2D Compressed Sensing Algorithm Based on Adaptive Blocking and Joint Optimization Smooth l0 Norm
-
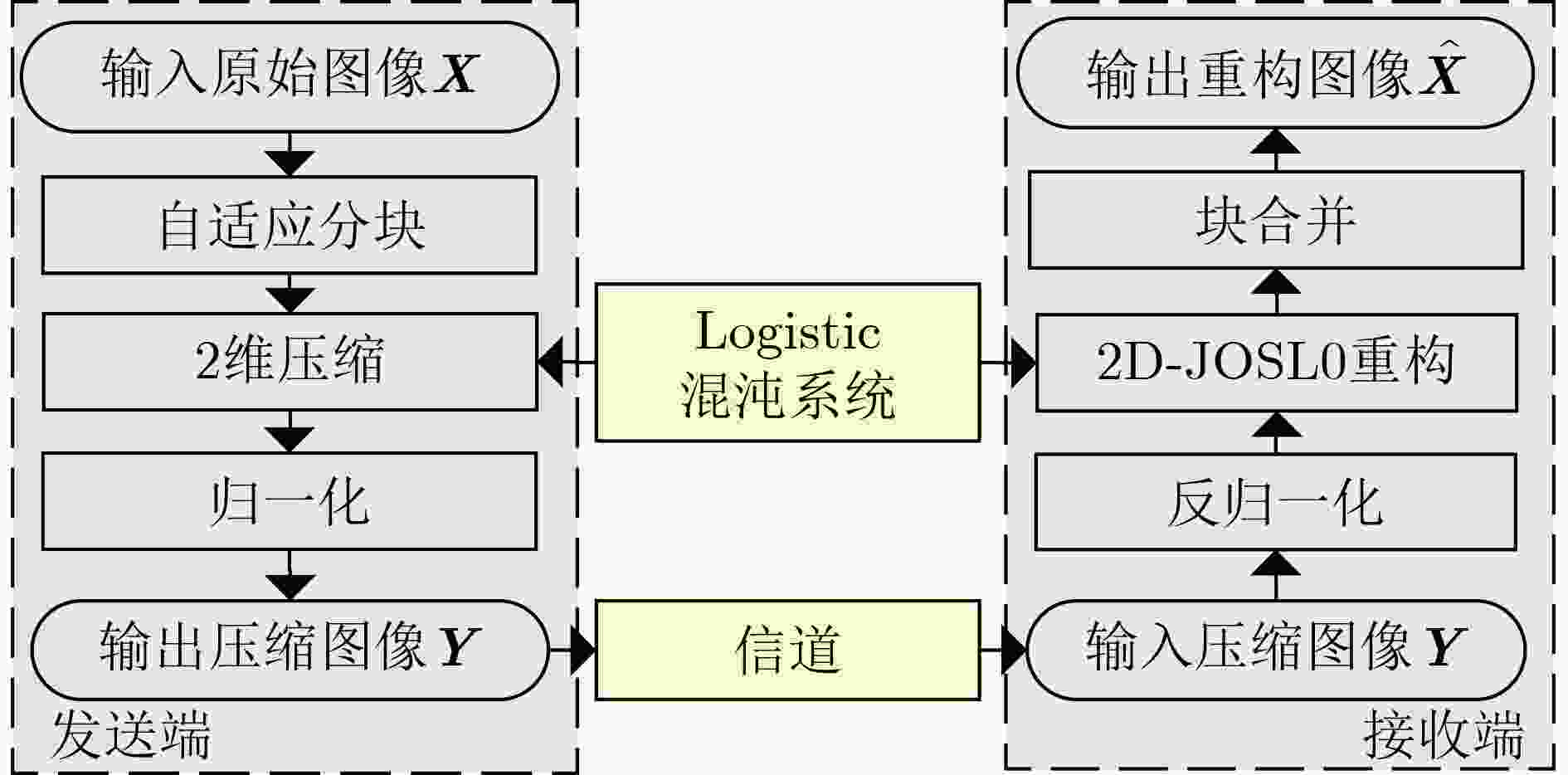
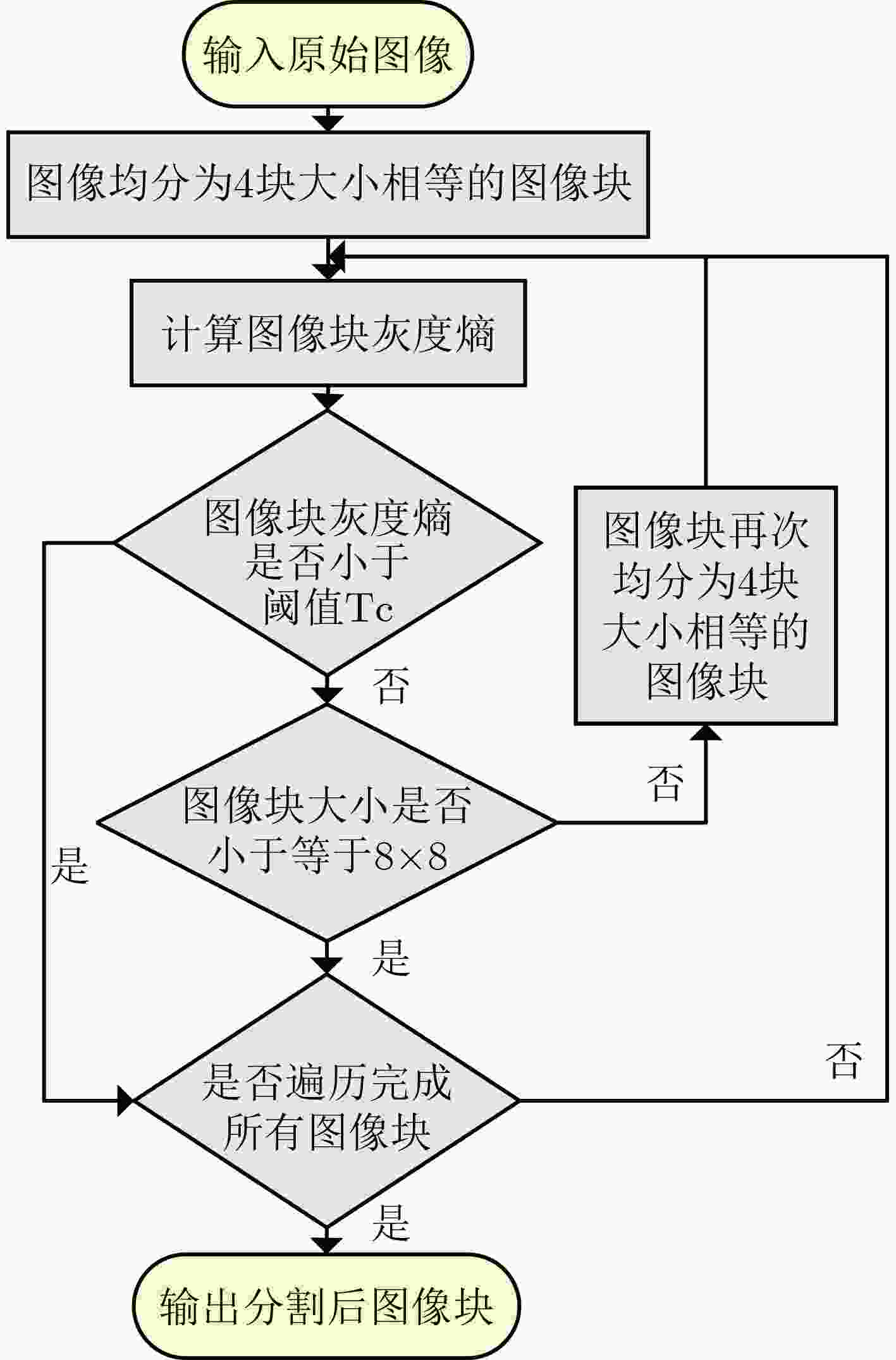
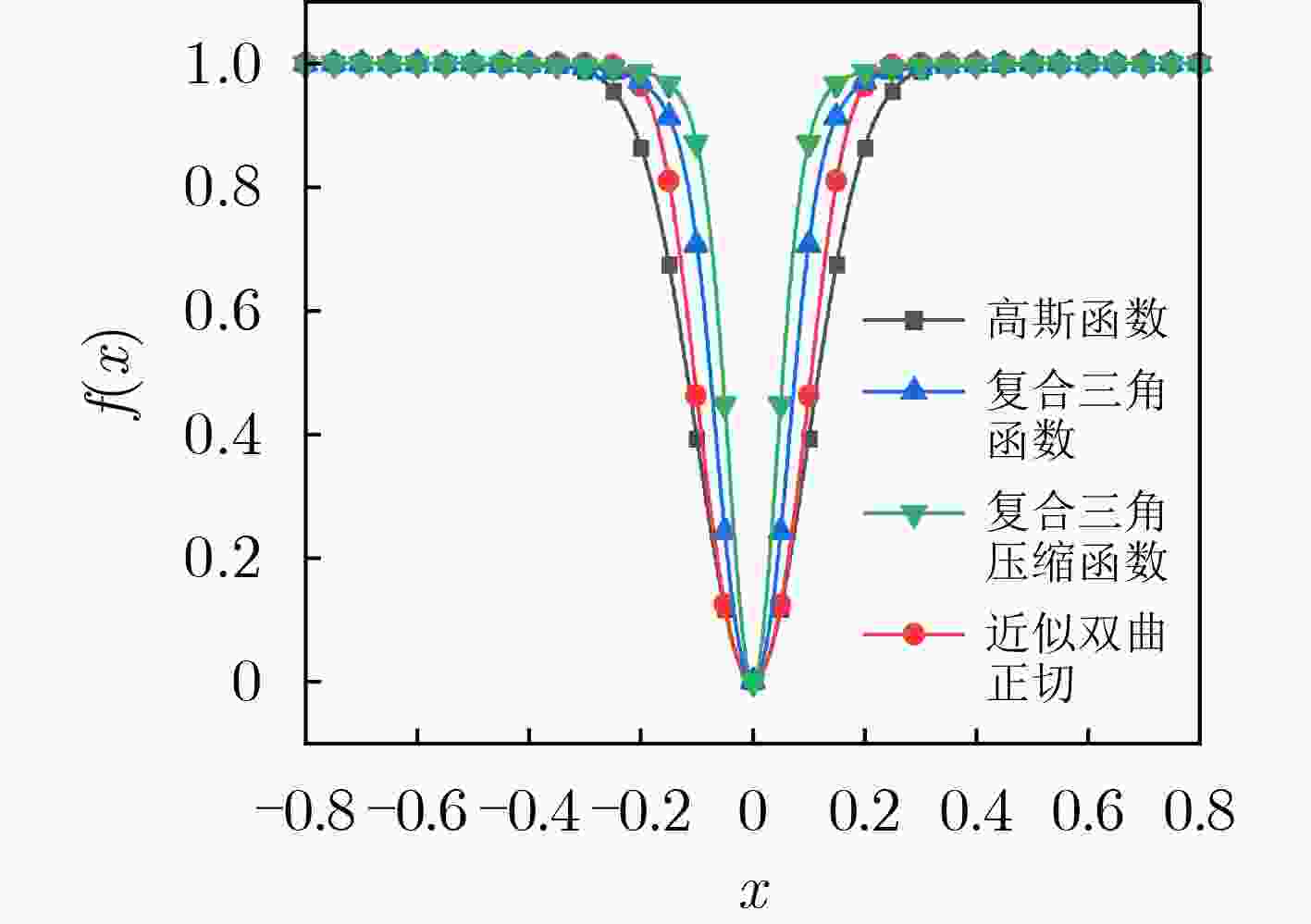
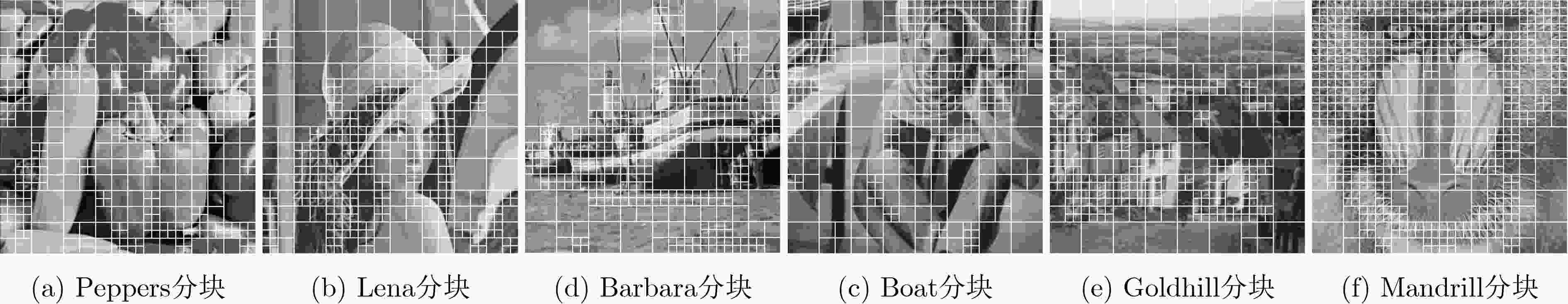
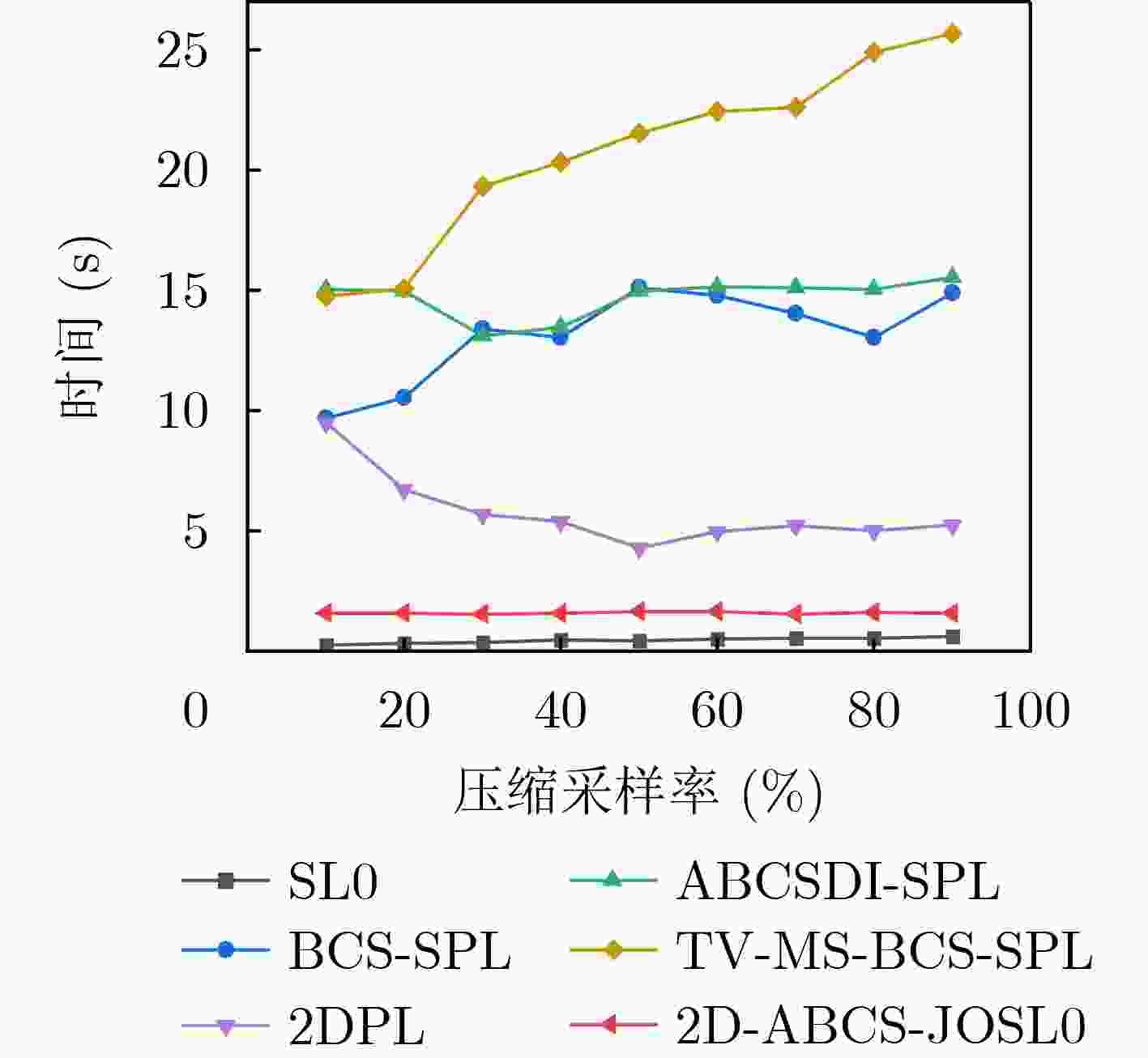
摘要: 传统的压缩感知模型和重构方法,虽能有效减少数据量,但压缩和重构性能不佳,故该文提出一种基于自适应分块和联合优化光滑l0范数(SL0)的2维压缩感知算法。压缩过程利用灰度熵和四叉树算法进行自适应分块和采样率分配,同时对压缩模型改进,使用混沌循环矩阵作为测量矩阵,提升了压缩性能。重构过程基于SL0算法,采用陡峭性更高的拟合函数,结合拟牛顿法和动态迭代的方案提高重构质量和效率。该算法峰值信噪比和结构相似性指数相比现有算法平均提升了5.44 dB和21.08%,平均计算时间仅需1.59 s,表明该算法能稳定、快速地实现图像的压缩感知和精确重构,为压缩感知和图像重构提供了新方法。Abstract: A 2-dimension compressed sensing algorithm based on adaptive blocking and joint optimization Smooth l0 (SL0) norm is proposed to solve the problem of poor compression and reconstruction performance of the traditional compressed sensing model and reconstruction method. In the compression process, gray entropy and quadtree algorithm are used for adaptive blocking and sample rate allocation. At the same time, the compressed sensing model is optimized and the chaotic cyclic matrix is used as the measure matrix, which improves the compression performance. In the reconstruction process based on SL0 algorithm, a fitting function with higher steepness and a scheme combined with Quasi-Newton method and dynamic iteration are adopted to improve the reconstruction quality and efficiency. Compared with other algorithms, the peak signal to noise ratio and structural similarity index of the proposed algorithm are improved by 5.44 dB and 21.08% on average respectively. The average calculation time is only 1.59 s. Based on realizing image compression and accurate reconstruction stably and quickly, the proposed algorithm provides a new method for compressed sensing and image reconstruction.
-
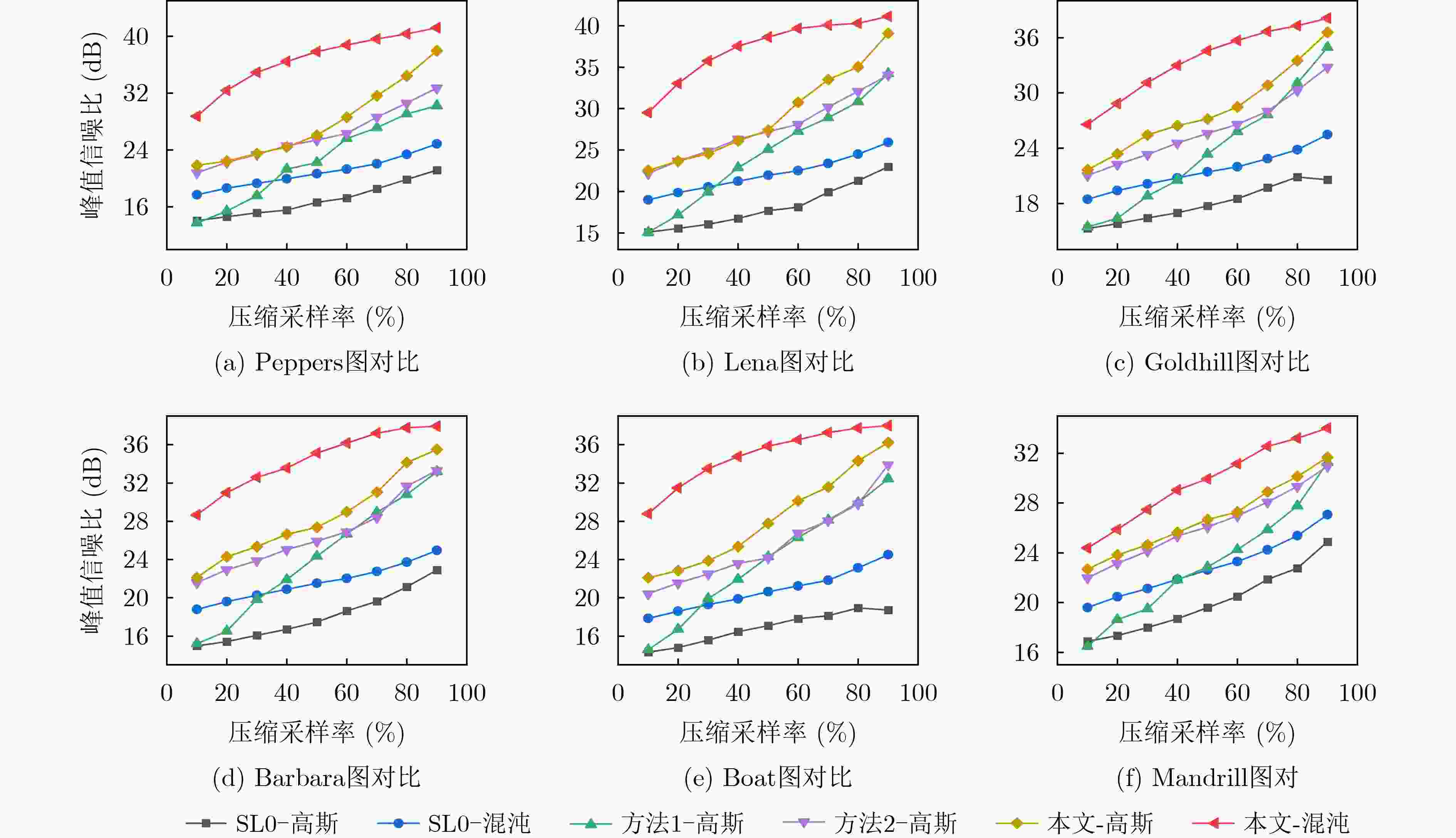
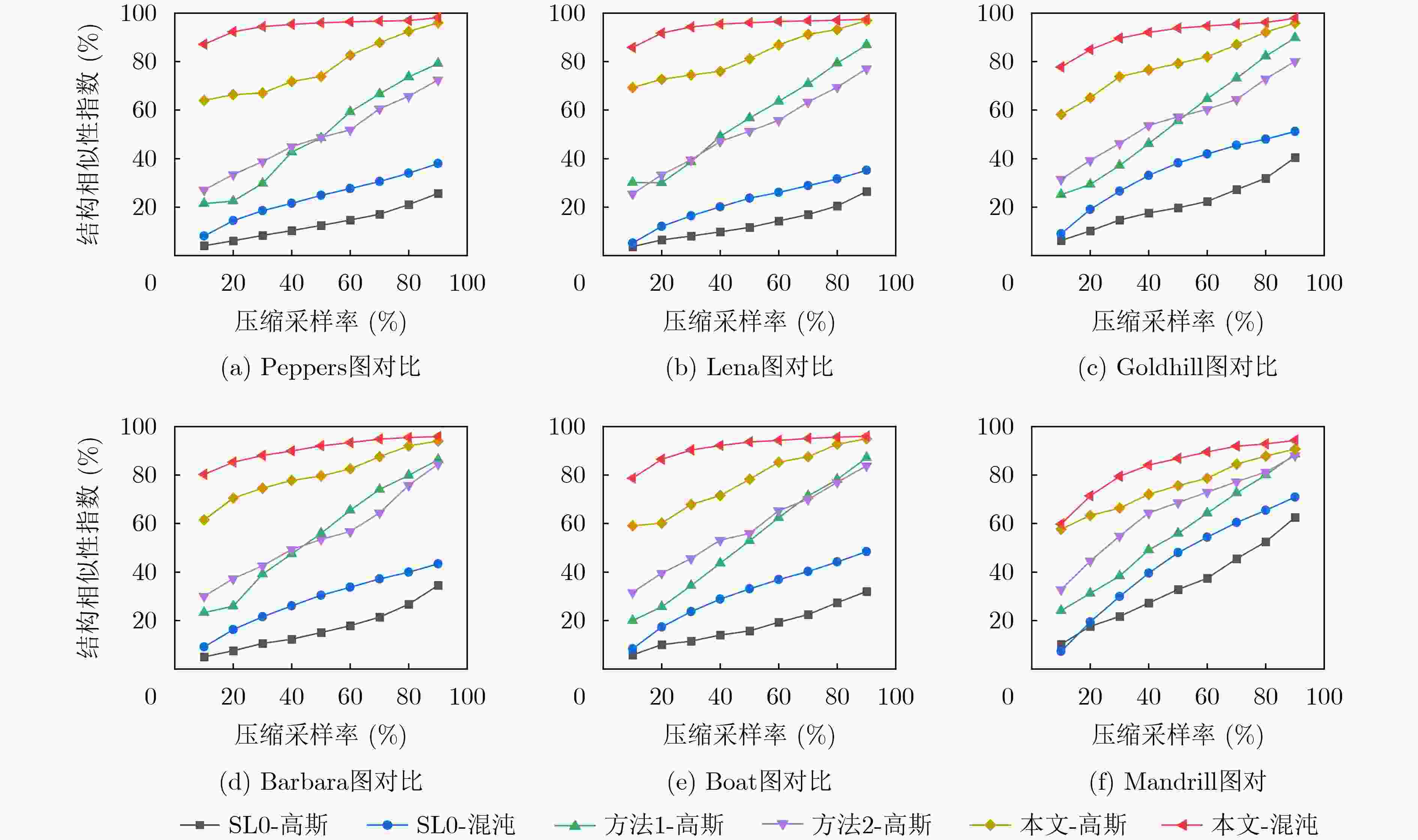
表 1 不同图像不同算法PSNR(dB)/SSIM(%))对比
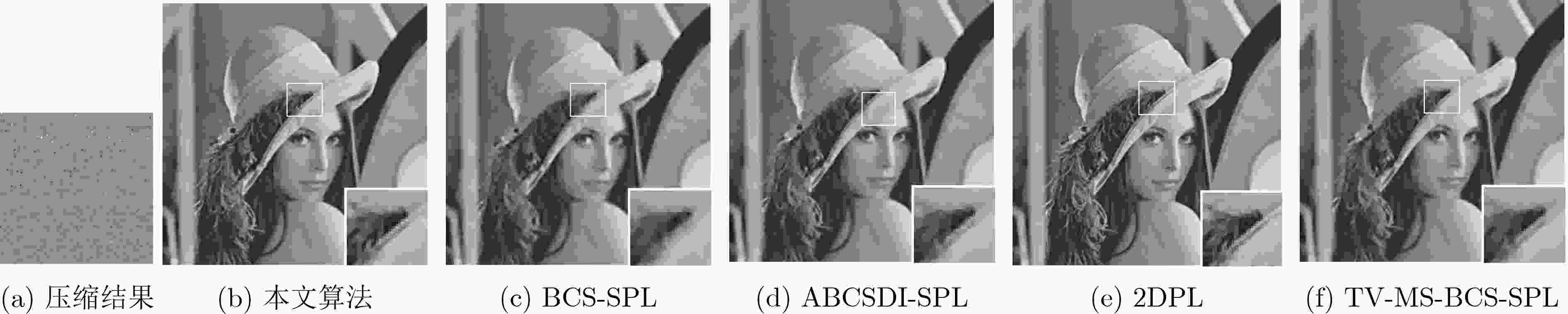
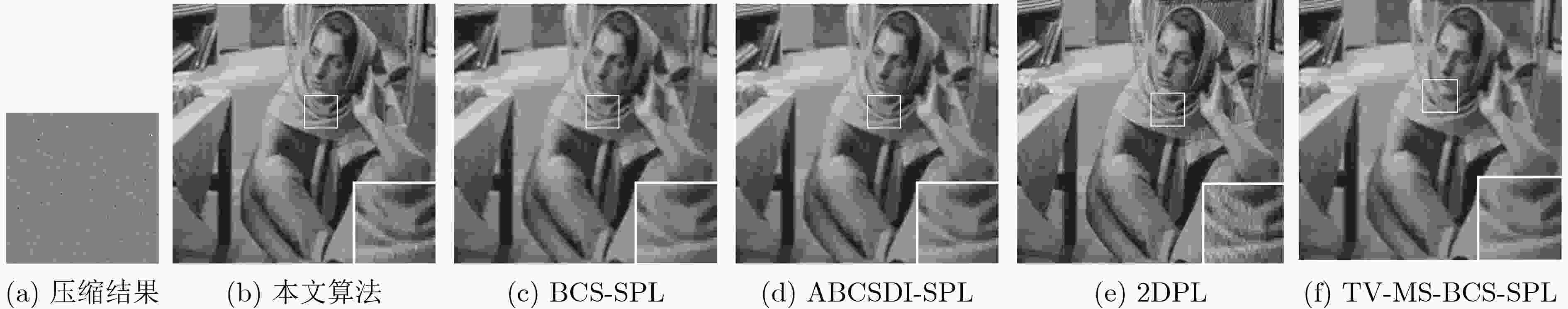
压缩采样率(%) 算法 Peppers Lena Goldhill Barbara Boat Mandrill 平均值 10 BCS-SPL 23.79/64.86 23.58/64.57 26.71/54.98 23.12/55.12 23.64/55.1 22.54/37.15 23.65/55.30 ABCSDI-SPL 24.79/72.09 24.05/73.87 27.57/57.26 23.97/55.52 24.28/56.54 20.81/36.02 24.24/58.55 2DPL 27.79/86.81 27.13/83.99 27.05/74.42 24.34/72.96 23.54/73.43 21.89/50.84 25.29/73.74 TV-MS-BCS-SPL 28.21/87.03 27.33/80.43 28.21/75.89 28.01/74.04 24.27/74.33 22.97/52.32 26.50/74.01 2D-ABCS-JOSL0 28.75/87.13 29.50/85.89 28.79/78.76 28.67/80.33 26.57/77.84 24.38/59.73 27.77/78.28 30 BCS-SPL 28.54/77.08 29.04/81.35 30.13/73.02 26.20/68.25 26.65/73.42 26.03/52.47 27.35/70.93 ABCSDI-SPL 29.93/82.50 29.92/87.12 32.09/72.25 30.39/70.01 27.65/73.43 24.54/52.59 29.09/72.98 2DPL 34.24/94.34 34.33/93.16 30.48/87.91 28.46/85.76 30.48/87.98 26.36/69.88 30.73/86.50 TV-MS-BCS-SPL 34.32/93.13 30.99/88.94 33.12/83.95 29.76/82.46 28.87/83.32 27.04/73.56 30.68/84.23 2D-ABCS-JOSL0 34.94/94.49 35.74/94.27 33.51/90.36 32.58/88.11 31.13/89.71 27.47/79.50 32.56/89.41 50 BCS-SPL 31.53/84.90 32.43/87.04 32.85/80.08 30.05/79.54 28.93/82.51 29.38/68.72 30.20/80.47 ABCSDI-SPL 33.02/88.45 33.72/92.65 33.84/81.54 33.12/81.11 30.02/82.50 26.85/70.32 31.76/82.76 2DPL 36.75/95.03 37.56/95.29 34.01/91.22 32.64/91.04 34.01/93.72 29.01/86.25 34.00/92.26 TV-MS-BCS-SPL 36.95/96.00 33.20/92.00 34.84/88.47 33.96/88.91 32.72/90.13 28.04/81.23 33.29/89.46 2D-ABCS-JOSL0 37.85/96.04 38.61/96.00 35.87/93.67 35.12/92.03 34.58/93.73 29.94/86.95 35.33/93.07 70 BCS-SPL 33.81/90.75 34.87/94.02 34.28/91.19 33.52/87.89 31.89/90.42 32.01/81.02 32.90/89.22 ABCSDI-SPL 36.71/94.34 38.12/96.14 34.95/89.26 36.01/88.14 33.38/90.99 28.55/82.34 34.62/90.20 2DPL 38.63/96.55 39.55/96.88 36.98/94.56 36.25/94.65 36.22/95.13 31.83/90.75 36.58/94.75 TV-MS-BCS-SPL 38.10/96.09 34.92/93.91 36.52/93.87 36.32/93.43 35.93/94.81 31.75/90.12 35.59/93.70 2D-ABCS-JOSL0 39.64/96.74 40.05/96.88 37.28/95.08 37.21/94.80 36.66/95.54 32.56/91.97 37.23/95.17 -
[1] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [2] 覃亚丽, 梅济才, 任宏亮, 等. 基于高斯平滑压缩感知分数阶全变分算法的图像重构[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 2105–2112. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200376QIN Yali, MEI Jicai, REN Hongliang, et al. Image reconstruction based on Gaussian smooth compressed sensing fractional order total variation algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 2105–2112. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200376 [3] 仲元红, 周宇杰, 张静, 等. 基于非局部先验的深度压缩感知图像重构网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 654–663. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211506ZHONG Yuanhong, ZHOU Yujie, ZHANG Jing, et al. Deep compressive sensing image reconstruction network based on non-local prior[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 654–663. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211506 [4] 方澄, 李慧娟, 路稳, 等. 基于形态学自适应分块的高分辨SAR多特征增强算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(2): 470–479. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.15FANG Cheng, LI Huijuan, LU Wen, et al. Multi-feature enhancement algorithm for high resolution SAR based on morphological auto-blocking[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 470–479. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.15 [5] MUN S and FOWLER J E. Block compressed sensing of images using directional transforms[C]. 2009 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Cairo, Egypt, 2009: 3021–3024. [6] 何敬禄. 基于压缩感知的块稀疏信号重构和图像分块采样算法研究[D]. [硕士论文]. 广西大学, 2017.HE Jinglu. Research on block-sparse signal reconstruction and image block sampling algorithm based on compressive sensing[D]. [Master dissertation], Guangxi University, 2017. [7] MOHIMAN I H, BABAIE-ZADEH M, and JUTTEN C. A fast approach for overcomplete sparse decomposition based on smoothed l 0 norm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(1): 289–301. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007606 [8] 孙娜, 刘继文, 肖东亮. 基于BFGS拟牛顿法的压缩感知SL0重构算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2408–2414. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170813SUN Na, LIU Jiwen, and XIAO Dongliang. SL0 reconstruction algorithm for compressive sensing based on BFGS quasi newton method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2408–2414. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170813 [9] CANDES E J and TAO T. Decoding by linear programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(12): 4203–4215. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.858979 [10] ZHANG Li and ZHOU Weijun. Spectral gradient projection method for solving nonlinear monotone equations[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2006, 196(2): 478–484. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2005.10.002 [11] GU Yuejianan, PIAO Yan, and HUANG Yufu. Adaptive block compressed sensing algorithm based on integral imaging[C]. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology, Shenzhen, China, 2020: 85–88. [12] 陈建, 苏凯雄, 杨秀芝, 等. 基于变分模型的块压缩感知重构算法[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(1): 100–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016011CHEN Jian, SU Kaixiong, YANG Xiuzhi, et al. Reconstruction algorithm for block compressed sensing based on variation model[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(1): 100–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016011 [13] YE Guodong, PAN Chen, HUANG Xiaoling, et al. An efficient pixel-level chaotic image encryption algorithm[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 94(1): 745–756. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4391-y [14] 王玥, 周城, 熊承义, 等. 基于纹理自适应全变分滤波的图像分块压缩感知优化算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2016, 43(2): 307–310,315. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.2.064WANG Yue, ZHOU Cheng, XIONG Chengyi, et al. Enhanced block compressed sensing of images based on total variation using texture information[J]. Computer Science, 2016, 43(2): 307–310,315. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.2.064 [15] YE Xinrong and ZHU Weiping. Sparse channel estimation of pulse-shaping multiple-input-multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing systems with an approximate gradient l 2–Sl0 reconstruction algorithm[J]. IET Communications, 2014, 8(7): 1124–1131. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2013.0571 [16] FANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Jiangshe, and LI Yingqi. Sparse signal reconstruction based on multiparameter approximation function with smoothed l0 norm[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, 2014: 416542. doi: 10.1155/2014/416542 [17] GENG Juan, WANG Laisheng, FU Aimin, et al. A smoothed rank function algorithm based Hyperbolic Tangent function for matrix completion[C]. 2012 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Xi’an, China, 2012: 1333–1338. [18] XIANG Jianhong, YUE Huihui, YIN Xiangjun, et al. A reweighted symmetric smoothed function approximating L0-norm regularized sparse reconstruction method[J]. Symmetry, 2018, 10(11): 583. doi: 10.3390/sym10110583 [19] 张巍, 朱正为, 汪亮, 等. 一种A-HNSL0压缩感知SAR图像重建方法[J]. 电光与控制, 2020, 27(8): 28–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2020.08.006ZHANG Wei, ZHU Zhengwei, WANG Liang, et al. An A-HNSL0 compressed sensing based SAR image reconstruction method[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2020, 27(8): 28–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2020.08.006 [20] PANT J K, LU Wusheng, and ANTONIOU A. Unconstrained regularized lp-norm based algorithm for the reconstruction of sparse signals[C]. 2011 IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011: 1740–1743. [21] ZHAO Hui, YE Hao, and WANG Ruyan. The construction of measurement matrices based on block weighing matrix in compressed sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 123: 64–74. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.12.016 [22] MAY R M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics[J]. Nature, 1976, 261(5560): 459–467. doi: 10.1038/261459a0 [23] ZHANG Bo, XIAO Di, ZHANG Zhenyu, et al. Compressing encrypted images by using 2D compressed sensing[C]. 2019 IEEE 21st International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 17th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 5th International Conference on Data Science and Systems, Zhangjiajie, China, 2019: 1914–1919. [24] WU Rui, FU Yusheng, and LEI Jianmin. Adaptive multiscale block compressed sensing algorithm based on total variation[C]. 2018 2nd IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Xi’an, China, 2018: 617–620. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
