Non-contact Liquid Level Detection Method Based on Multilayer Spiking Neural Network
-
摘要: 尽管基于深度学习的非接触液位检测方法能够较好地完成检测任务,但其对计算资源的较高要求使其不适用于算力受限的嵌入式设备。为解决上述问题,该文首先提出了基于多层脉冲神经网络的非接触液位检测方法;其次,提出了单帧和帧差脉冲编码方法将视频流时间动态性编码成可重构的脉冲模式;最后在实际场景中对模型进行测试。实验结果表明,所提方法具有较高应用价值。Abstract: Although the non-contact liquid level detection method based on deep learning can perform well, its high demand on computational resources makes it not suitable for embedded devices with limited resource. To solve this problem, a non-contact liquid level detection method is first proposed based on multilayer spiking neural network; Furthermore, spiking encoding methods based on single frame and frame difference are proposed to encode the temporal dynamics of video stream into reconfigurable spike patterns; Finally, the model is tested in the real scene. The experimental results show that the proposed method has high application value.
-
表 1 各类型样本数量
水杯类型 样本数量 玻璃杯 231 保温杯 30 不锈钢杯 93 马克杯 102 瓷杯 180 不透明塑料杯 102 纸杯 63 表 2 参数$ k $在注水量>70%时平均停水率
感受野尺寸k 纸杯(%) 瓷杯(%) 3 80 83 4 87 85 5 92 92 6 90 89 7 85 87 8 87 80 表 3 参数$ S $在注水量>70%时平均停水率
脉冲计算阈值 纸杯(%) 瓷杯(%) 130 79 77 135 85 84 140 90 89 145 92 92 150 92 87 155 84 81 160 85 86 表 4 模型参数取值
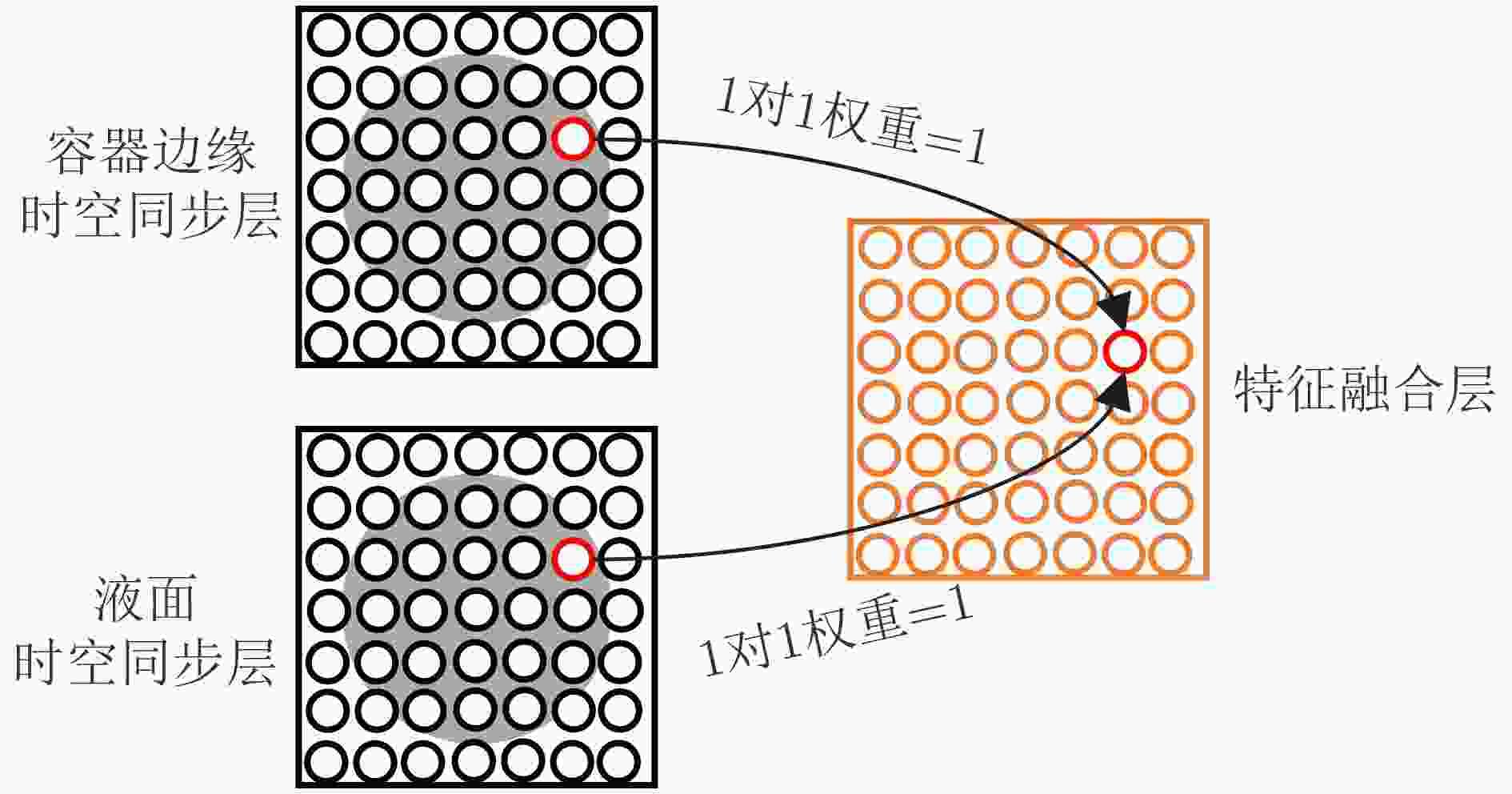
层 参数名称 参数值 容器边缘 TC编码阈值 0.5 液面编码层 TC编码阈值 0.5 容器边缘检测层 LIF神经元放电阈值 11 液面检测层 LIF神经元放电阈值 6 容器边缘检测层 侧向抑制范围 1 时空同步层 感受野尺寸k 5 输出与检测层 脉冲计数阈值 145 表 5 测试结果
序号 操作描述 数据示例 容器边缘编码 液面边缘编码 1 开始注水 


2 <20%水量 


3 20%~70%水量 


4 >70%水量 


表 6 杯子容量—材质阶梯准确率及时停水提示率(%)
容积材质 <20%水量 20%~70%水量 >70%水量 P $ {P_{\text{s}}} $ P $ {P_{\text{s}}} $ P $ {P_{\text{s}}} $ 马克杯 90 96 92 97 93 97 瓷杯 90 96 92 97 92 97 不透明塑料杯 90 96 93 97 95 97 纸杯 90 96 91 97 92 97 木杯 90 96 91 97 92 97 玻璃杯 – – 90 97 90 97 不锈钢水温杯 89 96 90 97 92 97 保温杯 – – 82 97 85 97 锥形玻璃杯 – – 82 81 83 81 注:表中的“–”表示该类型杯子在市面上不常见,无法采购得到。 -
[1] AREEKATH L, LODHA G, KUMAR SAHANA S, et al. Feasibility of a planar coil-based inductive-capacitive water level sensor with a quality-detection feature: An experimental study[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(15): 5508. doi: 10.3390/s22155508 [2] ISLAM T, MAURYA O P, and KHAN A U. Design and fabrication of fringing field capacitive sensor for non-contact liquid level measurement[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(21): 24812–24819. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2021.3112848 [3] ISMAEL M A, LAFTAH R M, and FALIH M N. Measurement of liquid level in partially-filled pipes using a noise of electromagnetic flowmeter[J]. Al-Qadisiyah Journal for Engineering Sciences, 2018, 10(4): 550–564. doi: 10.30772/qjes.v10i4.504 [4] 王路平, 魏勇, 汪玉祥, 等. 井下动液面声波信号处理方法研究[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44(22): 87–95. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2107326WANG Luping, WEI Yong, WANG Yuxiang, et al. Research on acoustic signal processing method of downhole moving liquid level[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(22): 87–95. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2107326 [5] 贾静, 吉娇, 檀洋阳, 等. 基于超声波的液面位置测量方法研究[J]. 应用物理, 2022, 12(5): 233–238. doi: 10.12677/app.2022.125026JIA Jing, JI Jiao, TAN Yangyang, et al. Research on liquid level position measurement method based on ultrasonic wave[J]. Applied Physics, 2022, 12(5): 233–238. doi: 10.12677/app.2022.125026 [6] HE Runjie, TENG Chuanxin, KUMAR S, et al. Polymer optical fiber liquid level sensor: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(2): 1081–1091. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2021.3132098 [7] LIAO Kaiyu, LI Yulong, LEI Min, et al. A liquid level sensor based on spiral macro-bending plastic optical fiber[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2022, 70: 102874. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2022.102874 [8] WEI Minghui, DENG Zigang, ZHENG Jun, et al. Magnetic float liquid level detection method for high-temperature superconducting flux-pinning maglev system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2022, 32(4): 9000105. doi: 10.1109/tasc.2021.3131398 [9] LAN Yanling, HAN Ding, BAI Fengshan, et al. Review of research and application of fluid flow detection based on computer vision[C]. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Science and Application Engineering, Sanya, China, 2020: 127. [10] SILVER D, HUANG A, MADDISON C J, et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 484–489. doi: 10.1038/nature16961 [11] SILVER D, SCHRITTWIESER J, SIMONYAN K, et al. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354–359. doi: 10.1038/nature24270 [12] LI Shutao, SONG Weiwei, FANG Leyuan, et al. Deep learning for hyperspectral image classification: An overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6690–6709. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2019.2907932 [13] CHAN T H, JIA Kui, GAO Shenghua, et al. PCANet: A simple deep learning baseline for image classification?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5017–5032. doi: 10.1109/tip.2015.2475625 [14] ZHANG Jianpeng, XIE Yutong, WU Qi, et al. Medical image classification using synergic deep learning[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2019, 54: 10–19. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.02.010 [15] JIAO Licheng, ZHANG Ruohan, LIU Fang, et al. New generation deep learning for video object detection: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 3195–3215. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2021.3053249 [16] 贺丰收, 何友, 刘准钆, 等. 卷积神经网络在雷达自动目标识别中的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899HE Fengshou, HE You, LIU Zhunga, et al. Research and development on applications of convolutional neural networks of radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899 [17] ESMAEILPOUR M, CARDINAL P, and KOERICH A L. Multidiscriminator sobolev defense-GAN against adversarial attacks for end-to-end speech systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 2044–2058. doi: 10.1109/tifs.2022.3175603 [18] ALI A, CHOWDHURY S, AFIFY M, et al. Connecting Arabs: Bridging the gap in dialectal speech recognition[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2021, 64(4): 124–129. doi: 10.1145/3451150 [19] 廖昭洋, 胡睿晗, 周雪峰, 等. 基于时空混合图卷积网络的机器人定位误差预测及补偿方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(5): 1539–1547. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211381LIAO Zhaoyang, HU Ruihan, ZHOU Xuefeng, et al. Prediction and compensation method of robot positioning error based on spatio-temporal graph convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(5): 1539–1547. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211381 [20] 张铁林, 徐波. 脉冲神经网络研究现状及展望[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(9): 1767–1785. doi: 10.11897/sp.j.1016.2021.01767ZHANG Tielin and XU Bo. Research advances and perspectives on spiking neural networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(9): 1767–1785. doi: 10.11897/sp.j.1016.2021.01767 [21] LUO Xiaoling, QU Hong, WANG Yuchen, et al. Supervised learning in multilayer spiking neural networks with spike temporal error backpropagation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, To be published. [22] MAASS W. Networks of spiking neurons: The third generation of neural network models[J]. Neural Networks, 1997, 10(9): 1659–1671. doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(97)00011-7 [23] 胡一凡, 李国齐, 吴郁杰, 等. 脉冲神经网络研究进展综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(1): 1–26. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1006HU Yifan, LI Guoqi, WU Yujie, et al. Spiking neural networks: A survey on recent advances and new directions[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(1): 1–26. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1006 [24] HAN Bing and ROY K. Deep spiking neural network: Energy efficiency through time based coding[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 388–404. [25] ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Shengyuan, ZHI Tian, et al. TDSNN: From deep neural networks to deep spike neural networks with temporal-coding[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 1319–1326. [26] KIM Y and PANDA P. Optimizing deeper spiking neural networks for dynamic vision sensing[J]. Neural Networks, 2021, 144: 686–698. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2021.09.022 [27] CAPORALE N and DAN Yang. Spike timing-dependent plasticity: A Hebbian learning rule[J]. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2008, 31: 25–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125639 [28] XU Qi, PENG Jianxin, SHEN Jiangrong, et al. Deep CovDenseSNN: A hierarchical event-driven dynamic framework with spiking neurons in noisy environment[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 121: 512–519. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.08.034 [29] XU Qi, SHEN Jiangrong, RAN Xuming, et al. Robust transcoding sensory information with neural spikes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(5): 1935–1946. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3107449 [30] 任明武, 杨万扣, 王欢, 等. 一种基于图像的水位自动测量新方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43(22): 204–206. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.22.061REN Mingwu, YANG Wankou, WANG Huan, et al. New algorithm of automatic water level measurement based on image processing[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2007, 43(22): 204–206. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.22.061 [31] SHEN Jun and CASTAN S. An optimal linear operator for step edge detection[J]. CVGIP:Graphical Models and Image Processing, 1992, 54(2): 112–133. doi: 10.1016/1049-9652(92)90060-b [32] 黄玲, 张叶林, 胡波, 等. 基于机器视觉的透明瓶装液体液位自动检测[J]. 自动化与仪表, 2012, 27(2): 57–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9944.2012.02.016HUANG Ling, ZHANG Yelin, HU Bo, et al. Automatic detection of liquid level in transparent bottle based on machine vision[J]. Automation &Instrumentation, 2012, 27(2): 57–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9944.2012.02.016 [33] 李博文. 基于机器视觉的饮水机取水杯液位检测系统开发研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华南理工大学, 2019.LI Bowen. Development of the machine vision-based liquid level detection system[D]. [Master dissertation], South China University of Technology, 2019. [34] 廖赟, 段清, 刘俊晖, 等. 基于深度学习的水位线检测算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(S1): 274–278. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019081360LIAO Yun, DUAN Qing, LIU Junhui, et al. Water line detection algorithm based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(S1): 274–278. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019081360 [35] JIANG Yijun, SCHENCK E, KRANZ S, et al. CNN-based non-contact detection of food level in bottles from RGB images[C]. 25th International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2019: 202–213. [36] WANG Ran, LIU Fengkai, HOU Fatao, et al. A non-contact fault diagnosis method for rolling bearings based on acoustic imaging and convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 132761–132774. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3010272 [37] QIAO Guangchao, YANG Mingxiang, and WANG Hao. A water level measurement approach based on YOLOv5s[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(10): 3714. doi: 10.3390/s22103714 [38] 梁霄, 李家炜, 赵小龙, 等. 基于深度学习的红外目标成像液位检测方法[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(21): 2110001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.2110001LIANG Xiao, LI Jiawei, ZHAO Xiaolong, et al. Infrared target imaging liquid level detection method based on deep learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(21): 2110001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.2110001 [39] HUANG Zeyong, LI Yuhong, ZHAO Tingting, et al. Infusion port level detection for intravenous infusion based on YOLO v3 neural network[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 3491–3501. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021175 [40] MAASS W and BISHOP C M. Pulsed Neural Networks[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2001. [41] LAPICQUE L. Recherches quantitatives sur l’excitation electrique des nerfs traitee comme une polarization[J]. Journal of Physiol Pathol Générale, 1907, 9: 620–635. [42] HODGKIN A L and HUXLEY A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1952, 117(4): 500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764 -





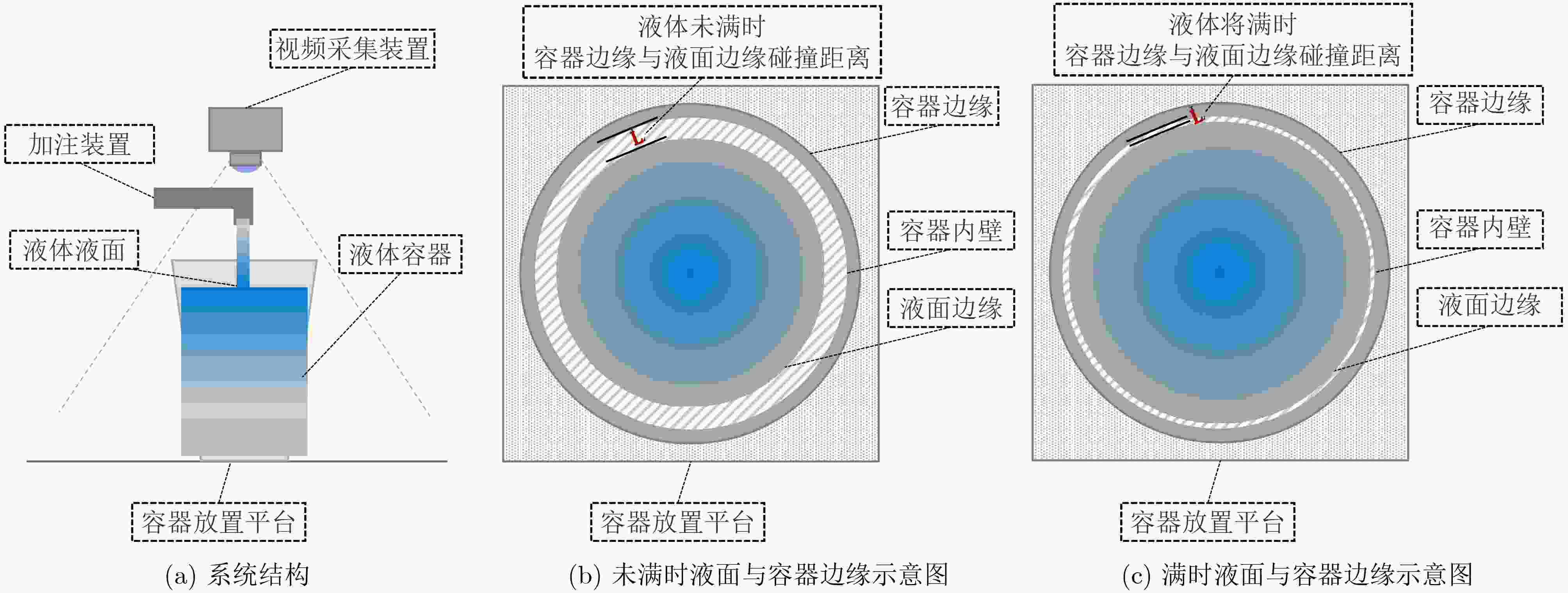
 下载:
下载:
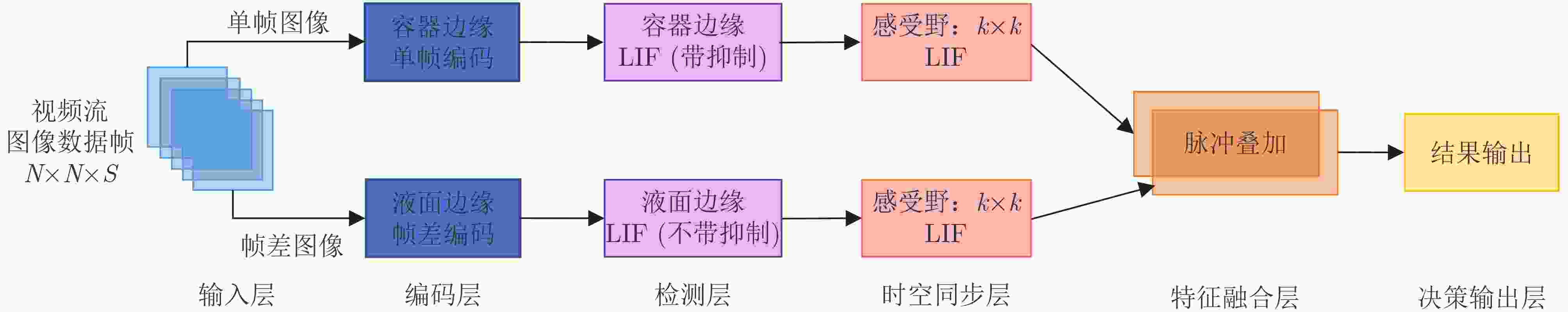
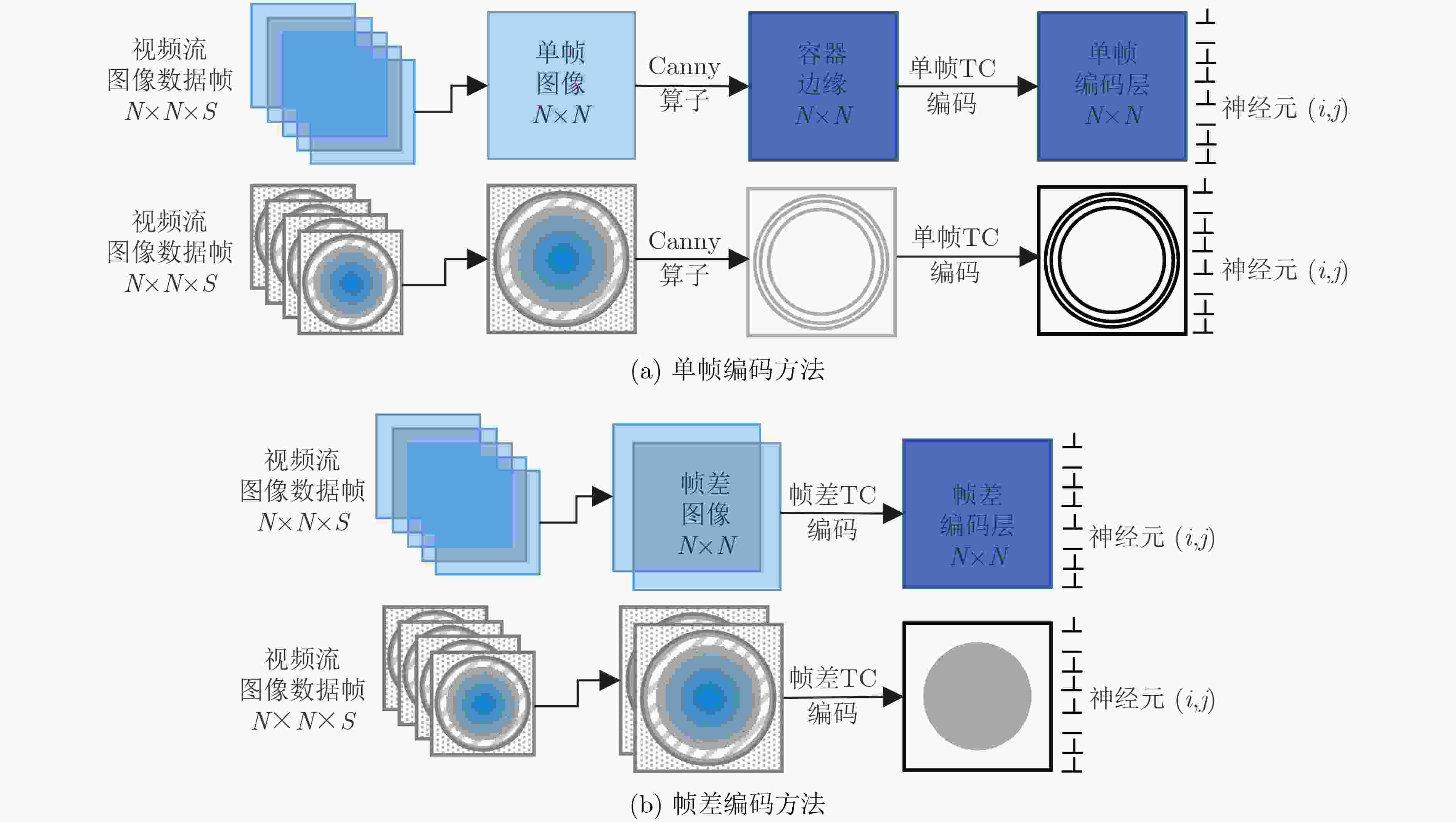
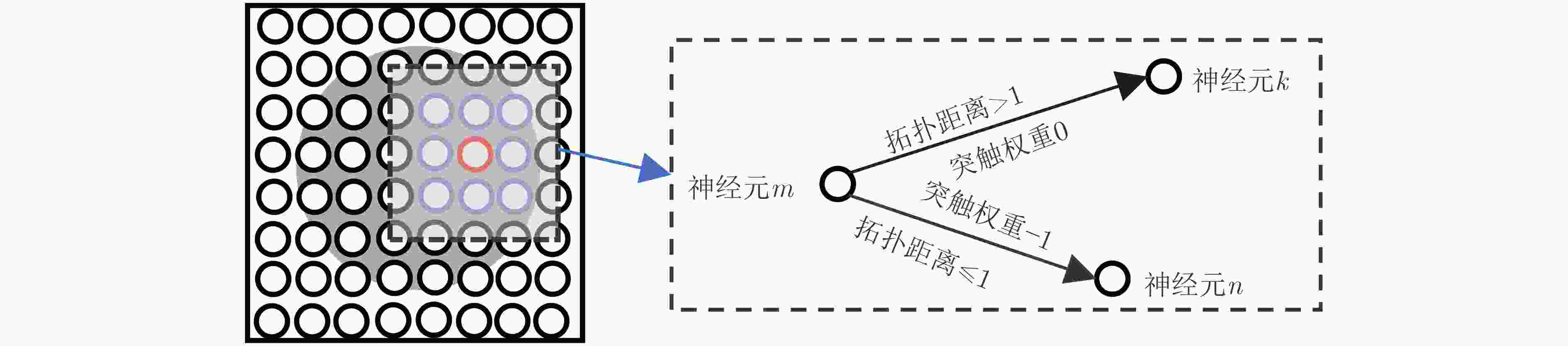



 下载:
下载:
