Design of Biological-inspired Low-light Video Adaptive Enhancement and FPGA Accelerated Implementation
-
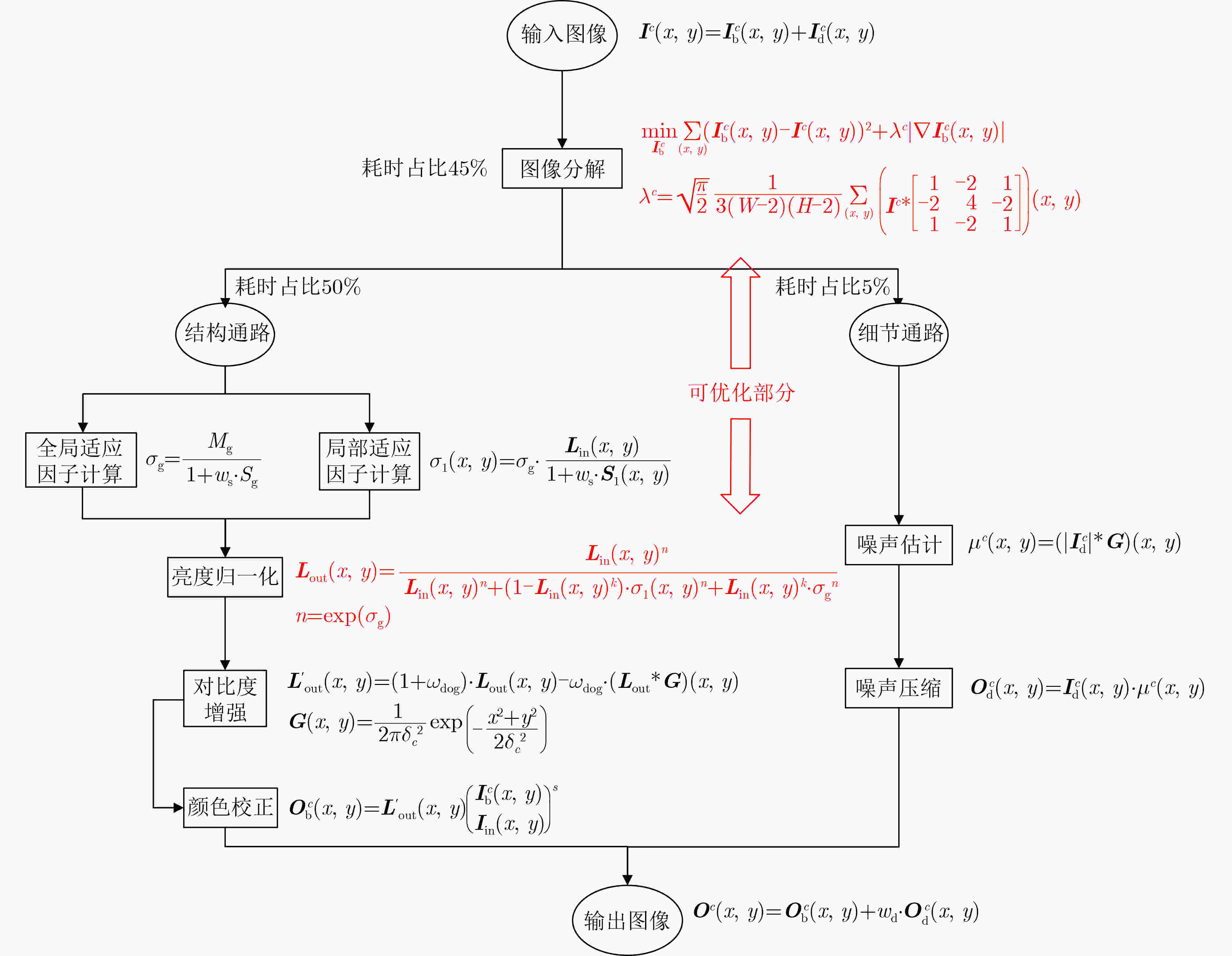
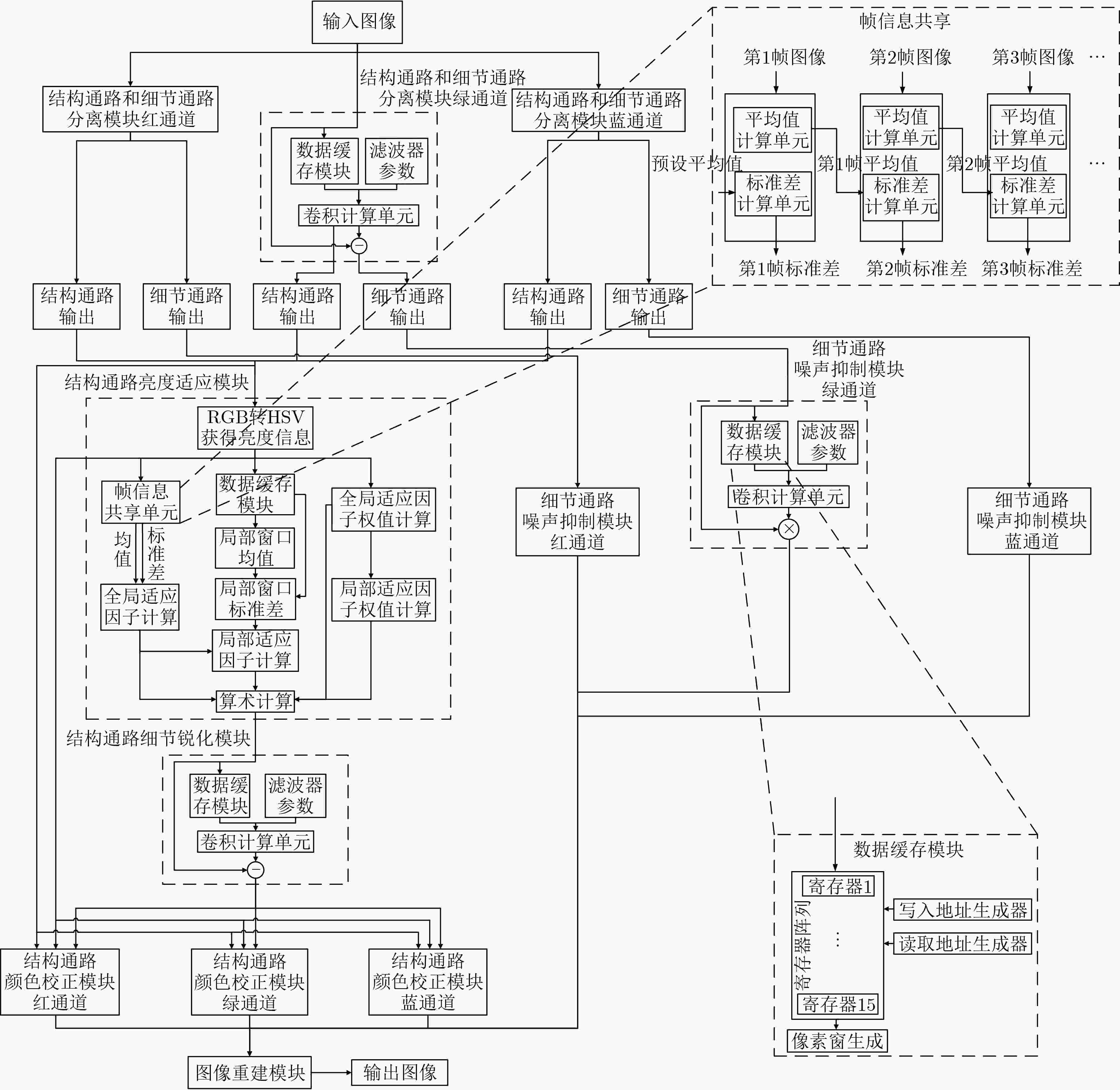
摘要: 该文基于现场可编程门阵列实现了受生物视觉机制启发的夜间图像增强模型,实时高效地对夜间低照度视频图像进行自适应增强。受初级视觉系统中大小细胞通路启发,该文采取独立的两条通路分别处理结构与细节信息,获得了较好的处理效果与处理效率。为了实现对高清视频的实时增强,基于现场可编程门阵列对该文算法进行了加速实现。通过滑动数据窗并行处理、相邻帧信息共享、多通道并行化等硬件设计保证高数据吞吐量。该设计在 XC7Z100现场可编程门阵列上达到对1080P@60 Hz彩色视频增强的实时性要求。与本领域已有设计相比,该文设计具有更高的数据吞吐量,适用于高分辨率实时图像增强应用。Abstract: A nighttime image enhancement model is proposed in this paper, which is inspired by biological vision mechanism and implemented on Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA) for real-time enhancement of low-light videos and images. Inspired by the Midget cells and the Parasol cells in the early visual system, the proposed method processes the structure and detail information through two independent pathways respectively, and obtains a nice effect and efficiency. To achieve real-time enhancement of high-resolution videos, this paper implements the proposed method on Field Programmable Gate Arrays. High data throughput is ensured through hardware design such as sliding data window parallel processing, adjacent frame information sharing, and multi-channel parallelization. Implemented on Field Programmable Gate Arrays XC7Z100, the proposed design achieves processing 60 frames per second for 1024 × 768 RGB images. Compared with existing designs in this field, the proposed design has higher data throughput and is suitable for high-resolution real-time image enhancement applications.
-
图 1 Yang等人[4]夜间图像增强模型的算法原理框架
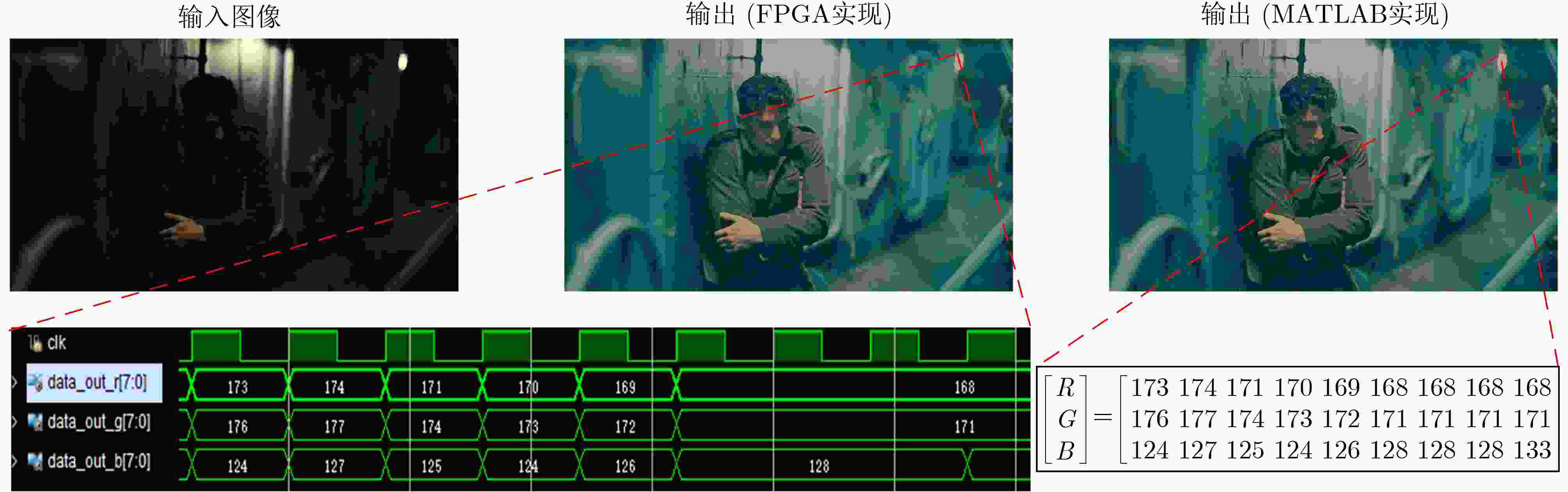
图 3 本文结果与文献[4]结果的比较
表 1 本文方法在LOL[10]图像库真实图像集上的测试结果
表 2 本文方法在SCIE[30]图像库真实图像集上的测试结果
表 3 夜间图像增强模型的FPGA实现的资源使用情况
资源 使用情况 使用率(%) 查找表 56673 20 查找表随机存取存储器 40604 38 块随机存取存储器 38 5 数字信号处理单元 7 1 输入和输出单元 108 30 区域时钟缓冲器 10 31 混合模式时钟管理器 4 50 锁相环 1 13 -
[1] 陈勇, 陈东, 刘焕淋, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的无参考低照度图像增强[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 2166–2174. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210386CHEN Yong, CHEN Dong, LIU Huanlin, et al. Unreferenced low-lighting image enhancement based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 2166–2174. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210386 [2] VELUCHAMY M, BHANDARI A K, and SUBRAMANI B. Optimized bezier curve based intensity mapping scheme for low light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2022, 6(3): 602–612. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2021.3053253 [3] KIM W. Low-light image enhancement: a comparative review and prospects[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 84535–84557. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3197629 [4] YANG Kaifu, ZHANG Xianshi, and LI Yongjie. A biological vision inspired framework for image enhancement in poor visibility conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 1493–1506. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2938310 [5] 向森, 王应锋, 邓慧萍, 等. 基于双重迭代的零样本低照度图像增强[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3379–3388. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211593XIANG Sen, WANG Yingfeng, DENG Huiping, et al. Zero-shot learning for low-light image enhancement based on dual iteration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3379–3388. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211593 [6] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, HAN Linghao, et al. Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 9396–9416. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3126387 [7] LI Mading, LIU Jiaying, YANG Wenhan, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828–2841. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539 [8] JIANG Xuesong, YAO Hongxun, and LIU Dilin. Nighttime image enhancement based on image decomposition[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2019, 13(1): 189–197. doi: 10.1007/s11760-018-1345-2 [9] GUO Xiaojie, LI Yu, and LING Haibin. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982–993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450 [10] YANG Wenhan, WANG Wenjing, HUANG Haofeng, et al. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2072–2086. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3050850 [11] ZHANG Yonghua, GUO Xiaojie, MA jiayi, et al. Beyond brightening low-light images[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(4): 1013–1037. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01407-x [12] LIU Risheng, MA Long, ZHANG Jiaao, et al. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10556–10565. [13] MA Long, LIU Risheng, WANG Yiyang, et al. Low-light image enhancement via self-reinforced retinex projection model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, To be published. [14] GUO Xiaojie and HU Qiming. Low-light image enhancement via breaking down the darkness[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131(1): 48–66. doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01667-9 [15] ZHANG Xianshi, YANG Kaifu, ZHOU Jun, et al. Retina inspired tone mapping method for high dynamic range images[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(5): 5953–5964. doi: 10.1364/OE.380555 [16] YANG Kaifu, CHENG Cheng, ZHAO Shixuan, et al. Learning to adapt to light[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131(4): 1022–1041. doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01745-y [17] LIU Xiaokai, MA Weihao, MA Xiaorui, et al. LAE-Net: A locally-adaptive embedding network for low-light image enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 133: 109039. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109039 [18] HAI Jiang, XUAN Zhu, YANG Ren, et al. R2RNet: Low-light image enhancement via real-low to real-normal network[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2023, 90: 103712. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2022.103712 [19] WU Yuhui, PAN Chen, WANG Guoqing, et al. Learning semantic-aware knowledge guidance for low-light image enhancement[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023. [20] FUTSCHIK D, RITLAND K, VECORE J, et al. Controllable light diffusion for portraits[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023. [21] UREÑA R, MARTÍNEZ-CAÑADA P, GÓMEZ-LÓPEZ J M, et al. Real-time tone mapping on GPU and FPGA[J]. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing, 2012, 2012: 1. doi: 10.1186/1687-5281-2012-1 [22] LAPRAY P J, HEYRMAN B, and GINHAC D. HDR-ARtiSt: An adaptive real-time smart camera for high dynamic range imaging[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2016, 12(4): 747–762. doi: 10.1007/s11554-013-0393-7 [23] CAÑADA P M, MORILLAS C, UREÑA R, et al. Embedded system for contrast enhancement in low-vision[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2013, 59(1): 30–38. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2012.10.005 [24] JOSEPH L M I L and RAJARAJAN S. Reconfigurable hybrid vision enhancement system using tone mapping and adaptive gamma correction algorithm for night surveillance robot[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(5): 6013–6032. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6321-x [25] AMBALATHANKANDY P, IKEBE M, YOSHIDA T, et al. An adaptive global and local tone mapping algorithm implemented on FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(9): 3015–3028. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2931510 [26] YANG Jie, HORE A, and YADID-PECHT O. Local tone mapping algorithm and hardware implementation[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(9): 560–562. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.3227 [27] SHAHNOVICH U, HORE A, and YADID-PECHT O. Hardware implementation of a real-time tone mapping algorithm based on a mantissa-exponent representation[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2016: 2210–2213. [28] AMBALATHANKANDY P, HORÉ A, and YADID-PECHT O. An FPGA implementation of a tone mapping algorithm with a halo-reducing filter[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2019, 16(4): 1317–1333. doi: 10.1007/s11554-016-0635-6 [29] FAIRCHILD M D. Seeing, adapting to, and reproducing the appearance of nature[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(4): B107–B116. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.00B107 [30] CAI Jianrui, GU Shuhang, and ZHANG Lei. Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 2049–2062. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2794218 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
