A Double Knowledge Distillation Model for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification
-
摘要: 为了提高轻型卷积神经网络(CNN)在遥感图像(RSI)场景分类任务中的精度,该文设计一个双注意力(DA)与空间结构(SS)相融合的双知识蒸馏(DKD)模型。首先,构造新的DA模块,将其嵌入到ResNet101与设计的轻型CNN,分别作为教师与学生网络;然后,构造DA蒸馏损失函数,将教师网络中的DA知识迁移到学生网络之中,从而增强其对RSI的局部特征提取能力;最后,构造SS蒸馏损失函数,将教师网络中的语义提取能力以空间结构的形式迁移到学生网络,以增强其对RSI的高层语义表示能力。基于两个标准数据集AID和NWPU-45的对比实验结果表明,在训练比例为20%的情况下,经知识蒸馏之后的学生网络性能分别提高了7.69%和7.39%,且在参量更少的情况下性能也优于其他方法。Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy of light-weight Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in the classification task of Remote Sensing Images (RSI) scene, a Double Knowledge Distillation (DKD) model combined with Dual-Attention (DA) and Spatial Structure (SS) is designed in this paper. First, new DA and SS modules are constructed and introduced into ResNet101 and lightweight CNN designed as teacher and student networks respectively. Then, a DA distillation loss function is constructed to transfer DA knowledge from teacher network to student network, so as to enhance their ability to extract local features from RSI. Finally, constructing a SS distillation loss function, migrating the semantic extraction ability in the teacher network to the student network in the form of a spatial structure to enhance its ability to express the high -level semantics of the RSI. The experimental results based on two standard data sets AID and NWPU-45 show that the performance of the student network after knowledge distillation is improved by 7.57% and 7.28% respectively under the condition of 20% training proportion, and the performance is still better than other methods under the condition of fewer parameters.
-
表 1 学生网络具体参数设计
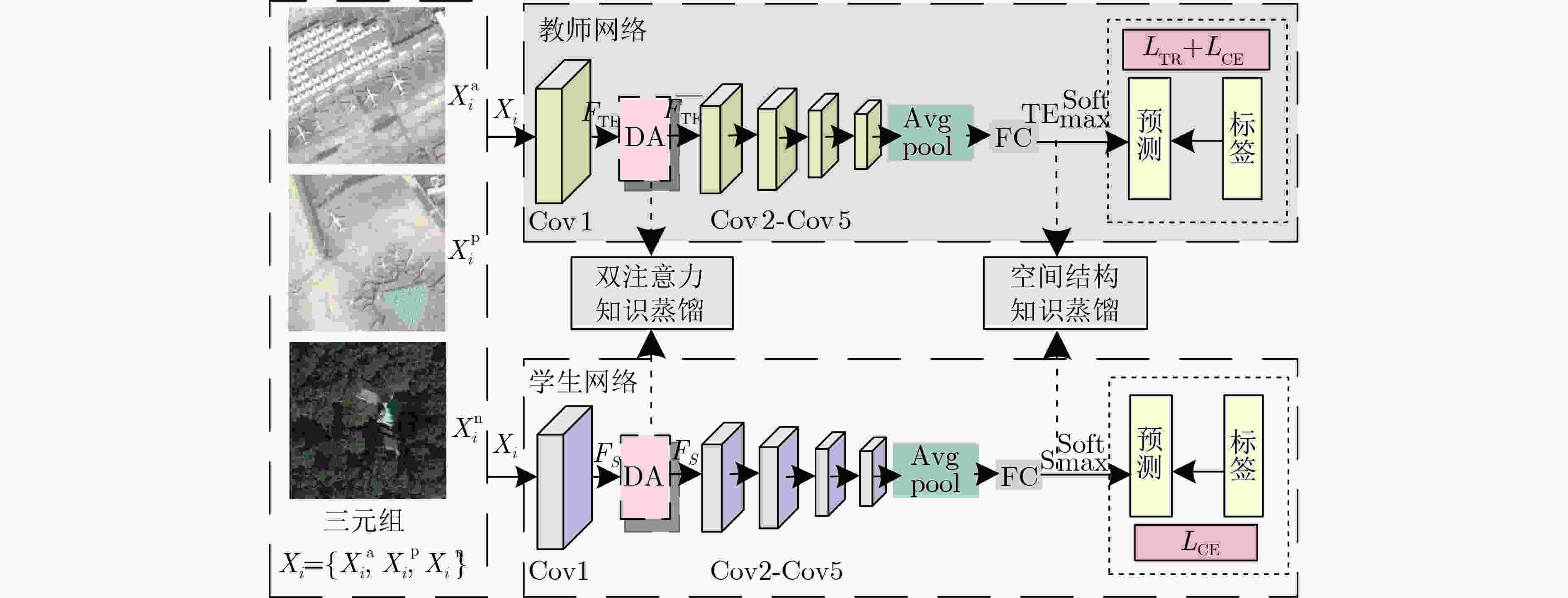
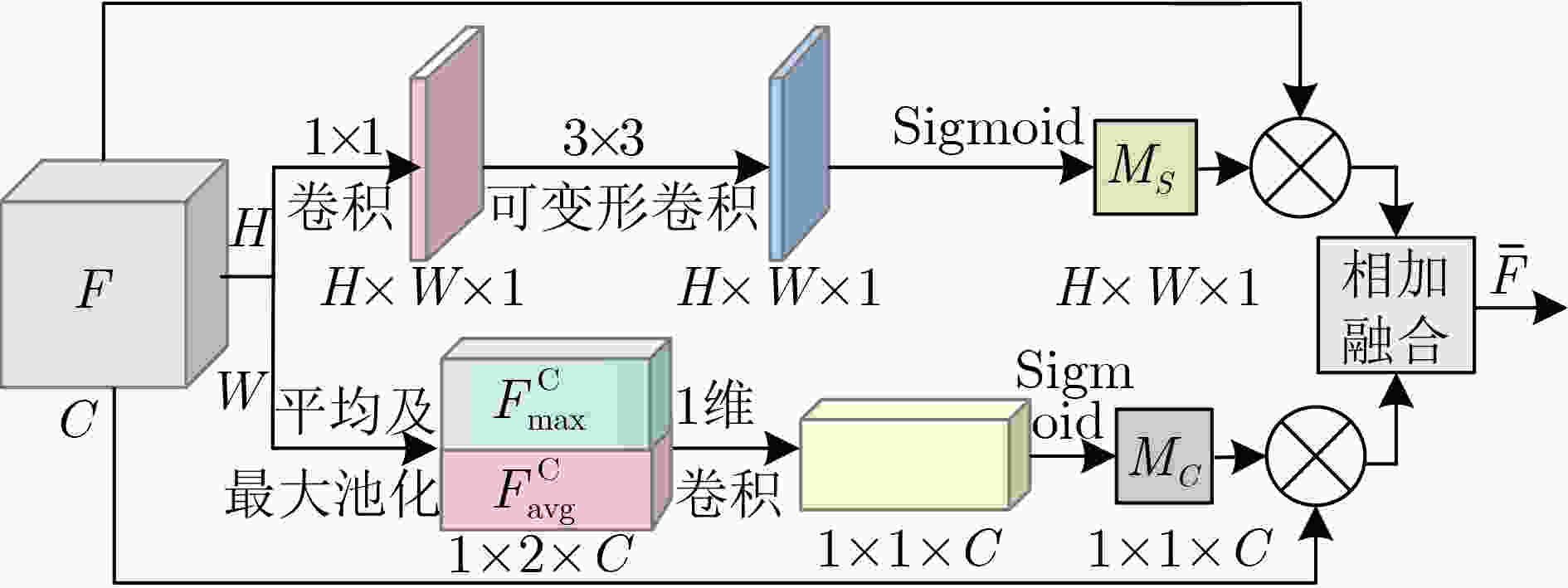
网络层名 输出尺寸 计算方法 Conv1 112×112 7×7,64,stride=2 DA 112×112 DA模块 Conv2_x 56×56 3×3 max pool, stride=2 [3×3, 64; 3×3,64] Conv3_x 28×28 [3×3, 128; 3×3,64] Conv4_x 14×14 [3×3, 256; 3×3,64] Conv5_x 7×7 [3×3, 512; 3×3,64] 1×1 average pool,45-d fc, softmax 算法1 双知识蒸馏(DKD)学生网络训练及测试 输入:训练图像$ D = \{ ({\text{IM}}{{\text{G}}_n},{y_n}):n = 1,2, \cdots ,N\} $,网络超参
(Epoches, BS与lr),测试图像
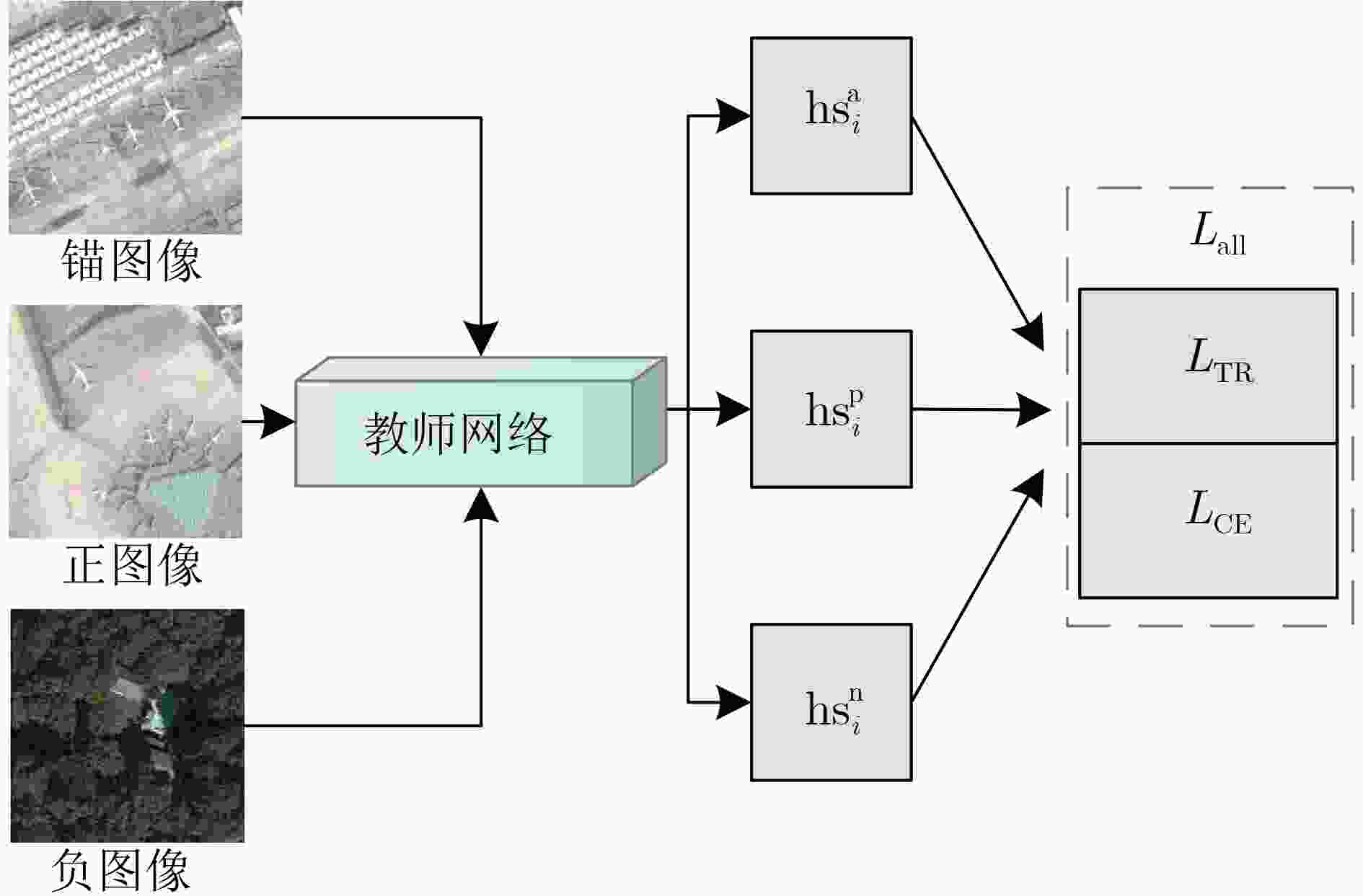
$ {\text{Tst}} = \{ ({\text{IM}}{{\text{G}}_m},{y_m}):m = 1,2, \cdots ,M\} $输出:学生网络参数${\varOmega _{\text{S} } }$及测试图像分类精度 准备:将D中的训练图像组成3元组,采用图3所示孪生框架训练
教师网络${\varOmega ^{ {\text{TE} } } }$;For epoch in Epoches: (1) 根据批大小BS,对D中的训练图像进行分批; (2) 每批图像送入教师网络${\varOmega ^{ {\text{TE} } } }$,得到的高层语义特征
${\text{Tb}} = \{ {t_i}|i = 1,2, \cdots ,{\text{BS}}\} $;(3) 每批图像送入学生网络${\varOmega _{\text{S} } }$,得到的高层语义特征
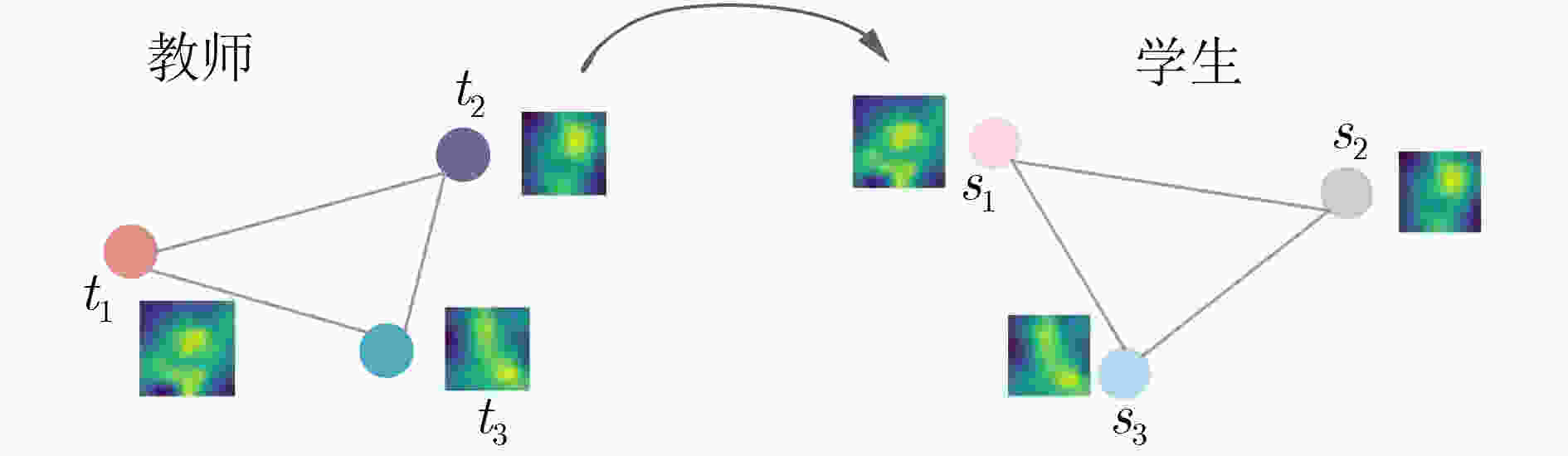
${\text{Sb}} = \{ {s_i}|i = 1,2, \cdots ,{\text{BS}}\} $及预测标签$\{ {\tilde y_i}\} _{i = 1}^{{\text{BS}}}$;(4) 用式(15)计算${L_{{\text{HTL}}}}$,优化器通过反向传播更新学生网络
参数${\varOmega _{\text{S} } }$;(5) 采用余弦衰减策略更新学习率lr。 End for (6) 对 $ \forall {\text{IM}}{{\text{G}}_m} \in {\text{Tst}} $,将${\text{IM}}{{\text{G}}_m}$输入学生网络${\varOmega _{\text{S} } }$,得到其
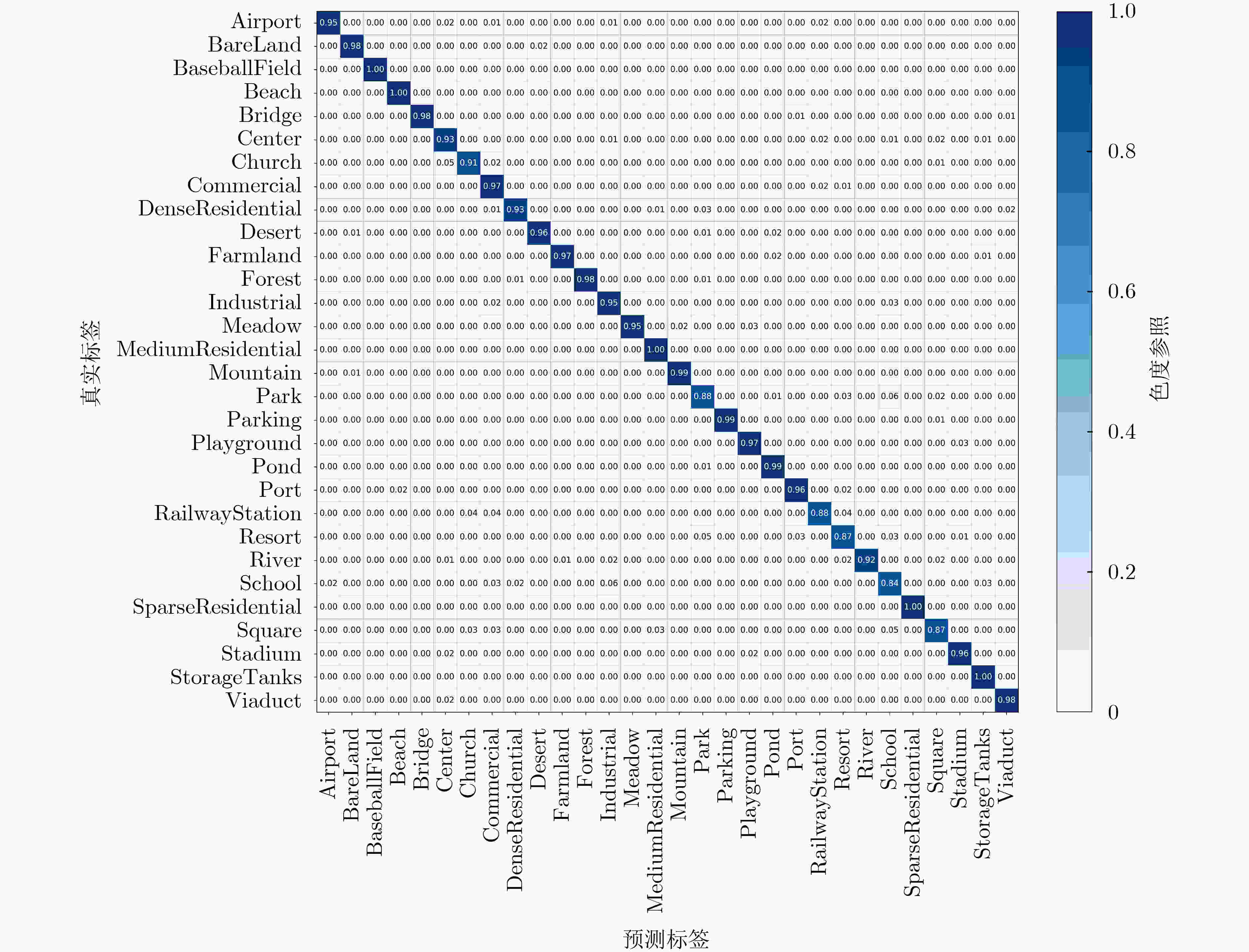
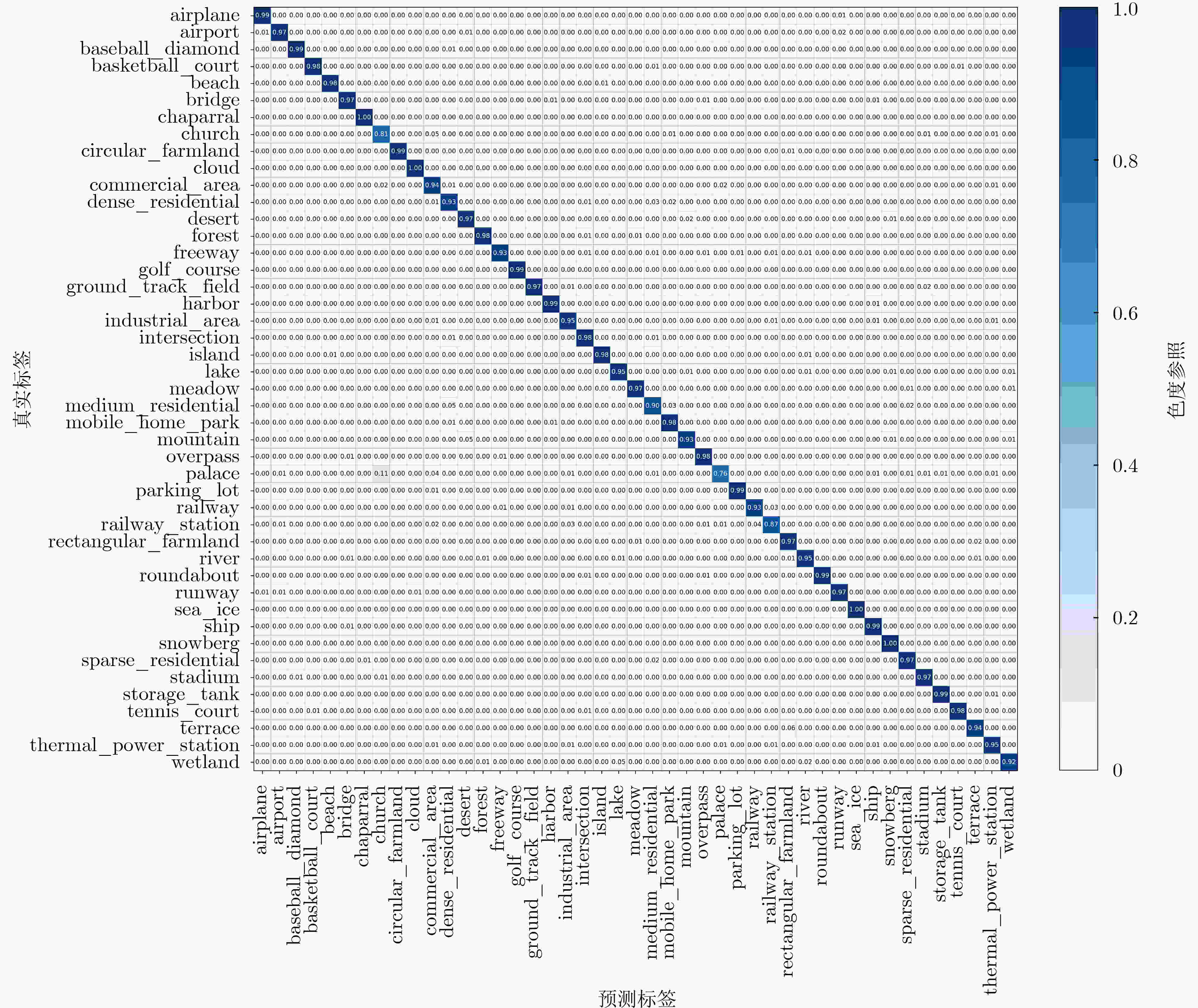
类别预测结果${ { {\tilde y} }_{{m} } }$;(7) 根据$ \{ ({\bar y_m},{y_m}):m = 1,2, \cdots ,M\} $,统计分类精度且输出。 表 2 不同训练比例下消融实验的OA值(%)
AID训练比例(%) NWPU-45训练比例(%) 20 50 10 20 基线 87.52 89.43 86.27 88.48 +DA 93.08 94.36 91.68 93.65 +SS 93.92 94.63 92.91 94.12 +DKD 95.21 97.04 93.88 95.87 教师 95.93 97.63 94.47 96.52 表 3 教师与学生网络性能比较(以AID数据集(50%)为例)
表 4 基于AID与NWPU-45数据集的综合对比实验结果(%)
方法 AID训练比例(%) NWPU-45训练比例(%) 20 50 10 20 VGG16+MSCP[22] 91.52 94.42 88.32 91.56 ARCNet-VGG[19] 88.75 93.10 85.60 90.87 CNN-CapsNet[23] 93.79 96.32 89.03 89.03 SCCov[24] 93.12 96.10 89.30 92.10 GBNet[25] 92.20 95.48 90.03 92.35 MF2Net[26] 93.82 95.93 90.17 92.73 MobileNet[20] 88.53 90.91 80.32 83.26 ViT-B-16[21] 93.81 95.90 90.96 93.36 XU et al.[27] 94.17 96.19 90.23 93.25 DKD (本文) 95.21 97.04 93.88 95.87 -
[1] 马少鹏, 梁路, 滕少华. 一种轻量级的高光谱遥感图像分类方法[J]. 广东工业大学学报, 2021, 38(3): 29–35. doi: 10.12052/gdutxb.200153MA Shaopeng, LIANG Lu, and TENG Shaohua. A lightweight hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology, 2021, 38(3): 29–35. doi: 10.12052/gdutxb.200153 [2] PAN Deng, ZHANG Meng, and ZHANG Bo. A generic FCN-based approach for the road-network extraction from VHR remote sensing images–using OpenStreetMap as benchmarks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2662–2673. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3058347 [3] 姜亚楠, 张欣, 张春雷, 等. 基于多尺度LBP特征融合的遥感图像分类[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2021, 33(3): 36–44. doi: 10.6046/zrzyyg.2020303JIANG Yanan, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Chunlei, et al. Classification of remote sensing images based on multi-scale feature fusion using local binary patterns[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2021, 33(3): 36–44. doi: 10.6046/zrzyyg.2020303 [4] CHAIB S, GU Yanfeng, and YAO Hongxun. An informative feature selection method based on sparse PCA for VHR scene classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 147–151. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2501383 [5] 李彦甫, 范习健, 杨绪兵, 等. 基于自注意力卷积网络的遥感图像分类[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(10): 81–88. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210196LI Yanfu, FAN Xijian, YANG Xubing, et al. Remote sensing image classification framework based on self-attention convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(10): 81–88. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210196 [6] XU Kejie, HUANG Hong, DENG Peifang, et al. Deep feature aggregation framework driven by graph convolutional network for scene classification in remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(10): 5751–5765. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3071369 [7] CHEN Sibao, WEI Qingsong, WANG Wenzhong, et al. Remote sensing scene classification via multi-branch local attention network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 31: 99–109. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3127851 [8] CHEN Xi, XING Zhiqiang, and CHENG Yuyang. Introduction to model compression knowledge distillation[C]. 2021 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing, Xi'an, China, 2021: 1464–1467. [9] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [10] LUO Yana and WANG Zhongsheng. An improved ResNet algorithm based on CBAM[C]. 2021 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation, Xi'an, China, 2021: 121–125. [11] KE Xiao, ZHANG Xiaoling, ZHANG Tianwen, et al. SAR ship detection based on an improved faster R-CNN using deformable convolution[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 3565–3568. [12] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. [13] ZENG Weiyu, WANG Tianlei, CAO Jiuwen, et al. Clustering-guided pairwise metric triplet loss for person reidentification[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(16): 15150–15160. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3147950 [14] PARK W, KIM D, LU Yan, et al. Relational knowledge distillation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3962–3971. [15] XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945 [16] CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and State of the Art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998 [17] TUN N L, GAVRILOV A, TUN N M, et al. Remote sensing data classification using A hybrid pre-trained VGG16 CNN-SVM classifier[C]. 2021 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, St. Petersburg, Russia, 2021: 2171–2175. [18] LV Pengyuan, WU Wenjun, ZHONG Yanfei, et al. SCViT: A spatial-channel feature preserving vision transformer for remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4409512. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3157671 [19] WANG Qi, LIU Shaoteng, CHANUSSOT J, et al. Scene classification with recurrent attention of VHR remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1155–1167. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864987 [20] PAN Haihong, PANG Zaijun, WANG Yaowei, et al. A new image recognition and classification method combining transfer learning algorithm and mobilenet model for welding defects[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 119951–119960. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005450 [21] DOSOVITSKI A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C/OL]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [22] HE Nanjun, FANG Leyuan, LI Shutao, et al. Remote sensing scene classification using multilayer stacked covariance pooling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(12): 6899–6910. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2845668 [23] ZHANG Wei, TANG Ping, and ZHAO Lijun. Remote sensing image scene classification using CNN-CapsNet[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 494. doi: 10.3390/rs11050494 [24] HE Nanjun, FANG Leyuan, LI Shutao, et al. Skip-connected covariance network for remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(5): 1461–1474. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2920374 [25] SUN Hao, LI Siyuan, ZHENG Xiangtao, et al. Remote sensing scene classification by gated bidirectional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(1): 82–96. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931801 [26] XU Kejie, HUANG Hong, LI Yuan, et al. Multilayer feature fusion network for scene classification in remote sensing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(11): 1894–1898. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2960026 [27] XU Chengjun, ZHU Guobin, and SHU Jingqian. A lightweight intrinsic mean for remote sensing classification with lie group kernel function[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 18(10): 1741–1745. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3007775 [28] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
