Infrared Small Target Detection Model with Multi-scale Fractal Attention
-
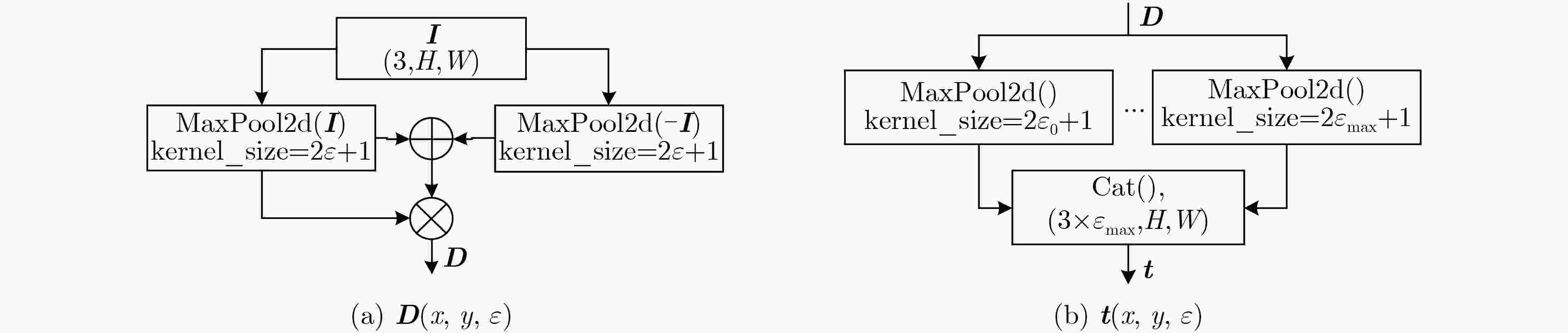
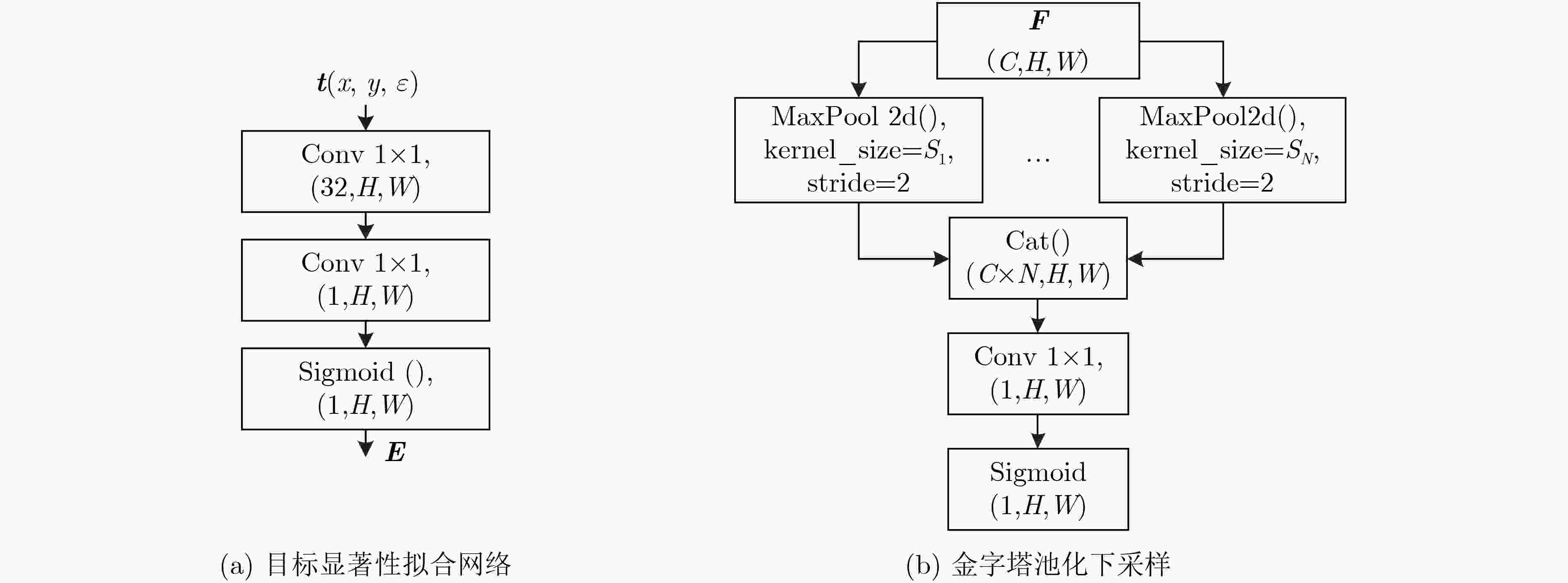
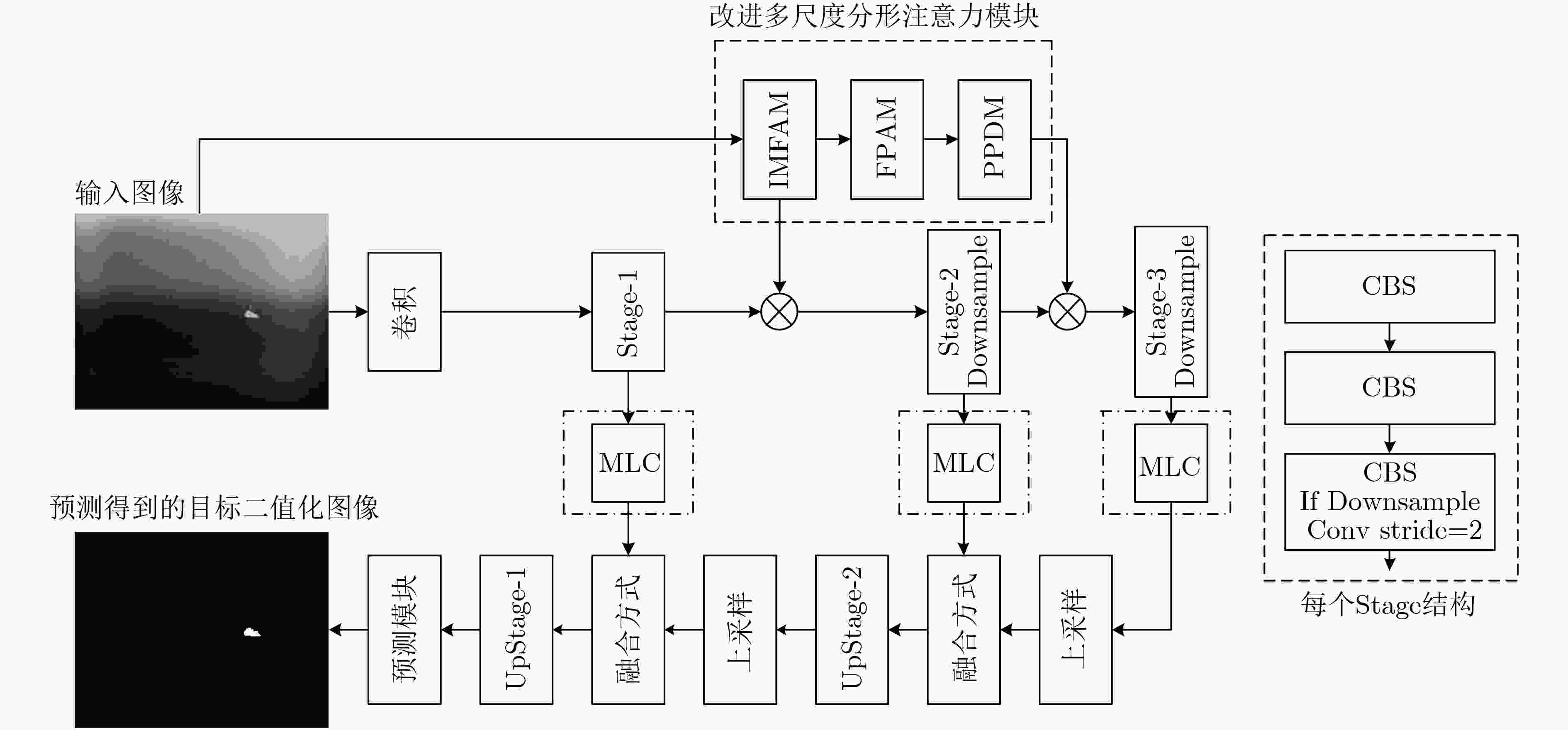
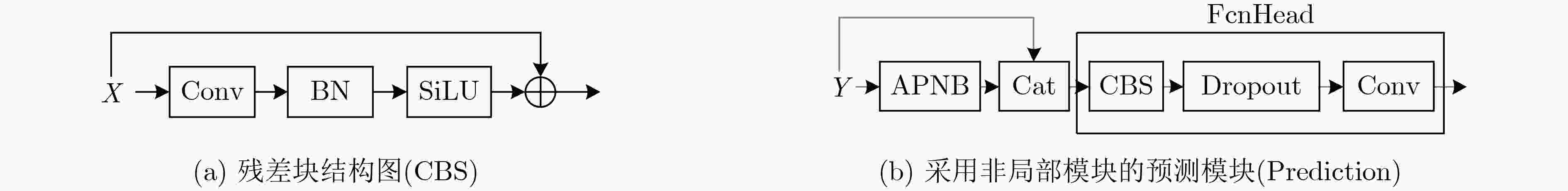
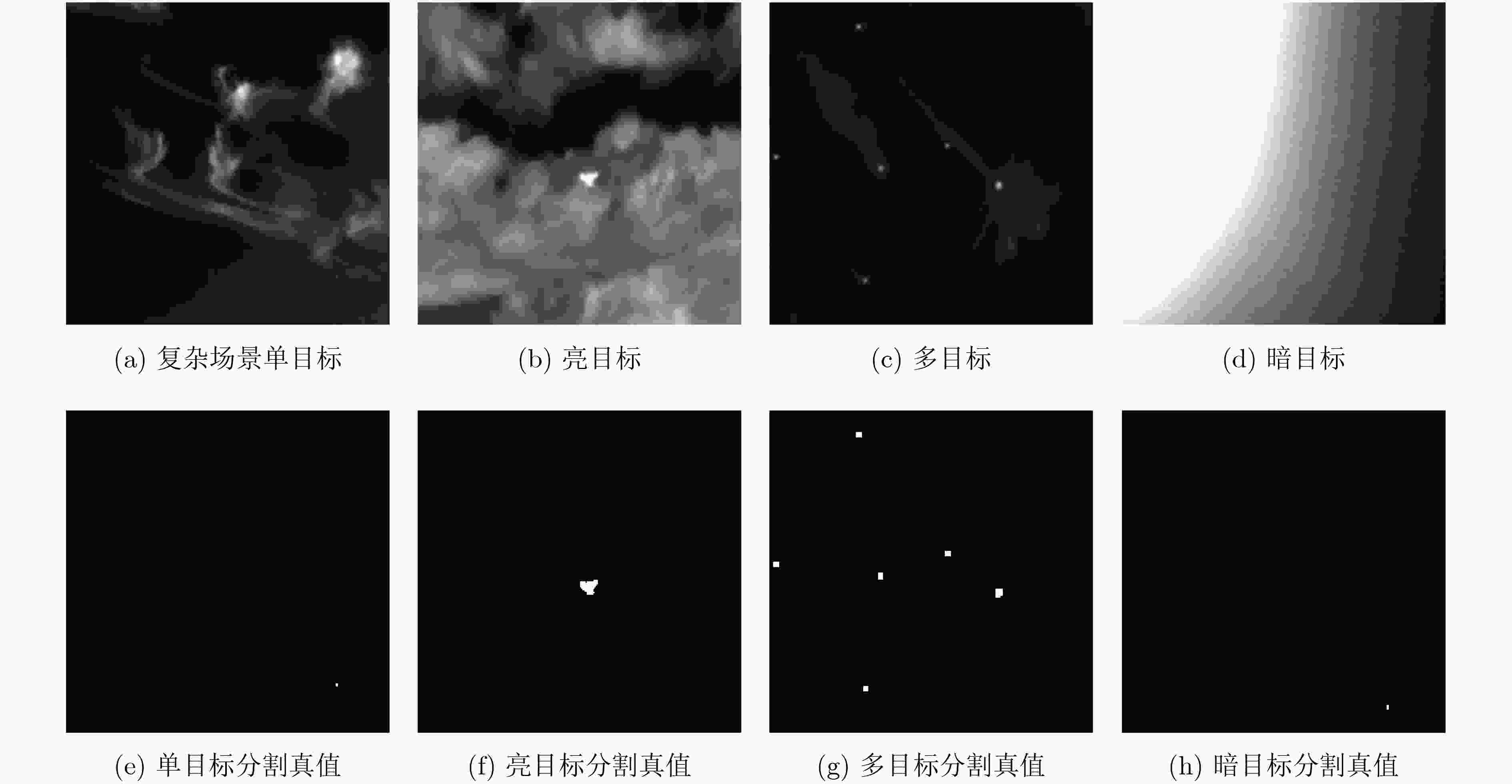
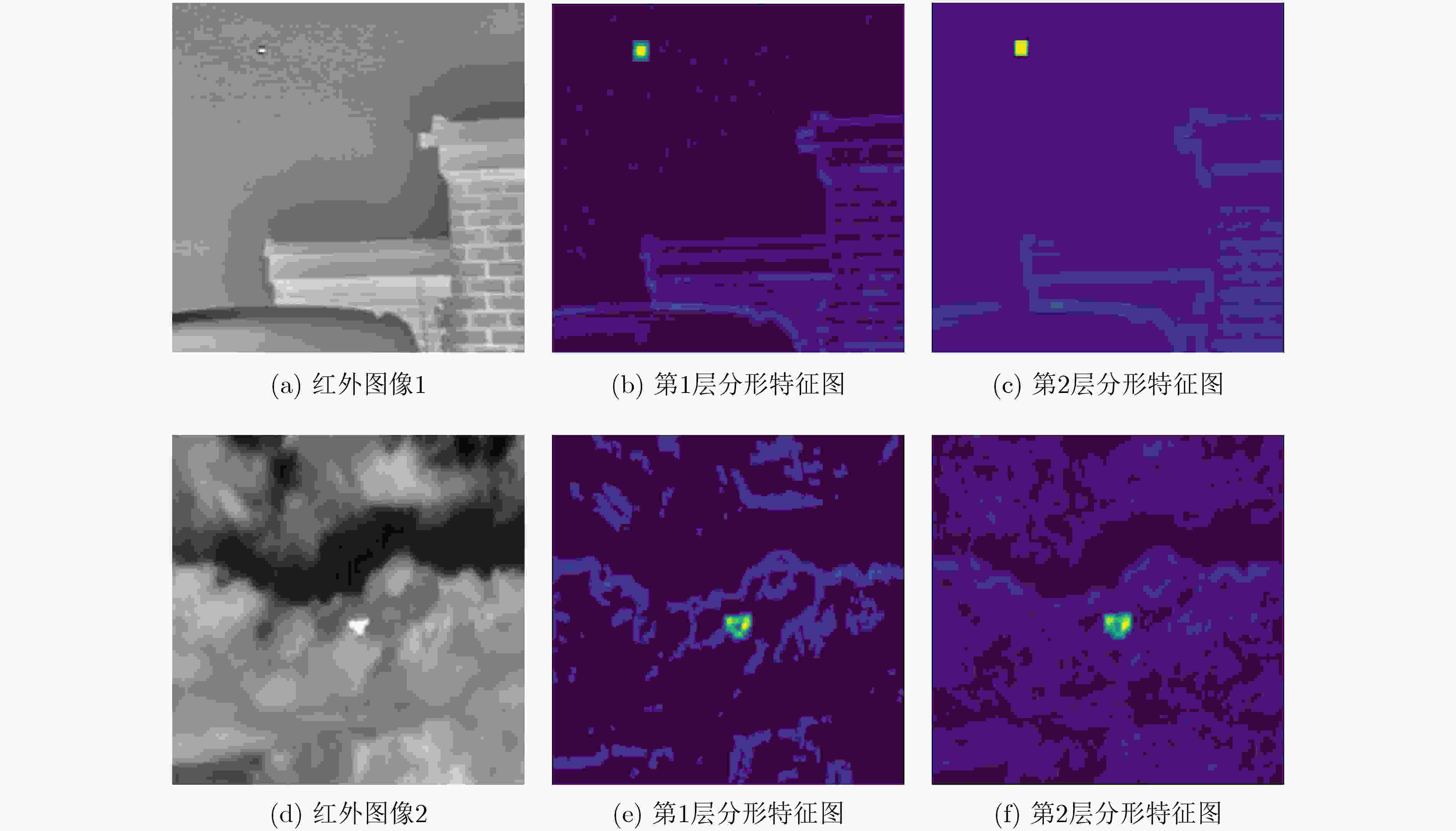
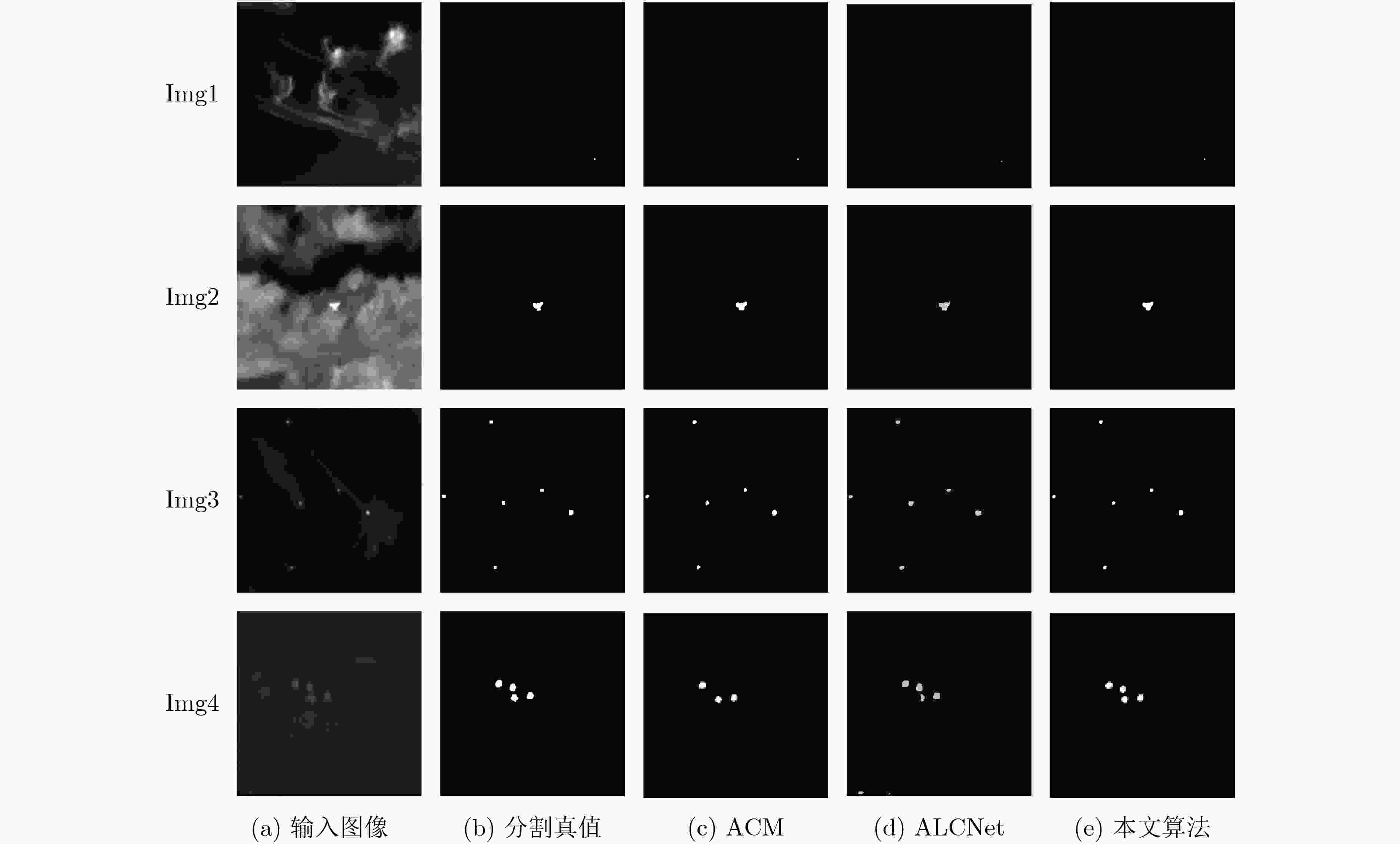
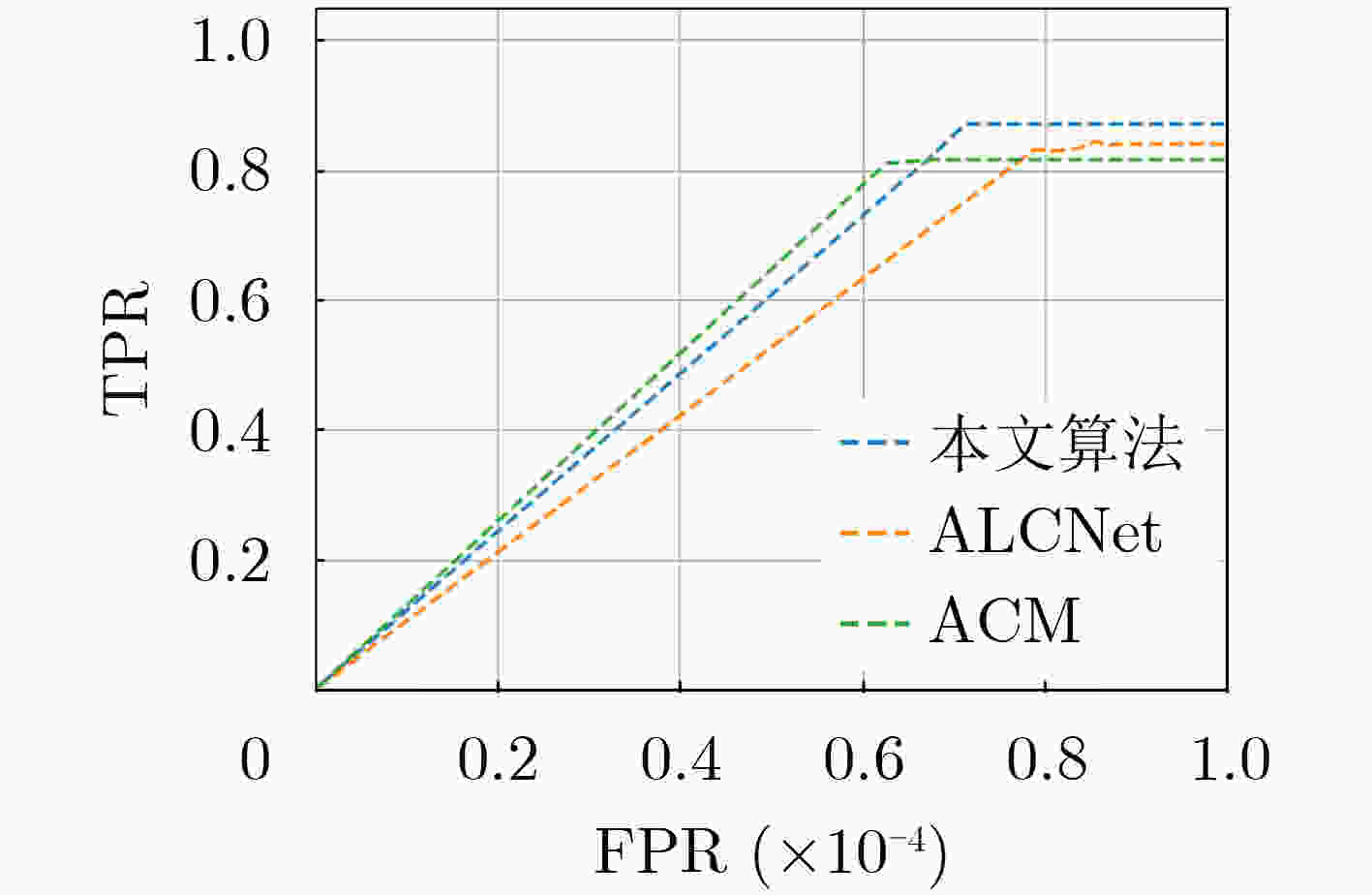
摘要: 为提高红外图像小目标检测的性能,融合传统方法的先验知识和深度学习方法的特征学习能力,该文设计了一种融合多尺度分形注意力的红外小目标端到端检测模型。首先,在对适用于红外图像弱小目标检测的多尺度分形特征分析基础上,给出了基于深度学习算子对其进行加速计算的过程。其次,设计卷积神经网络(CNN)学习度量得到目标显著性分布图,结合特征金字塔注意力模块和金字塔池化下采样模块,提出了一种基于多尺度分形特征的注意力模块。将其嵌入到红外目标语义分割模型时,采用非对称上下文融合机制提高浅层特征和深层特征的融合效果,并利用非对称金字塔非局部模块获取全局注意力,以提高红外小目标检测性能。最后,采用单帧红外小目标(SIRST)数据集验证提出算法的性能,所提模型交并比(IoU)和归一化交并比(nIoU)分别达到了77.4%和76.1%,优于目前已知方法的性能。同时通过迁移实验进一步验证了提出模型的有效性。由于有效地融合了传统方法和深度学习方法的优势,所提模型适用于复杂环境下的红外小目标检测。Abstract: In order to improve the performance of infrared image small target detection, an end-to-end infrared small target detection model that integrates multi-scale fractal attention is designed by combining prior knowledge of traditional methods and feature learning ability of deep learning methods. Firstly, the procedure of accelerating the calculation of multi-scale fractal feature with deep learning operator is proposed based on analysis of this feature, which is suitable for detecting dim and small targets in infrared images. Secondly, the Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) is designed to obtain the target significance distribution map, and a multi-scale fractal feature attention module is proposed by combining the feature pyramid attention and pyramid pooling downsampling module. When embedding it into the infrared target semantic segmentation model, asymmetric context modulation is adopted to improve fusion performance of shallow features and deep features, and asymmetric pyramid non-local block is used to obtain global attention to improve infrared small target detection performance. Finally, the performance of the proposed algorithm is verified by experiments on the Single-frame InfRared Small Target(SIRST) dataset, where Intersection over Union (IoU) and normalized IOU(nIoU) reach 77.4% and 76.1%, respectively, which is better than the performance of the currently known methods. Meanwhile, the effectiveness of the proposed model is further verified by migration experiments. Due to the effective integration of the advantages of traditional methods and deep learning methods, the proposed model is suitable for infrared small target detection in complex environments.
-
表 1 不同模块消融实验结果
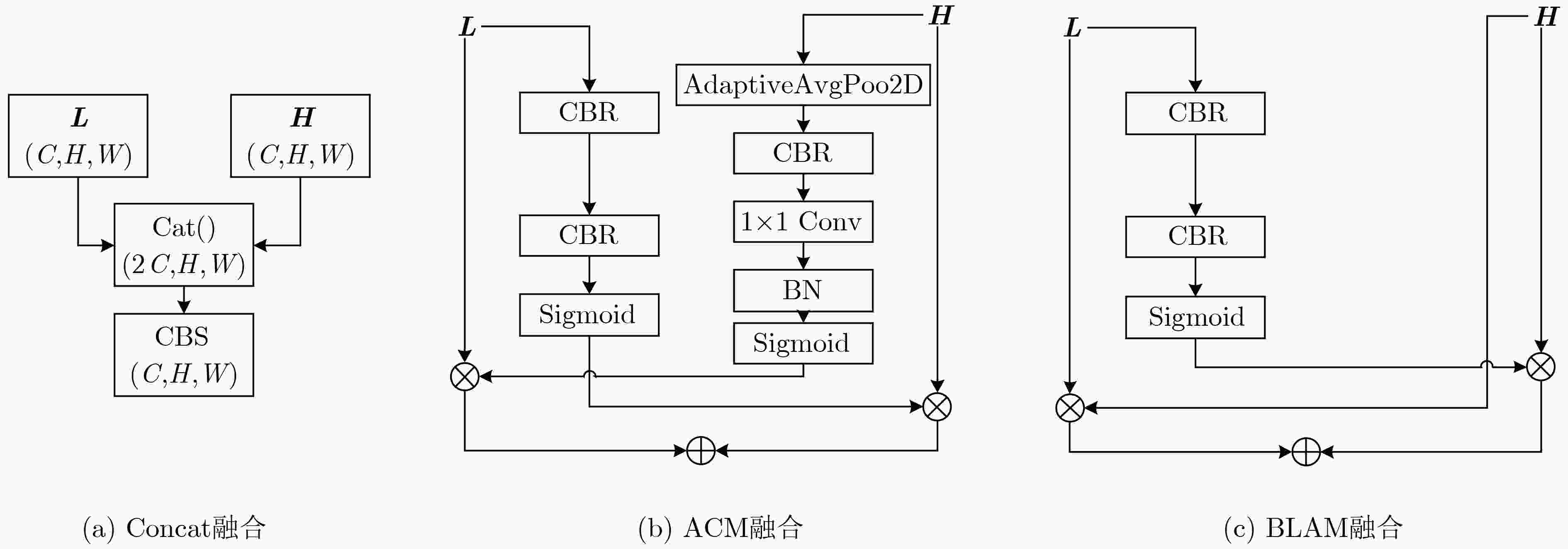
实验编号 改进多尺度分形注意力模块 融合方式 预测头 IoU nIoU 1 × Concat FcnHead 67.643 69.040 2 √ Concat FcnHead 71.842 74.656 3 √ Concat Prediction 73.636 74.649 4 × ACM FcnHead 73.450 74.083 5 √ ACM FcnHead 74.827 77.150 6 √ ACM Prediction 77.423 76.110 表 2 迁移实验结果
实验编号 改进多尺度分形注意力模块 融合方式 预测头 IoU nIoU 1 × Concat FcnHead 42.561 38.685 2 √ Concat FcnHead 43.740 36.882 3 √ Concat Prediction 46.138 40.211 4 × ACM FcnHead 46.948 42.846 5 √ ACM FcnHead 50.542 45.163 6 √ ACM Prediction 54.484 49.631 -
[1] LI Zhongmin, MEI Lifei, and SONG Mao. A survey on infrared weak small target detection method[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 945/949: 1558–1560. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.945-949.1558 [2] 李俊宏, 张萍, 王晓玮, 等. 红外弱小目标检测算法综述[J]. 中国图像图形学报, 2020, 25(9): 1739–1753. doi: 10.11834/jig.190574LI Junhong, ZHANG Ping, WANG Xiaowei, et al. Infrared small-target detection algorithms: A survey[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(9): 1739–1753. doi: 10.11834/jig.190574 [3] XU Yonghui and ZHANG J A. Real-time detection algorithm for small space targets based on max-median filter[J]. Journal of Information and Computational Science, 2014, 11(4): 1047–1055. doi: 10.12733/jics20102961 [4] 吴健, 陆书文, 芮大庆, 等. 基于背景抑制的改进Top-Hat红外小目标检测方法[J]. 电光与控制, 2018, 25(9): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2018.09.009WU Jian, LU Shuwen, RUI Daqing, et al. An improved Top-Hat infrared small target detection method based on background suppression[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2018, 25(9): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2018.09.009 [5] 侯旺, 孙晓亮, 尚洋, 等. 红外弱小目标检测技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 红外技术, 2015, 37(1): 1–10.HOU Wang, SUN Xiaoliang, SHANG Yang, et al. Present state and perspectives of small infrared targets detection technology[J]. Infrared Technology, 2015, 37(1): 1–10. [6] CHEN C L P, LI Hong, WEI Yantao, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574–581. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 [7] WEI Yantao, YOU Xinge, and LI Hong. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 58: 216–226. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.04.002 [8] GAO Chenqiang, MENG Deyu, YANG Yi, et al. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 4996–5009. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2281420 [9] WANG Huan, ZHOU Luping, and WANG Lei. Miss detection vs. false alarm: Adversarial learning for small object segmentation in infrared images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8508–8517. [10] 刘俊明, 孟卫华. 融合全卷积神经网络和视觉显著性的红外小目标检测[J]. 光子学报, 2020, 49(7): 0710003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204907.0710003LIU Junming and MENG Weihua. Infrared small target detection based on fully convolutional neural network and visual saliency[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(7): 0710003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204907.0710003 [11] DAI Yimian, WU Yiquan, ZHOU Fei, et al. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 949–958. [12] DAI Yimian, WU Yiquan, ZHOU Fei, et al. Attentional local contrast networks for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9813–9824. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3044958 [13] YU Chuang, LIU Yunpeng, WU Shuhang, et al. Infrared small target detection based on multiscale local contrast learning networks[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2022, 123: 104107. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2022.104107 [14] HUANG Lian, DAI Shaosheng, HUANG Tao, et al. Infrared small target segmentation with multiscale feature representation[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2021, 116: 103755. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2021.103755 [15] ZHANG Tianfang, CAO Siying, PU Tian, et al. AGPCNet: Attention-guided pyramid context networks for infrared small target detection[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.03580, 2021. [16] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. [17] LI Boyang, XIAO Chao, WANG Longguang, et al. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 1745–1758. [18] ZHOU Z W, SIDDIQUEE M R, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. UNet++: A nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis, Granada, Spain, 2018: 3–11. [19] TONG Xiaozhong, SUN Bei, WEI Junyu, et al. EAAU-Net: Enhanced asymmetric attention U-Net for infrared small target detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3200. doi: 10.3390/rs13163200 [20] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [21] 谷雨, 刘俊, 沈宏海, 等. 基于改进多尺度分形特征的红外图像弱小目标检测[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2020, 28(6): 1375–1386. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1375GU Yu, LIU Jun, SHEN Honghai, et al. Infrared dim-small target detection based on an improved multiscale fractal feature[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(6): 1375–1386. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1375 [22] LI Hanchao, XIONG Pengfei, AN Jie, et al. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation[C]. The British Machine Vision Conference 2018, Newcastle, UK, 2018: 285. [23] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2881–2890. [24] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [25] JOCHER G. Yolov5[EB/OL]. Https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5, 2020. [26] ZHU Zhen, XU Mengdu, BAI Song, et al. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 593–602. [27] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [28] RAHMAN A and WANG Yang. Optimizing intersection-over-union in deep neural networks for image segmentation[C]. The 12th International Symposium on Visual Computing, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 234–244. [29] BERMAN M, TRIKI A R, and BLASCHKO M B. The Lovasz-Softmax loss: A tractable surrogate for the optimization of the intersection-over-union measure in neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4413–4421. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
