Research on Wired and Wireless Time Slots Converged Scheduling Scheme for Satellite Formation Flying
-
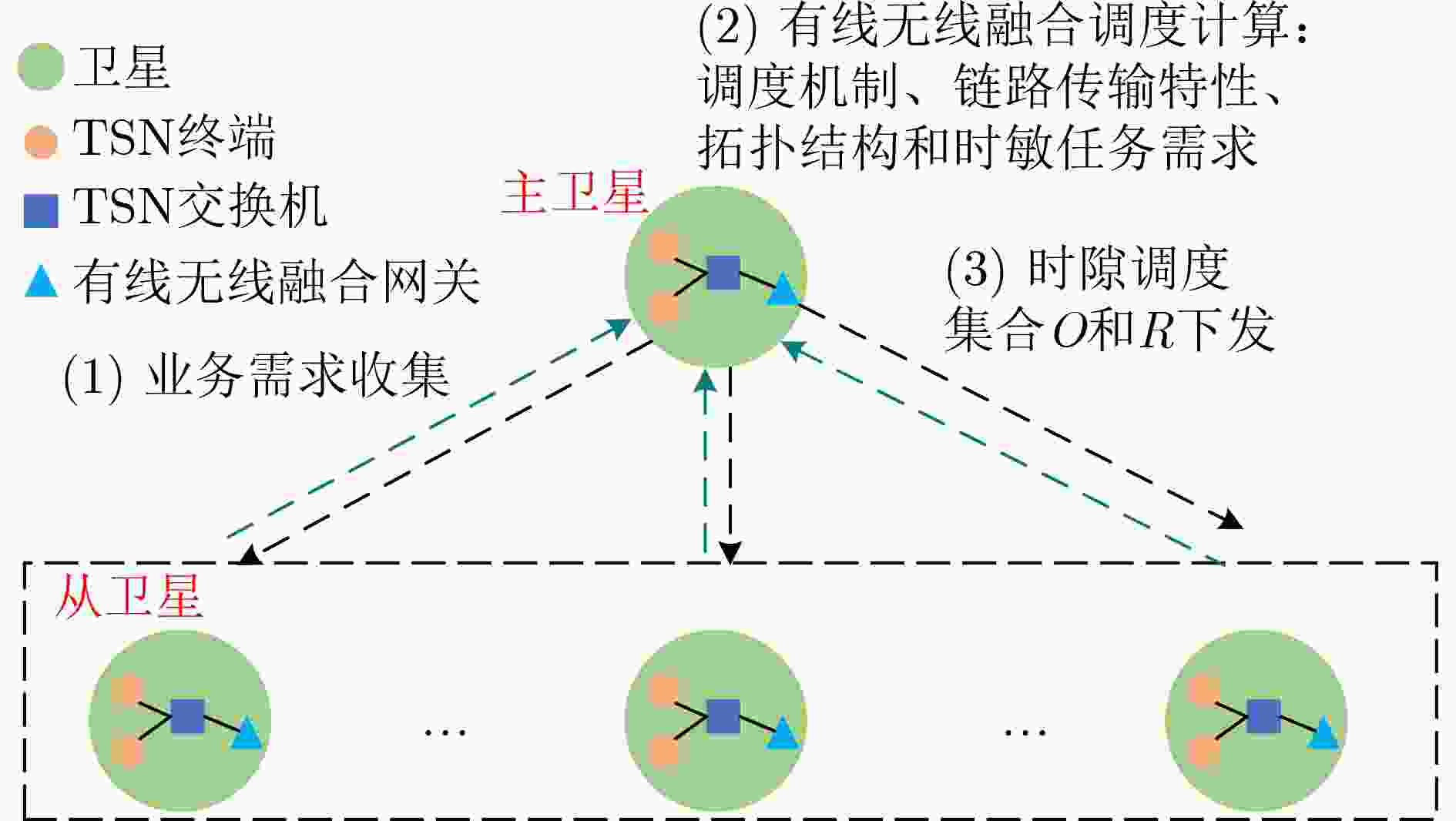
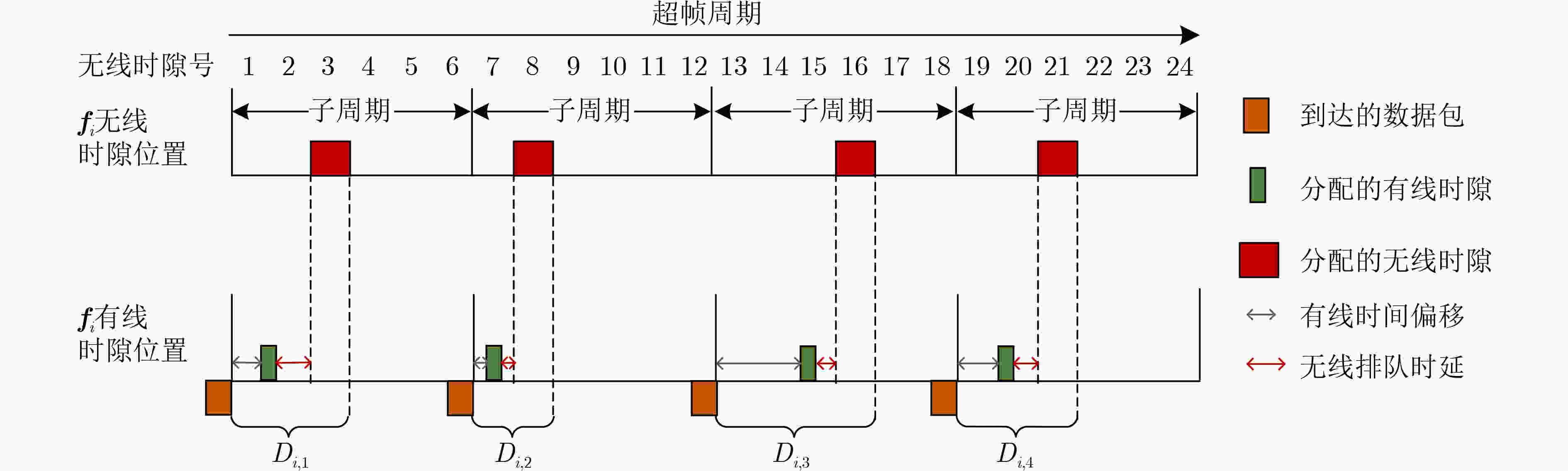
摘要: 针对卫星编队飞行场景中星内有线和星间无线链路传输速率以及调度机制的差异性引起的时敏任务在星上转发时延不确定性的问题,该文提出一种有线无线融合的时隙调度方案。首先,分别构建星间无线链路传输速率、星间无线调度以及星内有线调度模型;其次,联合有线和无线链路传输速率以及二者时隙位置关系,建立有线无线融合调度与星上转发时延关联分析模型;最后,为确保时敏业务每次在星上传输的时延稳定性,在时延分析模型基础上以抖动最小为融合调度优化目标,并采用遗传禁忌搜索算法进行求解。仿真结果表明,相比于非融合调度方案,所提融合调度方案的抖动不高于40 μs,转发时延平均降低了20%。Abstract: Considering the uncertainty of the forwarding delay of time sensitive missions on the satellite caused by the difference of the transmission rate and scheduling mechanism between the intra-satellite wired and inter-satellite wireless link in the satellite formation flying scenario, a wired and wireless converged time slot scheduling scheme is proposed. Firstly, the inter-satellite wireless link transmission rate, inter-satellite wireless scheduling and intra-satellite wired scheduling are constructed respectively. Secondly, the forwarding delay analysis model of the wired and wireless converged scheduling on the satellite is established by considering the transmission rate and the time slot position relationship between the wired and wireless link. Finally, to ensure the stability of delay when the time sensitive traffic is transmitted on the satellite each time, the converged scheduling optimization goal with the minimum jitter is constructed based on the delay analysis model, and the genetic tabu search algorithm is introduced to solve the problem. Simulation results indicate that, compared with the non-converged scheduling scheme, the jitter of the proposed converged scheduling scheme is not higher than 40 μs, and the forwarding delay is reduced by an average of 20%.
-
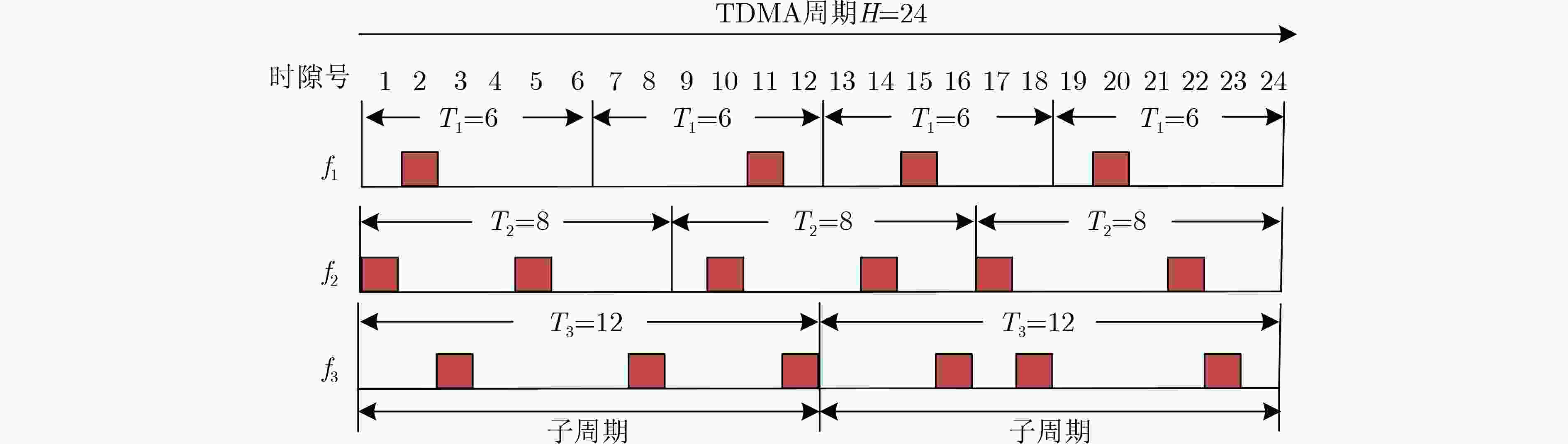
算法1 基于遗传禁忌搜索的融合调度算法(GTS-CSA) 输入:所有流fi的5元组信息,卫星编队拓扑信息,迭代次数Q 输出:平均抖动,有线时隙调度集合O,无线时隙调度集合R (1) 计算TDMA超帧长度H=lcm{T1, T2,···,TN}; (2) 计算流fi在一个TDMA超帧内的子周期数目Mi; (3) 计算流fi在第m个子周期内需要的时隙个数si,m; (4) 按照转发时延要求由高到低对流fi进行排序; (5) FOR EACH ${{\boldsymbol{f}}_i} \in F$ DO (6) 采用贪婪算法计算初始解; (7) WHILE q ≤Q DO (8) 锦标赛选择算法; (9) 两点交叉算法; (10) 基于禁忌搜索的变异算法; (11) q=q+1; (12) END WHILE (13) END FOR 表 1 仿真参数设置
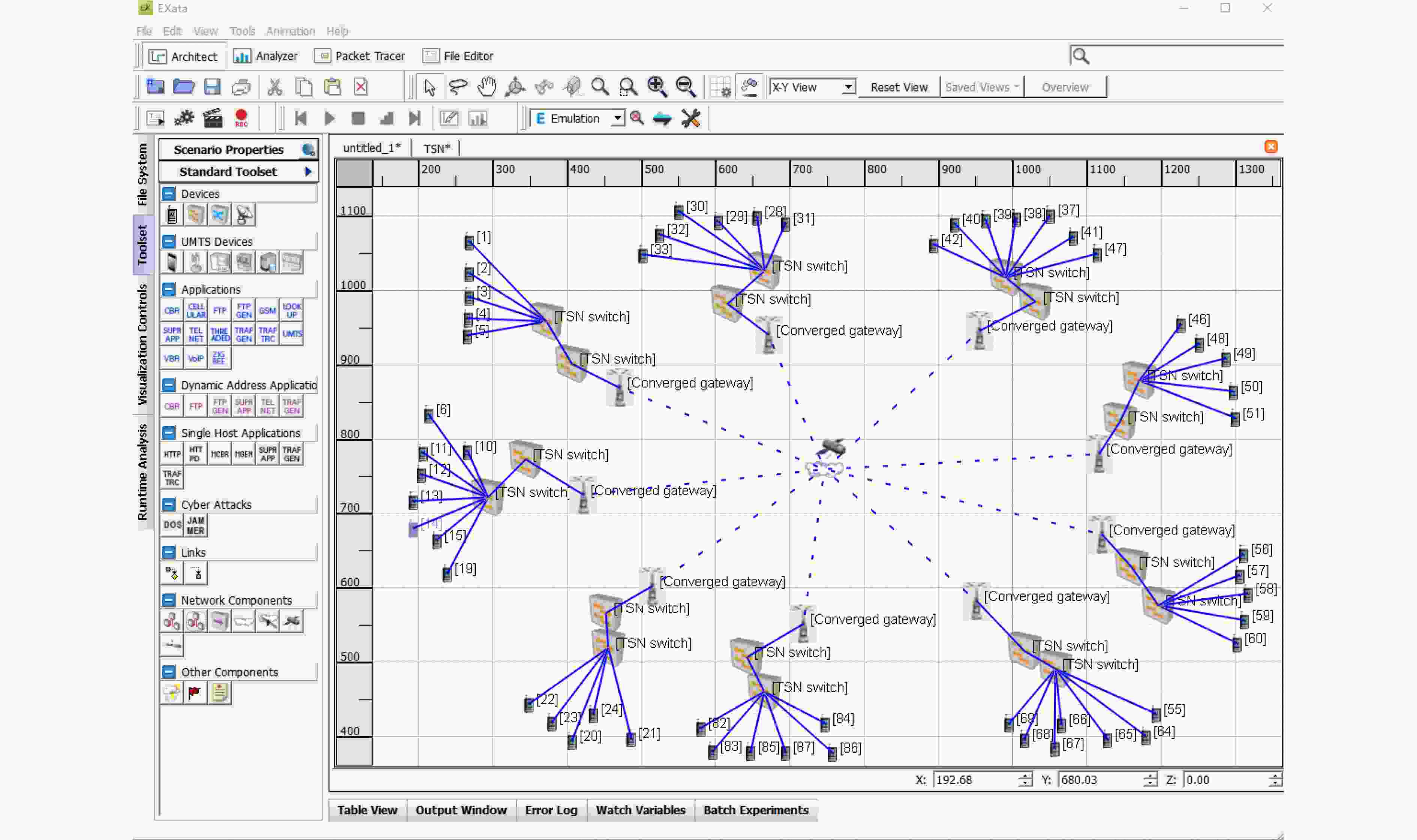
参数 值 编队中卫星的数目 10颗 卫星轨道高度 900 km 平均SNR 22.4 dB 每颗卫星内部终端数目 5~8台 时敏业务流数目 1~20条 有线链路传输速率 100 Mbit/s 无线链路传输速率 10~15 Mbit/s 单位无线时隙长度 500 μs 时敏业务发送周期取值范围 8~60 ms 时敏业务数据量大小取值范围 1~12 kbit 非时敏业务数据量大小取值范围 1~20 Mbit -
[1] DENG Ruoqi, DI Boya, and SONG Lingyang. Ultra-dense LEO satellite based formation flying[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3091–3105. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3058370 [2] CUI Zhaojing, DONG Zhenhui, ZHANG Hongjun, et al. A hybrid service scheduling strategy of satellite data based on TSN[C]. 9th International Conference in Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems, Singapore, 2020: 362–367. [3] NASRALLAH A, THYAGATURU A S, ALHARBI Z, et al. Ultra-low latency (ULL) networks: The IEEE TSN and IETF DetNet standards and related 5G ULL research[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(1): 88–145. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2869350 [4] 杨辉, 白巍, 张杰. 时间敏感空间信息网络关键技术研究[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2017, 43(3): 8–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2017.03.02YANG Hui, BAI Wei, and ZHANG Jie. Research on key technologies of time sensitive space information network[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2017, 43(3): 8–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2017.03.02 [5] 黄韬, 汪硕, 黄玉栋, 等. 确定性网络研究综述[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(6): 160–176. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019119HUANG Tao, WANG Shuo, HUANG Yudong, et al. Survey of the deterministic network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(6): 160–176. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019119 [6] CHAINE P J, BOYER M, PAGETTI C, et al. TSN support for quality of service in space[C]. 10th European Congress on Embedded Real Time Software and Systems (ERTS 2020), Toulouse, France, 2020: 1–11. [7] BOSK M, REZABEK F, HOLZINGER K, et al. Methodology and infrastructure for TSN-based reproducible network experiments[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 109203–109239. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3211969 [8] SANCHEZ-GARRIDO J, APARICIO B, RAMÍREZ J G, et al. Implementation of a time-sensitive networking (TSN) ethernet bus for microlaunchers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 2743–2758. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3061806 [9] REN Bo, LIU Jianping, LI Zhiyuan, et al. Satellite requirement preference driven TT&C resources scheduling algorithm for time sensitive missions[C]. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Shenzhen, China, 2020: 15–19. [10] 吕梦昭. 空间时延敏感通信关键技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.LV Mengzhao. Research on key technologies of space time delay sensitive communication[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. [11] SEIJO Ó, FERNÁNDEZ Z, VAL I, et al. SHARP: Towards the integration of time-sensitive communications in legacy LAN/WLAN[C]. 2018 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018: 1–7. [12] SEIJO Ó, ITURBE X, and VAL I. SHARP: Implementation of a hybrid wired-wireless TSN network to enable flexible smart factories[C]. 2021 17th IEEE International Conference on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS), Linz, Austria, 2021: 95–98. [13] SEIJO Ó, LÓPEZ-FERNÁNDEZ J A, and VAL I. w-SHARP: Implementation of a high-performance wireless time-sensitive network for low latency and ultra-low cycle time industrial applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(5): 3651–3662. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3007323 [14] VAL I, SEIJO Ó, TORREGO R, et al. IEEE 802.1AS clock synchronization performance evaluation of an integrated wired–wireless TSN architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(5): 2986–2999. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3106568 [15] CRUCES C, TORREGO R, ARRIOLA A, et al. Deterministic hybrid architecture with time sensitive network and wireless capabilities[C]. 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Turin, Italy, 2018: 1119–1122. [16] SEIJO Ó, ITURBE X, and VAL I. Tackling the challenges of the integration of wired and wireless TSN with a technology proof-of-concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(10): 7361–7372. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3131865 [17] ROST M P and KOLDING T. Performance of integrated 3GPP 5G and IEEE TSN networks[J]. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, 2022, 6(2): 51–56. doi: 10.1109/MCOMSTD.0001.2000013 [18] GINTHÖR D, GUILLAUME R, VON HOYNINGEN-HUENE J, et al. End-to-end optimized joint scheduling of converged wireless and wired time-sensitive networks[C]. 2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Vienna, Austria, 2020: 222–229. [19] ISO, IEC. 802.1Qbv-2015 IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks - bridges and bridged networks - amendment 25: Enhancements for scheduled traffic[S]. IEEE, 2016. [20] WANG Yin, LI Jinhong, CHEN Minglong, et al. Joint route selection and time-slot allocation for energy consumption optimization in satellite communication systems[C]. 2021 IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Fall), Norman, USA, 2021: 1–5. [21] GOLKAR A and CRUZ I L I. The federated satellite systems paradigm: Concept and business case evaluation[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2015, 111: 230–248. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.02.009 [22] 周笛. 面向任务的空间信息网络资源管理方法[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.ZHOU Di. Mission-oriented resource management technology in space information networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [23] ZHU Yan, SHENG Min, LI Jiandong, et al. Modeling and performance analysis for satellite data relay networks using two-dimensional Markov-modulated process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(6): 3894–3907. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2979126 [24] 徐川, 曾日辉, 邢媛, 等. 面向工业无线网络的动态TDMA系统设计与实现[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(11): 2812–2822. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190797XU Chuan, ZENG Rihui, XING Yuan, et al. Design and implementation of dynamic TDMA system for industrial wireless networks[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2812–2822. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190797 [25] WEI Y H, LENG Quan, HAN Song, et al. RT-WiFi: Real-time high-speed communication protocol for wireless cyber-physical control applications[C]. 2013 IEEE 34th Real-Time Systems Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2013: 140–149. -





 下载:
下载:
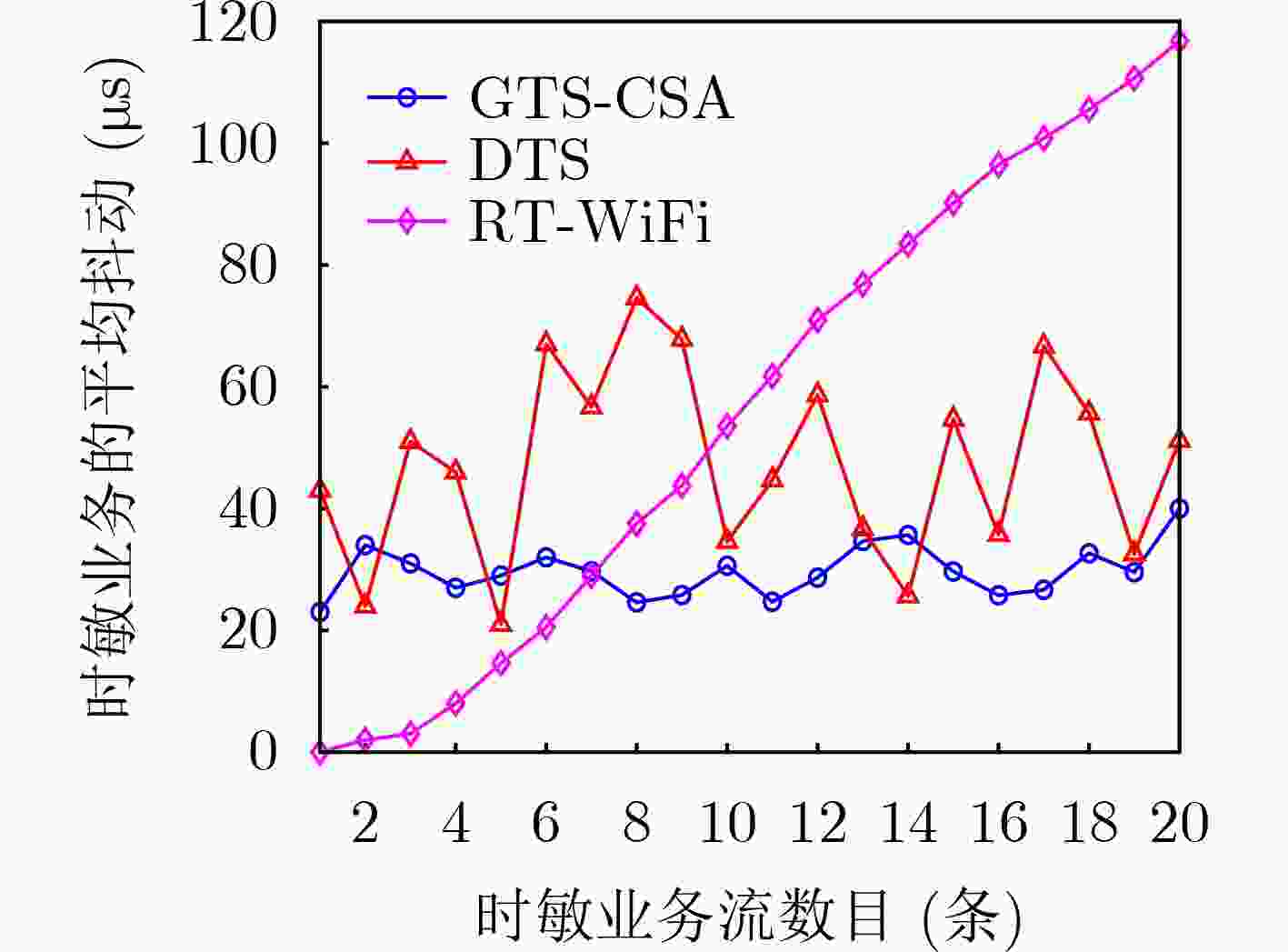
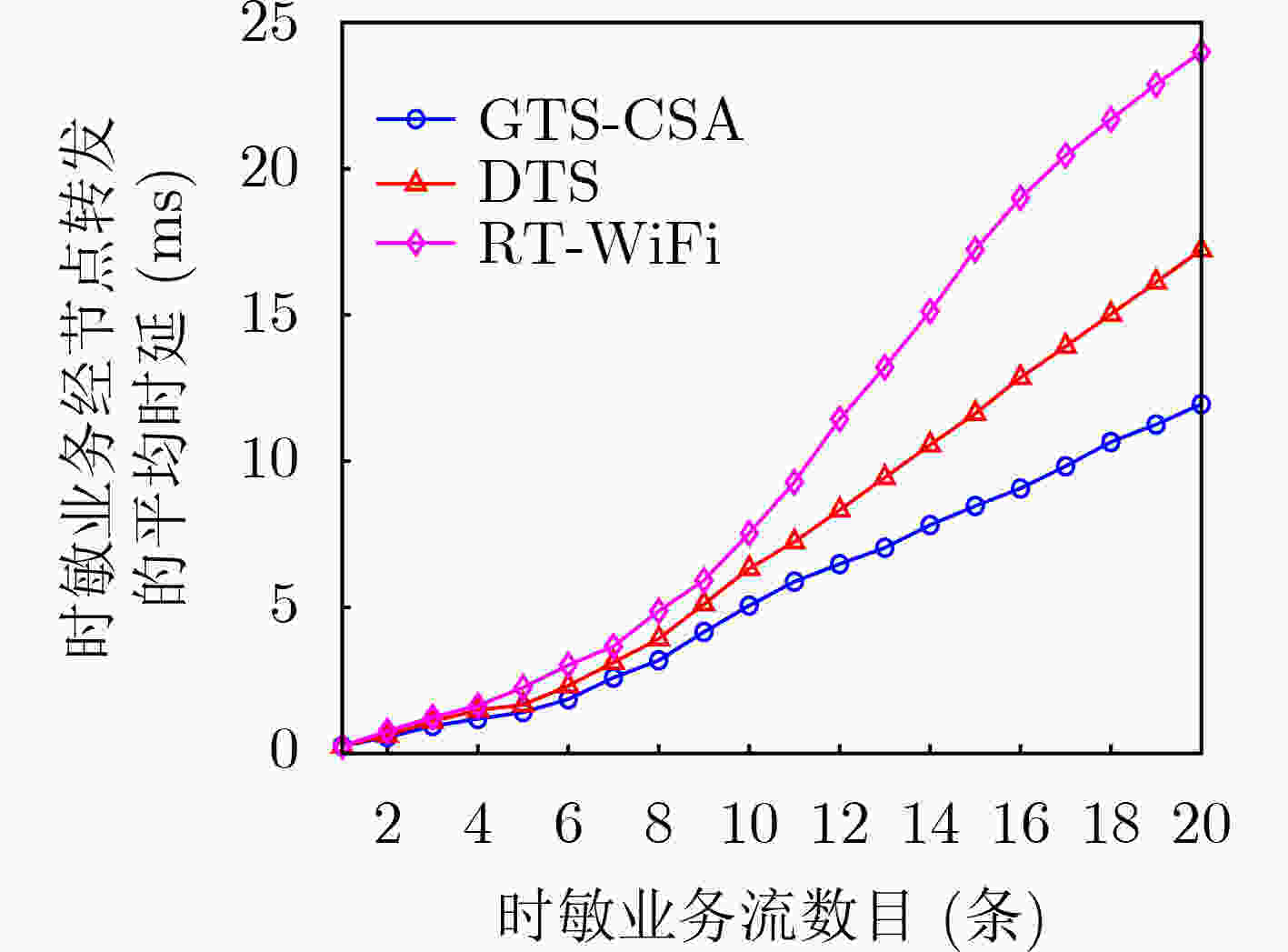


 下载:
下载:
