Saliency Detection Based on Context-aware Cross-layer Feature Fusion for Light Field Images
-
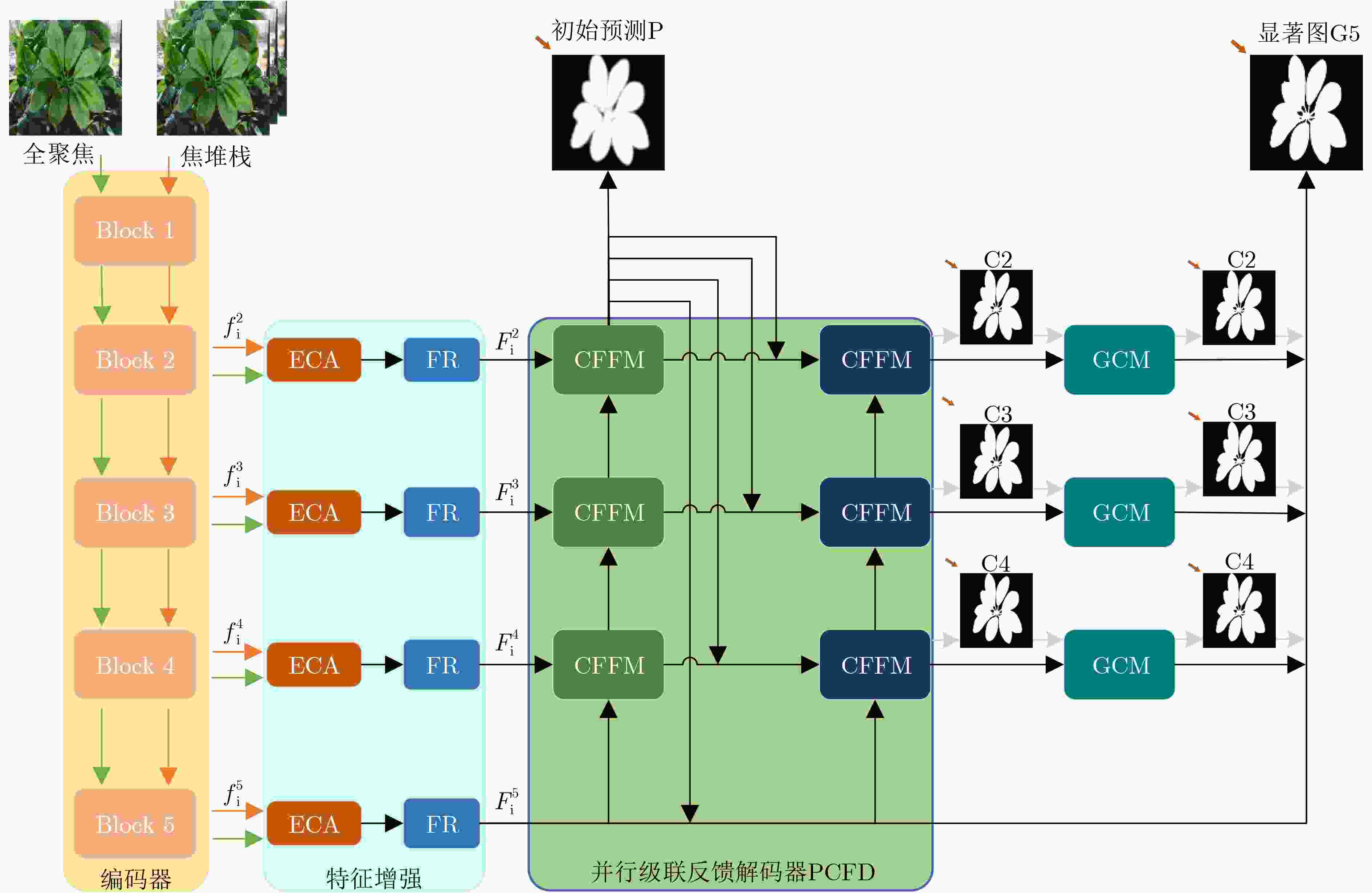
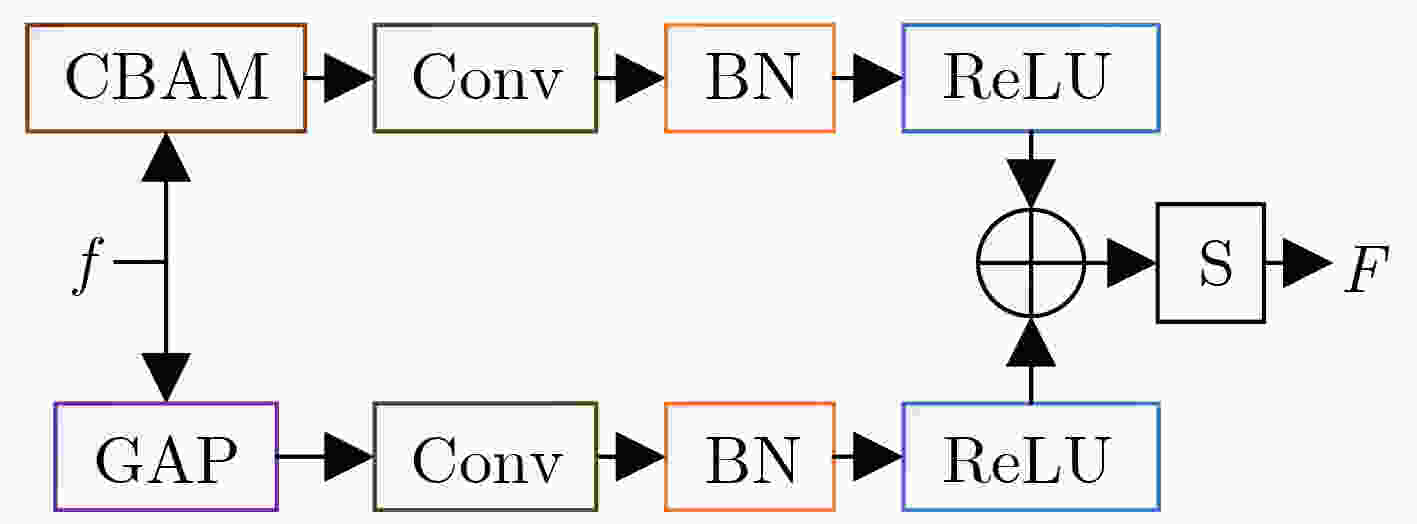
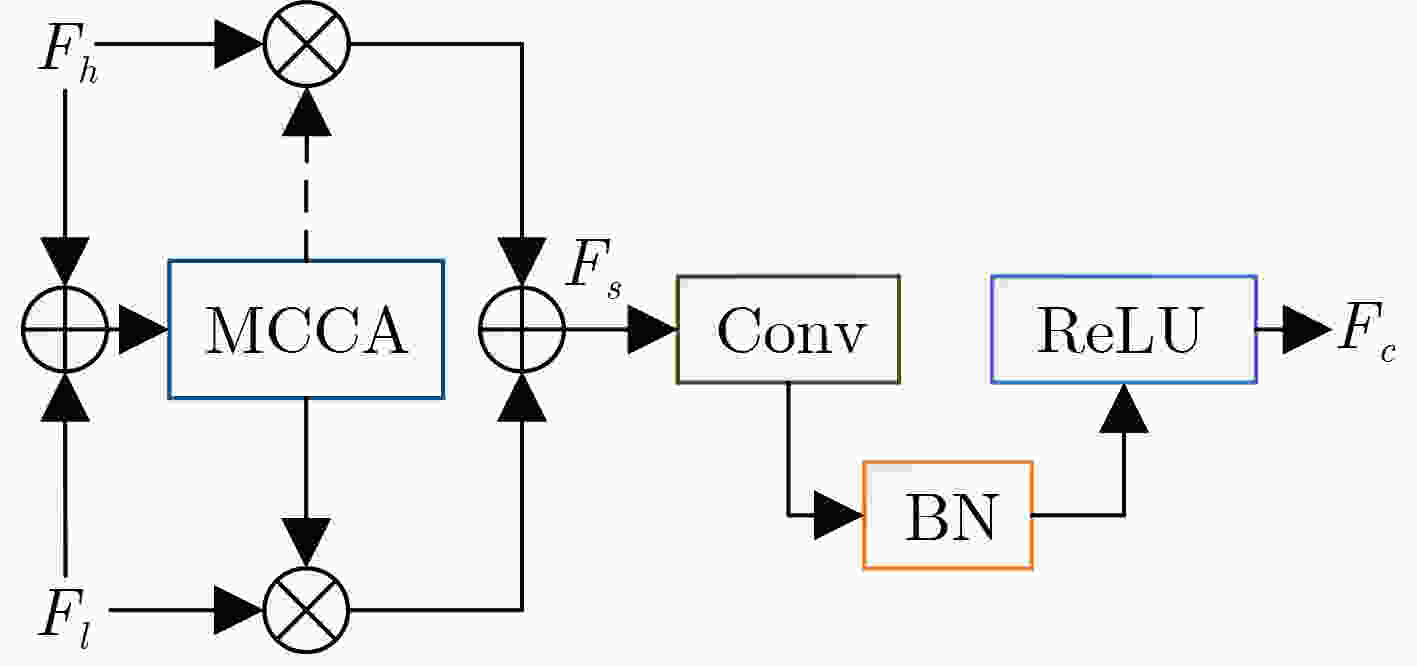
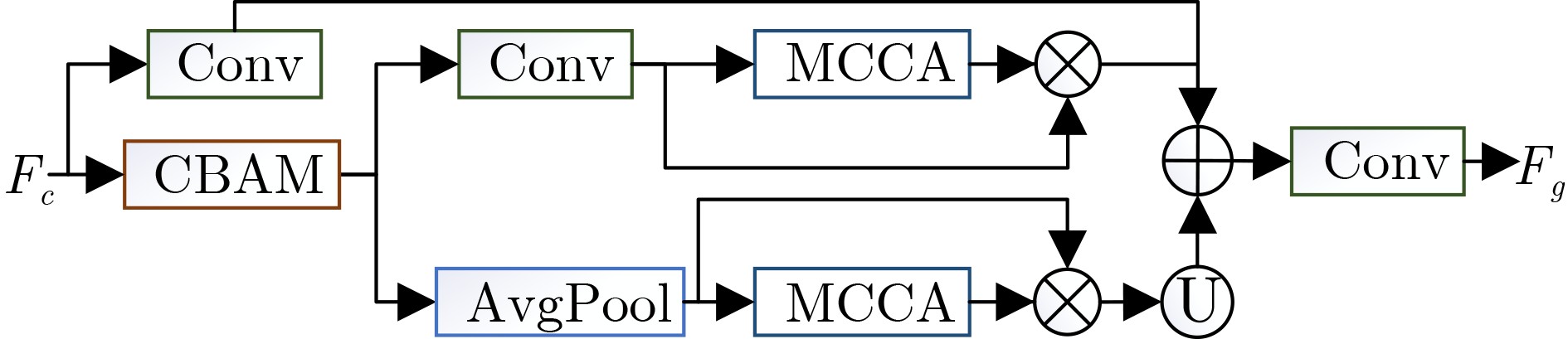
摘要: 光场图像的显著性检测是视觉跟踪、目标检测、图像压缩等应用中的关键技术。然而,现有深度学习方法在处理特征时,忽略特征差异和全局上下文信息,导致显著图模糊,甚至在前景与背景颜色、纹理相似或者背景杂乱的场景中,存在检测对象不完整以及背景难抑制的问题,因此该文提出一种基于上下文感知跨层特征融合的光场图像显著性检测网络。首先,构建跨层特征融合模块自适应地从输入特征中选择互补分量,减少特征差异,避免特征不准确整合,以更有效地融合相邻层特征和信息性系数;同时利用跨层特征融合模块构建了并行级联反馈解码器(PCFD),采用多级反馈机制重复迭代细化特征,避免特征丢失及高层上下文特征被稀释;最后构建全局上下文模块(GCM)产生多尺度特征以利用丰富的全局上下文信息,以此获取不同显著区域之间的关联并减轻高级特征的稀释。在最新光场数据集上的实验结果表明,该文方法在定量和定性上均优于所比较的方法,并且能够精确地从前/背景相似的场景中检测出完整的显著对象、获得清晰的显著图。Abstract: Saliency detection of light field images is a key technique in applications such as visual tracking, target detection, and image compression. However, the existing deep learning methods ignore feature differences and global contextual information when processing features, resulting in blurred saliency maps and even incomplete detection objects and difficult background suppression in scenes with similar foreground and background colors, textures, or background clutter. A context-aware cross-layer feature fusion-based saliency detection network for light field images is proposed. First, a cross-layer feature fusion module is built to select adaptively complementary components from input features to reduce feature differences and avoid inaccurate integration of features in order to more effectively fuse adjacent layer features and informative coefficients; Meanwhile, a Parallel Cascaded Feedback Decoder (PCFD) is constructed using the cross-layer feature fusion module to iteratively refine features using a multi-level feedback mechanism to avoid feature loss and dilution of high-level contextual features; Finally, a Global Context Module (GCM) generates multi-scale features to exploit the rich global context information in order to obtain the correlation between different salient regions and mitigate the dilution of high-level features. Experimental results on the latest light field dataset show that the textual method outperforms the compared methods both quantitatively and qualitatively, and is able to detect accurately complete salient objects and obtain clear saliency maps from similar front/background scenes.
-
Key words:
- Light field images /
- Saliency detection /
- Cross-layer feature fusion /
- Context-awareness
-
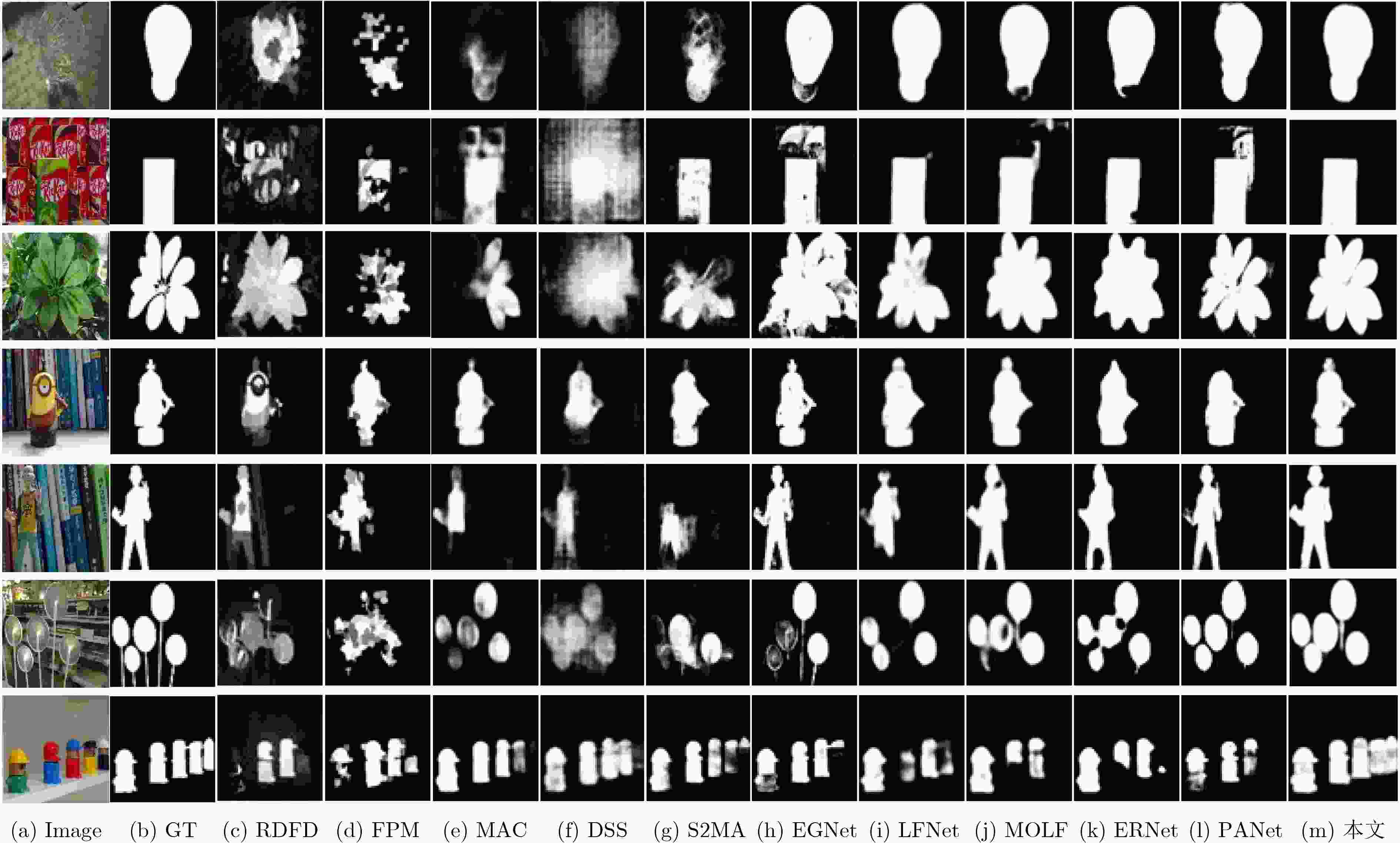
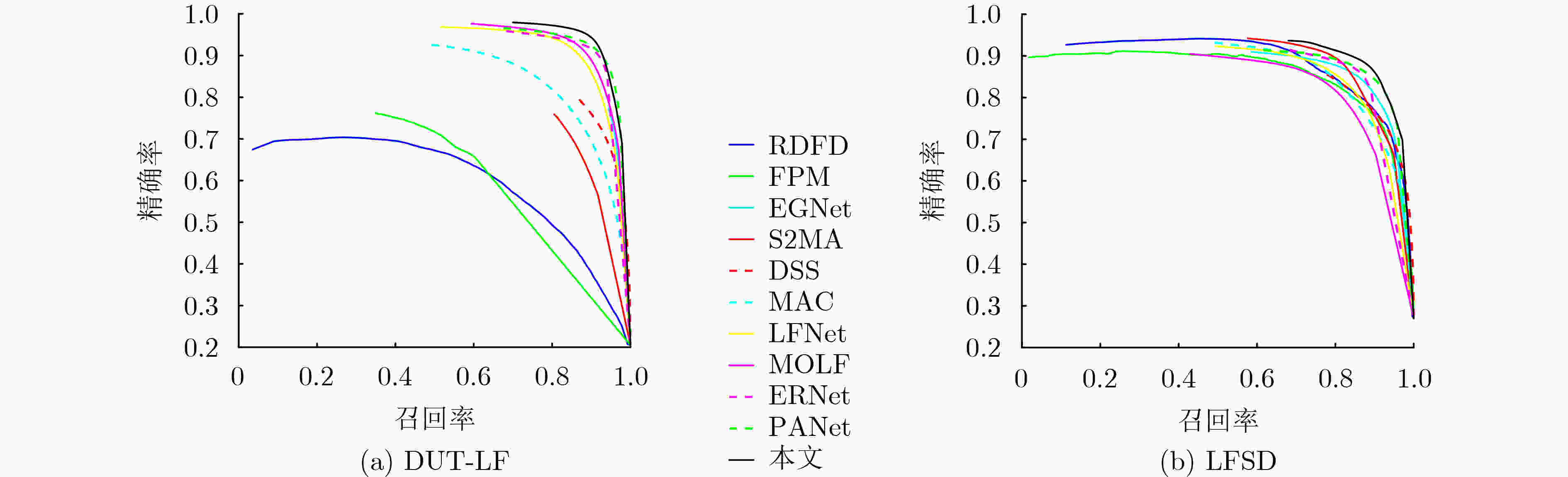
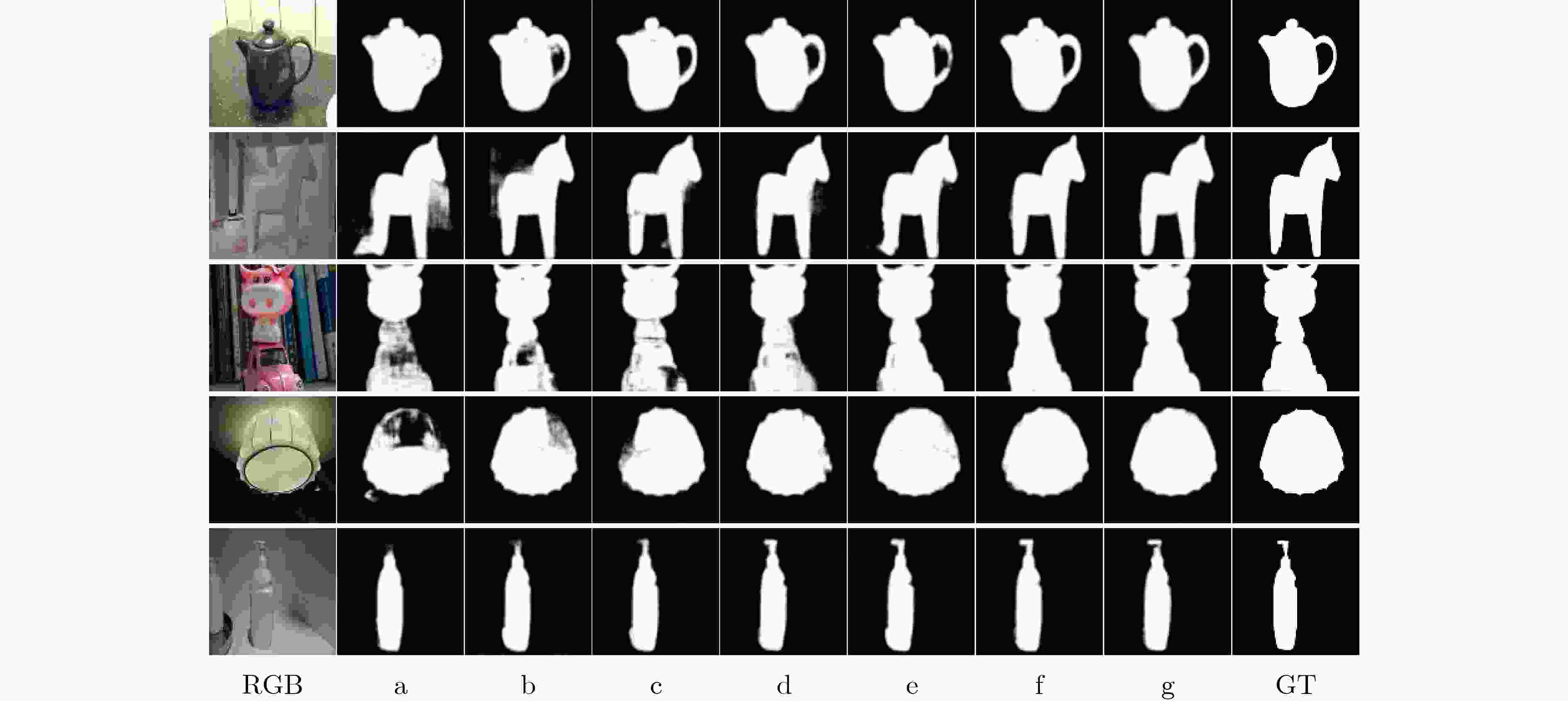
表 1 不同算法在DUT-LF数据集和LFSD数据集中的指标结果对比
类别 算法 DUT-LF LFSD Sα↑ Fβ↑ Eϕ↑ MAE↓ Sα↑ Fβ↑ Eϕ↑ MAE↓ 2d EGNet[16] 0.870 0.864 0.910 0.062 0.841 0.821 0.872 0.083 DSS[17] 0.764 0.728 0.827 0.128 0.677 0.644 0.749 0.190 3d S2MA[18] 0.729 0.650 0.777 0.112 0.837 0.835 0.833 0.094 ATSA[19] 0.772 0.729 0.833 0.084 0.858 0.866 0.902 0.068 4d RDFD[23] 0.658 0.599 0.774 0.191 0.786 0.802 0.834 0.136 FPM[21] 0.675 0.619 0.745 0.142 0.791 0.800 0.839 0.134 DILF[22] 0.705 0.641 0.805 0.168 0.755 0.728 0.810 0.168 MAC[19] 0.804 0.790 0.863 0.103 0.782 0.776 0.832 0.127 DLFS[6] 0.841 0.801 0.891 0.076 0.737 0.715 0.806 0.147 LFNet[13] 0.878 0.833 0.910 0.054 0.820 0.805 0.882 0.092 MoLF[14] 0.887 0.843 0.923 0.052 0.789 0.819 0.831 0.088 ERNet[12] 0.899 0.889 0.942 0.040 0.834 0.842 0.888 0.082 PANet[8] 0.897 0.892 0.941 0.042 0.842 0.853 0.882 0.080 本文 0.900 0.898 0.952 0.042 0.853 0.846 0.880 0.080 表 2 不同模块在DUT-LF和LFSD数据集的消融研究
实验 模型 DUT-LF LFSD Fβ↑ MAE↓ Fβ↑ MAE↓ a Baseline 0.851 0.066 0.776 0.118 b Baseline +FR 0.862 0.058 0.794 0.108 d Baseline +FR +PCFD 0.887 0.050 0.816 1.100 f Baseline +FR +PCFD +GCM 0.896 0.043 0.842 0.082 g 本文 0.898 0.042 0.846 0.080 表 3 MCCA在DUT-LF和LFSD数据集的消融研究
实验 模块 DUT-LF LFSD Fβ↑ MAE↓ Fβ↑ MAE↓ c +PCFD(w/o MCCA) 0.871 0.058 0.802 0.107 d +PCFD(with MCCA) 0.887 0.050 0.816 1.100 e +GCM(w/o MCCA) 0.890 0.046 0.829 0.096 f +GCM(with MCCA) 0.896 0.043 0.842 0.082 表 4 本文方法和其他方法复杂度比较
算法 主干 尺寸(MB) FPS(帧/s) DUT-LF LFSD Sα Sα 本文 VGG-19 175 29 0.900 0.853 PANet VGG-16 60 11 0.899 0.842 ERNet VGG-19 93 14 0.899 0.834 LFNet VGG-19 176 13 0.878 0.820 MoLF VGG-19 178 24 0.887 0.789 S2MA VGG-16 347 9 0.729 0.831 EGNet ResNet-50 412 21 0.870 0.843 -
[1] BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, JIANG Huaizhu, et al. Salient object detection: A benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5706–5722. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2487833 [2] LI Xi, HU Weiming, SHEN Chunhua, et al. A survey of appearance models in visual object tracking[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2013, 4(4): 58. doi: 10.1145/2508037.2508039 [3] HAN S and VASCONCELOS N. Object recognition with hierarchical discriminant saliency networks[J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2014, 8: 109. doi: 10.3389/FNCOM.2014.00109 [4] LI Nianyi, YE Jinwei, JI Yu, et al. Saliency detection on light field[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 2806–2813. [5] ZHANG Jun, WANG Meng, LIN Liang, et al. Saliency detection on light field: A multi-cue approach[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2017, 13(3): 32. doi: 10.1145/3107956 [6] PIAO Yongri, RONG Zhengkun, ZHANG Miao, et al. Deep light-field-driven saliency detection from a single view[C]. The 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 2019: 904–911. [7] WANG Tiantian, PIAO Yongri, LU Huchuan, et al. Deep learning for light field saliency detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 8837–8847. [8] PIAO Yongri, JIANG Yongyao, ZHANG Miao, et al. PANet: Patch-aware network for light field salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(1): 379–391. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3095512 [9] DAI Yimian, GIESEKE F, OEHMCKE S, et al. Attentional feature fusion[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 3559–3568. [10] 王安志, 任春洪, 何淋艳, 等. 基于多模态多级特征聚合网络的光场显著性目标检测[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(7): 227–233,240. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0061811WANG Anzhi, REN Chunhong, HE Linyan, et al. Light field salient object detection based on multi-modal multi-level feature aggregation network[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(7): 227–233,240. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0061811 [11] 冯洁, 王世刚, 韦健, 等. 结合相机阵列选择性光场重聚焦的显著性检测[J]. 中国光学, 2021, 14(3): 587–595. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0165FENG Jie, WANG Shigang, WEI Jian, et al. Saliency detection combined with selective light field refocusing of camera array[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 587–595. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0165 [12] PIAO Yongri, RONG Zhengkun, ZHANG Miao, et al. Exploit and replace: An asymmetrical two-stream architecture for versatile light field saliency detection[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 11865–11873. [13] ZHANG Miao, JI Wei, PIAO Yongri, et al. LFNet: Light field fusion network for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 6276–6287. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2990341 [14] ZHANG Miao, LI Jingjing, WEI Ji, et al. Memory-oriented decoder for light field salient object detection[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 81. [15] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. [16] ZHAO Jiaxing, LIU Jingjing, FAN Dengping, et al. EGNet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 8778–8787. [17] HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, HU Xiaowei, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5300–5309. [18] LIU Nian, ZHANG Ni, and HAN Junwei. Learning selective self-mutual attention for RGB-D saliency detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13753–13762. [19] ZHANG Miao, FEI Sunxiao, LIU Jie, et al. Asymmetric two-stream architecture for accurate RGB-D saliency detection[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 374–390. [20] ZHANG Qiudan, WANG Shiqi, WANG Xu, et al. A multi-task collaborative network for light field salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(5): 1849–1861. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3013119 [21] 李爽, 邓慧萍, 朱磊, 等. 联合聚焦度和传播机制的光场图像显著性检测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(12): 2578–2586. doi: 10.11834/jig.190675LI Shuang, DENG Huiping, ZHU Lei, et al. Saliency detection on a light field via the focusness and propagation mechanism[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(12): 2578–2586. doi: 10.11834/jig.190675 [22] ZHANG Jun, WANG Meng, GAO Jun, et al. Saliency detection with a deeper investigation of light field[C]. The 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015: 2212–2218. [23] WANG Xue, DONG Yingying, ZHANG Qi, et al. Region-based depth feature descriptor for saliency detection on light field[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(11): 16329–16346. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-08890-x -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
