Network Switching Algorithm Based on Mobile Trajectory Prediction in Ultra-dense Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
-
摘要: 随着5G技术的广泛应用,网络超密集化部署已成为必然趋势。超密集异构无线网络在实现网络高流量密度、高峰值速率性能的同时,给传统的网络切换算法带来了挑战,处于变速移动的终端会面临更频繁的切换问题,这将导致乒乓效应频率的显著提高,进而影响用户在网体验。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于终端移动轨迹预测的网络切换算法,适用于各类型用户在高密度无线网络中的垂直切换和水平切换问题。首先,为了更高精度的移动轨迹预测,提出一种基于模糊核聚类和长短期记忆(LSTM)神经网络的预测方法,可以有效预测不同移动模式下用户终端的短时移动轨迹;之后,基于用户当前和预测位置,获取候选网络集合,通过候选集交运算法和指标阈值判断网络切换时机;当切换触发时,使用帝企鹅算法最优化网络选择。仿真结果表明,相比于其他类型的时间序列预测算法,该文提出的轨迹预测算法精度较高;同时相较对比算法,该文所提网络切换算法的切换次数适中,有效避免了乒乓效应,且提高了用户连接的网络质量。Abstract: With the widespread adoption of 5G technology, network hyper-density deployment has become an inevitable trend. While achieving high traffic density and high peak rate performance, ultra-dense heterogeneous wireless networks pose challenges to traditional network switching algorithms. Terminals moving at variable speeds will face more frequent switching problems, which will lead to a much higher frequency of ping-pong effects, thus affecting the user experience of the network. To address these issues, a network switching algorithm based on terminal trajectory prediction is proposed, which is applicable to both vertical and horizontal switching for all types of users in high-density wireless networks. Firstly, to predict the mobile trajectory more accurately, a prediction method based on fuzzy kernel clustering and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks is proposed, which can effectively predict the short-term mobile trajectory of user terminals under different mobile modes. Afterwards, two sets of candidate networks are obtained based on the current and predicted positions of the user, and the network switching timing is judged by the candidate set swapping algorithm and indicator threshold; When the switching is triggered, the emperor penguin algorithm is used to select optimally the network at the time of switching. The simulation results show that the trajectory prediction algorithm proposed has higher accuracy compared to other types of time series prediction algorithms. At the same time, compared with the comparison algorithms, the proposed network switching algorithm has a moderate number of switches, which avoids effectively the ping-pong effect and improves the network quality of user connections.
-
表 1 网络仿真参数的设置
网络类型 宏蜂窝 微蜂窝 无线局域网络 网络数量 23 240 80 覆盖半径(m) 1000 60 100 基站发送功率(dBm) 46 30 35 路径损耗因子(dB) 26 32 35 通信时延(ms) [1,20] [10,50] [40,100] 时延抖动(ms) [1,10] [2,20] [15,30] 带宽(MHz) [5,10] [10,30] [25,40] 发送天线增益(dBm) 11 9 5 工作频率(GHz) 3.5 3.5 2.5 表 2 3种移动模式下,典型用户移动预测精度统计
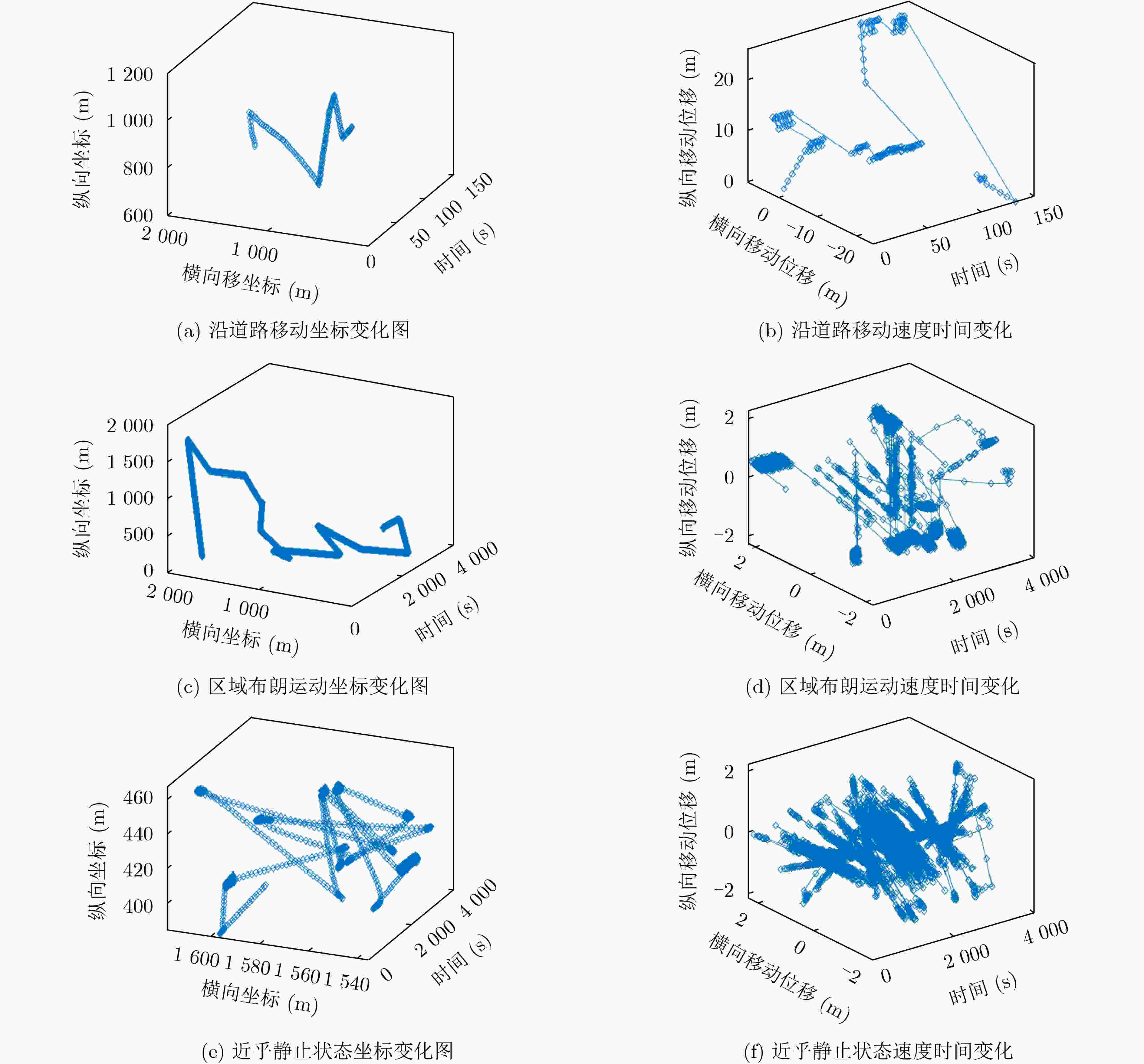
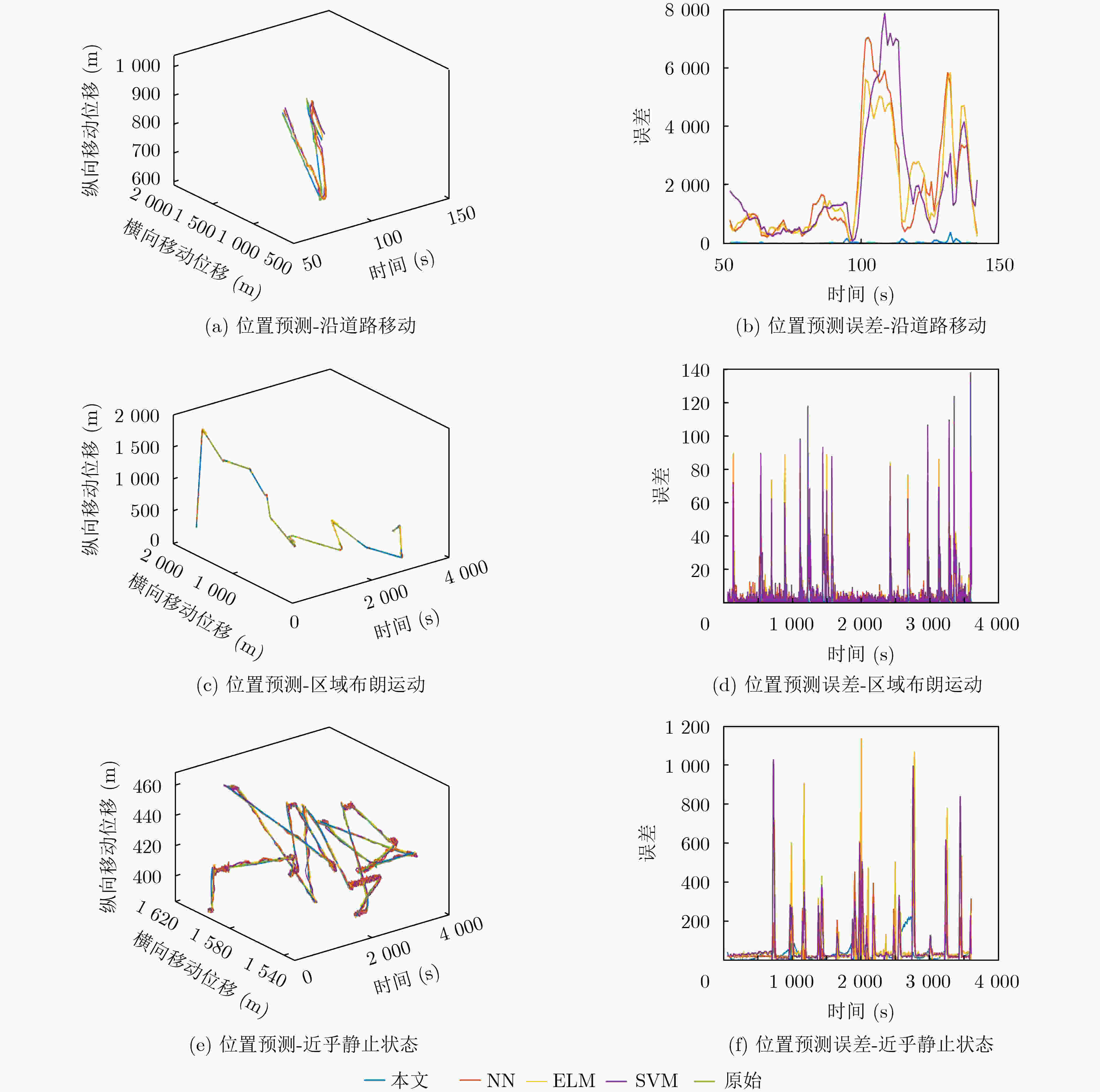
移动模式 指标 本文 NN ELM SVM 模式1 R2 0.99991 0.99405 0.99359 0.99178 RMSE 3.709 30.649 31.804 36.019 模式2 R2 0.99995 0.99989 0.99985 0.99990 RMSE 4.225 6.453 7.495 6.183 模式3 R2 0.99998 0.99988 0.99992 0.99992 RMSE 0.726 1.925 1.609 1.602 表 3 不同模式不同算法网络切换仿真——各项指标统计
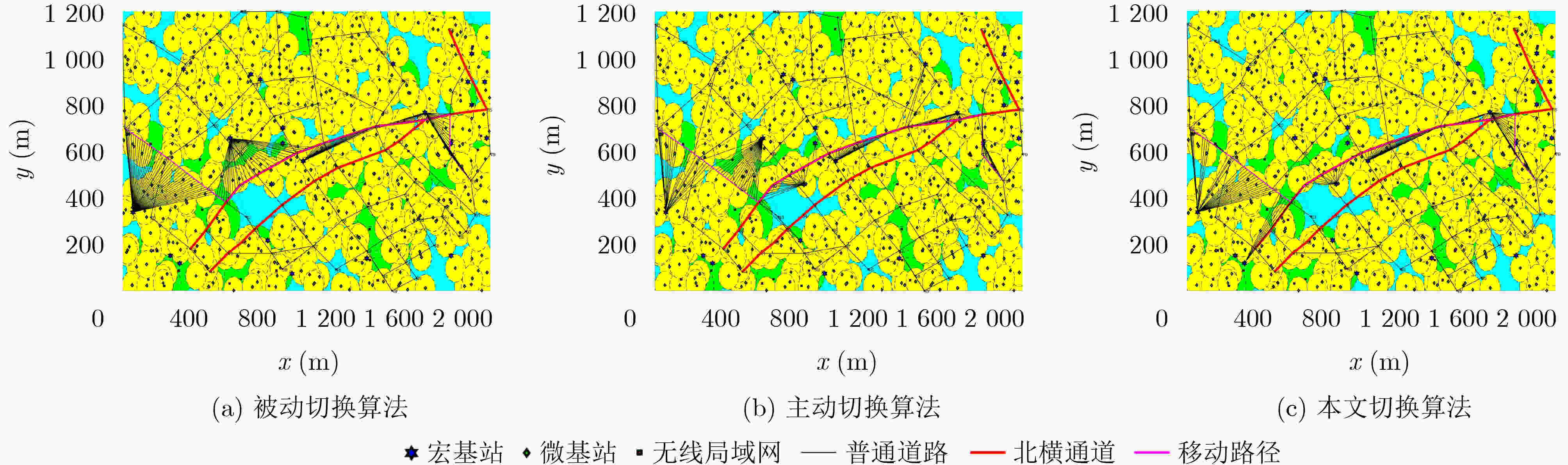
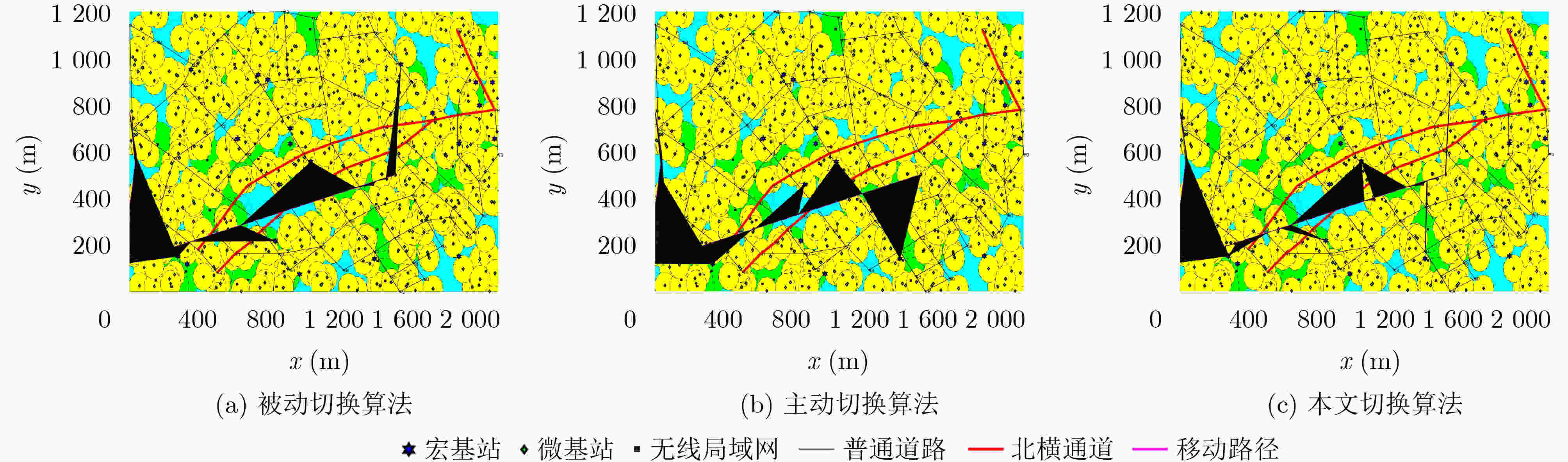
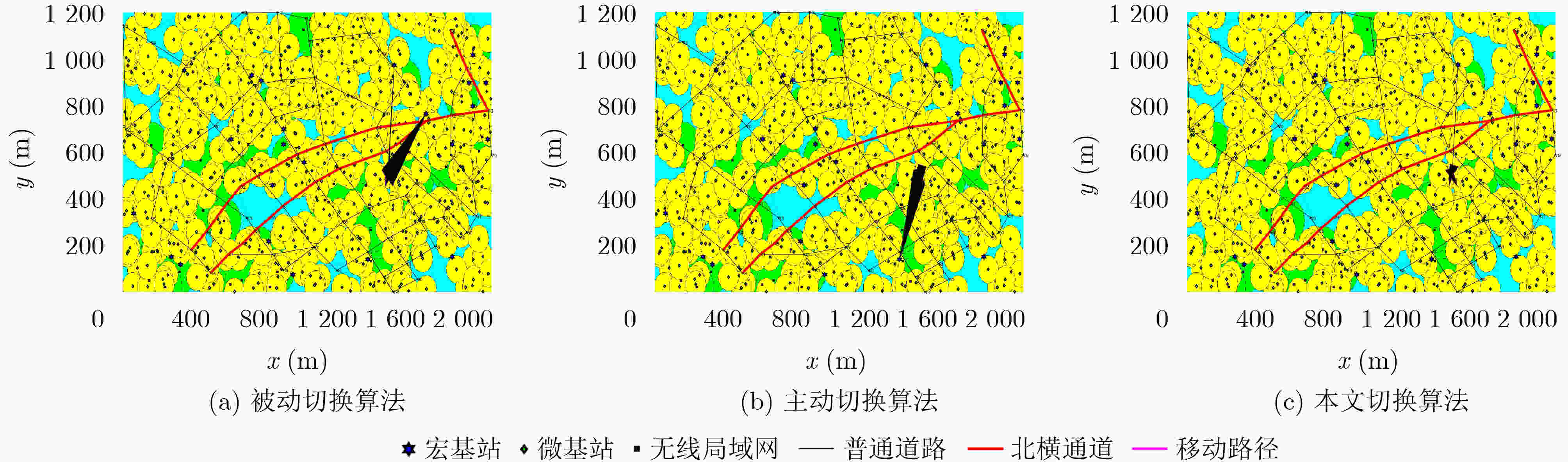
运动模式 切换算法 平均切换频率(次/s) 平均RSS(dBm) 平均时延(ms) 平均带宽(MHz) 平均传输速率(Mbs) 平均切换失败概率(%) 模式1 被动切换 0.033 –93.16 12.91 7.849 5.168 0.000 主动切换 0.044 –91.31 14.15 7.497 4.863 0.128 本文算法 0.085 –92.77 16.46 9.432 6.199 0.005 模式2 被动切换 0.003 –93.00 14.00 7.784 5.117 0 主动切换 0.007 –91.14 14.92 7.514 4.866 0.011 本文算法 0.013 –94.62 19.85 10.490 6.993 0 模式3 被动切换 0.001 –90.89 15.53 8.760 5.723 0 主动切换 0.005 –88.99 14.63 7.472 4.749 0 本文算法 0.002 –94.94 21.24 11.302 7.669 0 表 4 不同模式不同算法网络切换仿真-累计在网时长统计(s)
运动类型 切换算法 累计在网时长 宏蜂窝 微蜂窝 无线局域网 沿道路
移动被动切换 100746 904 863 主动切换 101833 425 255 本文算法 84870 10918 6725 局部布朗
运动被动切换 1186323 8776 4901 主动切换 1195642 3000 1358 本文算法 861756 251519 86725 近乎静止 被动切换 1135743 49857 14400 主动切换 1199044 810 146 本文算法 841921 292531 65548 -
[1] 李渝舟, 江涛, 曹洋, 等. 5G绿色超密集无线异构网络: 理念、技术及挑战[J]. 电信科学, 2017, 33(6): 34–40. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2017197LI Yuzhou, JIANG Tao, CAO Yang, et al. Green 5G ultra-dense wireless heterogeneous networks: Guidelines, techniques, and challenges[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2017, 33(6): 34–40. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2017197 [2] 辛杰, 赵力强, 张耀元. 超密集异构蜂窝网多维资源联合优化算法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2017, 15(1): 29–35. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201701.0029XIN Jie, ZHAO Liqiang, and ZHANG Yaoyuan. Joint radio resource allocation algorithm for ultra-dense heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2017, 15(1): 29–35. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201701.0029 [3] 李芦峰, 王燚, 贾桄宇. 面向无人机的无线网络应用场景分析[J]. 通信与信息技术, 2022(1): 45–48.LI Lufeng, WANG Yi, and JIA Guangyu. Analysis of wireless network application scenarios for UAVs[J]. Communication &Information Technology, 2022(1): 45–48. [4] 张富春, 周美辰, 宋晶. 毫米波5G通信系统动态链路及决策树切换算法[J]. 铁道通信信号, 2022, 58(2): 63–68. doi: 10.13879/j.issn.1000-7458.2022-02.21390ZHANG Fuchun, ZHOU Meichen, and SONG Jing. Dynamic link and decision tree switching algorithm of 5G communication system base on millimeter wave technology[J]. Railway Signalling &Communication, 2022, 58(2): 63–68. doi: 10.13879/j.issn.1000-7458.2022-02.21390 [5] 张燕燕, 王鹤鸣, 姬天相, 等. 机器学习在5G超密集网络切换中的应用[J]. 电讯技术, 2019, 59(12): 1371–1377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2019.12.001ZHANG Yanyan, WANG Heming, JI Tianxiang, et al. Application of machine learning in 5G ultra-dense network handover[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2019, 59(12): 1371–1377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2019.12.001 [6] 翟晨辉, 梁中华, 辛月, 等. 一种面向高速铁路通信的改进型基站切换优化算法[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2020, 48(2): 327–332,355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2020.02.012ZHAI Chenhui, LIANG Zhonghua, XIN Yue, et al. An improved base station switching optimized algorithm for high speed railway communication[J]. Computer and Digital Engineering, 2020, 48(2): 327–332,355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2020.02.012 [7] 马彬, 钟世林, 谢显中, 等. 考虑负载均衡和用户体验的垂直切换算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4218–4228. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210958MA Bin, ZHONG Shilin, XIE Xianzhong, et al. Vertical handoff algorithm considering load balance and user experience[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4218–4228. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210958 [8] 章广梅, 郑友亮, 童惠祺, 等. 异构无线网络资源管理与切换控制技术[J]. 电讯技术, 2023, 63(1): 70–76. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.211022002ZHANG Guangmei, ZHENG Youliang, TONG Huiqi, et al. Heterogeneous wireless network resource management and handoff control technology[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2023, 63(1): 70–76. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.211022002 [9] 张佳健, 李翠然, 谢健骊. 位置功率联合判决的高铁通信越区切换算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(10): 212–217. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0062701ZHANG Jiajian, LI Cuiran, and XIE Jianli. Handover algorithm with position-power joint decision for high-speed railway communication[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(10): 212–217. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0062701 [10] 杜涛, 陈永刚, 李德威. 基于实时动态迟滞的LTE-R切换算法优化研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2018, 62(4): 176–180. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.201704170003DU Tao, CHEN Yonggang, and LI Dewei. Research on optimization of LTE-R handover algorithm based on real-time dynamic hysteresis[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2018, 62(4): 176–180. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.201704170003 [11] 邓红. 基于驻留时间预测的车辆异构网络垂直切换算法[J]. 电子元器件与信息技术, 2020, 4(2): 56–58. doi: 10.19772/j.cnki.2096-4455.2020.2.021DENG Hong. Vertical switching algorithm for vehicle heterogeneous networks based on dwell time prediction[J]. Electronic Components and Information Technology, 2020, 4(2): 56–58. doi: 10.19772/j.cnki.2096-4455.2020.2.021 [12] 杨明极, 吴烨, 范华峰. 基于运动趋势预测的异构车联网垂直切换算法[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2018, 35(4): 119–123,129. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2018.04.024YANG Mingji, WU Ye, and FAN Huagnfeng. Vertical handoff algorithm for heterogeneous internet of vehicles based on motion trend prediction[J]. Microelectronics &Computer, 2018, 35(4): 119–123,129. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2018.04.024 [13] 梁颖, 马泳涛. 基于混合蜻蜓优化多核模糊聚类和特征子集选取的在线齿轮故障识别[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2022(1): 9–14,19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2022.01.003LIANG Yi and MA Yongtao. On line gear fault recognition based on multi-core fuzzy clustering and feature subset selection with hybrid dragonfly algorithm[J]. Machinery Design &Manufacture, 2022(1): 9–14,19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2022.01.003 [14] GIROLAMI M. Mercer kernel-based clustering in feature space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(3): 780–784. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2002.1000150 [15] 钟劲松, 王少林, 冉懿, 等. 基于互信息和LSTM的用户负荷短期预测[J]. 电力建设, 2022, 43(7): 96–102. doi: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.07.011ZHONG Jinsong, WANG Shaolin, RAN Yi, et al. Short-term consumer load forecasting based on mutual information and LSTM[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2022, 43(7): 96–102. doi: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.07.011 [16] YANG Zhe, DENG Libao, WANG Yuchen, et al. Aptenodytes Forsteri optimization: Algorithm and applications[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 232: 107483. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107483 [17] 杨鹏波. 基于用户移动性预测的切换优化算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2018.YANG Pengbo. Research of handoff optimization algorithm based on user mobility prediction[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018. [18] 姚力, 章江铭, 倪琳娜. 基于量子遗传和核模糊聚类的低压台区户变关系识别[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57(20): 106–113. doi: 10.19753/j.issn1001-1390.2020.20.015YAO Li, ZHANG Jiangming, and NI Linna. User-transformer relation identification of low voltage area based on quantum genetic and kernel fuzzy clustering[J]. Electrical Measurement &Instrumentation, 2020, 57(20): 106–113. doi: 10.19753/j.issn1001-1390.2020.20.015 [19] 李思思, 程良伦, 王涛, 等. 移动互联异构网络下多终端协同的垂直切换决策算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2018, 35(8): 2474–2476,2497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.08.059LI Sisi, CHENG Lianglun, WANG Tao, et al. Vertical handoff decision algorithm for multi-terminal cooperative in mobile interconnected heterogeneous networks[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(8): 2474–2476,2497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.08.059 [20] 张勇. 用户GPS轨迹数据支持下的出行周期活动模式分析及位置预测研究[D]. [硕士论文], 昆明理工大学, 2020.ZHANG Yong. Research on activity pattern analysis and location prediction of travel cycle supported by user GPS track data[D]. [Master dissertation], Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2020. [21] 李浡铭. 基于深度学习的用户移动性预测方法与应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆邮电大学, 2020.LI Boming. Research on user mobility prediction method and application based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020. [22] 吕邦国, 杨健, 于涛. 5G标准进展及关键技术[J]. 电信工程技术与标准化, 2016, 29(8): 39–43. doi: 10.13992/j.cnki.tetas.2016.08.012LV Bangguo, YANG Jian, and YU Tao. Brief introduction of 5G standard development and key technology[J]. Telecom Engineering Technics and Standardization, 2016, 29(8): 39–43. doi: 10.13992/j.cnki.tetas.2016.08.012 [23] 王煜尘, 窦银科, 孟润泉. 基于模糊C均值聚类-变分模态分解和群智能优化的多核神经网络短期负荷预测模型[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48(4): 1308–1319. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20210664WANG Yuchen, DOU Yinke, and MENG Runquan. Forecasting model for multicore neural network short-term load based on fuzzy c-mean clustering-variational modal decomposition and chaotic swarm intelligence optimization[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48(4): 1308–1319. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20210664 [24] KALBKHANI H, YOUSEFI S, and SHAYESTEH M G. Adaptive handover algorithm in heterogeneous femtocellular networks based on received signal strength and signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio prediction[J]. IET Communications, 2014, 8(17): 3061–3071. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2014.0230 [25] LEE C H and KIM J H. Time-of-stay estimation-based cell selection scheme in multitier heterogeneous mobile networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2015, 19(9): 1596–1599. doi: 10.1109/lcomm.2015.2422823 -





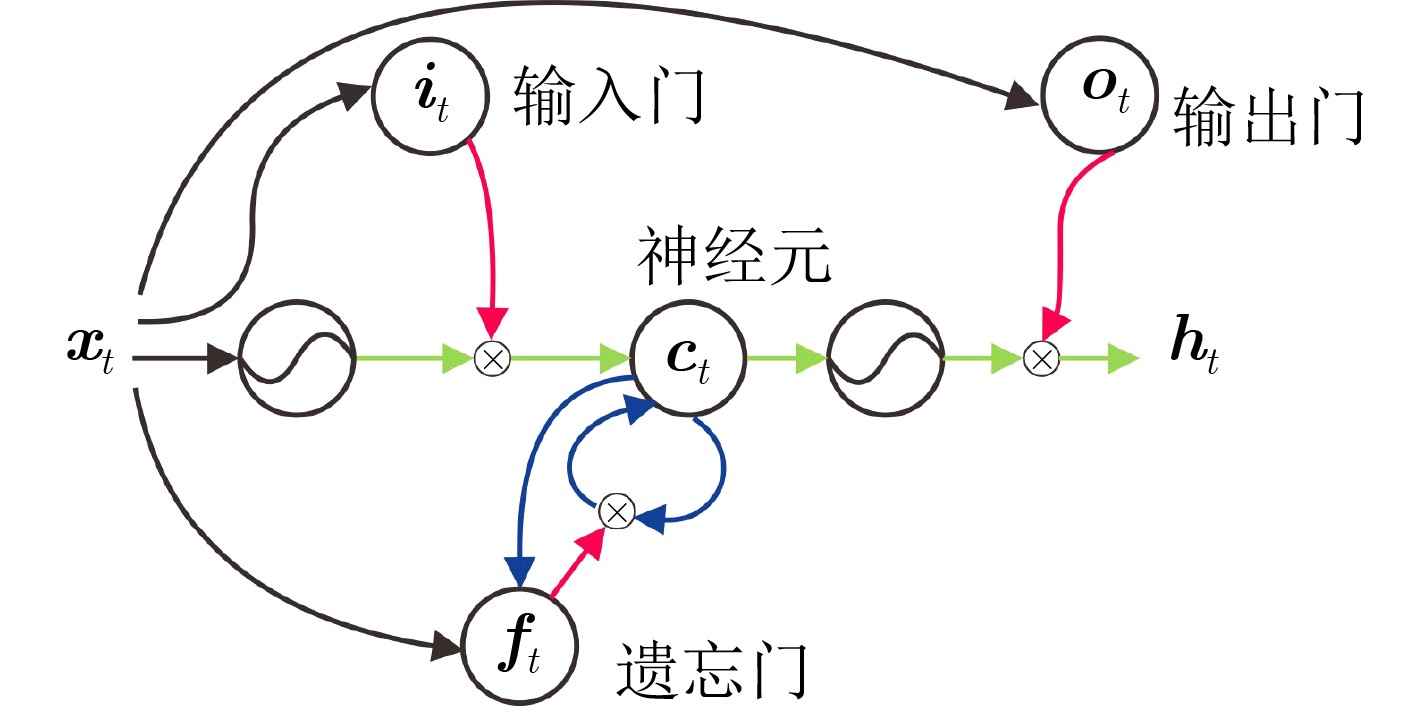
 下载:
下载:
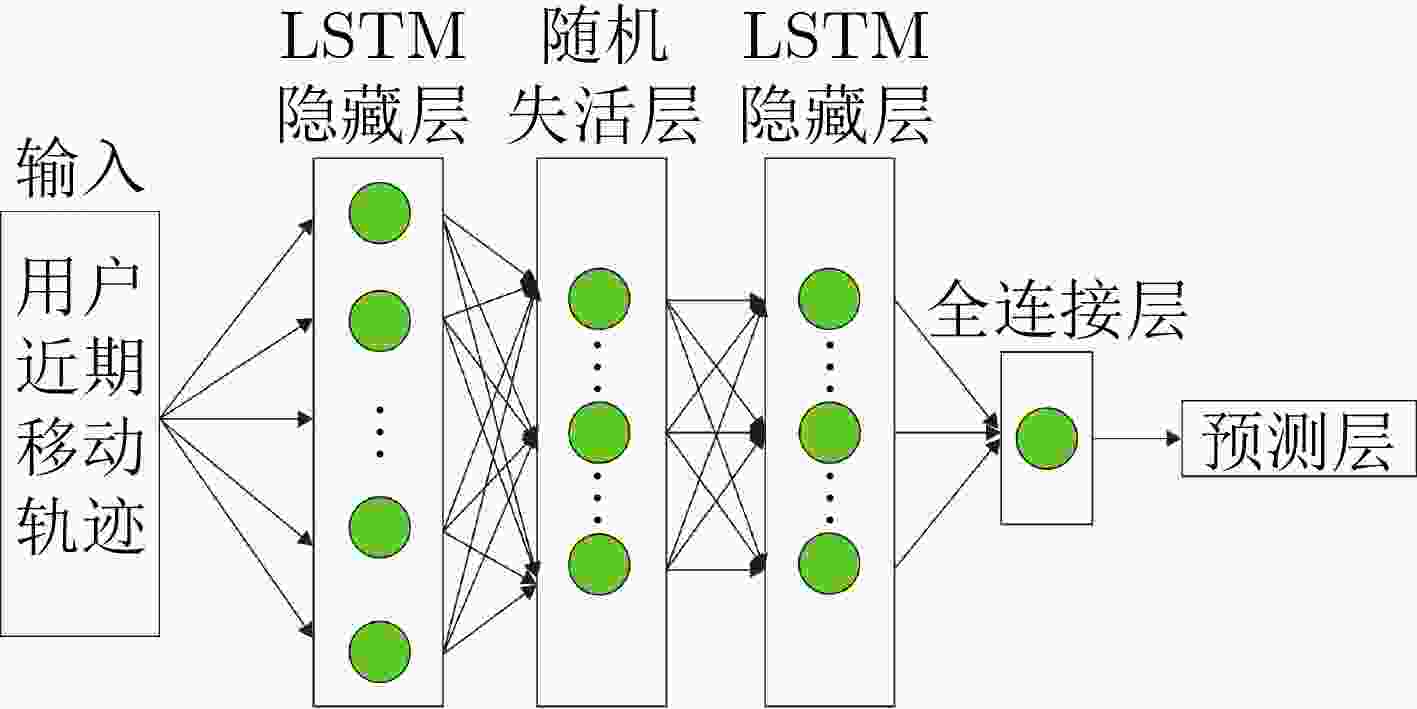

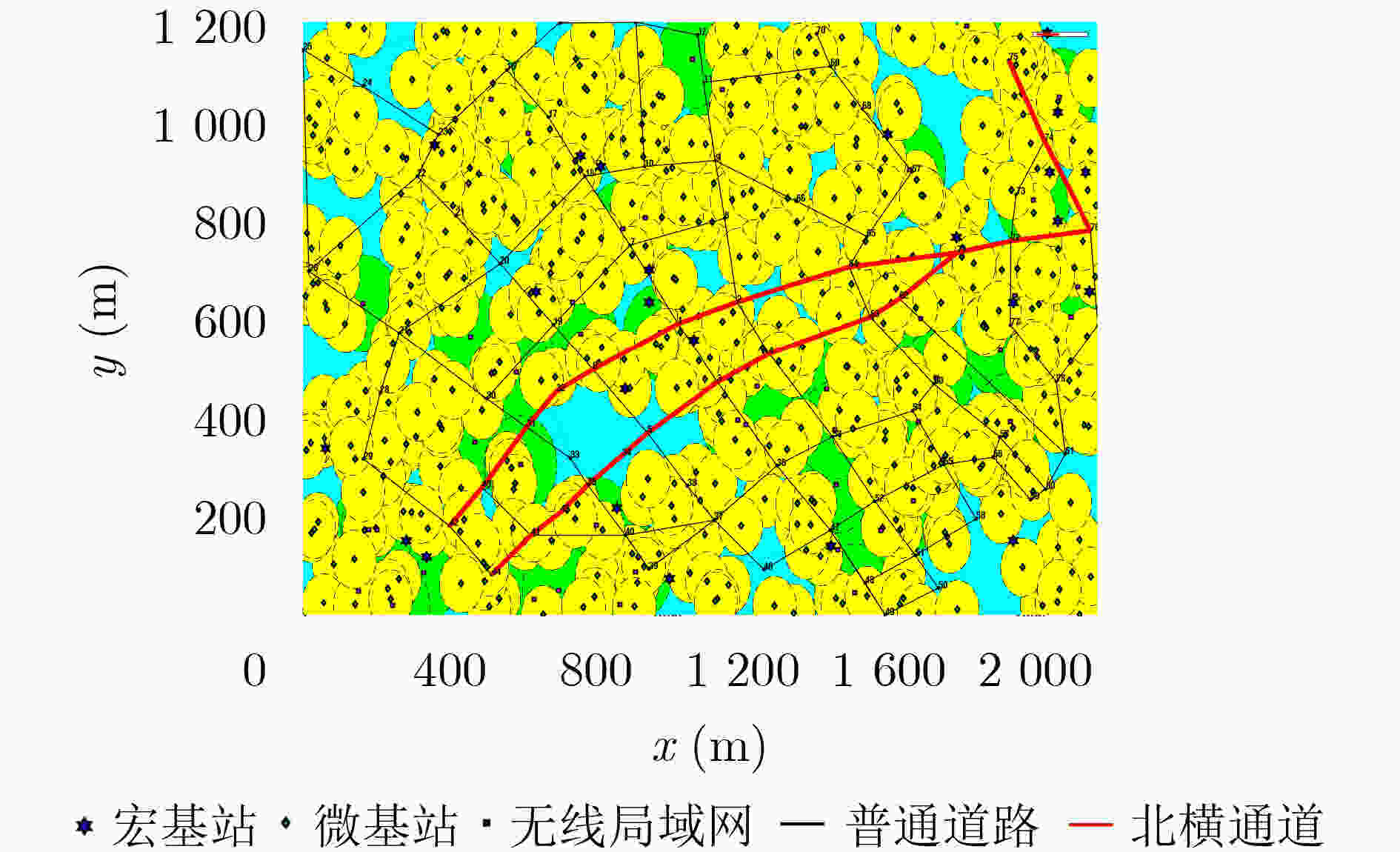


 下载:
下载:
