Review of Underwater Image Object Detection Based on Deep Learning
-
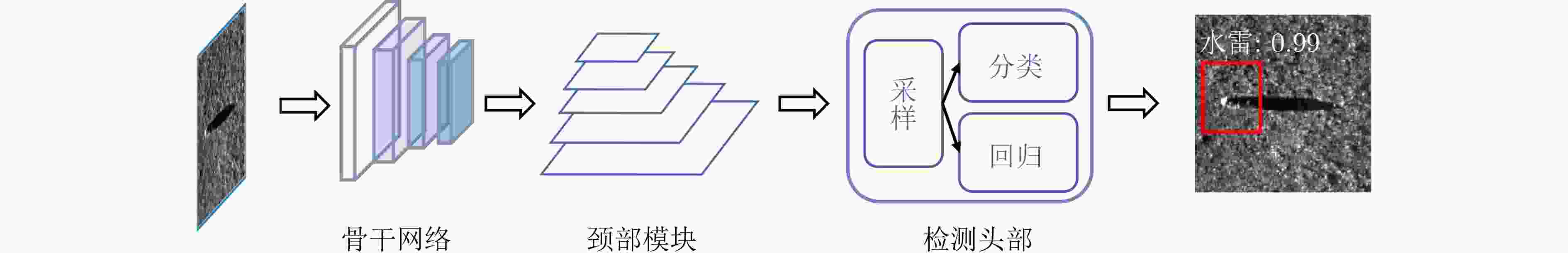
摘要: 水下图像目标检测是水下智能化探测的核心技术之一,广泛应用于工业及军事领域。深度学习相关技术的突破为水下图像目标检测的发展带来了新的机遇,但是目前该领域的综述较为陈旧,并且缺乏一定的系统性和全面性。该文对基于深度学习的水下可见光图像和声呐图像目标检测研究工作进行了详细总结与分析。首先,对基于深度学习的通用目标检测算法框架进行了梳理,包含骨干网络、颈部模块、检测头部、训练算法、推理策略、数据集6项要素,并系统性地总结了每个要素存在的问题及最新研究工作;然后,调研了水下可见光图像目标检测最新进展,分别从数据集发展、模型设计、训练算法进行总结;同时,归纳并分析了水下声呐图像目标检测相关工作,包含前视、侧扫、合成孔径3种声呐。最后,结合深度学习最新研究探讨了该领域的研究趋势。Abstract: Underwater image object detection is one of the core technologies of underwater intelligent exploration, which is widely used in industrial and military fields. The breakthrough of deep learning related technologies has brought new opportunities for the development of underwater image object detection, but the current reviews are relatively old and lack a certain degree of systematicness and comprehensiveness. In this paper, the research of underwater visible and sonar image detection based on deep learning is summarized and analyzed in detail. Firstly, the general object detection algorithm framework based on deep learning is sorted out, including six elements: backbone, neck, head, training algorithm, inference strategy, and evaluation criteria, and the problems of each element and the latest research work are systematically summarized; Then, the latest progresses of underwater visible image object detection are investigated and summarized from three aspects: data set, model design, and training method; Meanwhile, the works related to underwater sonar image detection are summarized and analyzed, including forward-looking sonar, side-scanning sonar and synthetic aperture sonar. Finally, the research trend of underwater image object detection is discussed based on the latest research on deep learning.
-
Key words:
- Underwater image object detection /
- Deep learning /
- Visible image /
- Sonar image /
- Data set
-
表 1 可用于水下可见光图像目标检测的数据集
数据集 训练集图像数 测试集图像数 类别数 类别描述 用途 年份 URPC2017[53] 17655 985* 3 海参、海胆、扇贝 目标检测 2017 URPC2018[53] 2901 800* 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2018 URPC2019[53] 4757 1029* 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2019 URPC2020-ZJ[53] 5543 2000* 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2020 URPC2020-DL[53] 6575 2400* 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2020 URPC2021[53] 7600 2400* 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2021 RUIE-UHTS[54] 300 – 3 海参、海胆、扇贝 目标检测 2020 UDD[55] 1827 400 3 海参、海胆、扇贝 目标检测 2022 UWD[56] 10000 – 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2020 DUO[57] 6671 1111 4 海参、海胆、扇贝、海星 目标检测 2021 Fish4Knowledge[58] 27370 – 23 海底鱼类 目标检测 2013 Brackish[59] 14518 – 6 大鱼、小鱼、水母、螃蟹等 目标检测 2019 Marine Litter[60] 5720 – 3 塑料垃圾、人为目标、生物 目标检测 2019 TrashCan[61] 7212 – 22 海底垃圾、动植物等 目标检测/分割 2020 SUIM[62] 1525 110 8 鱼类、珊瑚、植物、人、残骸等 目标检测/分割 2020 Kyutech10K[63] 10728 – 7 虾、鱿鱼、螃蟹、鲨鱼等 图像分类 2018 UIEB[64] 950 – 8 各类珊瑚与海洋生物等 图像增强 2020 MUED[65] 8600 – 430 430个海底物体 显著性检测 2019 UOT32[66] 24241 – 32 32个海底目标视频 目标跟踪 2019 UOT100[67] 74042 – 104 104个海底目标视频 目标跟踪 2021 -
[1] 郭戈, 王兴凯, 徐慧朴. 基于声呐图像的水下目标检测、识别与跟踪研究综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(5): 906–922. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.1678GUO Ge, WANG Xingkai, and XU Huipu. Review on underwater target detection, recognition and tracking based on sonar image[J]. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(5): 906–922. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.1678 [2] GOMES D, SAIF A F M S, and NANDI D. Robust underwater object detection with autonomous underwater vehicle: A comprehensive study[C]. 2020 International Conference on Computing Advancements, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2020, 17. [3] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [4] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG Jia, SU Hao, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211–252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [5] 檀盼龙, 吴小兵, 张晓宇. 基于声呐图像的水下目标识别研究综述[J]. 数字海洋与水下攻防, 2022, 5(4): 342–353. doi: 10.19838/j.issn.2096-5753.2022.04.010TAN Panlong, WU Xiaobing, and ZHANG Xiaoyu. Review on underwater target recognition based on sonar image[J]. Digital Ocean &Underwater Warfare, 2022, 5(4): 342–353. doi: 10.19838/j.issn.2096-5753.2022.04.010 [6] ZOU Zhengxia, CHEN Keyan, SHI Zhenwei, et al. Object detection in 20 years: A survey[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.05055.pdf, 2019. [7] 邵延华, 张铎, 楚红雨, 等. 基于深度学习的YOLO目标检测综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3697–3708. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210790SHAO Yanhua, ZHANG Duo, CHU Hongyu, et al. A review of YOLO object detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3697–3708. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210790 [8] ZAIDI S S A, ANSARI M S, ASLAM A, et al. A survey of modern deep learning based object detection models[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 126: 103514. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103514 [9] 林森, 赵颍. 水下光学图像中目标探测关键技术研究综述[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(6): 060002. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.060002LIN Sen and ZHAO Ying. Review on key technologies of target exploration in underwater optical images[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(6): 060002. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.060002 [10] FAYAZ S, PARAH S A, and QURESHI G J. Underwater object detection: Architectures and algorithms-a comprehensive review[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(15): 20871–20916. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12502-1 [11] GIRSHICK R B, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [12] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R B, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [13] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 386–397. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2844175 [14] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [15] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [16] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767.pdf, 2018. [17] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.10934.pdf, 2020. [18] DUAN Kaiwen, BAI Song, XIE Lingxi, et al. CenterNet: Keypoint triplets for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 6568–6577. [19] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 9626–9635. [20] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 213–229. [21] CHEN Kai, WANG Jiaqi, PANG Jiangmiao, et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab detection toolbox and benchmark[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.07155, 2019. [22] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [23] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. [24] ZHU Xizhou, HU Han, LIN S, et al. Deformable ConvNets V2: More deformable, better results[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9300–9308. [25] TOLSTIKHIN I O, HOULSBY N, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. MLP-mixer: An all-MLP architecture for vision[C/OL]. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 24261–24272. [26] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. [27] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN Bo, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 1314–1324. [28] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [29] LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifang, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759–8768. [30] ZONG Zhuofan, CAO Qianggang, and LENG Biao. RCNet: Reverse feature pyramid and cross-scale shift network for object detection[C]. The 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 2021: 5637–5645. [31] WANG Ning, GAO Yang, CHEN Hao, et al. NAS-FCOS: Fast neural architecture search for object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11940–11948. [32] WANG Jiaqi, ZHANG Wenwei, CAO Yuhang, et al. Side-aware boundary localization for more precise object detection[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 403–419. [33] WU Yue, CHEN Yinpeng, YUAN Lu, et al. Rethinking classification and localization for object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10183–10192. [34] FENG Chengjian, ZHONG Yujie, GAO Yu, et al. TOOD: Task-aligned one-stage object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 3490–3499. [35] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R B, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [36] PANG Jiangmiao, CHEN Kai, SHI Jianping, et al. Libra R-CNN: Towards balanced learning for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 821–830. [37] MA Yuchen, LIU Songtao, LI Zeming, et al. IQDet: Instance-wise quality distribution sampling for object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 1717–1725. [38] ZHANG Shifeng, CHI Cheng, YAO Yongqiang, et al. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9756–9765. [39] GE Zheng, LIU Songtao, LI Zeming, et al. OTA: Optimal transport assignment for object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 303–312. [40] OKSUZ K, CAM B C, AKBAS E, et al. Rank & sort loss for object detection and instance segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 2989–2998. [41] ZHANG Hongkai, CHANG Hong, MA Bingpeng, et al. Dynamic R-CNN: Towards high quality object detection via dynamic training[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 260–275. [42] GAO Yan, WANG Qimeng, TANG Xu, et al. Decoupled IoU regression for object detection[C]. The 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 2021: 5628–5636. [43] GUO M, HAQUE A, HUANG Dean, et al. Dynamic task prioritization for multitask learning[C]. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 282–299. [44] CAI Qi, PAN Yingwei, WANG Yu, et al. Learning a unified sample weighting network for object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 14161–14170. [45] LI Xiang, WANG Wenhai, HU Xiaolin, et al. Generalized focal loss V2: Learning reliable localization quality estimation for dense object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 11627–11636. [46] BODLA N, SINGH B, CHELLAPPA R, et al. Soft-NMS - Improving object detection with one line of code[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5562–5570. [47] LUO Zekun, FANG Zheng, ZHENG Sixiao, et al. NMS-loss: Learning with non-maximum suppression for crowded pedestrian detection[C]. 2021 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Taipei, China, 2021: 481–485. [48] SUN Peize, ZHANG Rufeng, JIANG Yi, et al. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-end object detection with learnable proposals[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 14449–14458. [49] WANG Jianfeng, SONG Lin, LI Zeming, et al. End-to-end object detection with fully convolutional network[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 15844–15853. [50] CAO Xiang, LUO Yihao, XIAO Yi, et al. Blind image super-resolution based on prior correction network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 463: 525–534. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.070 [51] EVERINGHAM M, VAN GOOL L, WILLIAMS C K I, et al. The PASCAL visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [52] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [53] URPC. Underwater robot professional contest[EB/OL]. http://www.urpc.org.cn/index.html, 2022. [54] LIU Risheng, FAN Xin, ZHU Ming, et al. Real-world underwater enhancement: Challenges, benchmarks, and solutions under natural light[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(12): 4861–4875. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2963772 [55] LIU Chongwei, WANG Zhihui, WANG Shijie, et al. A new dataset, Poisson GAN and AquaNet for underwater object grabbing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(5): 2831–2844. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3100059 [56] FAN Baojie, CHEN Wei, CONG Yang, et al. Dual refinement underwater object detection network[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 275–291. [57] LIU Chongwei, LI Haojie, WANG Shuchang, et al. A dataset and benchmark of underwater object detection for robot picking[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops, Shenzhen, China, 2021: 1–6. [58] Fish4Knowledge.https://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/Fish4Knowledge/index.html, 2013. [59] PEDERSEN M, HAURUM J B, GADE R, et al. Detection of marine animals in a new underwater dataset with varying visibility[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 18–26. [60] FULTON M, HONG J, ISLAM M J, et al. Robotic detection of marine litter using deep visual detection models[C]. 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, Canada, 2019: 5752–5758. [61] HONG J, FULTON M, and SATTAR J. TrashCan: A semantically-segmented dataset towards visual detection of marine debris[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.08097, 2020. [62] ISLAM M J, EDGE C, and XIAO Yuyang. Semantic segmentation of underwater imagery: Dataset and benchmark[C]. 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 1769–1776. [63] LU Huimin, LI Yujie, UEMURA T, et al. FDCNet: Filtering deep convolutional network for marine organism classification[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(17): 21847–21860. doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-4585-1 [64] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, REN Wenqi, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4376–4389. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241 [65] JIAN Muwei, QI Qiang, YU Hui, et al. The extended marine underwater environment database and baseline evaluations[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 80: 425–437. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.04.025 [66] KEZEBOU L, OLUDARE V, PANETTA K, et al. Underwater object tracking benchmark and dataset[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security, Woburn, USA, 2019: 1–6. [67] PANETTA K, KEZEBOU L, OLUDARE V, et al. Comprehensive underwater object tracking benchmark dataset and underwater image enhancement with GAN[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2022, 47(1): 59–75. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2021.3086907 [68] SUNG M, YU S C, and GIRDHAR Y. Vision based real-time fish detection using convolutional neural network[C]. OCEANS 2017, Aberdeen, UK, 2017: 1–6. [69] CHRISTENSEN J H, MOGENSEN L V, GALEAZZI R, et al. Detection, localization and classification of fish and fish species in poor conditions using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Workshop, Porto, Portugal, 2018: 1–6. [70] MANDAL R, CONNOLLY R M, SCHLACHER T A, et al. Assessing fish abundance from underwater video using deep neural networks[C]. 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018: 1–6. [71] KNAUSGÅRD K M, WIKLUND A, SØRDALEN T K, et al. Temperate fish detection and classification: A deep learning based approach[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(6): 6988–7001. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-02154-9 [72] 叶赵兵, 段先华, 赵楚. 改进YOLOv3-SPP水下目标检测研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(6): 231–240. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2204-0264YE Zhaobing, DUAN Xianhua, and ZHAO Chu. Research on underwater target detection by improved YOLOv3-SPP[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(6): 231–240. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2204-0264 [73] 张艳, 李星汕, 孙叶美, 等. 基于通道注意力与特征融合的水下目标检测算法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2022, 40(2): 433–441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.02.025ZHANG Yan, LI Xingshan, SUN Yemei, et al. Underwater object detection algorithm based on channel attention and feature fusion[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2022, 40(2): 433–441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.02.025 [74] 王蓉蓉, 蒋中云. 基于改进CenterNet的水下目标检测算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(2): 0215001.WANG Rongrong and JIANG Zhongyun. Underwater object detection algorithm based on improved CenterNet[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(2): 0215001. [75] 蔡达, 范保杰. 基于空间特征选择的水下目标检测方法[J]. 信息与控制, 2022, 51(2): 214–222. doi: 10.13976/j.cnki.xk.2022.1597CAI Da and FAN Baojie. Spatial feature selection for underwater object detection[J]. Information and Control, 2022, 51(2): 214–222. doi: 10.13976/j.cnki.xk.2022.1597 [76] 喻明毫, 高建瓴. 轻量级水下目标检测器LUDet[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2022, 44(9): 1638–1645. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2022.09.014YU Minghao and GAO Jianling. LUDet: A lightweight underwater object detector[J]. Computer Engineering &Science, 2022, 44(9): 1638–1645. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2022.09.014 [77] LIANG Xutao and SONG Pinhao. Excavating RoI attention for underwater object detection[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Bordeaux, France, 2022: 2651–2655. [78] LIN Weihong, ZHONG Jiaxing, LIU Shan, et al. ROIMIX: Proposal-fusion among multiple images for underwater object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 2022: 2588–2592. [79] 史朋飞, 韩松, 倪建军, 等. 结合数据增强和改进YOLOv4的水下目标检测算法[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2022, 36(3): 113–121. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2104168SHI Pengfei, HAN Song, NI Jianjun, et al. Underwater object detection algorithm combining data enhancement and improved YOLOv4[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2022, 36(3): 113–121. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2104168 [80] LI Xiuyuan, LI Fengchao, YU Jiangang, et al. A high-precision underwater object detection based on joint self-supervised deblurring and improved spatial transformer network[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.04822, 2022. [81] CHEN Long, LIU Zhihua, TONG Lei, et al. Underwater object detection using Invert Multi-Class Adaboost with deep learning[C]. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 1–8. [82] CHEN Long, ZHOU Feixiang, WANG Shengke, et al. SWIPENET: Object detection in noisy underwater scenes[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 132: 108926. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108926 [83] SONG Pinhao, LI Pengteng, DAI Linhui, et al. Boosting R-CNN: Reweighting R-CNN samples by RPN's error for underwater object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 530: 150–164. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.088 [84] Sound Metrics. Image Gallery[EB/OL]. http://www.soundmetrics.com/Image-Gallery, 2020. [85] SINGH D and VALDENEGRO-TORO M. The marine debris dataset for forward-looking sonar semantic segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 3734–3742. [86] BARNGROVER C, KASTNER R, and BELONGIE S. Semisynthetic versus real-world sonar training data for the classification of mine-like objects[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 40(1): 48–56. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2291634 [87] HUO Guanying, WU Ziyin, and LI Jiabiao. Underwater object classification in Sidescan sonar images using deep transfer learning and semisynthetic training data[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 47407–47418. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978880 [88] 周彦, 陈少昌, 吴可, 等. SCTD1.0: 声呐常见目标检测数据集[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(S2): 334–339. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210100138ZHOU Yan, CHEN Shaochang, WU Ke, et al. SCTD1.0: Sonar common target detection dataset[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(S2): 334–339. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210100138 [89] VALDENEGRO-TORO M. Object recognition in forward-looking sonar images with convolutional neural networks[C]. OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, Monterey, USA, 2016: 1–6. [90] VALDENEGRO-TORO M. End-to-end object detection and recognition in forward-looking sonar images with convolutional neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicles, Tokyo, Japan, 2016: 144–150. [91] PALOMERAS N, FURFARO T, WILLIAMS D P, et al. Automatic target recognition for mine countermeasure missions using forward-looking sonar data[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2022, 47(1): 141–161. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2021.3103269 [92] ZHOU Tian, SI Jikun, WANG Luyao, et al. Automatic detection of underwater small targets using forward-looking sonar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4207912. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3181417 [93] GEBHARDT D, PARIKH K, DZIECIUCH I, et al. Hunting for naval mines with deep neural networks[C]. OCEANS 2017, Anchorage, UK, 2017: 1–5. [94] HOANG T, DALTON K S, GERG I D, et al. Domain enriched deep networks for munition detection in underwater 3D sonar imagery[C]. 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 815–818. [95] FAN Zhimiao, XIA Weijie, LIU Xue, et al. Detection and segmentation of underwater objects from forward-looking sonar based on a modified Mask RCNN[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1135–1143. doi: 10.1007/s11760-020-01841-x [96] FAN Xinnan, LU Liang, SHI Pengfei, et al. A novel sonar target detection and classification algorithm[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(7): 10091–10106. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12054-4 [97] ZHANG Haoting, TIAN Mei, SHAO Gaoping, et al. Target detection of forward-looking sonar image based on improved YOLOv5[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 18023–18034. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3150339 [98] ZHU Xingyu, LIANG Yingshuo, ZHANG Jianlei, et al. STAFNet: Swin transformer based anchor-free network for detection of forward-looking sonar imagery[C]. The 2022 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Newark, USA, 2022: 443–450. [99] WANG Yanmei, LIU Jiaxin, YU Siquan, et al. Underwater object detection based on YOLO-v3 network[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems, Beijing, China, 2021: 571–575. [100] LI Jiawen and CAO Xiang. Target recognition and detection in side-scan sonar images based on YOLO v3 model[C]. 41st Chinese Control Conference, Hefei, China, 2022: 7186–7190. [101] 陈禹蒲, 马晓川, 李璇. 基于YOLOv3锚框优化的侧扫声呐图像目标检测[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(11): 2359–2371. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.11.013CHEN Yupu, MA Xiaochuan, and LI Xuan. Target detection in side scan sonar images based on YOLOv3 anchor boxes optimization[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(11): 2359–2371. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.11.013 [102] YU Yongcan, ZHAO Jianhu, GONG Quanhua, et al. Real-time underwater maritime object detection in side-scan sonar images based on transformer-YOLOv5[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3555. doi: 10.3390/rs13183555 [103] FU Shunan, XU Feng, LIU Jia, et al. Underwater small object detection in side-scan sonar images based on improved YOLOv5[C]. 3rd International Conference on Geology, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Zhoushan, China, 2022: 446–453. [104] 李宝奇, 黄海宁, 刘纪元, 等. 基于改进SSD的合成孔径声呐图像水下多尺度目标轻量化检测模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 2854–2862. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201042LI Baoqi, HUANG Haining, LIU Jiyuan, et al. Synthetic aperture sonar underwater multi-scale target efficient detection model based on improved single shot detector[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 2854–2862. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201042 [105] ZHANG Peng, TANG Jinsong, ZHONG Heping, et al. Self-trained target detection of radar and sonar images using automatic deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4701914. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3096011 [106] LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. [107] WU Meihan, WANG Qi, RIGALL e, et al. ECNet: Efficient convolutional networks for side scan sonar image segmentation[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(9): 2009. doi: 10.3390/s19092009 [108] SLEDGE I J, EMIGH M S, KING J L, et al. Target detection and segmentation in circular-scan synthetic aperture sonar images using Semisupervised convolutional encoder-decoders[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2022, 47(4): 1099–1128. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2022.3152863 [109] FUCHS L R, GÄLLSTRÖM A, and FOLKESSON J. Object recognition in forward looking sonar images using transfer learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Workshop, Porto, Portugal, 2018, 1–6. [110] LEE S, PARK B, and KIM A. Deep learning from shallow dives: Sonar image generation and training for underwater object detection[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.07990, 2018. [111] LOU Guanting, ZHENG Ronghao, LIU Meiqin, et al. Automatic target recognition in forward-looking sonar images using transfer learning[C]. Global Oceans 2020: Singapore – U. S. Gulf Coast, Biloxi, USA, 2020: 1–6. [112] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. [113] JEGOROVA M, KARJALAINEN A I, VAZQUEZ J, et al. Full-scale continuous synthetic sonar data generation with markov conditional generative adversarial networks[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Paris, France, 2020: 3168–3174. [114] 凡志邈, 夏伟杰, 刘雪. 基于修正Cycle GAN的声呐图像库构建方法研究[J]. 声学技术, 2021, 40(6): 890–894. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2021.06.023FAN Zhimiao, XIA Weijie, and LIU Xue. Modified CycleGAN based sonar image library construction[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2021, 40(6): 890–894. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2021.06.023 [115] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C] 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. [116] 盛子旗, 霍冠英. 样本仿真结合迁移学习的声呐图像水雷检测[J]. 智能系统学报, 2021, 16(2): 385–392. doi: 10.11992/tis.202101030SHENG Ziqi and HUO Guanying. Detection of underwater mine target in sidescan sonar image based on sample simulation and transfer learning[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2021, 16(2): 385–392. doi: 10.11992/tis.202101030 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
