Automatic Kidney CT Images Segmentation Algorithm Based on 3D Fuzzy Connectedness and Pulse Coupled Neural Network
-
摘要: 3维肾脏CT图像的自动准确分割对减轻医师阅片工作量和提高计算机辅助诊断效率具有重要意义。但是,由于肾脏器官的结构复杂性以及邻近部位的灰度相似性,3维肾脏的准确分割仍具有挑战性。该文基于简化脉冲耦合神经网络(SPCNN)结构简单、参数量少的特点,结合模糊连接度(FC)算法,提出一种3维肾脏CT图像的自动分割算法。主要贡献为:将SPCNN的2维模型扩展为3维模型,可以充分利用3维CT图像的层间信息;提出了一种基于感兴趣区域质心的3维种子点自动生成策略,可以有效提高算法的自动分割效率;实现了3维FC响应图与3维SPCNN的有效耦合。所提算法在自制数据集和公开数据集上进行了验证实验,结果表明该算法的性能优于现有的主流算法,其Dice系数、准确率、敏感度、体积误差、平均对称表面距离的平均值分别可以达到0.9095, 0.9969, 0.8517, 0.1749和0.8536。Abstract: Automatic and accurate segmentation of 3D kidney CT image is of great significance to reduce the workload of doctors and improve the efficiency of computer-aided diagnosis. However, due to the structural complexity of kidney organs and the gray similarity of adjacent parts, accurate segmentation of 3D kidney is still challenging. Based on the characteristics of simple structure and few parameters of Simplified Pulse Coupled Neural Network (SPCNN), combined with Fuzzy Connectedness (FC) algorithm, an automatic segmentation algorithm of three-dimensional kidney CT images is proposed in this paper. The main contributions of this paper are as follows: The 2D SPCNN is extended to 3D SPCNN, which can make full use of the inter-layer information of 3D CT images. A 3D seed point automatic generation strategy based on the centroid of region of interest is proposed, which can effectively improve the automatic segmentation efficiency of the algorithm. Effective coupling of 3D FC response map and 3D SPCNN is realized. The proposed algorithm is validated on self-made and public datasets, and the results show that the performance of the proposed algorithm is better than that of the existing mainstream algorithms. The average values of Dice coefficient, accuracy, sensitivity, volume error and average symmetric surface distance can achieve 0.9095, 0.9969, 0.8517, 0.1749 and 0.8536 respectively.
-
表 1 3D FC-SPCNN算法与不同算法在AHQU_K数据集上的分割结果比较
算法 Dice Acc Sen VE↓ ASSD↓ 3D FC-SPCNN 0.9175±0.0145 0.9969±0.0005 0.8533±0.0299 0.1749±0.0505 0.7903±0.1480 3D FC 0.9003±0.0396 0.9964±0.0012 0.8268±0.0658 0.2213±0.0723 0.9552±0.4141 3D 区域生长 0.8916±0.0589 0.9954±0.0058 0.8252±0.0501 0.3151±0.1442 1.2365±0.5071 3D Snakes 0.8058±0.0687 0.9928±0.0029 0.7369±0.1028 0.2374±0.1036 1.6287±0.9566 3D SPCNN 0.1481±0.0387 0.7433±0.0634 0.7376±0.0656 13.6017±3.3332 20.1676±3.8033 表 2 3D FC-SPCNN算法与不同算法在3Dircadb数据集上的分割结果比较
算法 Dice Acc Sen VE↓ ASSD↓ 3D FC-SPCNN 0.9119±0.0227 0.9972±0.0007 0.8519±0.0227 0.1865±0.0293 0.8107±0.1505 3D FC 0.8738±0.0769 0.9964±0.0019 0.7926±0.1011 0.2492±0.0962 1.0926±0.5016 3D 区域生长 0.8620±0.0816 0.9935±0.0053 0.8192±0.0635 0.2874±0.1331 1.2059±0.6009 3D Snakes 0.8063±0.0223 0.9863±0.0038 0.7586±0.0382 0.2206±0.0248 1.4037±0.1379 3D SPCNN 0.2208±0.0561 0.9182±0.2425 0.7027±0.0561 2.2117±1.4279 19.4560±5.1872 表 3 3D FC-SPCNN算法与不同算法在Kits19数据集上的分割结果比较
算法 Dice Acc Sen VE↓ ASSD↓ 3D FC-SPCNN 0.8991±0.0103 0.9966±0.0014 0.8499±0.0305 0.1633±0.0740 0.9598±0.2463 3D FC 0.8383±0.0370 0.9907±0.0088 0.8136±0.0590 0.3392±0.2089 1.5468±0.6721 3D 区域生长 0.8621±0.0516 0.9949±0.0039 0.7805±0.1010 0.3197±0.1357 1.6331±0.8665 3D Snakes 0.8329±0.0526 0.9908±0.0041 0.7495±0.1405 0.2083±0.0916 1.3861±0.3569 3D SPCNN 0.0487±0.0206 0.5312±0.0831 0.7392±0.0573 30.5897±7.7062 23.914±4.0112 表 4 相同参数、种子点个数不同的分割结果的评价指标对比
Dice Acc Sen VE↓ ASSD↓ 时间(s) Z/2 0.9197 0.9967 0.8551 0.1864 0.8150 3172 Z/2和Z/2–5 0.9208 0.9968 0.8572 0.1817 0.7919 3193 Z/2和Z/2–5和Z/2+5 0.9213 0.9968 0.8581 0.1804 0.7863 3200 -
[1] VAZIRI N D. Silva's diagnostic renal pathology[J]. Kidney International, 2010, 77(11): 939–940. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.392 [2] DOI K. Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2007, 31(4/5): 198–211. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2007.02.002 [3] TORRES H R, QUEIRÓS S, MORAIS P, et al. Kidney segmentation in ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography images: A systematic review[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018, 157: 49–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.01.014 [4] ZHANG Pin, LIANG Yanmei, CHANG Shengjiang, et al. Kidney segmentation in CT sequences using graph cuts based active contours model and contextual continuity[J]. Medical Physics, 2013, 40(8): 081905. doi: 10.1118/1.4812428 [5] LES T, MARKIEWICZ T, DZIEKIEWICZ M, et al. Adaptive two-way sweeping method to 3D kidney reconstruction[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 67: 102544. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102544 [6] JIN Chao, SHI Fei, XIANG Dehui, et al. 3D fast automatic segmentation of kidney based on modified AAM and random forest[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(6): 1395–1407. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2512606 [7] KHALIFA F, SOLIMAN A, TAKIELDEEN A, et al. Kidney segmentation from CT images using a 3D NMF-guided active contour model[C]. The 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Prague, Czech Republic, 2016: 432–435. [8] QAYYUM A, LALANDE A, and MERIAUDEAU F. Automatic segmentation of tumors and affected organs in the abdomen using a 3D hybrid model for computed tomography imaging[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2020, 127: 104097. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104097 [9] 胡敏, 周秀东, 黄宏程, 等. 基于改进U型神经网络的脑出血CT图像分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 127–137. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200996HU Min, ZHOU Xiudong, HUANG Hongcheng, et al. Computed-tomography image segmentation of cerebral hemorrhage based on improved U-shaped Neural Network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 127–137. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200996 [10] 刘侠, 甘权, 刘晓, 等. 基于超像素的联合能量主动轮廓CT图像分割方法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(1): 190104. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190104LIU Xia, GAN Quan, LIU Xiao, et al. Joint energy active contour CT image segmentation method based on super-pixel[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47(1): 190104. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190104 [11] ÇIÇEK Ö, ABDULKADIR A, LIENKAMP S S, et al. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation[C]. The 19th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Athens, Greece, 2016: 424–432. [12] KANG Li, ZHOU Ziqi, HUANG Jianjun, et al. Renal tumors segmentation in abdomen CT Images using 3D-CNN and ConvLSTM[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 72: 103334. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103334 [13] ZHAN Kun, SHI Jinhui, WANG Haibo, et al. Computational mechanisms of pulse-coupled neural networks: A comprehensive review[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2017, 24(3): 573–588. doi: 10.1007/s11831-016-9182-3 [14] BAI Peirui, YANG Kai, MIN Xiaolin, et al. A novel framework for improving Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks with fuzzy connectedness for medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 138129–138140. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012160 [15] 郑瑾, 柳肃, 孙炜. 用于自动识别遥感图像路网信息的改进模糊连接度方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 413–417. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150563ZHENG Jin, LIU Su, and SUN Wei. An improved fuzzy connectedness method to recognize automatically the road network information from remote sensing image[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 413–417. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150563 [16] DE MORAES BRAZ C, MIRANDA P A V, CIESIELSKI K C, et al. Optimum cuts in graphs by general fuzzy connectedness with local band constraints[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2020, 62(5): 659–672. doi: 10.1007/s10851-020-00953-w [17] 张睿, 吴薇薇, 周著黄, 等. 基于改进模糊连接度的CT图像肝脏血管三维分割方法[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2019, 38(1): 18–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2019.01.003ZHANG Rui, WU Weiwei, ZHOU Zhuhuang, et al. A three-dimensional liver vessel segmentation method for CT images using improved fuzzy connectedness[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 38(1): 18–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2019.01.003 [18] 李彬, 陈武凡. 基于模糊连接度的多发性硬化症MR图像自动分割算法[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2007, 26(5): 664–668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2007.05.005LI Bin and CHEN Wufan. Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions using fuzzy connectedness for MR images[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2007, 26(5): 664–668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2007.05.005 [19] ECKHORN R, REITBOECK H J, ARNDT M, et al. Feature linking via synchronization among distributed assemblies: Simulations of results from cat visual cortex[J]. Neural Computation, 1990, 2(3): 293–307. doi: 10.1162/neco.1990.2.3.293 [20] CHEN Yuli, PARK S K, MA Yide, et al. A new automatic parameter Setting method of a simplified PCNN for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(6): 880–892. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2128880 [21] UDUPA J K and SAMARASEKERA S. Fuzzy connectedness and object definition: Theory, algorithms, and applications in image segmentation[J]. Graphical Models and Image Processing, 1996, 58(3): 246–261. doi: 10.1006/gmip.1996.0021 -





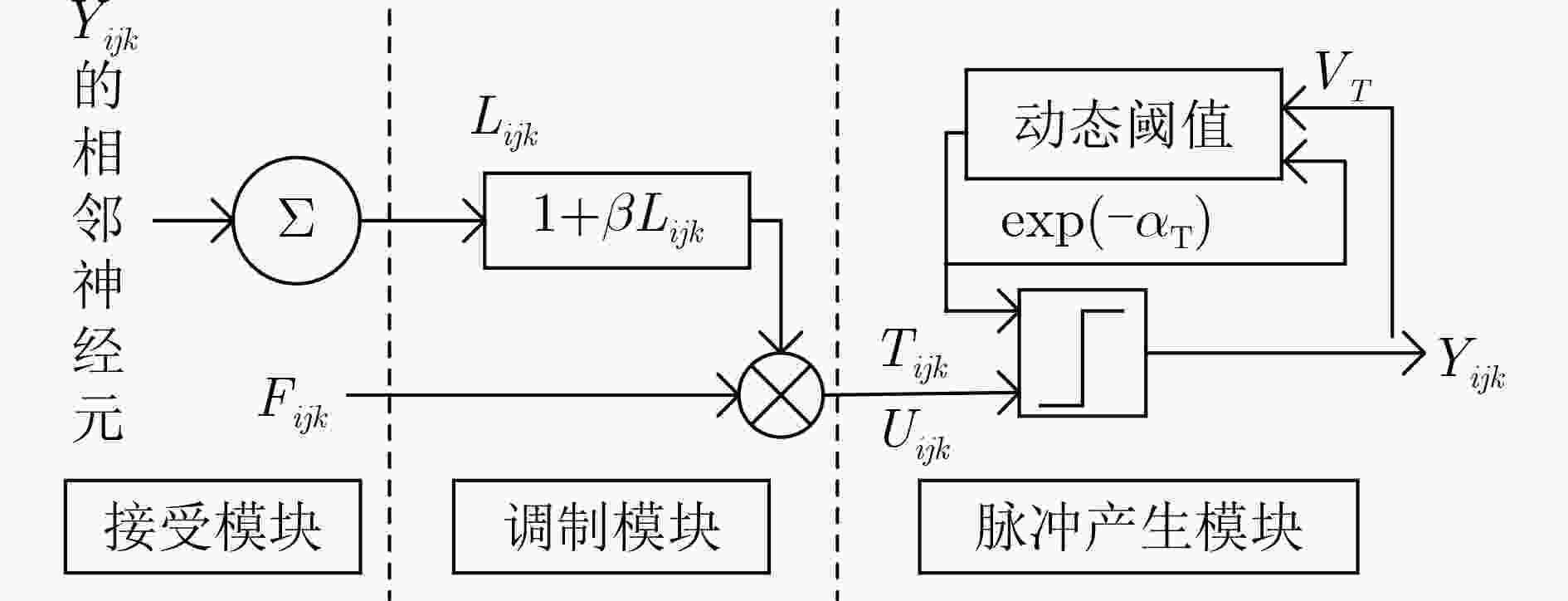
 下载:
下载:
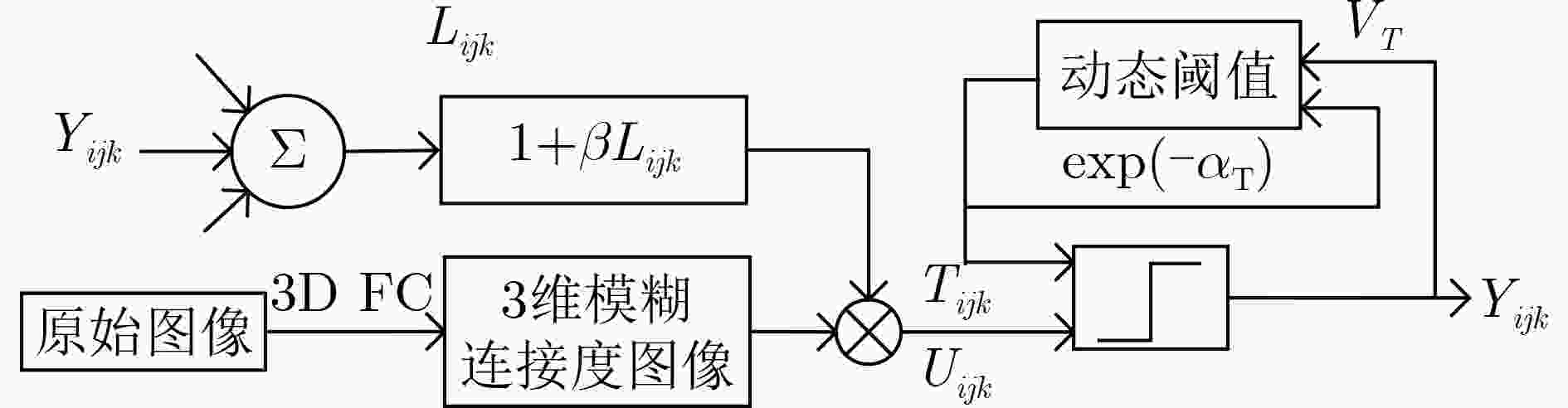
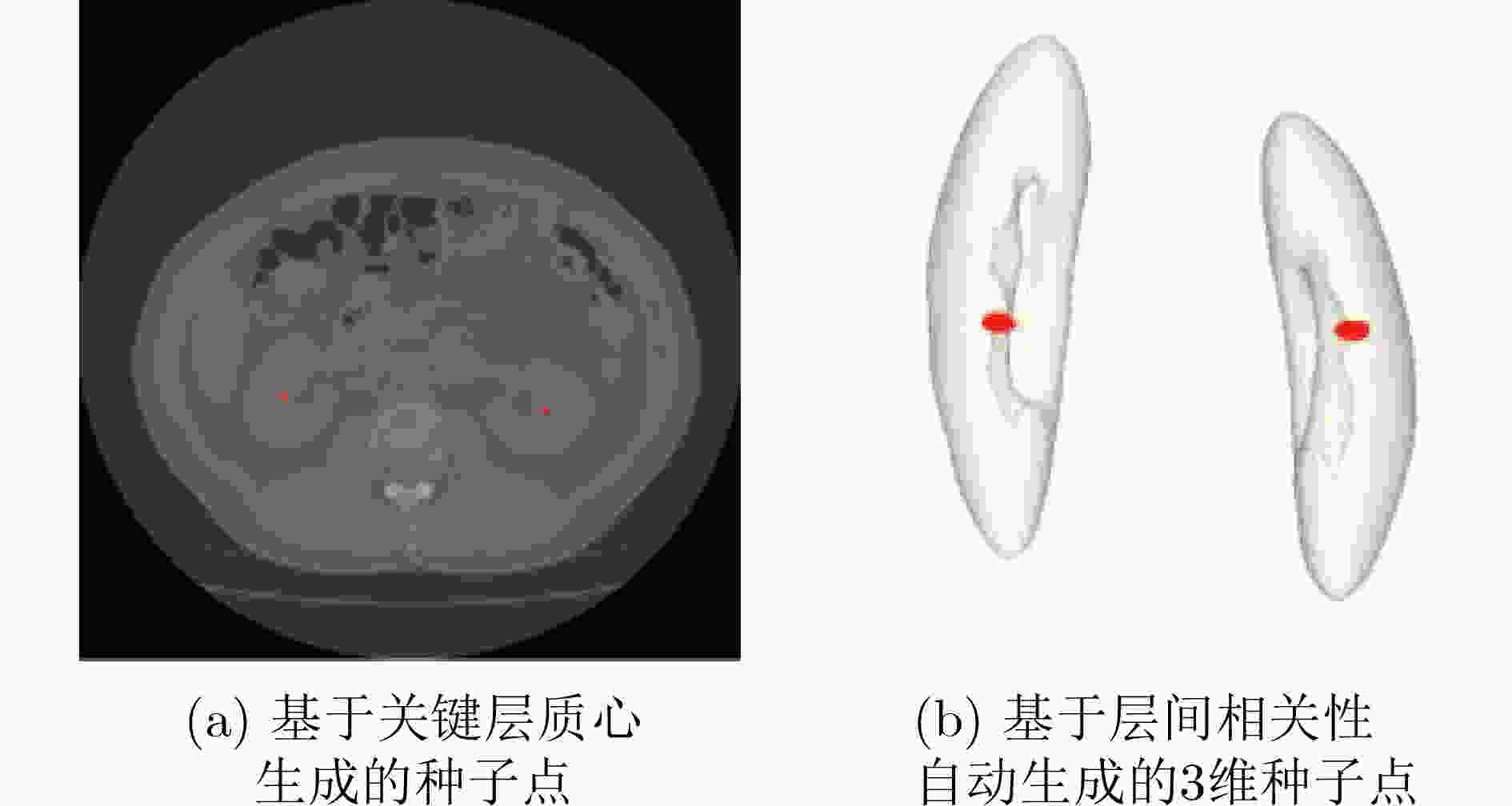
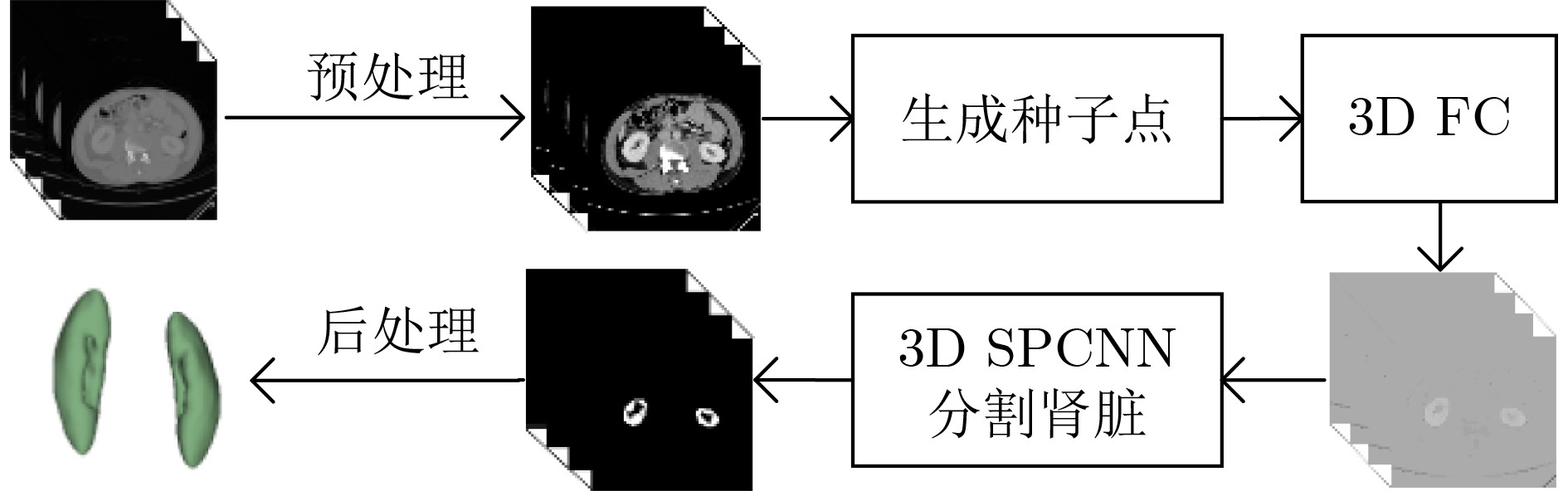
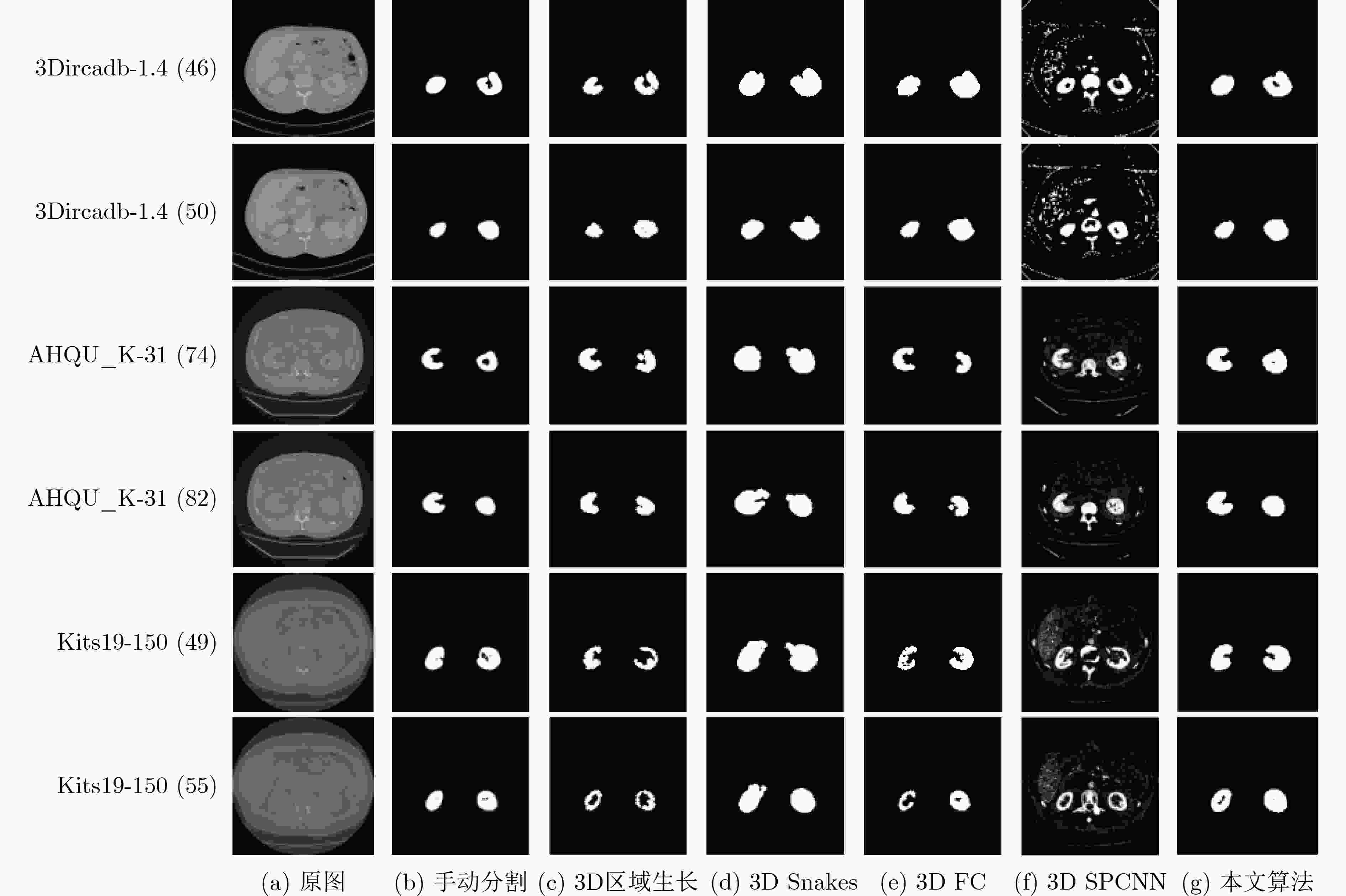
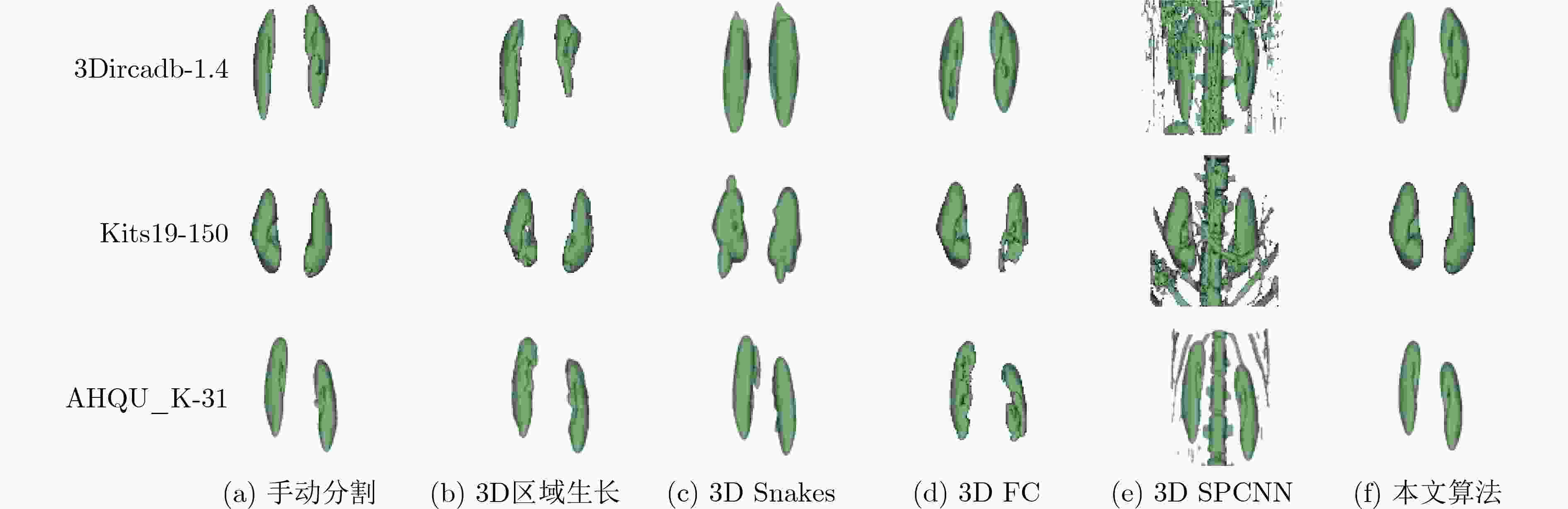
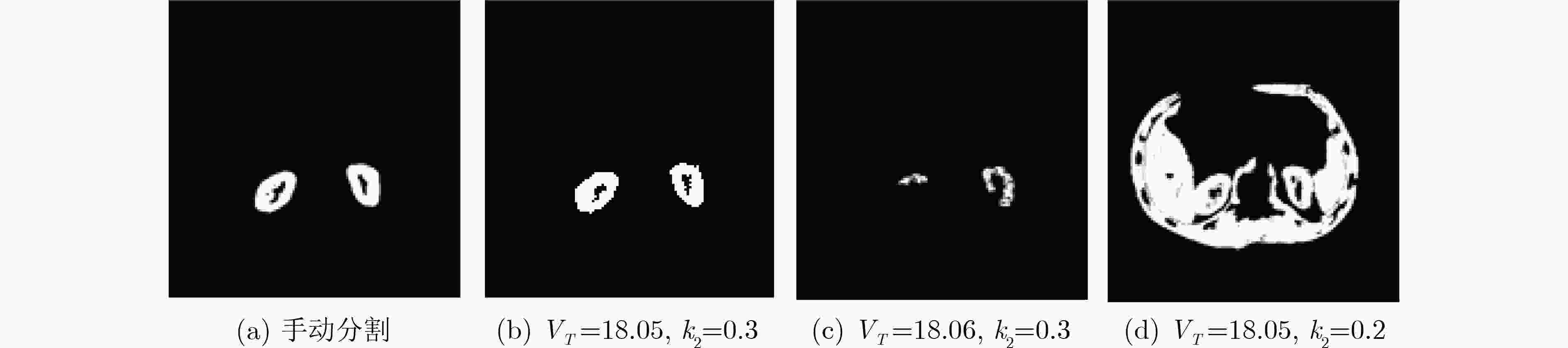
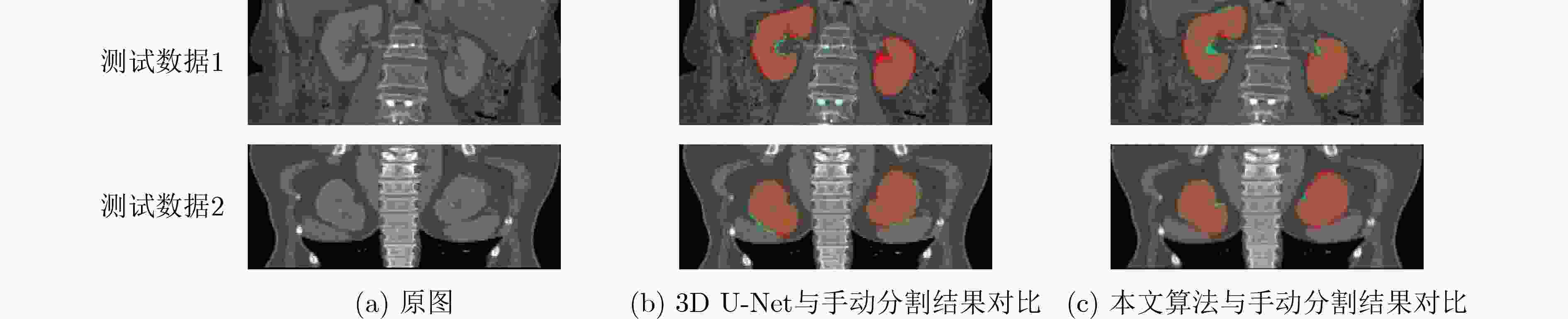


 下载:
下载:
