Differential Analysis of Reduced Rounds Block Cipher LEA
-
摘要: LEA算法是面向软件的轻量级加密算法,在2019年成为 ISO/IEC 国际标准轻量级加密算法,具有快速加密、占用运算资源少等优点。该文基于多条输入输出差分相同的路径计算了差分概率,首次对LEA-128进行了13轮和14轮的密钥恢复攻击;采用提前抛弃技术,分别在12轮和13轮差分特征后面添加了1轮,恢复了96 bit密钥;其中13轮的密钥恢复攻击数据复杂度为298个明文,时间复杂度为286.7次13轮LEA-128解密;14轮的密钥恢复攻击数据复杂度为2118个明文,时间复杂度为2110.6次14轮LEA-128解密。Abstract: The LEA algorithm is a software-oriented lightweight encryption algorithm, which became the ISO/IEC international standard lightweight encryption algorithm in 2019. It has the advantages of fast encryption and less computing resources. The differential probability is calculated based on multiple paths with the same input-output difference, 13 and 14 rounds of key recovery attacks of LEA-128 are given for the first time. Using the early abort technology, one round is added after the 12-round and 13-round differential characteristic, and a total of 96 bit keys are recovered. The 13-round key recovery attack has a data complexity of 298 plaintext and a time complexity of 286.7 times of 13 rounds of LEA-128 decryption; the 14-round key recovery attack has a data complexity of 2118 plaintext and a time complexity of 2110.6 times of 14 rounds of LEA-128 decryption.
-
Key words:
- Lightweight block cipher /
- ARX /
- Differential analysis /
- Key recovery attack
-
表 1 LEA-128攻击分析结果比较
算法1 最优特征的差分概率 输入:对于 r 轮密码的原始MILP模型。 输出:最优特征的概率多项式。 (1) 求解原始MILP模型并获得最优差分特征的概率 d 和
$(\varDelta _{ {\text{in} } }^ * ,\varDelta _{ {\text{out} } }^ * )$;(2) 令 j = –1 ; (3) 重复: (4) j = j + 1 ; (5) 将原始MILP模型中的输入输出差分设为$(\varDelta _{ {\text{in} } }^ * ,\varDelta _{ {\text{out} } }^ * )$; (6) 令原始MILP模型中的目标函数 = d + j ; (7) 求解模型和不同特征的数量值$ {p_j} $;
(8) 直到${p_j}{2^{ - (d + j)} } \ge \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 0}^{j - 1} { {p_i}{2^{ - (d + i)} } }$;(9) 令N = j – 1; (10) 返回:概率多项式。 表 2 LEA算法的12轮差分特征及概率
轮数 $\Delta {X_0}$ $ \Delta {X_{\text{1}}} $ $\Delta {X_{\text{2}}}$ $\Delta {X_{\text{3}}}$ ${\log _2}p$ 0 C0000000 C0400080 40400010 40400012 – 1 80010000 8000000C 40000004 C0000000 –13 2 02001800 82000000 80000000 80010000 –8 3 00300100 00100000 00002000 02001800 –4 4 00020000 0001FF00 00400100 00300100 –15 5 00020000 00020000 00020000 00020000 –25 6 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000 –5 7 00000000 00000000 00004000 00000000 –1 8 00000000 00000200 00000800 00000000 –2 9 00040000 00000030 00000100 00000000 –5 10 08002000 80000008 00000020 00040000 –7 11 00401110 C4000000 00008004 08002000 –8 12 80222188 22200400 81001400 00401110 –14 表 3 LEA算法的13轮差分特征及概率
轮数 $\Delta {X_0}$ $ \Delta {X_{\text{1}}} $ $\Delta {X_{\text{2}}}$ $\Delta {X_{\text{3}}}$ ${\log _2}p$ 0 C0000000 C0400080 40400010 40400012 – 1 80010000 8000000C 40000004 C0000000 –13 2 02001800 82000000 80000000 80010000 –8 3 00300100 00100000 00002000 02001800 –4 4 00020000 0001FF00 00400100 00300100 –15 5 00020000 00020000 00020000 00020000 –25 6 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000 –5 7 00000000 00000000 00004000 00000000 –1 8 00000000 00000200 00000800 00000000 –2 9 00040000 00000030 00000100 00000000 –5 10 08002000 80000008 00000020 00040000 –7 11 00401110 C4000000 00008004 08002000 –8 12 80222188 22200400 81001400 00401110 –14 13 04491144 05190080 102800A1 80222088 –20 -
[1] HONG D, LEE J K, KIM D C, et al. LEA: A 128-bit block cipher for fast encryption on common processors[C]. The 14th International Workshop on Information Security Applications, Jeju Island, Korea, 2013: 3–27. [2] BEAULIEU R, SHORS D, SMITH J, et al. The SIMON and SPECK lightweight block ciphers[C]. The 52nd Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2015: 175. [3] HONG D, SUNG J, HONG S, et al. HIGHT: A new block cipher suitable for low-resource device[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 2006: 46–59. [4] GUO Ying, LI Lang, and LIU Botao. Shadow: A lightweight block cipher for IoT nodes[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(16): 13014–13023. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3064203 [5] KANG Man, LI Yongqiang, JIAO Lin, et al. Differential analysis of ARX block ciphers based on an improved genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2023, 32(2): 225–236. doi: 10.23919/cje.2021.00.415 [6] AZIMI S A, RANEA A, SALMASIZADEH M, et al. A bit-vector differential model for the modular addition by a constant and its applications to differential and impossible-differential cryptanalysis[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2022, 90(8): 1797–1855. doi: 10.1007/s10623-022-01074-8 [7] COUTINHO M and SOUZA NETO T C. Improved linear approximations to ARX ciphers and attacks against ChaCha[C]. The 40th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Zagreb, Croatia, 2021: 711–740. [8] WANG Feifan and WANG Gaoli. Improved differential-linear attack with application to round-reduced Speck32/64[C]. The 20th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Rome, Italy, 2022: 792–808. [9] ZHANG Kai, GUAN Jie, and HU Bin. Zero correlation linear cryptanalysis on LEA family ciphers[J]. Journal of Communications, 2016, 11(7): 677–685. doi: 10.12720/jcm.11.7.677-685 [10] SUN Ling, WANG Wei, LIU Ru, et al. MILP-aided bit-based division property for ARX ciphers[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(11): 118102. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9321-7 [11] 崔婷婷. 分组密码算法和流密码算法的安全性分析[D]. [博士论文], 山东大学, 2018.CUI Tingting. Security analysis of block ciphers and stream ciphers[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Shandong University, 2018. [12] 孙玲. 分组密码攻击模型的构建和自动化密码分析[D]. [博士论文], 山东大学, 2019.SUN Ling. The construction of attack model for block ciphers and automatic cryptanalysis[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Shandong University, 2019. [13] 李航, 任炯炯, 陈少真. 减轮LEA密码算法的积分攻击[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(1): 17–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.003LI Hang, REN Jiongjiong, and CHEN Shaozhen. Integral attack on reduced-round LEA cipher[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(1): 17–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.003 [14] 刘晟源. 基于MILP对WARP、GOST2和LEA算法的密码分析[D]. [硕士论文], 华东师范大学, 2022.LIU Shengyuan. Cryptanalysis of WARP, GOST2 and LEA algorithms based on MILP[D]. [Master dissertation], East China Normal University, 2022. [15] MOUHA N, WANG Qingju, GU Dawu, et al. Differential and linear cryptanalysis using mixed-integer linear programming[C]. The 7th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Beijing, China, 2011: 57–76. [16] WU Shengbao and WANG Mingsheng. Security evaluation against differential cryptanalysis for block cipher structures[R]. Paper 2011/551, 2011. [17] SUN Siwei, HU Lei, WANG Peng, et al. Automatic security evaluation and (related-key) differential characteristic search: Application to SIMON, PRESENT, LBlock, DES(L) and other bit-oriented block ciphers[C]. The 20th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Taipei, China, 2014: 158–178. [18] SUN Siwei, HU Lei, WANG Meiqin, et al. Towards finding the best characteristics of some bit-oriented block ciphers and automatic enumeration of (related-key) differential and linear characteristics with predefined properties[R]. Paper 2014/747, 2014: 747. [19] LIPMAA H and MORIAI S. Efficient algorithms for computing differential properties of addition[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Yokohama, Japan, 2001: 336–350. [20] FU Kai, WANG Meiqin, GUO Yinghua, et al. MILP-based automatic search algorithms for differential and linear trails for speck[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Fast Software Encryption, Bochum, Germany, 2016: 268–288. [21] LAI Xuejia, MASSEY J L, and MURPHY S. Markov ciphers and differential cryptanalysis[C]. 1991 Workshop on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Brighton, UK, 1991: 17–38. [22] BAGHERZADEH E and AHMADIAN Z. MILP‐based automatic differential search for LEA and HIGHT block ciphers[J]. IET Information Security, 2020, 14(5): 595–603. doi: 10.1049/iet-ifs.2018.5539 -





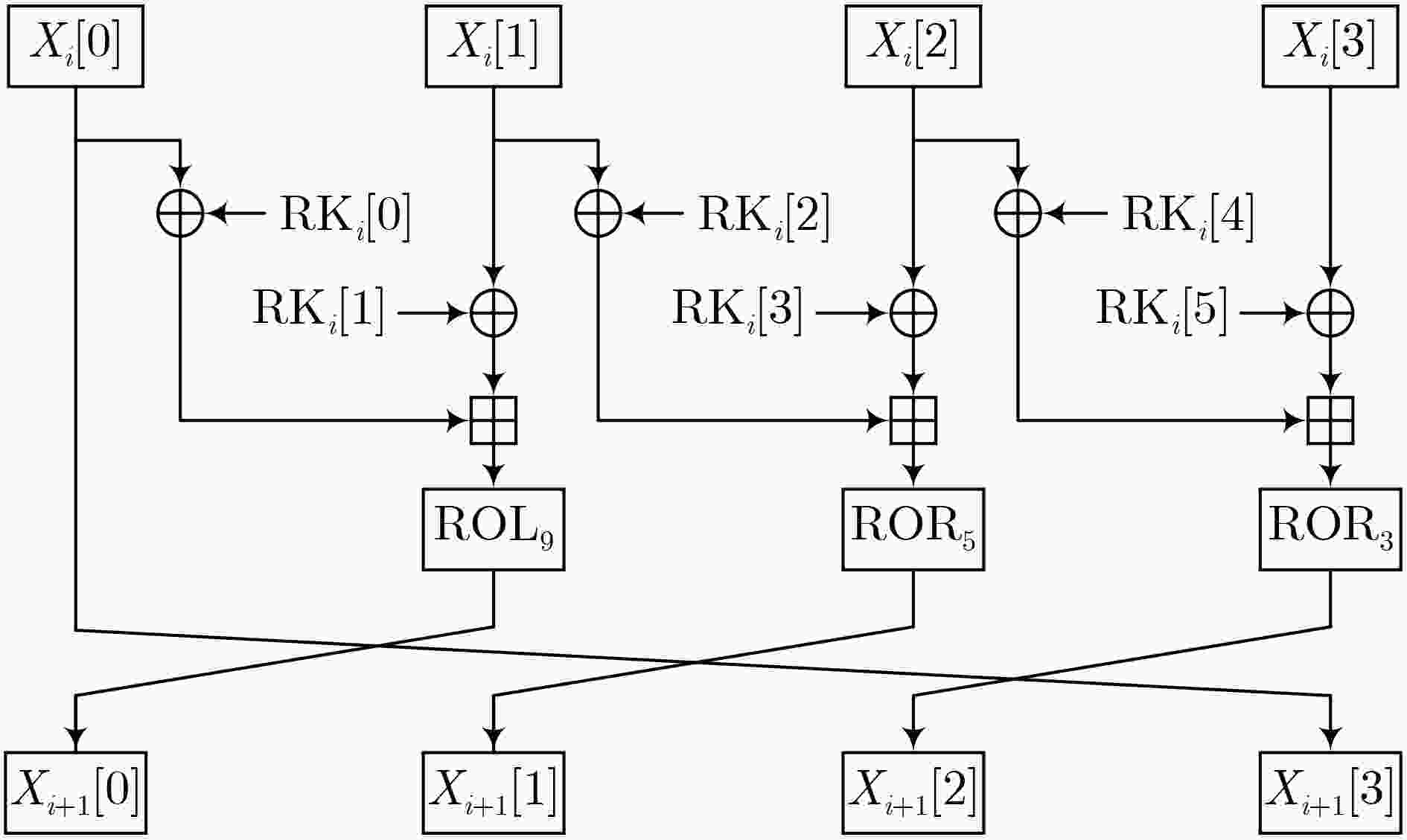
 下载:
下载:

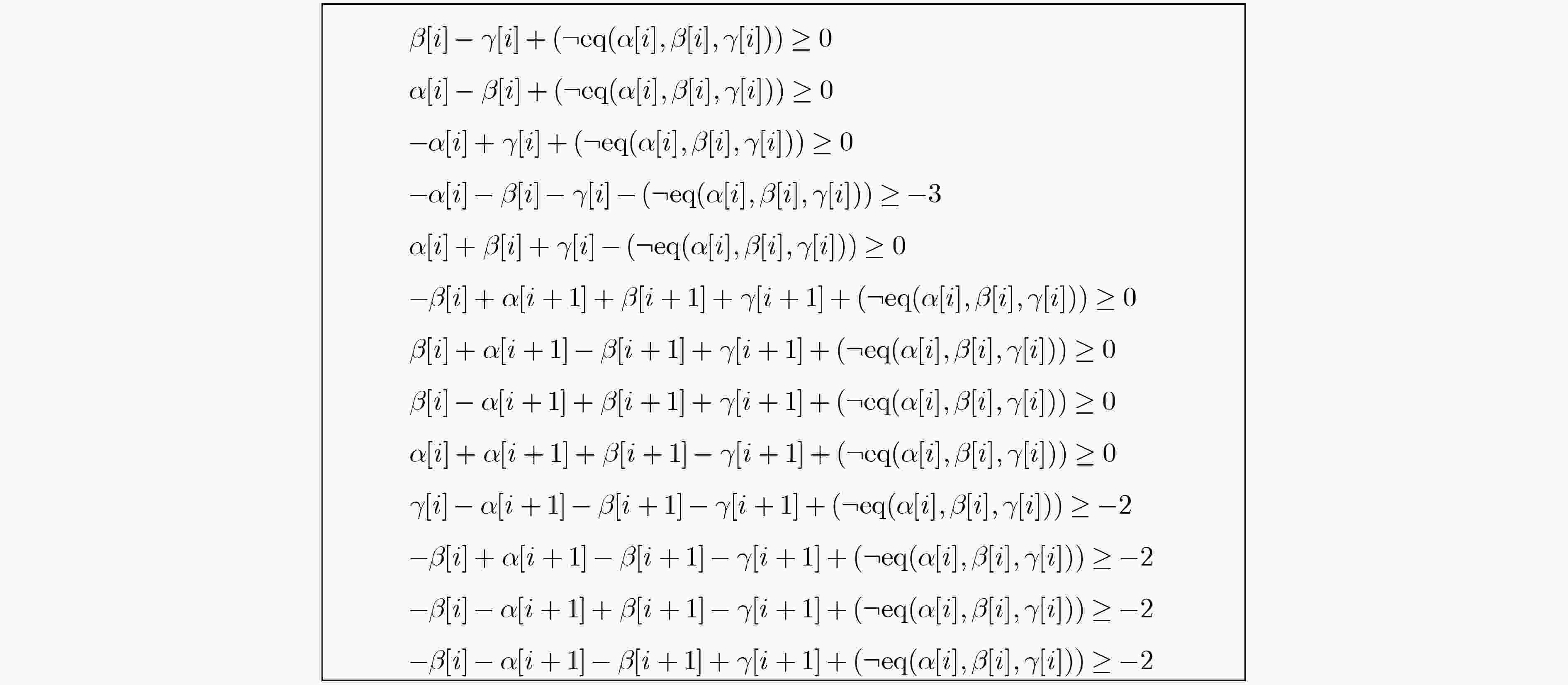
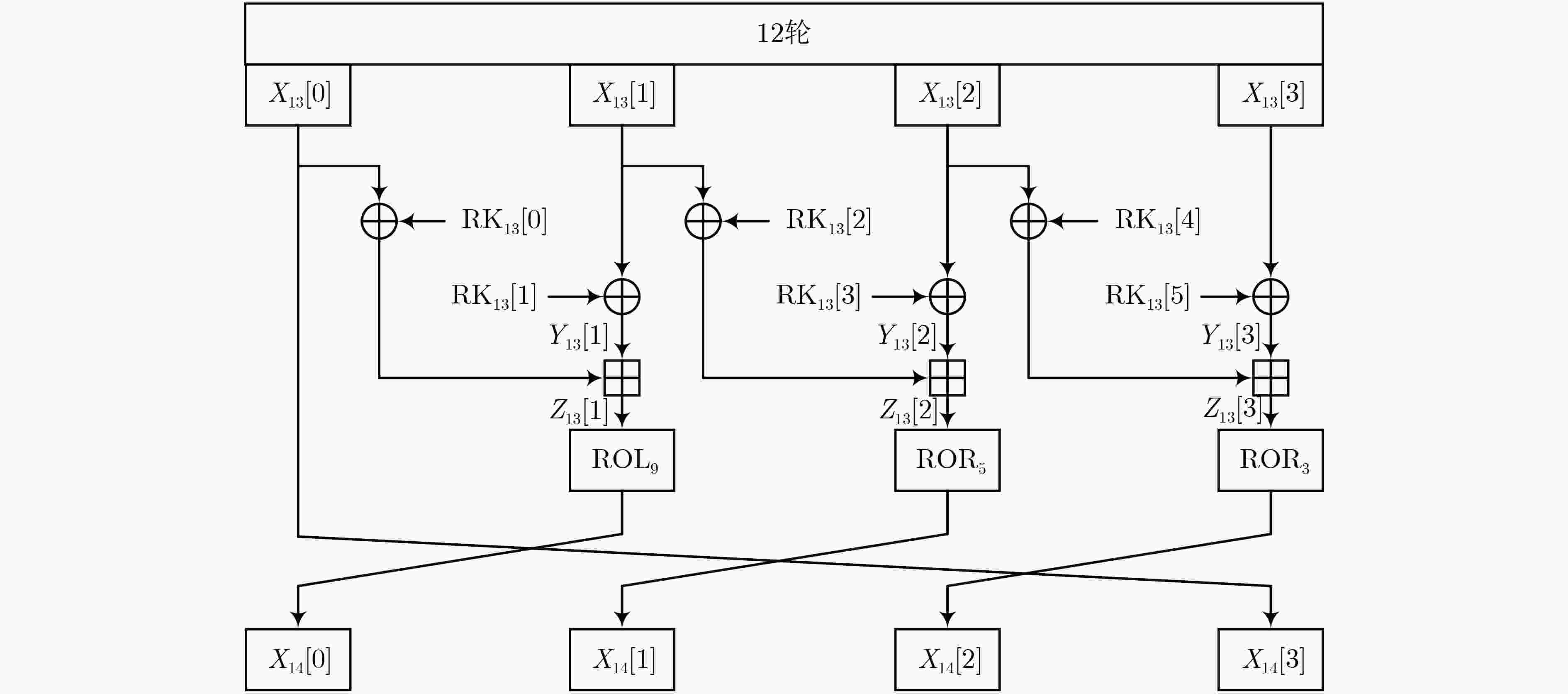
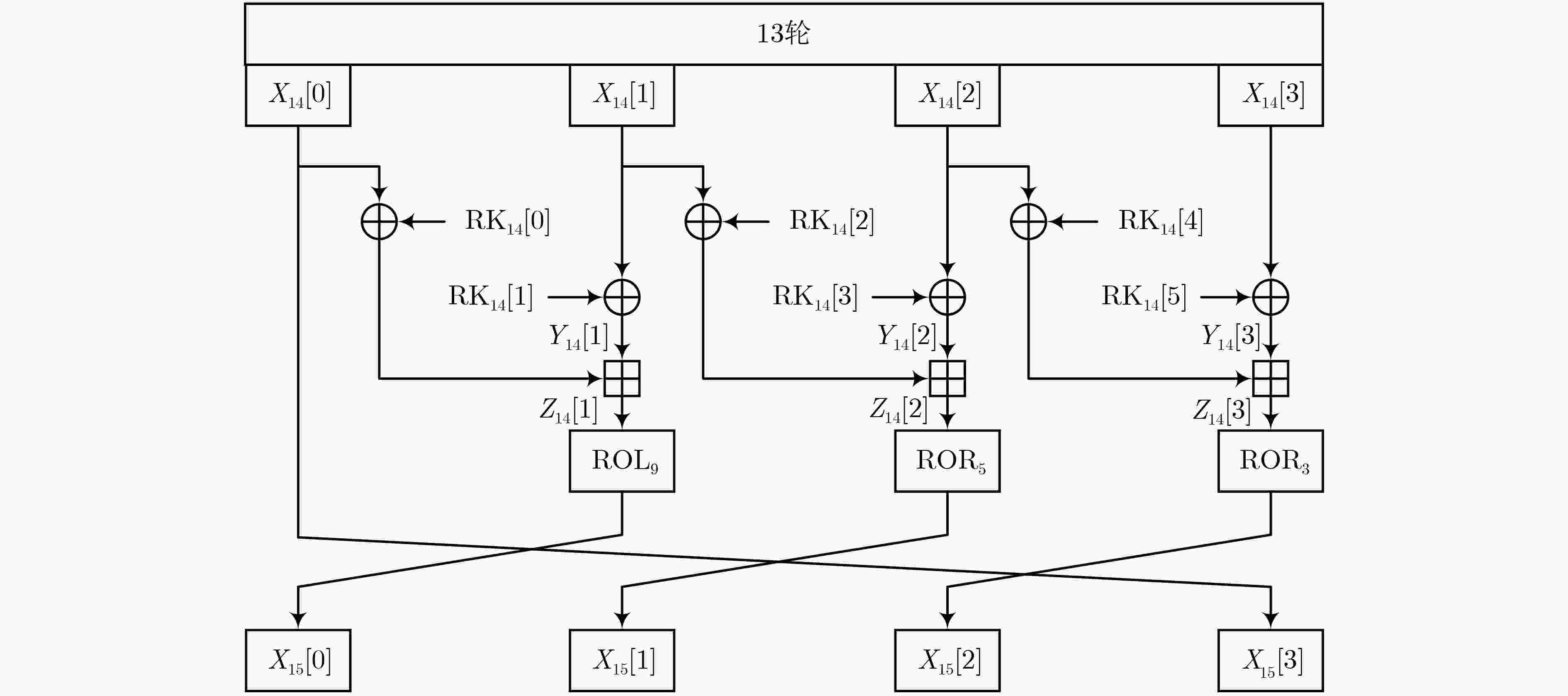


 下载:
下载:
