Fusion Recognition of Space Targets with Micro-Motion Based on a Sparse Auto-Encoder
-
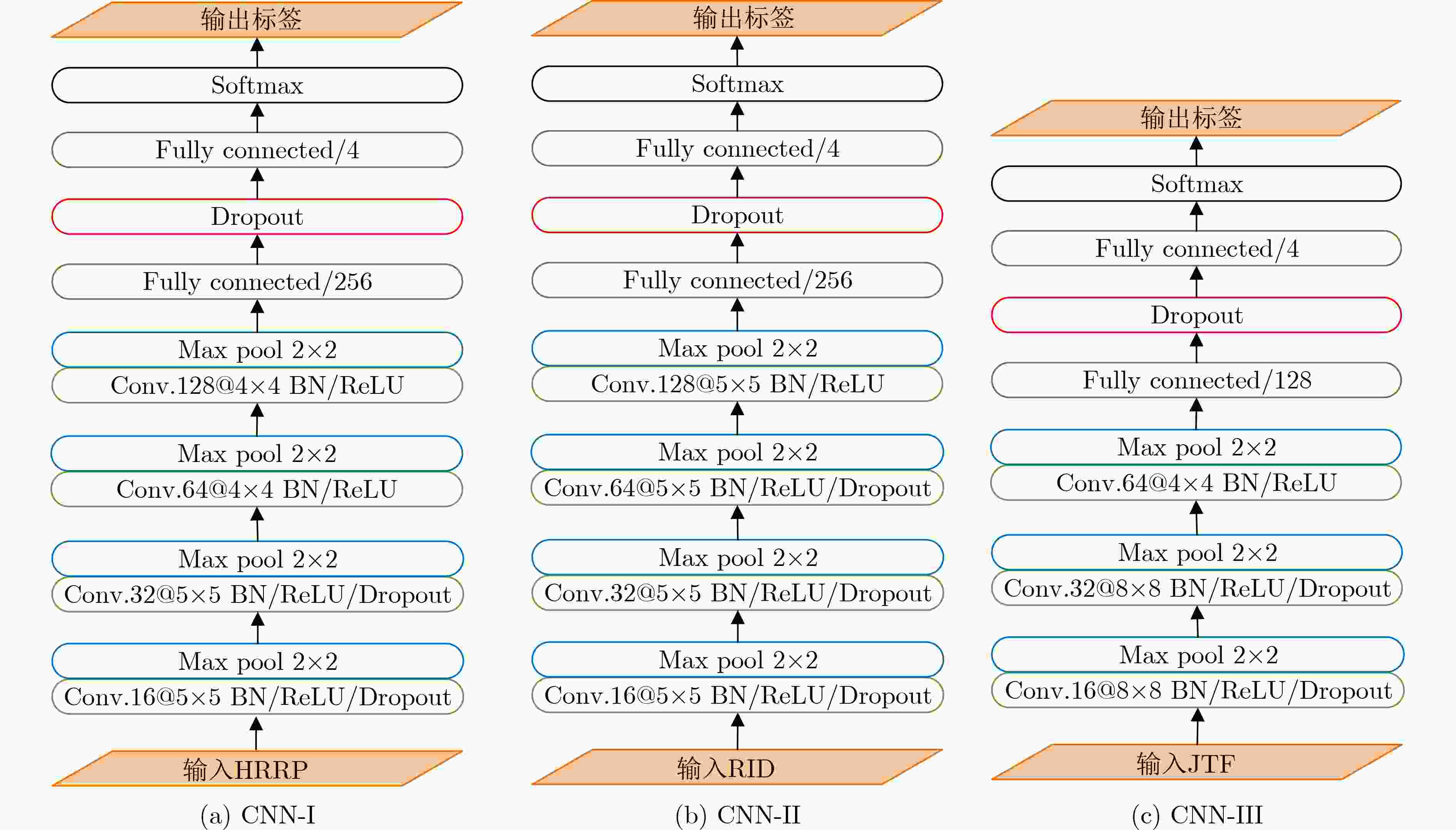
摘要: 当采用高分辨雷达对空间微动目标进行观测时,往往能同时获得其窄带、宽带回波。为充分利用其中蕴含的丰富电磁散射、形状、结构及运动信息,该文提出基于稀疏自编码器(SAE)的空间微动目标特征级融合识别方法。在训练阶段,首先采用卷积神经网络(CNN)分别提取训练集中微动目标回波的1维高分辨距离像(HRRP)、时频图(JTF)及距离-瞬时多普勒像(RID)层级特征。随后,将提取的3个深层特征进行1维拼接形成联合特征向量,并采用SAE自动学习联合特征向量的隐层特征。进而剔除SAE解码部分并在编码器后接入Softmax分类器构成识别网络。最后,利用SAE网络参数对识别网络进行初始化,并利用上述联合特征向量对其进行微调得到训练好的识别网络。在测试阶段,将CNN所提测试集的联合特征向量直接输入训练好的识别网络以得到融合识别结果。不同条件下的电磁仿真数据识别结果证明了所提方法的有效性及稳健性。Abstract: During the observation of micro-motion targets in space, high resolution radar collects the narrowband and wideband echoes simultaneously. This paper proposes a fusion method based on a Sparse Auto-Encoder (SAE) for recognizing space micro-motion targets to exploit their rich electromagnetic scattering, shape, structure, and motion information. In the training phase, the proposed method extracts the hierarchical features from High Resolution Range Profiles (HRRP), Joint Time-Frequency (JTF) images, and Range-Instantaneous-Doppler (RID) images using Convolution Neural Networks (CNN). The joint feature vector is then created by concatenating the relevant deep features, and SAE learns autonomously its hidden features unsupervised. After that, the decoder is removed and the Softmax classifier is introduced after the encoder to create the recognition network. Finally, parameters of the optimized SAE network are used for the initialization of the recognition network, which is then fine-tuned by the joint feature vectors of training samples. In the test phase, the trained recognition network is supplied directly with the joint feature vectors of the test samples recovered by CNN to produce the fusion recognition results. Experimental results of simulated EM data under different conditions show the efficacy and robustness of the proposed method.
-
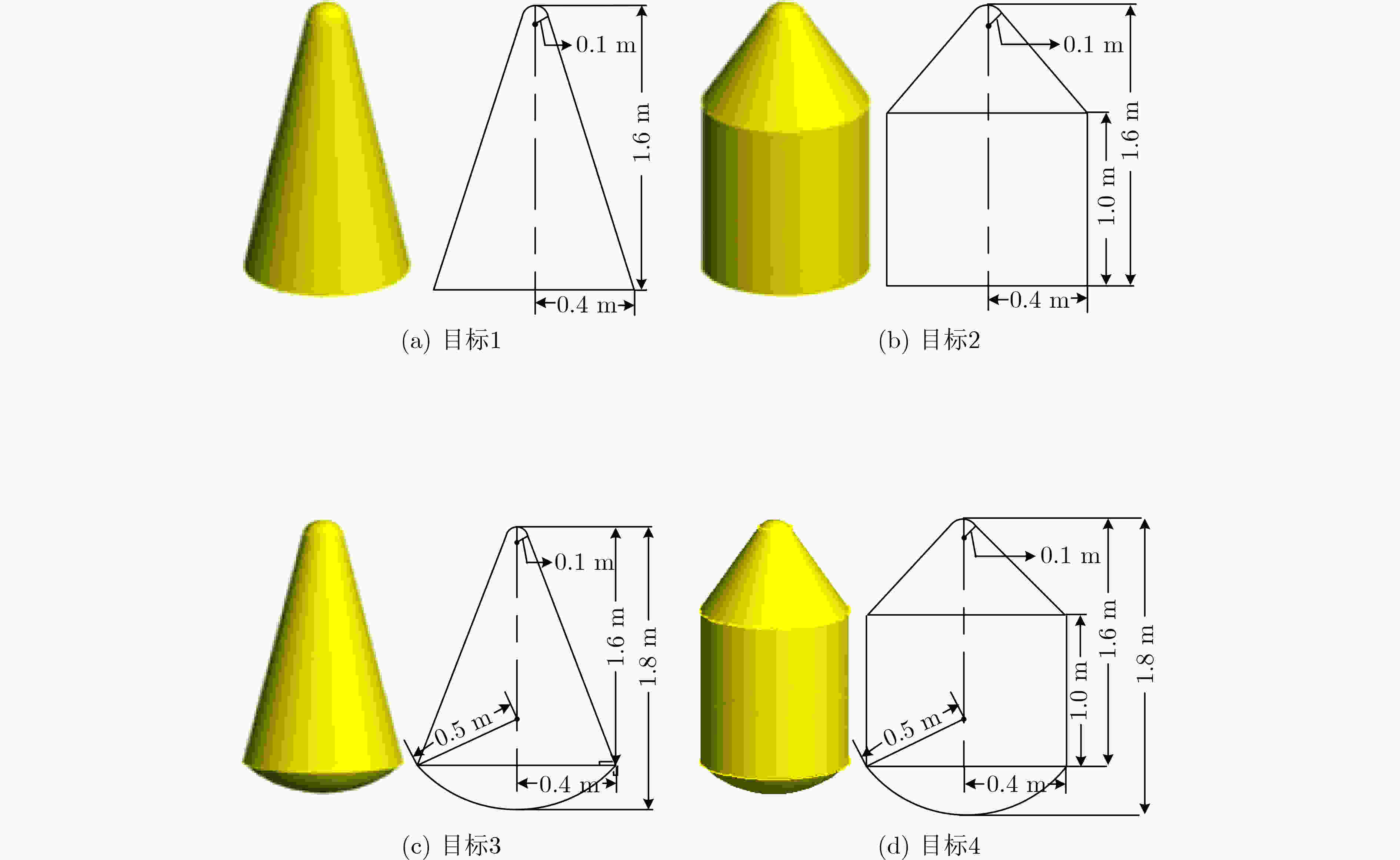
表 1 4类目标微动参数
目标 俯仰角(°) 自旋频率(Hz) 进动频率(Hz) 进动角(°) 目标1 21~30 3.0 2.0~4.0 4.0~5.5 目标2 21~30 1.5 1.5~3.5 2.0~3.5 目标3 21~30 2.0 1.0~3.0 3.0~4.5 目标4 21~30 1.0 0.5~2.5 1.0~2.5 表 2 网络超参数
网络模块 SGD优化器 学习率 迭代次数 批处理大小 $ \alpha $ $ \beta $ $ {\eta _0} $ $ d $ ${{\rm{tb}}}$ Batch Size 特征提取 0.5 0.01 0.1 0.94 50 64 SAE 0.5 0.001 0.1 0.96 50 64 识别网络 0.5 0 0.1 0.94 50 64 表 3 所提方法在各SNR下识别结果(%)
实验结果 SNR(dB) 0 5 10 15 20 识别率 95.00 96.69 97.27 97.52 97.64 表 4 所提方法与单一回波识别结果对比(%)
识别特征 SNR(dB) 0 5 10 15 20 JTF 86.41 89.46 90.58 91.74 92.64 HRRP 86.00 86.74 88.84 88.93 89.96 RID 85.58 87.40 88.10 88.51 88.64 所提方法 95.00 96.69 97.27 97.52 97.64 表 5 实验对比结果(%)
融合方法 SNR(dB) 0 5 10 15 20 特征拼接 92.93 93.93 94.01 94.26 95.79 特征相加 92.31 93.76 94.05 94.17 95.95 所提方法 95.00 96.69 97.27 97.52 97.64 -
[1] BAI Xueru, XING Mengdao, ZHOU Feng, et al. High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of spinning space debris[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 2352–2362. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010854 [2] 李瑞, 李开明, 张群, 等. 基于角多普勒效应的自旋目标微动特征提取[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 547–554. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200595LI Rui, LI Kaiming, ZHANG Qun, et al. Micro-motion feature extraction of spinning target based on angular Doppler effect[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 547–554. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200595 [3] 冯存前, 李江, 黄大荣, 等. 弹道中段不同平动多目标的平动参数估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 564–571. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200075FENG Cunqian, LI Jiang, HUANG Darong, et al. Estimation method of translational parameters for different translational of ballistic targets in midcourse[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 564–571. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200075 [4] CHOI I O, PARK S H, KIM M, et al. Efficient discrimination of ballistic targets with micromotions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1243–1261. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2928611 [5] GAO Hongwei, XIE Lianggui, WEN Shuliang, et al. Micro-Doppler signature extraction from ballistic target with micro-motions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(4): 1969–1982. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5595607 [6] SHI Xiaoran, ZHOU Feng, LIU Lei, et al. Textural feature extraction based on time–frequency spectrograms of humans and vehicles[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1251–1259. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0432 [7] PERSICO A R, CLEMENTE C, GAGLIONE D, et al. On model, algorithms, and experiment for micro-Doppler-based recognition of ballistic targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1088–1108. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2665258 [8] LUO Ying, ZHANG Qun, QIU Chengwei, et al. Micro-Doppler effect analysis and feature extraction in ISAR imaging with stepped-frequency chirp signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2087–2098. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2034367 [9] PERSICO A R, ILIOUDIS C V, CLEMENTE C, et al. Novel classification algorithm for ballistic target based on HRRP frame[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3168–3189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2905281 [10] 杨敏佳, 白雪茹, 刘士豪, 等. 基于高斯原型网络的小样本逆合成孔径雷达目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3566–3573. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210724YANG Minjia, BAI Xueru, LIU Shihao, et al. Small-data inverse synthetic aperture radar object recognition based on Gaussian prototypical network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3566–3573. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210724 [11] BAI Xueru and PENG Xin. Radar image series denoising of space targets based on Gaussian process regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(7): 4659–4669. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2892183 [12] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [13] GLOROT X, BORDES A, and BENGIO Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2011: 315–323. [14] 张淑军, 张群, 李辉. 基于深度学习的手语识别综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1021–1032. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190416ZHANG Shujun, ZHANG Qun, and LI Hui. Review of sign language recognition based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1021–1032. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190416 [15] 袁野, 贾克斌, 刘鹏宇. 基于深度卷积神经网络的多元医学信号多级上下文自编码器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 371–378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190135YUAN Ye, JIA Kebin, and LIU Pengyu. Multi-context autoencoders for multivariate medical signals based on deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 371–378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190135 [16] 唐伦, 王恺, 张月, 等. 网络切片场景下基于分布式生成对抗网络的服务功能链异常检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(1): 262–271. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211261TANG Lun, WANG Kai, ZHANG Yue, et al. Service function chain anomaly detection based on distributed generative adversarial network in network slicing scenario[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(1): 262–271. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211261 [17] TIAN Xudong, BAI Xueru, XUE Ruihang, et al. Fusion recognition of space targets with micromotion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3116–3125. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3145303 [18] ZHANG Yuanpeng, ZHANG Qun, KANG Le, et al. End-to-end recognition of similar space cone-cylinder targets based on complex-valued coordinate attention networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5106214. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3115624 [19] BINGLE M, GARCIA-AGUILAR A, ILLENSEER F, et al. Overview of the latest electromagnetic solver features in FEKO suite 7.0[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 31st International Review of Progress in Applied Computational Electromagnetics, Williamsburg, USA, 2015: 1–2. [20] BAI Xueru and BAO Zheng. Imaging of rotation-symmetric space targets based on electromagnetic modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 1680–1689. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120772 [21] LECUN Y, BOSER B, DENKER J S, et al. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541–551. doi: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541 [22] RUDER S. An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04747, 2017. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
