A Privacy Protection Scheme Based on Attribute Encryption in Mobile Social Networks
-
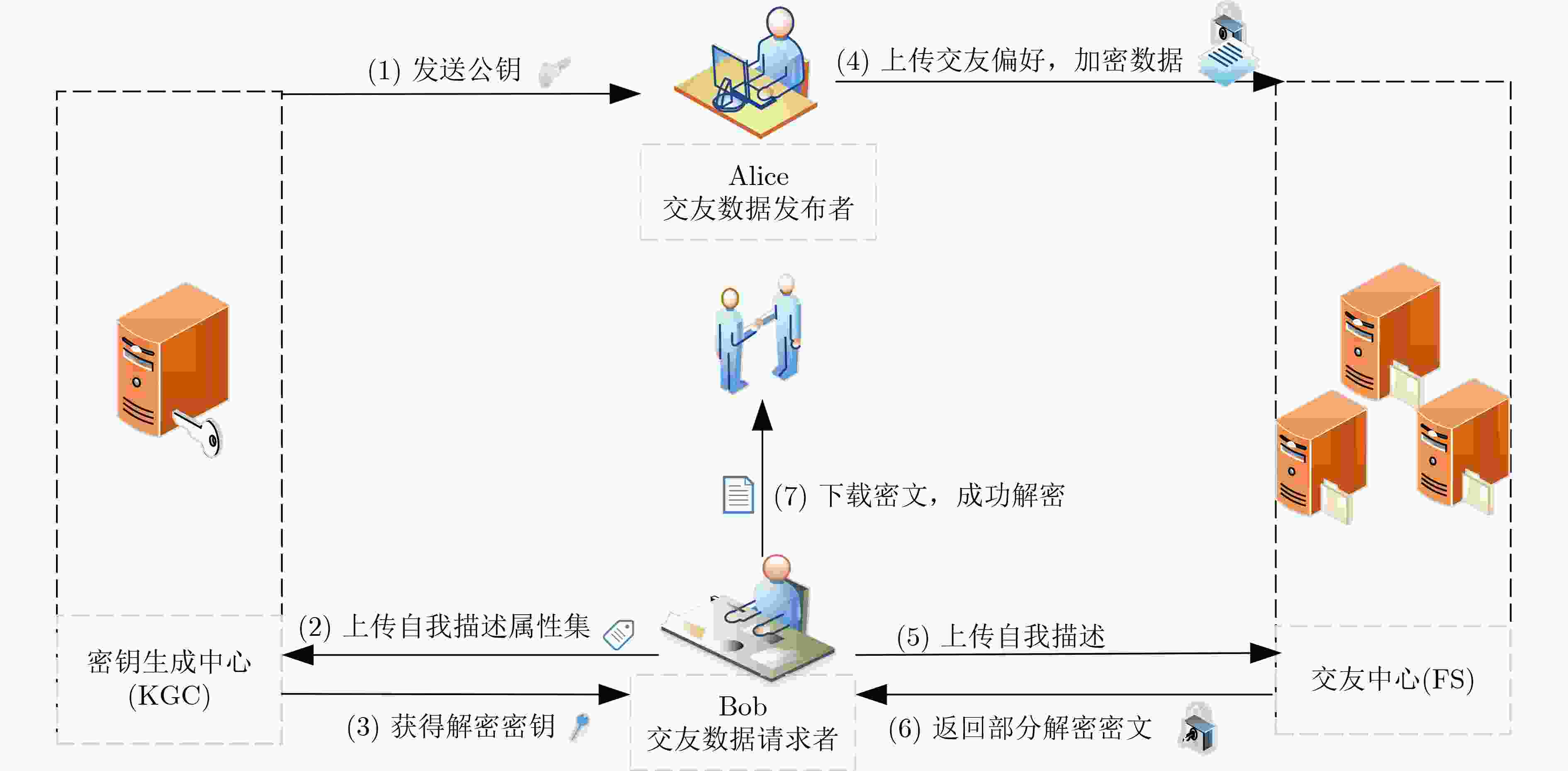
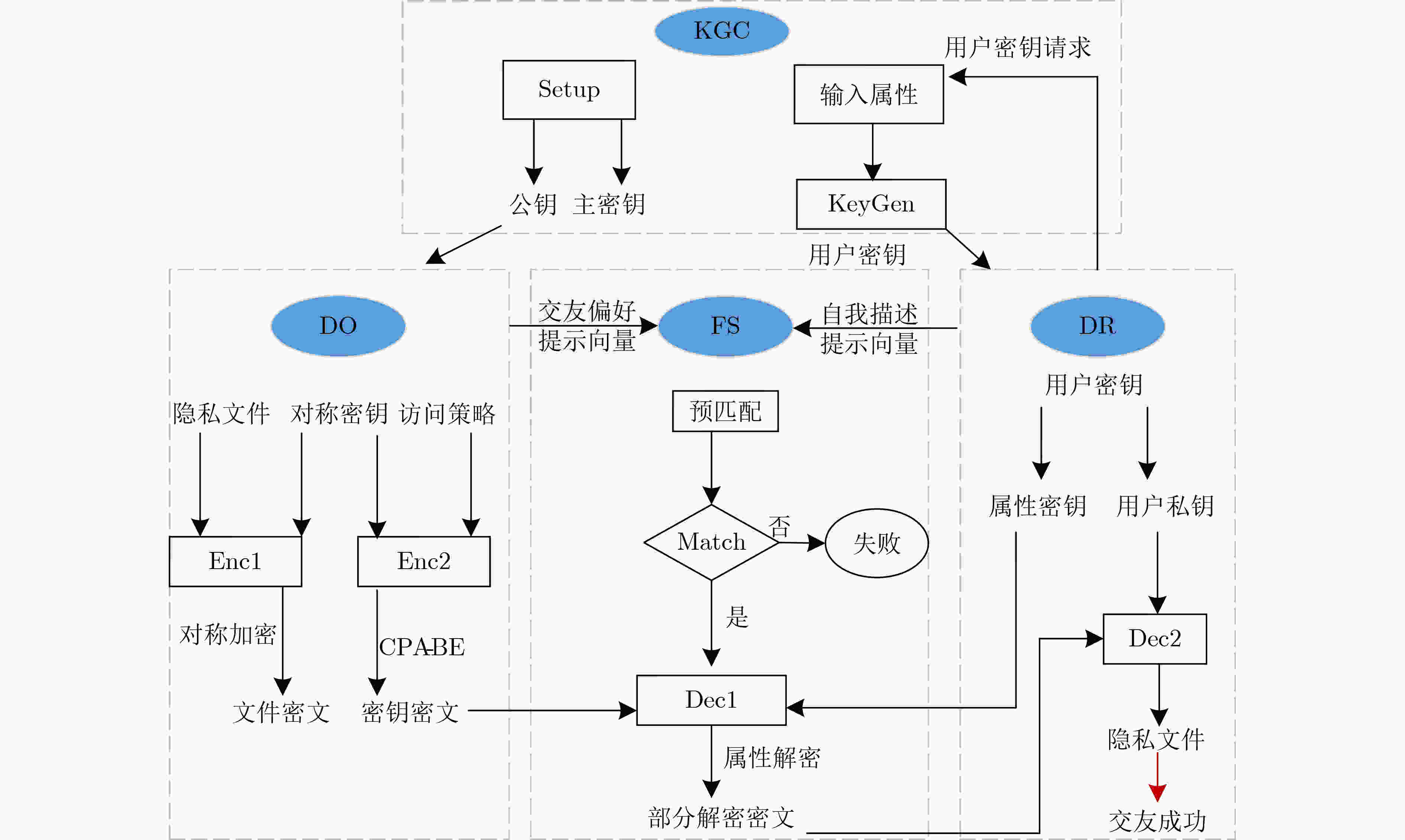
摘要: 为了保护用户在移动社交网络中的个人信息和交友偏好等隐私,该文提出支持外包解密的基于密文策略的属性基加密(CP-ABE)方案。在该方案中,将用户的交友偏好和自我描述分别生成属性列表,通过将交友偏好转换为密文控制策略,自我描述转化为属性密钥来隐藏属性,从而实现隐私保护。该方案提出了先匹配后解密的算法机制:社交平台对用户信息进行匹配验证,当满足相应的匹配条件时,该算法将计算量较大的双线性对运算外包给交友中心,之后用户再对密文解密。通过快速排除不匹配用户,避免了无效解密。外包解密在保护信息的同时,减少了移动设备的计算负担和通信开销。安全性分析表明,该方案是安全有效的,此外性能评估显示所提方案在计算和通信开销方面是高效且实用的。Abstract: In order to protect the privacy of
${\rm{users}}' $ personal information and friend preferences in social networks, a Ciphertext-Policy Attribute Based Encryption (CP-ABE) scheme that supports outsourced decryption is proposed. In this scheme, attribute lists are generated for the${\rm{users}}' $ dating preference and self-description respectively, and attributes are hidden by converting the dating preference into ciphertext control policy and self-description into attribute key, thus realizing privacy protection. The proposed algorithm mechanism matches${\rm{users}}' $ information and then decrypts it.${\rm{Users}}' $ information is matched and verified by social platform. When the corresponding matching conditions are met, the algorithm outsources the computationally expensive bilinear pairing operation to the dating center. The user then decrypts the ciphertext. Invalid decryption is avoided by quickly eliminating mismatched users. Outsourced decryption reduces the computational burden and communication overhead of mobile devices while protecting information. Security analysis shows that the scheme is safe and effective, furthermore, performance evaluation shows that the proposed scheme is efficient and practical in terms of computational and communication overhead. -
表 1 数据请求者的自我描述列表
列表名 用户名 年龄 性别 血型 职业 住址 爱好 ${S_{{\text{Bob}}}}$ Bob 26 男 AB 教师 北京 音乐、旅游、打羽毛球······ ${S_{{\text{Ada}}}}$ Ada 22 女 O 空姐 上海 游泳、瑜伽、音乐、电影······ ${S_{{\text{Leo}}}}$ Leo 35 男 B 警察 深圳 跑步、健身、做饭、画画······ 表 2 通信量分析
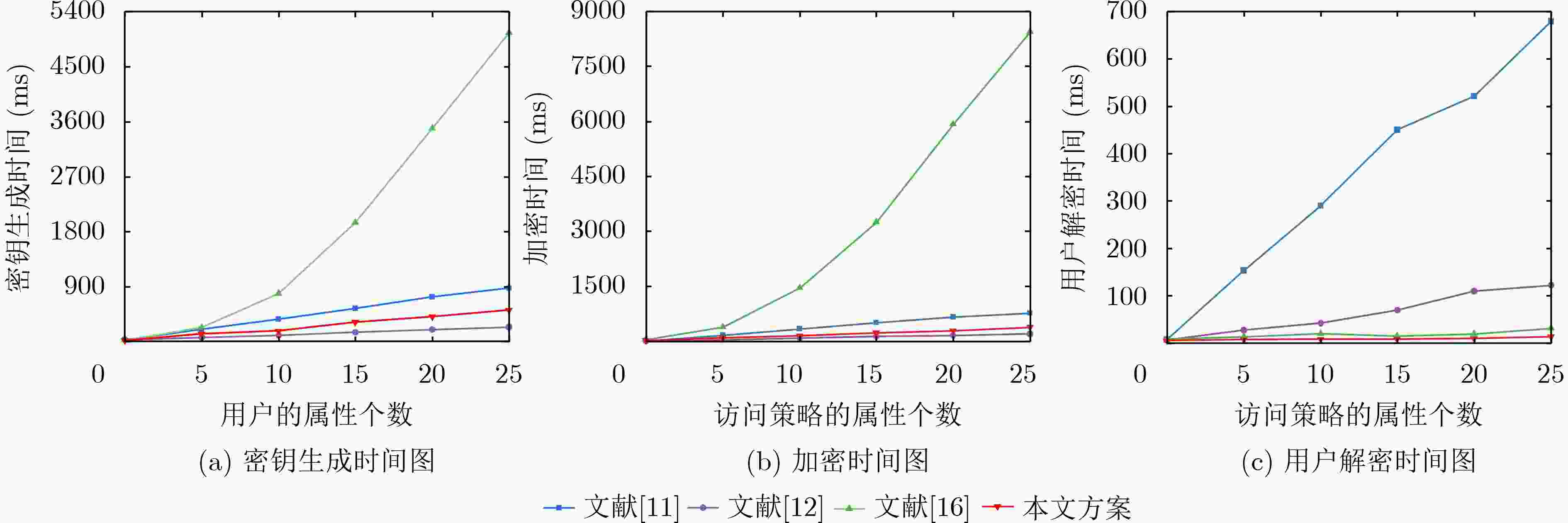
方案 系统公钥 系统主密钥 用户密钥 加密密文 文献[11] $ 9\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| + \left| H \right| $ $ \left| G \right| + 4\left| {{Z_p}} \right| $ $ (2 + 5u)\left| G \right| $ $ (6l + 1)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| + \left| {({\mathbf{M}},\rho )} \right| $ 文献[12] $ (2 + N)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| $ $ \left| G \right| $ $ (2 + u)\left| G \right| $ $ (l + 1)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| + \left| {({\mathbf{M}},\rho )} \right| $ 文献[16] $ (5 + N)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| $ $ (1 + N)\left| {{Z_p}} \right| $ $ 2\left| G \right| $ $ 5\left| G \right| + 2\left| {{G_1}} \right| $ 本文 $ (2 + N)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| $ $ 3\left| G \right| $ $ (3 + u)\left| G \right| $ $ (2l + 1)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_1}} \right| + \left| {({\mathbf{M}},\rho )} \right| $ 表 3 计算量分析
方案 密钥生成 数据加密 数据解密 文献[11] $(u + 2){ {T_{\rm e}} } + { {T_{\rm m}} }$ $(8l + 2){ {T_{\rm e}} } + (l + 3){ {T_{\rm m}} }$ $ u{T_{\rm e}} + (6u + 1){T_{\rm p}} + (5u + 1){T_{\rm m}} $ 文献[12] $(u + 2){{T_{\rm e}} }$ $ (2l + 2){T_{\rm e}} + (l + 1){T_{\rm m}} $ $ u{T_{\rm e}} + (2u + 1){T_{\rm p}} + (u + 2){T_{\rm m}} $ 文献[16] $(5u + 3){ {T_{\rm e}} } + 4{ {T_{\rm m}} }$ $(2l + 6){T_{\rm e} } + (2l + 4){T_{\rm m} } + 2{T_{\rm{h}}}$ $ 8{T_{\rm p}} + 8{T_{\rm m}} $ 本文 $(u + 3){ {T_{\rm e}} }$ $ (3l + 2){T_{\rm e}} + (l + 1){T_{\rm m}} $ $ {T_{\rm e}} + {T_{\rm p}} $ -
[1] QIU Tie, CHEN Baochao, SANGAIAH A K, et al. A survey of mobile social networks: Applications, social characteristics, and challenges[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(4): 3932–3947. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2764479 [2] SAHAI A and WATERS B. Fuzzy identity-based encryption[C]. The 24th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Aarhus, Denmark, 2005: 457–473. [3] SAIDI A, NOUALI O, and AMIRA A. SHARE-ABE: An efficient and secure data sharing framework based on ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption and Fog computing[J]. Cluster Computing, 2022, 25(1): 167–185. doi: 10.1007/s10586-021-03382-5 [4] FU Xingbing, WANG Yinglun, YOU Lin, et al. Offline/Online lattice-based ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2022, 130: 102684. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102684 [5] DENG Shijie, YANG Gaobo, DONG Wen, et al. Flexible revocation in ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption with verifiable ciphertext delegation[J/OL]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022. [6] LI Jiguo, ZHANG Yichen, NING Jianting, et al. Attribute based encryption with privacy protection and accountability for CloudIoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2022, 10(2): 762–773. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2020.2975184 [7] WANG Shulan, ZHOU Junwei, LIU J K, et al. An efficient file hierarchy attribute-based encryption scheme in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(6): 1265–1277. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2523941 [8] HUANG Qinlong, YANG Yixian, and FU Jingyi. PRECISE: Identity-based private data sharing with conditional proxy re-encryption in online social networks[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 86: 1523–1533. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.05.026 [9] ZHOU Lei, LUO Entao, WANG Guojun, et al. Secure fine-grained friend-making scheme based on hierarchical management in mobile social networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 554: 15–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.12.012 [10] CUI Weirong, DU Chenglie, CHEN Jinchao, et al. CP-ABE based privacy-preserving user profile matching in mobile social networks[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(6): e0157933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157933 [11] CUI Hui, DENG R H, LAI Junzuo, et al. An efficient and expressive ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption scheme with partially hidden access structures, revisited[J]. Computer Networks, 2018, 133: 157–165. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2018.01.034 [12] YANG Kan, HAN Qi, LI Hui, et al. An efficient and fine-grained big data access control scheme with privacy-preserving policy[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(2): 563–571. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2571718 [13] PREMKAMAL P K, PASUPULETI S K, and ALPHONSE P J A. A new verifiable outsourced ciphertext-policy attribute based encryption for big data privacy and access control in cloud[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2019, 10(7): 2693–2707. doi: 10.1007/s12652-018-0967-0 [14] ZHANG Zhishuo and ZHOU Shijie. A decentralized strongly secure attribute-based encryption and authentication scheme for distributed Internet of Mobile Things[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 201: 108553. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108553 [15] FENG Chaosheng, YU Keping, ALOQAILY M, et al. Attribute-based encryption with parallel outsourced decryption for edge intelligent IoV[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 13784–13795. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3027568 [16] LI Jiguo, SHA Fengjie, ZHANG Yichen, et al. Verifiable outsourced decryption of attribute-based encryption with constant ciphertext length[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2017, 2017: 3596205. doi: 10.1155/2017/3596205 -







 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
