Invertible Color Image Decolorization Based on Variable Augmented Network
-
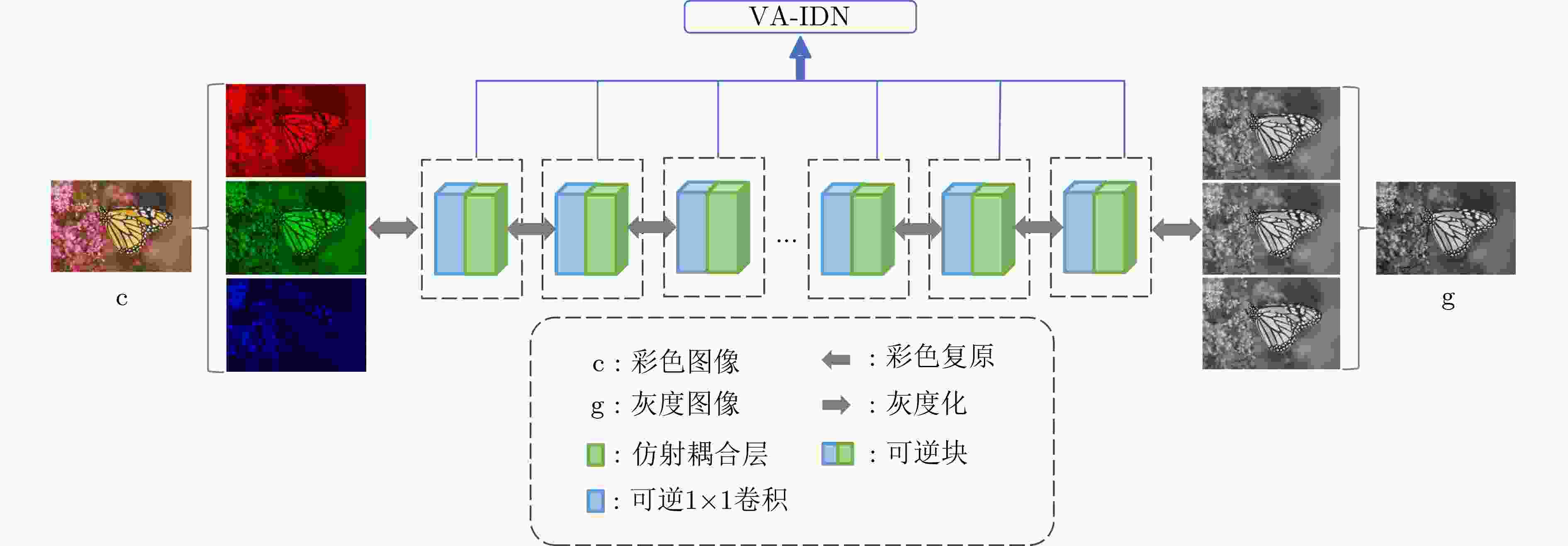
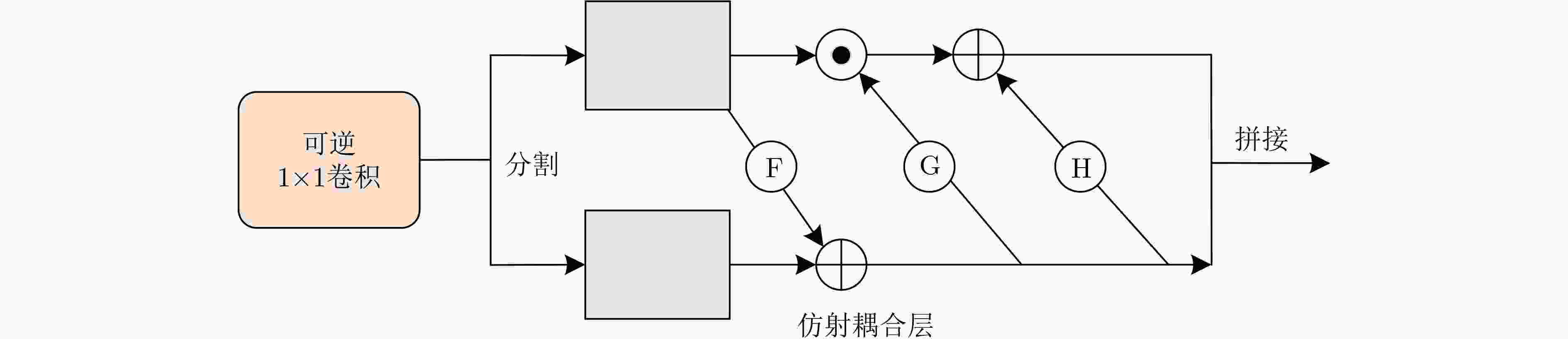
摘要: 彩色图像灰度化是一种被广泛应用于各个领域的图像压缩方式,但很少有研究关注彩色图像与灰度图像之间的相互转换技术。该文运用深度学习,创新性地提出了一种基于辅助变量增强的可逆彩色图像灰度化方法。该方法使用变量增强技术来保证输出与输入变量通道数相同以满足网络的可逆特性。具体来说,该方法通过可逆神经网络的正向过程实现彩色图像灰度化,逆向过程实现灰度图像的色彩复原。将所提方法在VOC2012, NCD和Wallpaper数据集上进行定性和定量比较。实验结果表明,所提方法在评价指标上均获得了更好的结果。无论是在全局还是局部,生成图像都可以最大程度地保留亮度、颜色对比度和结构相关性等特征。Abstract: Decolorization is an image compression method widely used in various fields, but few researches focus on the mutual conversion technology of color image and grayscale image. In this paper, a deep learning method is used to propose innovatively an invertible decolorization method based on variable augmentation. This method uses variable augmentation technology to ensure that the output has the same number of channels as the input variable, which satisfies the reversible characteristics of the network. Specifically, the proposed method realizes the decolorization through the forward process of the invertible neural network, and realizes the color restoration of grayscale images through the reverse process. The proposed method performs qualitative and quantitative comparisons on VOC2012, NCD, Wallpaper datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better results in the evaluation indicators. The quality of the generated images can preserve the characteristics of brightness, color contrast and structural correlation to the greatest extent, both globally and locally.
-
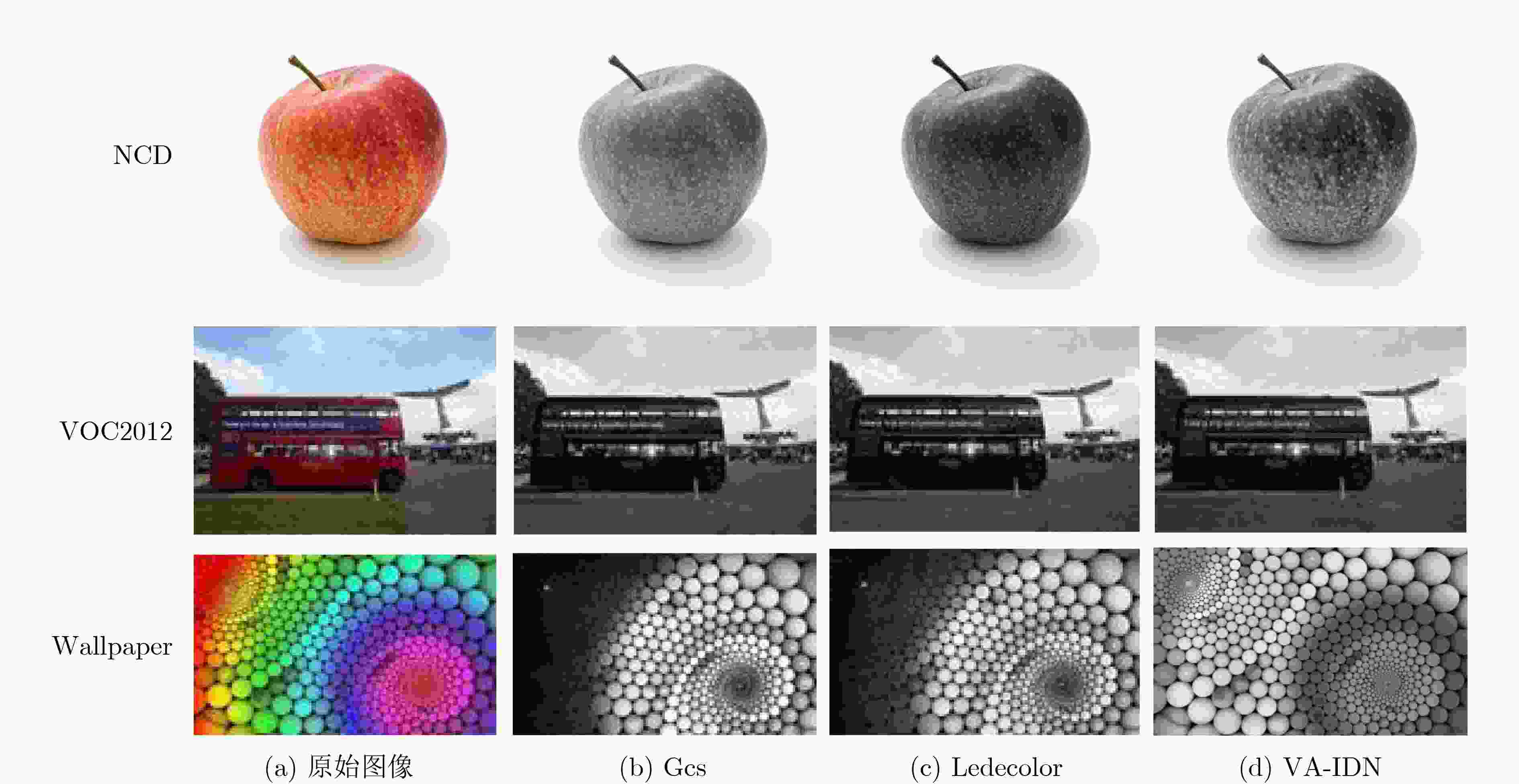
表 1 Wallpaper数据集的CCPR, CCFR和E-score结果
τ CCPR CCFR E-score Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN 1 0.9578 0.9638 0.9555 0.9275 0.9294 0.9729 0.9418 0.9456 0.9637 2 0.9281 0.9361 0.9218 0.8850 0.8885 0.9634 0.9048 0.9105 0.9414 3 0.9065 0.9151 0.8973 0.8648 0.8687 0.9586 0.8840 0.8902 0.9261 4 0.8863 0.8951 0.8743 0.8556 0.8595 0.9555 0.8694 0.8759 0.9122 5 0.8685 0.8773 0.8538 0.8503 0.8547 0.9536 0.8581 0.8649 0.9000 6 0.8515 0.8601 0.8346 0.8480 0.8517 0.9518 0.8484 0.8550 0.8884 7 0.8352 0.8437 0.8160 0.8462 0.8495 0.9499 0.8393 0.8457 0.8768 8 0.8197 0.8279 0.7979 0.8455 0.8490 0.9479 0.8310 0.8375 0.8654 9 0.8044 0.8124 0.7805 0.8458 0.8489 0.9456 0.8232 0.8294 0.8539 10 0.7894 0.7971 0.7633 0.8461 0.8485 0.9440 0.8154 0.8212 0.8428 表 2 VOC2012数据集的CCPR, CCFR和E-score结果
τ CCPR CCFR E-score Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN 1 0.9687 0.9710 0.9683 0.9382 0.9378 0.9708 0.9531 0.9539 0.9695 2 0.9404 0.9446 0.9404 0.8640 0.8630 0.9557 0.9002 0.9016 0.9479 3 0.9185 0.9244 0.9195 0.8130 0.8113 0.9518 0.8621 0.8637 0.9352 4 0.8972 0.9052 0.8989 0.7835 0.7812 0.9530 0.8360 0.8381 0.9249 5 0.8788 0.8887 0.8810 0.7667 0.7639 0.9546 0.8183 0.8209 0.9159 6 0.8617 0.8736 0.8642 0.7589 0.7551 0.9558 0.8062 0.8092 0.9072 7 0.8458 0.8595 0.8483 0.7560 0.7516 0.9580 0.7973 0.8009 0.8992 8 0.8308 0.8461 0.8334 0.7563 0.7512 0.9597 0.7906 0.7947 0.8913 9 0.8166 0.8333 0.8191 0.7589 0.7529 0.9609 0.7853 0.7898 0.8833 10 0.8031 0.8211 0.8055 0.7628 0.7568 0.9620 0.7809 0.7863 0.8755 表 3 NCD数据集的CCPR, CCFR和E-score结果
τ CCPR CCFR E-score Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN Gcs Ledecolor VA-IDN 1 0.9503 0.9587 0.9451 0.9466 0.9389 0.9716 0.9480 0.9483 0.9579 2 0.9493 0.9581 0.9431 0.9184 0.8976 0.9644 0.9327 0.9261 0.9533 3 0.9471 0.9568 0.9431 0.9010 0.8729 0.9611 0.9223 0.9119 0.9516 4 0.9424 0.9535 0.9399 0.8925 0.8572 0.9604 0.9153 0.9015 0.9496 5 0.9376 0.9507 0.9362 0.8883 0.8481 0.9612 0.9104 0.8948 0.9480 6 0.9317 0.9477 0.9311 0.8867 0.8429 0.9619 0.9064 0.8903 0.9456 7 0.9252 0.9450 0.9251 0.8887 0.8405 0.9625 0.9040 0.8876 0.9427 8 0.9203 0.9432 0.9205 0.8900 0.8398 0.9630 0.9020 0.8862 0.9403 9 0.9131 0.9410 0.9127 0.8936 0.8407 0.9637 0.8999 0.8856 0.9362 10 0.9058 0.9390 0.9039 0.8971 0.8426 0.9645 0.8977 0.8856 0.9315 表 4 彩色图像灰度化的PSNR和SSIM值
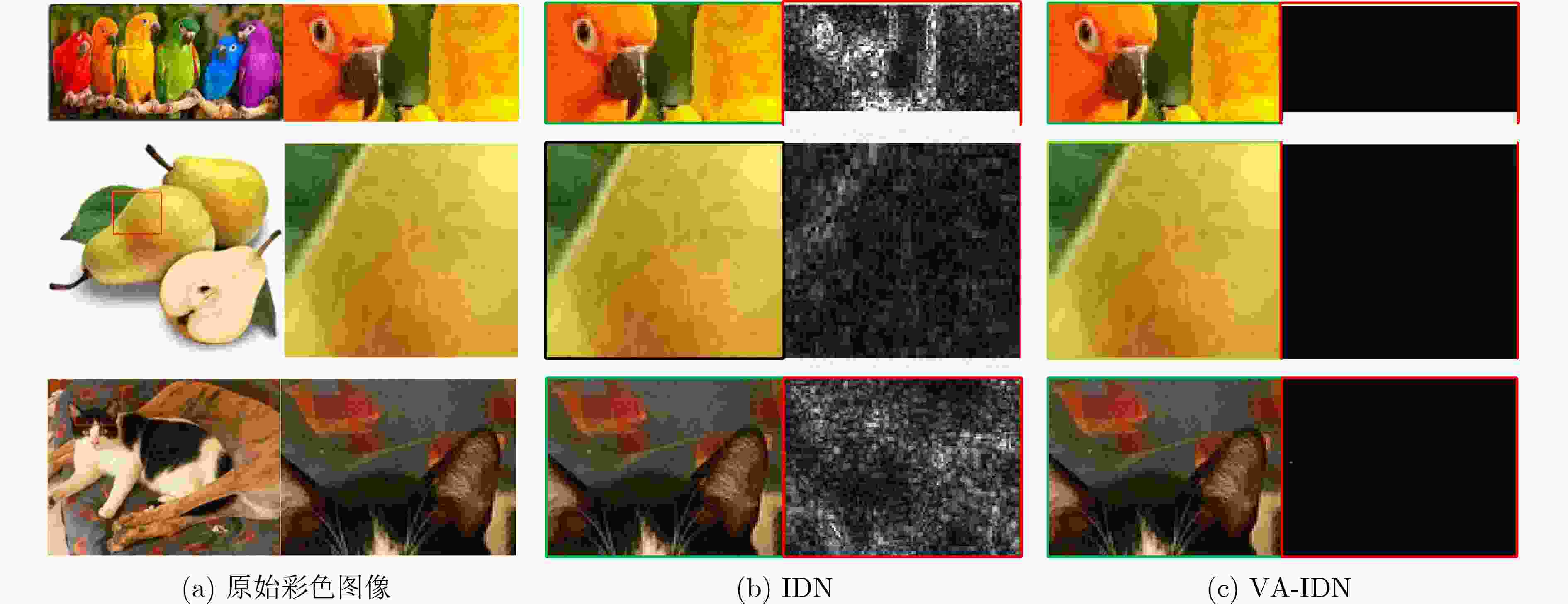
数据指标 VOC2012 Wallpaper NCD IDN VA-IDN IDN VA-IDN IDN VA-IDN PSNR (dB) 40.660 45.648 34.969 37.781 43.611 45.639 SSIM 0.9790 0.9982 0.9092 0.9913 0.9791 0.9988 表 5 灰度图像色彩复原的PSNR和SSIM值
数据指标 VOC2012 Wallpaper NCD IDN VA-IDN IDN VA-IDN IDN VA-IDN PSNR (dB) 39.505 64.759 35.068 64.696 42.245 45.777 SSIM 0.9868 0.9998 0.9553 0.9998 0.9884 0.9969 -
[1] LIU Qiegen, XIONG Jiaojiao, LI Zhu, et al. Extended RGB2Gray conversion model for efficient contrast preserving decolorization[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(12): 14055–14074. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-3748-9 [2] ZHANG Lina and YI Wan. Color-to-gray conversion based on boundary points[C]. 11th International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems, Chengdu, China, 2022: 241–245. [3] LIU Qiegen, LI Sanqian, XIONG Jiaojiao, et al. WpmDecolor: Weighted projection maximum solver for contrast-preserving decolorization[J]. The Visual Computer, 2019, 35(2): 205–221. doi: 10.1007/s00371-017-1464-8 [4] 朱波, 汶德胜, 王飞, 等. 应用字典学习算法改善Bayer格式图像彩色恢复效果[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(4): 812–819. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00947ZHU Bo, WEN Desheng, WANG Fei, et al. Improvement of Bayer-pattern demosaicking with dictionary learning algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(4): 812–819. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00947 [5] ZHU Wen, HU Ruizhen, and LIU Ligang. Grey conversion via perceived-contrast[J]. The Visual Computer, 2014, 30(3): 299–309. doi: 10.1007/s00371-013-0854-9 [6] 卢红阳, 刘且根, 熊娇娇, 等. 基于最大加权投影求解的彩色图像灰度化对比度保留算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 843–854. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160077LU Hongyang, LIU Qiegen, XIONG Jiaojiao, et al. Maximum weighted projection solver for contrast preserving decolorization[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 843–854. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160077 [7] LU Cewu, XU Li, and JIA Jiaya. Contrast preserving decolorization[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, Seattle, USA, 2012: 1–7. [8] LU Cewu, XU Li, and JIA Jiaya. Real-time contrast preserving decolorization[C]. SIGGRAPH Asia 2012 Technical Briefs, Singapore, 2012: 34. [9] LIU Qiegen, LIU P X, WANG Yuhao, et al. Semiparametric decolorization with Laplacian-based perceptual quality metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(9): 1856–1868. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2555779 [10] HSIN C, LE H N, and SHIN S J. Color to grayscale transform preserving natural order of hues[C]. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Bandung, Indonesia, 2011: 1–6. [11] ANCUTI C and ANCUTI C O. Laplacian-guided image decolorization[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 4107–4111. [12] AN Jiancheng, KPEYITON K G, and SHI Qingnan. Grayscale images colorization with convolutional neural networks[J]. Soft Computing, 2020, 24(7): 4751–4758. doi: 10.1007/s00500-020-04711-3 [13] DU Kangning, LIU Changtong, CAO Lin, et al. Double-channel guided generative adversarial network for image colorization[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 21604–21617. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3055575 [14] VITORIA P, RAAD L, and BALLESTER C. ChromaGAN: Adversarial picture colorization with semantic class distribution[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass, USA, 2020: 2434–2443. [15] XIA Menghan, LIU Xueting, and WONG T T. Invertible grayscale[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37(6): 246. doi: 10.1145/3272127.3275080 [16] ZHAO Rui, LIU Tianshan, XIAO Jun, et al. Invertible image decolorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 6081–6095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3091902 [17] LIU Qiegen and LEUNG H. Variable augmented neural network for decolorization and multi-exposure fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 46: 114–127. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.05.007 [18] XING Yazhou, QIAN Zian, and CHEN Qifeng. Invertible image signal processing[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 6283–6292. [19] XIAO Mingqing, ZHENG Shuxin, LIU Chang, et al. Invertible image rescaling[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 126–144. [20] KINGMA D P and DHARIWAL P. Glow: Generative flow with invertible 1x1 convolutions[C]. Proceedings of International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2018, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 10236-10245. [21] LIU Qiegen, LIU P X, XIE Weisi, et al. GcsDecolor: Gradient correlation similarity for efficient contrast preserving decolorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(9): 2889–2904. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2423615 [22] LIU Qiegen, Shao Guangpu, WANG Yuhao, et al. Log-Euclidean metrics for contrast preserving decolorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(12): 5772–5783. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2745104 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
