Adaptive Noise Reduction Algorithm for Chaotic Signals Based on Wavelet Packet Transform
-
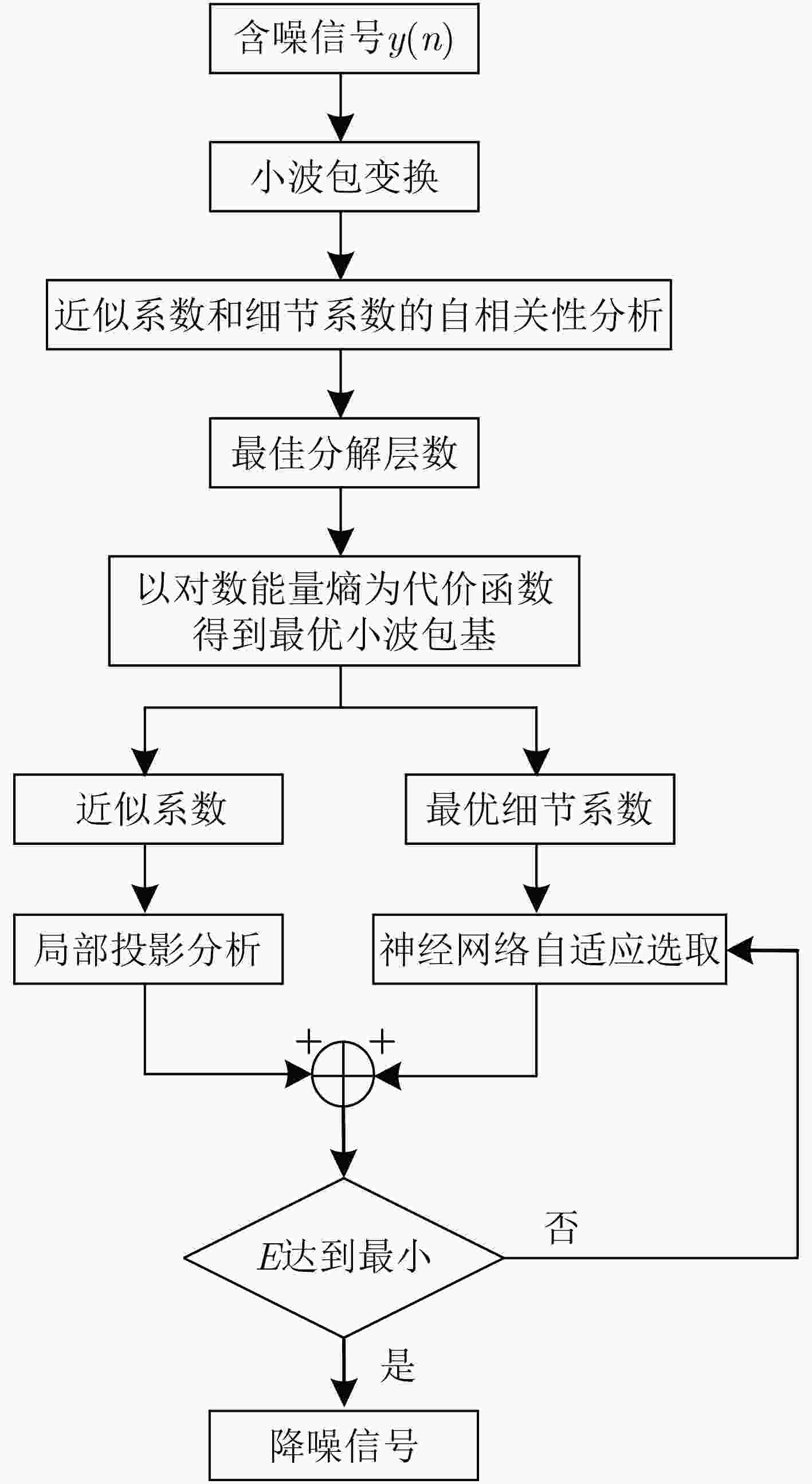
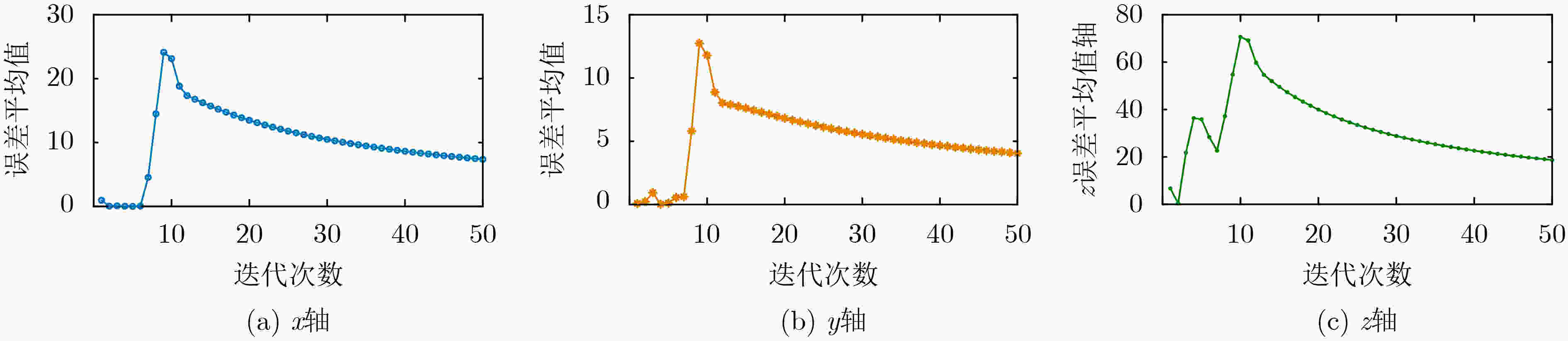
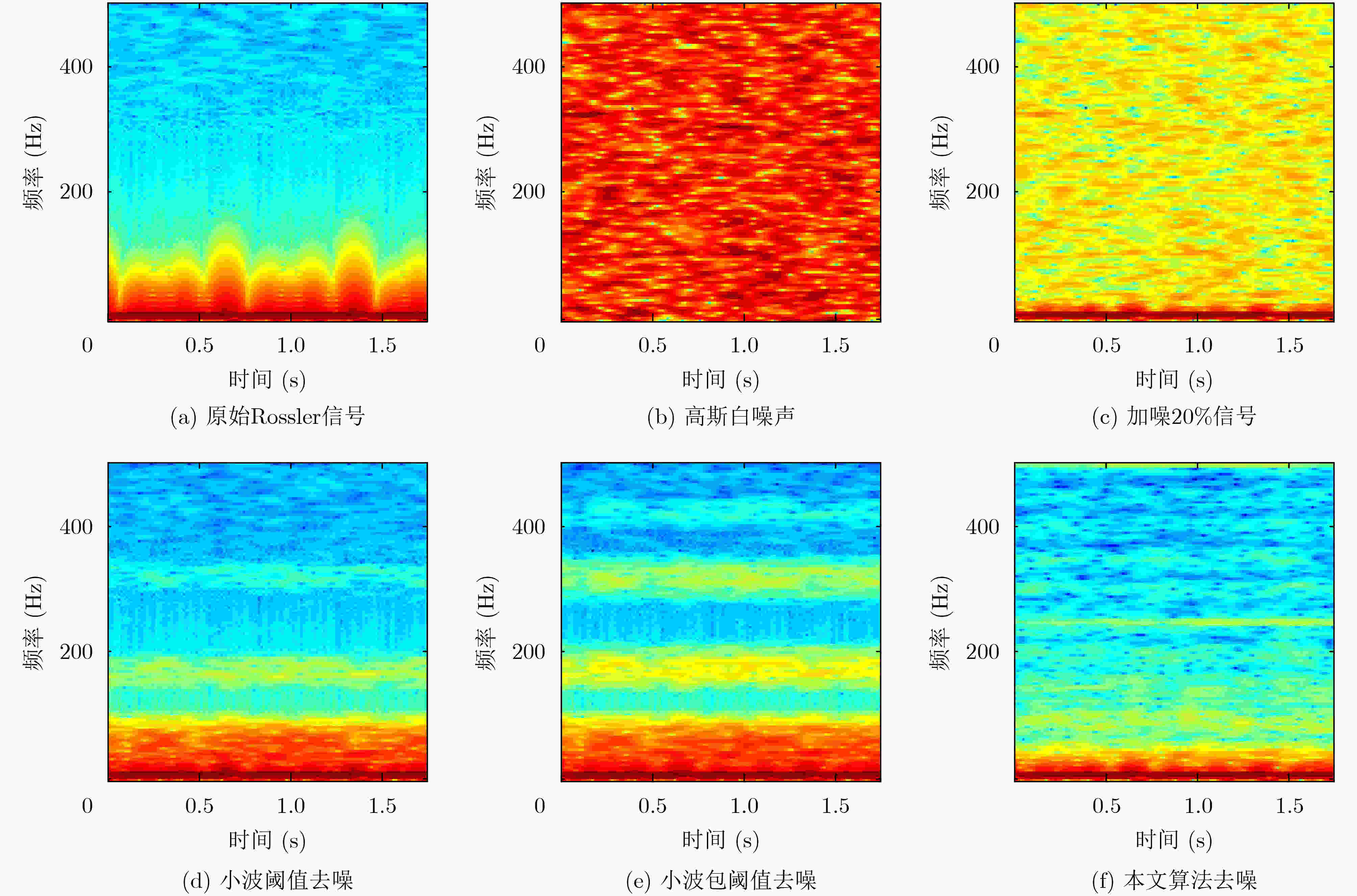
摘要: 为了更好地体现混沌系统的内在特征,该文提出一种基于小波包变换的自适应混沌信号降噪算法。首先,该算法根据不同分解尺度小波包系数的相关性不同,确定了最佳分解层数;以对数能量熵为代价函数,得到了最优小波包基。然后,在局部邻域内对近似系数进行投影分析,利用神经网络梯度下降法对细节系数进行自适应选择。通过最小化损失函数,最大限度降低噪声对混沌信号的影响。最后,通过对来自Rossler混沌模型的状态变量进行仿真分析,证实了该算法对混沌信号降噪的优越性。Abstract: To reflect better the inherent characteristics of chaotic systems, an adaptive noise reduction algorithm for chaotic signals based on wavelet packet transform is proposed. Firstly, the best decomposition level is determined according to the different correlation of wavelet packet coefficients in different decomposition scales, while the optimal wavelet packet basis is obtained with the logarithmic energy entropy as the cost function. Then, the approximate coefficients are projected in the local neighborhood and the detail coefficients are adaptively selected with the gradient descent algorithm in neural network. By minimizing the loss function, the influence of noises on chaotic signals is reduced to the greatest extent. Finally, simulations on the state variables originating from Rossler chaotic model verify the denoising superiority of the proposed algorithm for the chaotic signals.
-
Key words:
- Wavelet packet /
- Local projection /
- Neural network /
- Chaos /
- Noise reduction
-
表 1 不同噪声水平下的最优小波包基
噪声水平(%) 坐标轴 近似系数 细节系数 5 x, y $ s_3^1 $ $ s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4,\;s_3^5,\;s_3^6,\;s_3^7,\;s_3^8 $ 10 x, y $ s_3^1 $ $ s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4,\;s_3^5,\;s_3^6,\;s_3^7,\;s_3^8 $ 20 x, y $ s_3^1 $ $ s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4,\;s_3^5,\;s_3^6,\;s_3^7,\;s_3^8 $ 35 x, y $ s_3^1 $ $ s_2^4,\;s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4,\;s_3^5,\;s_3^6 $ 60 x, y $ s_3^1 $ $ s_2^3,\;s_2^4,\;s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4 $ 90 x $ s_3^1 $ $ s_1^2,\;s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4 $ y $ s_3^1 $ $ s_2^3,\;s_2^4,\;s_3^2,\;s_3^3,\;s_3^4 $ 5~90 z $ s_2^1 $ $ s_2^2,\;s_2^3,\;s_2^4 $ 表 2 SNR和RMSE对比表(x轴)
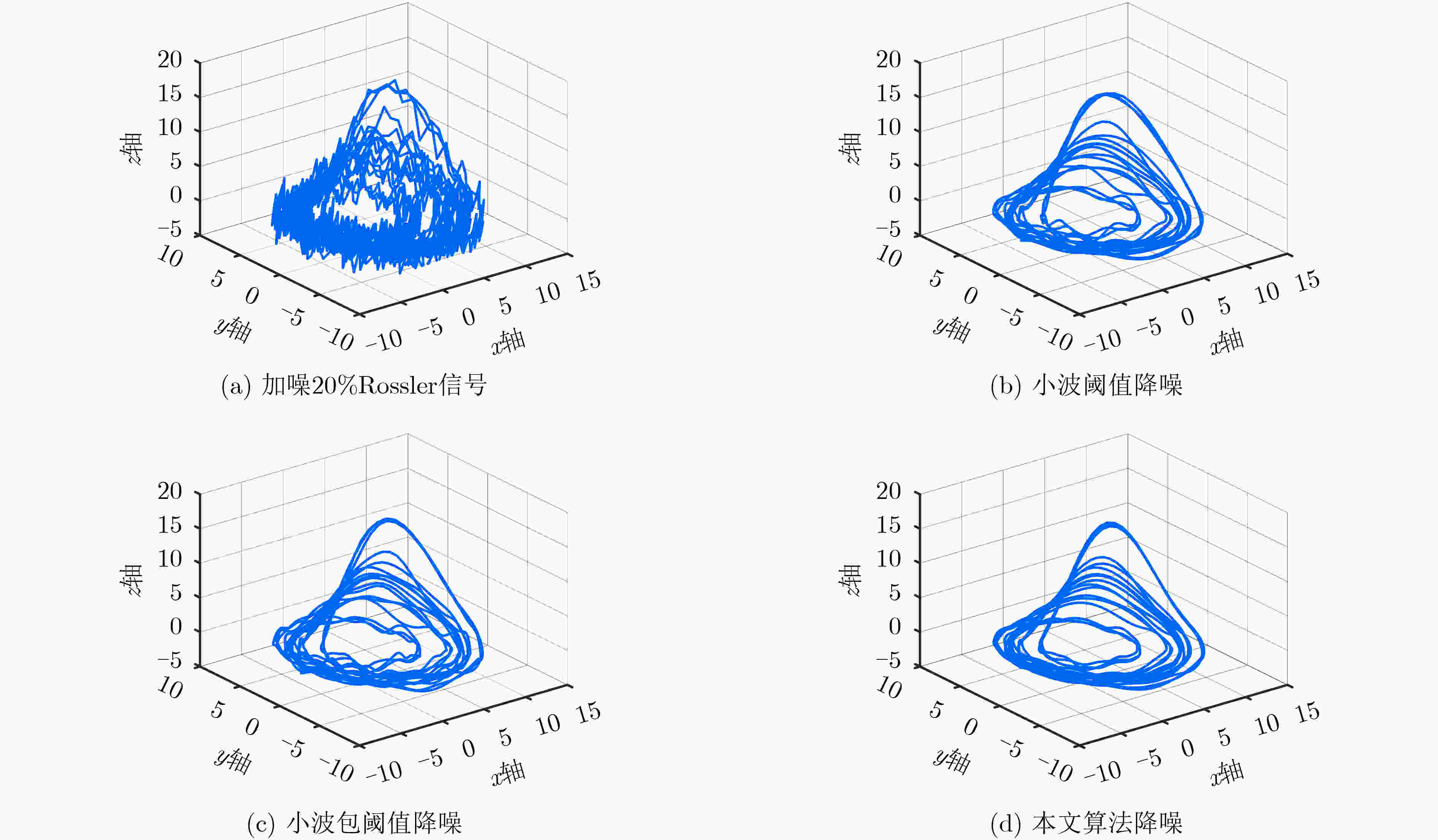
降噪指标 噪声水平(%) 降噪前 小波阈值降噪 小波包阈值降噪 本文算法降噪 SNR 5 26.115 8 34.414 2 34.223 6 34.681 2 10 20.095 2 28.880 6 28.507 3 29.632 4 20 14.074 6 23.581 5 22.568 6 24.660 0 35 9.213 9 18.781 0 17.677 5 20.736 2 60 4.532 2 14.898 4 11.920 3 17.144 2 90 1.010 4 11.359 3 6.676 8 14.668 1 RMSE 5 0.174 2 0.067 0 0.068 5 0.065 0 10 0.348 3 0.126 7 0.132 2 0.116 2 20 0.696 6 0.233 2 0.262 0 0.205 9 35 1.219 1 0.405 2 0.460 1 0.323 5 60 2.089 8 0.633 6 0.892 7 0.489 2 90 3.134 8 0.952 3 1.632 6 0.650 6 表 3 SNR和RMSE对比表(y轴和z轴)
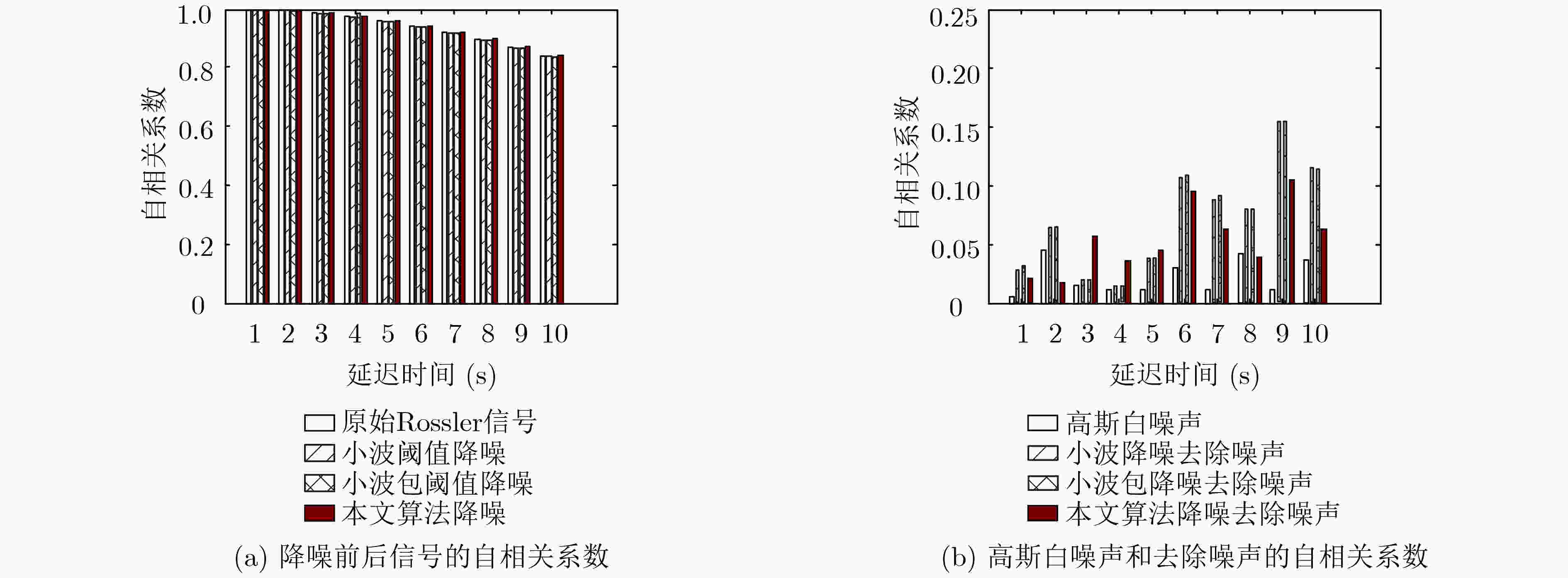
坐标轴 降噪指标 降噪前 小波阈值降噪 小波包阈值降噪 本文算法降噪 y SNR 14.074 6 22.589 2 22.589 2 25.895 2 RMSE 0.639 3 0.239 9 0.239 9 0.208 4 z SNR 14.074 6 20.336 5 19.751 8 21.650 9 RMSE 0.310 0 0.150 7 0.161 2 0.129 6 表 4 信号的自相关函数值
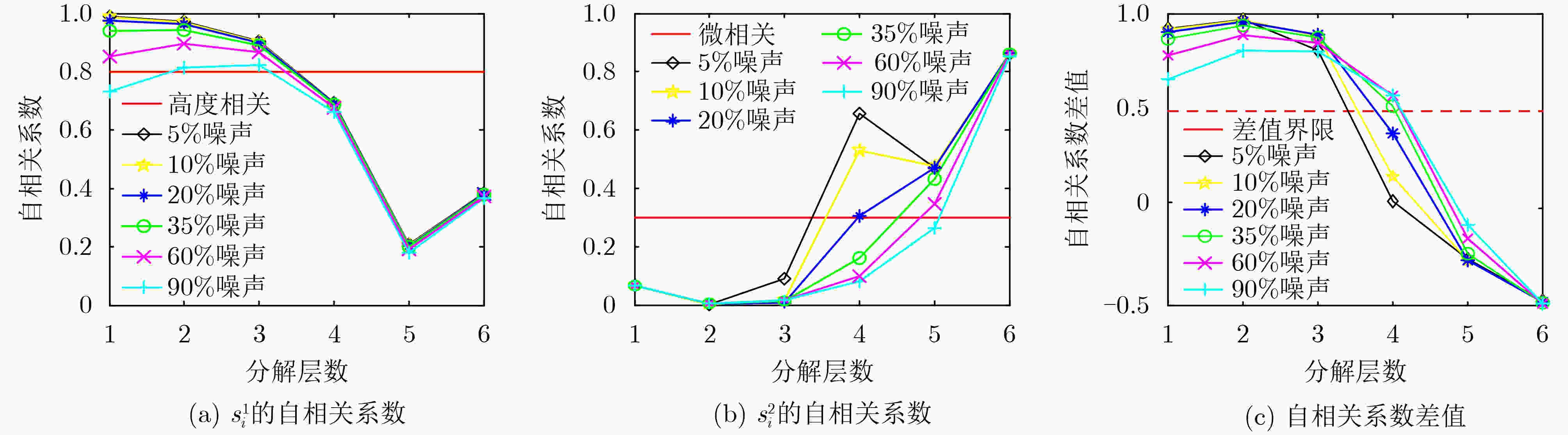
延迟时间(s) 噪声水平(%) 加噪信号 小波阈值降噪 小波包阈值降噪 本文算法降噪 1 5 0.995 0 0.997 3 0.997 3 0.997 4 10 0.988 1 0.997 3 0.997 3 0.997 4 20 0.961 5 0.997 3 0.997 2 0.997 4 35 0.896 1 0.997 3 0.996 7 0.997 4 60 0.752 7 0.996 7 0.981 4 0.997 5 90 0.583 4 0.996 6 0.904 0 0.997 7 2 5 0.989 1 0.991 5 0.991 5 0.991 6 10 0.981 9 0.991 5 0.991 4 0.991 7 20 0.954 2 0.991 4 0.991 0 0.991 7 35 0.886 1 0.991 2 0.989 7 0.991 8 60 0.736 8 0.989 3 0.970 6 0.992 1 90 0.560 7 0.988 5 0.885 0 0.992 5 5 5 0.953 2 0.955 6 0.955 5 0.955 9 10 0.946 1 0.955 4 0.955 1 0.956 1 20 0.918 9 0.954 9 0.953 3 0.956 6 35 0.852 2 0.953 8 0.948 0 0.956 9 60 0.705 8 0.943 9 0.919 6 0.958 4 90 0.532 9 0.938 8 0.823 3 0.959 6 -
[1] 黄丽莲, 姚文举, 项建弘, 等. 一种具有多对称同质吸引子的四维混沌系统的超级多稳定性研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 390–399. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201095HUANG Lilian, YAO Wenju, XIANG Jianhong, et al. Extreme multi-stability of a four-dimensional chaotic system with infinitely many symmetric homogeneous attractors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 390–399. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201095 [2] 金江涛, 许子非, 李春, 等. 基于深度学习与混沌特征融合的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(1): 109–116. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10177JIN Jiangtao, XU Zifei, LI Chun, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on deep learning and chaotic feature fusion[J]. Control Theory &Applications, 2022, 39(1): 109–116. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10177 [3] 毛北行, 王东晓. 不确定分数阶高维混沌系统的自适应滑模同步[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(4): 775–780. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200316MAO Beixing and WANG Dongxiao. Self-adaptive sliding mode synchronization of uncertain fractional-order high-dimension chaotic systems[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(4): 775–780. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200316 [4] 郭业才, 姚文强. 基于信噪比分类网络的调制信号分类识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825GUO Yecai and YAO Wenqiang. Modulation signal classification and recognition algorithm based on signal to noise ratio classification network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825 [5] LIU Yunxia, LU Xiao, PENG Wei, et al. Compression and regularized optimization of modules stacked residual deep fuzzy system with application to time series prediction[J]. Information Sciences, 2022, 608: 551–577. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.06.088 [6] KADAM S T, DHAIMODKER V M N, PATIL M M, et al. EIQ: EEG based IQ test using wavelet packet transform and hierarchical extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2019, 322: 71–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.04.008 [7] LOU Shuting, DENG Jiarui, and LYU Shanxiang. Chaotic signal denoising based on simplified convolutional denoising auto-encoder[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2022, 161: 112333. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112333 [8] CHEN Yue and ZHANG Yu. Chaotic signal denoising using an improved wavelet thresholding algorithm[C]. 2021 International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering, Beijing, China, 2021: 200–203. [9] 罗勇江, 杨腾飞, 赵冬. 色噪声下基于白化频谱重排鲁棒主成分分析的语音增强算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3671–3679. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200594LUO Yongjiang, YANG Tengfei, and ZHAO Dong. Speech enhancement algorithm based on robust principal component analysis with whitened spectrogram rearrangement in colored noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3671–3679. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200594 [10] 郭文博, 林朗, 赵宏志, 等. 频谱共生干扰主动抑制技术研究[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2022, 52(10): 1915–1928. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0160GUO Wenbo, LIN Lang, ZHAO Hongzhi, et al. Research on the active cancellation technology of spectrum symbiotic interference[J]. Scientia Sinica (Informationis), 2022, 52(10): 1915–1928. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0160 [11] MORADI M. Wavelet transform approach for denoising and decomposition of satellite-derived ocean color time-series: Selection of optimal mother wavelet[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 69(7): 2724–2744. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.01.023 [12] 江莉, 尚文擎, 周军妮, 等. 一种用于地震信号分析的二阶挤压小波变换算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3710–3717. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200753JIANG Li, SHANG Wenqing, ZHOU Junni, et al. A second-order squeezed wavelet transform algorithm for seismic signal analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3710–3717. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200753 [13] JIANG Feibo, DONG Li, DAI Qianwei, et al. Using wavelet packet denoising and ANFIS networks based on COSFLA optimization for electrical resistivity imaging inversion[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2018, 337: 93–112. doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2017.07.009 [14] DASS R. Speckle noise reduction of ultrasound images using BFO cascaded with wiener filter and discrete wavelet transform in homomorphic region[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 132: 1543–1551. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.05.118 [15] CUI Huimin, ZHAO Ruimei, and HOU Yanli. Improved threshold denoising method based on wavelet transform[J]. Physics Procedia, 2012, 33: 1354–1359. doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2012.05.222 [16] GHANBARI Y and KARAMI-MOLLAEI M R. A new approach for speech enhancement based on the adaptive thresholding of the wavelet packets[J]. Speech Communication, 2006, 48(8): 927–940. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2005.12.002 [17] LU Yibin, LI Min, WU Biteng, et al. Denoising of pulse wave signal by wavelet packet transform[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Sanya, China, 2021: 232–236. [18] ISLAM T, SHAHNAZ C, ZHU Weiping, et al. Rayleigh modeling of teager energy operated perceptual wavelet packet coefficients for enhancing noisy speech[J]. Speech Communication, 2017, 86: 64–74. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2016.11.002 [19] ZAHHAD M A, AHMED S M, and ABBAS S N. Biometrics from heart sounds: Evaluation of a new approach based on wavelet packet cepstral features using HSCT-11 database[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2016, 53: 346–358. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2016.05.004 [20] DONG Wenyong and DING Hong. Full frequency de-noising method based on wavelet decomposition and noise-type detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 214: 902–909. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.06.072 [21] SWAMI P D, SHARMA R, JAIN A, et al. Speech enhancement by noise driven adaptation of perceptual scales and thresholds of continuous wavelet transform coefficients[J]. Speech Communication, 2015, 70: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2015.02.007 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
