Traffic Flow Combined Prediction Model Based on Complementary Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit Optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm
-
摘要: 该文针对短时交通流预测过程呈现的非线性、非平稳性及时序相关性特征,为提升预测的精度及收敛速度,提出一种基于互补集合经验模态分解(CEEMD)和改进麻雀搜索算法(ISSA)优化双向门控循环单元(BiGRU)的组合预测模型。首先,考虑到端点飞翼问题,通过改进CEEMD算法将交通流量序列分解为体现路网交通趋势性、周期性及随机性的本征模态函数(IMF)分量,有效提取了其中的先验特征;随后,利用BiGRU网络挖掘交通流量序列中的时序相关性特征,为避免局部最优,并提高麻雀搜索算法(SSA)全局搜索及局部开发能力,采用ISSA对BiGRU网络权值参数迭代择优。实验结果表明,该组合预测模型中各组件对提高预测精度均起到正向作用,同时在不同交通流量数据集下的预测性能较对比算法均更优,展现了精准、快速的预测表现以及良好的泛化能力。
-
关键词:
- 短时交通流预测 /
- 互补集合经验模态分解 /
- 麻雀搜索算法 /
- 双向门控循环单元 /
- 边界局部特征延拓
Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy and convergence speed of prediction, a combined prediction model, based on Complementary Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (CEEMD) and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU) optimized by Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm (ISSA), is proposed to deal with the nonlinear, non-stationary and temporal correlation of short-term traffic flow prediction. Firstly, considering the end-point flying wing problem, the traffic flow sequence is decomposed into Intrinsic Mode Function (IMF) components that reflect the trend, periodicity and randomness of road network traffic by improved CEEMD algorithm, which extracts effectively the prior features; Then, the BiGRU network is used to mine the temporal correlation in traffic flow sequence. To fear the local optimum, and improve the global search and local mining ability of Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA), ISSA is used instead of gradient descent method to iterate the BiGRU network weights. The ablation experiment results show that each component in the combined prediction model plays a positive role in improving the prediction accuracy. The prediction performance under different traffic flow sets is better than the compared algorithm, showing accurate and fast prediction performance with good generalization ability. -
表 1 仿真参数设置
仿真参数 参数值 ISSA仿真参数 参数值 信噪比$ {\text{Nstd}} $ 0.2 dB 初始权重${w_{\rm{b}}}$ 0.9 噪声添加次数$ {\text{NE}} $ 500 次 终止权重${w_{\rm{e}}}$ 0.4 最大迭代次数$ {\text{iter}} $ 2 000 次 麻雀种族数量$ {\text{Np}} $ 50 个 模态分量总数$ m $ 9 个 最大迭代次数$ {\text{ite}}{{\text{r}}_M} $ 100 次 学习率$ {\text{lr}} $ 0.001 预警值$ {R_2} $ 0.5 隐含层神经元个数${N_{{\text{ly}}}}$ 64 个 安全值$ {\text{ST}} $ 0.8 表 2 各预测模型的误差对比
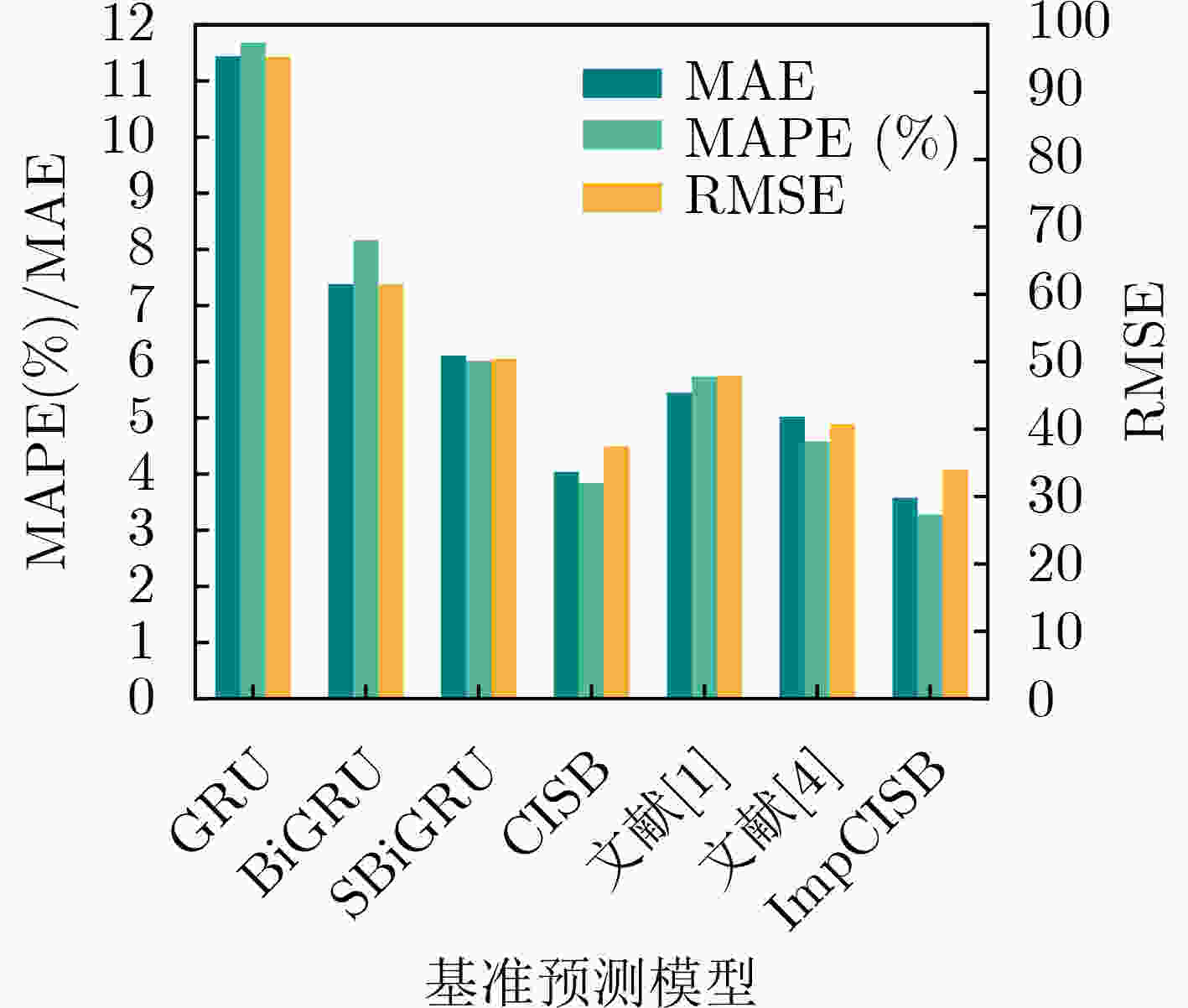
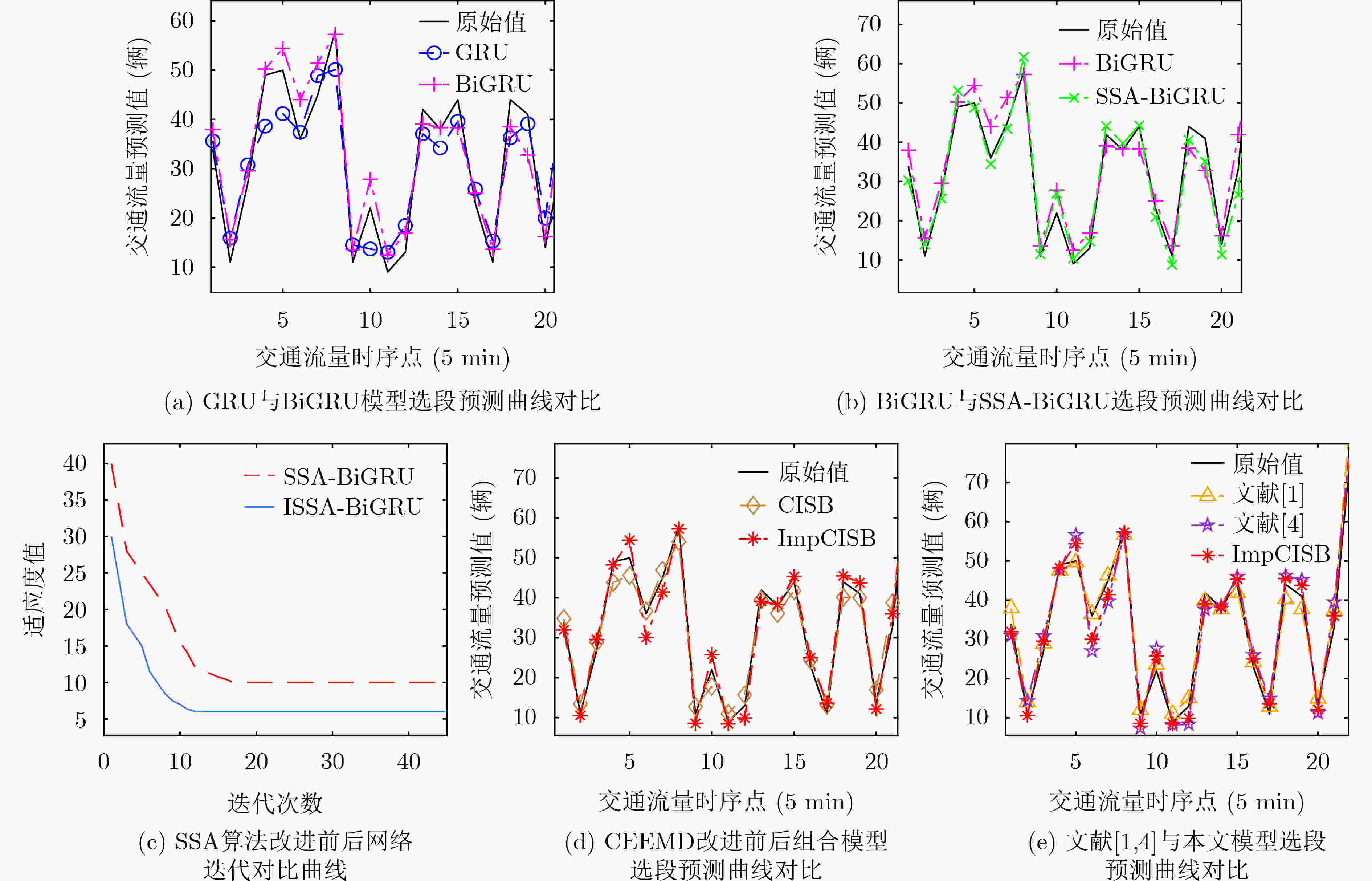
基准预测模型 MAE MAPE(%) RMSE 该组合模型与基准模型相比各指标变化 MAE MAPE(%) RMSE GRU 11.44 11.68 95.25 –7.86 –8.40 –61.31 BiGRU 7.38 8.16 61.51 –3.80 –4.88 –27.57 SSA-BiGRU 6.11 6.01 50.44 –2.53 –2.73 –16.50 CEEMD-ISSA-BiGRU 4.04 3.84 37.43 –0.46 –0.56 –3.49 文献[4] 5.45 5.74 47.98 –1.87 –2.46 –14.04 文献[1] 5.02 4.58 40.74 –1.44 –1.30 –6.80 改进CEEMD-ISSA-BiGRU(本文) 3.58 3.28 33.94 – – – -
[1] 殷礼胜, 魏帅康, 孙双晨, 等. 基于FEEMD-SAPSO-BiLSTM组合模型的短时交通流预测[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2021, 35(10): 72–81. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2103878YIN Lisheng, WEI Shuaikang, SUN Shuangchen, et al. Short-term traffic flow forecast based on FEEMD-SAPSO-BiLSTM[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2021, 35(10): 72–81. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2103878 [2] QU Zhaowei, LI Haitao, LI Zhihui, et al. Short-term traffic flow forecasting method with M-B-LSTM hybrid network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(1): 225–235. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3009725 [3] 陈如清, 李嘉春, 俞金寿. 基于FWADE-ELM的短时交通流预测方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(4): 925–932. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2019.1103CHEN Ruqing, LI Jiachun, and YU Jinshou. Short-term traffic flow forecasting based on hybrid FWADE-ELM[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(4): 925–932. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2019.1103 [4] 王博文, 王景升, 朱茵, 等. 基于ARMA-SVR的短时交通流量预测模型研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(11): 126–133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.11.015WANG Bowen, WANG Jingsheng, ZHU Yin, et al. Study on short-term traffic volume prediction model based on ARMA-SVR[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2021, 38(11): 126–133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.11.015 [5] 于德新, 邱实, 周户星, 等. 基于GRU-RNN模型的交叉口短时交通流预测研究[J]. 公路工程, 2020, 45(4): 109–114. doi: 10.19782/j.cnki.1674-0610.2020.04.018YU Dexin, QIU Shi, ZHOU Huxing, et al. Research on short-term traffic flow prediction of intersections based on GRU-RNN model[J]. Highway Engineering, 2020, 45(4): 109–114. doi: 10.19782/j.cnki.1674-0610.2020.04.018 [6] 聂铃, 张剑, 胡茂政. 基于CEEMDAN分解的短时交通流组合预测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(11): 279–286. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2106-0305NIE Ling, ZHANG Jian, and HU Maozheng. Short-term traffic flow combination prediction based on CEEMDAN decomposition[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(11): 279–286. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2106-0305 [7] LIU Hui, ZHANG Xinyu, YANG Yuxiang, et al. Hourly traffic flow forecasting using a new hybrid modelling method[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2022, 29(4): 1389–1402. doi: 10.1007/s11771-022-5000-2 [8] YANG Haofan and CHEN Y P P. Hybrid deep learning and empirical mode decomposition model for time series applications[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 120: 128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.11.019 [9] HAN Tian, LIU Qiannan, ZHANG Li, et al. Fault feature extraction of low speed roller bearing based on Teager energy operator and CEEMD[J]. Measurement, 2019, 138: 400–408. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.02.053 [10] 李雅丽, 王淑琴, 陈倩茹, 等. 若干新型群智能优化算法的对比研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(22): 1–12. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2006-0291LI Yali, WANG Shuqin, CHEN Qianru, et al. Comparative study of several new swarm intelligence optimization algorithms[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(22): 1–12. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2006-0291 [11] BAO Kexin, BI Jinqiang, GAO Miao, et al. An improved ship trajectory prediction based on AIS data using MHA-BiGRU[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(6): 804. doi: 10.3390/jmse10060804 [12] DING Yunfei, CHEN Zijun, ZHANG Hongwei, et al. A short-term wind power prediction model based on CEEMD and WOA-KELM[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 189: 188–198. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.02.108 [13] MA Yangling, LUO Yixin, and YANG Zhouwang. PCFNet: Deep neural network with predefined convolutional filters[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 382: 32–39. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.11.075 [14] ZHANG Yituo, LI Chaolin, JIANG Yiqi, et al. Accurate prediction of water quality in urban drainage network with integrated EMD-LSTM model[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 354: 131724. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131724 [15] LIU Die, BAO Yihao, HE Yingying, et al. A data loss recovery technique using EMD-BiGRU algorithm for structural health monitoring[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(21): 10072. doi: 10.3390/app112110072 [16] 张训杰, 张敏, 李贤均. 基于二维图像和CNN-BiGRU网络的滚动轴承故障模式识别[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(23): 194–201,207. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.23.026ZHANG Xunjie, ZHANG Min, and LI Xianjun. Rolling bearing fault mode recognition based on 2D image and CNN-BiGRU[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(23): 194–201,207. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.23.026 [17] SUN Peng, BOUKERCHE A, and TAO Yanjie. SSGRU: A novel hybrid stacked GRU-based traffic volume prediction approach in a road network[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 160: 502–511. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.06.028 [18] XUE Jiankai and SHEN Bo. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm[J]. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2020, 8(1): 22–34. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2019.1708830 [19] 桑海峰, 陈紫珍. 基于双向门控循环单元的3D人体运动预测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2256–2263. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180978SANG Haifeng and CHEN Zizhen. 3D human motion prediction based on bi-directional gated recurrent unit[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2256–2263. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180978 -





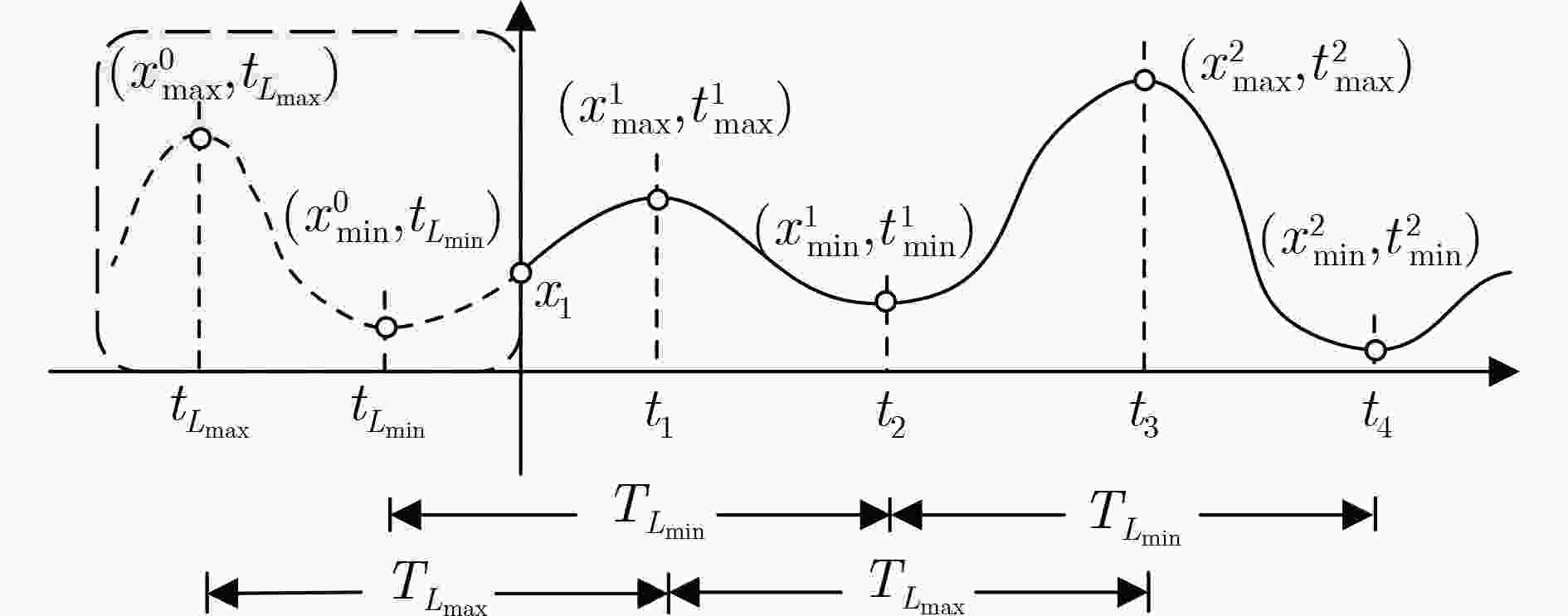
 下载:
下载:
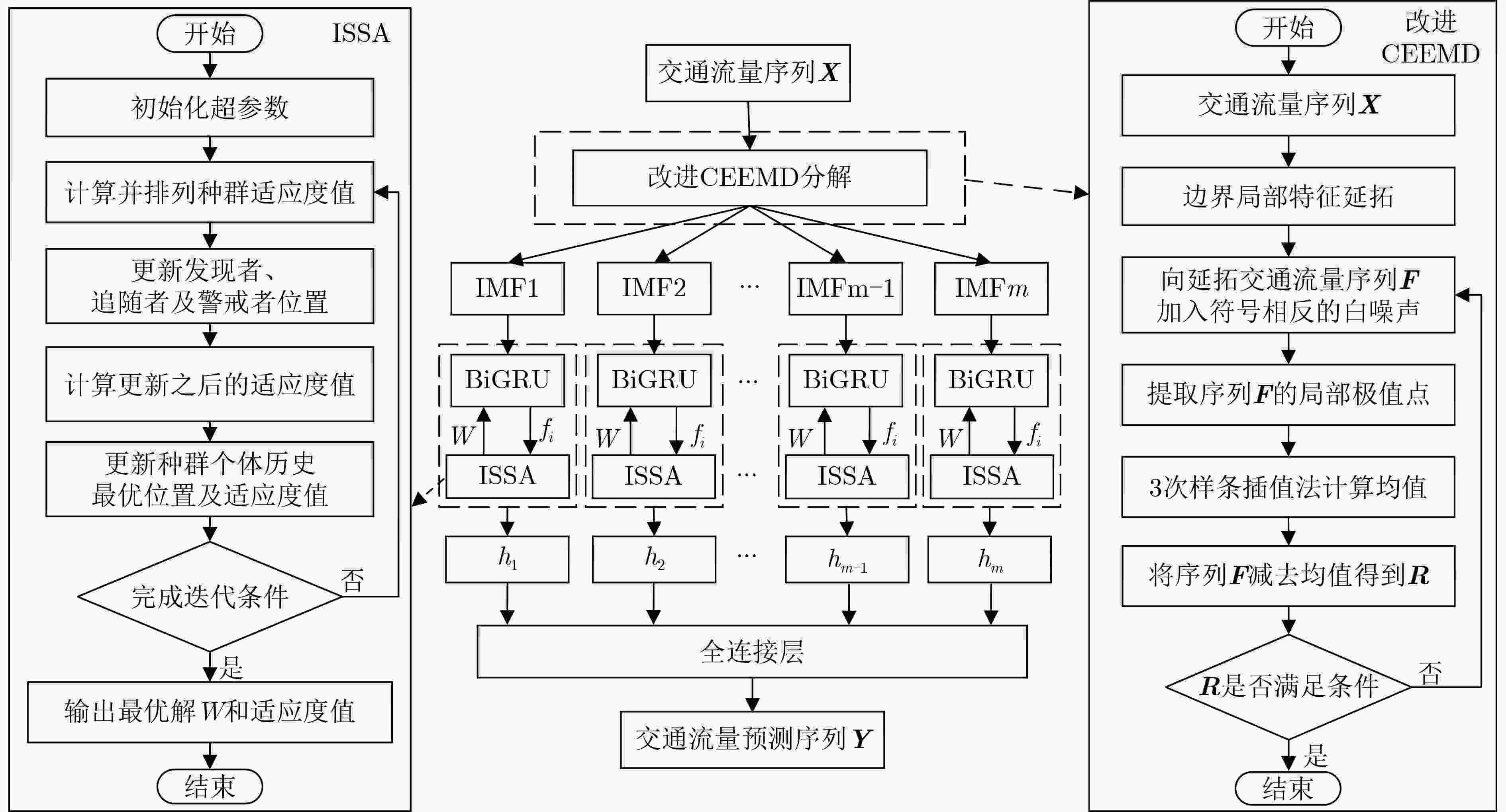
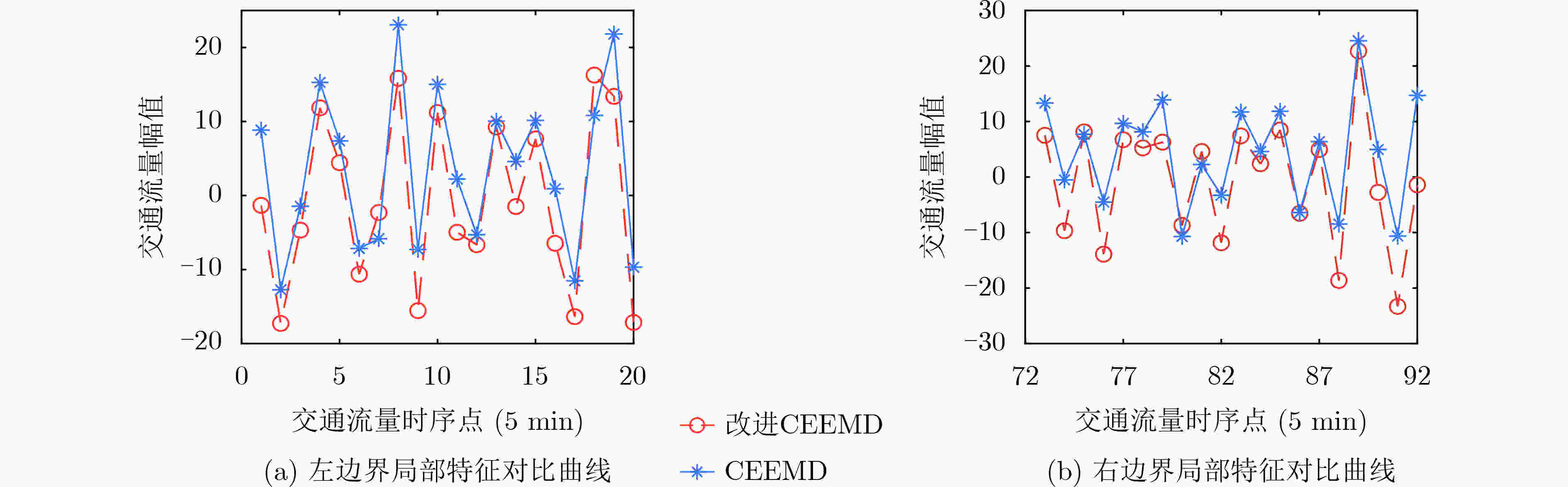
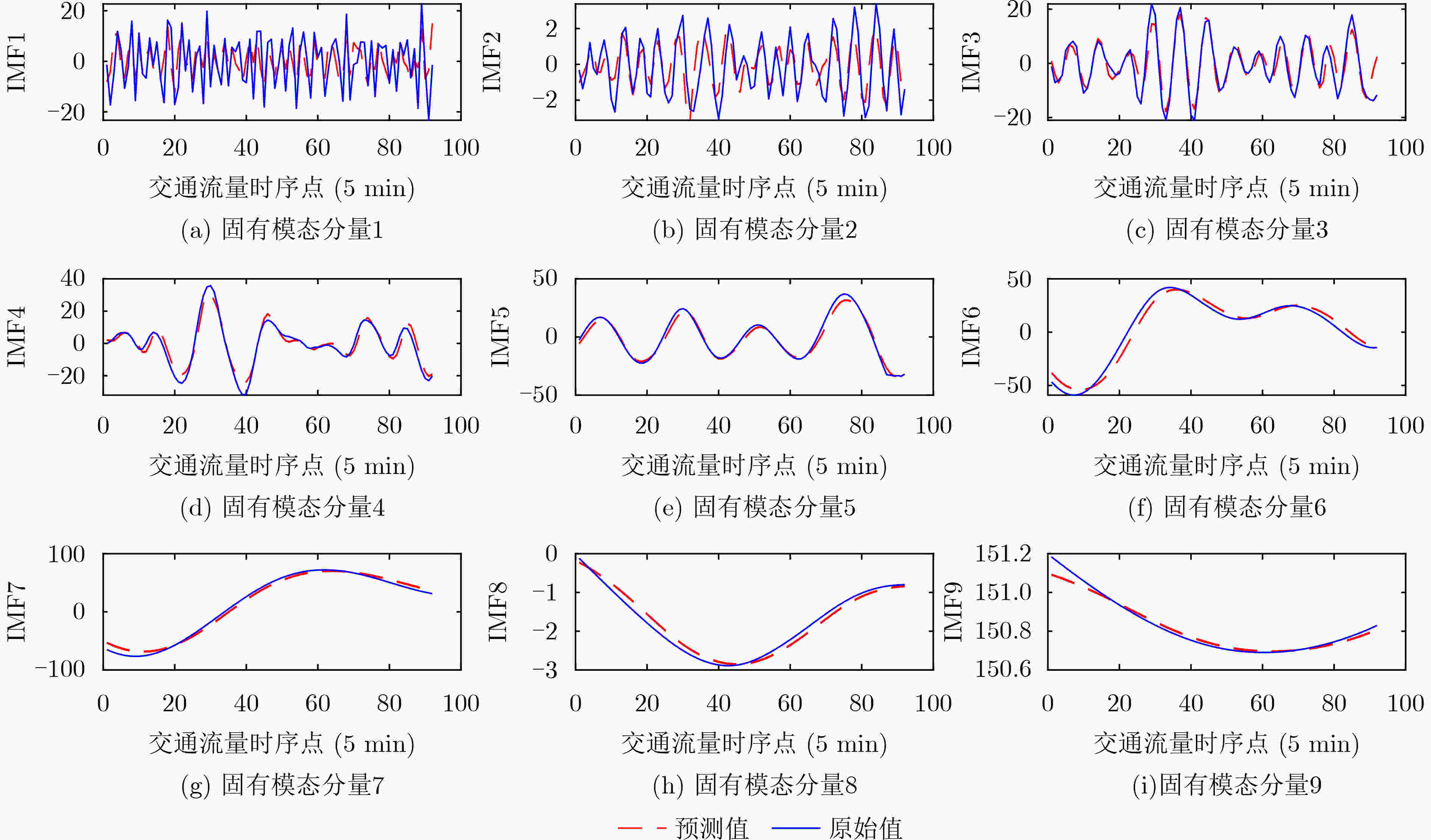



 下载:
下载:
