True Digital Ortho Maps Production for Target Structure Information of SAR Remote Sensing Images
-
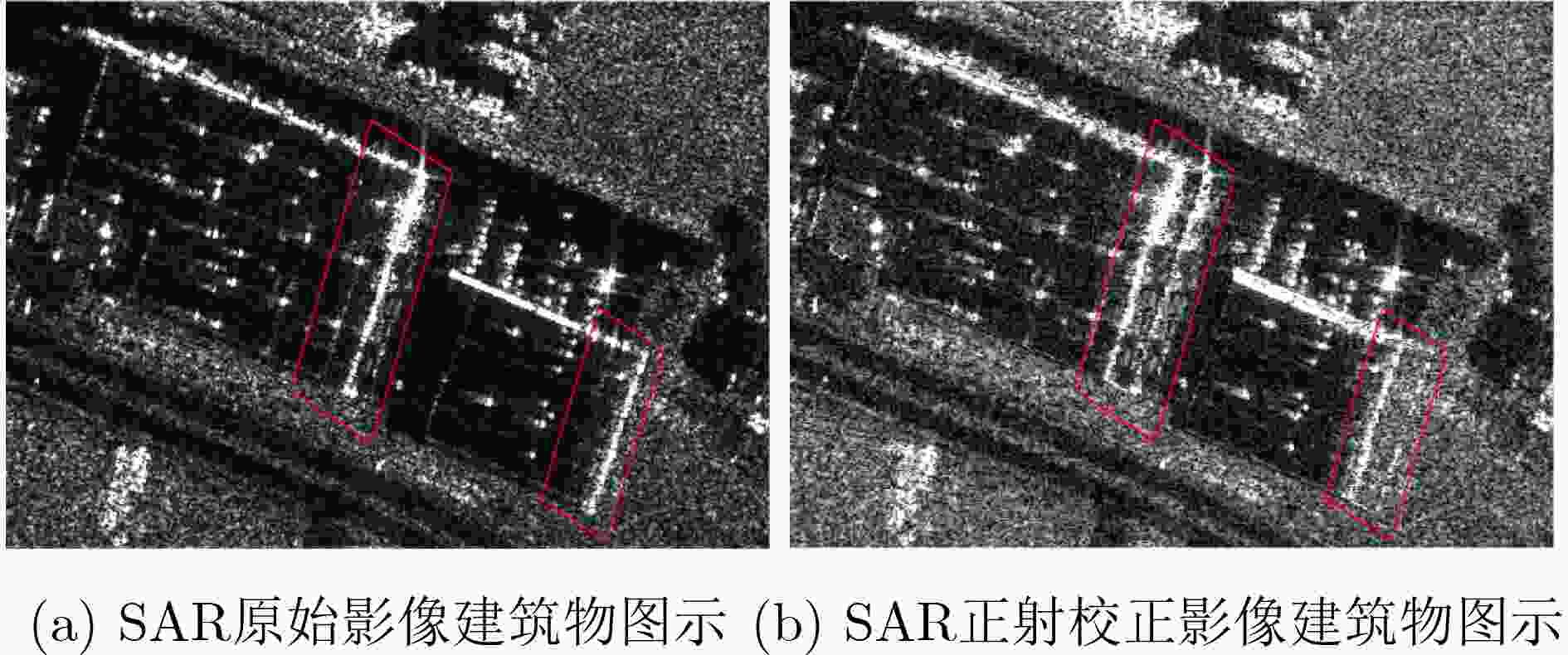
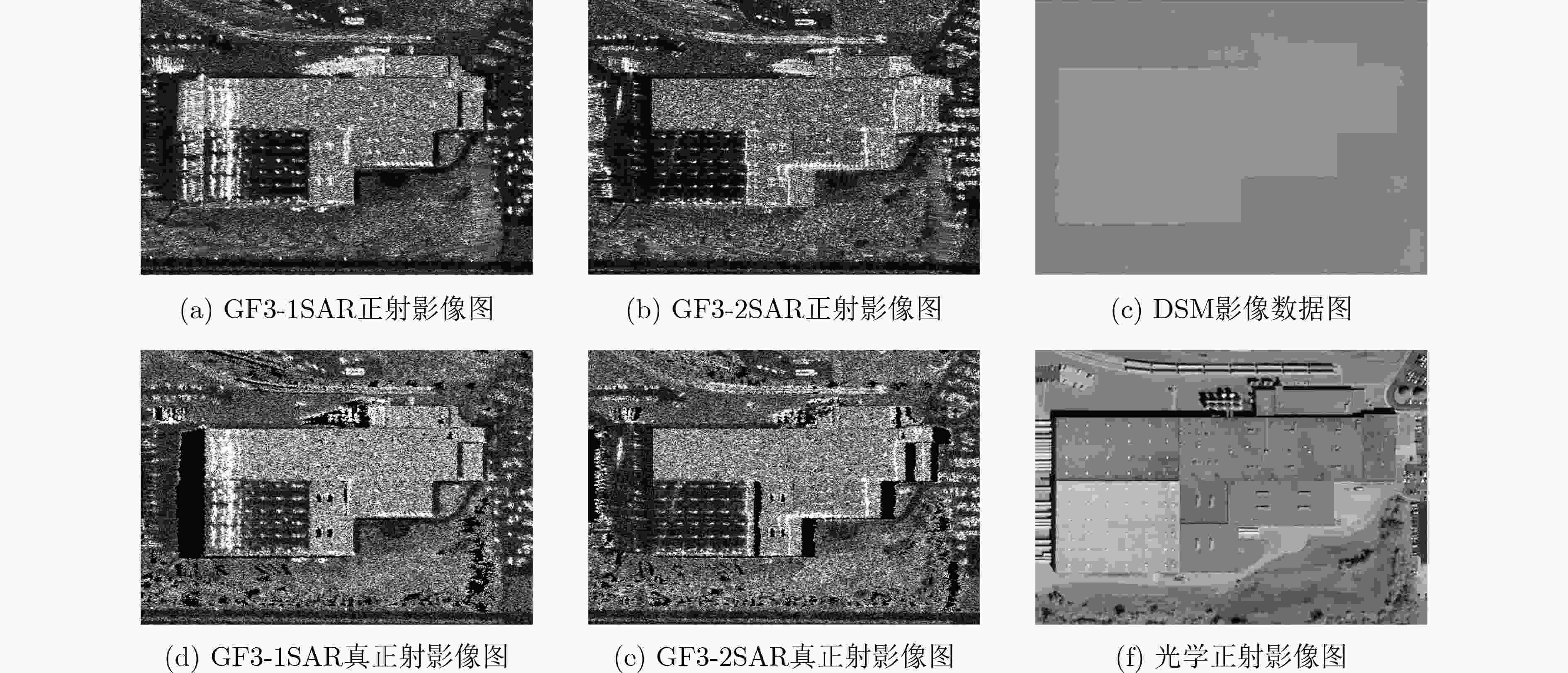
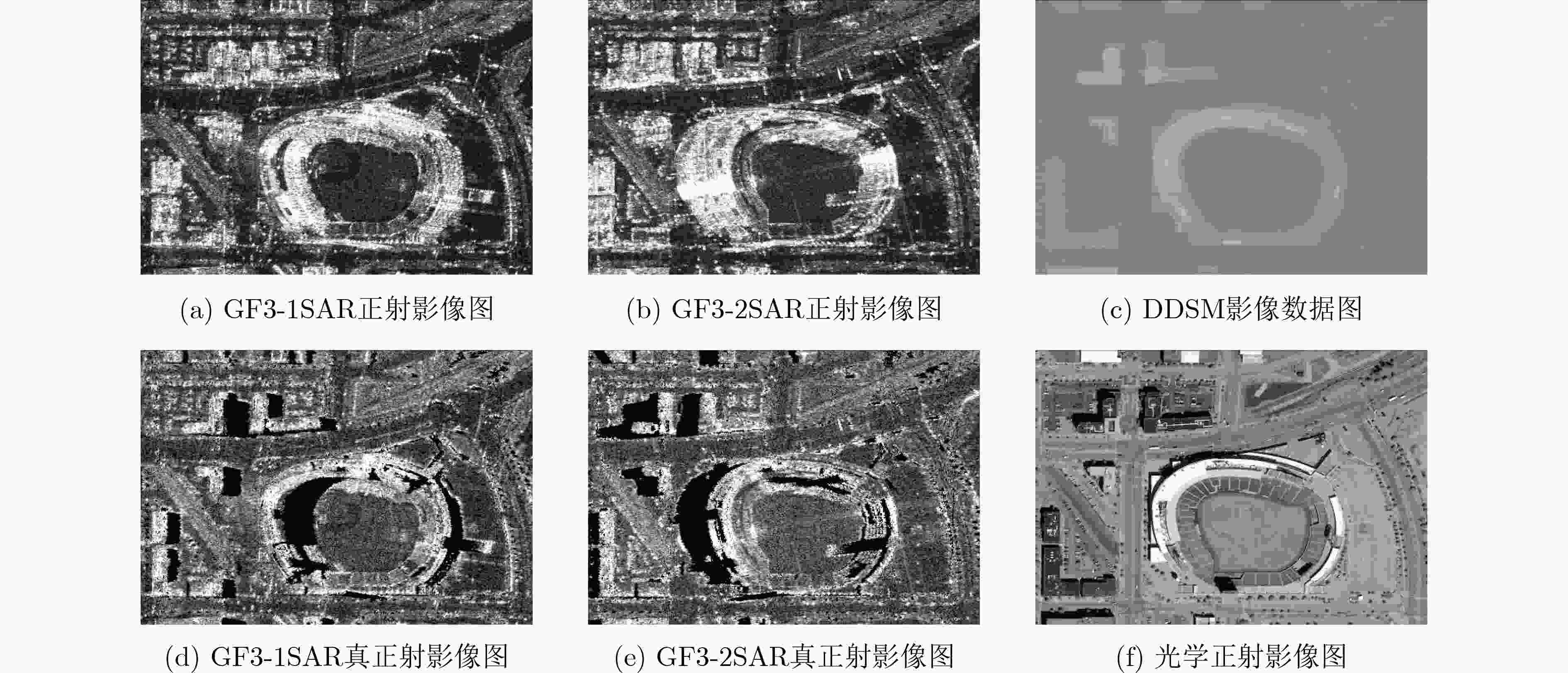
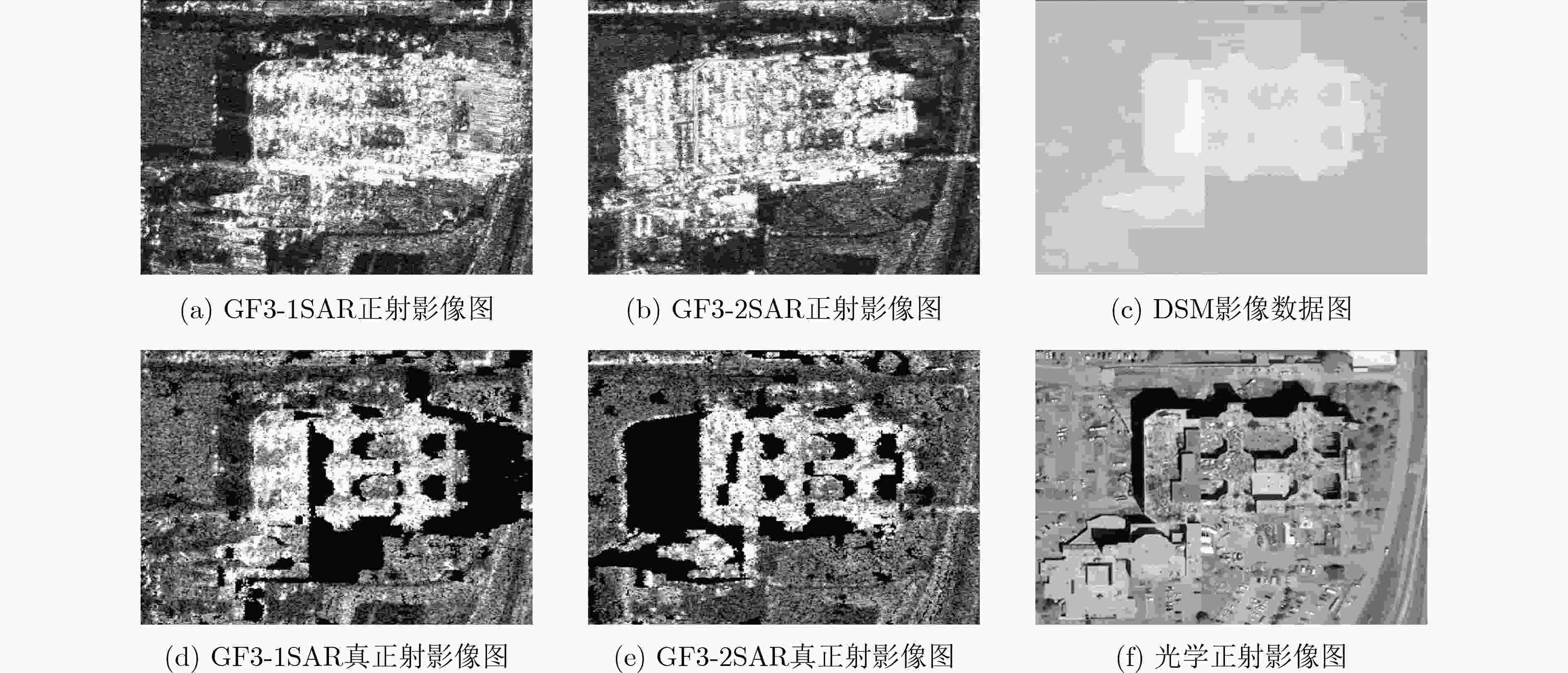
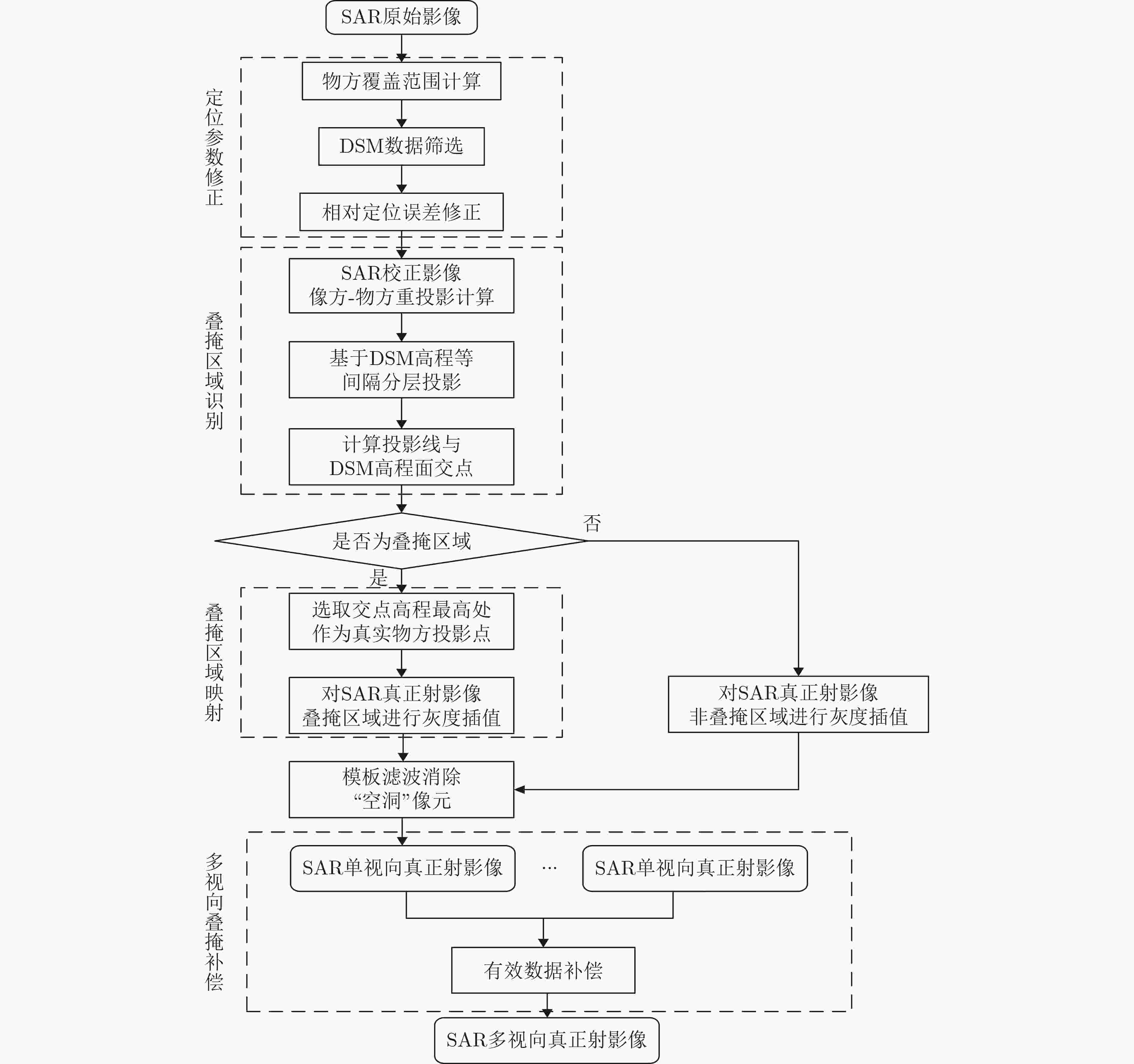
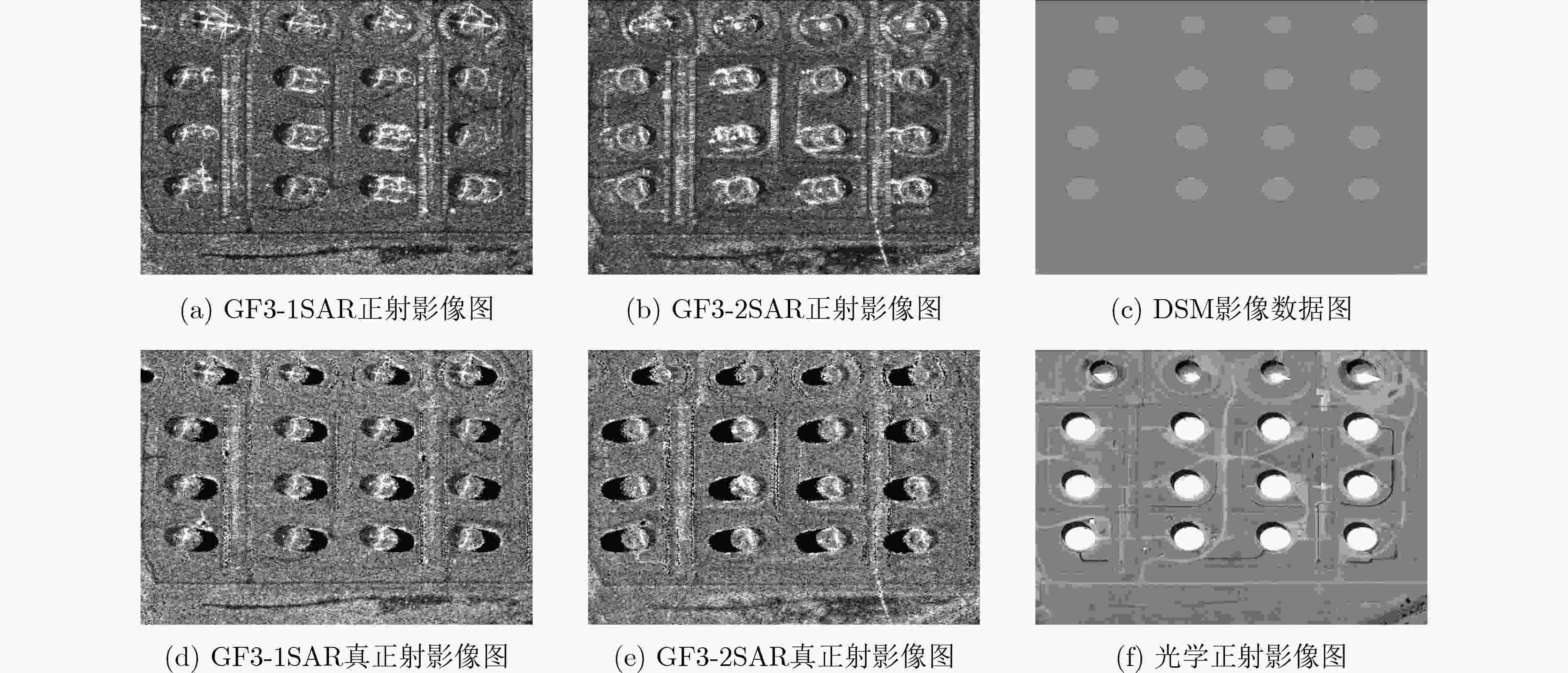
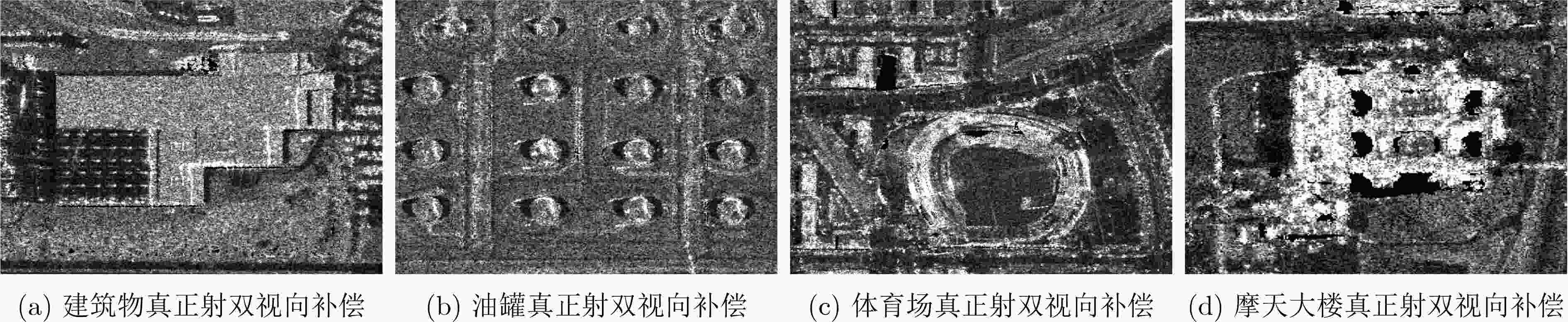
摘要: SAR遥感影像中的几何结构信息对于目标识别和判读具有十分重要的意义。现有SAR遥感影像的正射校正方法沿用光学正射影像(DOM)的校正思路,直接利用物方-像方采样进行,SAR遥感影像叠掩现象所引起的几何畸变会对目标结构信息提取造成干扰。针对以上问题,该文提出一种面向目标结构信息保持的SAR真正射影像(TDOM)制作方法,基于高精度数字表面模型(DSM),通过像方-物方反投影提取像方影像中的叠掩区域;然后,针对叠掩区域进行多高程面投影拟合分析,将雷达波与物方高程最高处的交点作为真实物方投影点,生成单视向SAR真正射影像;最后,利用不同视向的SAR真正射影像进行缺失信息补偿,得到融合后的多视向SAR真正射影像。以高分三号SAR影像作为研究对象,实验结果表明,相比于传统SAR正射影像,该文所提方法能够更好地保持目标结构信息,有效提升处理后SAR影像的目标识别和判读能力。Abstract: The restoration of geometric structural information in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) remote sensing images is of great significance for target recognition and interpretation. Existed Digital Ortho Map (DOM) production methods for SAR images follow the traditional ortho-rectification methods of optical images. The application of directly object image sampling can not eliminate the geometric distortion caused by the layovers of SAR remote sensing images. Therefore, a method for the production of SAR True Digital Ortho Map (TDOM) is proposed in this paper. With the help of high-precision Digital Surface Model (DSM) data, the layover area is extracted through the back-projection from image-space to object-space. The highest intersection of the DSM and the back-projected lines are considered as the object mapping of the coordinates in layover area to generate the single-view SAR TDOM. Finally, single-view SAR TDOMs are fused together for information compensation, and the multi-view SAR TDOM is produced with multiple information. Images obtained from the GF-3 SAR satellite are experimented, and the results indicate that the structural information of the target in the TDOMs produced by the proposed method is more clearly than traditional produced DOMs. The application of the proposed method can effectively improve the efficiency of target recognition and interpretation in SAR images.
-
表 1 SAR影像详情表
序号 成像模式 分辨率(m) 入射角(°) 升降轨 左右视 平均高程(m) 标称分辨率(m) 方位向 距离向 GF3-1 聚束模式 0.33 0.56 31.77 降轨 右视 296 1 GF3-2 聚束模式 0.31 0.56 27.17 升轨 右视 300 1 表 2 SAR影像相对校正前后定位误差统计表(m)
控制点编号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 RMSE GF3-1 校正前 38.65 37.92 39.23 38.71 38.66 39.47 39.88 36.95 37.48 39.12 38.62 校正后 0.76 0.64 0.96 0.63 0.95 0.82 1.06 0.77 0.86 0.99 0.86 GF3-2 校正前 33.14 34.26 35.11 36.25 35.77 34.92 36.28 37.39 34.21 35.72 35.32 校正后 0.58 0.69 0.93 0.97 0.84 0.92 0.88 0.83 0.91 1.04 0.87 -
[1] SHEN Shengyu, CHEN Jiasheng, ZHANG Shaoyi, et al. Deep fusion of DOM and DSM features for benggang discovery[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2021, 10(8): 556. doi: 10.3390/ijgi10080556 [2] WANG Chen and GU Yanfeng. A method for generating true digital orthophoto map of UAV platform push-broom hyperspectral scanners assisted by lidar[C]. 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 7523–7526. [3] DU Shuhan, ZHENG Fengjie, CHEN Xiangning, et al. Research on a true digital orthophoto map generation technology based on 3D point cloud geometry[C]. SPIE 12155, International Conference on Computer Vision, Application, and Design, Sanya, China, 2021, 1215516. [4] HÖHLE J. Automated mapping of buildings through classification of DSM-based ortho-images and cartographic enhancement[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2021, 95: 102237. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2020.102237 [5] AMHAR F, JANSA J, and RIES C. The generation of true orthophotos using a 3D building model in conjunction with a conventional DTM[J]. International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 1998, 32(4): 16–22. [6] HABIB A F, KIM E M, and KIM C J. New methodologies for true orthophoto generation[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2007, 73(1): 25–36. doi: 10.14358/PERS.73.1.25 [7] BAND K I, HABIB A F, SHIN S W, et al. Comparative analysis of alternative methodologies for true ortho-photo generation from high resolution satellite imagery[C]. ASPRS Annual Conference 2007, Tampa, USA, 2007: 34–45. [8] DENG Xingsheng, TANG Guo, WANG Qingyang, et al. A method for forest vegetation height modeling based on aerial digital orthophoto map and digital surface model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 4404307. [9] 刘佳音, 韩冰, 洪文. 一种新的SAR图像斜距多普勒定位模型的直接解法[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2012, 27(5): 716–721. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2012.5.716LIU Jiayin, HAN Bing, and HONG Wen. A new direct solution of range-doppler model for SAR image[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2012, 27(5): 716–721. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2012.5.716 [10] 黄志杨, 曹永锋. 基于影像模拟的多山地区SAR影像正射校正[J]. 现代计算机, 2015(36): 21–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2015.36.005HUANG Zhiyang and CAO Yongfeng. Ortho-rectification of mountain region SAR image based on image simulation[J]. Modern Computer, 2015(36): 21–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2015.36.005 [11] 万紫, 邵芸, 谢酬, 等. 基于RADARSAT-2数据的SAR图像双视向几何校正方法研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2011, 30(2): 167–172.WAN Zi, SHAO Yun, XIE Chou, et al. The dual-aspect geometric correction method based on DEM using Radarsat-2 data[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2011, 30(2): 167–172. [12] ZHANG J X, WEI J, HUANG G, et al. Fusion of ascending and descending polarimetric SAR data for colour Orthophoto generation[C]. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Vienna, Austria, 2010: 323–328. [13] SANSOSTI E, BERARDINO P, MANUNTA M, et al. Geometrical SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(10): 2861–2870. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.875787 [14] 陈晓轩, 周荣荣, 丁明涛, 等. 基于模拟影像的山地SAR影像配准方法研究[J]. 河南科学, 2019, 37(1): 86–92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2019.01.015CHEN Xiaoxuan, ZHOU Rongrong, DING Mingtao, et al. The registration method of mountainous SAR image based on simulated image[J]. Henan Science, 2019, 37(1): 86–92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2019.01.015 [15] ARAI K. Ground control point generation from simulated sar image derived from digital terrain model and its application to texture feature extraction[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2021, 12(1): 89–94. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2021.0120112 -





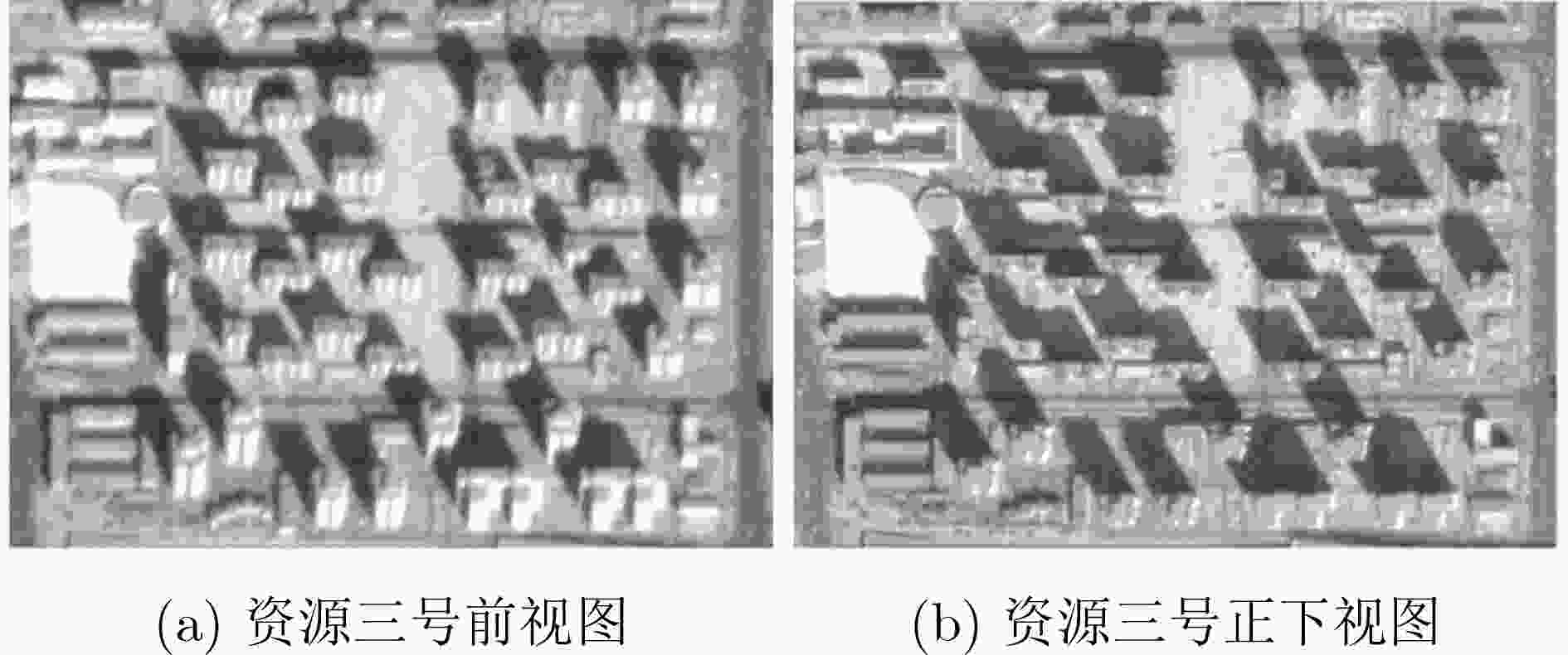
 下载:
下载:



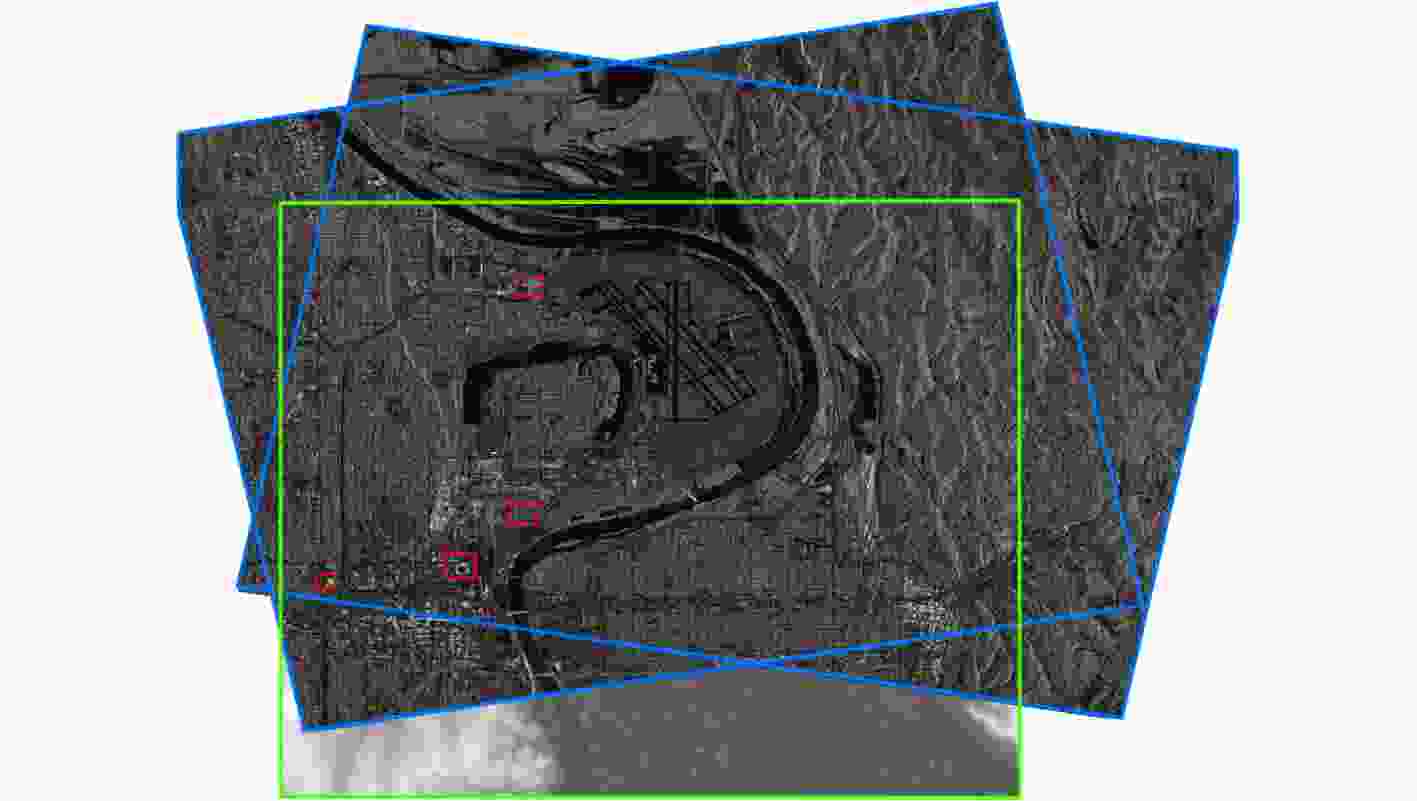
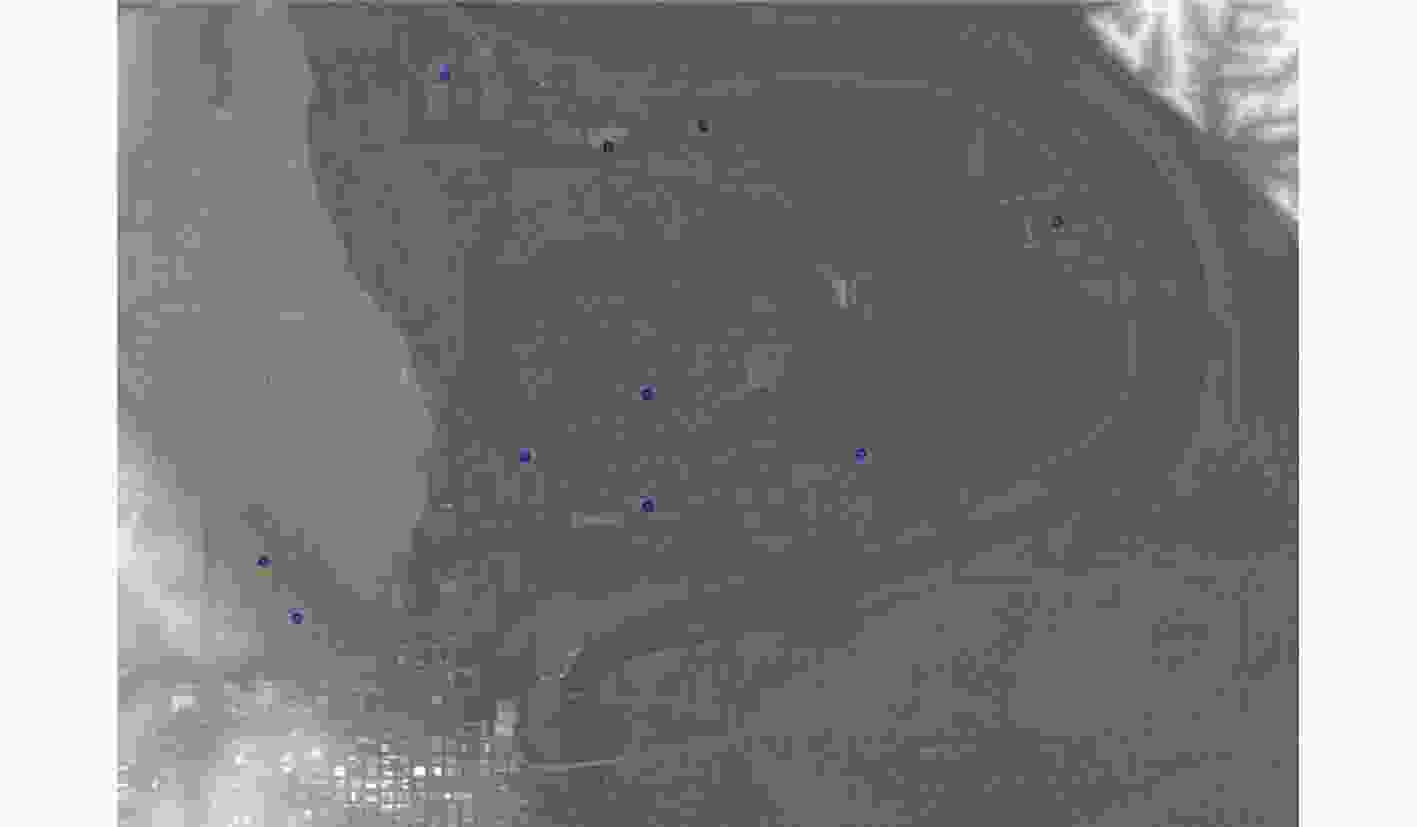





 下载:
下载:
