| [1] |
IMT-2030 (6G)推进组. 6G典型场景和关键能力[R]. 北京: IMT-2030 (6G)推进组, 2022.IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. 6G typical scenarios and key capabilities[R]. Beijing: IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group, 2022.
|
| [2] |
WANG Kunlun, ZHOU Yong, LIU Zening, et al. Online task scheduling and resource allocation for intelligent NOMA-based industrial Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(5): 803–815. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.2980908
|
| [3] |
WEN Xiangming, ZHANG Huiwen, ZHANG Haijun, et al. Interference pricing resource allocation and user-subchannel matching for NOMA hierarchy fog networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(3): 467–479. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2899238
|
| [4] |
WU Qingqing, ZHANG Shuowen, ZHENG Beixiong, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications: A tutorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313–3351. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051897
|
| [5] |
LI Yun, LIAO Chao, WANG Yong, et al. Energy-efficient optimal relay selection in cooperative cellular networks based on double auction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(8): 4093–4104. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2416715
|
| [6] |
PANG Weina, WANG Ping, HAN Maojie, et al. Optical intelligent reflecting surface for mixed Dual-Hop FSO and beamforming-based RF system in C-RAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(10): 8489–8506. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3166756
|
| [7] |
SHAWAQFEH M K and BADARNEH O S. Performance of mobile networks under composite $ \mathcal{F}$ fading channels[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2022, 8(1): 25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2021.01.001
|
| [8] |
HOU Tianwei, LIU Yuanwei, SONG Zhengyu, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface aided NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2575–2588. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007039
|
| [9] |
YU Xianhua, LI Dong, XU Yongjun, et al. Convolutional autoencoder-based phase shift feedback compression for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted wireless systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(1): 89–93. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3123941
|
| [10] |
DU Hongyang, ZHANG Jiayi, PEPPAS K P, et al. On the distribution of the ratio of products of Fisher-Snedecor $ \mathcal{F} $ random variables and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(2): 1855–1866. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2961427
|
| [11] |
ZWILLINGER D and JEFFREY A. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products[M]. 7th ed. Burlington: Academic Press, 2007.
|
| [12] |
BASAR E. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for Doppler effect and multipath fading mitigation[J]. Frontiers in Communications and Networks, 2021, 2: 672857. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2021.672857
|
| [13] |
BLOCH M, BARROS J Ã, RODRIGUES M R D, et al. Wireless information-theoretic security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(6): 2515–2534. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2008.921908
|
| [14] |
YAKUBOVICH S B and NGUYEN T H. The Double Mellin-Barnes Type Integrals and Their Applications To Convolution Theory[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 1992.
|
| [15] |
MATHAI A M, SAXENA R K, and HAUBOLD H J. The H-Function: Theory and Applications[M]. New York: Springer, 2009.
|
| [16] |
KILBAS A A. H-transforms: Theory and Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2004.
|
| [17] |
LI Dong. How many reflecting elements are needed for energy- and spectral-efficient intelligent reflecting surface-assisted communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1320–1331. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3128544
|
| [18] |
LI Dong. Bound analysis of number configuration for reflecting elements in IRS-Assisted D2D communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(10): 2220–2224. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3197614
|
| [19] |
MOHJAZI L, BARIAH L, MUHAIDAT S, et al. Performance of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in the presence of generalized Gaussian noise[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(4): 773–777. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3145291
|
| [20] |
FENG Youhong, YAN Shihao, YANG Nan, et al. Safeguarding non-orthogonal multiple access with physical layer techniques[J]. IEEE Network, 2022, 36(3): 145–151. doi: 10.1109/MNET.014.2100091
|
| [21] |
XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, OHTSUKI T, et al. Robust resource allocation for two-tier HetNets: An interference-efficiency perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2021, 5(3): 1514–1528. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2021.3090592
|





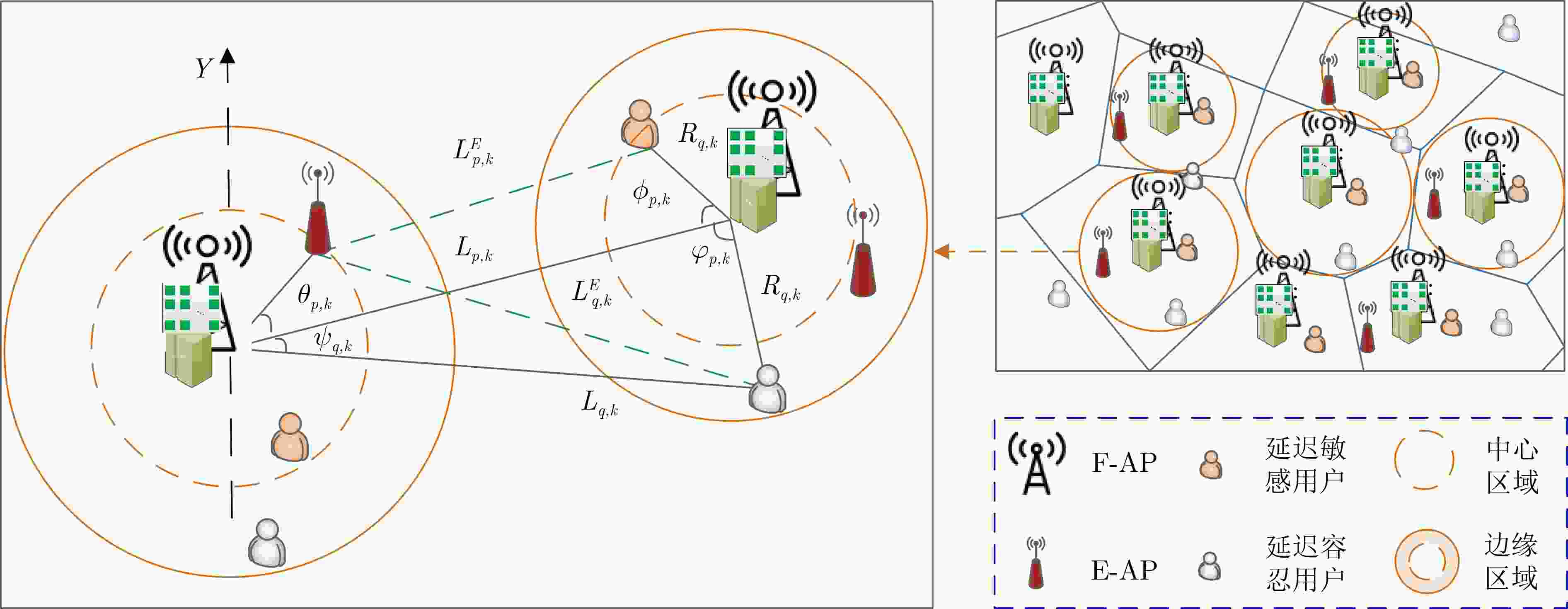
 下载:
下载:
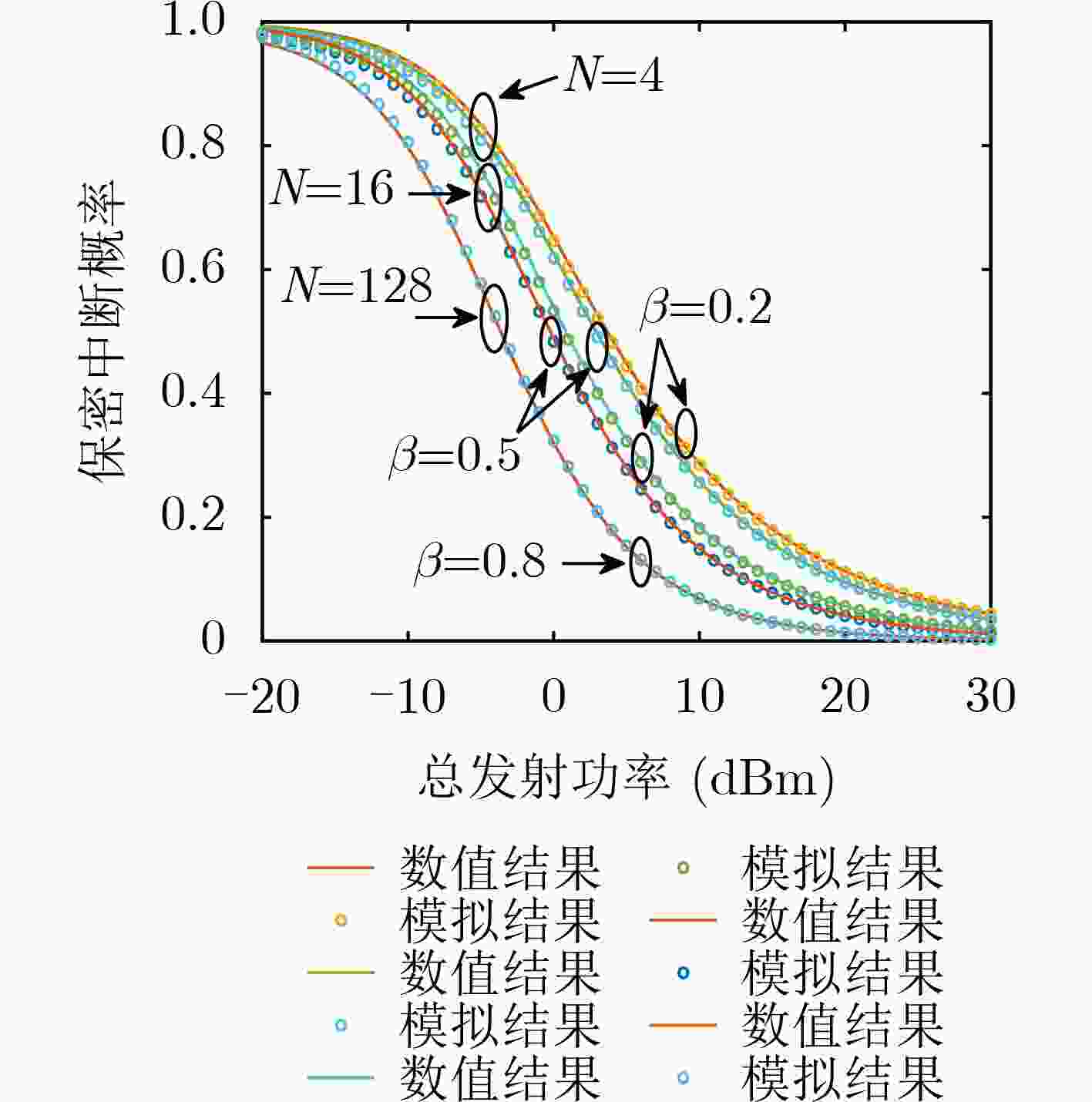
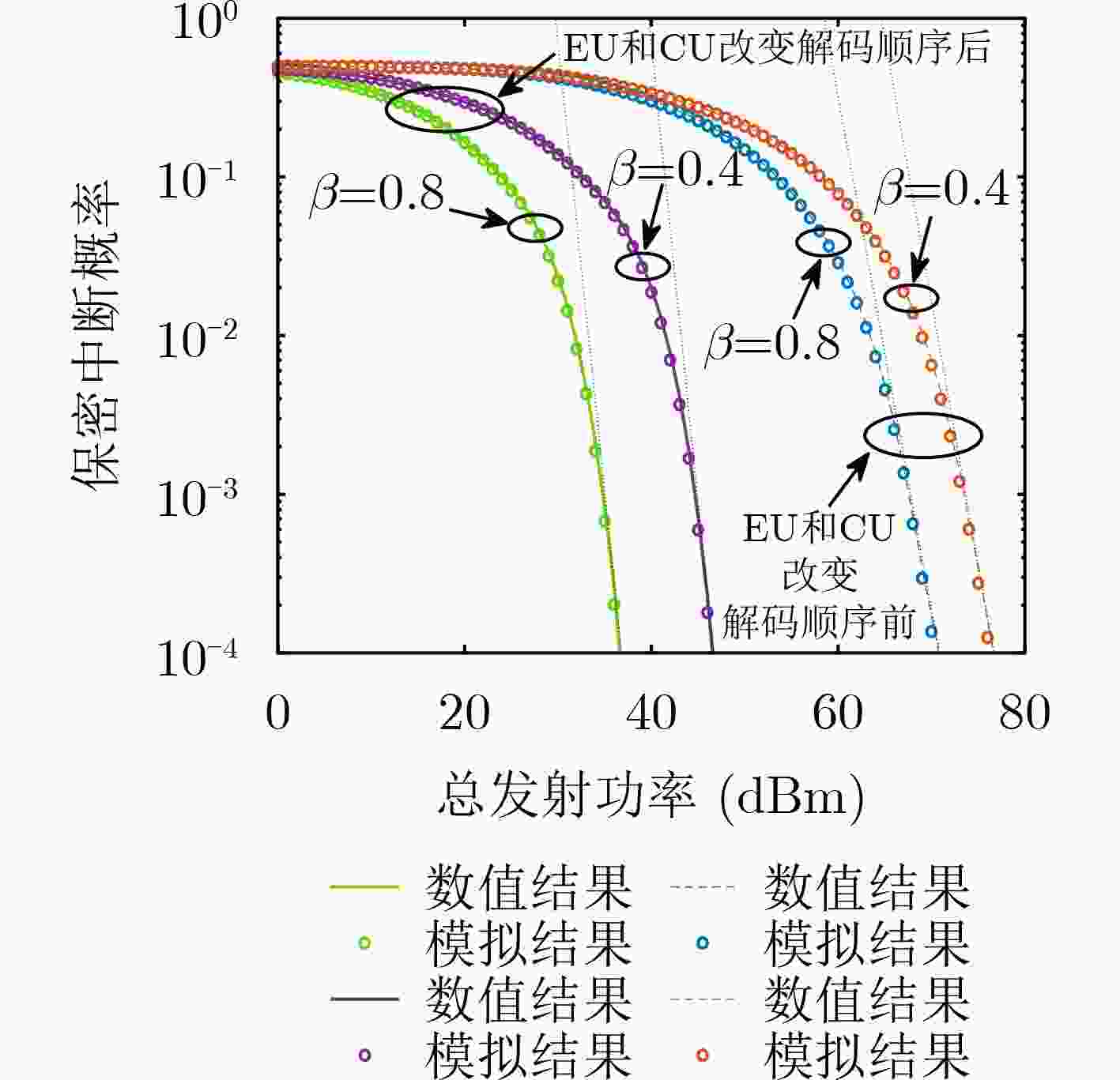
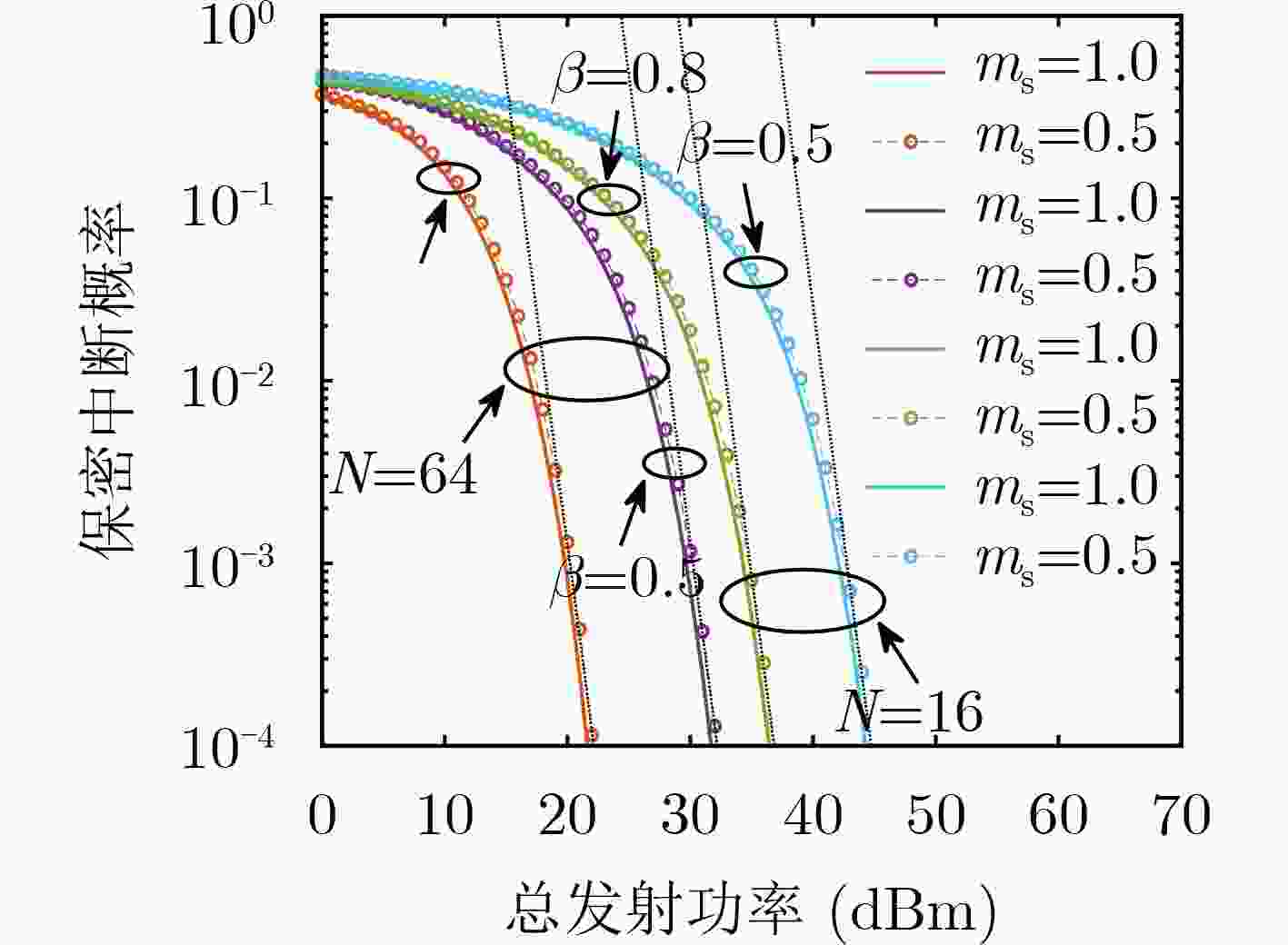
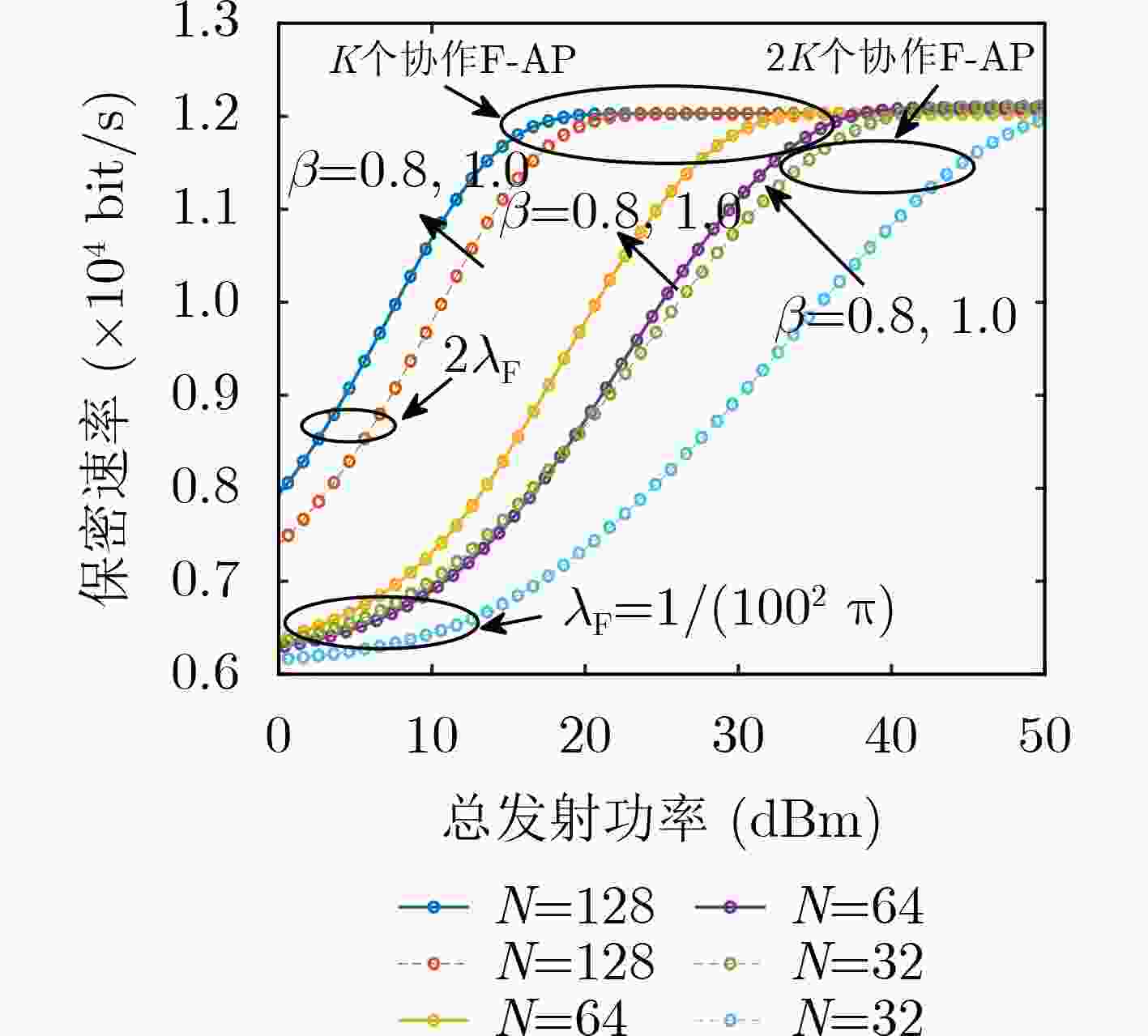


 下载:
下载:
