A MEMS-based Electric Field Sensor with Self-compensation for Sensitivity Drift
-
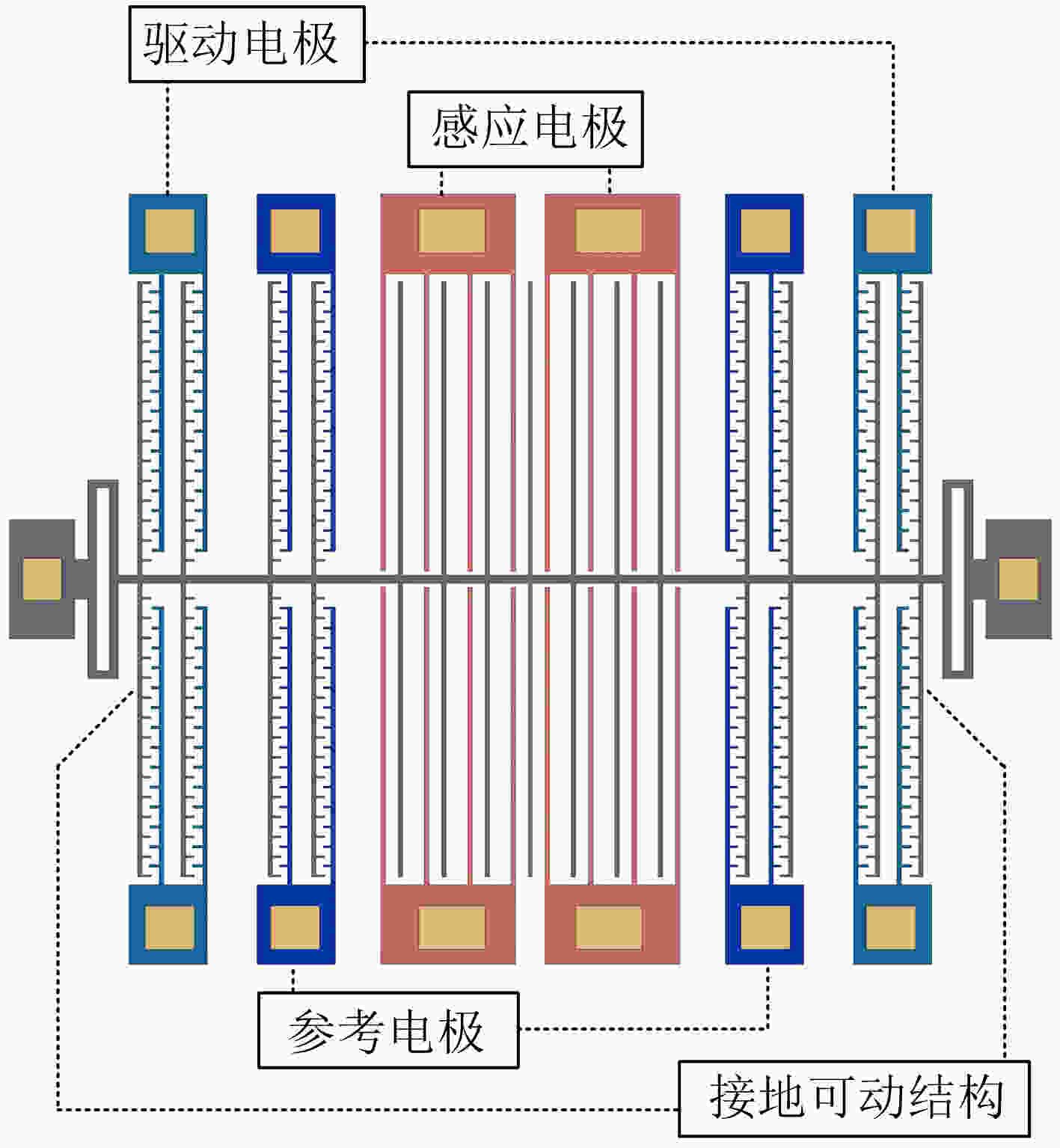
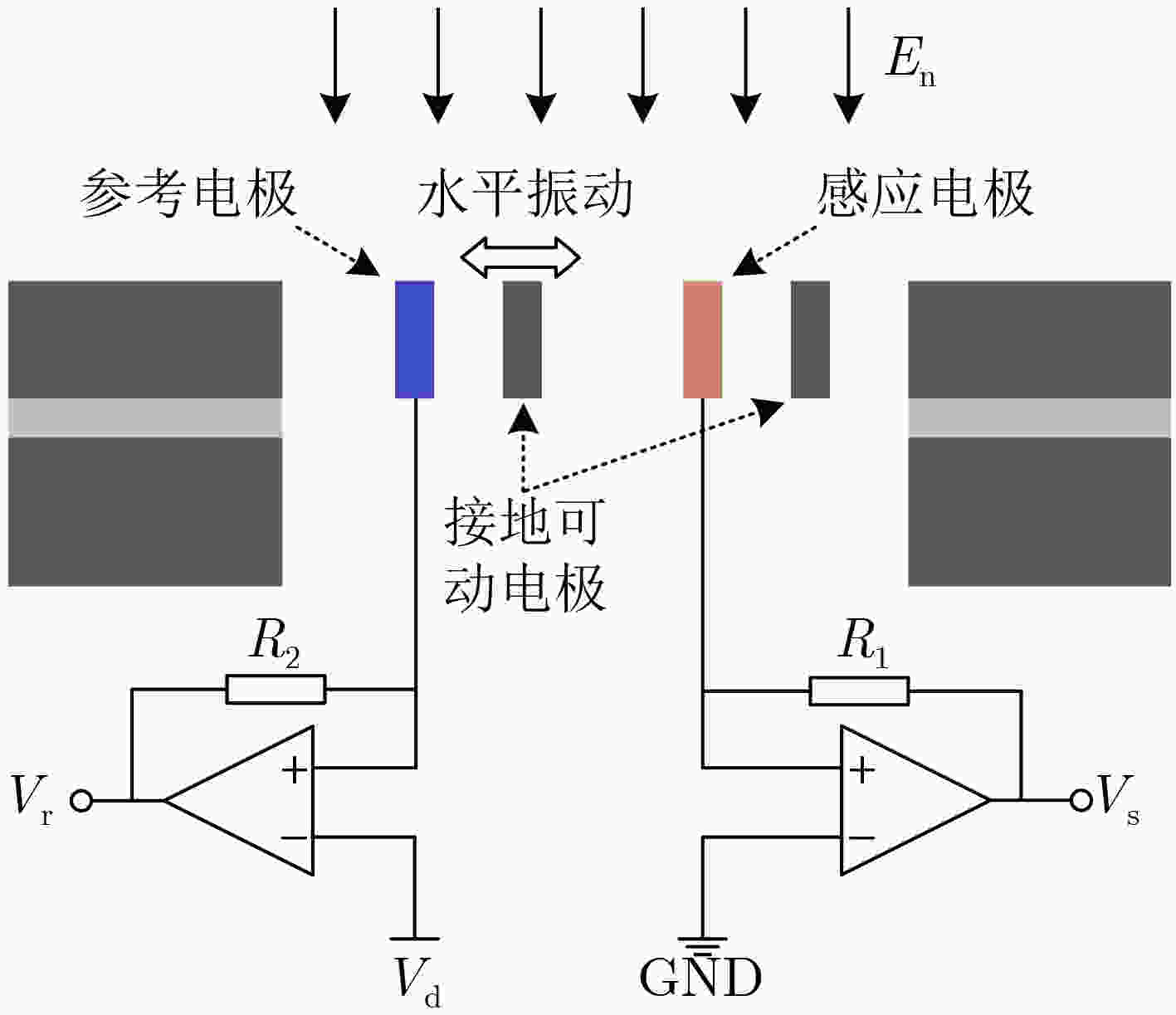
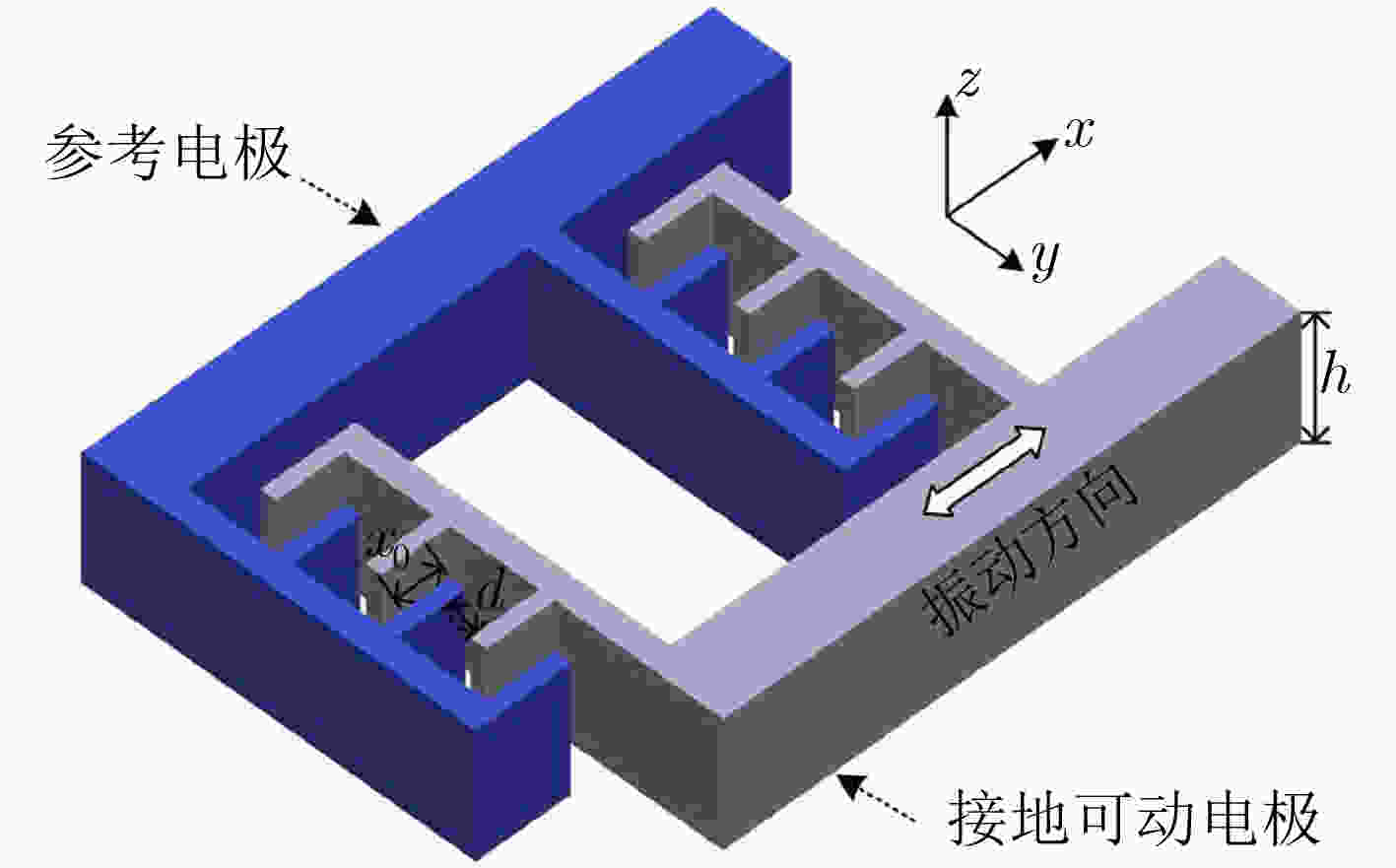
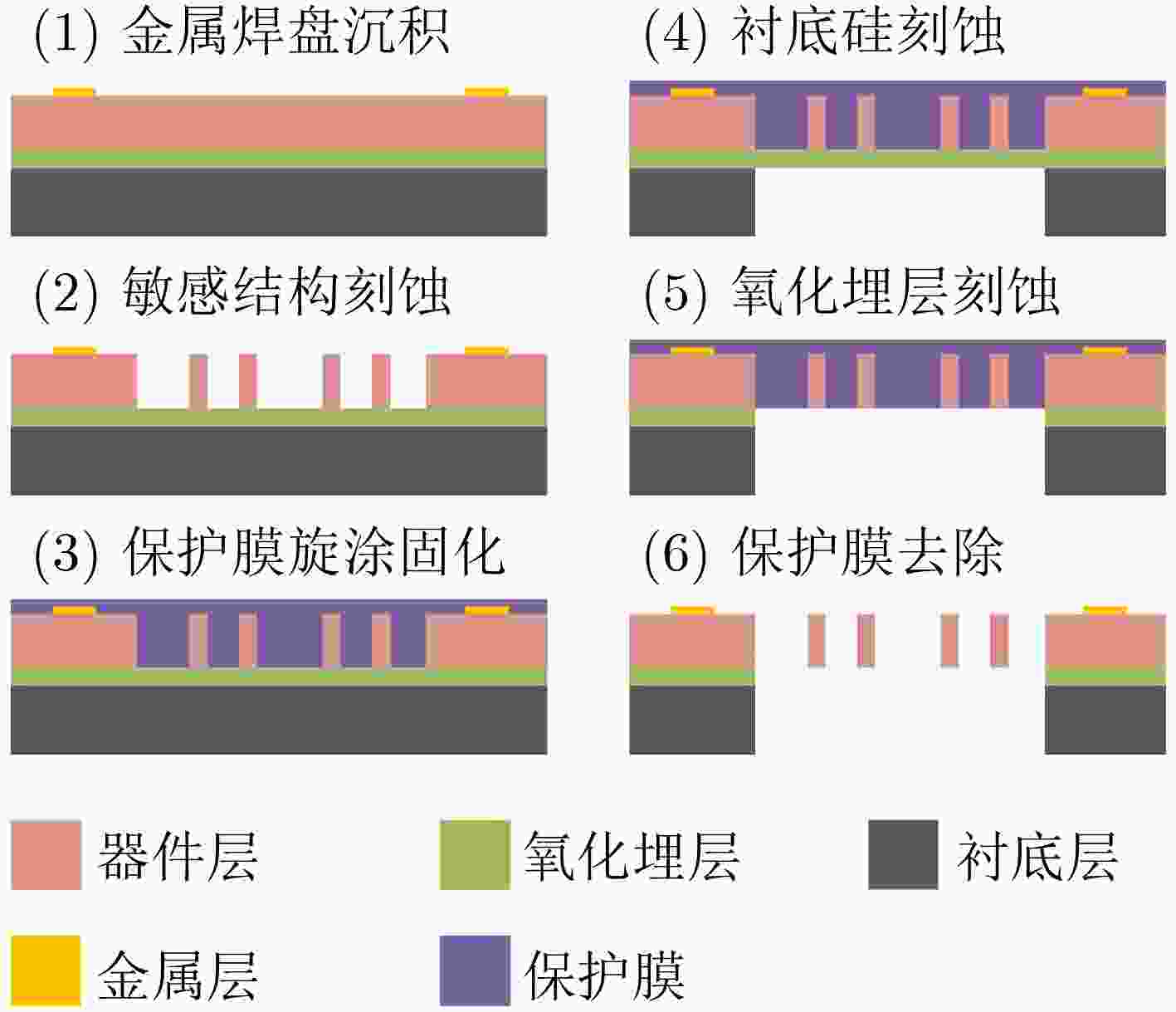
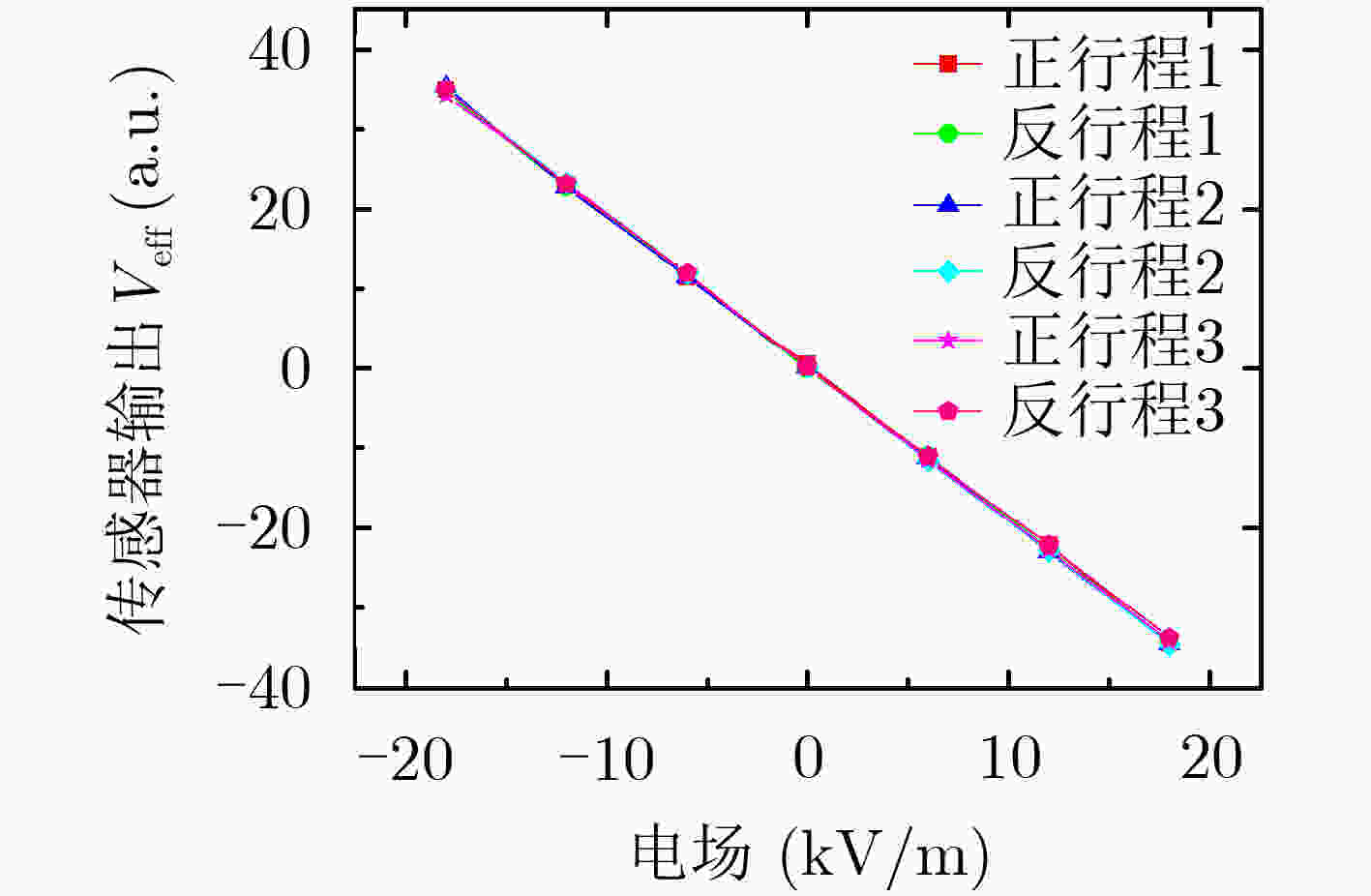
摘要: 针对温度和应力变化带来的电场传感器灵敏度漂移和测量误差问题,该文提出一种具有灵敏度漂移自补偿功能的微机电系统(MEMS)谐振式电场传感器。传感器结构中,感应电极用于测量外部电场,参考电极用于监测可动结构振动信息;基于振动相位和锁相环技术实现传感器谐振频率自动跟踪,利用参考电极输出信号对感应电极输出信号进行实时补偿,提高传感器灵敏度的稳定性。该文开展了敏感结构设计和理论分析,研制出传感器样机,并进行了样机标定测试。测试结果表明,在±18 kV/m电场范围内,传感器线性度达到0.21%,3个往返行程总不确定度达到1.34%;在–40°C~70°C温度范围内,灵敏度相对漂移量小于3.0%,具有良好的灵敏度漂移自补偿效果。Abstract: To reduce the sensitivity drift caused by working temperature and structural parameters change, an electric field sensor with self-compensation based on Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) is proposed. The sensor structure includes the sensing electrodes for measuring the external electric field and the reference electrodes for monitoring the movable structure vibration. With the reference electrodes output, this sensor can track the resonant frequency automatically, and correct the sensing output in real time. Experimental results show that this sensor can achieve a linearity of 0.21% and an accuracy of 1.34% in the electric field range of –18~+18 kV/m, and a less sensitivity drift within 3.0% in the temperature range of –40~70°C, realizing a good self-compensation performance.
-
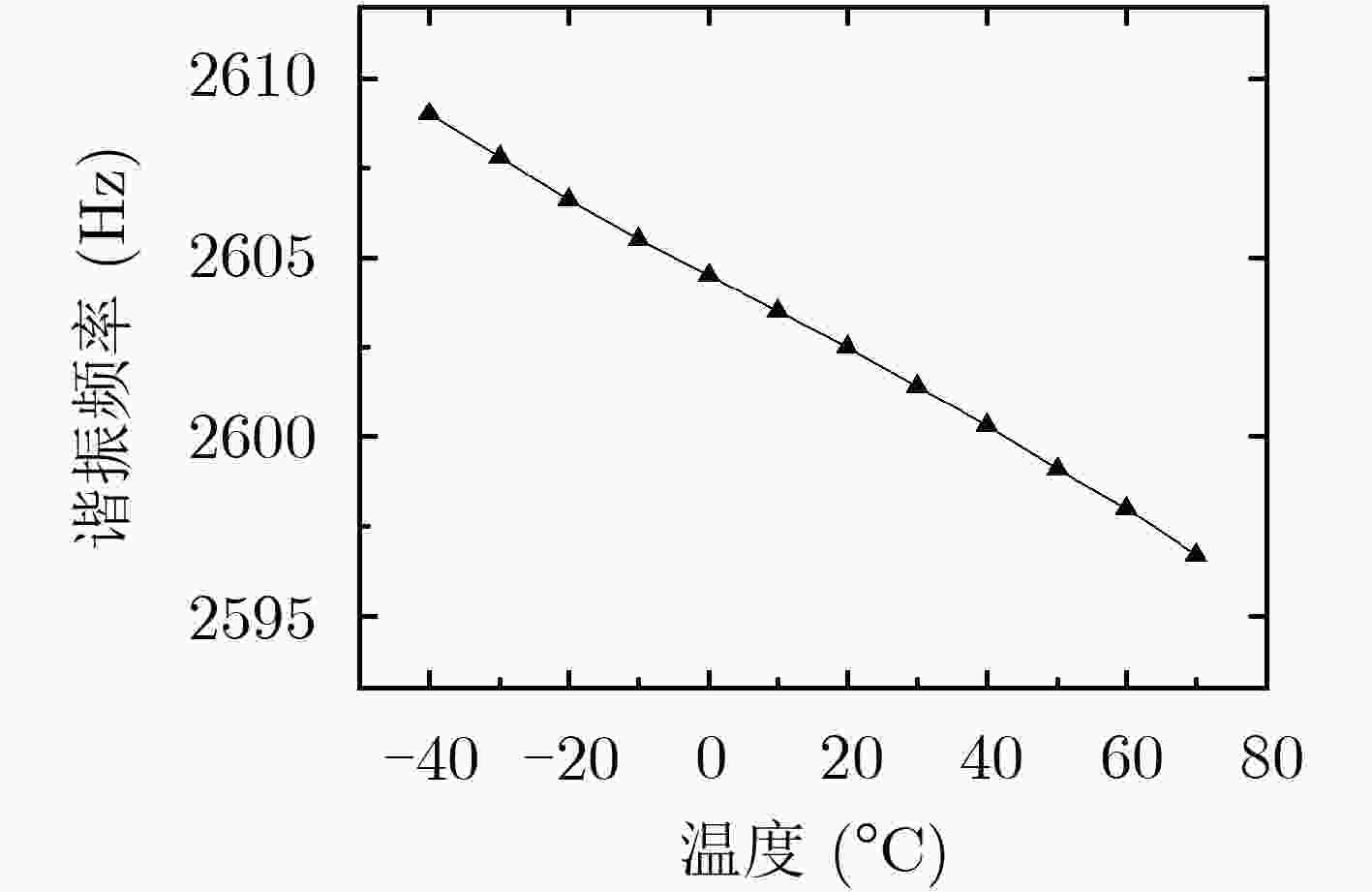
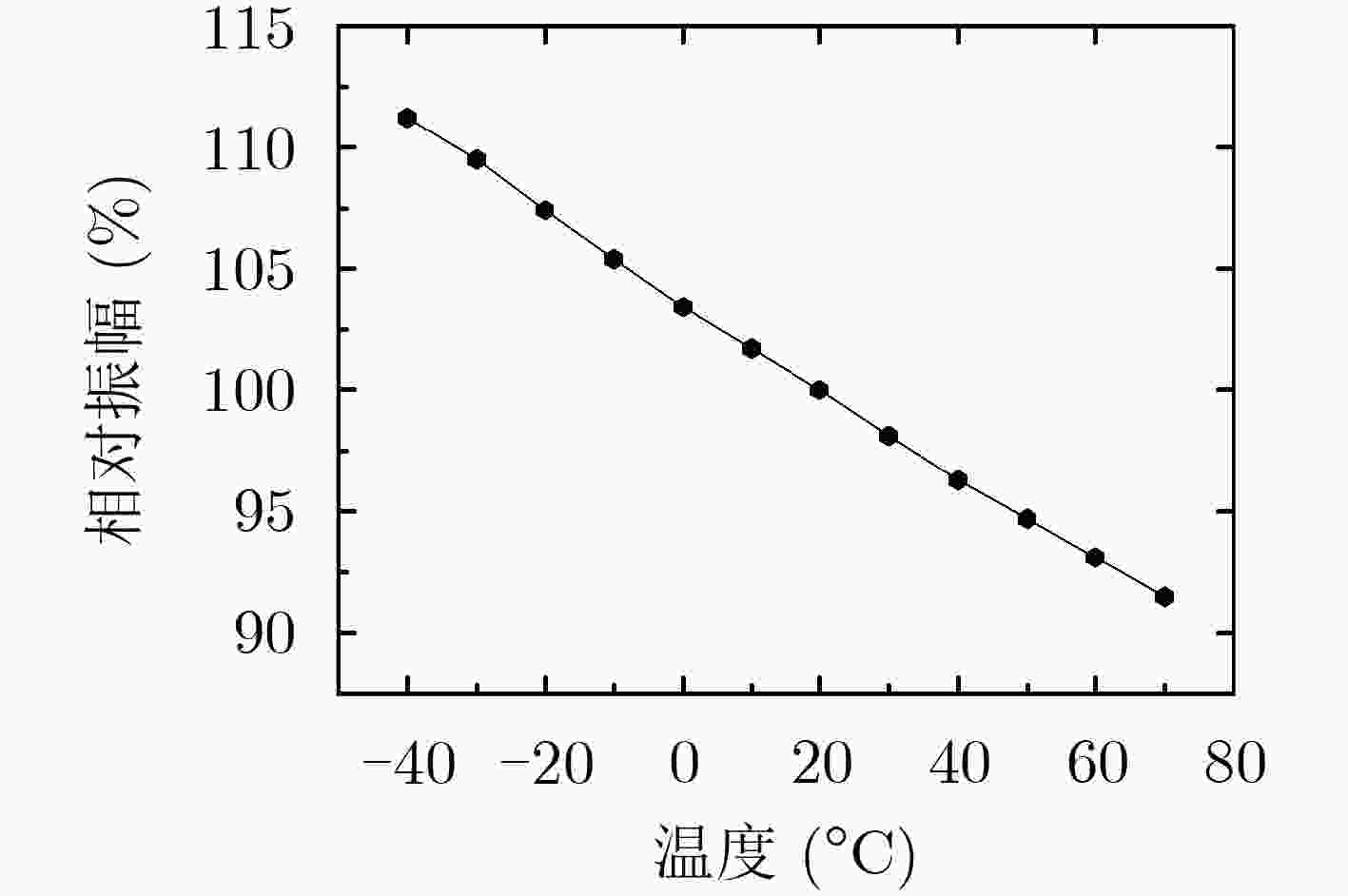
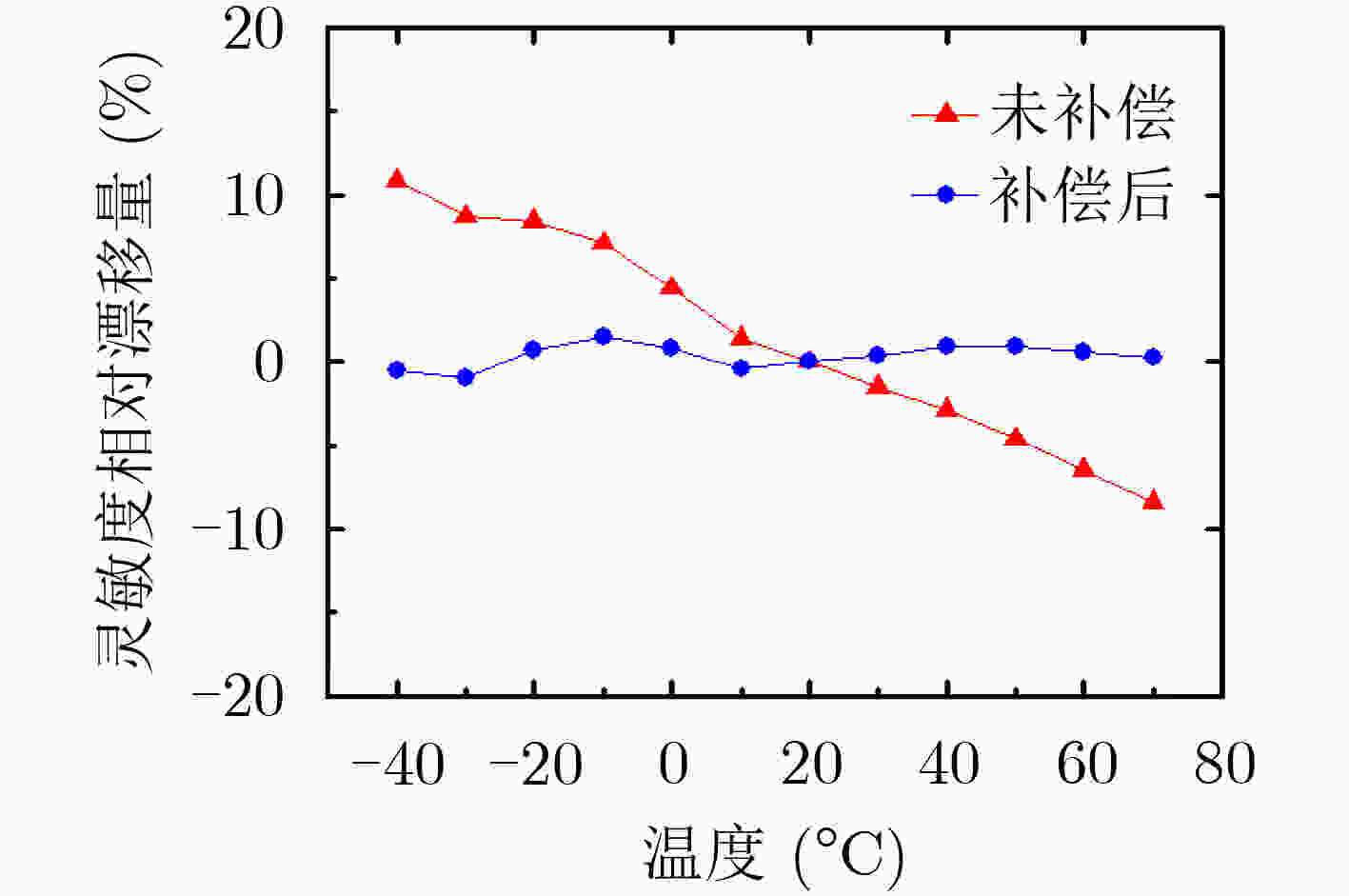
表 1 传感器灵敏度相对漂移量随温度变化的测试结果(%)
温度(°C) 1号传感器 2号传感器 3号传感器 4号传感器 5号传感器 6号传感器 未补偿 补偿后 未补偿 补偿后 未补偿 补偿后 未补偿 补偿后 未补偿 补偿后 未补偿 补偿后 –40 10.9 –0.5 12.1 –0.4 12.1 –0.2 12.8 0.7 8.1 –1.1 18.1 –0.9 –30 8.7 –1.0 9.4 –1.2 10.4 –0.2 10.4 0.0 6.7 –1.3 15.5 –0.2 –20 8.4 0.7 7.4 –1.0 7.8 –0.7 8.4 0.0 6.3 –0.2 10.3 1.0 –10 7.1 1.5 5.8 –0.3 5.6 –0.5 6.7 0.4 5.6 0.6 6.8 1.0 0 4.4 0.8 3.7 –0.2 3.6 –0.3 3.9 –0.1 3.7 0.4 5.2 1.3 10 1.4 –0.4 –1.2 –3.0 1.5 –0.5 2.4 0.4 1.2 –0.4 2.1 0.3 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 30 –1.5 0.4 –1.7 0.4 –1.1 1.1 –1.5 0.6 –1.7 –0.2 –1.2 0.6 40 –2.9 0.9 –3.1 1.0 –3.3 0.8 –5.1 –1.2 –3.8 –0.7 –3.9 0.3 50 –4.6 0.9 –5.4 0.6 –5.2 0.8 –8.1 –2.5 –5.4 –0.8 –5.9 0.4 60 –6.5 0.6 –7.0 0.8 –6.5 1.3 –9.3 –1.9 –7.4 –1.3 –9.2 –1.3 70 –8.4 0.3 –9.9 –0.4 –7.2 2.4 –11.4 –2.2 –9.8 –2.2 –10.9 –0.8 表 2 传感器灵敏度相对漂移量的平均值及标准差(%)
1号 2号 3号 4号 5号 6号 未补偿 平均值 1.4 0.8 1.5 0.8 0.3 2.2 标准差 6.2 6.6 6.2 7.7 5.7 8.9 补偿后 平均值 0.4 –0.3 0.3 –0.5 –0.6 0.1 标准差 0.7 1.0 0.9 1.1 0.8 0.8 -
[1] MONTANYA J, BERGAS J, and HERMOSO B. Electric field measurements at ground level as a basis for lightning hazard warning[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2004, 60(2/4): 241–246. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2004.01.009 [2] 王德才. 电线电压与电流非接触检测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 重庆大学, 2018.WANG Decai. Study on non-contact detecting technology for electric power line-voltage and current[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Chongqing University, 2018. [3] PAILLAT T, MOREAU E, and TOUCHARD G. Space charge density at the wall in the case of heptane flowing through an insulating pipe[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2001, 53(2): 171–182. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3886(01)00139-5 [4] 李亮亮, 赵清山, 李义鹏, 等. 电导率对成品油静电特性影响试验研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2018, 44(7): 9–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2018.07.003LI Liangliang, ZHAO Qingshan, LI Yipeng, et al. Experimental study on the effect of conductivity on the electrostatic characteristics of petroleum products[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 44(7): 9–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2018.07.003 [5] RIEHL P S, SCOTT K L, MULLER R S, et al. Electrostatic charge and field sensors based on micromechanical resonators[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2003, 12(5): 577–589. doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2003.818066 [6] PENG Chunrong, CHEN Xianxiang, YE Cao, et al. Design and testing of a micromechanical resonant electrostatic field sensor[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2006, 16(5): 914–919. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/16/5/006 [7] BAHREYNI B, WIJEWEERA G, SHAFAI C, et al. Analysis and design of a micromachined electric-field sensor[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2008, 17(1): 31–36. doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2007.911870 [8] YANG Pengfei, PENG Chunrong, FANG Dongming, et al. Design, fabrication and application of an SOI-based resonant electric field microsensor with coplanar comb-shaped electrodes[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2013, 23(5): 055002. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/23/5/055002 [9] WANG Yu, FANG Dongming, FENG Ke, et al. A novel micro electric field sensor with X–Y dual axis sensitive differential structure[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2015, 229: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2015.03.013 [10] CHU Zhaozhi, PENG Chunrong, REN Ren, et al. A high sensitivity electric field microsensor based on torsional resonance[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 286. doi: 10.3390/s18010286 [11] LING Biyun, PENG Chunrong, REN Ren, et al. Design, fabrication and characterization of a MEMS-based three-dimensional electric field sensor with low cross-axis coupling interference[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 870. doi: 10.3390/s18030870 [12] YANG Pengfei, WEN Xiaolong, CHU Zhaozhi, et al. Non-intrusive DC voltage measurement based on resonant electric field microsensors[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2021, 31(6): 064001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6439/abf631 [13] WEN Xiaolong, YANG Pengfei, CHU Zhaozhi, et al. Toward atmospheric electricity research: A low-cost, highly sensitive and robust balloon-borne electric field sounding sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(12): 13405–13416. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3070130 [14] WEN Xiaolong, YANG Pengfei, ZHANG Zhouwei, et al. Resolution-enhancing structure for the electric field microsensor chip[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(8): 936. doi: 10.3390/mi12080936 [15] YANG Pengfei, WEN Xiaolong, LV Yao, et al. A non-intrusive voltage measurement scheme based on MEMS electric field sensors: Theoretical analysis and experimental verification of AC power lines[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(6): 065002. doi: 10.1063/5.0052678 [16] LEI Hucheng, XIA Shanhong, CHU Zhaozhi, et al. An electric field microsensor with mutual shielding electrodes[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(4): 360. doi: 10.3390/mi12040360 [17] YANG Pengfei, WEN Xiaolong, LV Yao, et al. Improved Microsensor-based fieldmeter for ground-level atmospheric electric field measurements[C]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 2001510. [18] LIU Jun, XIA Shanhong, PENG Chunrong, et al. Wafer-level vacuum-packaged electric field microsensor: Structure design, theoretical model, microfabrication, and characterization[J]. Micromachines, 2022, 13(6): 928. doi: 10.3390/mi13060928 [19] 杨鹏飞, 陈博, 闻小龙, 等. 一种基于MEMS芯片的新型地面大气电场传感器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1536–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150994YANG Pengfei, CHEN Bo, WEN Xiaolong, et al. A novel MEMS chip-based ground atmospheric electric field sensor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1536–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150994 [20] 闻小龙, 杨鹏飞, 储昭志, 等. 基于MEMS的距离自适应型非接触静电仪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 3068–3074. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200571WEN Xiaolong, YANG Pengfei, CHU Zhaozhi, et al. A daptive-distance noncontact electrostatic meter based on MEMS technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 3068–3074. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200571 -





 下载:
下载:
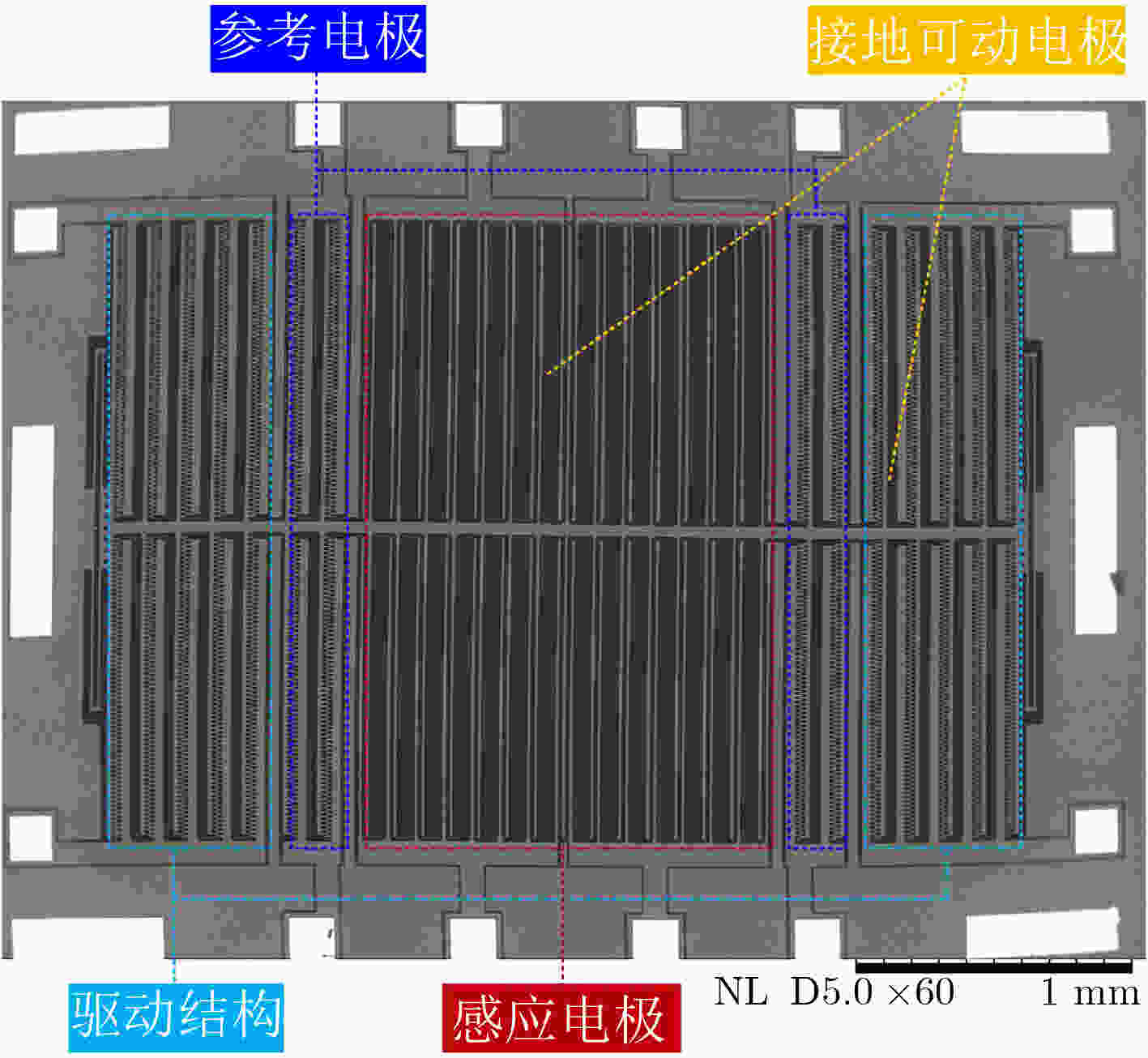
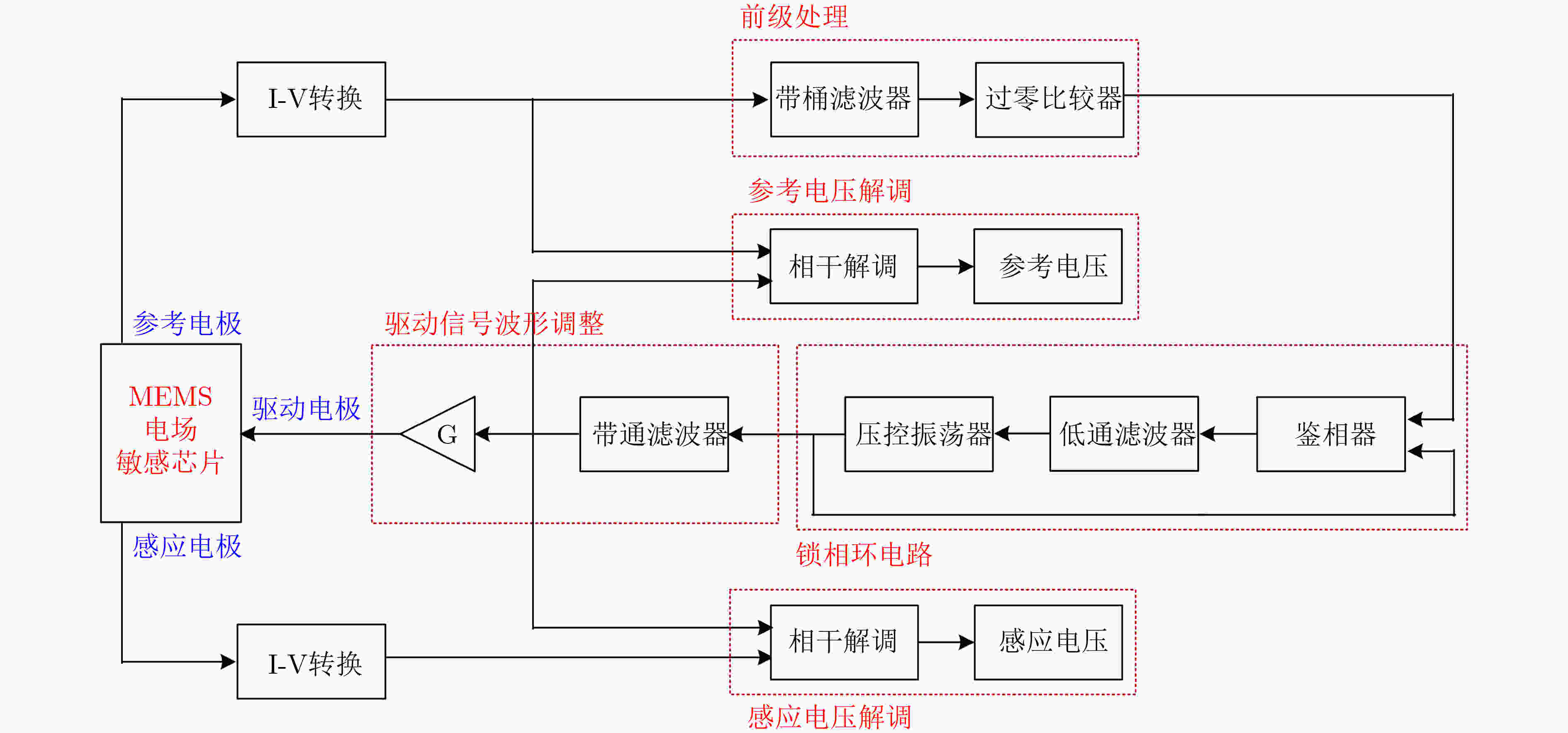
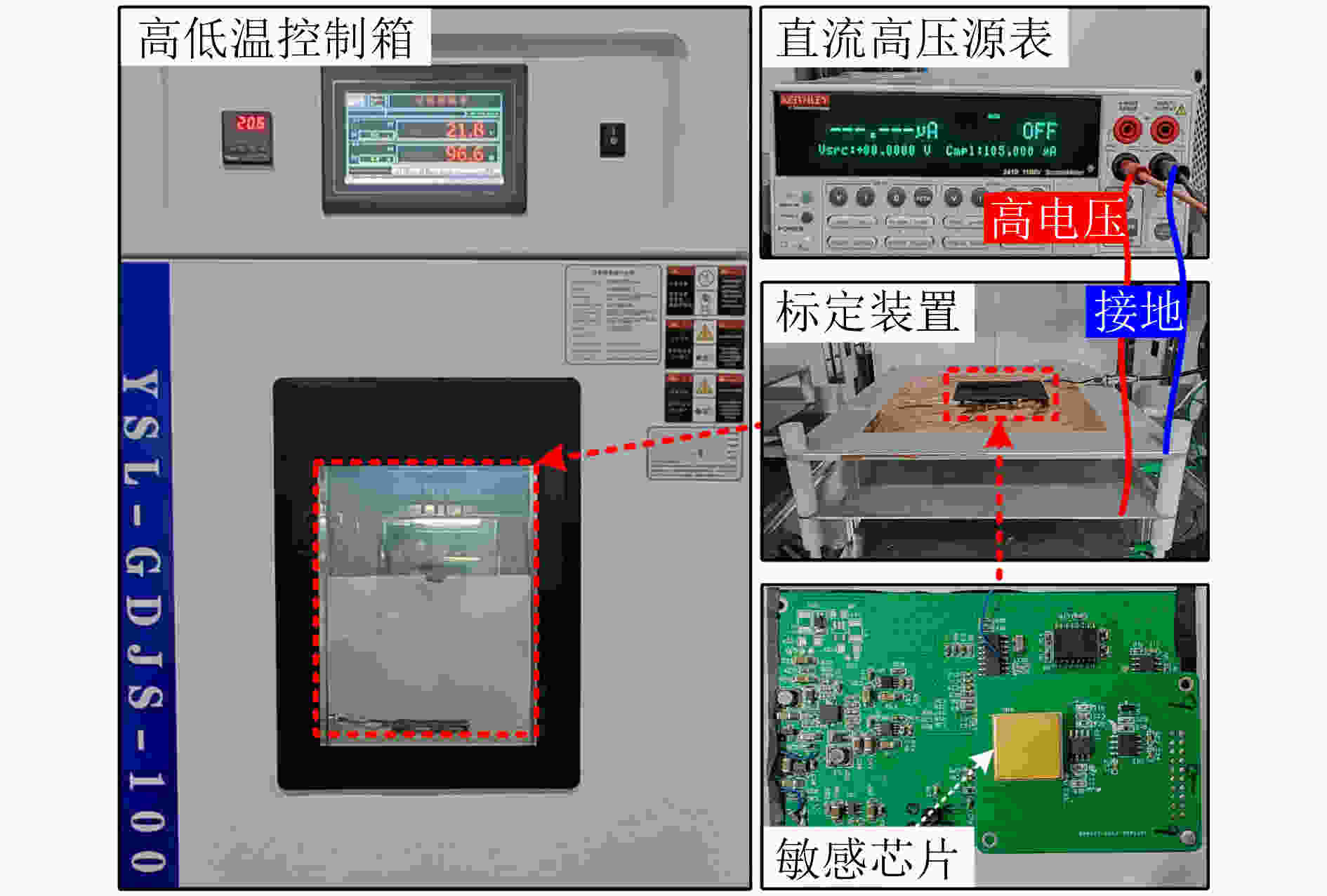


 下载:
下载:
