An Encryption Algorithm Based on Optical Chaos and Image Quotient and Residue Preprocessing
-
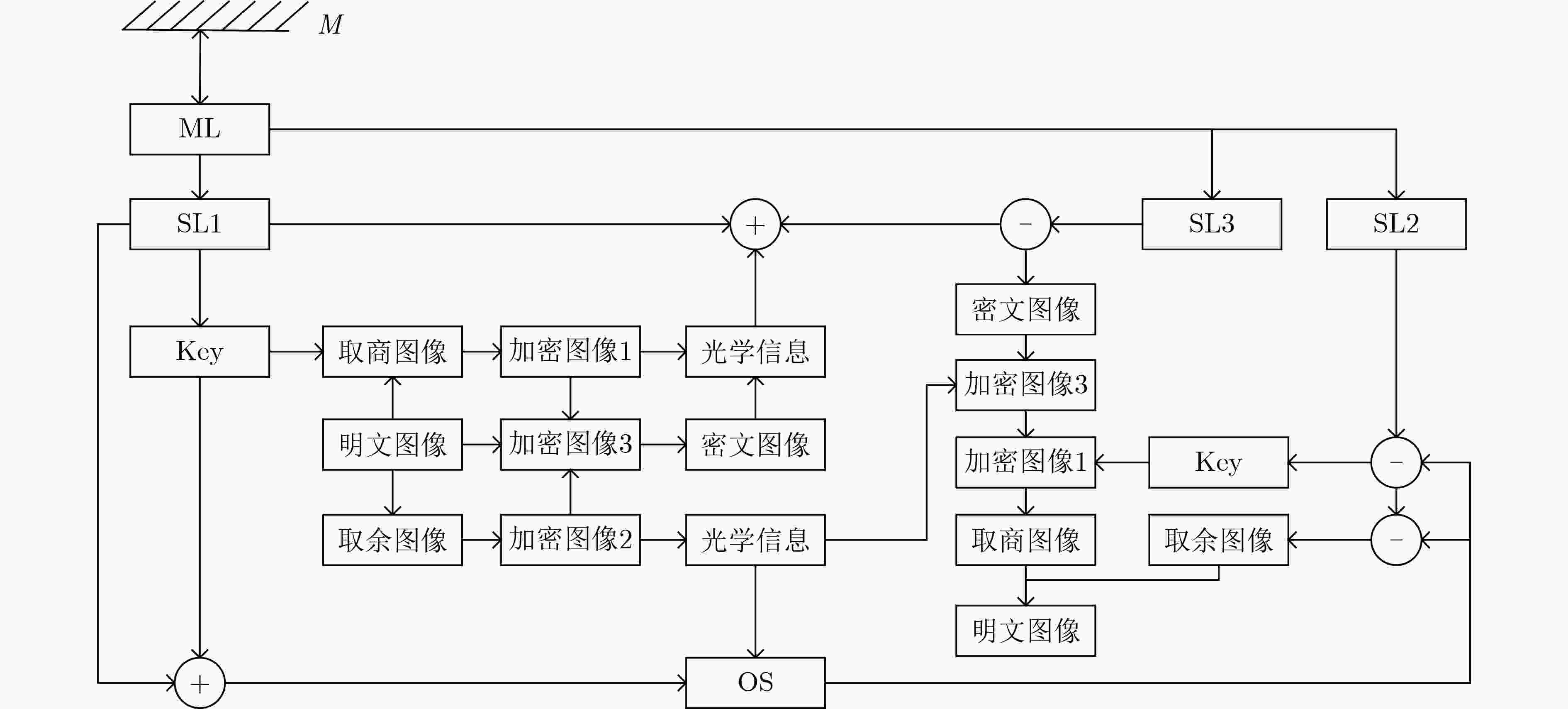
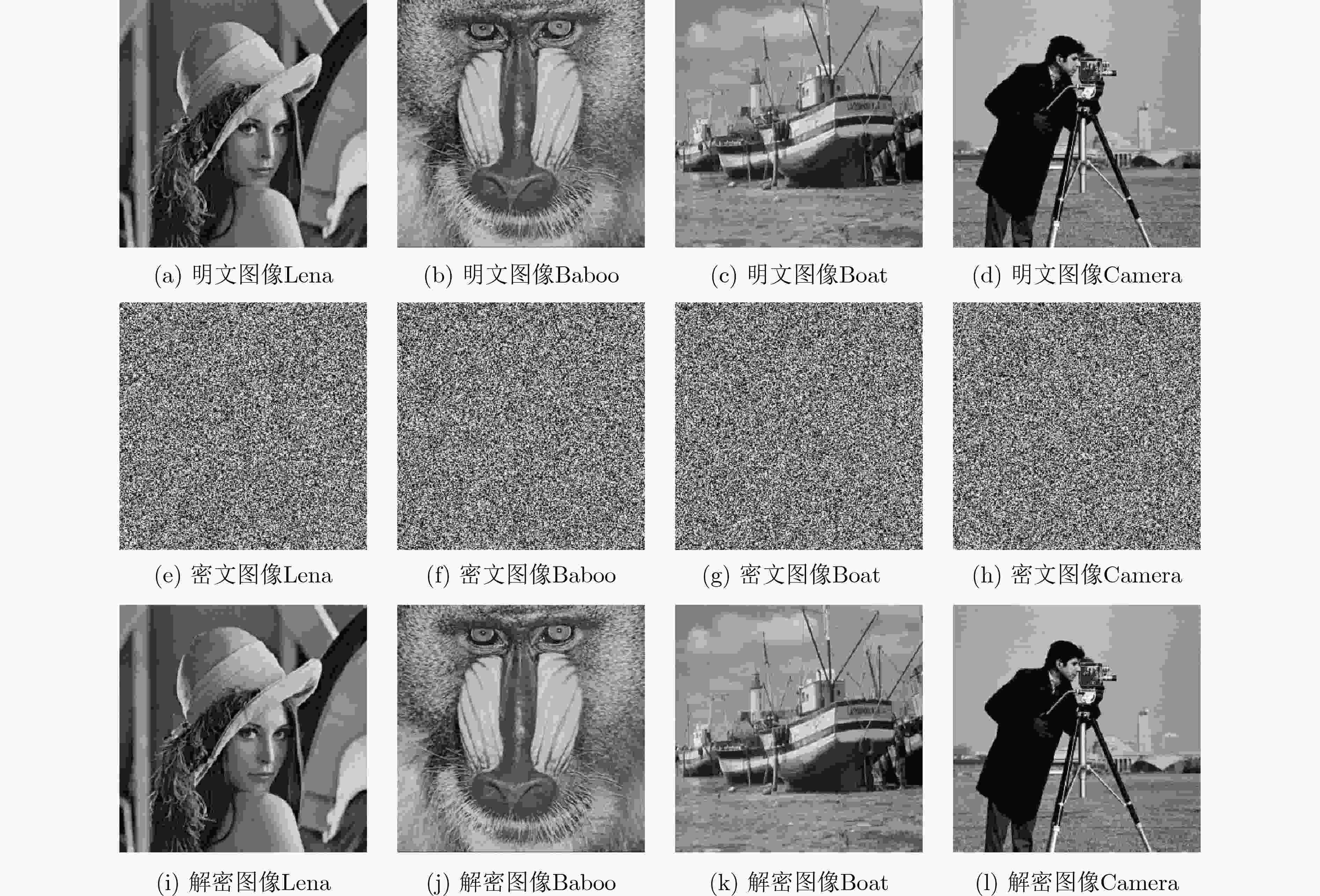
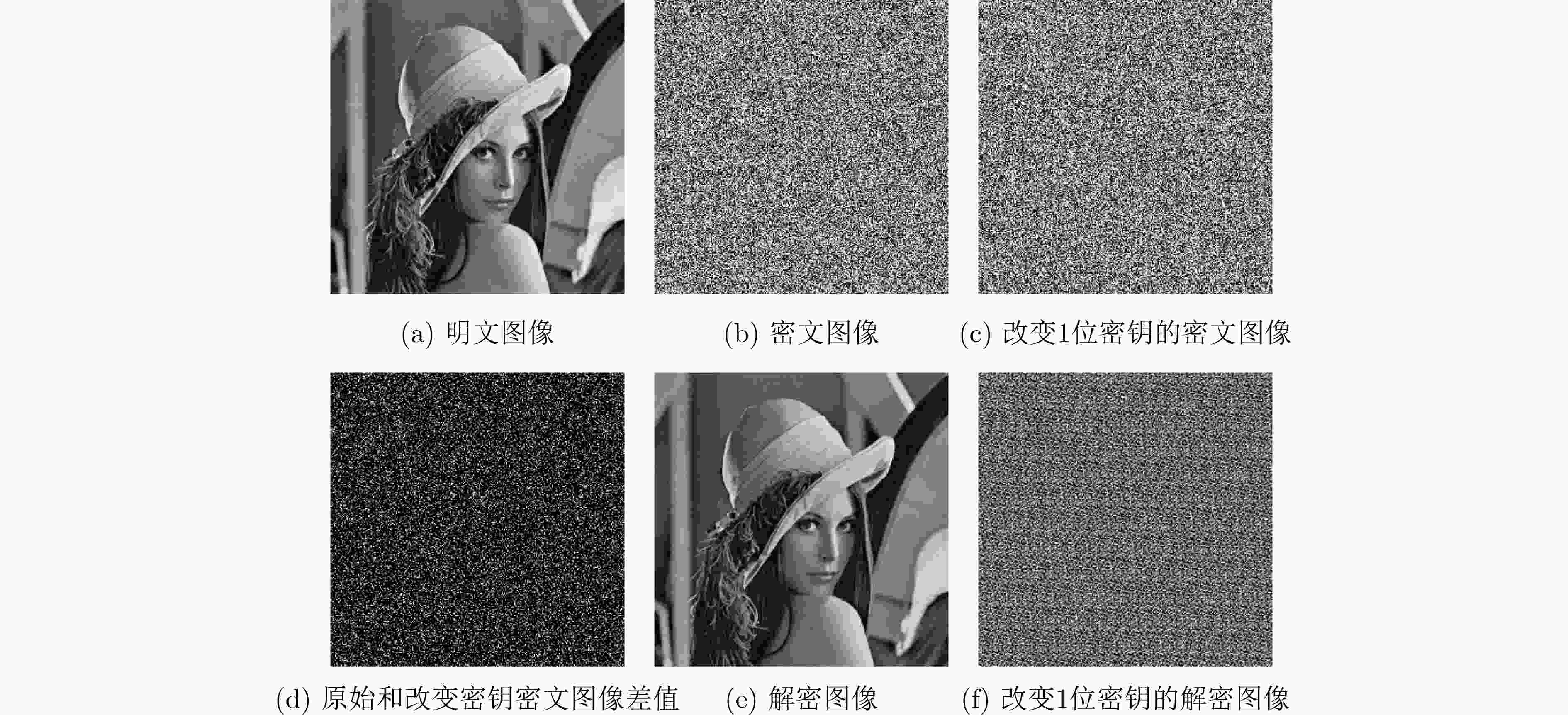
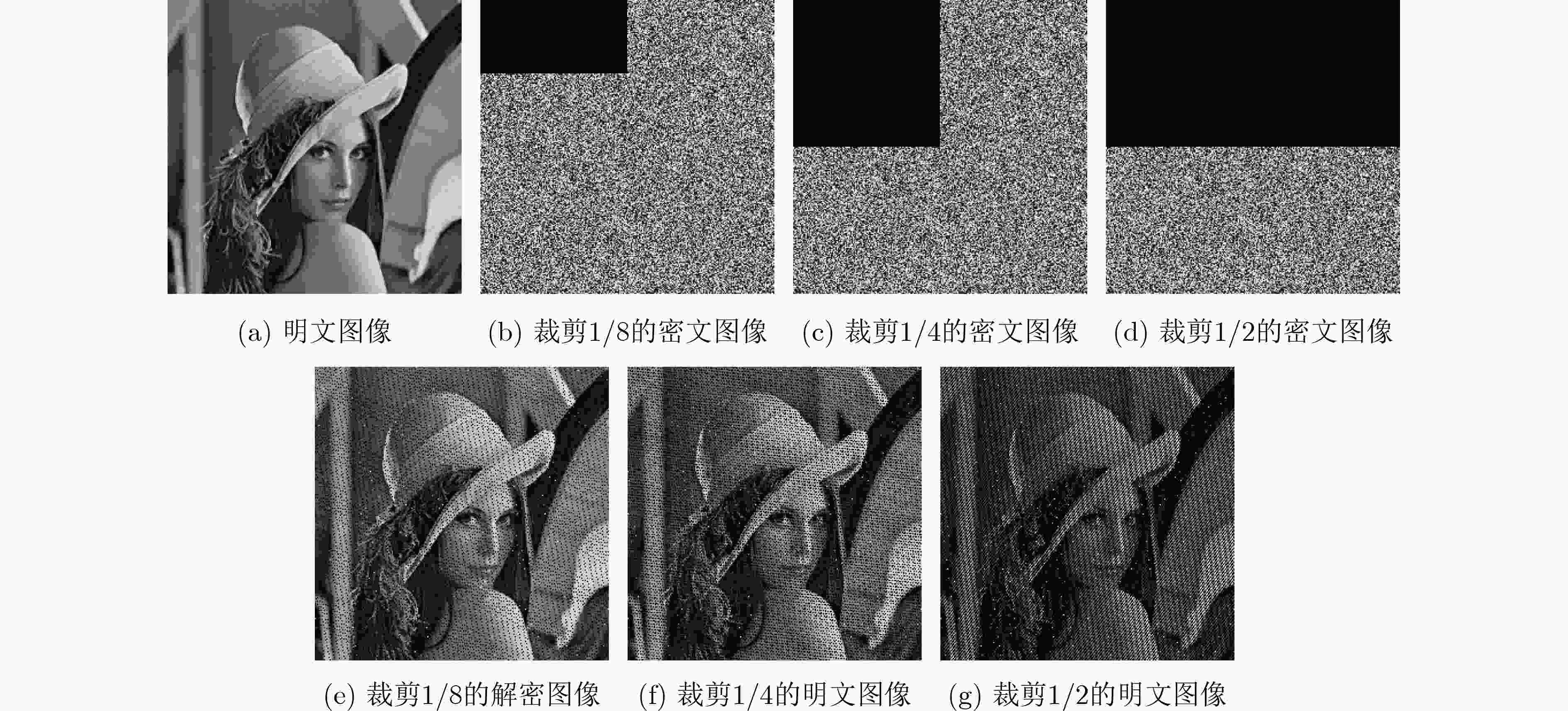
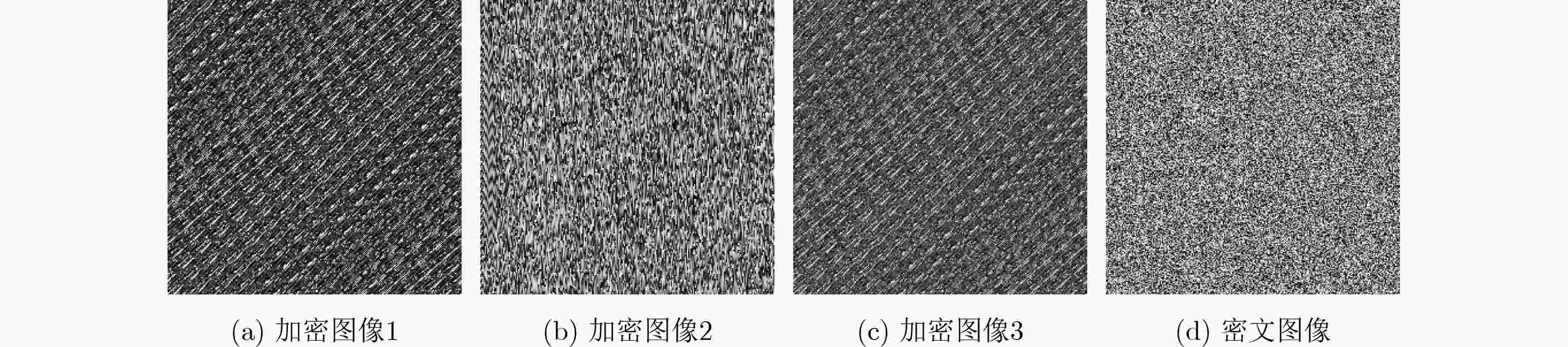
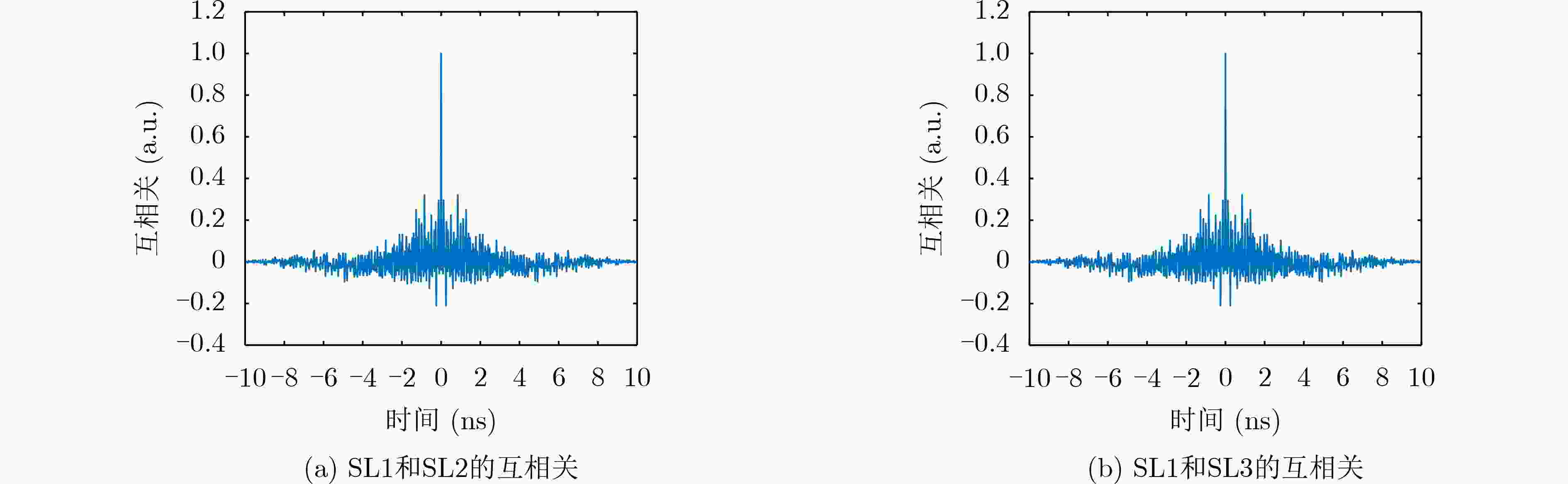
摘要: 随着现代科学技术的发展,人们对图像信息传输的安全性要求越来越高,以混沌理论为基础的图像加密方案更加受到重视。该文提出一种新型的光混沌图像加密传输系统以及图像“自加密”算法,该系统的主激光器(ML)经全光反馈后分别注入到3个半导体激光器(SLs)中,从而产生3个同步的混沌序列。在图像加密之前,先对明文图像进行预处理,得到两幅图像,一幅是明文图像取商的图像,另一幅是明文图像取余的图像。利用发送端的混沌序列对预处理的两幅图像进行多次加密、隐写以及扩散等操作,得到密文图像。实验结果表明:该文的密文图像像素值分布均匀,各像素间的相关性被打破,NPCR和UACI均接近理想值。该图像预处理的方法能够有效地使图像像素值更为集中、分布更加均匀,同时结合光混沌对图像进行加密,大大地提高传输图像的安全性。Abstract: With the development of modern science and technology, people have higher and higher requirements for the security of image information transmission, and the image encryption scheme based on chaos theory has attracted more and more attention. In this paper, a novel optical chaotic image encryption transmission system and a “self-encryption” algorithm for images are proposed and demonstrated. The Master Laser (ML) of the system is injected into the other three Semiconductor Lasers (SLs) respectively after full-optical feedback, then three synchronous chaotic sequences are generated. Before encrypting the image, the plaintext image is preprocessed, and two images are obtained, one is the image after the quotient of the plain image, the other is the image after the redundancy of the plain image. The chaotic sequence of the sender is used to encrypt, steganograph and spread the two preprocessed images for many times, and then the ciphertext image is obtained. The experimental results show that the pixel values of the ciphertext images obtained in this paper are evenly distributed, the correlation between each pixel is broken, and both NPCR and UACI are close to the ideal value. The image preprocessing method proposed in this paper can effectively make the image pixel value more concentrated, more uniform distribution. Combining with the optical chaos to encrypt the image, it greatly improves the security of the transmitted image.
-
Key words:
- Semiconductor Laser (SL) /
- Optical chaos /
- Image encryption /
- Image processing
-
表 1 激光器的参数
参数 数值 参数 数值 $ \partial $ 3 $ {C} $ 3×108 $ {{K}_{f}} $ 30 ns $ {g} $ 1.2×10–5 $ {\tau _{f}} $ 1.2 ns $ {{N}_0} $ 1.25×108 $ {{K}_{{inj}}} $ 50 $ {s} $ 5×10–7 ${{e} }$ 1.6×10–19 $ \gamma $ 496 $ {\gamma _{e}} $ 0.65 表 2 直方图检测
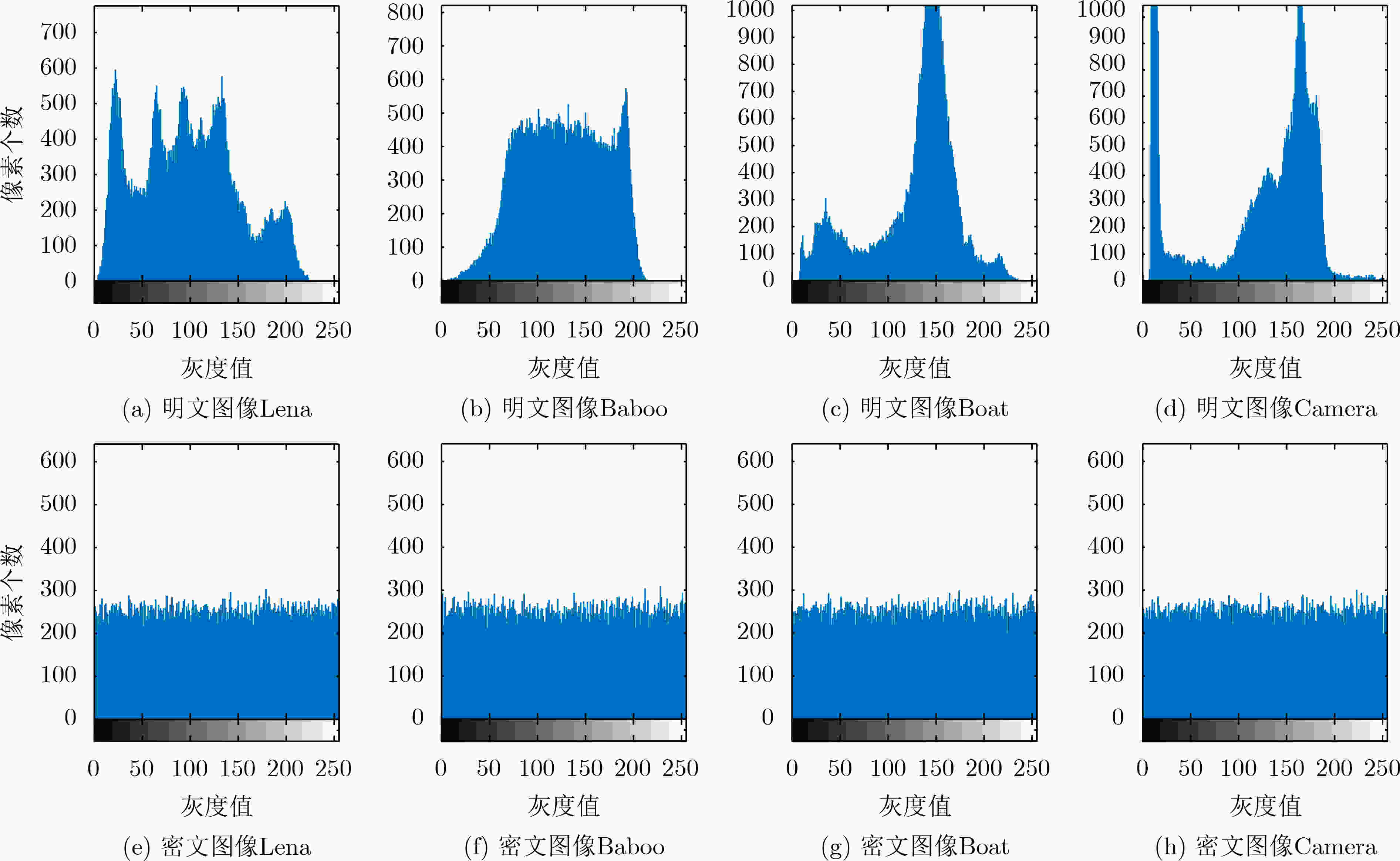
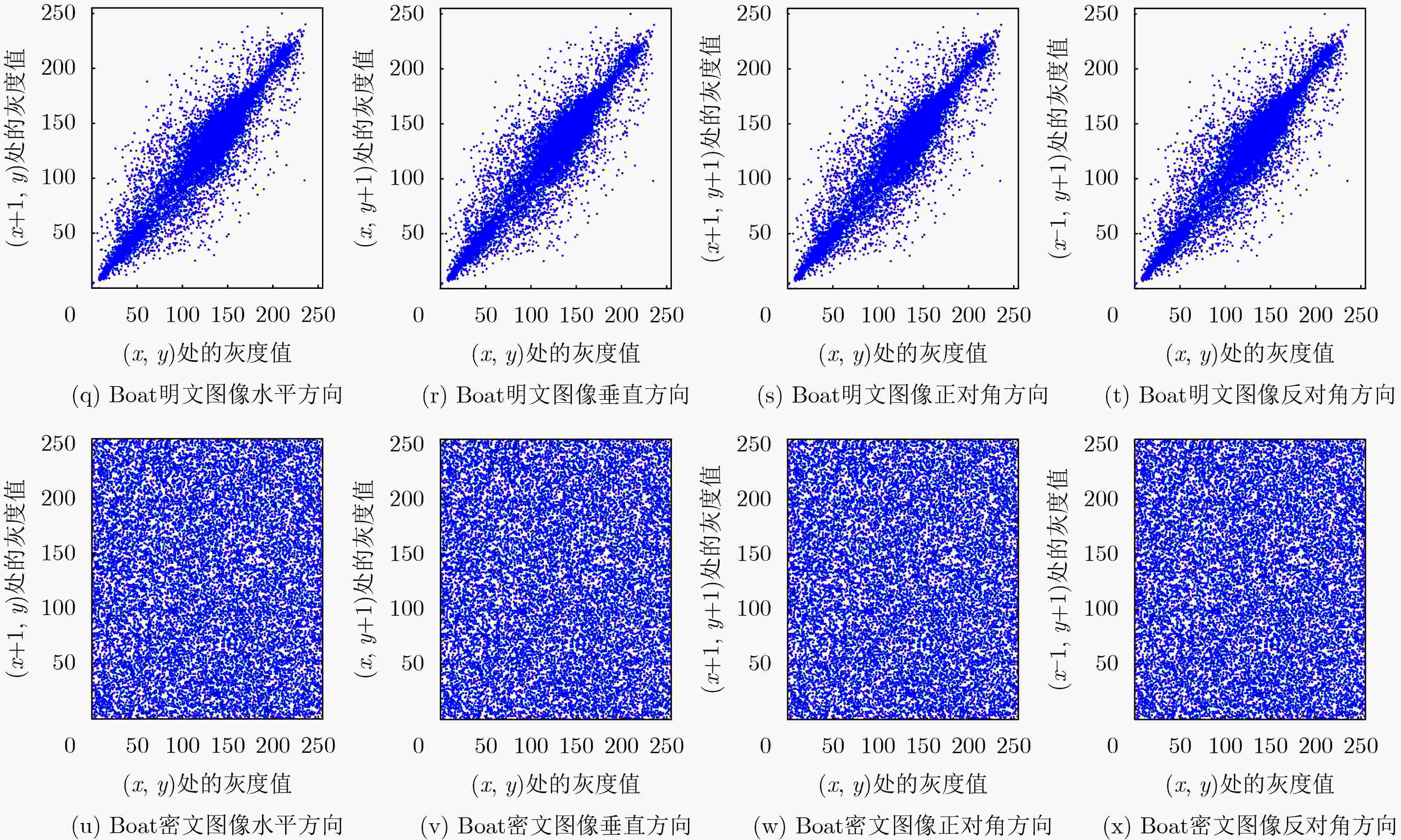
图像 $ \chi _{{\text{test}}}^2 $ 结果 明文Lena 30665.7031 不通过 密文Lena 243.7188 通过 明文Baboo 42256.0859 不通过 密文Baboo 232.8672 通过 明文Boat 100313.132 不通过 密文Boat 226.4297 通过 明文Camera 109020.992 不通过 密文Camera 247.4375 通过 表 3 相关性检测
表 4 不同图像的NPCR和UACI
-
[1] LORENZ E N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1963, 20(2): 130–141. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0130:DNF>2.0.CO;2 [2] 梁颖, 张绍武. 位级同步置乱扩散和像素级环形扩散图像加密算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(6): 814–826. doi: 10.11834/jig.170433LIANG Ying and ZHANG Shaowu. Image encryption algorithm based on bit-level synchronous permutation diffusion and pixel-level annular diffusion[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(6): 814–826. doi: 10.11834/jig.170433 [3] LIN Hairong, WANG Chunhua, CUI Li, et al. Brain-like initial-boosted hyperchaos and application in biomedical image encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(12): 8839–8850. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3155599 [4] JIANG Xiao, XIAO Ying, XIE Yiyuan, et al. Exploiting optical chaos for double images encryption with compressive sensing and double random phase encoding[J]. Optics Communications, 2021, 484: 126683. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126683 [5] HAKEN H. Analogy between higher instabilities in fluids and lasers[J]. Physics Letters A, 1975, 53(1): 77–78. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(75)90353-9 [6] 义理林, 柯俊翔. 混沌保密光通信研究进展[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(3): 168–181. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020008YI Lilin and KE Junxiang. Research progress of chaotic secure optical communication[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(3): 168–181. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020008 [7] 郑亮, 李秀玲, 王瑛剑. 半导体激光器混沌通信研究进展[J]. 光通信技术, 2020, 44(1): 1–5. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2020.01.001ZHENG Liang, LI Xiuling, and WANG Yingjian. Research progress on chaotic communication of semiconductor lasers[J]. Optical Communication Technology, 2020, 44(1): 1–5. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2020.01.001 [8] XIE Yiyuan, LI Jiachao, KONG Zhoufan, et al. Exploiting optics chaos for image encryption-then-transmission[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2016, 34(22): 5101–5109. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2606121 [9] SIVAPRAKASAM S and SHORE K A. Signal masking for chaotic optical communication using external-cavity diode lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 1999, 24(17): 1200–1202. doi: 10.1364/OL.24.001200 [10] FU Xingquan, LIU Bocheng, XIE Yiyuan, et al. Image encryption-then-transmission using DNA encryption algorithm and the double chaos[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2018, 10(3): 3900515. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2018.2827165 [11] LI Jiafu, XIANG Shuiying, WANG Haoning, et al. A novel image encryption algorithm based on synchronized random bit generated in cascade-coupled chaotic semiconductor ring lasers[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 102: 170–180. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.11.001 [12] WU Ting, LI Qiliang, BAO Xiaobin, et al. Time-delay signature concealment in chaotic secure communication system combining optical intensity with phase feedback[J]. Optics Communications, 2020, 475: 126042. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126042 [13] GHANBARI-GHALEHJOUGHI H, ESLAMI M, AHMADI-KANDJANI S, et al. Multiple layer encryption and steganography via multi-channel ghost imaging[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 134: 106227. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106227 [14] DONG Wenlong, LI Qiliang, and TANG Yiwen. Image encryption-then-transmission combining random sub-block scrambling and loop DNA algorithm in an optical chaotic system[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2021, 153: 111539. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111539 [15] LANG R and KOBAYASHI K. External optical feedback effects on semiconductor injection laser properties[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1980, 16(3): 347–355. doi: 10.1109/JQE.1980.1070479 [16] PETERS-FLYNN S, SPENCER P S, SIVAPRAKASAM S, et al. Identification of the optimum time-delay for chaos synchronization regimes of semiconductor lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2006, 42(4): 427–434. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2006.872312 [17] 刘劲杨, 周雪芳, 毕美华, 等. 光混沌保密通信系统在MATLAB与OptiSystem中的协同实现[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(9): 210146. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210146LIU Jinyang, ZHOU Xuefang, BI Meihua, et al. Co-simulation of optical chaotic secure communication systems in MATLAB and OptiSystem[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2021, 48(9): 210146. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210146 [18] LI Zhen, PENG Changgen, TAN Weijie, et al. An efficient plaintext-related chaotic image encryption scheme based on compressive sensing[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(3): 758. doi: 10.3390/S21030758 [19] SHA Yuwen, BO Sun, YANG Chenxiao, et al. A chaotic image encryption scheme based on genetic central dogma and KMP method[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2022, 32(12): 2250186. doi: 10.1142/S0218127422501863 [20] ZHAO Chaofeng and REN Haipeng. Image encryption based on hyper-chaotic multi-attractors[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2020, 100(1): 679–698. doi: 10.1007/s11071-020-05526-5 [21] HUA Zhongyun, ZHOU Yicong, PUN C M, et al. 2D Sine Logistic modulation map for image encryption[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 297: 80–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.11.018 [22] VIDHYA R and BRINDHA M. A novel dynamic chaotic image encryption using butterfly network topology based diffusion and decision based permutation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(41): 30281–30310. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-09462-9 [23] SEYEDZADEH S M and MIRZAKUCHAKI S. A fast color image encryption algorithm based on coupled two-dimensional piecewise chaotic map[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(5): 1202–1215. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.11.004 [24] SHI Hang, YAN Dengwei, WANG Lidan, et al. A novel memristor-based chaotic image encryption algorithm with Hash process and S-box[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2022, 231(3): 465–480. doi: 10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00365-w [25] KHAIRULLAH M K, ALKAHTANI A A, BIN BAHARUDDIN M Z, et al. Designing 1D chaotic maps for fast chaotic image encryption[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(17): 2116. doi: 10.3390/ELECTRONICS10172116 [26] ZHANG Xuncai, WU Tao, WANG Yanfeng, et al. A novel chaotic image encryption algorithm based on Latin square and random shift[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2021, 2021: 2091053. doi: 10.1155/2021/2091053 [27] YAN Xiaopeng, WANG Xingyuan, and XIAN Yongjin. Chaotic image encryption algorithm based on arithmetic sequence scrambling model and DNA encoding operation[J]. Multimedia Tools and applications, 2021, 80(7): 10949–10983. doi: 10.1007/S11042-020-10218-8 [28] VIDHYA R and BRINDHA M. A novel conditional butterfly network topology based chaotic image encryption[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2020, 52: 102484. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2020.102484 [29] WEN Wenying, HONG Yukun, FANG Yuming, et al. A visually secure image encryption scheme based on semi-tensor product compressed sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 173: 107580. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107580 [30] LI Ming, WANG Mengdie, FAN Haiju, et al. A novel plaintext-related chaotic image encryption scheme with no additional plaintext information[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2022, 158: 111989. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.111989 [31] ZHANG Xiaoqiang and YAN Xuangang. Adaptive chaotic image encryption algorithm based on RNA and pixel depth[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(15): 1770. doi: 10.3390/electronics10151770 [32] SHAKIBA A. A novel randomized bit-level two-dimensional hyperchaotic image encryption algorithm[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(43/44): 32575–32605. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-09434-z [33] CHENG Guangfeng, WANG Chunhua, and XU Cong. A novel hyper-chaotic image encryption scheme based on quantum genetic algorithm and compressive sensing[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(39/40): 29243–29263. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-09542-w -





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
