Optoelectronic Tweezers — A Versatile Micro/Nano Operation Technique
-
摘要: 光电镊(OET)是一种基于光致介电泳效应的微尺度光操控技术,可在流体场、光电场、生物力场耦合的复杂环境下对微小目标进行精准操控,在细胞操作、微机械系统等领域有着重要的应用。光电镊技术可以单独使用或与其他技术协同使用,应用十分广泛。迄今为止,基于光电镊的研究主要集中在:微纳米材料的操作、组装和合成;单个细胞/分子的操作、分离和分析;细胞固有特性的分析和获取;细胞的电穿孔、融合和裂解;细胞封装生物材料和生物结构的制备;流体传输的光流体器件的开发。这些工作展示了光电镊技术优越的性能和独特的通用性和灵活性。该文系统地介绍了光电镊技术的现有应用,总结了该技术的应用前景、局限性及发展趋势。Abstract: OptoElectronic Tweezer (OET) is a micro-scale optical manipulation technology based on photoinduced electrophoretic effect. It can accurately control small targets in the complex environment of fluid field, photoelectric field and biological force field, and has important applications to cell operation, micromechanical system and other fields. Optoelectronic tweezers technology can be used alone or in conjunction with other technologies, and has been widely used. To date, research based on optoelectronic tweezers has focused on manipulation, assembly, and synthesis of micro and nanomaterials; manipulation, isolation, and analysis of individual cells/molecules; analysis and acquisition of cell intrinsic properties; electroporation, fusion, and lysis of cells; preparation of cell-encapsulated biomaterials and biological structures; development of optical fluid devices for fluid transport. These works demonstrate the superior performance and unique versatility and flexibility of the optoelectronic tweezers technology. The existing application of optoelectronic tweezers technology are systematically presented in the paper and the application prospect, limitation and development trend of this technology are summarised.
-
Key words:
- Optical manipulation /
- Micromachine /
- Optoelectronic tweezers /
- Micromanipulation /
- Dielectrophoresis
-
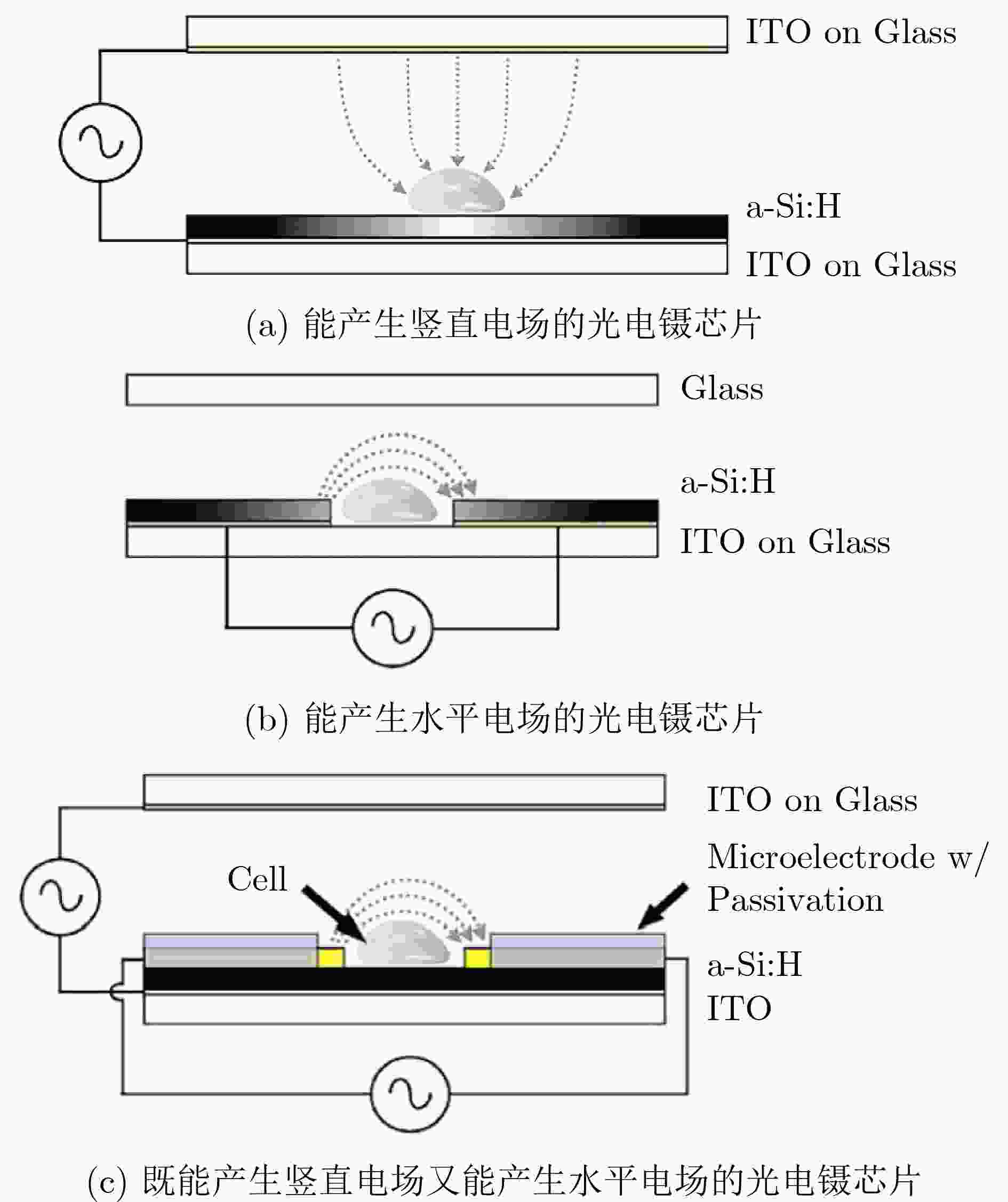
图 1 3种光电镊设备[10]
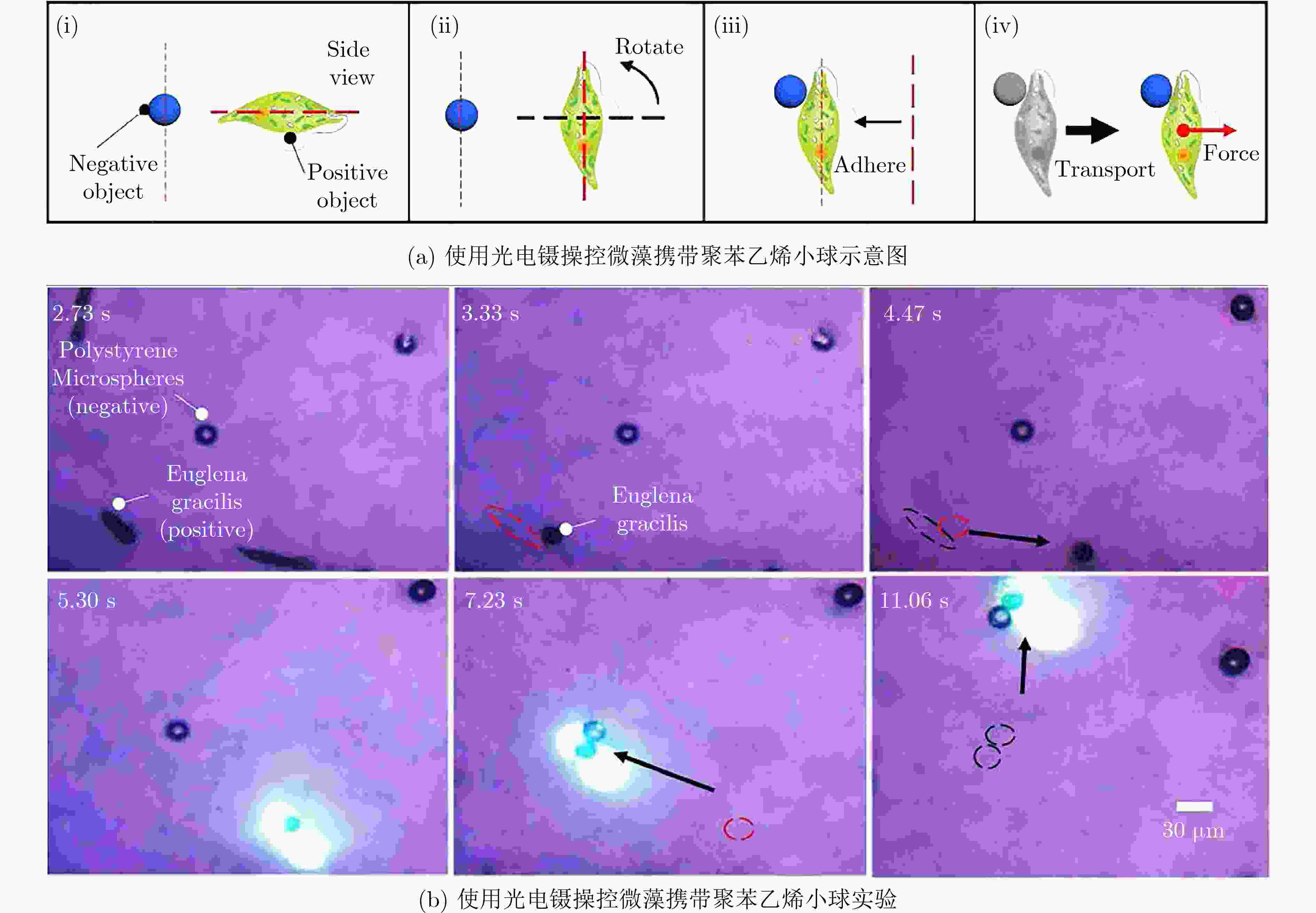
图 2 使用微生物运输微小物体[11]
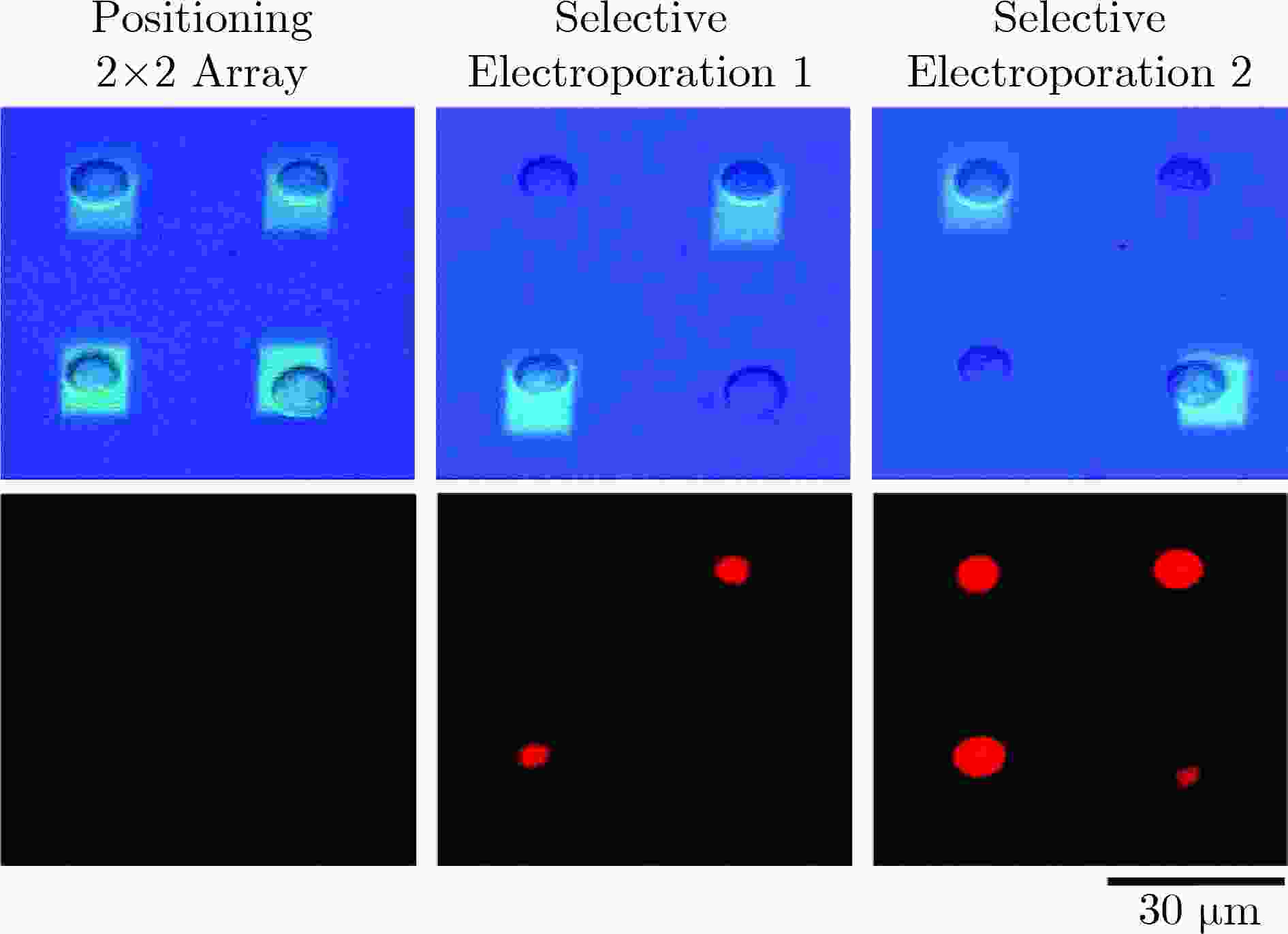
图 3 光诱导单细胞电穿孔[12]
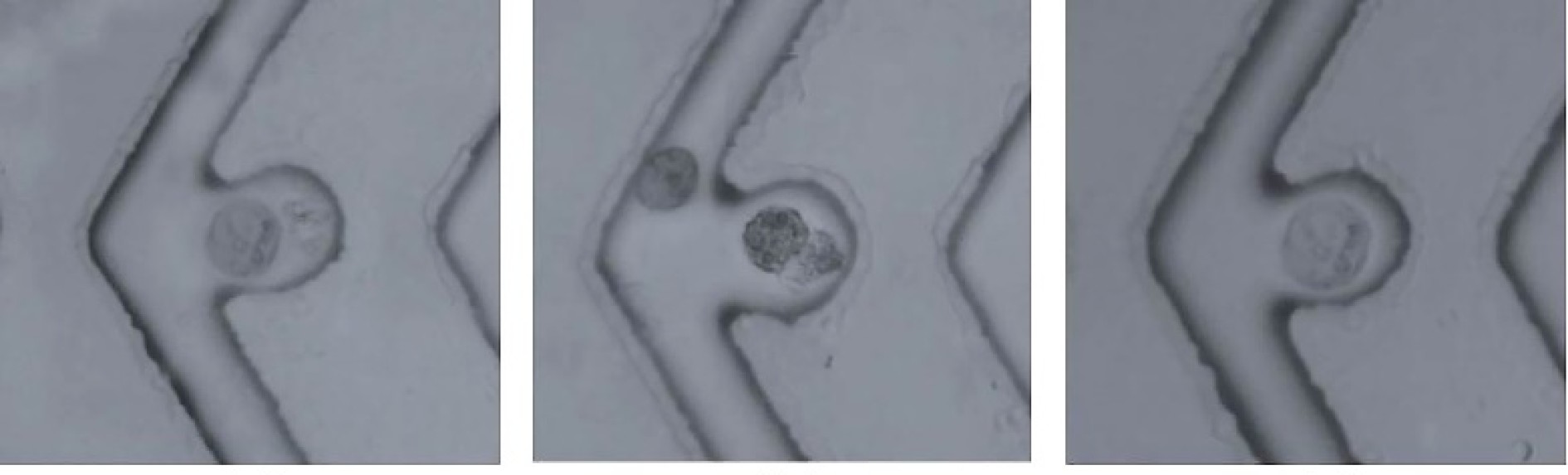
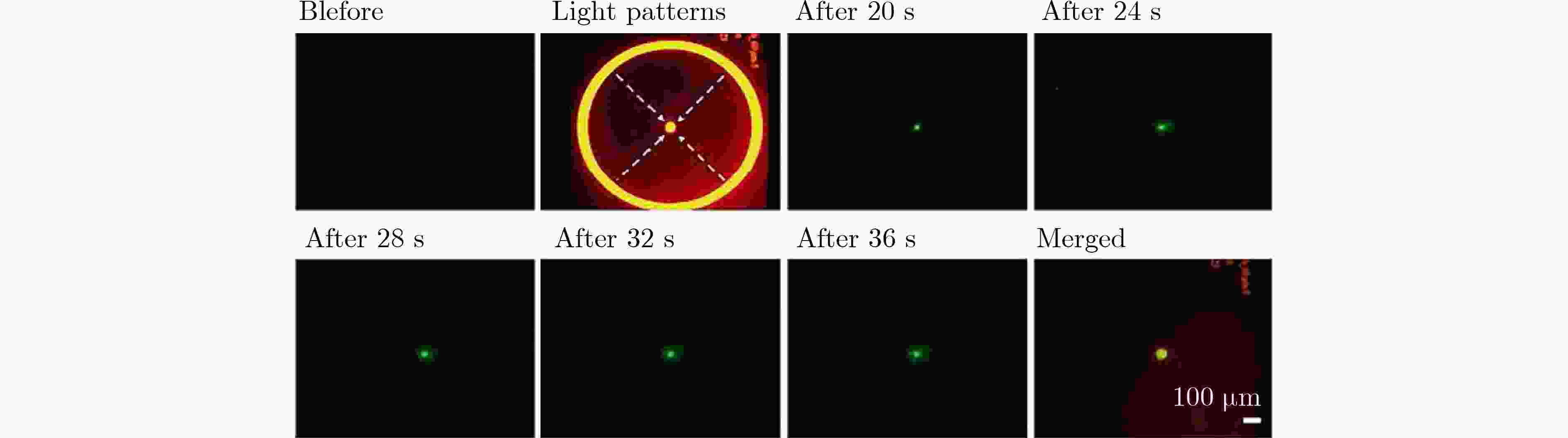
图 4 细胞在接收点进行光诱导细胞融合[13]
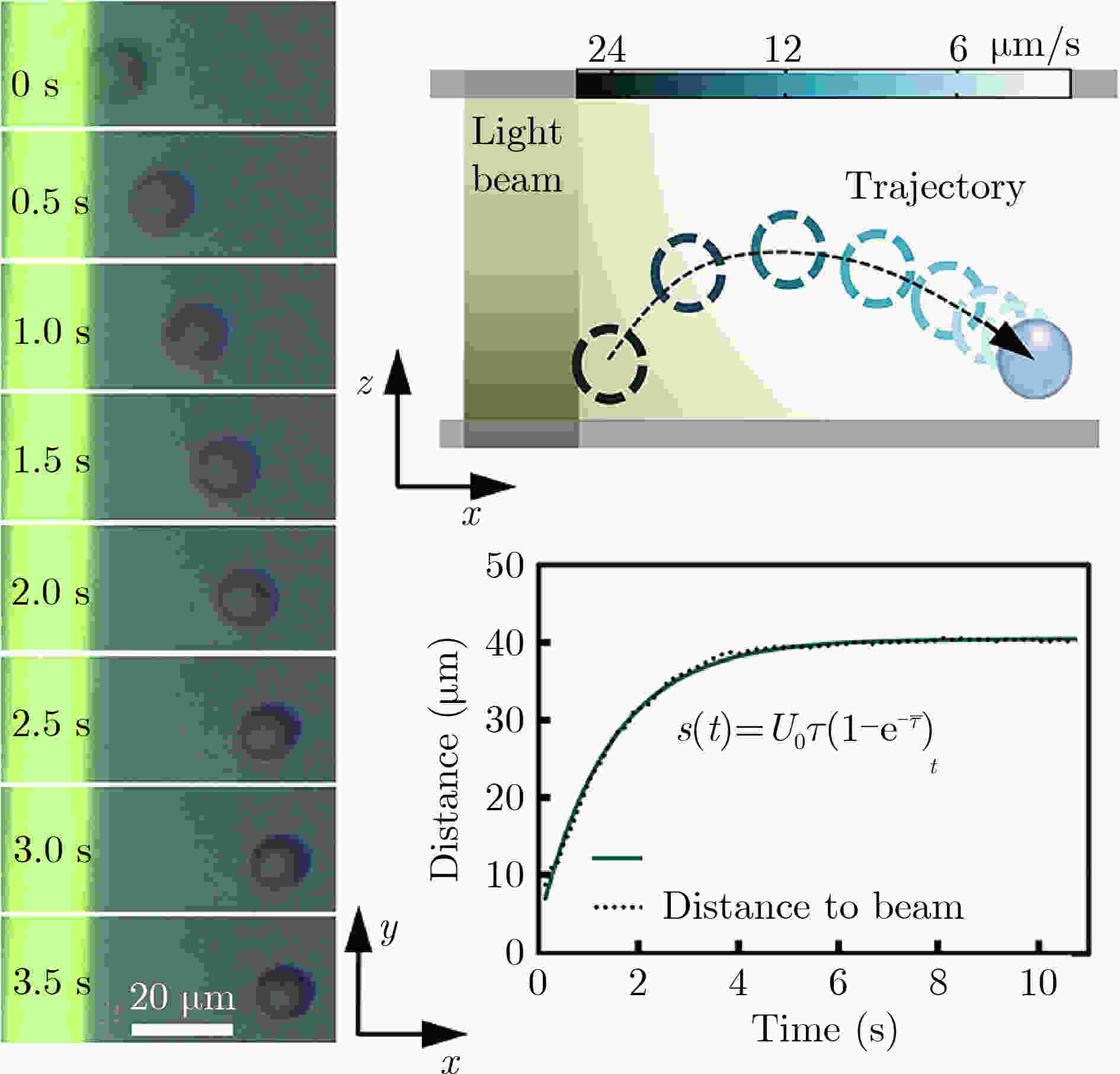
图 5 细胞基于光电镊的1阶响应[14]
图 6 利用收缩光圈富集细胞外囊泡[15]
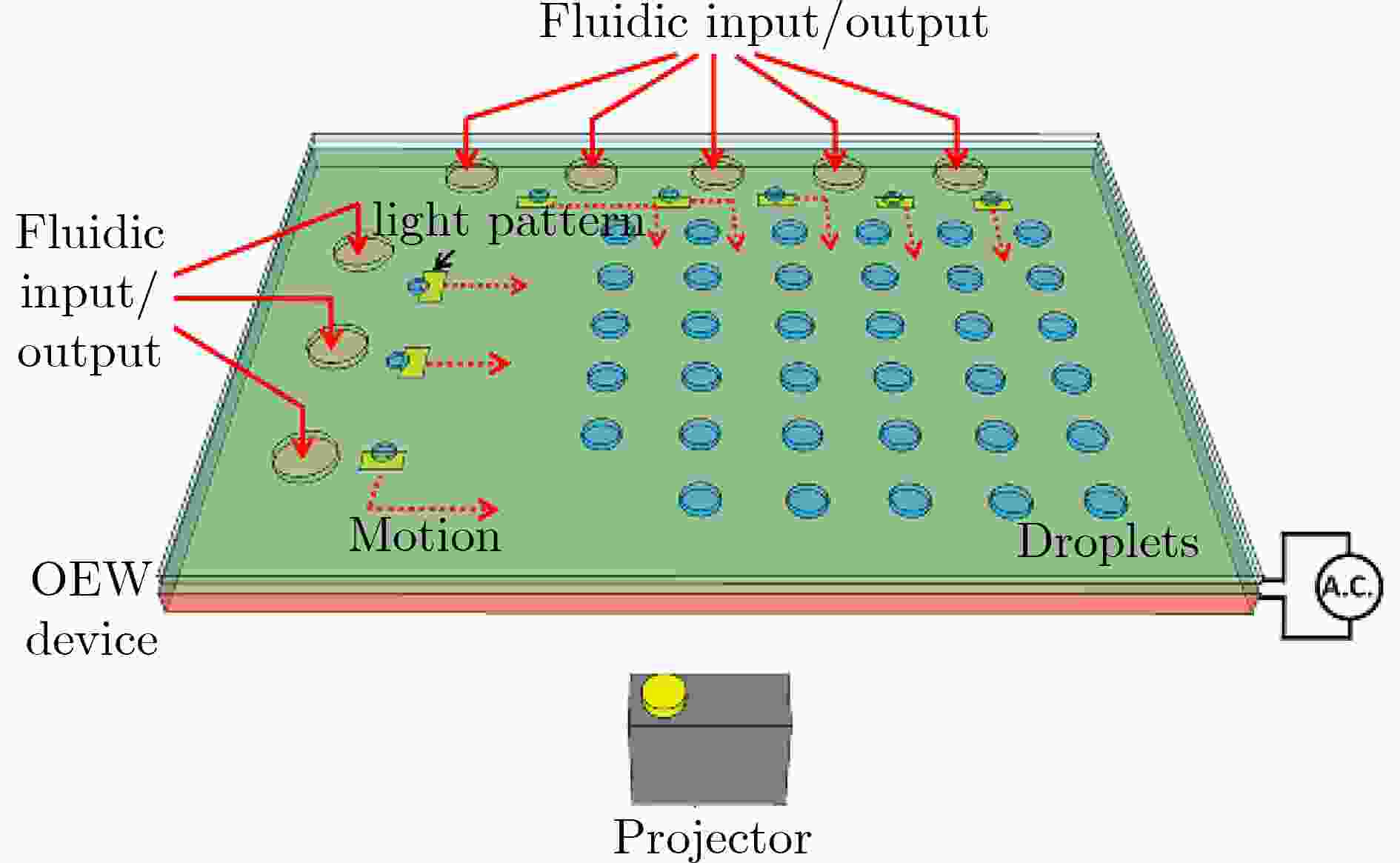
图 7 光电镊结合数字微流控技术[16]
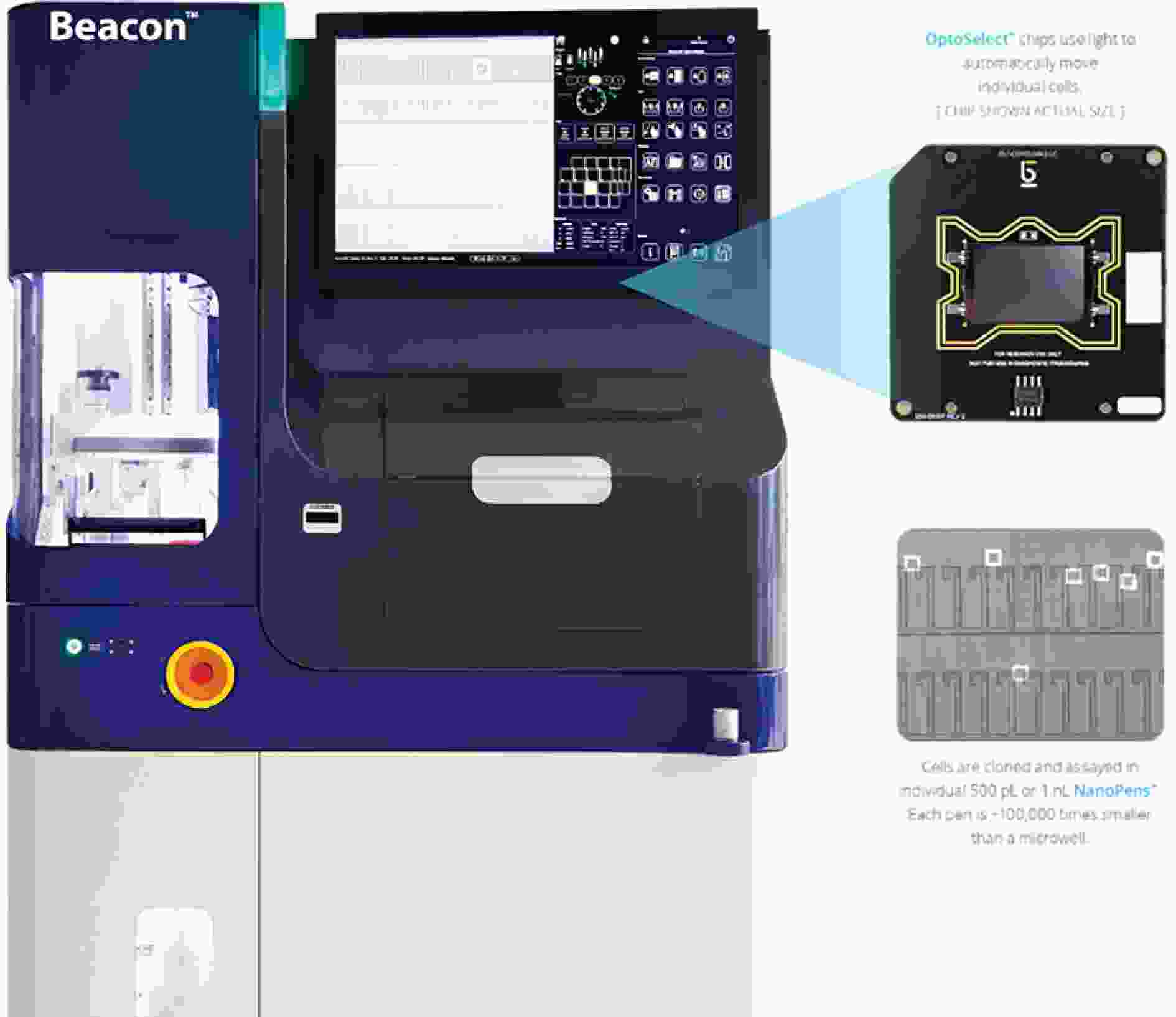
图 8 Beacon光电镊平台[17]
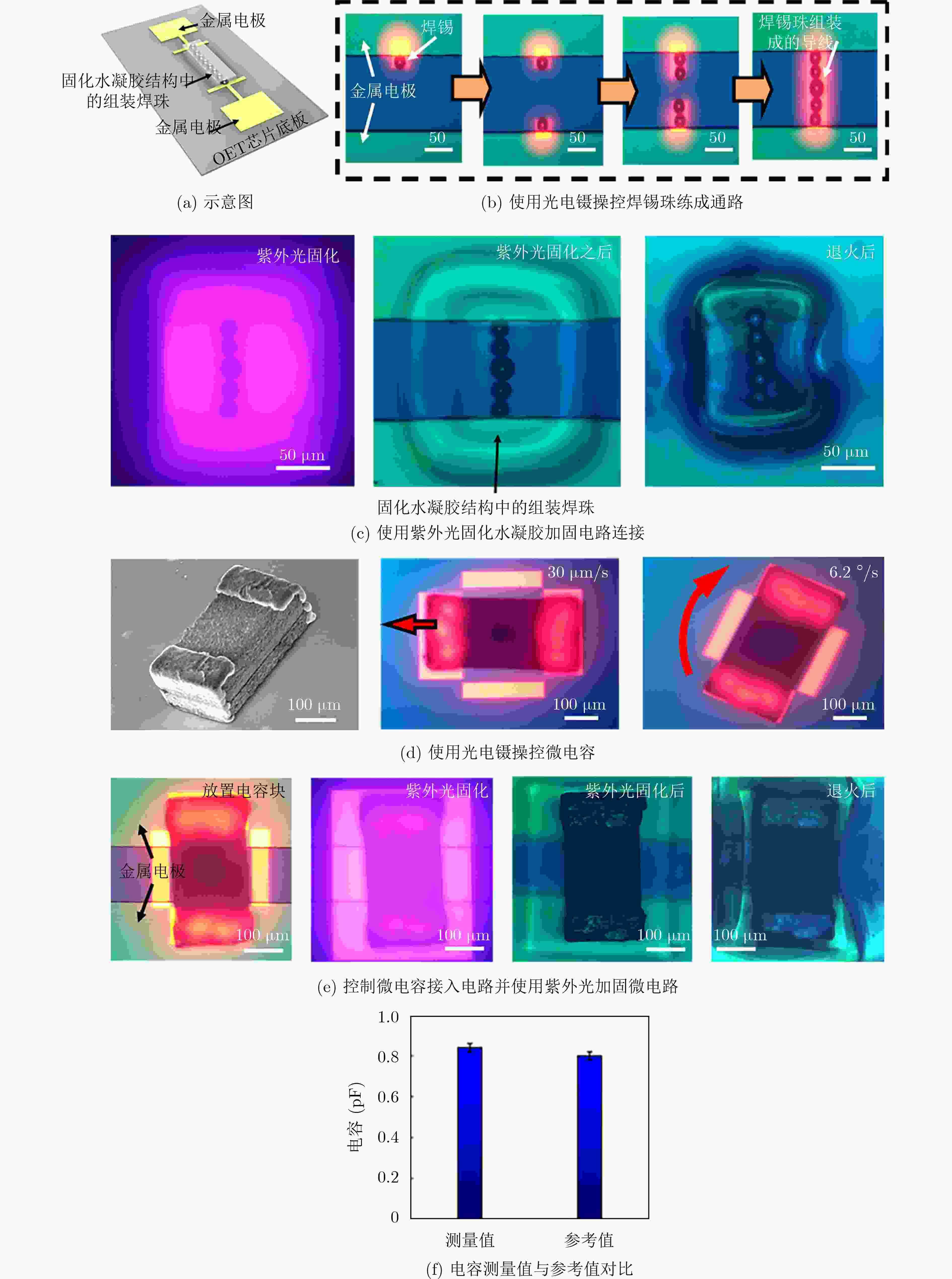
图 9 基于光电镊技术印制微电路[19]
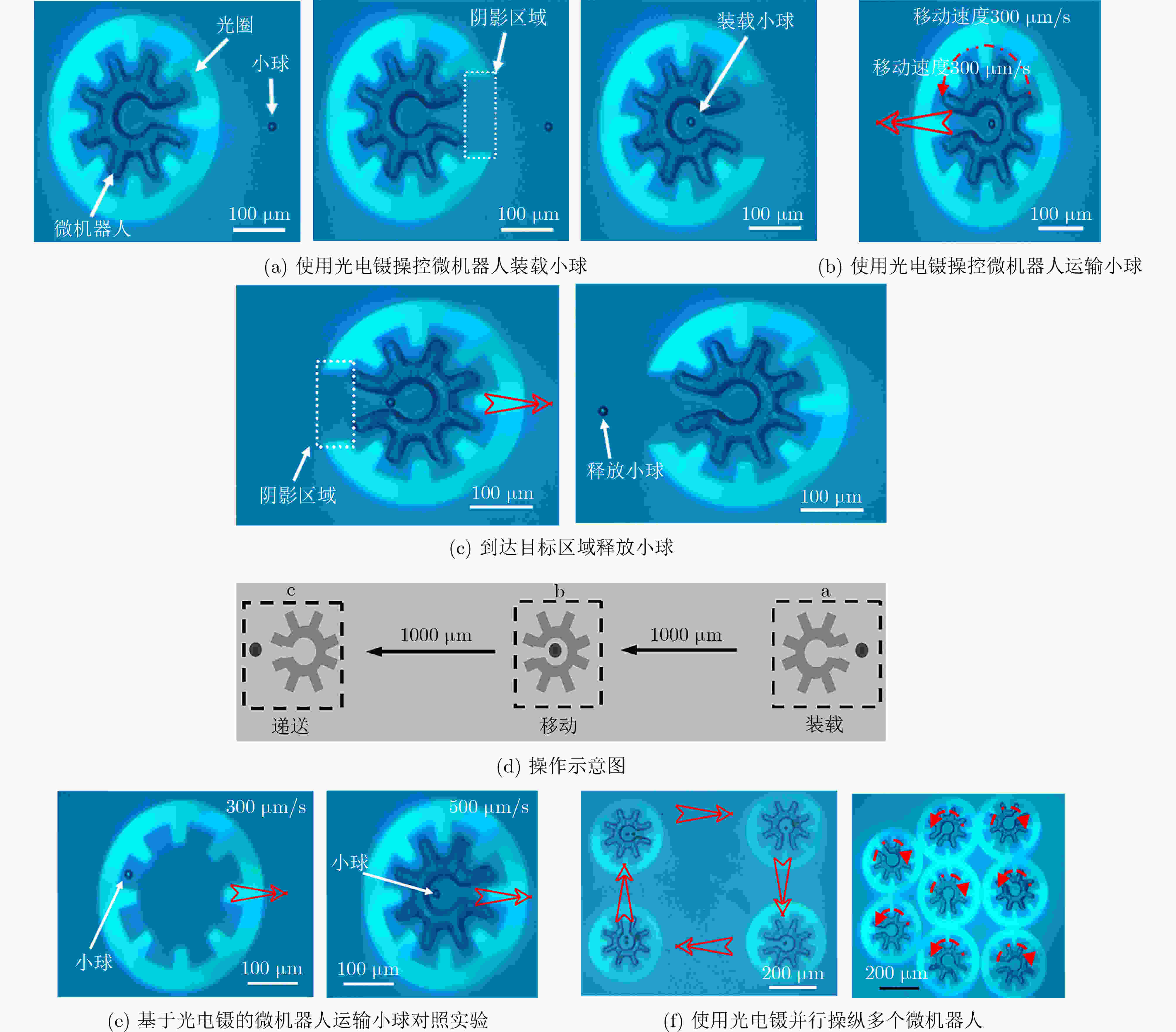
图 10 可进行并行操作的光电镊微机器人[20]
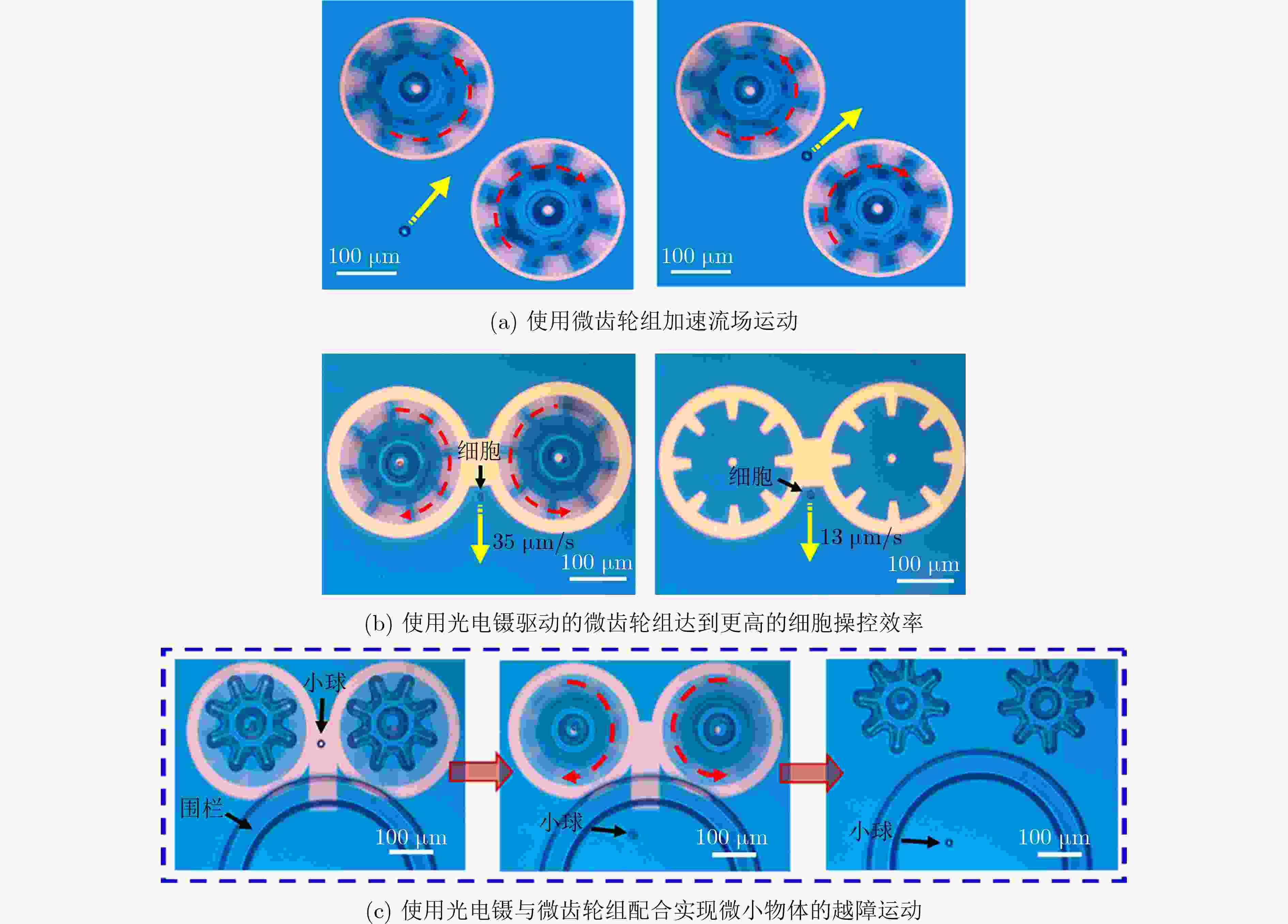
图 11 光电镊驱动微齿轮组实现物体的3维运输[21]
-
[1] LI Jinxing, DE ÁVILA B E F, GAO Wei, et al. Micro/nanorobots for biomedicine: Delivery, surgery, sensing, and detoxification[J]. Science Robotics, 2017, 2(4): eaam6431. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aam6431 [2] ZHANG Yong, CHEN B K, LIU Xinyu, et al. Autonomous robotic pick-and-place of microobjects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2009, 26(1): 200–207. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2009.2034831 [3] ZHU Wei, LI Jinxing, LEONG Y J, et al. 3D-printed artificial microfish[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(30): 4411–4417. doi: 10.1002/adma.201501372 [4] XU Xiaobin, LIU Chao, KIM K, et al. Electric-driven rotation of silicon nanowires and silicon nanowire motors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(30): 4843–4850. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201303505 [5] XIE Hui, SUN Mengmeng, FAN Xinjian, et al. Reconfigurable magnetic microrobot swarm: Multimode transformation, locomotion, and manipulation[J]. Science Robotics, 2019, 4(28): eaav8006. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aav8006 [6] WANG Wei, LI Sixing, MAIR L, et al. Acoustic propulsion of nanorod motors inside living cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(12): 3201–3204. doi: 10.1002/anie.201309629 [7] PALIMA D and GLÜCKSTAD J. Gearing up for optical microrobotics: Micromanipulation and actuation of synthetic microstructures by optical forces[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2013, 7(4): 478–494. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201200030 [8] ASHKIN A and DZIEDZIC J M. Optical trapping and manipulation of viruses and bacteria[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4795): 1517–1520. doi: 10.1126/science.3547653 [9] WU M C. Optoelectronic tweezers[J]. Nature Photonics, 2011, 5(6): 322–324. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.98 [10] VALLEY J K, OHTA A T, HSAN-YIN H, et al. Optoelectronic tweezers as a tool for parallel single-cell manipulation and stimulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2009, 3(6): 424–431. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2009.2031329 [11] LIANG Shuzhang, GAN Chunyuan, DAI Yuguo, et al. Interaction between positive and negative dielectric microparticles/microorganism in optoelectronic tweezers[J]. Lab on A Chip, 2021, 21(22): 4379–4389. doi: 10.1039/D1LC00610J [12] VALLEY J K, NEALE S, HSU H Y, et al. Parallel single-cell light-induced electroporation and dielectrophoretic manipulation[J]. Lab on A Chip, 2009, 9(12): 1714–1720. doi: 10.1039/b821678a [13] HSIAO Y C, WANG C H, LEE W B, et al. Automatic cell fusion via optically-induced dielectrophoresis and optically-induced locally-enhanced electric field on a microfluidic chip[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2018, 12(3): 034108. doi: 10.1063/1.5028158 [14] ZHAO Yuliang, LIANG Wenfeng, ZHANG Guanglie, et al. Distinguishing cells by their first-order transient motion response under an optically induced dielectrophoretic force field[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103(18): 183702. doi: 10.1063/1.4827300 [15] CHEN Y S, LAI C P K, CHEN C, et al. Isolation and recovery of extracellular vesicles using optically-induced dielectrophoresis on an integrated microfluidic platform[J]. Lab on A Chip, 2021, 21(8): 1475–1483. doi: 10.1039/D1LC00093D [16] PEI Shaoning, VALLEY J K, WANG Yilun, et al. Distributed circuit model for multi-color light-actuated opto-electrowetting microfluidic device[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2015, 33(16): 3486–3493. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2405076 [17] Berkeley Lights[EB/OL]. https://www.berkeleylights.com/systems/beacon/, 2022. [18] CHO H, GONZALES-WARTZ K K, HUANG Deli, et al. Bispecific antibodies targeting distinct regions of the spike protein potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2021, 13(616): eabj5413. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj5413 [19] ZHANG Shuailong, LI Weizhen, ELSAYED M, et al. Integrated assembly and photopreservation of topographical micropatterns[J]. Small, 2021, 17(37): 2103702. doi: 10.1002/smll.202103702 [20] ZHANG Shuailong, SCOTT E Y, SINGH J, et al. The optoelectronic microrobot: A versatile toolbox for micromanipulation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(30): 14823–14828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903406116 [21] ZHANG Shuailong, ELSAYED M, PENG Ran, et al. Reconfigurable multi-component micromachines driven by optoelectronic tweezers[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5349. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25582-8 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
