Anomaly Detection Method of Network Traffic Based on Secondary Feature Extraction and BiLSTM-Attention
-
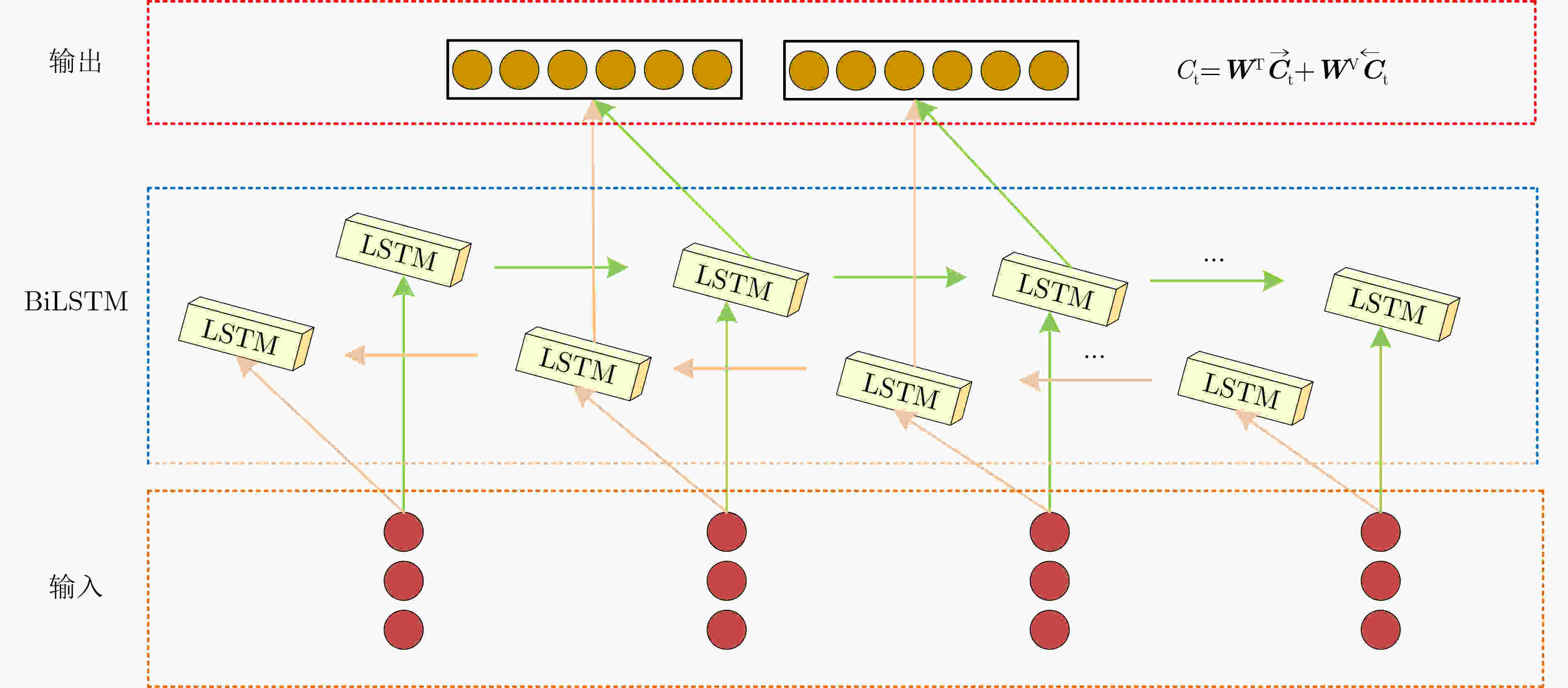
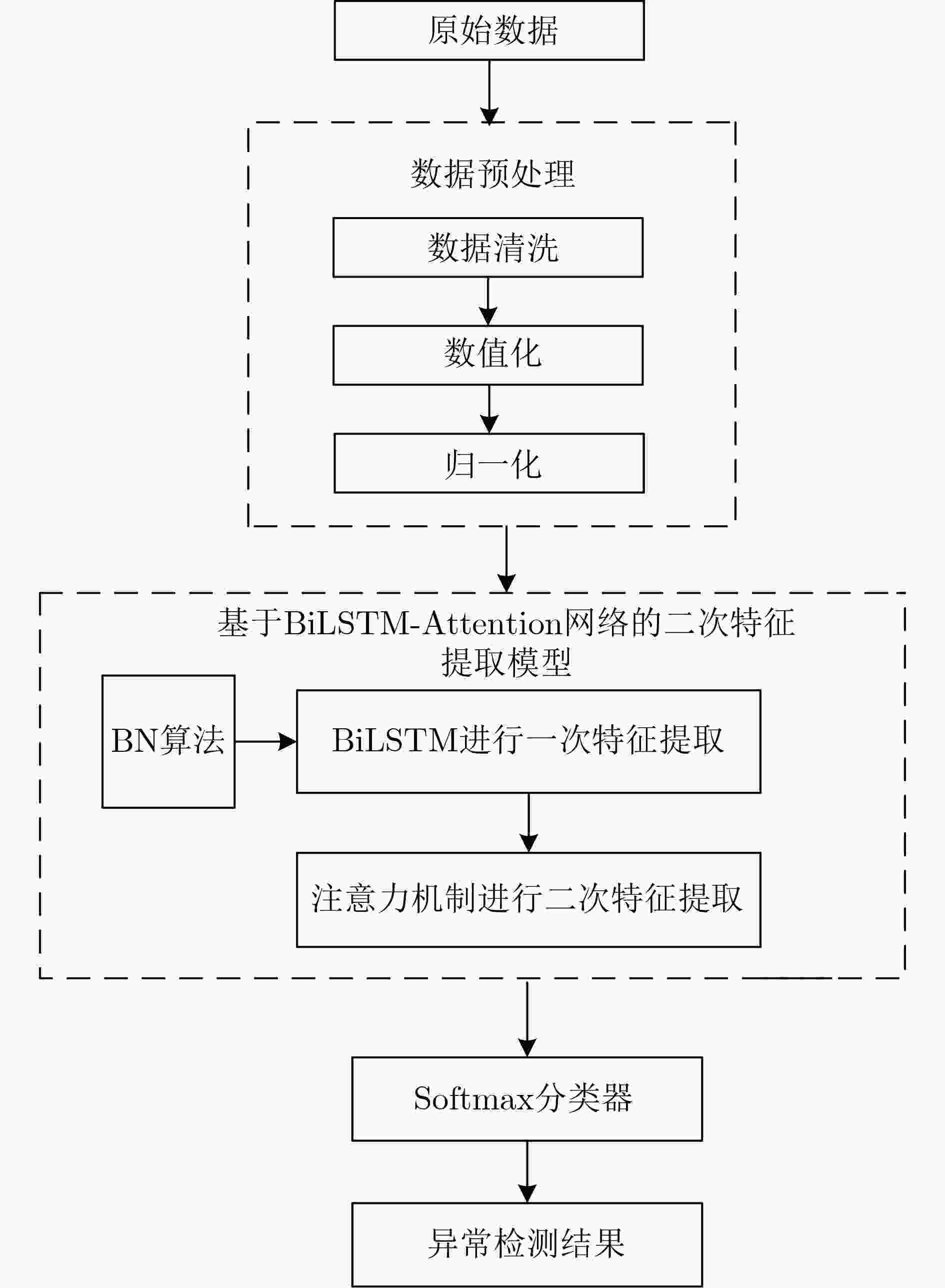
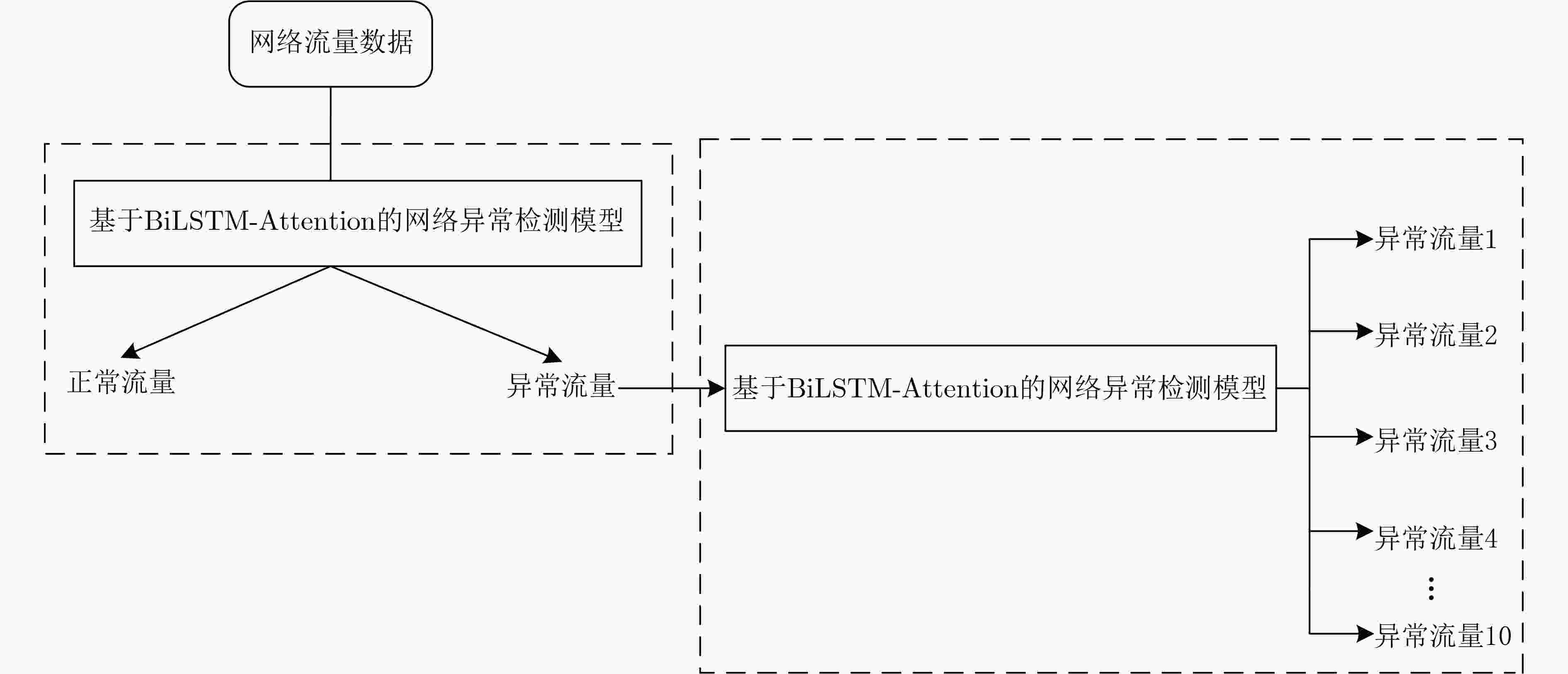
摘要: 针对传统的网络流量异常检测方法存在识别准确度低、表征能力弱、泛化能力差,忽略了特征之间的相互关系等问题,该文提出一种基于二次特征提取和BiLSTM-Attention的网络流量异常检测方法。通过使用双向长短期记忆网络(BiLSTM)学习数据之间的特征关系,完成数据的一次特征提取,在此基础上,定义一种基于注意力机制的特征重要性权重评估规则,依据特征重要性大小对BiLSTM生成的特征向量给予相应的权重,完成数据的二次特征提取。最后,提出一种“先总分后细分”的设计思想构建网络流量异常检测模型,实现多分类网络流量的异常检测。实验结果表明,该文所提方法在性能上要优于传统单一的模型,并且具有良好的表征能力和泛化能力。Abstract: Focusing on the problems of the traditional network traffic anomaly detection methods, such as low recognition accuracy, weak representation ability, poor generalization ability, and ignoring the relationship between features, a network traffic anomaly detection method based on quadratic feature extraction and BiLSTM-Attention is proposed. By using the Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory network (BiLSTM) to learn the feature relationship between the data, the feature of the data is extracted, on this basis, a feature importance weight evaluation rule based on attention mechanism is defined, and the feature vector generated by BiLSTM is given corresponding weight according to the feature importance to complete the secondary feature extraction of data. Finally, a design idea of “total score first and then subdivision” is proposed to construct a network traffic anomaly detection model to implement anomaly detection of multi-classified network traffic. The experimental results show that the method proposed in this paper is better than the traditional single model in performance, and has good representation ability and generalization ability.
-
表 1 混淆矩阵
混淆矩阵 预测值 正常 异常 实际值 正常 TP FN 异常 FP TN 表 2 CICIDS2017数据集
数据流类型 数量 占比(%) Benign 342 465 61.15 Dos GlodenEye 7 320 1.31 Dos Hulk 14 575 2.60 Dos Slowhttp 4 230 0.76 Dos Slowloris 3 915 0.70 SSH Patator 2 270 0.41 FTP Patator 3 895 0.70 Web Attack 2 040 0.36 BotNet 1 020 0.18 Port Scan 162 425 29.00 DDoS 15 845 2.83 表 3 注意力机制对实验结果(%)的影响
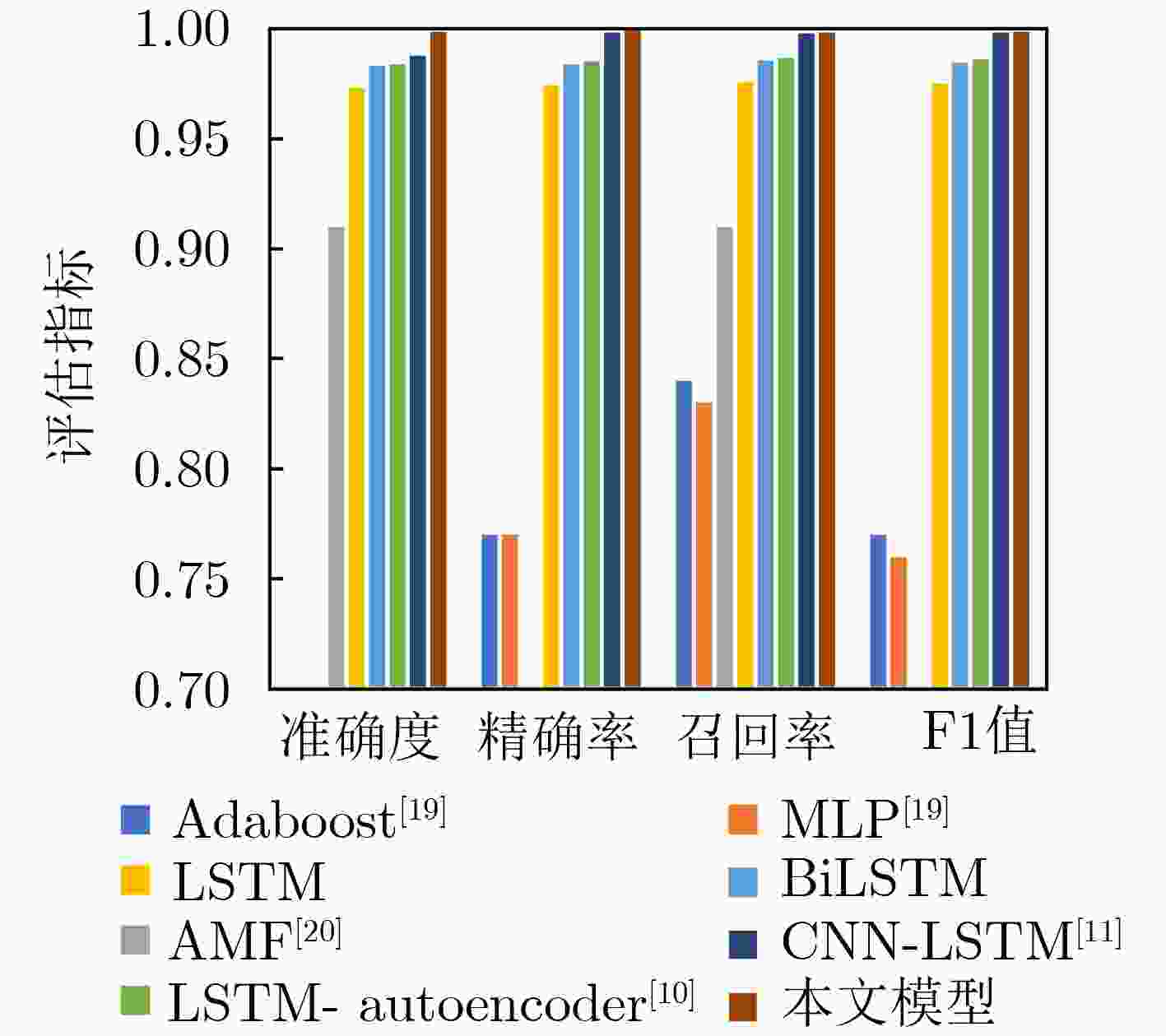
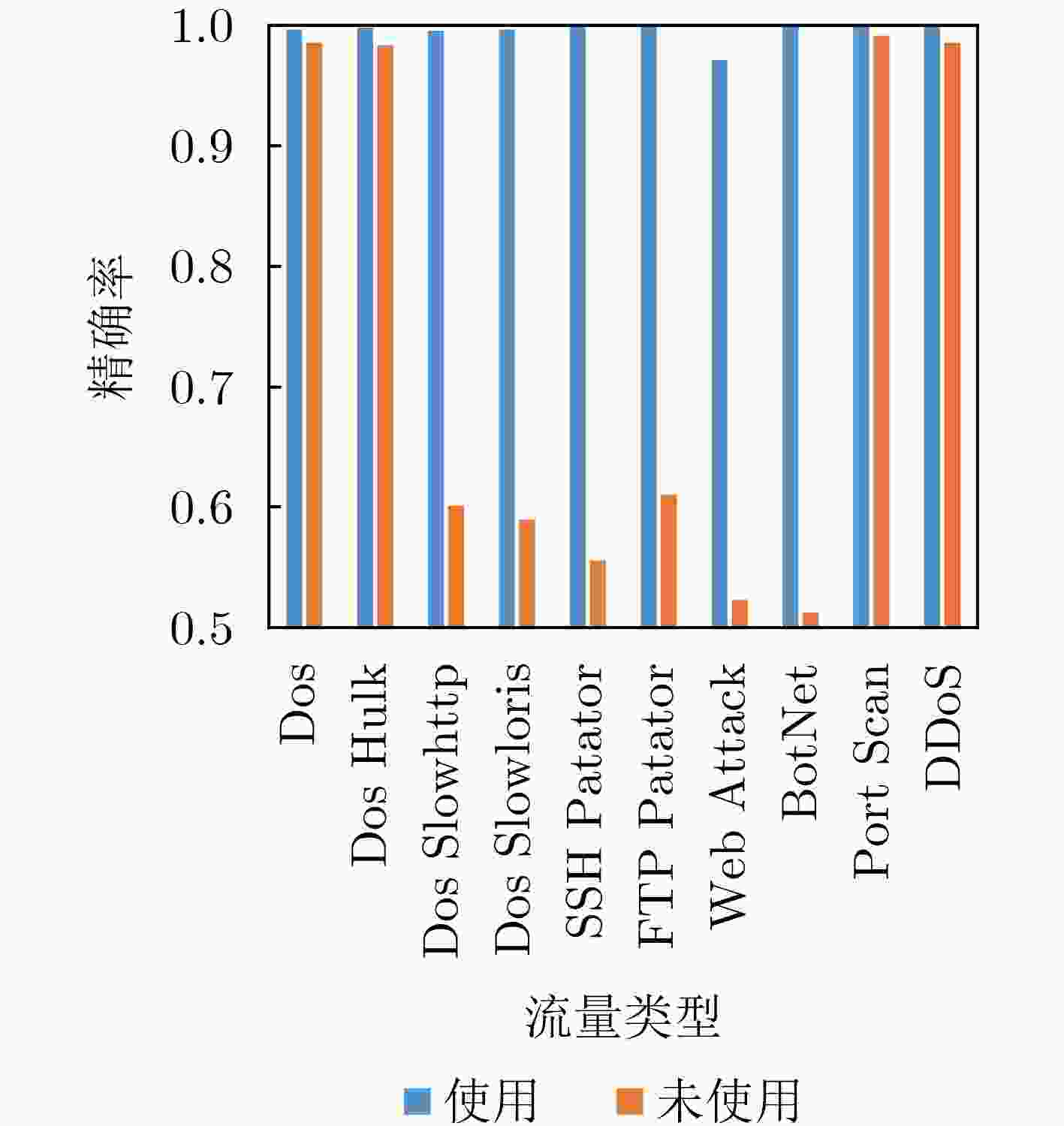
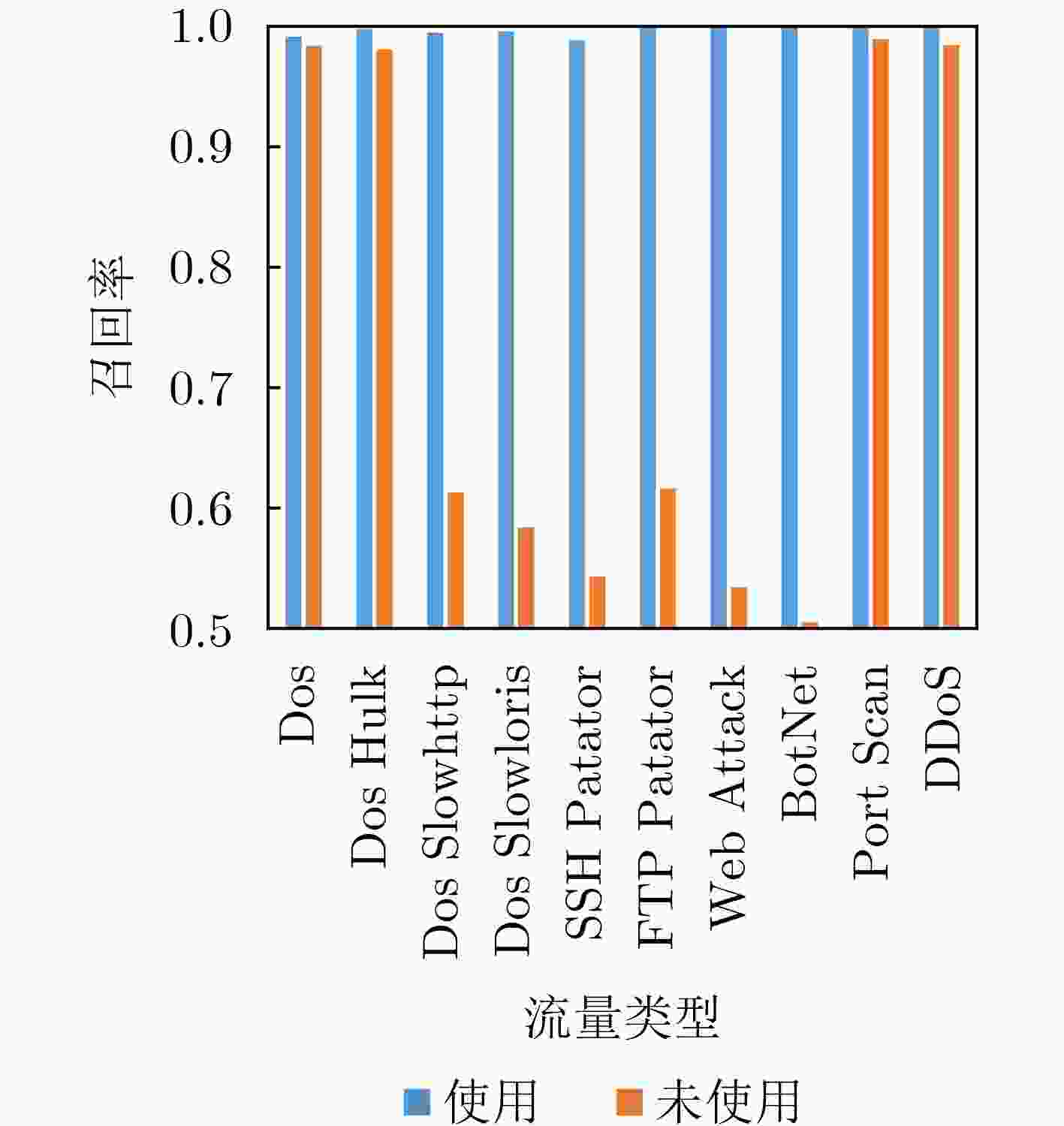
有无注意力机制 准确度 精确率 召回率 有 99.88 99.93 99.83 无 98.53 98.43 98.62 表 4 不同子数据集在准确度、精确率、召回率和F1 值指标上的比较(%)
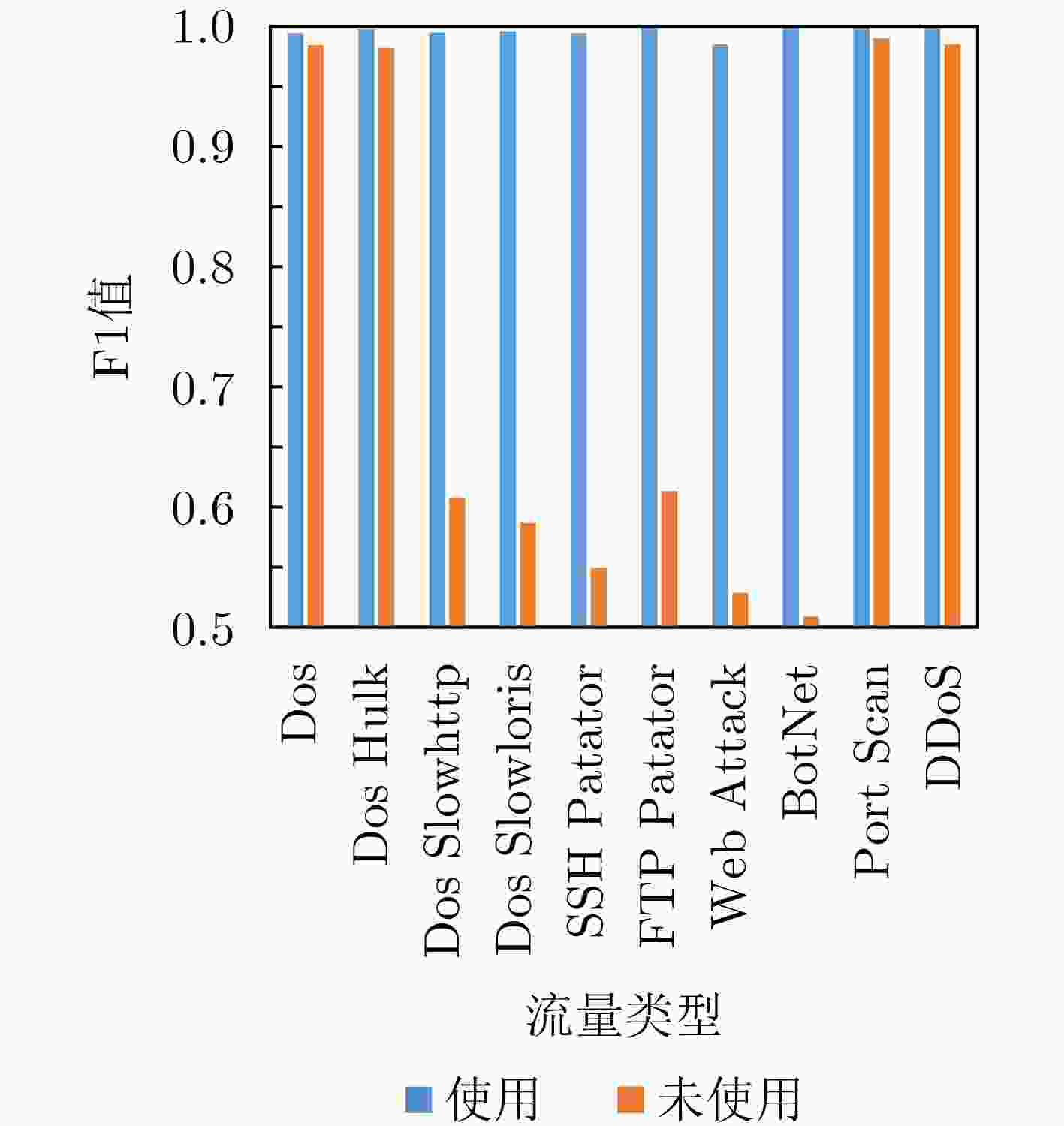
数据集 准确度 精确率 召回率 F1值 LSTM 本文模型 LSTM 本文模型 LSTM 本文模型 LSTM 本文模型 P1 75.96 99.58 73.68 99.77 75.54 99.15 74.62 99.46 P2 73.18 99.65 73.18 99.87 74.23 98.83 74.12 99.34 P3 76.23 99.69 76.16 99.21 76.72 99.68 75.82 99.45 P4 78.42 99.45 68.34 99.13 70.39 98.53 69.03 98.83 P5 74.73 99.37 56.31 99.43 59.73 99.35 58.28 99.39 P6 70.25 99.35 65.29 99.62 68.62 98.36 67.19 98.99 均值 74.80 99.52 68.83 99.51 70.87 98.98 69.84 99.24 -
[1] 康潆允, 孟凡宇, 冯永新. 一种面向军事物联网的网络流量异常检测模型[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2021, 46(2): 120–125,132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.02.021KANG Yingyun, MENG Fanyu, and FENG Yongxin. A network traffic anomaly detection model for military internet of things[J]. Fire Control &Command Control, 2021, 46(2): 120–125,132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.02.021 [2] 王馨彤, 王璇, 孙知信. 基于多尺度记忆残差网络的网络流量异常检测模型[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(8): 314–322. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.220200011WANG Xintong, WANG Xuan, and SUN Zhixin. Network traffic anomaly detection method based on multi-scale memory residual network[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(8): 314–322. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.220200011 [3] WESTER P, HEIDING F and LAGERSTROM R. Anomaly-based intrusion detection using tree augmented naive Bayes[C]. 2021 IEEE 25th International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Workshop (EDOCW), Gold Coast, Australia, 2021: 112–121. [4] HUANG Meigen and CAI Yunqiang. A DDoS attack detection method based on time series and random forest in SDN[C]. 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Automation and Systems (ICICAS), Chongqing, China, 2021: 323–327. [5] EL-SAYED R, EL-GHAMRY A, GABER T, et al. Zero-day malware classification using deep features with support vector machines[C]. 2021 Tenth International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Information Systems (ICICIS), Cairo, Egypt, 2021: 311–317. [6] KACHAVIMATH A V, NAZARE S V, and AKKI S S. Distributed denial of Service attack detection using naive Bayes and k-nearest neighbor for network forensics[C]. 2020 2nd International Conference on Innovative Mechanisms for Industry Applications (ICIMIA), Bangalore, India, 2020: 711–717. [7] NGUYEN T T T and ARMITAGE G. A survey of techniques for internet traffic classification using machine learning[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2008, 10(4): 56–76. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2008.080406 [8] 杭梦鑫, 陈伟, 张仁杰. 基于改进的一维卷积神经网络的异常流量检测[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(2): 433–440. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020050734HANG Mengxin, CHEN Wei, and ZHANG Renjie. Abnormal flow detection based on improved one-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(2): 433–440. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020050734 [9] YIN Chuanlong, ZHU Yuefei, FEI Jinlong, et al. A deep learning approach for intrusion detection using recurrent neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 21954–21961. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2762418 [10] PEI Jiaming, ZHONG Kaiyang, JAN M A, et al. Personalized federated learning framework for network traffic anomaly detection[J]. Computer Networks, 2022, 209: 108906. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.108906 [11] FOTIADOU K, VELIVASSAKI T H, VOULKIDIS A, et al. Network traffic anomaly detection via deep learning[J]. Information, 2021, 12(5): 215. doi: 10.3390/info12050215 [12] 皇甫雨婷, 李丽颖, 王海洲, 等. 自注意力的多特征网络流量异常检测与分类[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2021(6): 161–173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5641.2021.06.016HUANGFU Yuting, LI Liying, WANG Haizhou, et al. Multi-feature network traffic anomaly detection and classification based on self-attention[J]. Journal of East China Normal University:Natural Science, 2021(6): 161–173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5641.2021.06.016 [13] DING Defeng, ZHU Lu, XIE Jiaying, et al. In-vehicle network intrusion detection system based on Bi-LSTM[C]. 2022 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 2022: 580–583. [14] ZHANG Xin, CHEN Zhuang, and WEI Qingjie. Research and application of facial expression recognition based on attention mechanism[C]. 2021 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Image Processing, Electronics and Computers (IPEC), Dalian, China, 2021: 282–285. [15] ANDERSON J P. Computer security threat monitoring and surveillance[R]. Washington: James P. Anderson Company, 1980. [16] THAKKAR V, TEWARY S, and CHAKRABORTY C. Batch normalization in convolutional neural networks — a comparative study with CIFAR-10 data[C]. 2018 Fifth International Conference on Emerging Applications of Information Technology (EAIT), Kolkata, India, 2018: 1–5. [17] CAI Ningning, MA Can, WANG Weiping et al. Effective Self Attention modeling for aspect based sentiment analysis[C]. 19th International Conference on Computational Science, Faro, Portugal, 2019: 3–14. [18] SHARAFALDIN I, LASHKARI A H, and GHORBANI A A. A detailed analysis of the CICIDS2017 data set[C]. 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Funchal-Madeira, Portugal, 2019: 172–188. [19] SHARAFALDIN I, LASHKARI A H, and GHORBANI A A. Toward generating a new intrusion detection dataset and intrusion traffic characterization[C]. The 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Funchal-Madeira, Portugal, 2018: 108–116. [20] ZHU Mingyi, YE Kejiang, WANG Yang, et al. A deep learning approach for network anomaly detection based on AMF-LSTM[C]. The 15th IFIP WG 10.3 International Conference on Network and Parallel Computing, Muroran, Japan, 2018: 137–141. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
