Cooperative VLC User Access and Dynamic Power Adjustment in Indoor Cell-free VLC Network
-
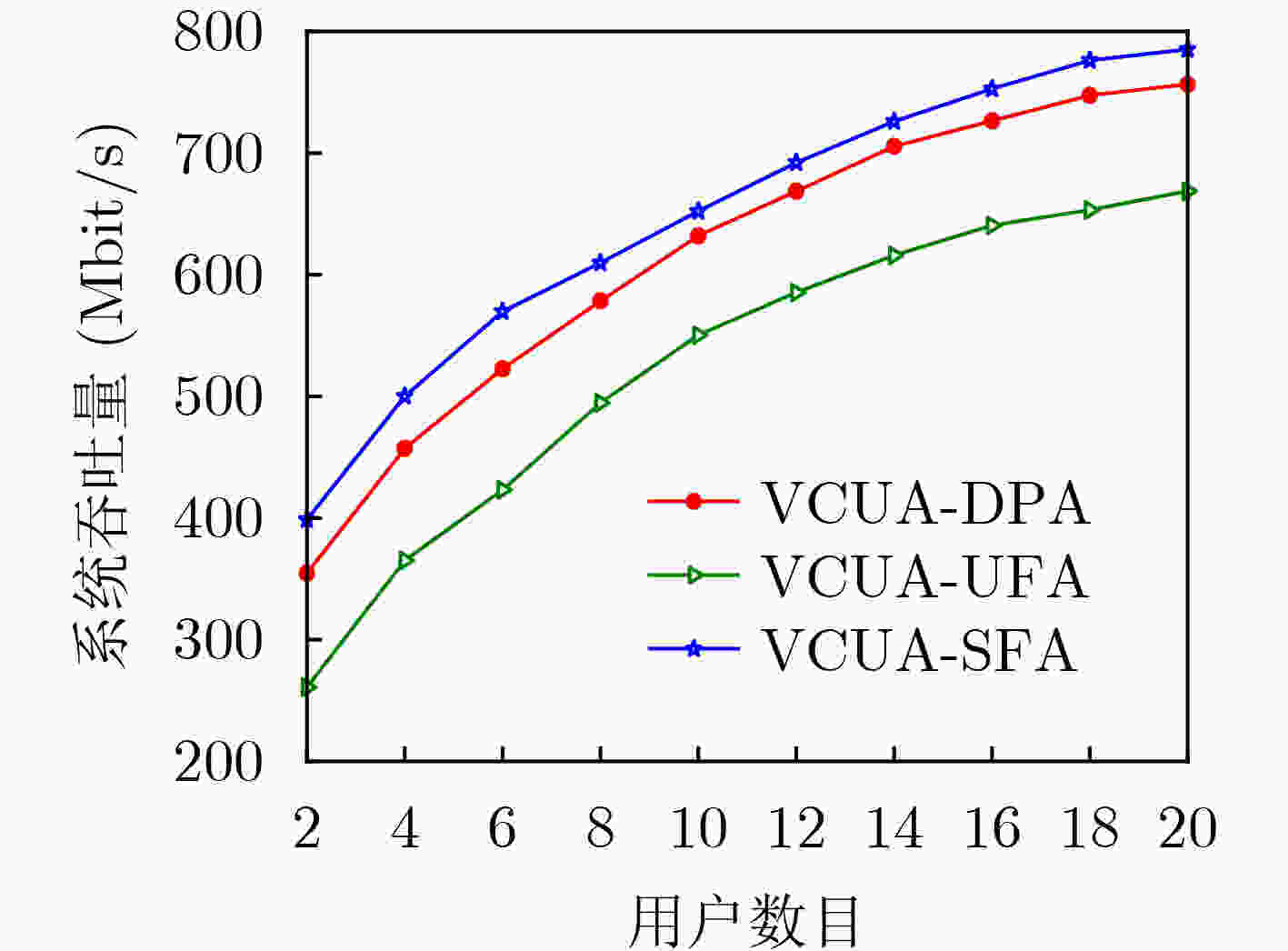
摘要: 针对室内自由小区VLC网络照明和吞吐量联合优化困难的问题,该文提出VLC协作用户接入和功率动态调整(VCUA-DPA)方法。在用户接入阶段,设计考虑网络的负载均衡、用户速率需求和协作小区数目限制的用户和VLC协作的用户接入算法;在功率分配阶段,设计联合优化照明均匀度和系统吞吐量的功率动态调整分配算法。仿真结果表明,所提VCUA-DPA在明显提升系统吞吐量的同时能优化室内照明均匀度。
-
关键词:
- 室内自由小区 VLC网络 /
- 用户接入 /
- 功率分配 /
- 系统吞吐量 /
- 照明均匀度
Abstract: Focusing on the difficulty of jointly optimizing lighting and throughput in indoor cell-free Visible Light Communication (VLC) network, a method of VLC Cooperative User Access and Dynamic Power Adjustment (VCUA-DPA) is proposed. In the user access stage, by considering the network load balance, user rate demands and the limitation of the number of cooperative cells, a user access algorithm through user and VLC cooperating is designed in this paper. In the power allocation stage, a dynamic power adjustment algorithm is designed to optimize jointly illumination uniformity and system throughput. Simulation results show that the proposed VCUA-DPA can significantly improve the system throughput and optimize the indoor illumination uniformity. -
算法1 基于用户需求的VLC协作用户接入(VCUA) 算法 输入:NA, MU, B,用户的信道增益矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{H}} = {[{h_{i,j}}]_{M \times N}} $、初始发射功率$ {{\boldsymbol{P}}^{(0)}} $、用户满意度阈值$ {\rho _{{\text{th}}}} $; 输出:用户和AP接入矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{A}} = {[{a_{i,j}}]_{M \times N}} $; (1) 根据式(2),计算用户和候选AP的信道增益值,分别建立用户i关联AP的关联集合,各AP j关联用户的AP关联集合,i∈MU, j∈NA; (2) 所有用户i从候选AP集中选择信道增益值最大的AP,记为AP j*,令${a_{i,j^*} } = 1$,并删除AP j*的关联集合; (3) repeat (4) 选择剩余带宽最大的AP j*为本轮迭代的提供者,则AP j*的候选用户为本轮迭代的需求者; (5) 由式(9)和式(10),分别计算用户i的需求权重因子和AP j的供应权重因子,i∈MU, j∈NA; (6) 由式(11),计算各候选AP j的用户接入优先级,j∈NA; (7) 从用户的关联集合中,选择用户接入优先级最高的候选AP j,分别记为用户i*和AP j*,令${a_{i^*,j^*} } = 1$; (8) 计算AP j*的剩余带宽,计算用户i*的需求权重因子; (9) 若$B_{j^*}^R \le 0$,删除AP j*的关联集合; (10) 若${\rho _{i^*} } \le {\rho _{ {\text{th} } } }$,则删除用户i*的关联集合; (11) until 所有用户确定关联的协作VLC AP. 算法2 联合优化照明和吞吐量的动态功率调整 (DPA) 算法 输入:N,M,B,μmin,接收点的信道增益矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_s} = {[{h_{s,j}}]_{S \times N}} $、AP j的服务用户集合Aj、AP j的干扰用户集合Qj、用户i的服务VLC
AP集合Ci、迭代次数t=1、最大迭代次数$ {T_{{\text{max}}}} $、最小和最大照明强度$ {E_{{\text{min}}}} $和$ {E_{{\text{max}}}} $、基准发射功率增量$ \Delta P $、基准发射功率增量最
小值$ \Delta {P_{\min }} $、发射功率增量的调整系数ε,0 < ε < 1;输出:联合优化照明和吞吐量的各AP发射功率$ {P^*} = [{P_1},{\text{ }}{P_2},{\text{ }} \cdots ,{\text{ }}{P_N}] $; (1) 根据式(15),执行Dinkelbach单纯形法[6]求解优化目标O3'的各VLC AP发射功率Pl; (2) for $ j = 1,2, \cdots ,N $ do (3) 由式(17)计算AP j的基准发射功率增加$ \Delta P $时吞吐量增益$G_j^{ {{\rm{in}}} }$,由式(18)计算AP j的基准发射功率减少$ \Delta P $时吞吐量增益$G_j^{{\rm{de}}}$; (4) 若$G_j^{ {{\rm{in}}} } > G_j^{{\rm{de}}}$,则AP的编号j加入Vin集合;否则,AP的编号j加入Vde集合; (5) end for (6) while $ t < {T_{{\text{max}}}} $ do (7) for $j \in {V_{ {\rm{in} } } }$ do (8) 由式(17)计算AP j的基准发射功率增加$ \Delta P$时的吞吐量增益$G_j^{ {{\rm{in}}} }$,若$G_j^{ {{\rm{in}}} } > 0$且$({P_{\max } } - P_j^l) \ge \Delta P$,进一步判断AP j的所有干扰用户
是否都能满足用户速率需求,若是,则AP j加入G集合;(9) end for (10) for $j \in {V_{{\rm{de}}} }$ do (11) 由式(18)计算AP j的基准发射功率减少$\Delta P $时的吞吐量增益$G_j^{ {{\rm{de}}} }$,若$G_j^{ {{\rm{de}}} } > 0$且$({P_{\max } } - P_j^l) \ge \Delta P$,进一步判断AP j的所有服务用户
是否都能满足用户速率需求,若是,则AP j加入G集合;(12) end for (13) 若G集合为空集,则转步骤(18);否则,转步骤(14); (14) 按照吞吐量增益值大小对G集合中的AP进行降序排序; (15) 记G集合中第一个AP为 j*,若AP j*为Vin集合中的AP,则转步骤(16);否则,转步骤(17); (16) 由式(5)和式(6)分别计算AP j*的基准发射功率为$P_{j^*}^l + \Delta P$时各接收点的Es和$\mu^*$,若${E_{\min } } \le {E_s} \le {E_{\max } },\forall s$且$\mu^* \ge {\mu _{\min } }$,则AP j*
的发射功率调整为$ P_j^l = P_j^l + \Delta P $,令t = t+1,转步骤(6);否则,从G集合中删除AP j*,转步骤(13);(17) 由式(5)和式(6)分别计算AP j*的基准发射功率为$ P_{j*}^l - \Delta P $时各接收点的Es和$\mu^*$,若${E_{\min } } \le {E_s} \le {E_{\max } },\forall s$且$\mu^* \ge {\mu _{\min } }$,则AP j*
的发射功率调整为$ P_j^l = P_j^l - \Delta P $,令t = t+1,转步骤(6);否则,从G集合中删除AP j*,转步骤(13);(18) 令$\Delta P$=$\varDelta$×ε,若$\varDelta$>$\Delta P_{\min} $,则转步骤(7);否则,转步骤(20); (19) end while (20) 令P*=Pl,输出联合优化照明和吞吐量的各AP发射功率P*。 表 1 仿真参数
参数 含义 数值 参数 含义 数值 h PD的高度 0.85 m $ {\mu _{\min }} $ 最小照明均匀度 0.7 $ {P_{{\text{min}}}} $ VLC AP的最小发射功率 3 W $ {E_{\min }} $ 最小照明强度 300 lx $ {P_{\max }} $ VLC AP的最大发射功率 10 W $ {E_{\max }} $ 最大照明强度 1500 lx B VLC系统带宽 40 MHz $ \Delta P $ 基准发射功率的增量 1.5 W $ {\phi _{1/2}} $ 发射机的半功率角 60° $ \Delta {P_{\min }} $ 基准发射功率增量最小值 0.3 W $ {\psi _c} $ 接收机视场角 60° $ \varepsilon $ 基准发射功率增量调整系数 0.8 $ {A_{{\text{PD}}}} $ PD的接收面积 1 cm2 $ {T_{\max }} $ 功率调整的最大迭代次数 20 $ \gamma $ 光电转换系数 0.53 A/W $ \delta $ LED发射光功率和光通量的转换系数 2.1 mW/lm -
[1] 徐常志, 靳一, 李立, 等. 面向6G的星地融合无线传输技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 28–36. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200363XU Changzhi, JIN Yi, LI Li, et al. Wireless transmission technology of satellite-terrestrial integration for 6G mobile communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 28–36. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200363 [2] 谢显中, 高龙龙, 卢华兵. VLC网络中兼顾QoS和公平性的协作子载波与功率分配算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 33(1): 7–17. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201904090122XIE Xianzhong, GAO Longlong, and LU Huabing. Coordinated subcarrier and power allocation algorithms considering both QoS and fairness for VLC networks[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2021, 33(1): 7–17. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201904090122 [3] 付亚伟. 大数据互联网时代光纤通信技术的发展与挑战[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 33(1): 52–58. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201905080181FU Yawei. Development and challenge of optical fiber communication technology in the era of big data internet[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2021, 33(1): 52–58. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201905080181 [4] DENG Jiajun, JIN Xianqing, MA Xiaoting, et al. Graph-based multi-user scheduling for indoor cooperative visible light transmission[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(11): 15984–16002. doi: 10.1364/OE.392353 [5] CHEN Jiaxuan and WANG Zhaocheng. Joint design of user scheduling and precoding for interference management in cell-free VLC network[C]. IEEE Global Communications Conference, Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. [6] JIANG Rui, WANG Qi, HAAS H, et al. Joint user association and power allocation for cell-free visible light communication networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(1): 136–148. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2774400 [7] CHEN Jiaxuan, WANG Zhaocheng, and JIANG Rui. Downlink interference management in cell-free VLC network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(9): 9007–9017. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2931698 [8] 刘焕淋, 吴兰, 陈勇, 等. 基于QoS决策的异构VLC/WiFi网络联合收发端需求的接入点选择[J]. 中国激光, 2019, 46(8): 0806002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0806002LIU Huanlin, WU Lan, CHEN Yong, et al. QoS-based decision-making access-point selection under joint demands of transmitting and receiving in heterogeneous VLC/WiFi networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(8): 0806002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0806002 [9] YANG Helin, ZHONG Wende, CHEN Chen, et al. QoS-driven optimized design-based integrated visible light communication and positioning for indoor IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(1): 269–283. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2951396 [10] FENG Simeng, ZHANG Rong, XU Wei, et al. Multiple access design for ultra-dense VLC networks: Orthogonal vs non-orthogonal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(3): 2218–2232. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2884482 [11] OBEED M, SALHAB A M, ZUMMO S A, et al. New algorithms for energy-efficient VLC networks with user-centric cell formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2019, 3(1): 108–121. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2018.2886605 [12] 刘焕淋, 蒲欣, 陈勇, 等. 室内VLC-WiFi异构网络基于动态载波分配的干扰管理策略[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(10): 1920–1926. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210072LIU Huanlin, PU Xin, CHEN Yong, et al. Interference management strategy based on dynamic carrier allocation for indoor VLC-WiFi heterogeneous network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(10): 1920–1926. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210072 [13] 雷新颖, 王成. 一种多孔径接收器的设计及其可见光通信系统[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 33(1): 59–66. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201902150057LEI Xinying and WANG Cheng. Design of amultiple bore diameter receiver and its visible communication system[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2021, 33(1): 59–66. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201902150057 [14] GIANG D T, PHAM T S, NGO Q M, et al. An alternative approach for high uniformity distribution of indoor lighting LED[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2020, 12(2): 7100810. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2020.2979609 [15] LIU Huanlin, LIN Zhenyu, XU Yang, et al. Coverage uniformity with improved genetic simulated annealing algorithm for indoor Visible Light Communications[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 439: 156–163. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.12.084 [16] MUSHFIQUE S I, ALSHAROA A, and YUKSEL M. Optimization of SINR and illumination uniformity in multi-LED multi-datastream VLC networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(3): 1108–1121. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.2972310 [17] MA Shuai, ZHANG Fan, LI Hang, et al. Aggregated VLC-RF systems: Achievable rates, optimal power allocation, and energy efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7265–7278. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3010294 [18] WEI Zhengyuan, HU Haiying, and HUANG Huamao. Optimization of location, power allocation and orientation for lighting lamps in a visible light communication system using the firefly algorithm[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(6): 8796–8808. doi: 10.1364/OE.420773 -





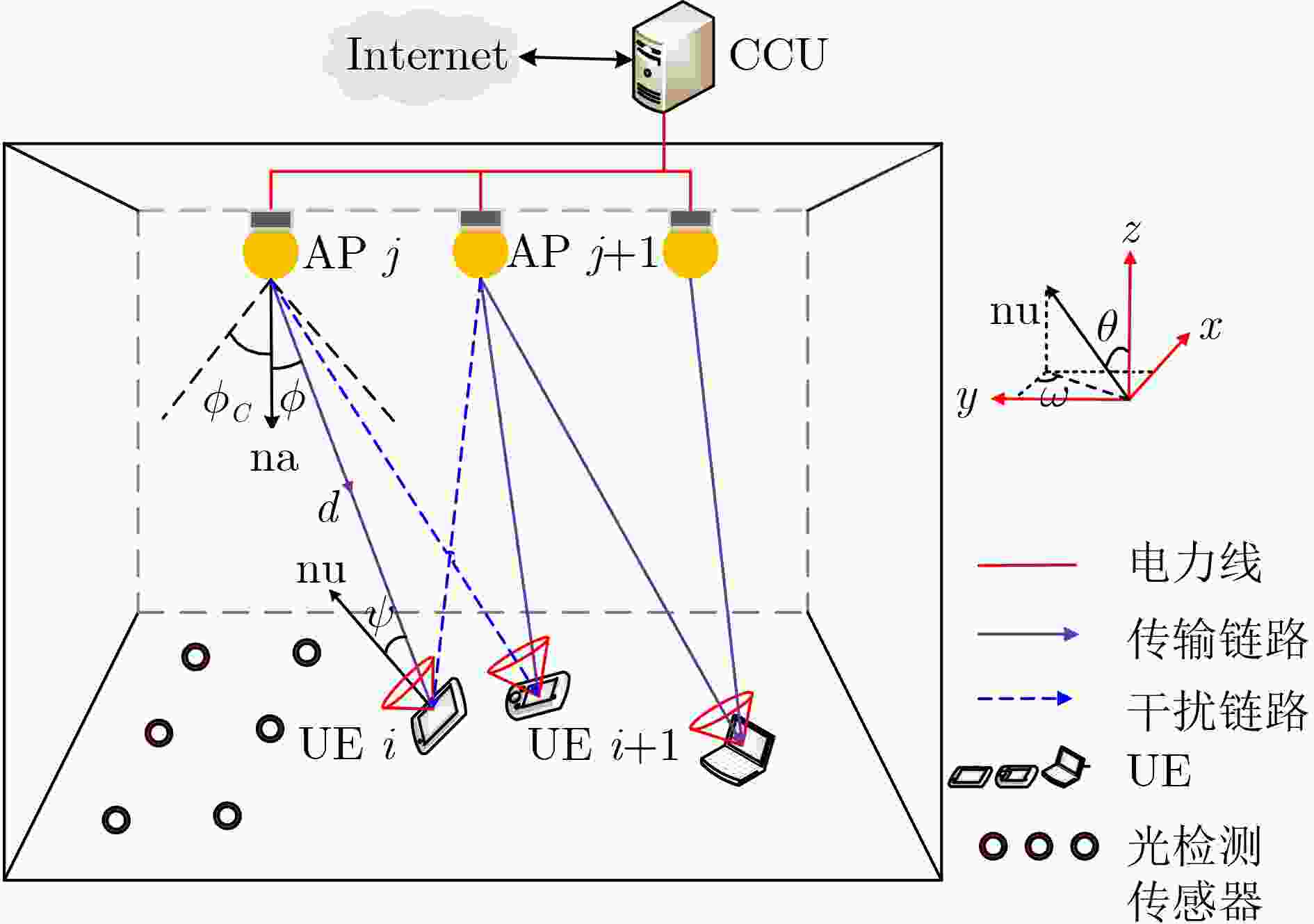
 下载:
下载:
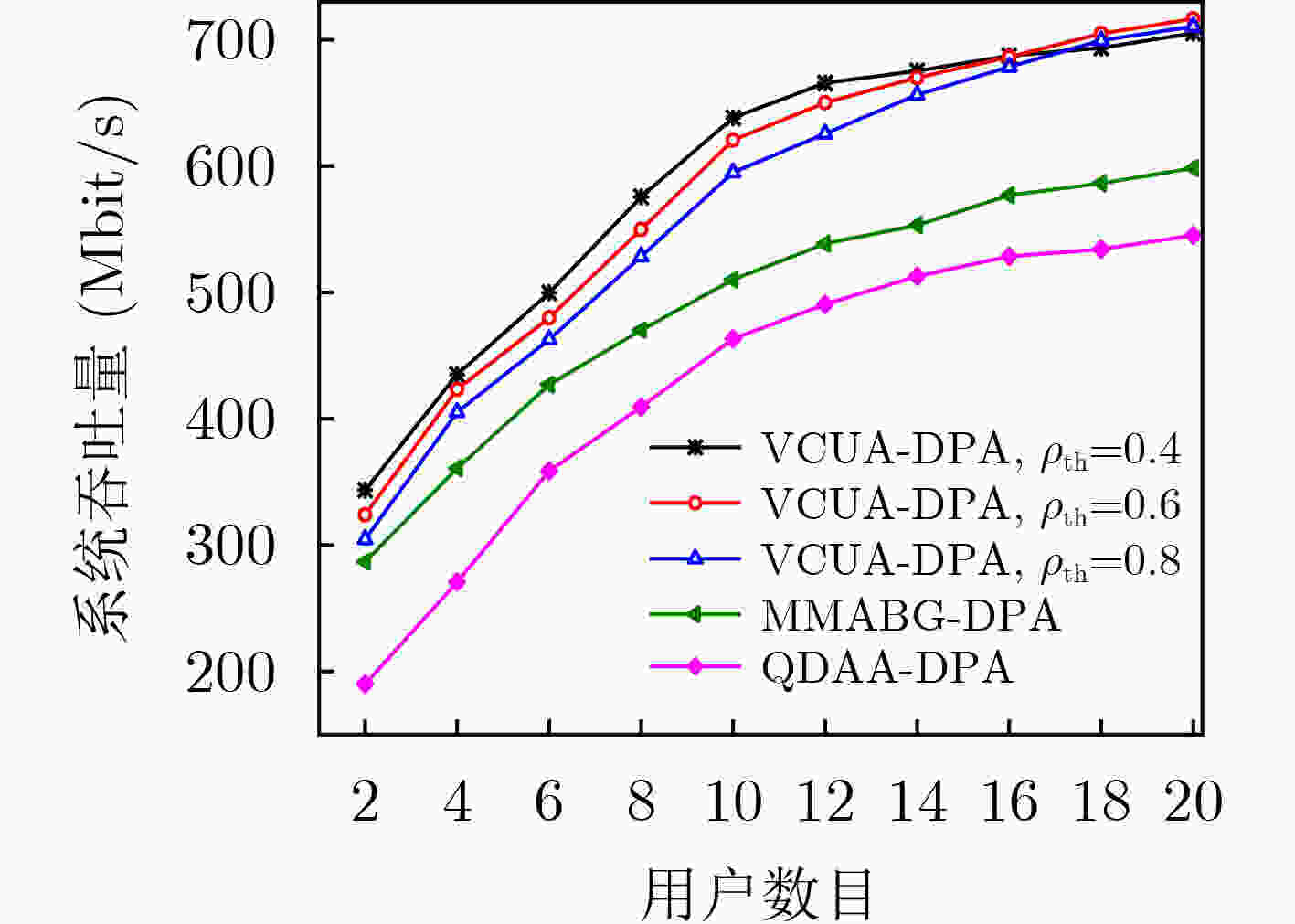
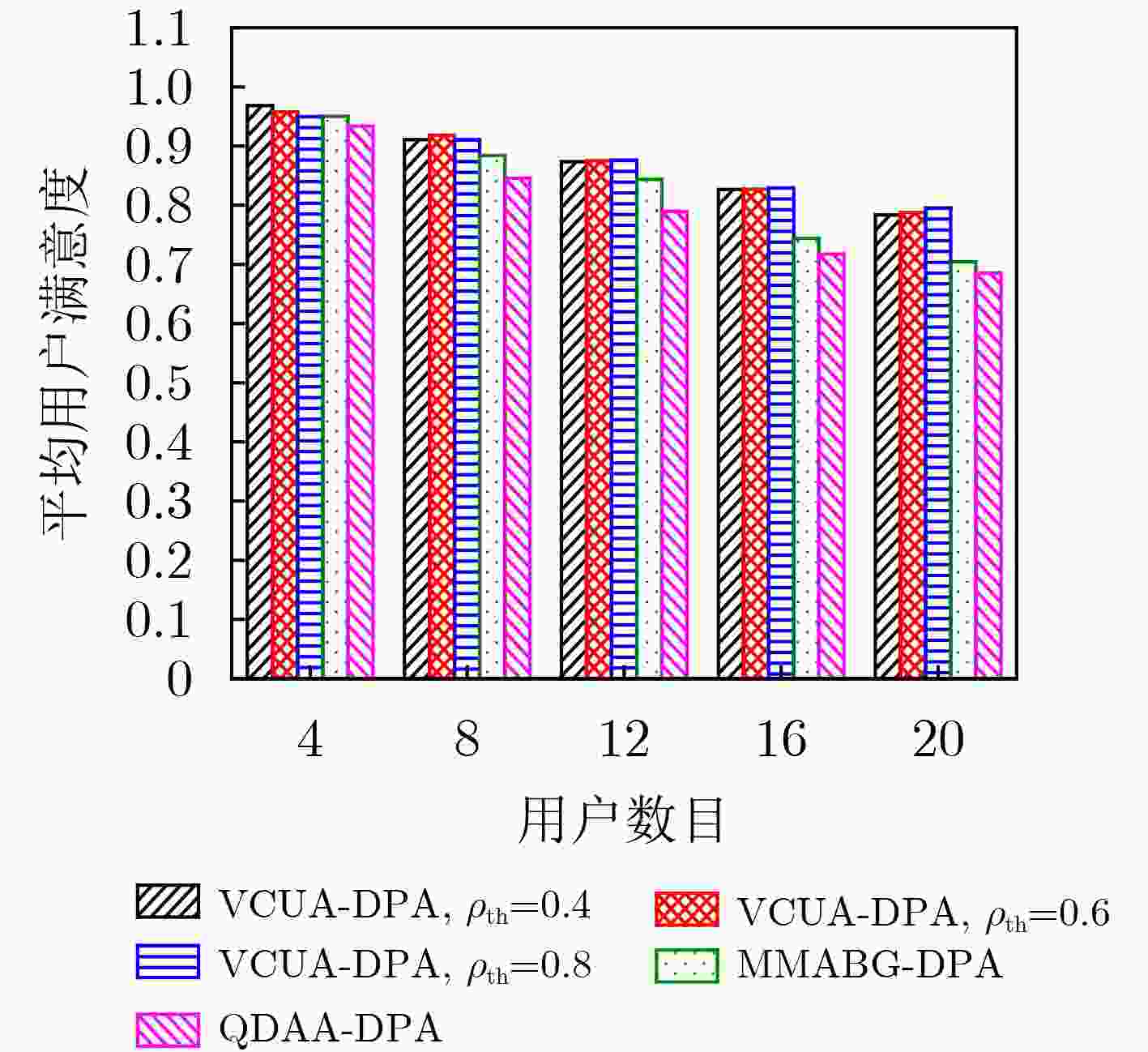
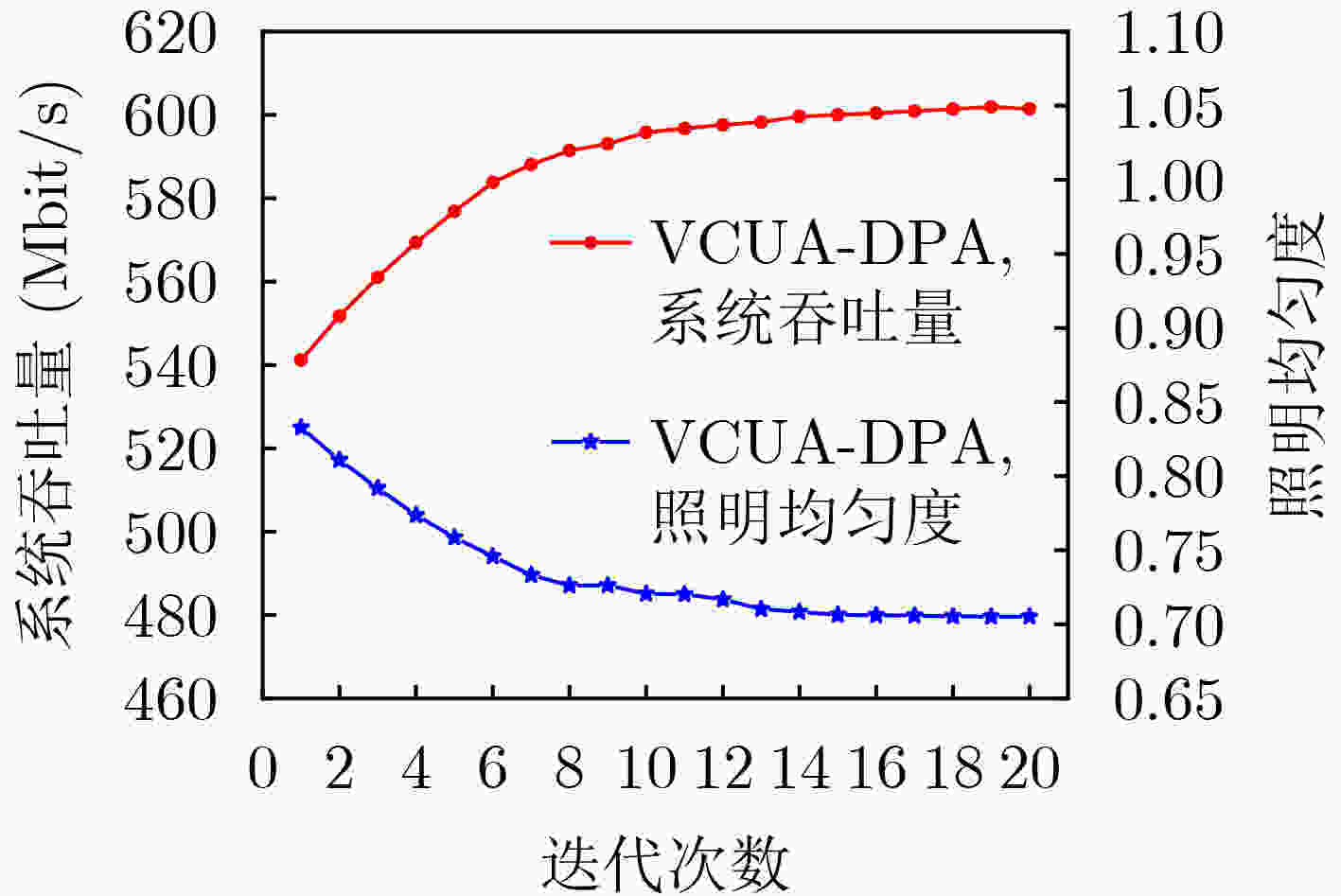


 下载:
下载:
