Overview on Intelligent Wireless Resource Management of Millimeter Wave Communications under High-speed Railway
-
摘要: 为满足高速铁路智能化发展对铁路移动通信系统提出的新需求,基于第5代(5G)无线通信技术的高铁移动网络将采用宽带毫米波频段以提高传输容量。基于此,该文首先结合高铁传输需求及场景特殊性,分析了定向毫米波通信在网络覆盖鲁棒性、移动支持能力及链路稳定性与管理方面的问题。然后,探讨了通过融合传统6 GHz以下频段(简称sub-6 GHz)与毫米波频段以兼顾网络覆盖与传输容量的新一代高铁无线接入网络架构,其中全向覆盖的sub-6GHz频段提供鲁棒覆盖,定向毫米波通信提升传输速率。最后,在该网络架构基础上,研究了如何利用深度学习算法进行业务特征与传输环境的预测,并智能决策sub-6 GHz与毫米波双频段的无线资源分配、波束对齐及切换优化,最终实现高可靠、低时延、大容量新一代高铁移动通信系统。Abstract: To satisfy the new requirements brought by the intelligent development of high-speed railways, future railway mobile networks based on the Fifth Generation (5G) wireless technologies will apply broadband millimeter wave bands to enhance the transmission capability. Therefore, in this paper, considering the transmission requirements and scenario characteristics of high-speed railways, the problems of millimeter wave communications in network coverage robustness, mobility support capability, link stability and management are analyzed. Then, to guarantee the network coverage while improving the transmission capacity, future high-speed railway wireless network architecture based on the integration of conventional sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave bands is discussed, where the omni-directional sub-6 GHz bands provide robust coverage, and the directional millimeter wave communications improve transmission rate. Finally, under this network architecture, this paper investigates how to employ deep learning algorithms to predict the service characteristics and propagation environments, and make decisions for radio resource allocation, beam alignment, and handover optimization for sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave bands, to realize eventually the high reliability, low latency, and large capacity for the future high-speed railway mobile systems.
-
表 1 面向高铁毫米波通信的相关研究
研究内容 关键技术与智能算法 达成目标 参考文献 通信网络架构 网络切片
控制面与数据面解耦
sub-6 GHz与毫米波融合
云接入网络架构
车车通信实现定制化服务
大幅度提升容量
保障移动性能
满足应急通信需求[12,13,15,16] 业务与信道特征 业务预测,长短期记忆网络(Long Short
Term Memory, LSTM)及变种等
信道预测,LSTM及变种等
智能反射面,强化学习等预测传输需求
预测传输环境
改变传输环境[22,23,27–32] 无线资源分配 区分业务的资源调度,强化学习等
网络切片资源预留,强化学习等保障资源可用性
保障资源隔离性[40–47] 切换优化 切换参数自适应优化,深度神经网络等
快速波束对齐、跟踪,强化学习等提高切换成功率
提高链路稳定性[51–55] 表 2 业务预测时间尺度与预测算法需求及网络资源配置
业务预测时间尺度 预测算法需求 网络资源配置 大尺度 (周、月) 指数平滑、线性回归、
支持向量机等网络功能单元配置、工作频段及
带宽配置、RRU资源配置等中尺度 (分、时) LSTM算法及其变种等 为不同切片预留网络功能模块、
为不同切片预留传输带宽等小尺度 (毫秒、秒) LSTM算法及其变种等 时隙分配、子载波分配、空间流分配、
功率分配、调制编码方式等表 3 业务预测参数设置
切片
类型业务参数(模式1/模式2/模式3) URLLC切片 数据包个数:均匀分布 (4000, 4500)/ (1500, 2000)/(500,600)
包内字节数(B): 均匀分布(500, 600)/ (100, 200)/(20,30)
移动速度(m/s): 均匀分布(100, 138)/ (10, 30)/ (1, 3)
用户量: 均匀分布(2, 5)/ (2, 8)/ (6, 16)eMBB切片 数据包个数:泊松分布(密度) 6000/ 2400/240
包内字节数(B): 均匀分布(3000, 3500)/ (300, 400)/(100,200)
移动速度(m/s): 均匀分布(100, 138)/ (10, 30)/ (1, 3)
用户量: 均匀分布(2, 5)/ (2, 8)/ (6, 16)mMTC切片 数据包个数:均匀分布 (200, 500)/ (1000, 1100)/(10,100)
包内字节数(B): 均匀分布(100, 110)/ (200, 210)/(50,70)
移动速度(m/s): 均匀分布(100, 138)/ (10, 20)/ 0
用户量: 均匀分布(4, 10)/ (1, 10)/ (1, 20) -
[1] HE Ruisi, AI Bo, WANG Gongpu, et al. High-speed railway communications: From GSM-R to LTE-R[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2016, 11(3): 49–58. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2016.2564446 [2] RAPPAPORT T S, SUN Shu, MAYZUS R, et al. Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: It will work![J]. IEEE Access, 2013, 1: 335–349. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2013.2260813 [3] AI Bo, MOLISCH A F, RUPP M, et al. 5G key technologies for smart railways[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(6): 856–893. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.2988595 [4] 卢永忠, 戚建淮, 胡福强, 等. 探索毫米波通信技术在高铁旅客服务中的应用[J]. 铁道通信信号, 2018, 54(5): 50–53. doi: 10.13879/j.issn1000-7458.2018-05.17567LU Yongzhong, QI Jianhuai, HU Fuqiang, et al. Application of millimeter wave communication in high-speed railway passenger services[J]. Railway Signalling &Communication, 2018, 54(5): 50–53. doi: 10.13879/j.issn1000-7458.2018-05.17567 [5] 3GPP TR 38. 913 (V17.0. 0), Technical specification group radio access network. Study on scenarios and requirements for next generation access technologies (Release 17), 2022. [6] CHEN W E, FAN Xiangyuan, and CHEN Lixian. A CNN-based packet classification of eMBB, mMTC and URLLC applications for 5G[C]. 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and its Emerging Applications, Tainan, China, 2019: 140–145. [7] WANG Chengxiang, GHAZAL A, AI Bo, et al. Channel measurements and models for high-speed train communication systems: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(2): 974–987. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2508442 [8] 闫莉, 方旭明. 高铁基于毫米波的自适应波束分合传输方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(1): 146–152. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150396YAN Li and FANG Xuming. Adaptive beam splitting or integrating scheme for railway millimeter wave wireless communications[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 146–152. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150396 [9] SONG Hao, FANG Xuming, and FANG Yuguang. Millimeter-wave network architectures for future high-speed railway communications: Challenges and solutions[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2016, 23(6): 114–122. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2016.1500255WC [10] 艾渤, 章嘉懿, 何睿斯, 等. 面向智能高铁业务和应用的5G基础理论与关键技术[J]. 中国科学基金, 2020, 34(2): 133–141. doi: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2020.02.003AI Bo, ZHANG Jiayi, HE Ruisi, et al. Fundamental theory and key technologies of 5G for service and application of intelligent high-speed railway[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2020, 34(2): 133–141. doi: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2020.02.003 [11] GUAN Ke, AI Bo, PENG Bile, et al. Towards realistic high-speed train channels at 5G millimeter-wave band—Part II: Case study for paradigm implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(10): 9129–9144. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2865530 [12] VALASTRO G C, PANNO D, and RIOLO S. A SDN/NFV based C-RAN architecture for 5G Mobile networks[C]. 2018 International Conference on Selected Topics in Mobile and Wireless Networking, Tangier, Morocco, 2018: 1–8. [13] WANG Kai, LIU Liu, HAN Botao, et al. High-speed railway communication based on dynamic mapping of BBU-RRH using cloud radio access network[C]. The 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2019: 901–905. [14] LAURIDSEN M, GIMENEZ L C, RODRIGUEZ I, et al. From LTE to 5G for connected mobility[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(3): 156–162. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600778CM [15] SONG Hao, FANG Xuming, and YAN Li. Handover scheme for 5G C/U plane split heterogeneous network in high-speed railway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(9): 4633–4646. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2315231 [16] YAN Li, FANG Xuming, and FANG Yuguang. Control and data signaling decoupled architecture for railway wireless networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(1): 103–111. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2015.7054725 [17] YAN Li, FANG Xuming, WANG Xianbin, et al. AI-enabled Sub-6-GHz and mm-Wave hybrid communications: Considerations for use with future HSR wireless systems[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2020, 15(3): 59–67. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2020.2969528 [18] ZHANG Jianping, SHEN Chunzi, WANG Shuo, et al. The design and performance test of train control data communication systems based on train-to-train communication[C]. 2020 Chinese Automation Congress, Shanghai, China, 2020: 588–592. [19] WANG Xiaoxuan, LIU Lingjia, TANG Tao, et al. Enhancing communication-based train control systems through train-to-train communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(4): 1544–1561. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2856635 [20] XU Chenren, WANG Jing, MA Zhiyao, et al. A first look at disconnection-centric TCP performance on high-speed railways[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(12): 2723–2733. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3005486 [21] XU Junyi, WEI Zhenchun, LYU Z W, et al. Throughput maximization of offloading tasks in multi-access edge computing networks for high-speed railways[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(9): 9525–9539. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3101571 [22] WANG Wei, ZHOU Conghao, HE Hongli, et al. Cellular traffic load prediction with LSTM and gaussian process regression[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. [23] ZHANG He and WONG V W S. A two-timescale approach for network slicing in C-RAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6656–6669. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2985289 [24] 黄阿琼, 关伟. 不同时间尺度下短期交通流的可预测性[J]. 系统工程, 2010, 28(5): 75–80.HUANG Aqiong and GUAN Wei. The predictability of short-term traffic flow in different temporal scales[J]. Systems Engineering, 2010, 28(5): 75–80. [25] BERLIN E and VAN LAERHOVEN K. Sensor networks for railway monitoring: Detecting trains from their distributed vibration footprints[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems, Cambridge, USA, 2013: 80–87. [26] ZHOU Tao, TAO Cheng, SALOUS S, et al. Implementation of an LTE-based channel measurement method for high-speed railway scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(1): 25–36. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2015.2477166 [27] ZHOU Tao, ZHANG Haitong, AI Bo, et al. Deep-learning-based spatial-temporal channel prediction for smart high-speed railway communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(7): 5333–5345. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3139384 [28] XUE Chen, ZHOU Tao, ZHANG Haitong, et al. Deep learning based channel prediction for massive MIMO systems in high-speed railway scenarios[C]. The 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Helsinki, Finland, 2021: 1–5. [29] MA Zheng, WU Yanliang, XIAO Ming, et al. Interference suppression for railway wireless communication systems: A reconfigurable intelligent surface approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(11): 11593–11603. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3111646 [30] 王丹, 梁家敏, 梅志强, 等. 基于矢量近似消息传递的智能反射面辅助毫米波信道估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2400–2406. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211271WANG Dan, LIANG Jiamin, MEI Zhiqiang, et al. Millimeter-wave channel estimation with intelligent reflecting surface assisted based on vector approximate message passing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2400–2406. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211271 [31] XU Jianpeng and AI Bo. When mmwave high-speed railway networks meet reconfigurable intelligent surface: A deep reinforcement learning method[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(3): 533–537. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3135602 [32] 王靖瑜, 鞠宏浩, 方旭明. 智能反射面在高铁通信下的应用研究[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2021, 27(4): 14–17,35. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202104004WANG Jingyu, JU Honghao, and FANG Xuming. Applications of intelligent reflecting surface in high-speed railway communications[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2021, 27(4): 14–17,35. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202104004 [33] GUAN Ke, AI Bo, PENG Bile, et al. Towards realistic high-speed train channels at 5G millimeter-wave band—Part I: Paradigm, significance analysis, and scenario reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(10): 9112–9128. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2865498 [34] PARK J J, LEE J, KIM K W, et al. Large- and small-scale fading characteristics of mmwave HST propagation channel based on 28-GHz measurements[C]. The 2021 15th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Dusseldorf, Germany, 2021: 1–5. [35] HE Danping, AI Bo, GUAN Ke, et al. Channel measurement, simulation, and analysis for high-speed railway communications in 5G millimeter-wave band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(10): 3144–3158. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2771559 [36] ALI A, GONZÁLEZ-PRELCIC N, and HEATH R W. Millimeter wave beam-selection using out-of-band spatial information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(2): 1038–1052. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2773532 [37] MASCHIETTI F, GESBERT D, and DE KERRET P. Coordinated beam selection in millimeter wave multi-user MIMO using out-of-band information[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. [38] LI Tianyou, XU Youyun, TONG Huawei, et al. Low-band information and historical data aided non-uniform millimeter wave beam selection algorithm in 5G-R high-speed railway communication scene[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 2809–2823. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3138152 [39] LIU Ziyue and FAN Pingzhi. An effective handover scheme based on antenna selection in ground–train distributed antenna systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(7): 3342–3350. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2300154 [40] WANG Ke, LI Suoping, LIN Ying, et al. Performance analysis of high-speed railway handover scheme with different network architecture[C]. The 2019 IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, Chongqing, China, 2019: 1894–1898. [41] 张睿, 马钰昕, 黄辉, 等. LTE-M系统的通信时延分析[J]. 工业控制计算机, 2018, 31(5): 20–22,24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-182X.2018.05.008ZHANG Rui, MA Yuxin, HUANG Hui, et al. Communication delay analysis of LTE-M system[J]. Industrial Control Computer, 2018, 31(5): 20–22,24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-182X.2018.05.008 [42] 李莎莎, 方旭明, 罗万团. 一种提升高速铁路无线通信网络HARQ性能的方法[J]. 铁道学报, 2014, 36(10): 53–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.10.009LI Shasha, FANG Xuming, and LUO Wantuan. Method for improving HARQ performance of mobile communication system of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(10): 53–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.10.009 [43] GARCIA M H C, MOLINA-GALAN A, BOBAN M, et al. A tutorial on 5G NR V2X communications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(3): 1972–2026. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3057017 [44] FENG Mingjie and MAO Shiwen. Dealing with limited backhaul capacity in millimeter-wave systems: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(3): 50–55. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1800565 [45] XU Jianpeng and AI Bo. Artificial intelligence empowered power allocation for smart railway[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(2): 28–33. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000634 [46] HAN Shuangfeng, I C L, XIE Tian, et al. Achieving high spectrum efficiency on high speed train for 5G new radio and beyond[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(5): 62–69. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1800260 [47] SONG Haifeng and SCHNIEDER E. Availability and performance analysis of train-to-train data communication system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(7): 2786–2795. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2914701 [48] WANG Xiaoxuan, LIU Lingjia, ZHU Li, et al. Train-centric CBTC meets age of information in train-to-train communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(10): 4072–4085. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2936219 [49] ZHAO Junhui, ZHANG Yang, NIE Yiwen, et al. Intelligent resource allocation for train-to-train communication: A multi-agent deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 8032–8040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963751 [50] OH S, YOON B, KIM D, et al. Handover impact on E2E delay of multimedia service in high-speed railway system[C]. 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence, Jeju, Korea (South), 2020: 1709–1713. [51] 陈永, 陈耀, 张薇. 基于SPN的LTE-R无线通信可靠性建模与分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(9): 111–119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.09.014CHEN Yong, CHEN Yao, and ZHANG Wei. Modeling and analysis of LTE-R wireless communication reliability based on SPN[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(9): 111–119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.09.014 [52] ABDELMOHSEN A, ABDELWAHAB M, ADEL M, et al. LTE handover parameters optimization using q-learning technique[C]. The 2018 IEEE 61st International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Windsor, Canada, 2018: 194–197. [53] WU Cheng, CAI Xingqiang, SHENG Jie, et al. Parameter adaptation and situation awareness of LTE-R handover for high-speed railway communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(3): 1767–1781. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3026195 [54] 3GPP TR 38.804 V14.0. 0. Technical specification group radio access network; study on new radio access technology[S]. Radio Interface Protocol Aspects (Release 14), 2017. [55] YAN Li, FANG Xuming, HAO Li, et al. A fast beam alignment scheme for dual-band HSR wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 3968–3979. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2971856 -





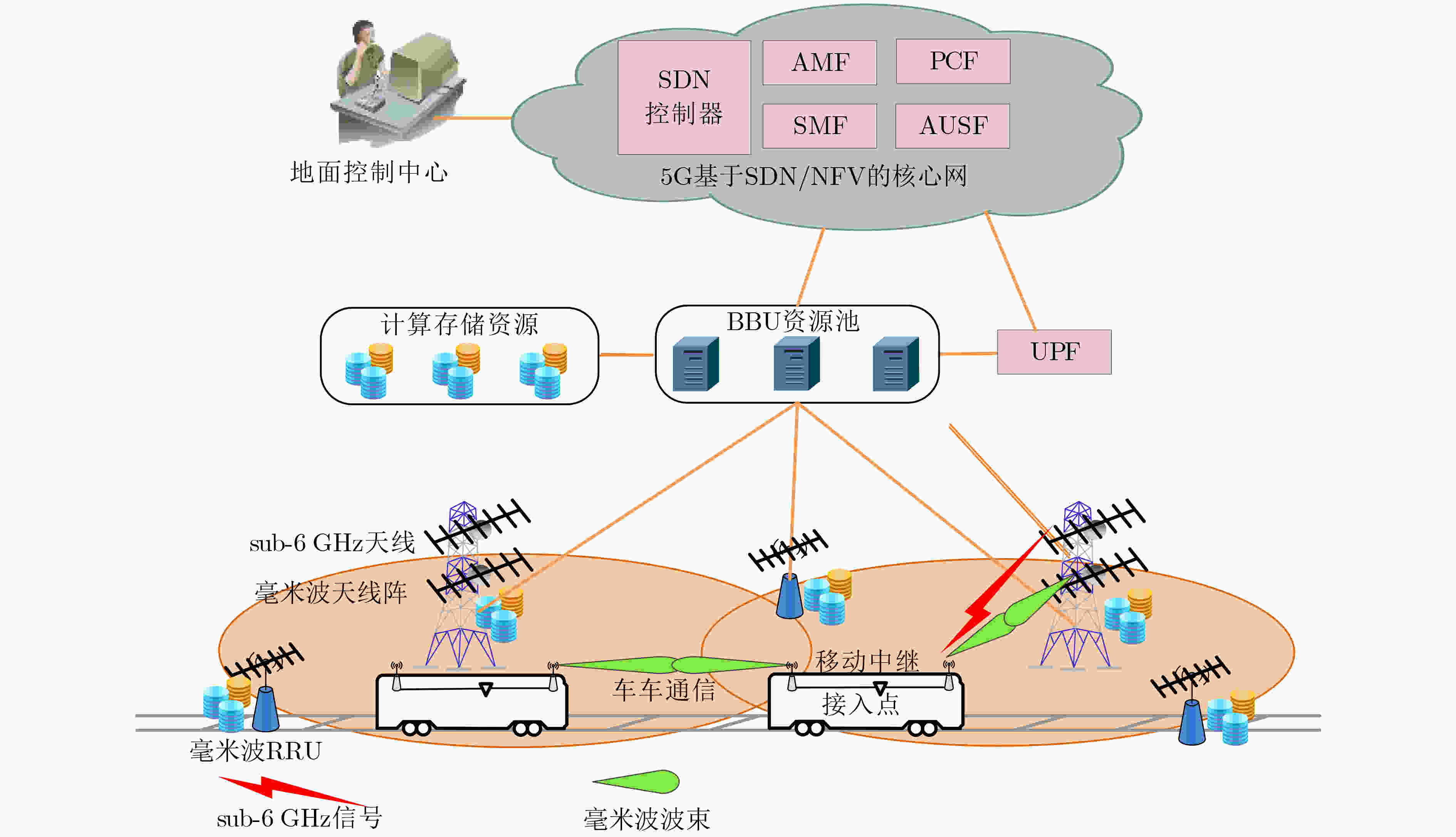
 下载:
下载:
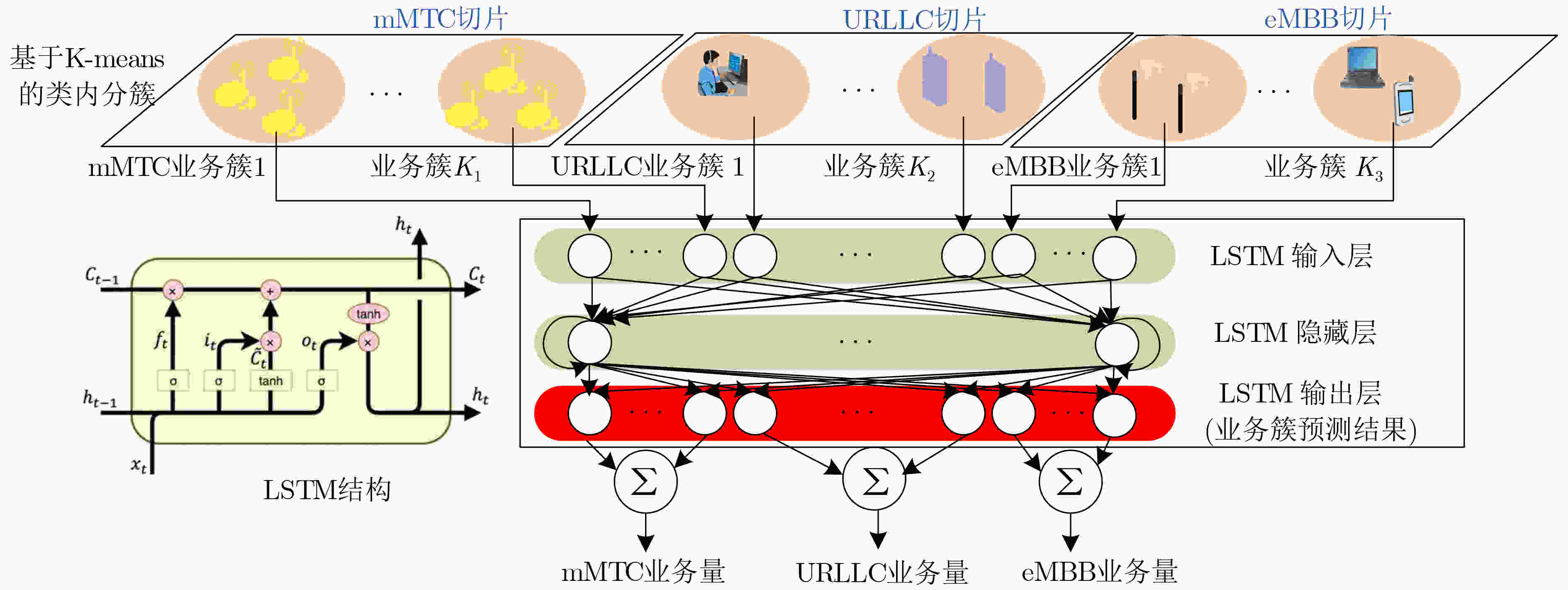
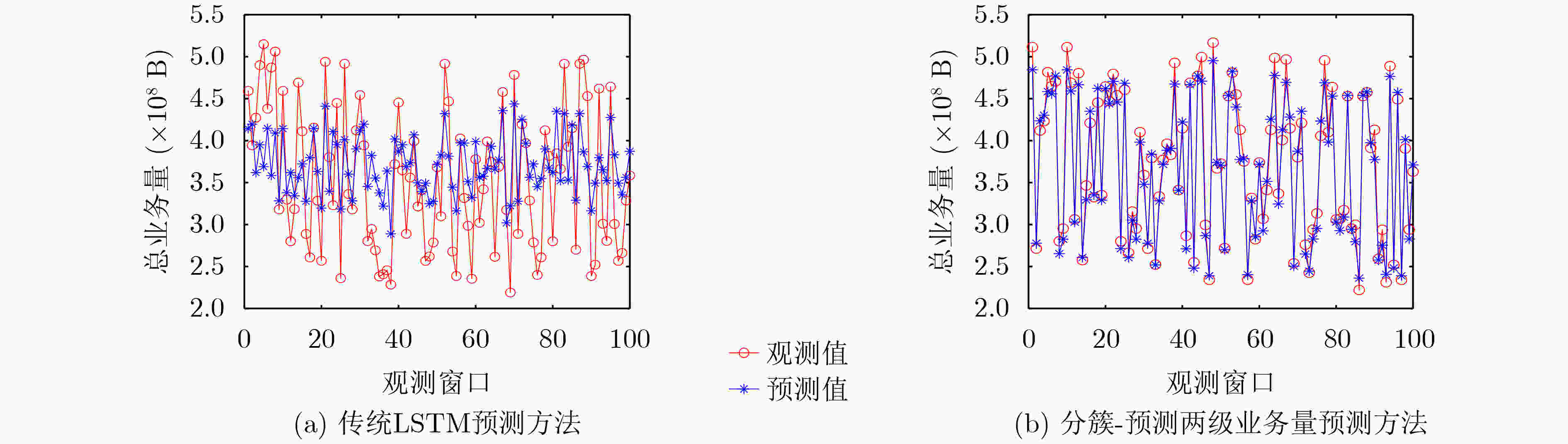
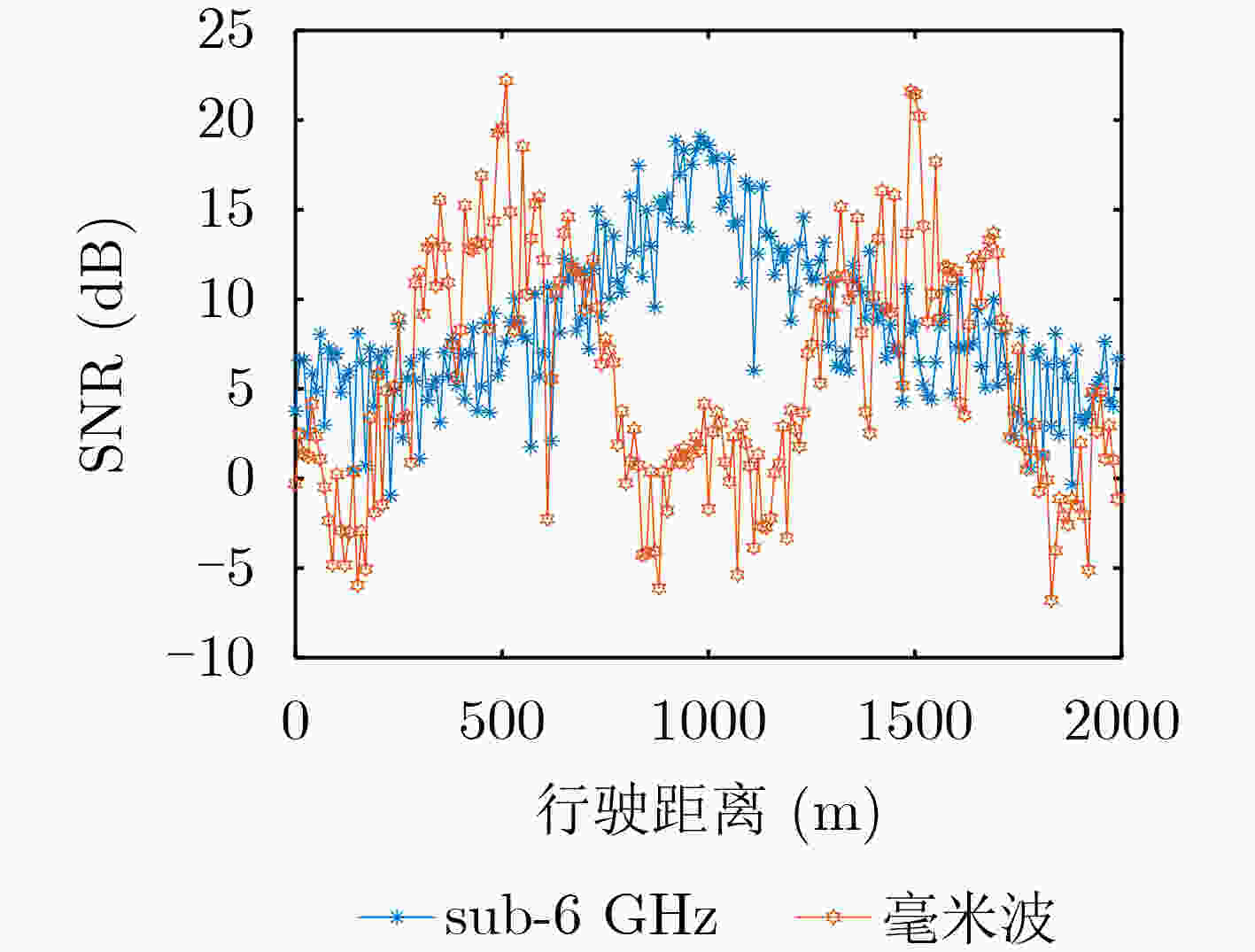
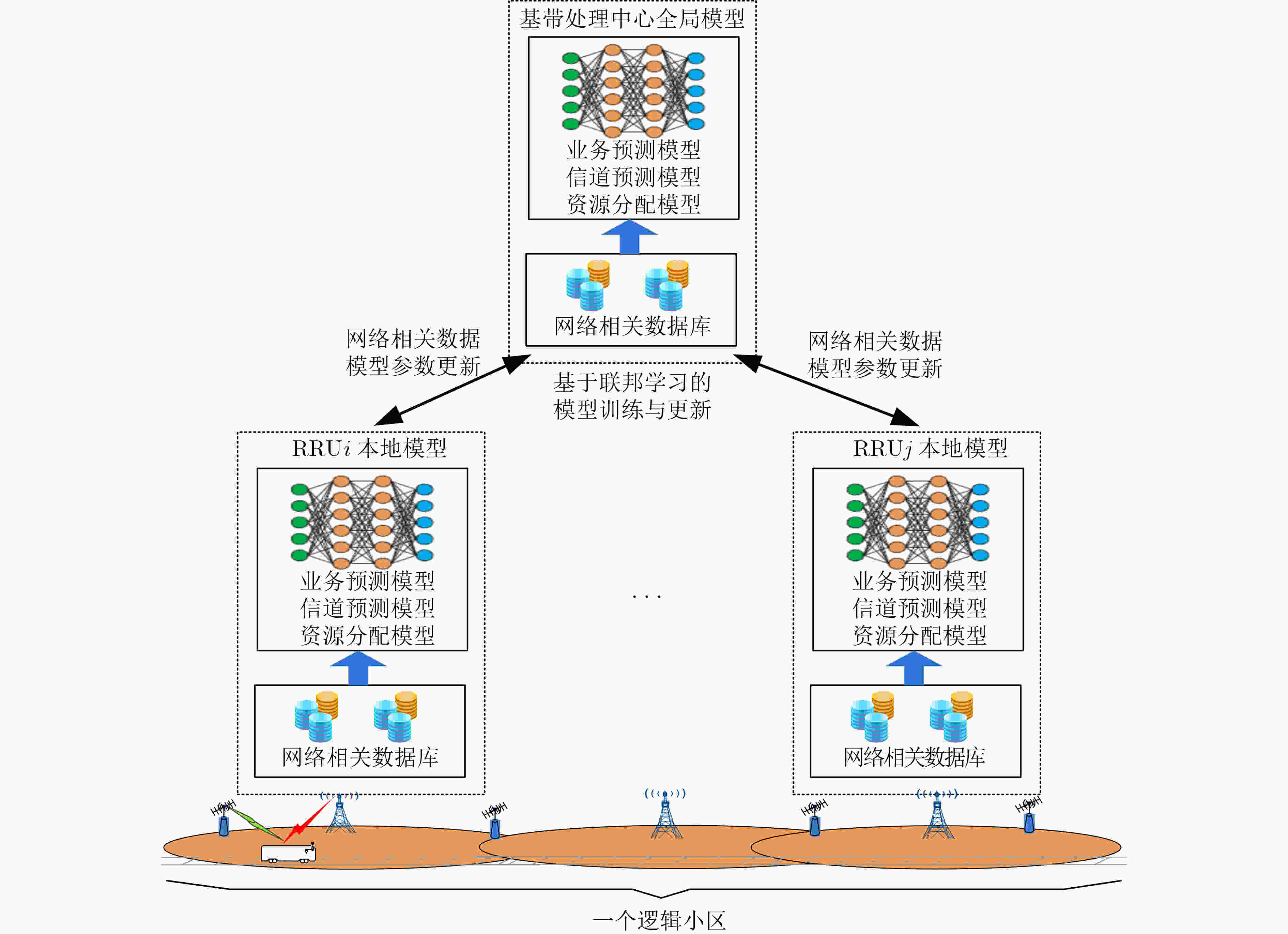
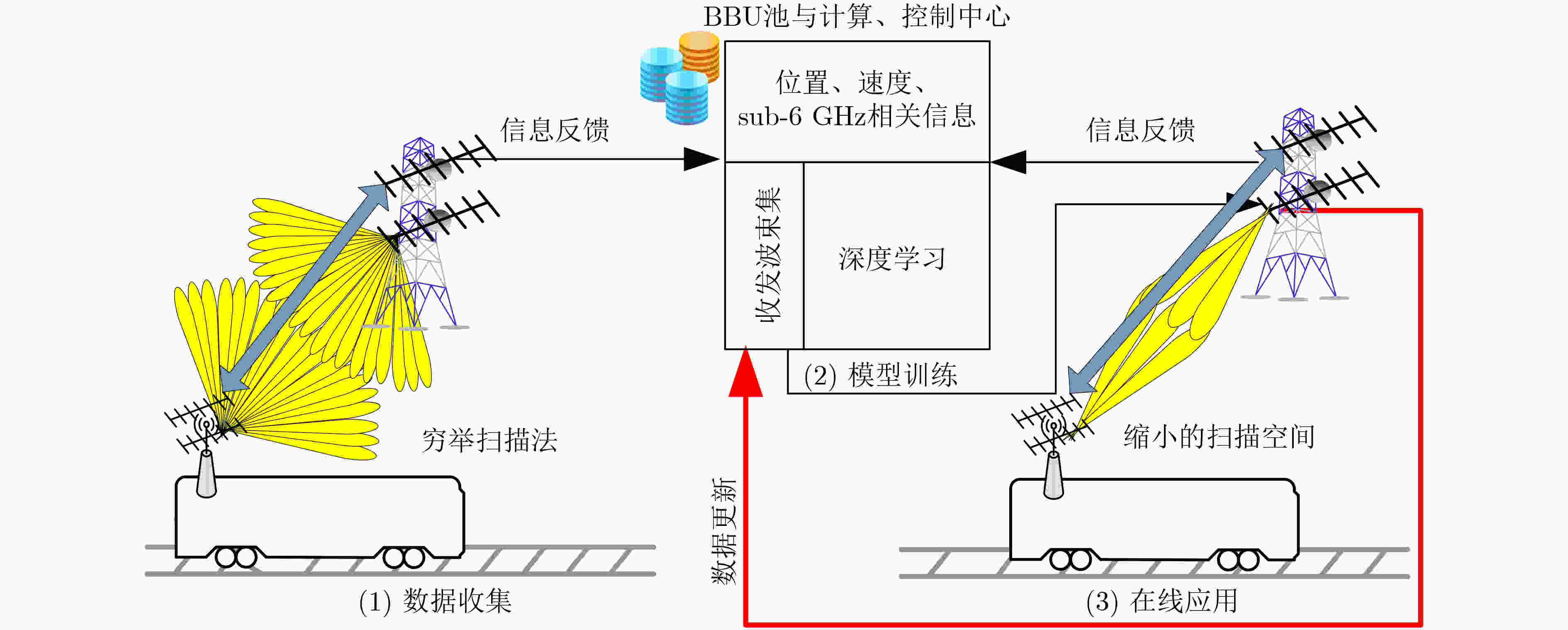


 下载:
下载:
