Research on Highly Portable Lightweight Physical Unclonable Functions Using Multiplexer Entropy Sources
-
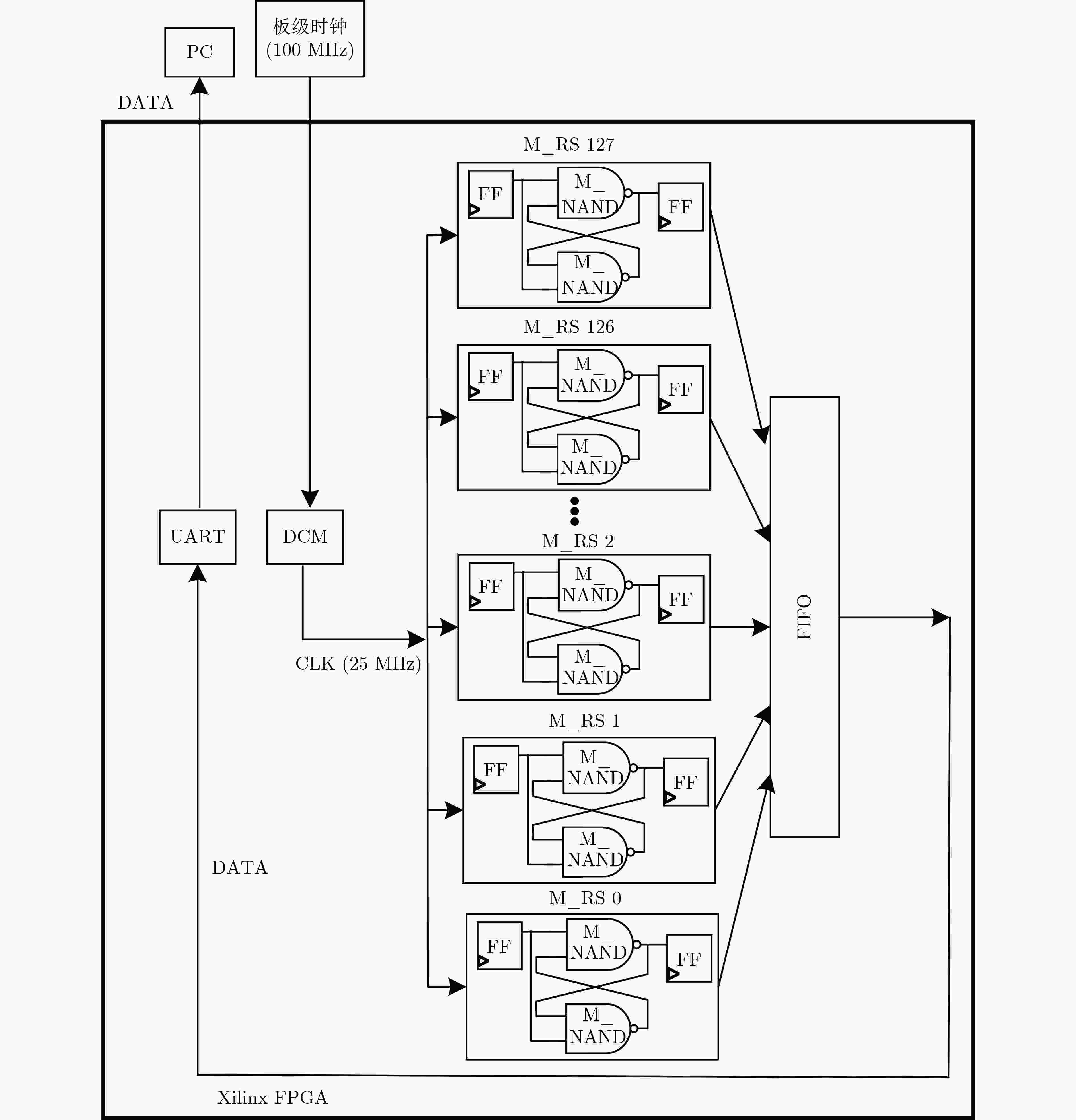
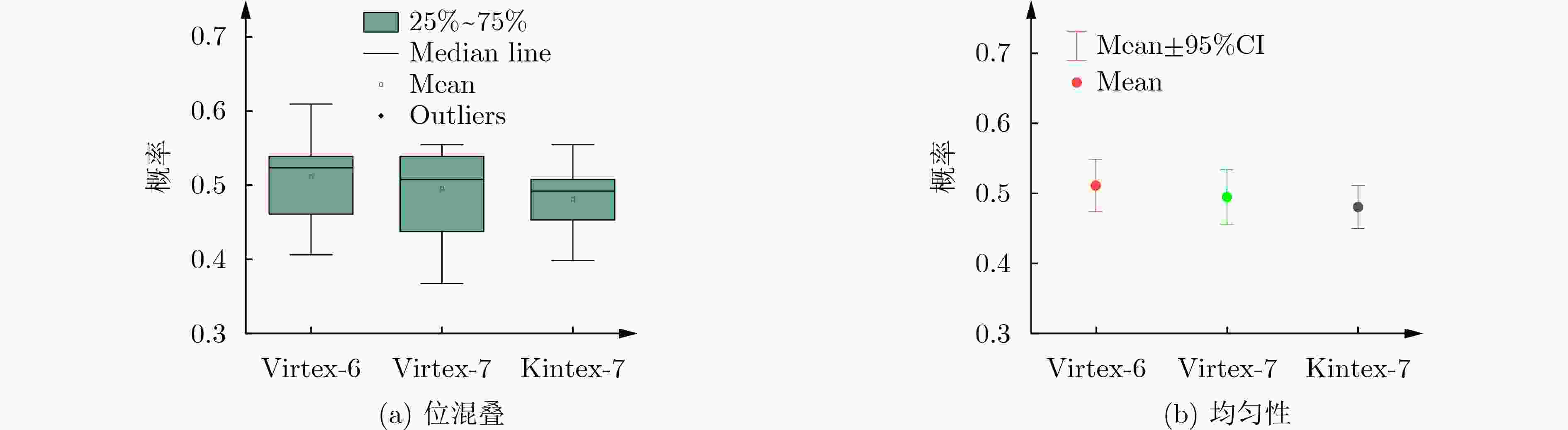
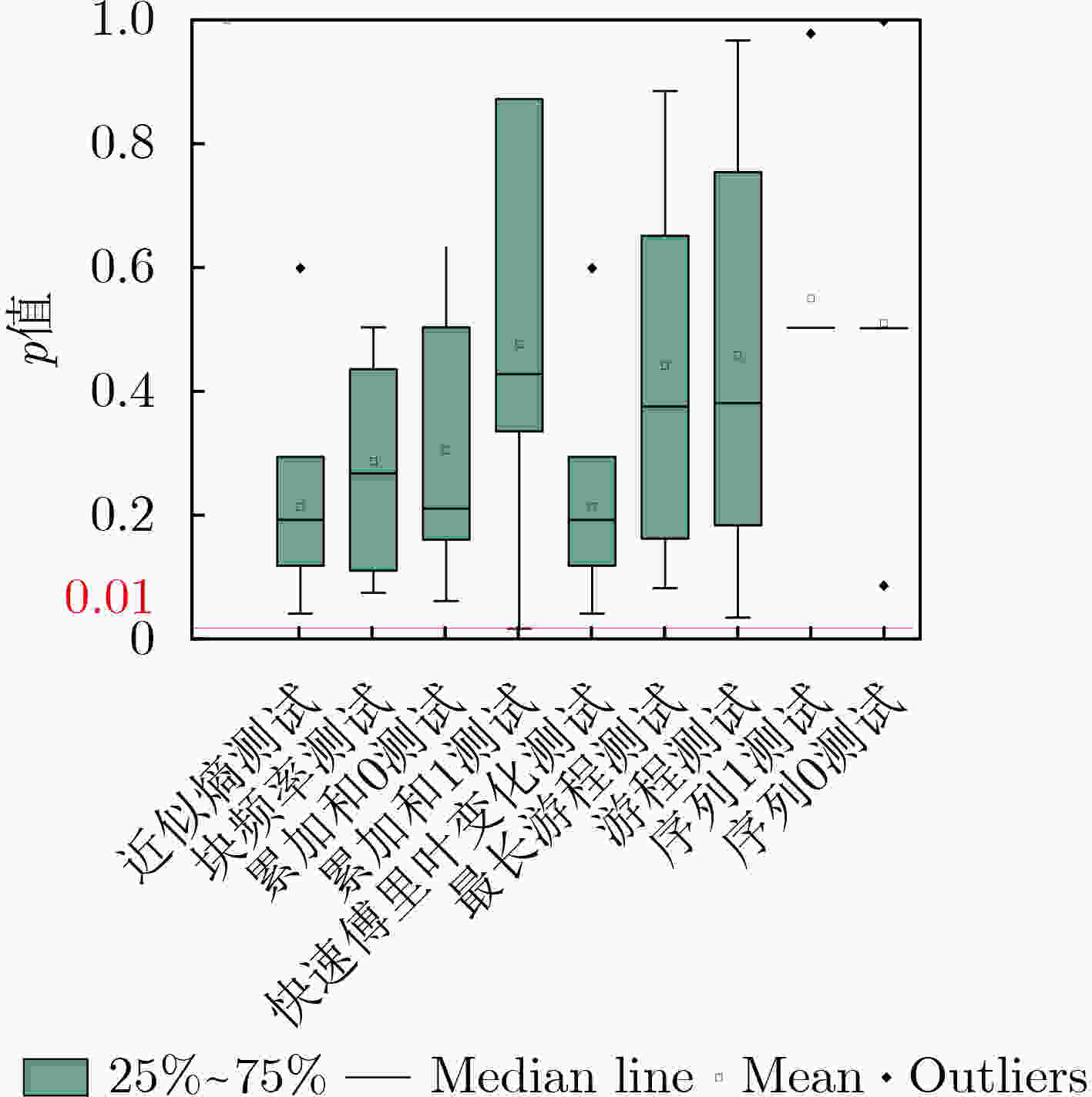
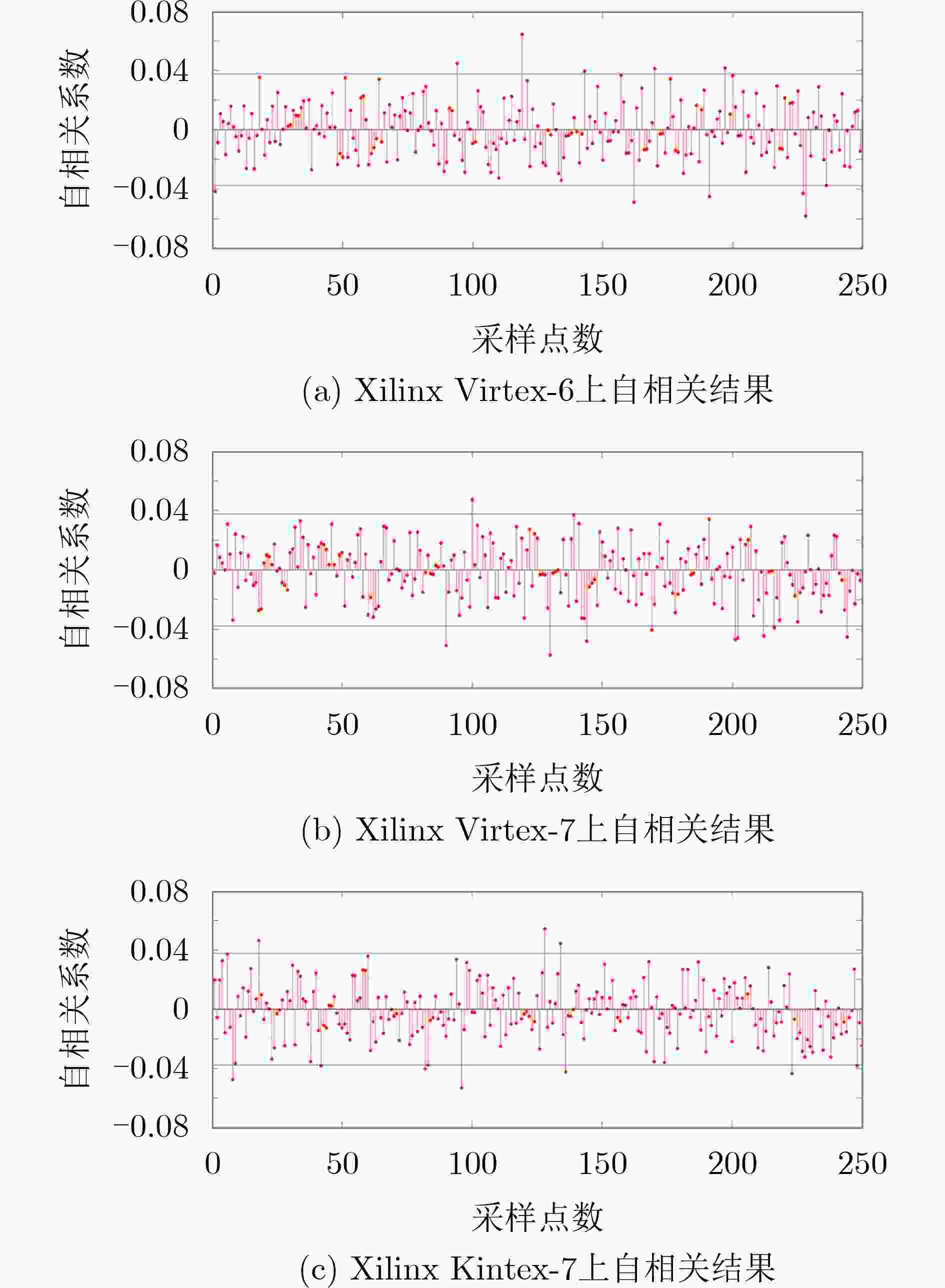
摘要: SR锁存器物理不可克隆函数 (Physical Unclonable Function, PUF) 是基于 FPGA 实现的最流行加密应用,在轻量级物联网设备中拥有广阔的市场。为了实现对称无偏SR锁存PUF,研究人员提出了不同的实现方法,这些方法增加了面积消耗。该文提出一种新型的基于MUX单元的延迟门来构成M_SR PUF单元,并将稳定状态下SR锁存器的输出提取作为PUF的响应。为了验证所提出的 M_SR PUF,该文在 Xilinx Virtex-6,Virtex-7 和 Kintex-7 3个系列的 FPGA 上进行了实现。值得一提的是,对称布局通过“硬宏”实现相对简单,保证了PUF更好的性能。实验结果表明,所提出的M_SR PUF可以在超宽范围的环境变化(温度:0°C~80°C;电压:0.8~1.2 V)下稳定工作,平均唯一性为50.125%。此外,所提出的 M_SR PUF 单元具有低开销的特点,仅消耗 4个 MUX 和 2个 DFF,并产生适合硬件安全应用的高熵响应。Abstract: SR Latches Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs) are the most popular FPGA-based cryptographic applications and have a broad market in lightweight IoT devices. To realize a symmetric unbiased SR latch PUF, different implementation methods that increase area consumption have been proposed. In this paper, a novel MUX-unit-based delay gate is proposed to form the M_SR PUF unit, and the output of the SR latch in the steady state is extracted as the response of the PUF. To verify the proposed M_SR PUF, it is implemented on three series of FPGAs from Xilinx Virtex-6, Virtex-7 and Kintex-7. It is worth mentioning that the symmetrical layout is relatively simple to implement through “hard macros”, which ensures better performance of PUF. The experimental results show that the proposed M_SR PUF can work stably under an ultra-wide range of environmental changes (temperature: 0°C ~80 °C; voltage: 0.8~1.2 V) with an average uniqueness of 50.125%. Furthermore, the proposed M_SR PUF unit is characterized by low overhead, consuming only 4 MUXs and 2 DFFs, and produces a high-entropy response suitable for hardware security applications.
-
表 1 相关PUF的性能比较
PUF 设计 FPGA平台 PUF 响应 唯一性(%) 可靠性(%) 资源消耗 不同电压 不同温度 文献[8] Spartan-3 128 49.200 80.000* 435×CLB 文献[16] Artix 128 51.700 94.500* – 文献[27] Kintex-7 256 47.300 – 96.650 – Artix-7 256 40.100 94.000 96.000 文献[9] Spartan-3 128 46.000 >87.000 2×128 SLICEs 文献[17] Virtex-6 128 48.438 98.242 98.326 256×CLB 本文 M_SR PUF Virtex-6 128 50.423 94.879 97.118 4×128 MUXs
2×128 DFFVirtex-7 49.902 94.010 96.806 Kintex-7 50.051 91.884 94.861 注1:*表示文献没有说明获得可靠性结果的情况.
注2:1个CLB包含2 SLICEs, 1个SLICE包含4个LUTs和8个DFFs. -
[1] SUNAR B, MARTIN W J, and STINSON D R. A provably secure true random number generator with built-in tolerance to active attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2007, 56(1): 109–119. doi: 10.1109/TC.2007.250627 [2] TANEJA S, RAJANNA V K, and ALIOTO M. 36.1 Unified in-memory dynamic TRNG and multi-bit static PUF entropy generation for ubiquitous hardware security[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2021: 498–500. [3] SURAGANI R, NAZARENKO E, ANAGNOSTOPOULOS N A, et al. Identification and classification of corrupted PUF responses via machine learning[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), McLean, USA, 2022: 137–140. [4] KROEGER T, CHENG Wei, GUILLEY S, et al. Cross-PUF attacks on arbiter-PUFs through their power side-channel[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Test Conference (ITC), Washington, USA, 2020: 1–5. [5] CHANG Zhengtai, SHI Shanshan, SONG Binwei, et al. Modeling attack resistant arbiter PUF with time-variant obfuscation scheme[C]. Proceedings of 2021 31st International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Dresden, Germany, 2021: 60–63. [6] YAO Liang, LIANG Huaguo, HAN Qian, et al. M-RO PUF: A portable pure digital RO PUF based on MUX unit[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2022, 119: 105314. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2021.105314 [7] OKUMURA S, YOSHIMOTO S, KAWAGUCHI H, et al. A 128-bit chip identification generating scheme exploiting load transistors' variation in SRAM bitcells[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2012, E95.A(12): 2226–2233. doi: 10.1587/transfun.E95.A.2226 [8] ARDAKANI A and SHOKOUHI S B. A secure and area-efficient FPGA-based SR-Latch PUF[C]. Proceedings of 2016 8th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran, 2016: 94–99. [9] YAMAMOTO D, SAKIYAMA K, IWAMOTO M, et al. Uniqueness enhancement of PUF responses based on the locations of random outputting RS latches[C]. Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Nara, Japan, 2011: 390–496. [10] DANGER J L, YASHIRO R, GRABA T, et al. Analysis of mixed PUF-TRNG circuit based on SR-latches in FD-SOI technology[C]. Proceedings of the 21st Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Prague, Czech Republic, 2018: 508–515. [11] XU Xiumin, LIANG Huaguo, HUANG Zhengfeng, et al. A highly reliable butterfly PUF in SRAM-based FPGAs[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2017, 14(14): 20170551. doi: 10.1587/elex.14.20170551 [12] LOTFY A, KAVEH M, MARTÍN D, et al. An efficient design of anderson PUF by utilization of the xilinx primitives in the SLICEM[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 23025–23034. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3056291 [13] NOZAKI Y, TAKEMOTO S, IKEZAKI Y, et al. Performance evaluation of unrolled cipher based glitch PUF implemented on virtex-7[C]. Proceedings of 2021 International Symposium on Devices, Circuits and Systems (ISDCS), Higashihiroshima, Japan, 2021: 1–4. [14] ZHOU Kai, LIANG Huaguo, JIANG Yue, et al. FPGA-based RO PUF with low overhead and high stability[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(9): 510–513. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.0451 [15] CUI Yijun, CHEN Yunpeng, WANG Chenghua, et al. Programmable ring oscillator PUF based on switch matrix[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seville, Spain, 2020: 1–4. [16] ZHOU Ting, JI Yuxin, CHEN Mingyi, et al. PL-MRO PUF: High speed pseudo-LFSR PUF based on multiple ring oscillators[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seville, Spain, 2020: 1–5. [17] YAO Liang, LIANG Huaguo, HUANG Zhengfeng, et al. A lightweight configurable XOR RO-PUF design based on xilinx FPGA[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, China, 2021: 83–88. [18] YAMAMOTO D, SAKIYAMA K, IWAMOTO M, et al. Variety enhancement of PUF responses using the locations of random outputting RS latches[J]. Journal of Cryptographic Engineering, 2013, 3(4): 197–211. doi: 10.1007/s13389-012-0044-0 [19] CHALLA R P, ISLAM S A, and KATKOORI S. An SR flip-flop based physical unclonable functions for hardware security[C]. Proceedings of the 62nd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Dallas, USA, 2019: 574–577. [20] WANG Jiadong, CUI Aijiao, LI Mengyang, et al. An ultra-low overhead LUT-based PUF for FPGA[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Asian Hardware-oriented Security and Trust, Yilan, China, 2016: 1–6. [21] 孙子文, 叶乔. 利用震荡环频率特性提取多位可靠信息熵的物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013SUN Ziwen and YE Qiao. Study on the physical unclonable function of the reliable information entropy extracted by the frequency characteristic of oscillating ring[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013 [22] HATA H and ICHIKAWA S. FPGA implementation of metastability-based true random number generator[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2012, E95.D(2): 426–436. doi: 10.1587/transinf.E95.D.426 [23] XILINX Corporation. 7 series FPGAs configurable logic block user guide[EB/OL]. https://www.xilinx.com/content/dam/xilinx/support/documentation/user_guides/ug474_7Series_CLB.pdf, 2020. [24] GE Lulu and PARHI K K. Molecular MUX-based physical unclonable functions[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Limassol, Cyprus, 2020: 482–487. [25] RAMANUJAM S and BURLESON W. Reconfiguring the mux-based arbiter PUF using FeFETs[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), Santa Clara, USA, 2021: 257–262. [26] RUKHIN A, SOTO J, NECHVATAL J, et al. A statistical test suite for random and pseudorandom number generators for cryptographic applications[R]. NIST Special Publication 800-220, 2001. [27] CUI Yijun, GU Chongyan, MA Qingqing, et al. Lightweight modeling attack-resistant multiplexer-based multi-PUF (MMPUF) design on FPGA[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(5): 815. doi: 10.3390/electronics9050815 -





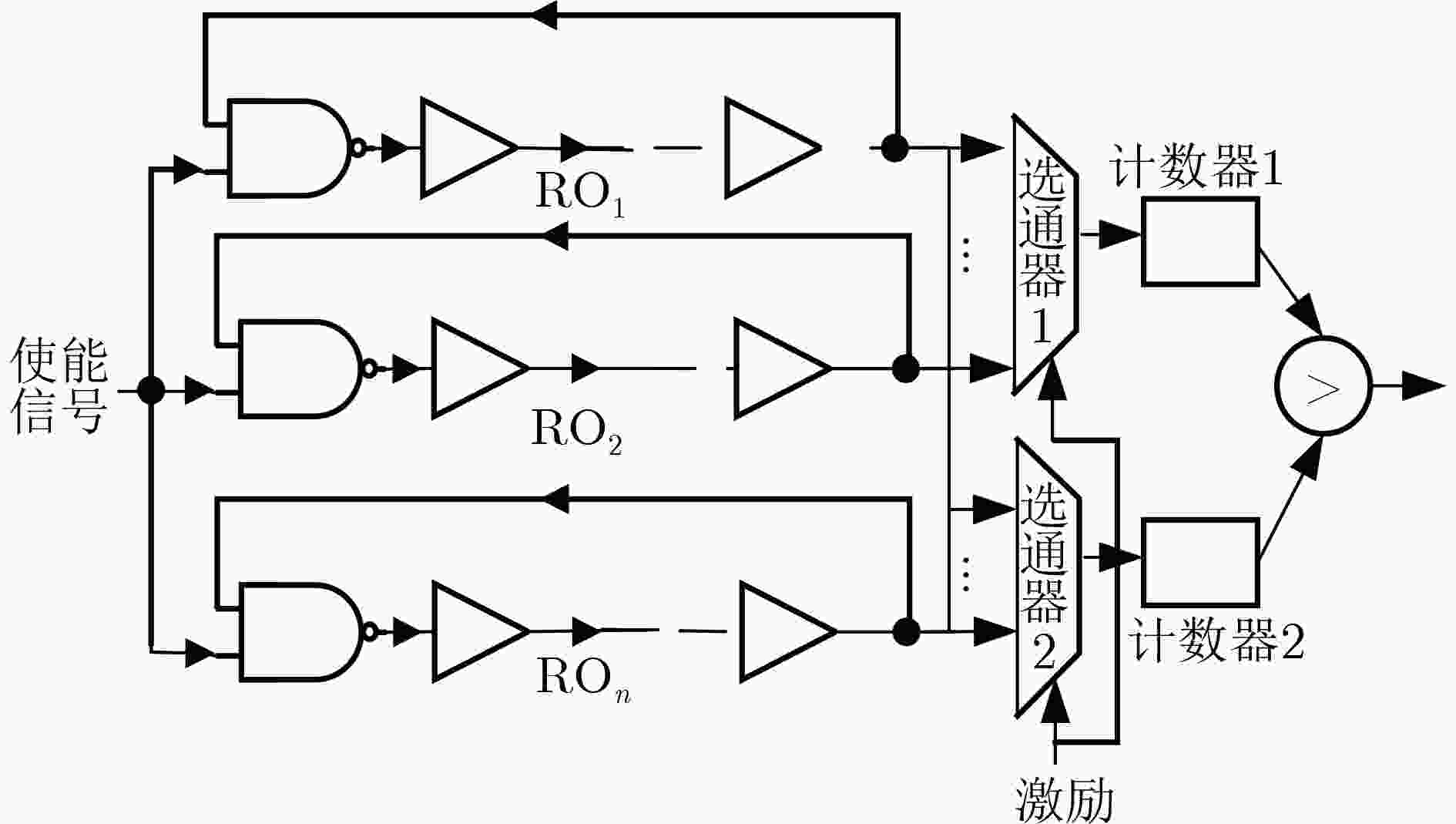
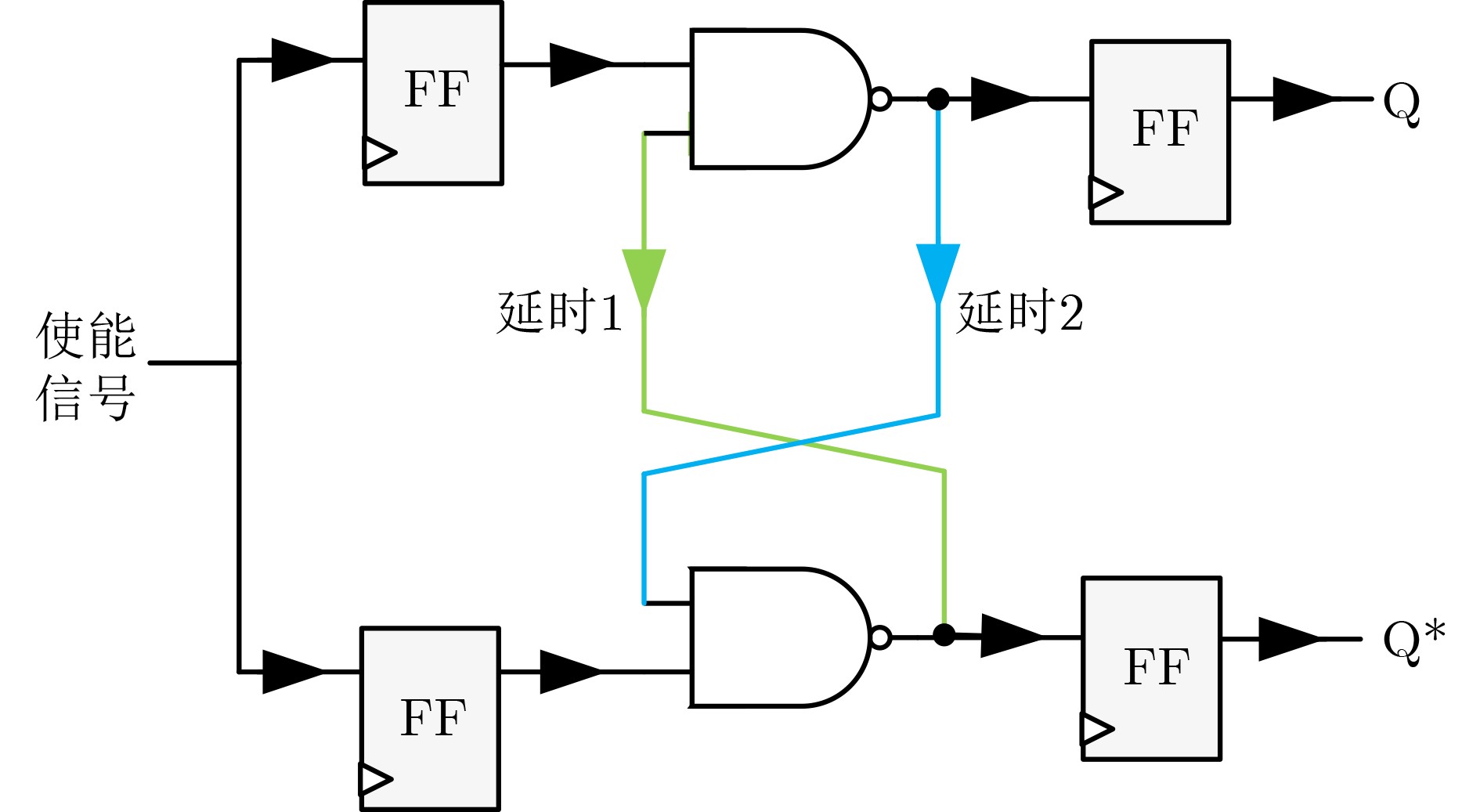
 下载:
下载:
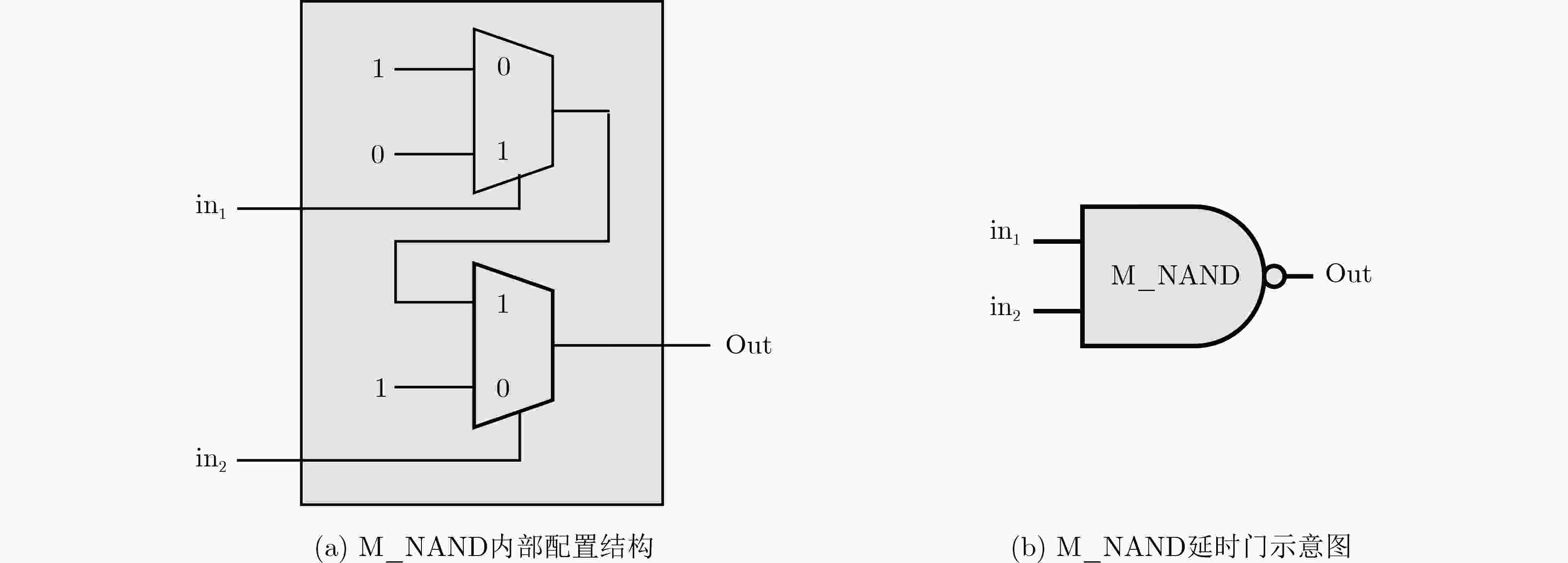

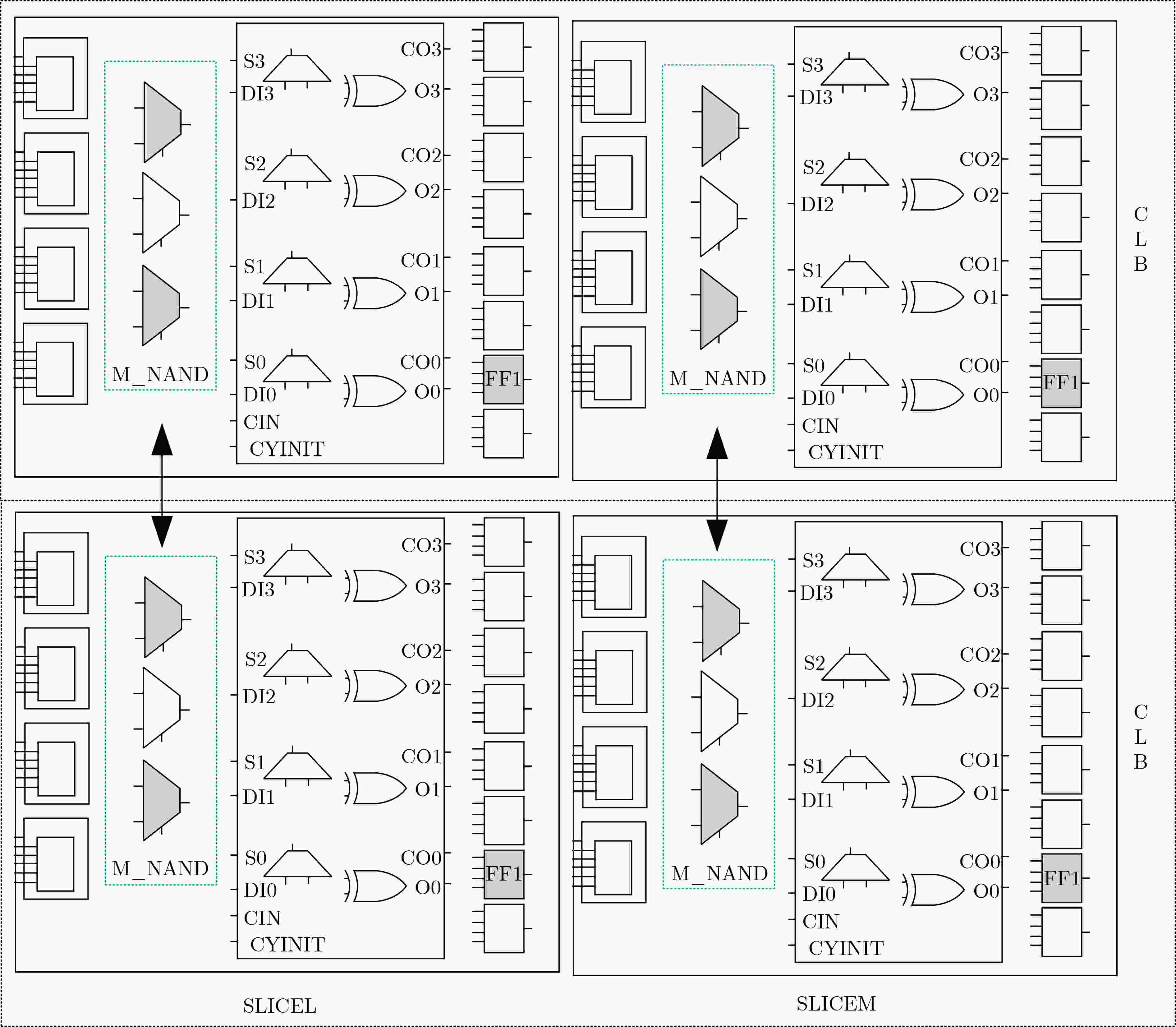

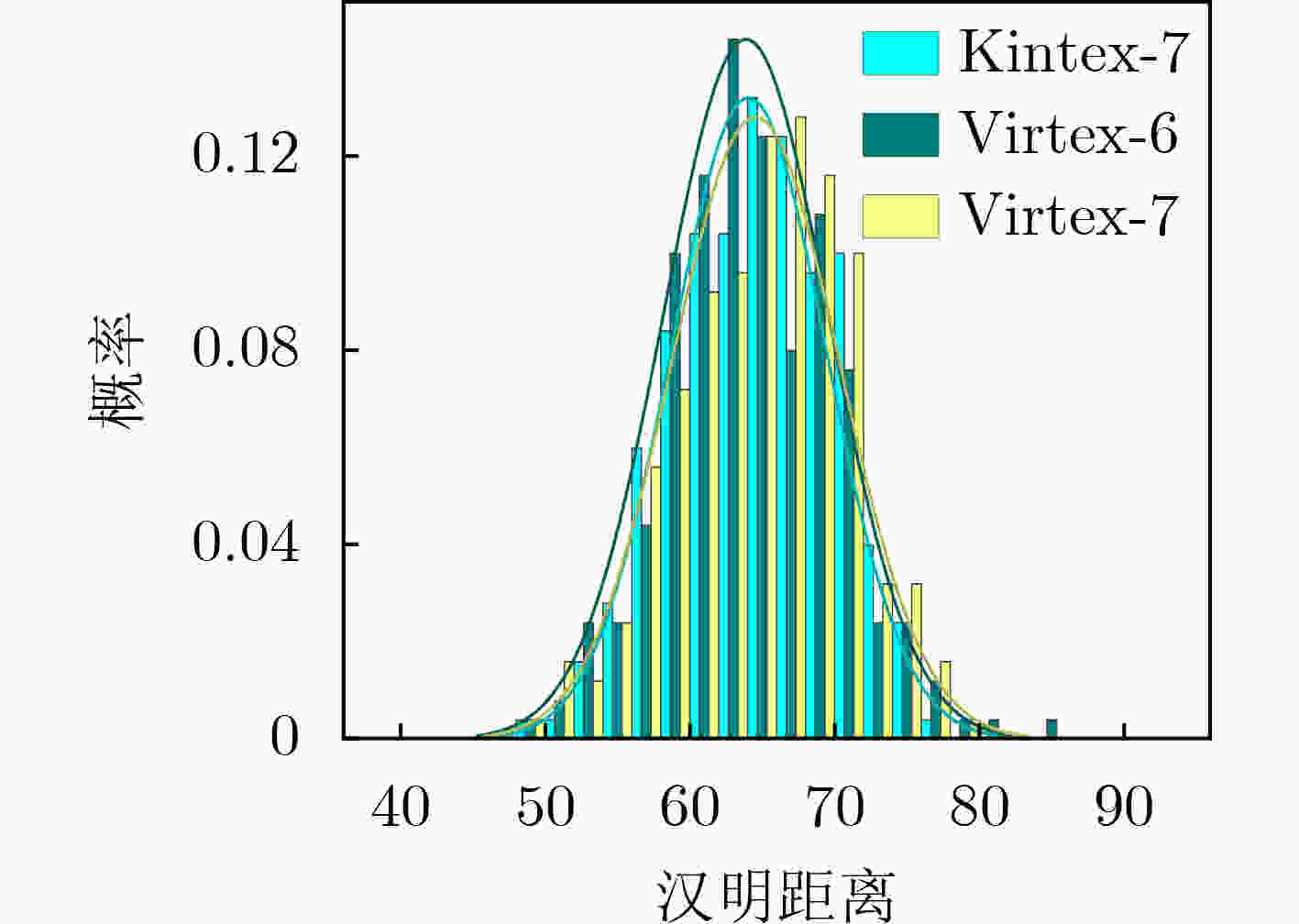
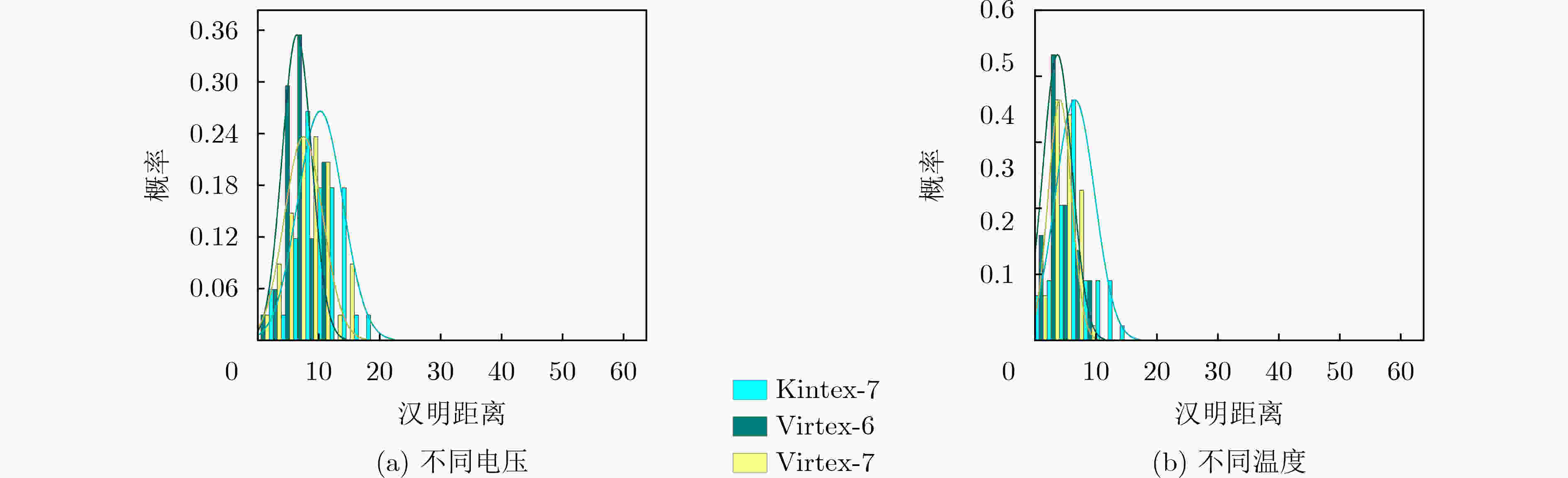
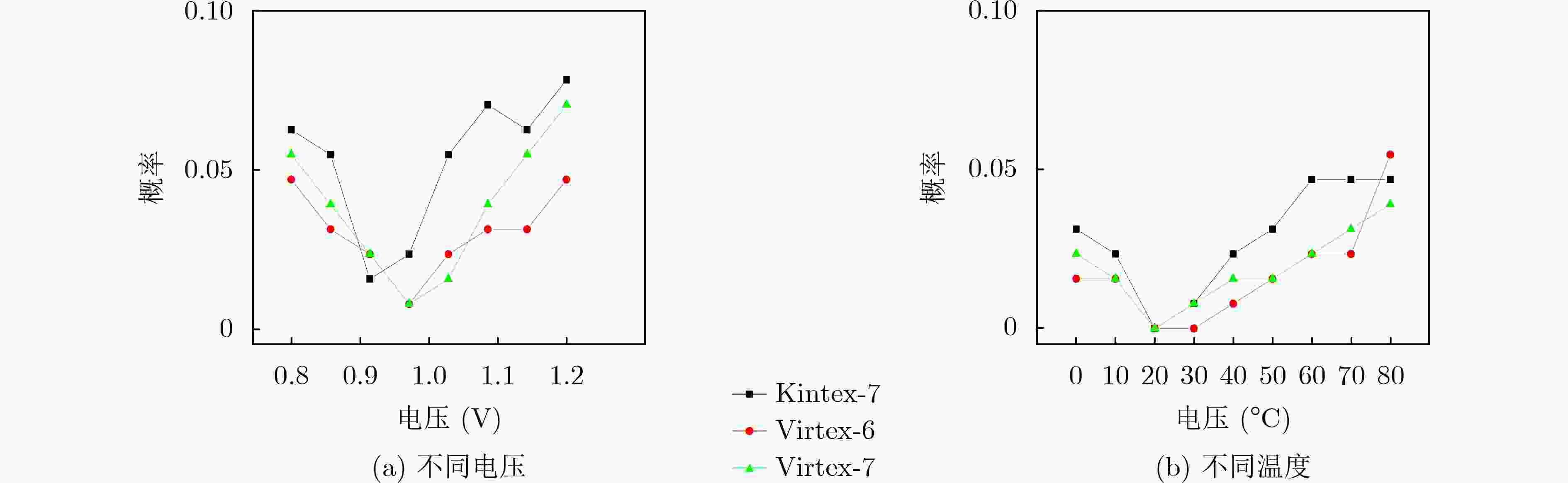


 下载:
下载:
