A Highly Robust Indoor Location Algorithm Using WiFi Channel State Information Based on Transfer Learning Reinforcement
-
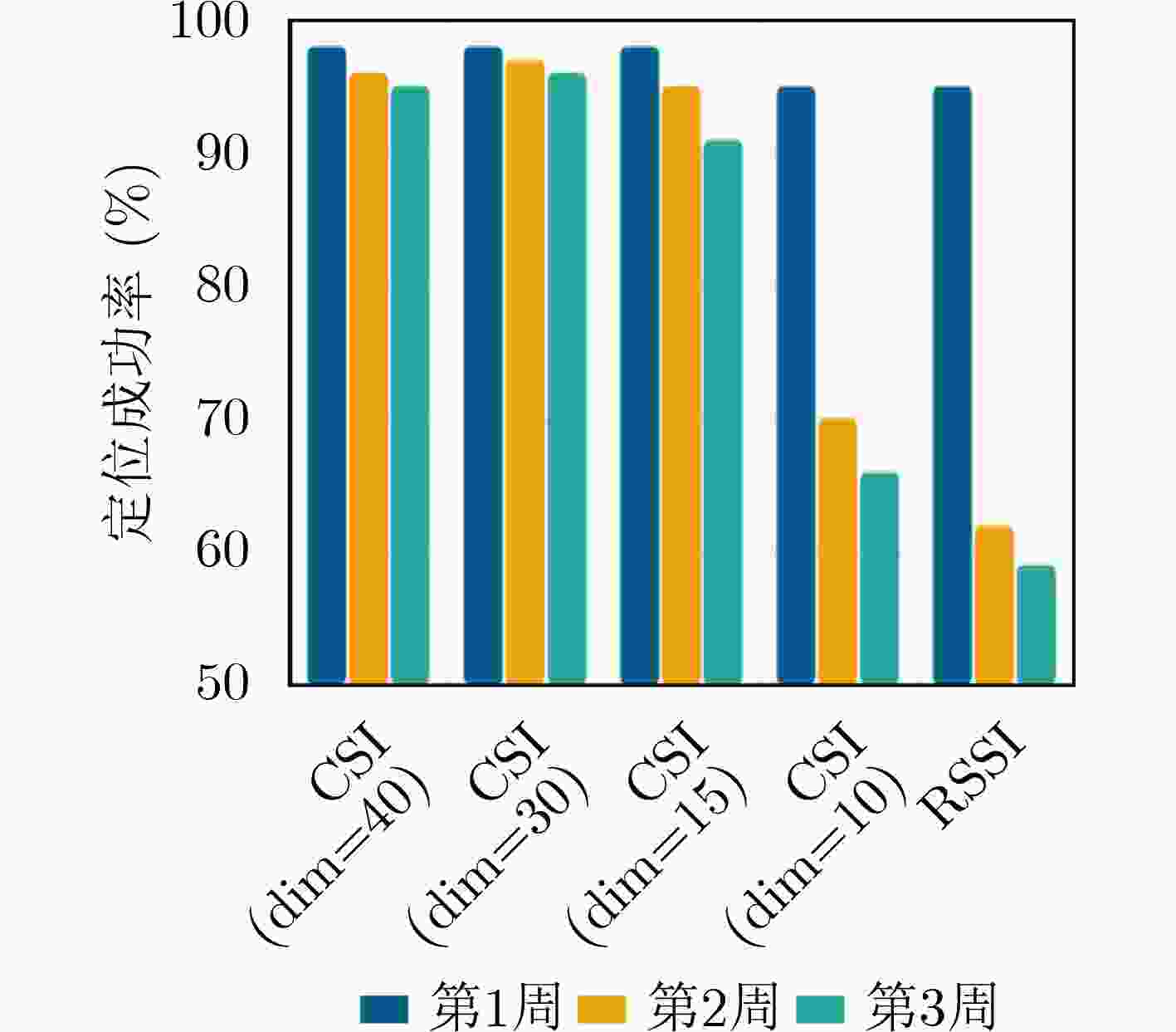
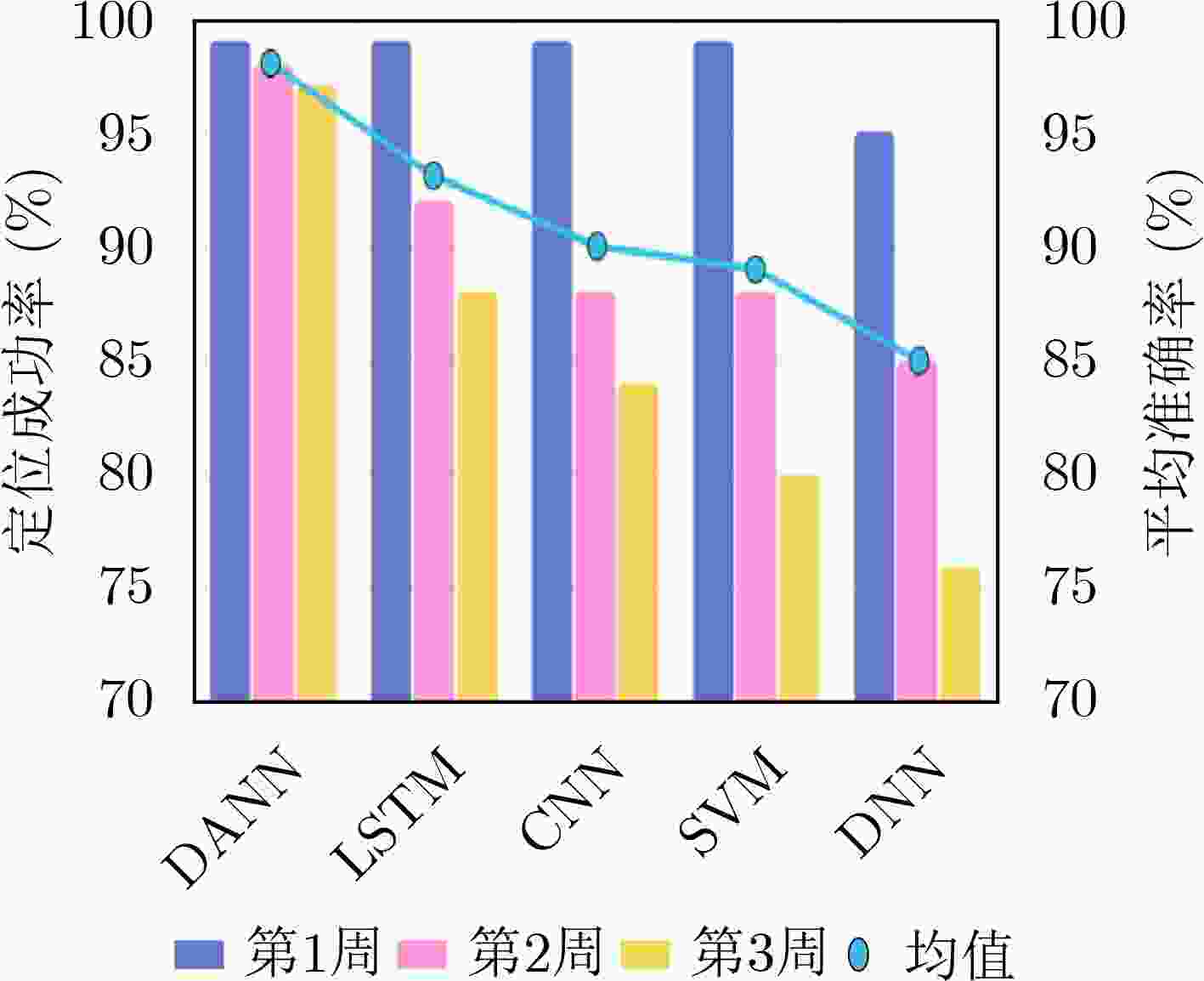
摘要: 基于信道状态信息(CSI)数据的WiFi指纹可用于室内定位。与信号强度值(RSSI)数据相比,CSI具有更高的数据信息粒度,并且可以在多个子载波上获得。当使用CSI数据进行室内定位时,相对于RSSI可以获得更好的结果。然而,无论使用RSSI还是CSI信号,在室内定位部署期间的一段时间后,室内环境通常会发生变化,并且基于测试数据的指纹数据库通常会恶化甚至失效。该文提出使用迁移学习算法来建立用于室内定位的指纹数据库。迁移学习的优势在于,可以使用较少的数据来获得更好的迁移训练结果。该文使用迁移学习来迁移指纹数据库的预测,延长指纹数据库的生命周期,并提高室内定位的鲁棒性。经过实验,1周后室内定位准确率保持在98%,两周后保持在97%。在相同成本下,该模型的生命周期和定位精度高于长短期记忆网络(LSTM)、卷积神经网络(CNN)、支持向量机(SVM)、深度神经网络(DNN)和其他定位系统。Abstract: The WiFi fingerprint based on Channel State Information (CSI) data can be used for indoor positioning. Compared to Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) data, CSI has a higher granularity of data information and can be obtained over multiple subcarriers. Better results can be achieved when using CSI data for indoor localization. However, regardless of whether RSSI or CSI signals are used, the indoor environment often changes after a period of time during the deployment of indoor localization, and the fingerprint database based on the test data often deteriorates or even becomes invalid. In this paper, using a transfer learning algorithm to establish a fingerprint database for indoor positioning is proposed. The advantage of transfer learning is that it can use less data to obtain better transfer training results. Transfer learning is used to migrate the prediction of fingerprint database, the life cycle of fingerprint database is prolonged, and robustness in indoor positioning is improved. The indoor positioning accuracy is maintained at 98% after one week and 97% after two weeks. At the same cost, the life cycle and positioning accuracy of the proposed model are higher than Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Deep Neural Networks (DNN), and other positioning systems.
-
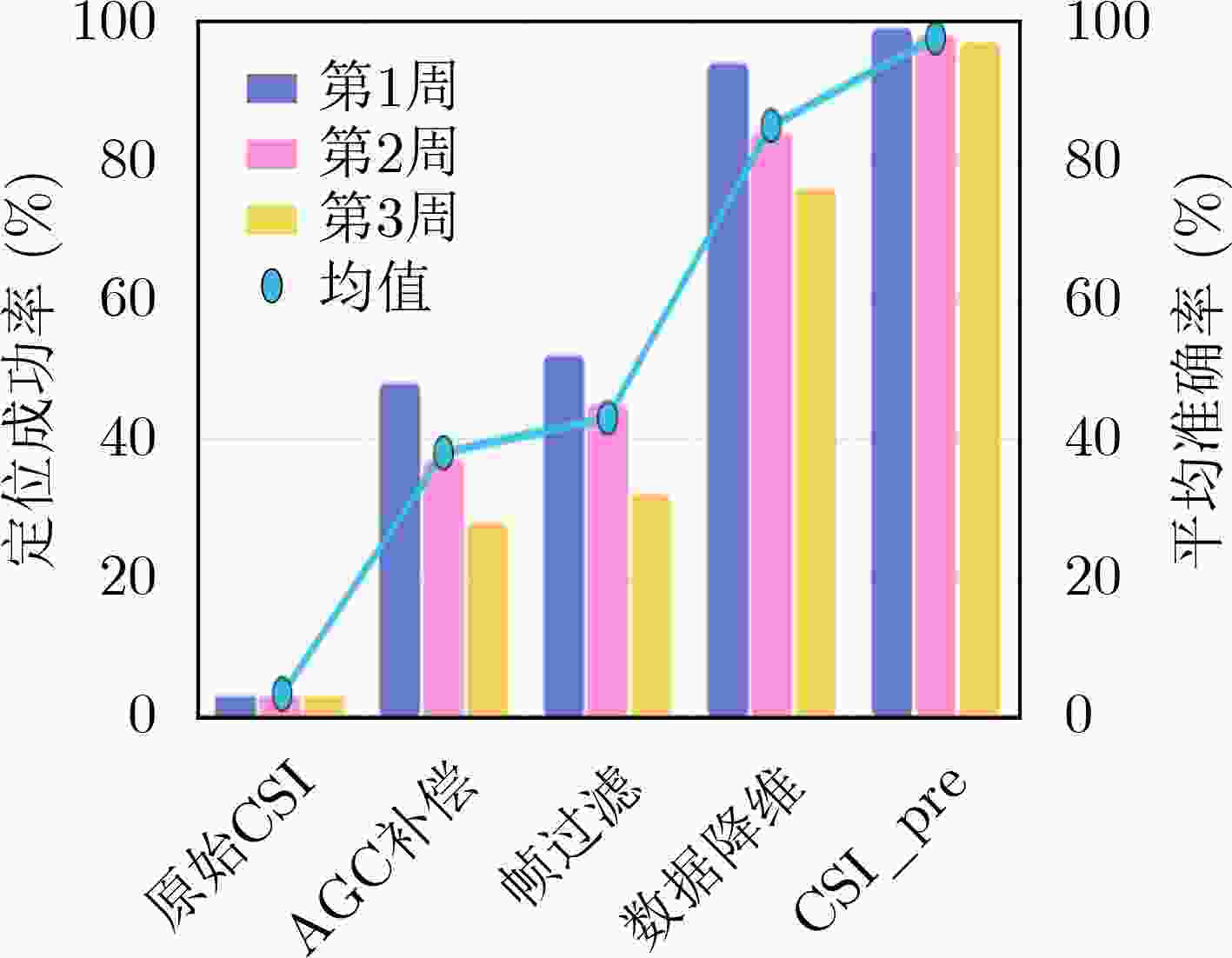
算法1 数据预处理算法 输入:${\bf{CSI} }_{i}$, ${\rm{RS}}\mathrm{S}{\mathrm{I} }_{i}$ 输出:预处理后的${\bf{CSI} }_{i}$ (1) for ${\bf{CSI} }_{i}$ do (2) for ${\bf{CSI} }_{ij}$ do (3) 通过式(5)计算$ s; $ (4) 通过式(6)修正${\bf{CSI} }_{i}$; (5) end (6) if ${\bf{CSI} }_{i}$ 不是最大的聚类部分 then (7) 删除${\bf{CSI} }_{i}$; (8) end (9) 删除非数据子载波; (10) 利用PCA算法进行降维; (11) end 算法2 迁移学习训练与位置预测 输入:经过数据预处理后的训练数据${ {\bf{CSI} } } _{i}^{S}$,测试数据${\bf{CSI}}_{i}^{T}$ 输出:训练好的指纹库,预测位置 (1) for ${{\bf{CSI}}}_{i}^{S}$ do (2) 输入到特征提取器以获得$ {Z}_{i}^{S}; $ (3) 通过式(10)计算${y}_{i}^{\left(S;{M}_{{\rm{P}}}\right)}$; (4) 通过式(11)计算$ {L}_{\mathrm{a}} $; (5) 计算域间损失$ {L}_{\mathrm{d}} $; (6) 反向传播更新网络参数; (7) end (8) for ${\bf{CSI}} _{i}^{T}$ do (9) 输入到特征提取器以获得${{\boldsymbol{Z}}}_{i}^{T}$; (10) 通过式(10)计算${y}_{i}^{\left(T;{M}_{{\rm{P}}}\right)}$; (11) 输出位置预测结果。 (12) end 算法3 网络更新算法 输入:测试数据${\bf{C}\bf{S}{\bf{I} }}_{i}^{ {\rm{t} } }$,信标数据${\bf{C}\bf{S}{\bf{I} }}_{i}^{{\rm{b}}}$ 输出:更新后的网络 (1) for ${\bf{C}\bf{S}{\bf{I} }}_{i}^{{\rm{t}}}$ do (2) 执行算法1:数据预处理算法; (3) if $D\left(\bf{C}\bf{S}{\bf{I} }_{i}\right) < \mathrm{\delta }$且无异常值then (4) 作为训练数据执行算法2:迁移学习训练算法; (5) end (6) end (7) for ${\bf{C}\bf{S}{\bf{I} }}_{i}^{{\rm{b}}}$ do (8) 执行算法1:数据预处理算法; (9) 作为训练数据执行算法2:迁移学习训练算法; (10) end 表 1 数据降维带来的精度提升(%)
CSI_pre 帧过滤 提升 第1周 99 52 47 第2周 98 45 53 第3周 97 32 65 数据降维 AGC补偿 提升 第1周 94 48 46 第2周 84 37 47 第3周 76 28 48 -
[1] SADRUDDIN H, MAHMOUD A, and ATIA M M. Enhancing body-mounted LiDAR SLAM using an IMU-based pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) model[C]. The 2020 IEEE 63rd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Springfield, USA, 2020: 901–904. [2] BAI Lu, CIRAVEGNA F, BOND R, et al. A low cost indoor positioning system using bluetooth low energy[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 136858–136871. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012342 [3] CHÓLIZ J, EGUIZÁBAL M, HERNÁNDEZ-SOLANA Á, et al. Comparison of algorithms for UWB indoor location and tracking systems[C]. The 2011 IEEE 73rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Budapest, Hungary, 2011: 1–5. [4] LIU Fen, LIU Jing, YIN Yuqing, et al. Survey on WiFi-based indoor positioning techniques[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(9): 1372–1383. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2019.1059 [5] GAN Xingli, HUO Zhihui, SUN Lu, et al. An approach to improve the indoor positioning performance of pseudolite/UWB system with ambiguity resolution[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2022, 2022: 3962014. doi: 10.1155/2022/3962014 [6] JEDARI E, WU Zheng, RASHIDZADEH R, et al. Wi-Fi based indoor location positioning employing random forest classifier[C]. 2015 International conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Banff, Canada, 2015: 1–5. [7] FANG S H and LIN T N. Indoor location system based on discriminant-adaptive neural network in IEEE 802.11 environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2008, 19(11): 1973–1978. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2005494 [8] SHAO Wenhua, LUO Haiyong, ZHAO Fang, et al. Indoor positioning based on fingerprint-image and deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 74699–74712. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2884193 [9] NESSA A, ADHIKARI B, HUSSAIN F, et al. A survey of machine learning for indoor positioning[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 214945–214965. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3039271 [10] SEIDEL S Y and RAPPAPORT T S. 914 MHz path loss prediction models for indoor wireless communications in multifloored buildings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1992, 40(2): 207–217. doi: 10.1109/8.127405 [11] YE Hongyun, YANG Biao, LONG Zhiqiang, et al. A method of indoor positioning by signal fitting and PDDA algorithm using BLE AOA device[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(8): 7877–7887. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3141739 [12] WANG Mei, CHEN Zhao, ZHOU Zou, et al. Analysis of the applicability of dilution of precision in the base station configuration optimization of ultrawideband indoor TDOA positioning system[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 225076–225087. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3045189 [13] WANG Jingjing and PARK J. An enhanced indoor positioning algorithm based on fingerprint using fine-grained CSI and RSSI measurements of IEEE 802.11n WLAN[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(8): 2769. doi: 10.3390/s21082769 [14] GÖNÜLTAŞŞ E, LEI E, LANGERMAN J, et al. CSI-based multi-antenna and multi-point indoor positioning using probability fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(4): 2162–2176. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3109789 [15] AYABAKAN T and KERESTECIOĞLU F. RSSI-based indoor positioning via adaptive federated Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5302–5308. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3097249 [16] SILVA I, PENDÃO C, TORRES-SOSPEDRA J, et al. TrackInFactory: A tight coupling particle filter for industrial vehicle tracking in indoor environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2022, 52(7): 4151–4162. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3091987 [17] IBRAHIM M, TORKI M, and ELNAINAY M. CNN based indoor localization using RSS time-series[C]. 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Natal, Brazil, 2018: 1044–1049. [18] EDEL M and KÖPPE E. Binarized-BLSTM-RNN based human activity recognition[C]. 2016 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Alcala de Henares, Spain, 2016: 1–7. [19] GAO Zhihui, GAO Yunfan, WANG Sulei, et al. CRISLoc: Reconstructable CSI fingerprinting for indoor smartphone localization[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(5): 3422–3437. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3022573 [20] LI Danyang, XU Jingao, YANG Zheng, et al. Train once, locate anytime for anyone: Adversarial learning based wireless localization[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Vancouver, Canada, 2021: 1–10. [21] GHIFARY M, KLEIJN W B, and ZHANG Mengjie. Domain adaptive neural networks for object recognition[C]. The 13th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Gold Coast, Australia, 2014: 898–904. [22] LONG Mingsheng, CAO Yue, WANG Jianmin, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 97–105. [23] ZHU Yongchun, ZHUANG Fuzhen, WANG Jindong, et al. Deep subdomain adaptation network for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(4): 1713–1722. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2988928 [24] SHEORAN V, JOSHI S, and BHAYANI T R. Age and gender prediction using deep CNNs and transfer learning[C]. The 5th International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing, Prayagraj, India, 2020: 293–304. [25] ANEJA S, ANEJA N, ABAS P E, et al. Transfer learning for cancer diagnosis in histopathological images[J]. arXiv: 2112.15523, 2021. [26] HORRY M J, CHAKRABORTY S, PAUL M, et al. COVID-19 detection through transfer learning using multimodal imaging data[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 149808–149824. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016780 [27] PATHAK Y, SHUKLA P K, TIWARI A, et al. Deep transfer learning based classification model for COVID-19 disease[J]. IRBM, 2022, 43(2): 87–92. doi: 10.1016/j.irbm.2020.05.003 [28] ALEGRE PÉREZ J P, CELMA PUEYO S, and LÓPEZ B C. Automatic Gain Control[M]. New York: Springer, 2011. [29] 王迪也. 5G辅助的室内外融合定位技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022.WANG Diye. Research on 5G-assisted indoor and outdoor fusion positioning technology[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. [30] ZHANG Yong, QU Chen, and WANG Yujie. An indoor positioning method based on CSI by using features optimization mechanism with LSTM[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(9): 4868–4878. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2965590 [31] BORGWARDT K M, GRETTON A, RASCH M J, et al. Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy[J]. Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(14): e49–e57. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl242 [32] SCHULZ M, WEGEMER D, and HOLLICK M. Nexmon: The c-based firmware patching framework. 2017. [33] GRINGOLI F, SCHULZ M, LINK J, et al. Free your CSI: A channel state information extraction platform for modern Wi-Fi chipsets[C]. The 13th International Workshop on Wireless Network Testbeds, Experimental Evaluation & Characterization, Los Cabos, Mexico, 2019: 21–28. -





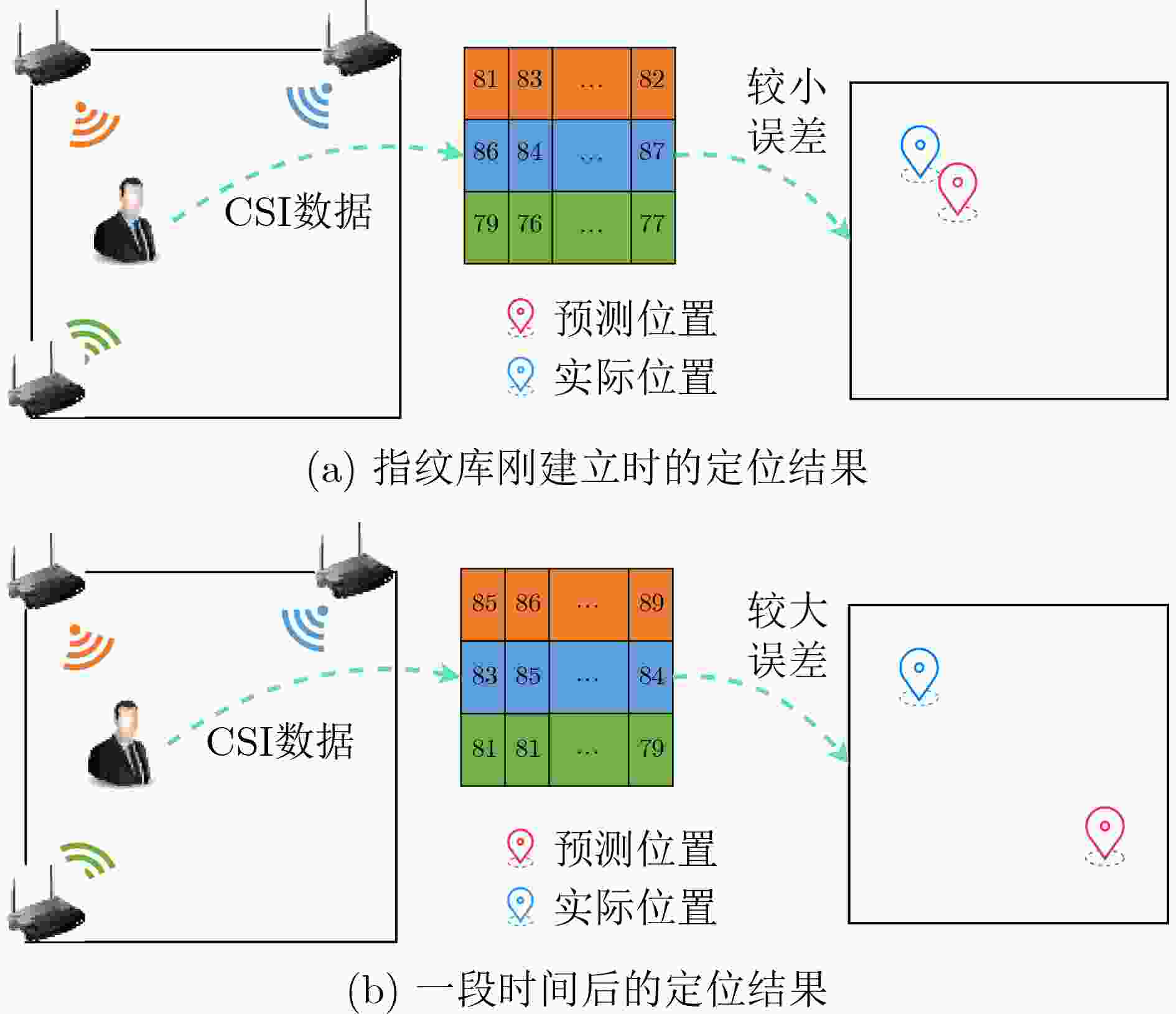
 下载:
下载:
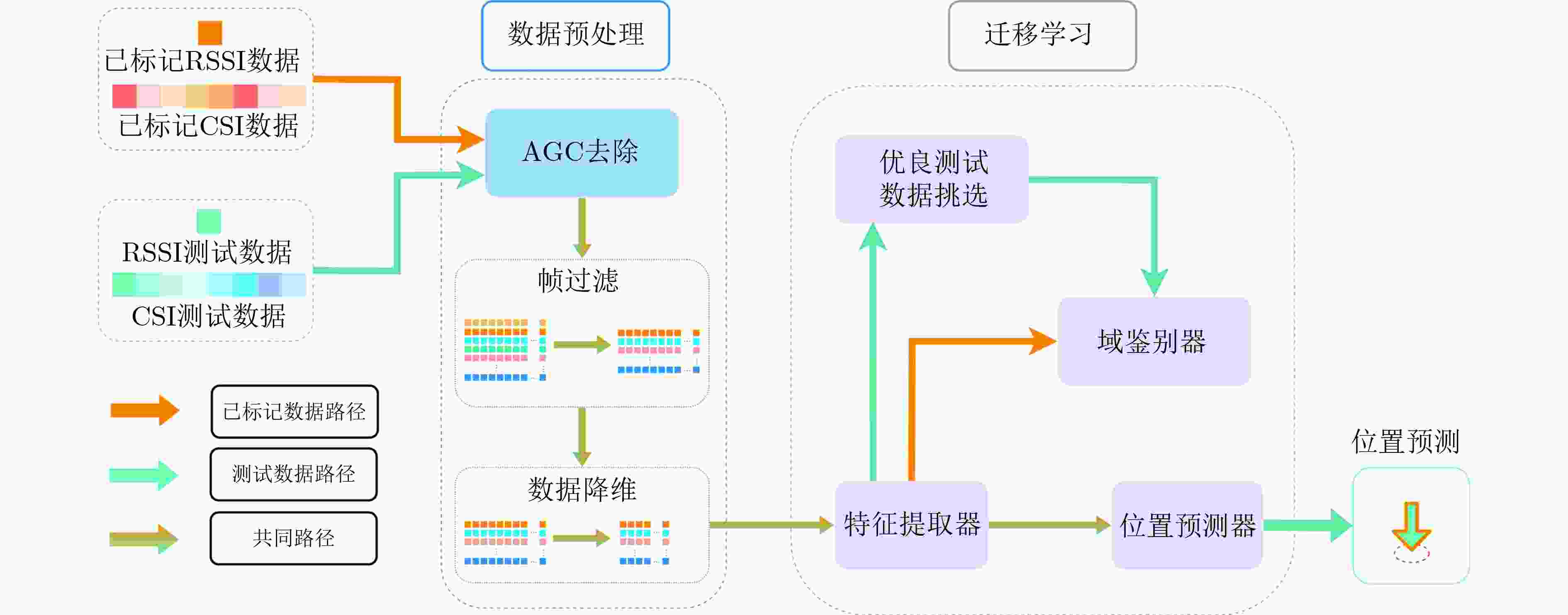


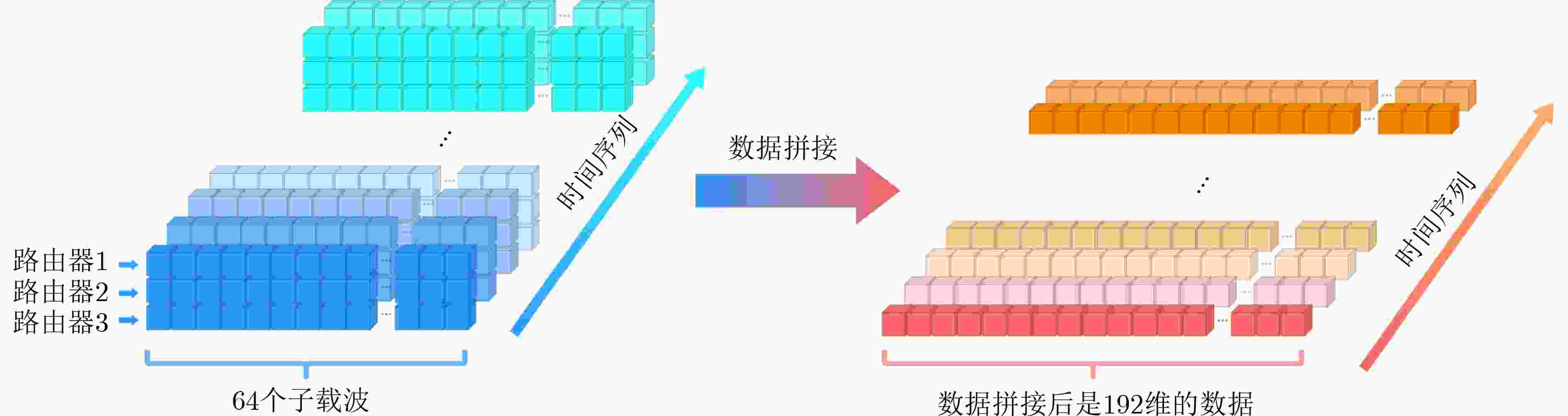
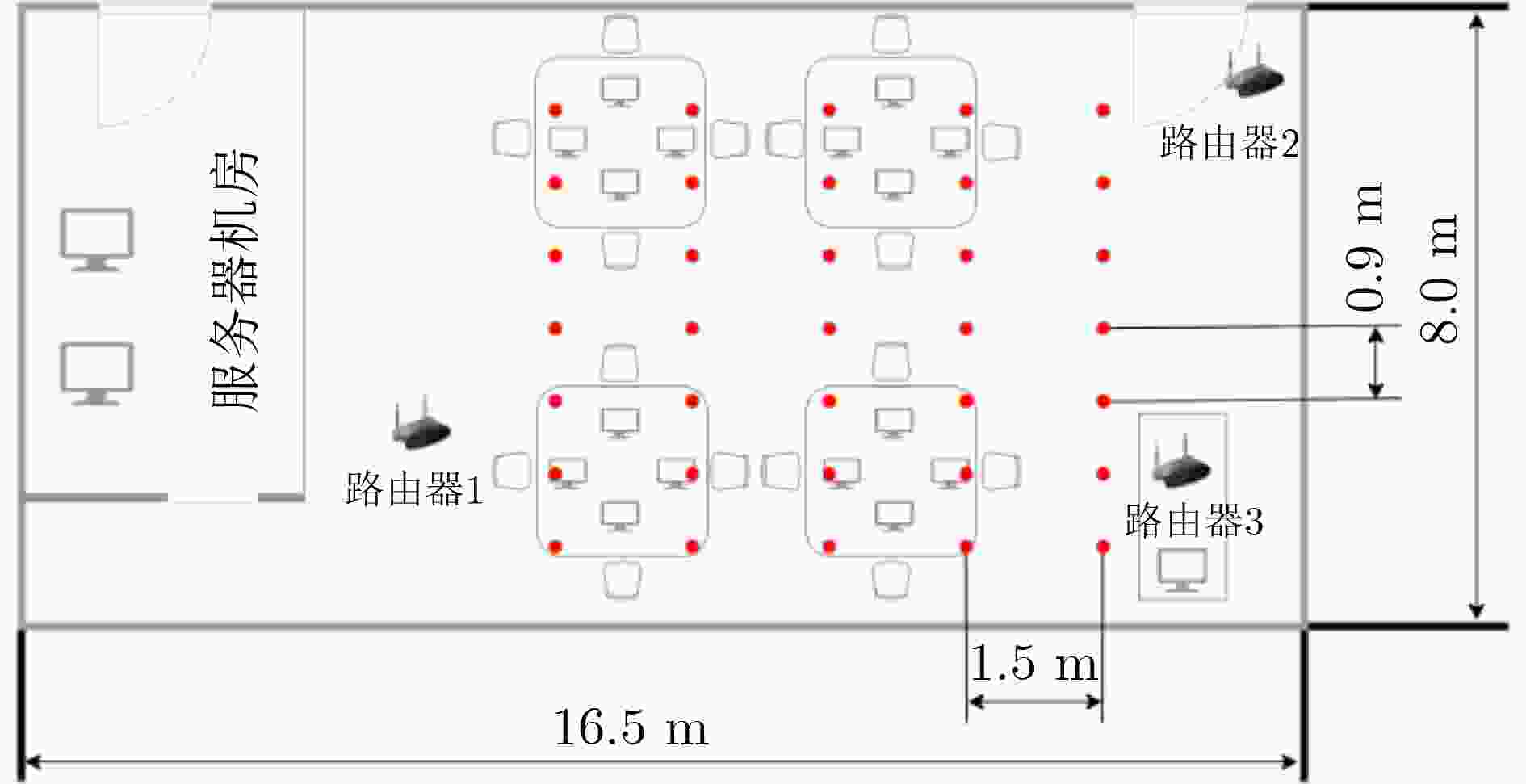


 下载:
下载:
