Research on Satellite Virtual Network Admission Control and Resource Allocation Based on Robust Optimization
-
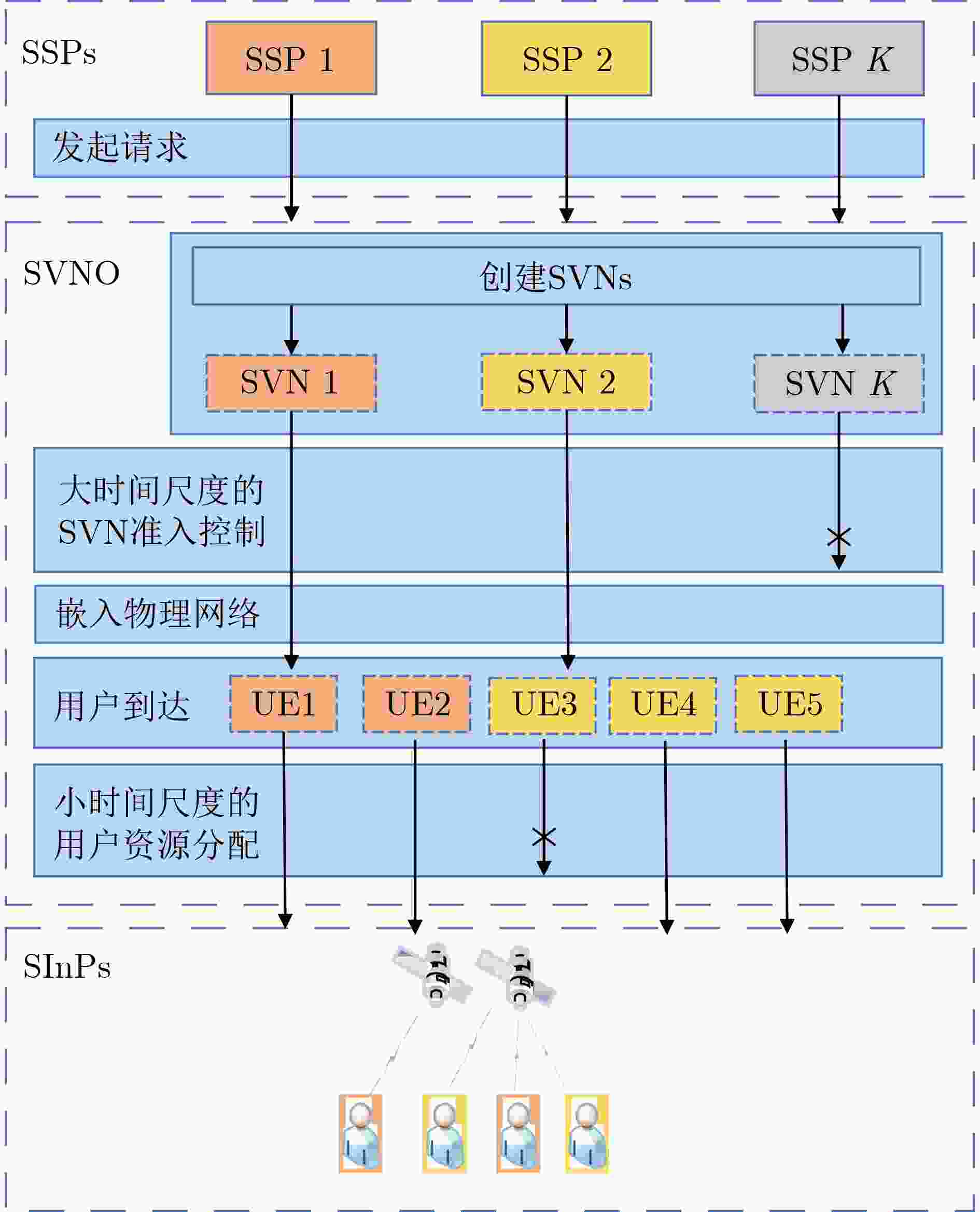
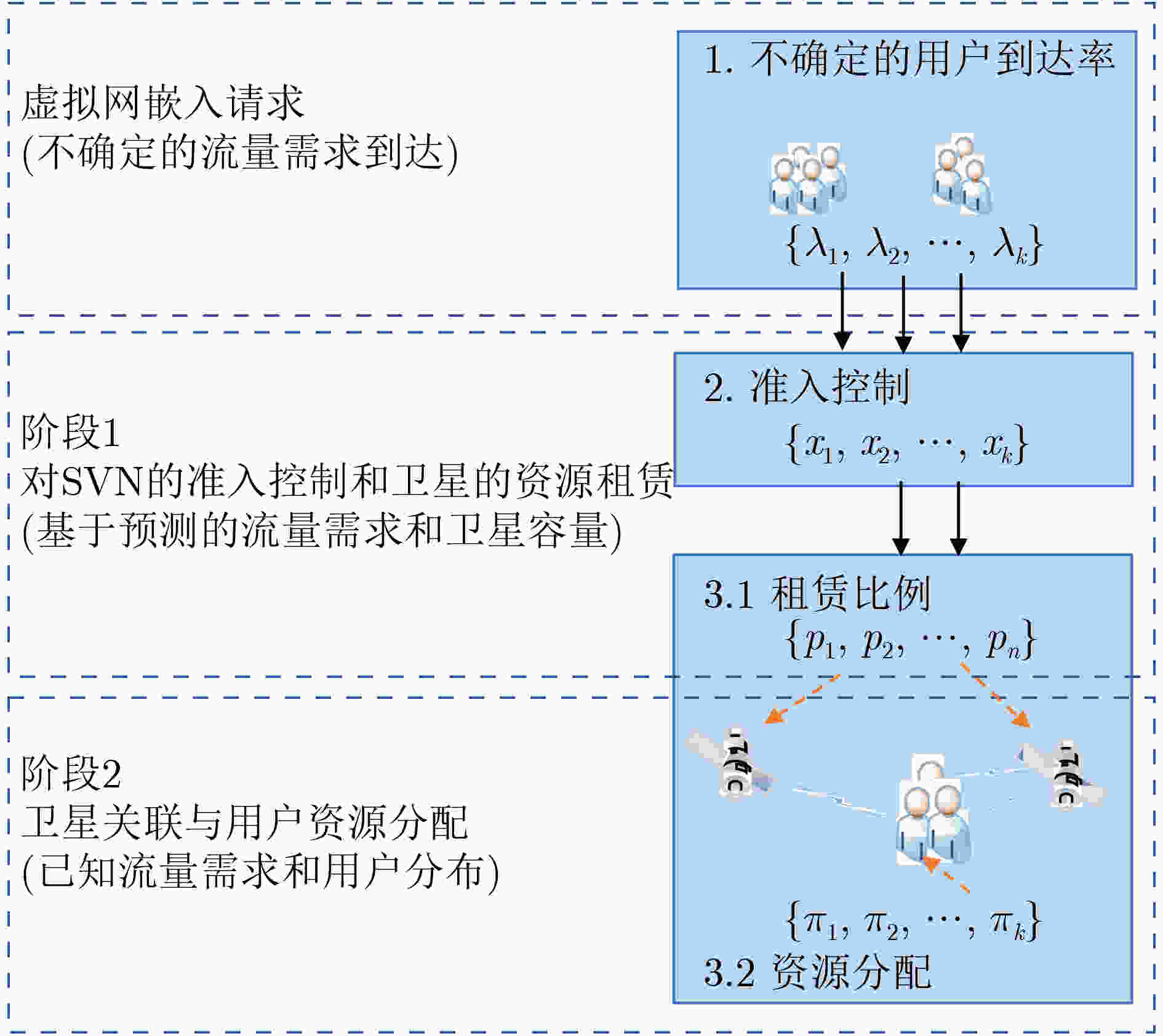
摘要: 网络虚拟化是一项未来网络发展的重要技术。针对卫星虚拟网络(SVN)中用户服务质量(QoS)可能受到严重影响的问题,该文提出一种用于SVN准入控制的方法,通过限制嵌入卫星物理网络中SVN的数量可以有效保证用户的QoS。具体而言,首先,该文提出一种两阶段SVN嵌入机制,该机制将短期资源分配与长期准入控制和资源租赁解耦。其次,该文同时考虑用户到达率时变导致流量需求不确定和卫星网络拓扑高动态性导致系统容量不确定的情况,将第1阶段的准入控制和资源租赁问题描述为鲁棒优化问题,再利用伯恩施坦近似将其转化为凸问题进行求解。最后,该文将第2阶段的资源分配问题转化为最大化公平带宽分配的凸问题进行求解。仿真结果表明了该文所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Network virtualization is a significant technology for future network development. A method for Satellite Virtual Network (SVN) admission control is proposed in this paper to address the problem that user Quality of Service (QoS) may be severely affected in SVN, which can effectively guarantee user QoS by limiting the number of SVNs embedded in the satellite physical network. Specifically, firstly, a two-stage SVN embedding mechanism is proposed, which decouples short-term resource allocation from long-term admission control and resource leasing. Secondly, considering the uncertainty of traffic demand due to time-varying user arrival rate and the uncertainty of system capacity due to the highly dynamic nature of satellite network topology, the admission control and resource leasing problems in the first stage are described as robust optimization problems, which are then transformed into convex problems using the Bernstein approximation for solution. Finally, the article transforms the resource allocation problem in the second stage into a convex problem that maximizes fair bandwidth allocation for solution. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme in this paper.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
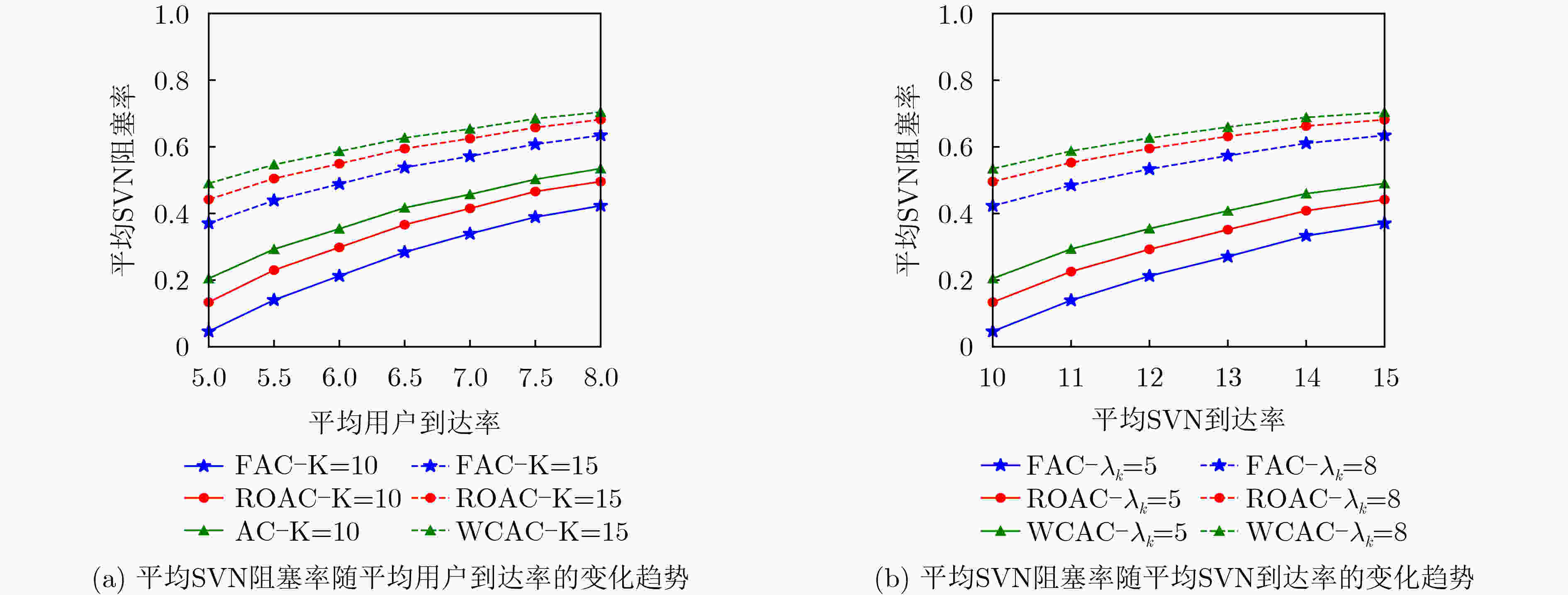
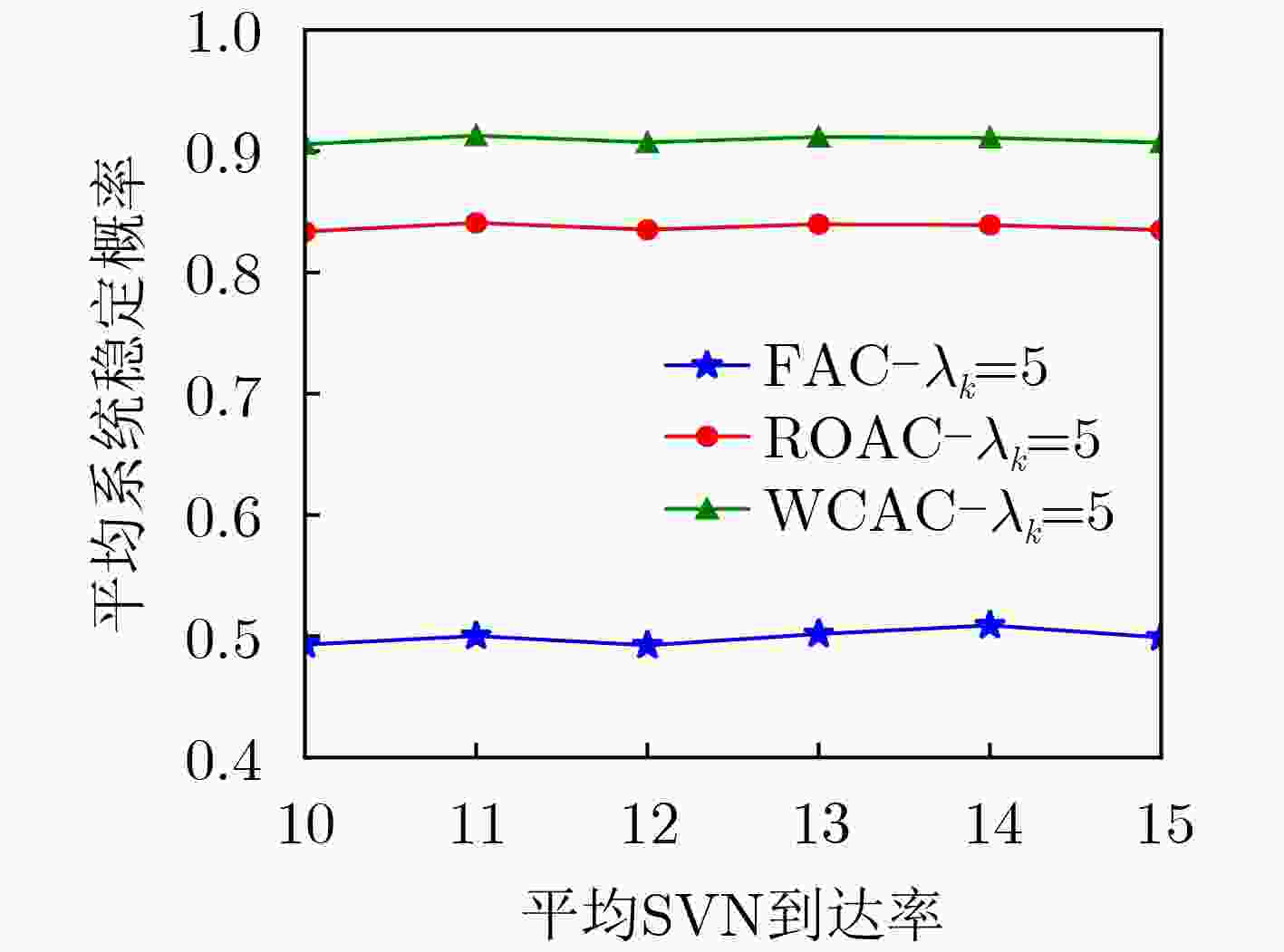
参数名称 取值 参数名称 取值 卫星数 5 平均用户到达率最大不确定性 ±20% 卫星轨道高度 781 km 卫星容量估计最大不确定性 ±10% 卫星均匀分布范围 (89°W ~91°W, 44°N~46°N) 卫星可租赁资源上限$p_n^{\max }$ Uniform[0.85,0.95] 用户随机分布范围 (85°W~95°W, 40°N~50°N) 网络状态比例常数${\alpha _n}$ 0.5 下行链路工作频段 1616~1626.5 MHz 租赁价格 2 unit/MHz 卫星最大发射天线增益 41.6 dBi 准入SVN收入 1 unit/SVN 用户接收天线增益 20 dBi 拒绝SVN惩罚 2 unit/SVN 噪声功率密度 –174 dBm/Hz 用户数据速率 {0.5,0.6,0.7} Mbit/s -
[1] GIORDANI M and ZORZI M. Non-terrestrial networks in the 6G era: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(2): 244–251. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000493 [2] WANG Ruibo, KISHK M A, and ALOUINI M S. Ultra-dense LEO satellite-based communication systems: A novel modeling technique[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2022, 60(4): 25–31. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2100800 [3] LIU Shicong, GAO Zhen, WU Yongpeng, et al. LEO satellite constellations for 5G and beyond: How will they reshape vertical domains?[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(7): 30–36. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2001081 [4] CAO Suzhi, WEI Junyong, HAN Hao, et al. Space edge cloud enabling network slicing for 5G satellite network[C]. 2019 15th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference, Tangier, Morocco, 2019: 787–792. [5] RODRIGUES T K and KATO N. Network slicing with centralized and distributed reinforcement learning for combined satellite/ground networks in a 6G environment[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(1): 104–110. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100287 [6] MENDOZA F, MINARDI M, CHATZINOTAS S, et al. An SDN based testbed for dynamic network slicing in satellite-terrestrial networks[C]. 2021 IEEE International Mediterranean Conference on Communications and Networking, Athens, Greece, 2021: 36–41. [7] BARAKABITZE A A, AHMAD A, MIJUMBI R, et al. 5G network slicing using SDN and NFV: A survey of taxonomy, architectures and future challenges[J]. Computer Networks, 2020, 167: 106984. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2019.106984 [8] KODHELI O, LAGUNAS E, MATURO N, et al. Satellite communications in the new space era: A survey and future challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(1): 70–109. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.3028247 [9] HAN Bin, FENG Di, JI Lianghai, et al. A profit-maximizing strategy of network resource management for 5G tenant slices[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1709.09229, 2017. [10] CHALLA R, ZALYUBOVSKIY V V, RAZA S M, et al. Network slice admission model: Tradeoff between monetization and rejections[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(1): 657–660. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2904667 [11] SCIANCALEPORE V, COSTA-PEREZ X, and BANCHS A. RL-NSB: Reinforcement learning-based 5G network slice broker[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(4): 1543–1557. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2019.2924471 [12] LIU Jiang, HE Xiaochun, CHEN Tianjiao, et al. SN-VNE: A virtual network embedding algorithm for satellite networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications Workshops in China, Changchun, China, 2019: 1–6. [13] LIU Zhiguo and WU Junhua. Mobile satellite network virtual mapping algorithm based on node risk[C]. 2016 International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers, Wuhan, China, 2016: 76–79. [14] LIANG Chengchao and YU F R. Wireless virtualization for next generation mobile cellular networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(1): 61–69. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2015.7054720 [15] WANG Xin, KRISHNAMURTHY P, and TIPPER D. Wireless network virtualization[C]. 2013 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications, San Diego, USA, 2013: 818–822. [16] RENGARAJAN B and DE VECIANA G. Architecture and abstractions for environment and traffic-aware system-level coordination of wireless networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2011, 19(3): 721–734. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2010.2098043 [17] International Telecommunication Union-Radio (ITU-R). ITU-R S. 1528 Satellite antenna radiation patterns for non-geostationary orbit satellite antennas operating in the fixed-satellite service below 30 GHz[S]. 2001. [18] ZAKI Y. Future Mobile Communications: LTE Optimization and Mobile Network Virtualization[M]. Wiesbaden: Springer, 2012. [19] BEN-TAL A and NEMIROVSKI A. Selected topics in robust convex optimization[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2008, 112(1): 125–158. doi: 10.1007/s10107-006-0092-2 [20] LIU Zhixin, XIE Yuan’ai, CHAN K Y, et al. Chance-constrained optimization in D2D-based vehicular communication network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 5045–5058. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2904291 -





 下载:
下载:
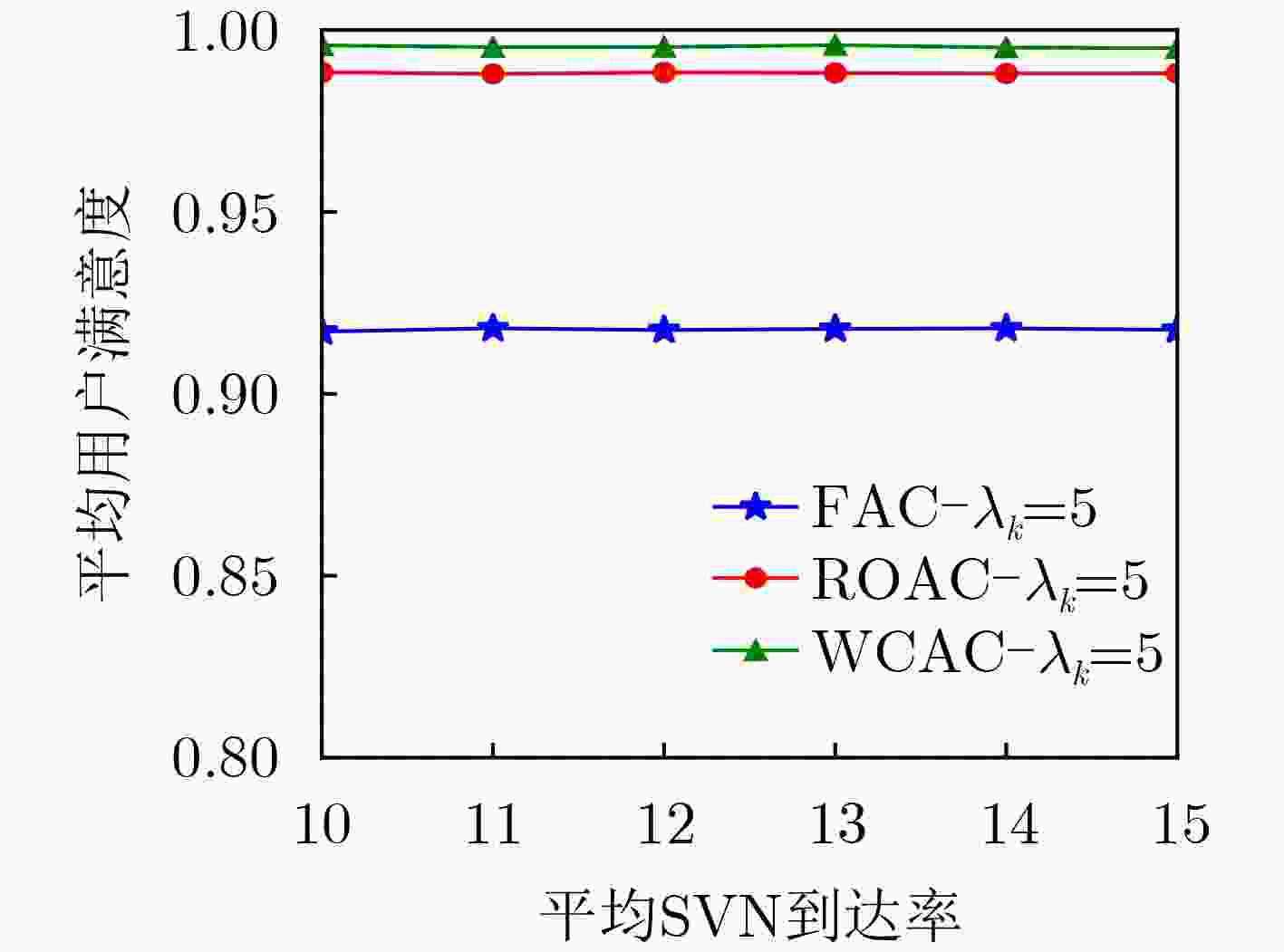
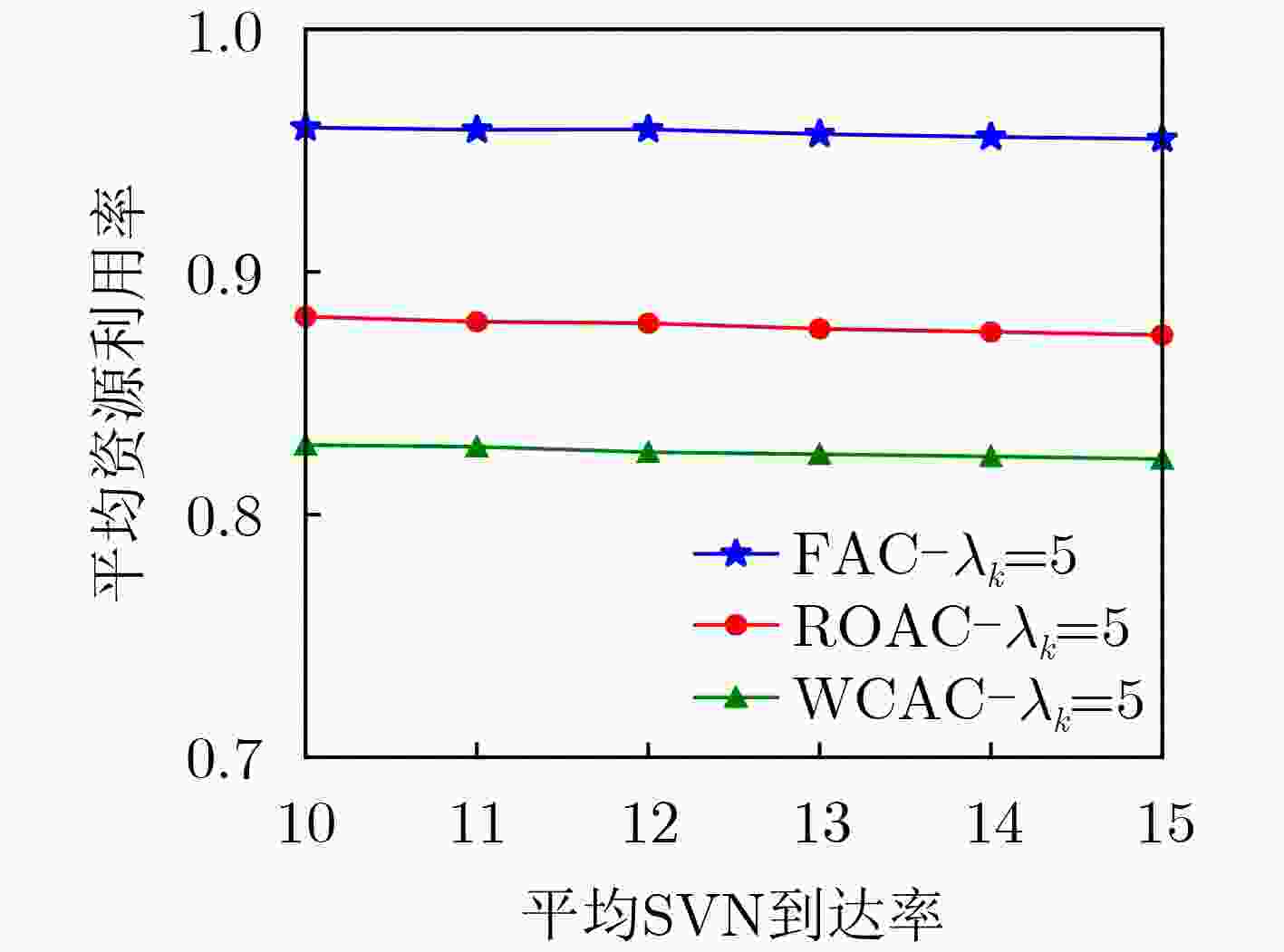


 下载:
下载:
