Research on Data Heterogeneous Robust Federated Learning with Privacy Protection in Internet of Things
-
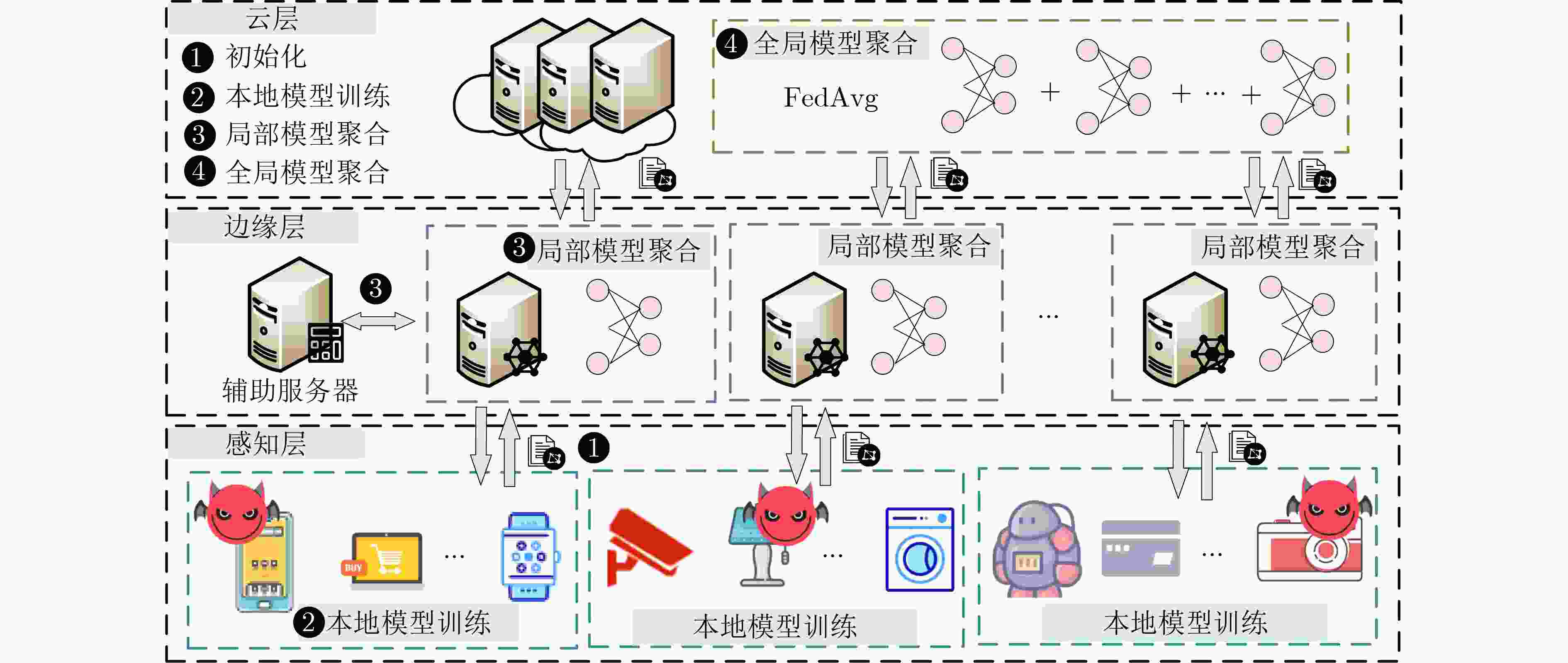
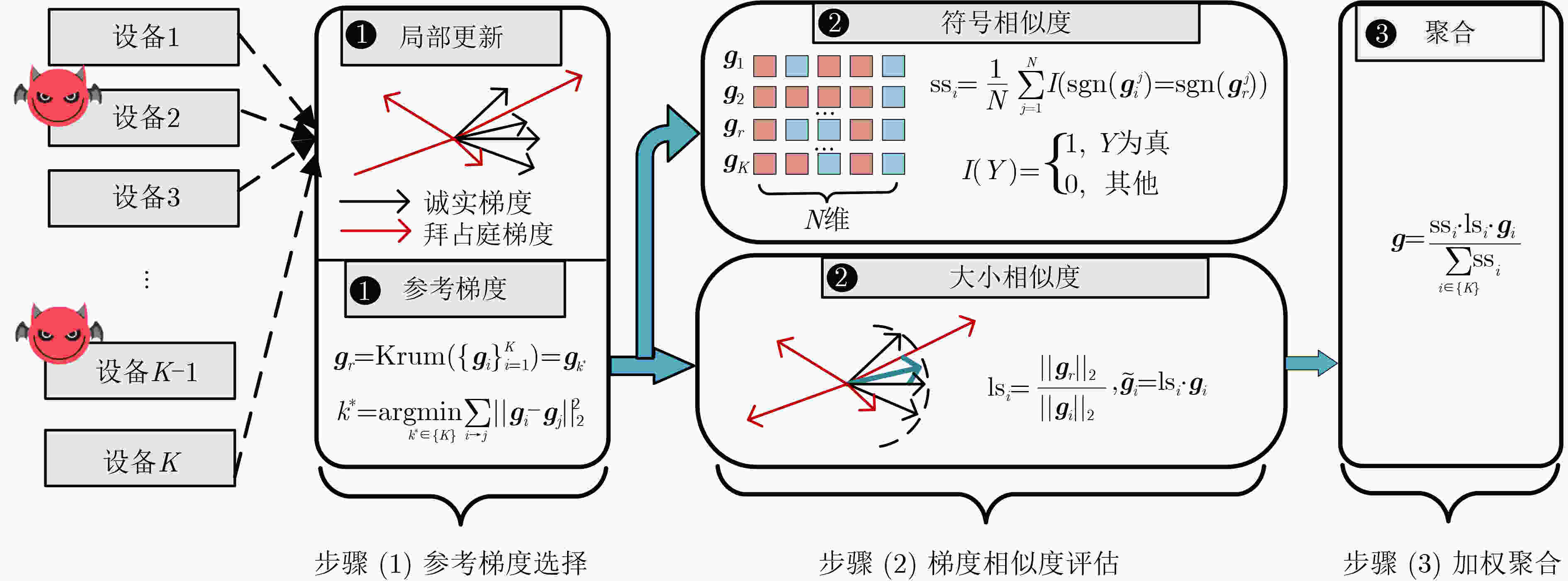
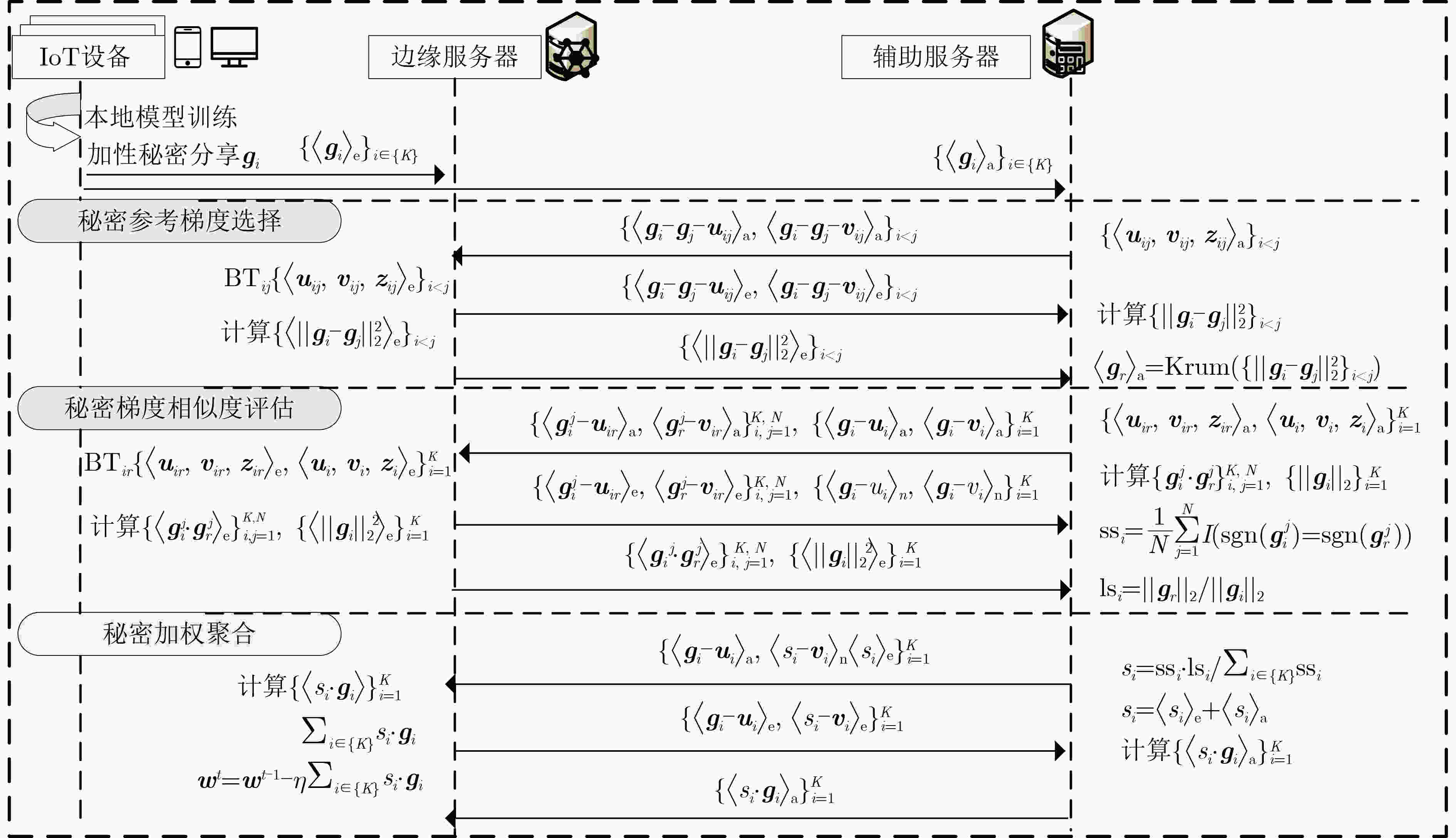
摘要: 联邦学习允许数据不出本地的情况下实现数据价值的有效流动,被认为是物联网(IoT)场景下兼顾数据共享与隐私保护的有效方法。然而,联邦学习系统易受拜占庭攻击和推理攻击的影响,导致系统的鲁棒性和数据的隐私性受损。物联网设备的数据异构性和资源瓶颈,也为带有隐私保护的鲁棒聚合算法设计带来巨大挑战。该文提出面向异构物联网的带有数据重采样的鲁棒聚合方法Re-Sim,通过测量方向相似性和标准化更新幅度实现模型的鲁棒聚合,并采用数据重采样技术增强数据异构环境下模型的鲁棒性。同时构建轻量安全聚合协议(LSA),在保证数据隐私性的同时兼顾模型鲁棒性、准确性和计算开销,并从理论上对协议的隐私性进行了分析。仿真结果表明,该方案能在数据异构情况下有效抵抗拜占庭攻击和推理攻击,与基线方法相比,该文所提方案精度提高1%~3%,同时减轻客户端侧计算开销79%。Abstract: Federated learning allows the effective flow of data value without leaving the local data, which is considered to be an effective way to balance data sharing and privacy protection in the Internet of Things (IoT) scenario. However, federated learning systems are vulnerable to Byzantine attacks and inference attacks, leading to the robustness of the system and the privacy of the data being compromised. The data heterogeneity and resource bottlenecks of IoT devices also pose significant challenges to the design of privacy-preserving and Byzantine-robust algorithms. In this paper, a data resampling of robust aggregation method Re-Sim applicable to heterogeneous IoT is proposed, which achieves robust aggregation by measuring directional similarity and normalized update magnitude, and uses data resampling to enhance robustness in data heterogeneous environments. Meanwhile, a Lightweight Security Aggregation (LSA) protocol is proposed to ensure data privacy while taking into account model robustness, accuracy and computational overhead, and the privacy of the protocol is theoretically analyzed. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme can effectively resist Byzantine attacks and inference attacks in the case of data heterogeneity. The proposed scheme improves the accuracy by 1%~3% compared to the baseline method, while reducing the client-side computational overhead by 79%.
-
Key words:
- Internet of Things (IoT) /
- Federated learning /
- Robust aggregation /
- Secret sharing
-
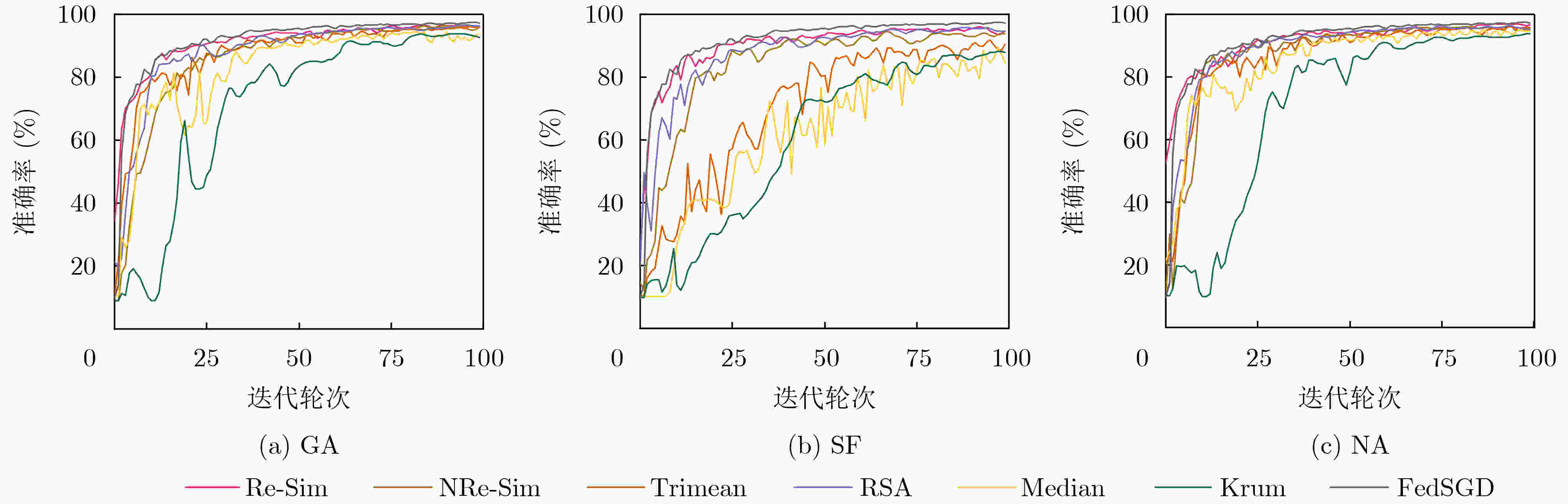
表 1 MNIST和Fashion MNIST在IID设置下的算法准确度(%)
数据集 模型 攻击方式 FedSGD Krum Median Trimean RSA NRe-Sim MNIST LeNet-5 无攻击 97.14 94.49 96.78 96.79 96.94 97.16 SF 11.35 94.40 95.10 94.73 95.32 96.21 GA 12.41 95.07 95.73 96.28 96.68 96.76 NA 81.74 94.46 96.49 96.87 96.58 97.03 Fashion MNIST LeNet-5 无攻击 85.17 82.80 85.68 85.73 85.76 85.89 SF 9.98 81.76 82.88 83.39 82.57 83.43 GA 16.17 82.77 85.27 84.97 85.16 85.44 NA 62.92 82.15 85.46 85.41 85.33 85.64 -
[1] 黄新林, 郑人华. 基于强化学习的802.11ax上行链路调度算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(5): 1800–1808. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210590HUANG Xinlin and ZHENG Renhua. 802.11ax uplink scheduling algorithm based on reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(5): 1800–1808. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210590 [2] MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282. [3] BLANCHARD P, EL MHAMDI E M, GUERRAOUI R, et al. Machine learning with adversaries: Byzantine tolerant gradient descent[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 118–128. [4] YIN Dong, CHEN Yudong, RAMCHANDRAN K, et al. Byzantine-robust distributed learning: Towards optimal statistical rates[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 5636–5645. [5] MELIS L, SONG Congzheng, DE CRISTOFARO E, et al. Exploiting unintended feature leakage in collaborative learning[C]. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, USA, 2019: 691–706. [6] XIONG Jinbo, BI Renwan, TIAN Youliang, et al. Toward lightweight, privacy-preserving cooperative object classification for connected autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(4): 2787–2801. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3093573 [7] BI Renwan, XIONG Jinbo, TIAN Youliang, et al. Achieving lightweight and privacy-preserving object detection for connected autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(3): 2314–2329. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3212464 [8] ZAWAD S, ALI A, CHEN Pinyu, et al. Curse or redemption? How data heterogeneity affects the robustness of federated learning[C]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 2021: 10807–10814. [9] ZHAI Kun, REN Qiang, WANG Junli, et al. Byzantine-robust federated learning via credibility assessment on non-IID data[J]. arXiv: 2109.02396, 2021. [10] LI Liping, XU Wei, CHEN Tianyi, et al. RSA: Byzantine-robust stochastic aggregation methods for distributed learning from heterogeneous datasets[C]. The 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hawaii, USA, 2019: 1544–1551. [11] ZHANG Chengliang, LI Suyi, XIA Junzhe, et al. BatchCrypt: Efficient homomorphic encryption for cross-silo federated learning[C]. The 2020 USENIX Conference on Usenix Annual Technical Conference, Boston, USA, 2020: 33. [12] FU Anmin, ZHANG Xianglong, XIONG Naixue, et al. VFL: A verifiable federated learning with privacy-preserving for big data in industrial IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(5): 3316–3326. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3036166 [13] SO J, GÜLER B, and AVESTIMEHR A S. Byzantine-resilient secure federated learning[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(7): 2168–2181. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3041404 [14] LIU Xiaoyuan, LI Hongwei, XU Guowen, et al. Privacy-enhanced federated learning against poisoning adversaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 4574–4588. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3108434 [15] HSIEH K, HARLAP A, VIJAYKUMAR N, et al. Gaia: Geo-distributed machine learning approaching LAN speeds[C]. The 14th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Boston, USA, 2017: 629–647. [16] LI Yiran, LI Hongwei, XU Guowen, et al. Efficient privacy-preserving federated learning with unreliable users[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(13): 11590–11603. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3130115 [17] ZHU Wanchuang, ZHAO B Z H, LUO S, et al. MANDERA: Malicious node detection in federated learning via ranking[J]. arXiv: 2110.11736, 2021. [18] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [19] XIAO Han, RASUL K, and VOLLGRAF R. Fashion-MNIST: A novel image dataset for benchmarking machine learning algorithms[J]. arXiv: 1708.07747, 2017. [20] WANG Hao, KAPLAN Z, NIU Di, et al. Optimizing federated learning on non-IID data with reinforcement learning[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2020 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, Canada, 2020: 1698–1707. -





 下载:
下载:
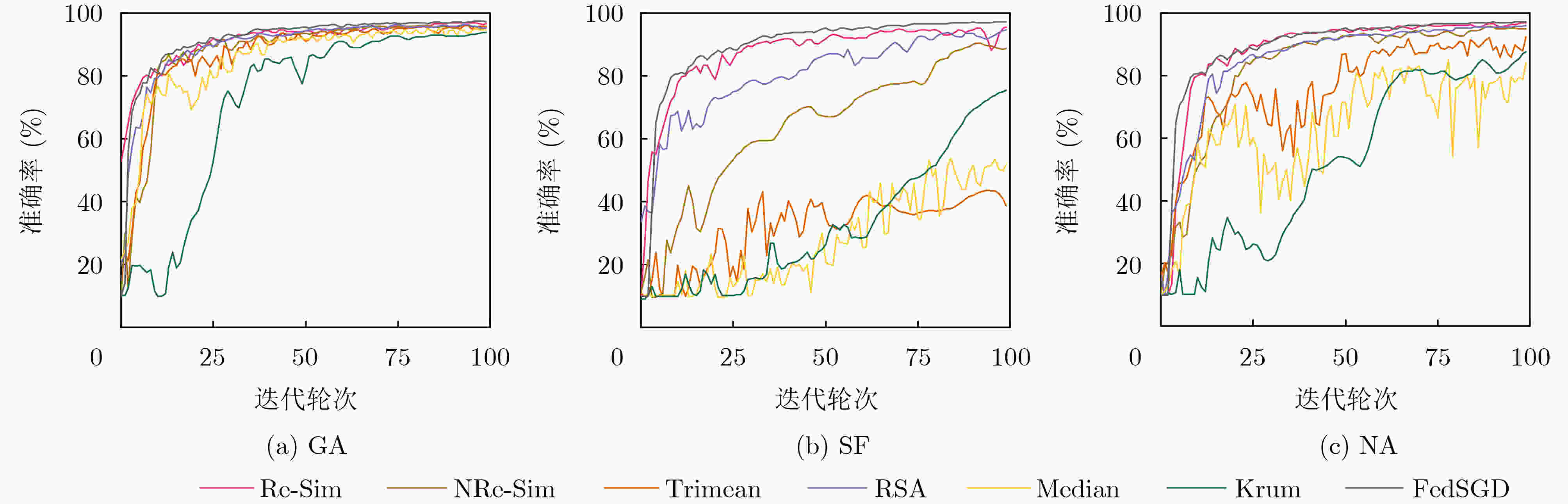
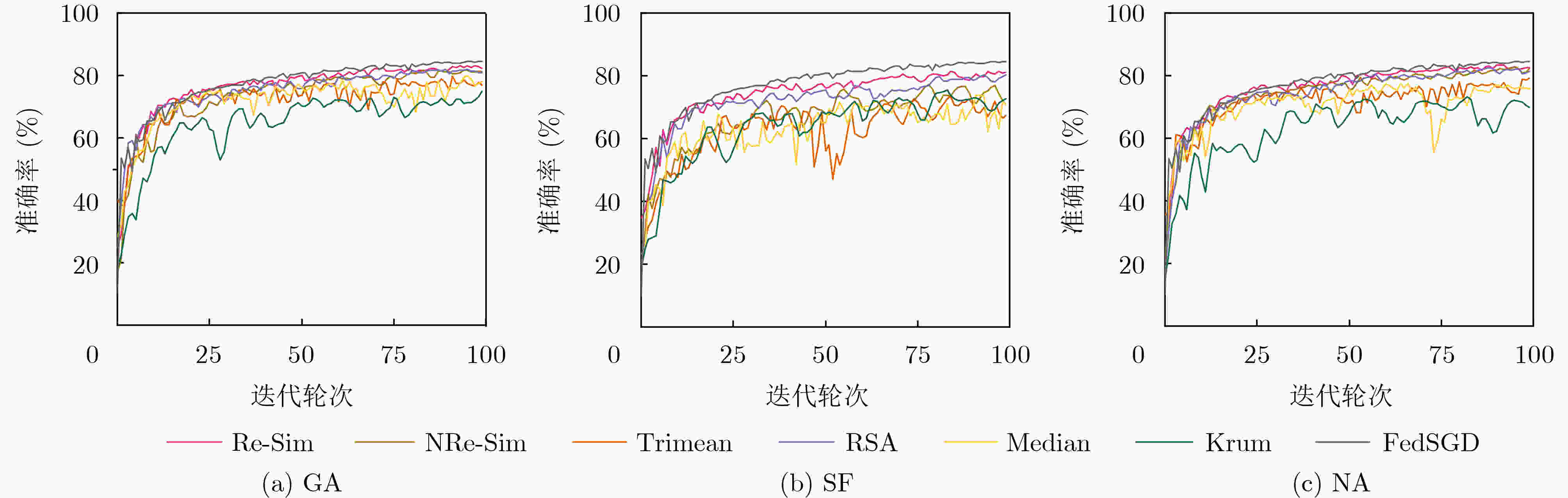
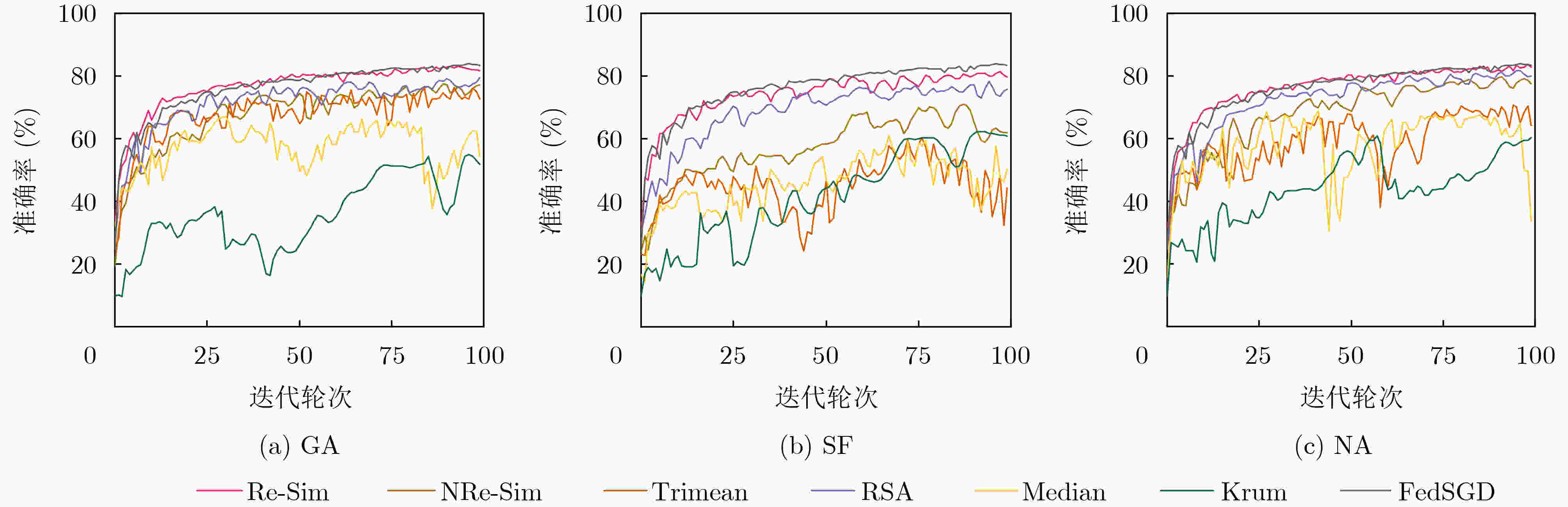
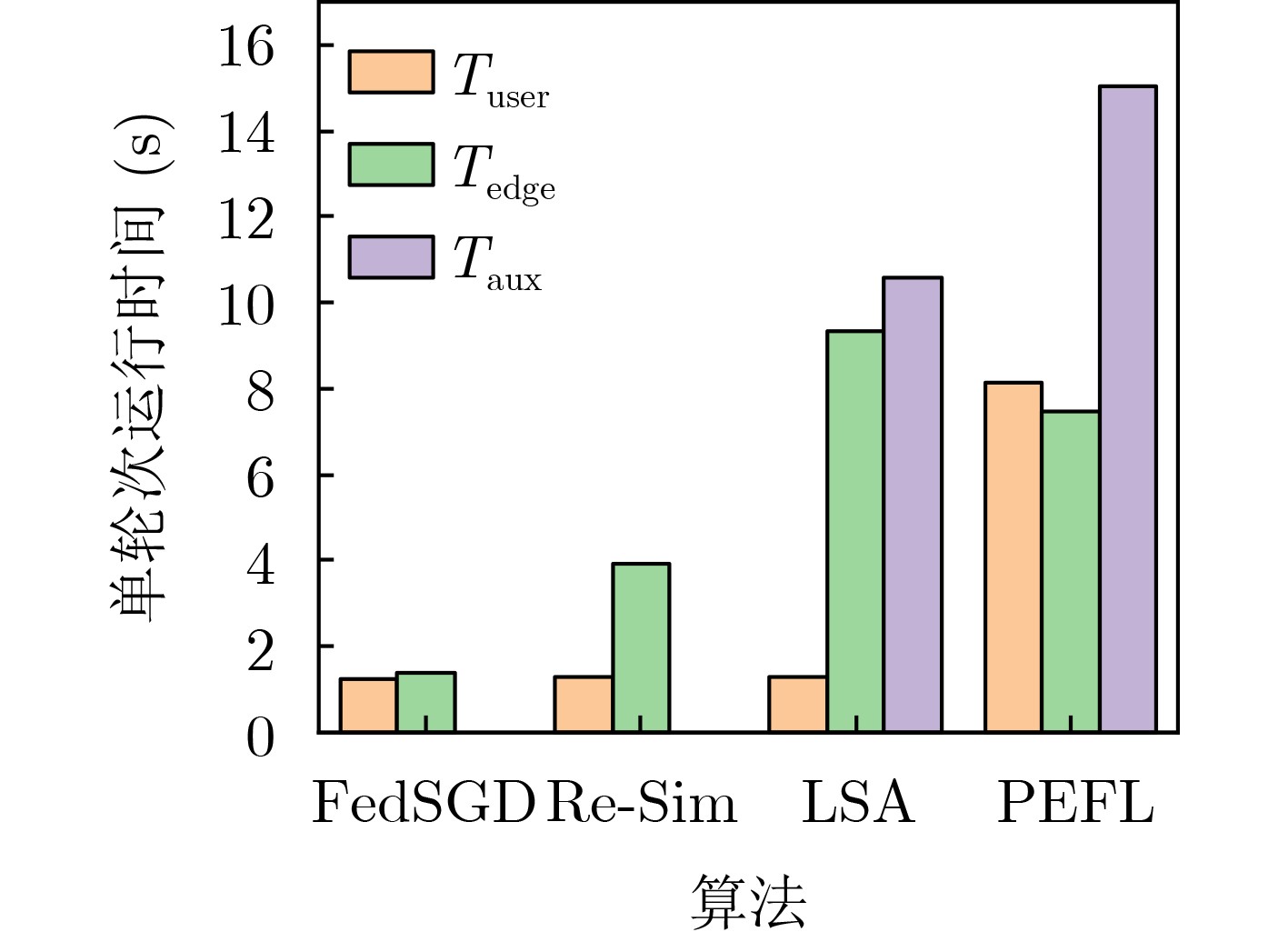


 下载:
下载:
