Joint Optimization of Content Caching and Power Distribution for Internet of Vehicles Based on Parametric Reinforcement Learning
-
摘要: 车联网场景下的业务内容具有海量和高度动态的特性,使得传统缓存机制无法较好地感知内容动态变化,且巨量接入设备与边缘缓存设备的有限资源之间的矛盾会引起系统时延性能差的问题。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于强化学习的联合内容缓存和功率分配算法。首先,考虑联合优化内容缓存和功率分配,建立最小化系统整体时延的优化模型。其次,将该优化问题建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),并进一步将内容缓存和内容提供者的选择映射为离散动作集,并将功率分配映射为与离散动作相对应的连续参数。最后,借助参数化深度Q-Networks (P-DQN)算法求解这个具有离散-连续混合动作空间的问题。仿真结果表明,相较对比算法,该文所提算法能提高本地缓存命中率并降低系统传输时延。Abstract: The service content in the Internet of Vehicles scenario is massive and highly dynamic, which makes the traditional caching mechanism unable to perceive better the dynamic changes of the content, and the contradiction between the huge number of access devices and the limited resources of edge cache devices will cause the problem of poor system latency performance. In view of the above problems, a reinforcement learning-based joint content caching and power allocation algorithm is proposed. First, considering the joint optimization of content caching and power allocation, an optimization model is established to minimize the overall system delay. Second, this optimization problem is modeled as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), and the selection of content caches and content providers is further mapped as discrete action sets, and power allocation is mapped as continuous parameters corresponding to discrete actions. Finally, this problem with a discrete-continuous mixed action space is solved with the aid of the Parametric Deep Q-Networks (P-DQN) algorithm. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can improve the local cache hit rate and reduce the system transmission delay compared with the comparison algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Internet of vehicles /
- Content caching /
- Power distribution /
- Deep reinforcement learning
-
算法1 基于P-DQN的联合优化算法 初始化:设置最大训练轮数$T$、学习率$\{ \alpha ,\beta \} $、探索参数$\varepsilon $、概
率分布参数$\xi $、mini-batch大小为$B$、经验回放池$\varGamma$、
网络权重${\varphi _1}$和${\theta _1}$1: for $t = 1$ to $T$do 2: for $k = 1$ to $K$do 3: 计算动作参数${p_d} \leftarrow {p_d}({s_t};{\theta _t})$。 4: 使用$\varepsilon $-greedy策略选择动作${a_t} = ({d_t},{p_{{d_t}}})$,其中 5: ${d_t} = \arg {\max _{d \in D}}Q({s_t},d,{p_d};{\varphi _t})$ 6: ${a}_{t}=\left\{\begin{array}{lllll}以概率\xi 采样,& \varepsilon \\ ({d}_{t},{p}_{ {d}_{t} }),& 1-\varepsilon \end{array} \right.$ 7: 执行${a_t}$,并获取时延和命中率,观测奖励${r_t}$和下一状态${s_{t + 1}}$ 8: 将$[{s_t},{a_t},{r_t},{s_{t + 1}}]$存入$\varGamma$ 9: 从$\varGamma$中采集$B$个${\{ {s_b},{a_b},{r_b},{s_{b + 1}}\} _{b \in [B]}}$样本 10: ${y_b} = {r_b} + {\max _{d \in D}}\varphi Q({s_{b + 1}},d,{p_d}({s_{b + 1}};{\theta _t});{\varphi _t})$ 11: 使用${\{ {y_b},{s_b},{a_b}\} _{b \in [B]}}$计算${\nabla _\varphi }\ell _t^Q(\varphi )$和${\nabla _\theta }\ell _t^\varTheta (\theta )$ 12: 计算${\varphi _{t + 1}} \leftarrow {\varphi _t} - {\alpha _t}{\nabla _\varphi }\ell _t^Q(\varphi )$和${\theta _{t + 1} } \leftarrow {\theta _t} - {\beta _t}{\nabla _\theta }\ell _t^\varTheta (\theta )$ 13: end for 14: end for 表 1 仿真参数
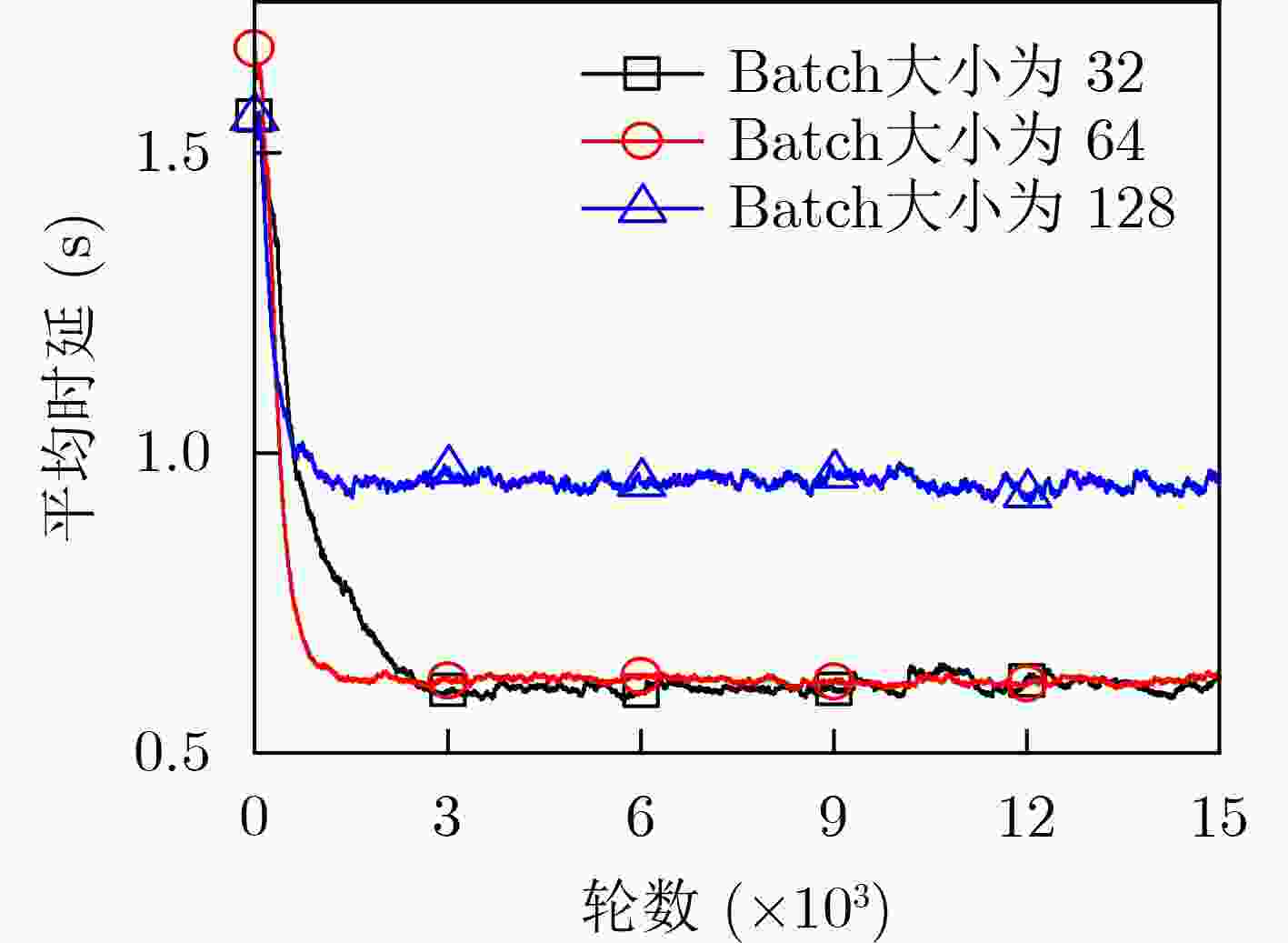
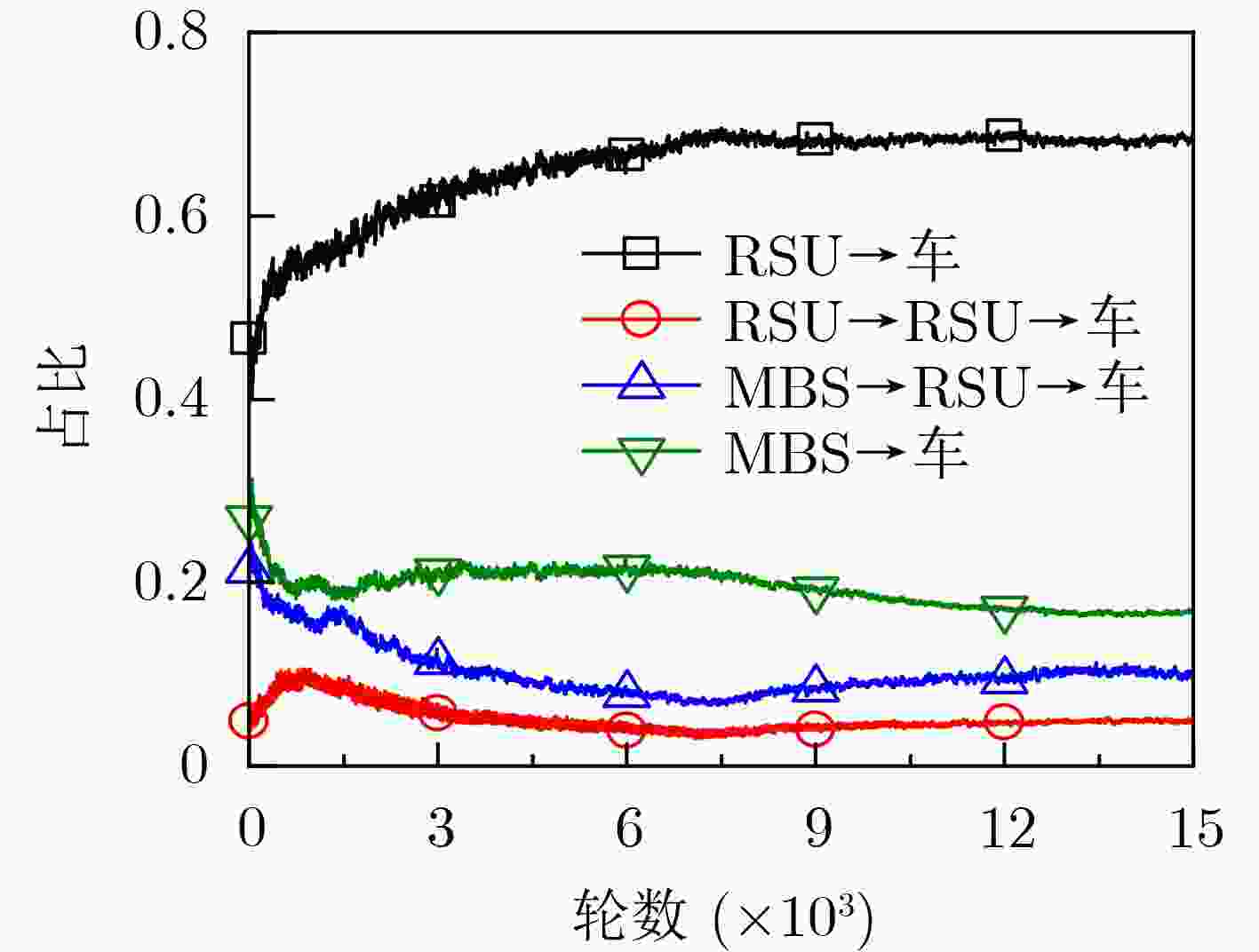
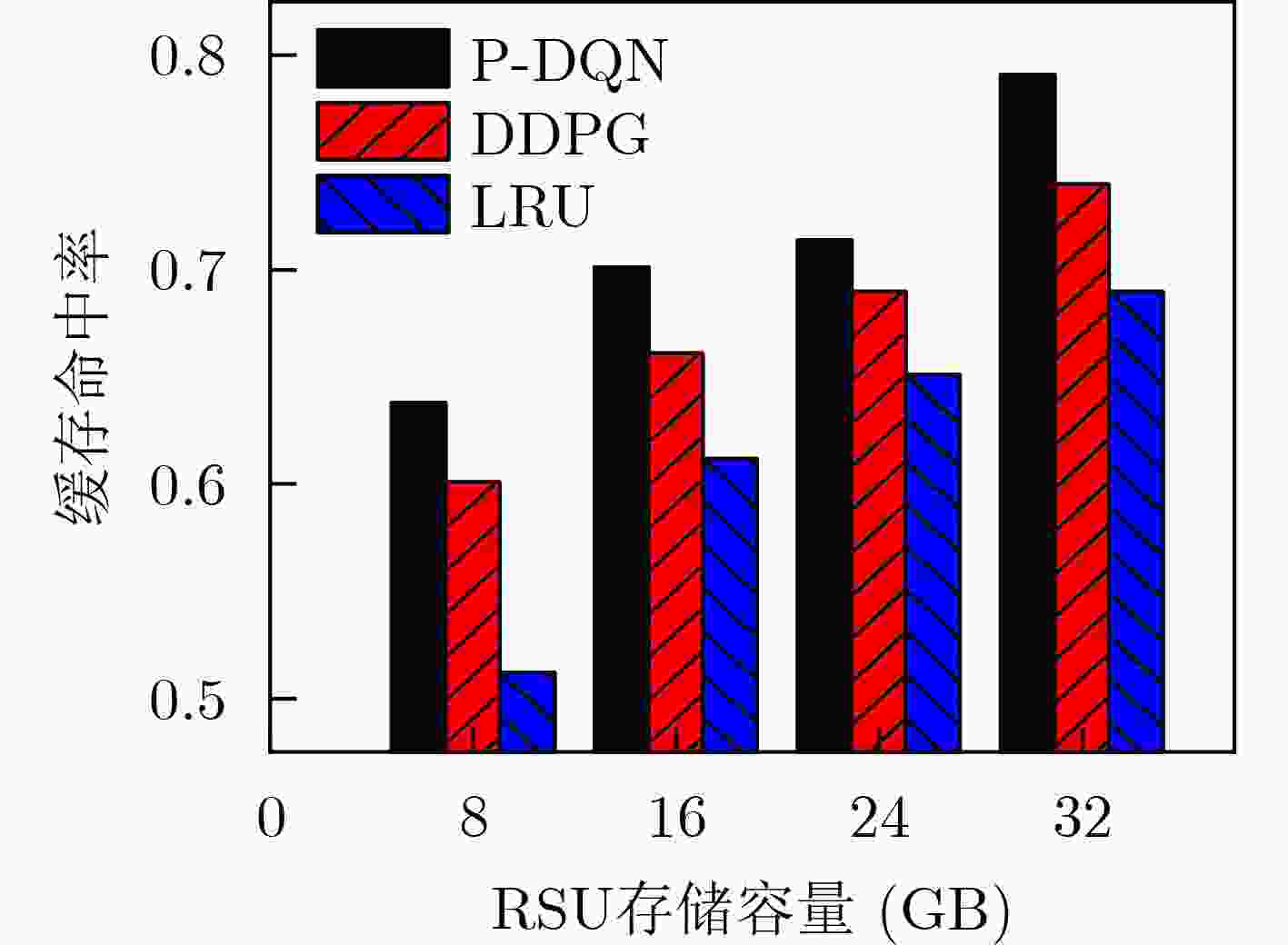
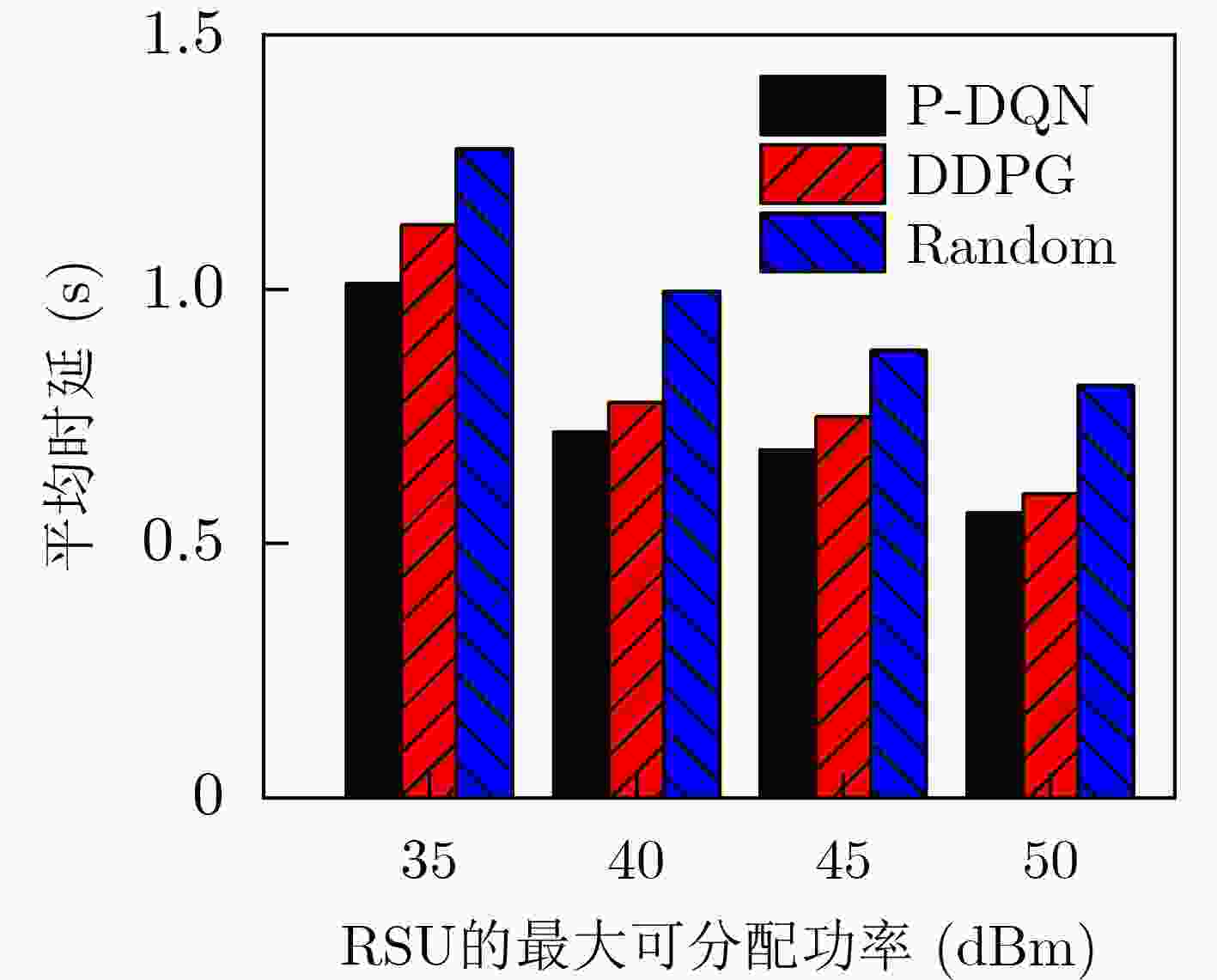
参数 数值 RSU覆盖半径 (m) 250 RSU数量 4 RSU存储容量 (GB) 16 RSU总功率 (dBm) 40 内容大小 (MB) [8,12] 车辆数量 100 带宽 (MHz) 10 噪声功率 (dBm) –60 SINR门限 (dB) 20 路径损耗模型 128.1+37.61lg(d) $ \mathrm{p} $和Q网络的隐藏层 128×64 mini-batch大小 64 经验回放池容量 5000 学习率$\alpha = \beta $ 0.001 折扣因子$\gamma $ 0.95 -
[1] YOUSEFPOUR A, ISHIGAKI G, GOUR R, et al. On reducing IoT service delay via fog offloading[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(2): 998–1010. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2788802 [2] HE Ying, ZHAO Nan, and YIN Hongxi. Integrated networking, caching, and computing for connected vehicles: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(1): 44–55. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2760281 [3] TANG Fengxiao, MAO Bomin, KATO N, et al. Comprehensive survey on machine learning in vehicular network: Technology, applications and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(3): 2027–2057. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3089688 [4] XU Lianming, YANG Zexuan, WU Huaqing, et al. Socially driven joint optimization of communication, caching, and computing resources in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(1): 461–476. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3096881 [5] KAZMI S M A, DANG T N, YAQOOB I, et al. Infotainment enabled smart cars: A joint communication, caching, and computation approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(9): 8408–8420. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2930601 [6] ZHANG Shan, LI Junjie, LUO Hongbin, et al. Towards fresh and low-latency content delivery in vehicular networks: An edge caching aspect[C]. 2018 10th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2018: 1–6. [7] CHEN Jiayin, WU Huaqing, YANG Peng, et al. Cooperative edge caching with location-based and popular contents for vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 10291–10305. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3004720 [8] SUN Yaohua, PENG Mugen, and MAO Shiwen. A game-theoretic approach to cache and radio resource management in fog radio access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(10): 10145–10159. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2935098 [9] YU Zhengxin, HU Jia, MIN Geyong, et al. Proactive content caching for internet-of-vehicles based on peer-to-peer federated learning[C]. 2020 IEEE 26th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Hong Kong, China, 2020: 601–608. [10] XING Yuping, SUN Yanhua, QIAO Lan, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for cooperative edge caching in vehicular networks[C]. 2021 13th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Chongqing, China, 2021: 144–149. [11] QIAO Guanhua, LENG Supeng, MAHARJAN S, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for cooperative content caching in vehicular edge computing and networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(1): 247–257. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2945640 [12] DAI Yueyue, XU Du, LU Yunlong, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for edge caching and content delivery in internet of vehicles[C]. 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Changchun, China, 2019: 134–139. [13] CHEN Shuangwu, YAO Zhen, JIANG Xiaofeng, et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning-based cooperative edge caching for ultra-dense next-generation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(4): 2441–2456. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3044298 [14] CHETLUR V V and DHILLON H S. Coverage and rate analysis of downlink cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X) communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(3): 1738–1753. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2957222 [15] ASHERALIEVA A and NIYATO D. Game theory and lyapunov optimization for cloud-based content delivery networks with device-to-device and UAV-enabled caching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(10): 10094–10110. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2934027 [16] HAO Linchun, REN Pinyi, and DU Qinghe. Satellite QoS routing algorithm based on energy aware and load balancing[C]. 2020 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 2020: 685–690. -





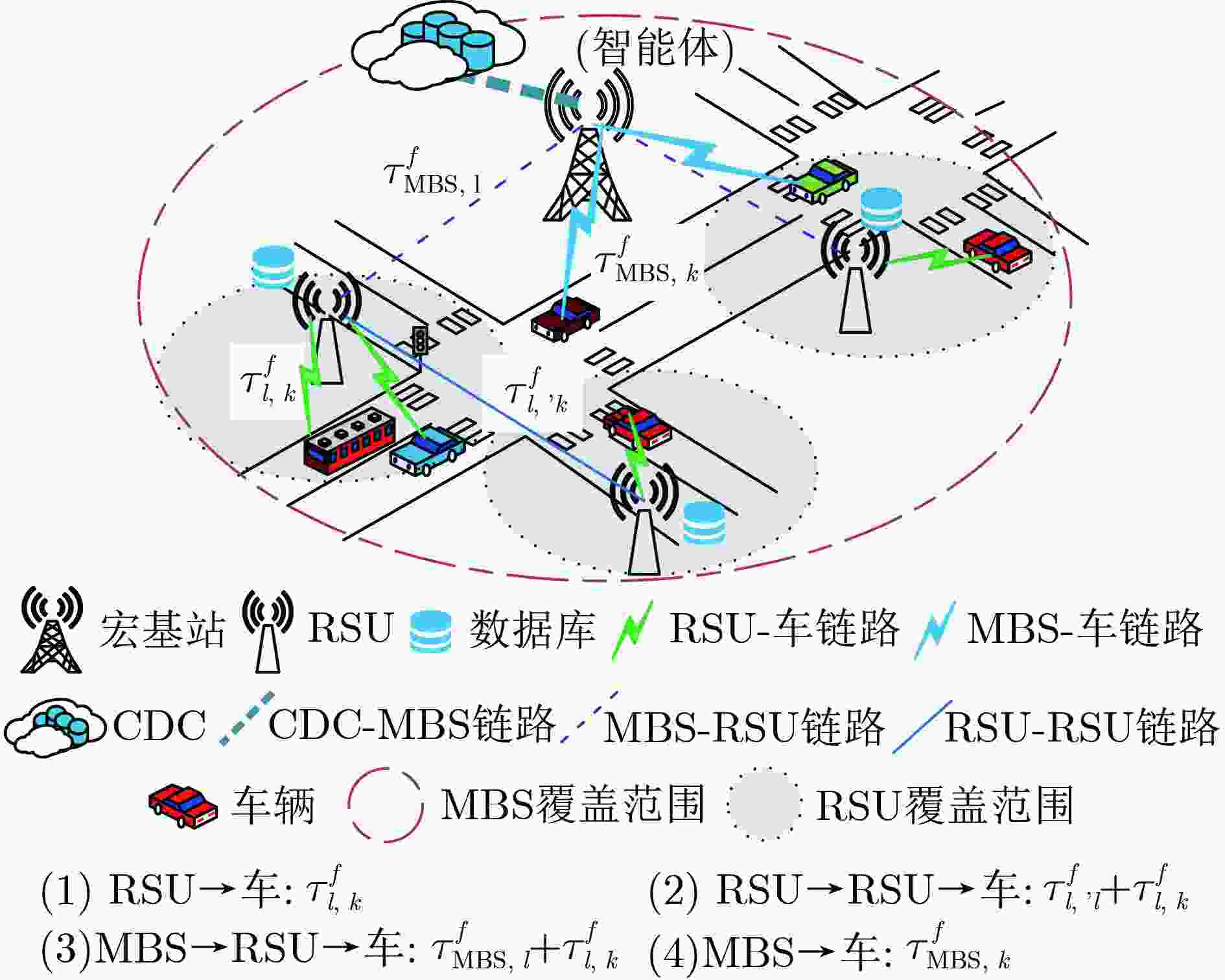
 下载:
下载:
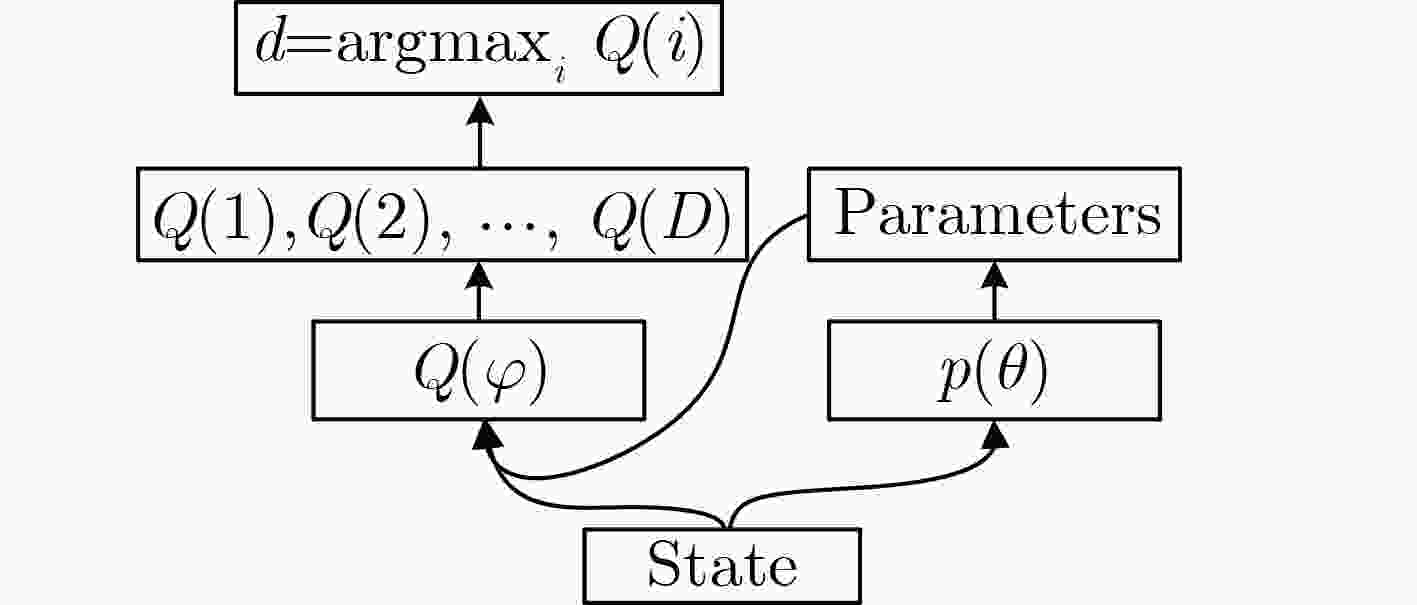
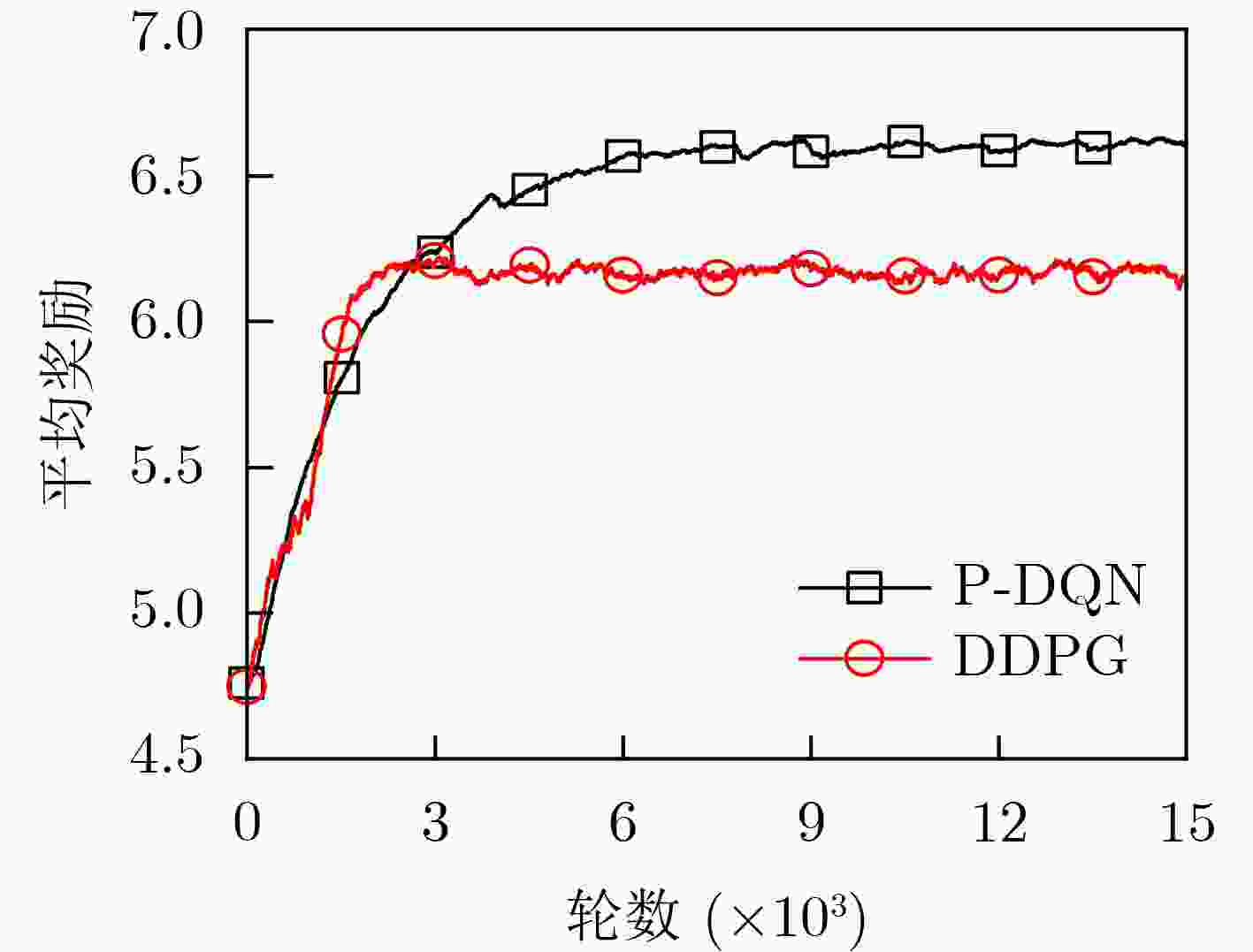
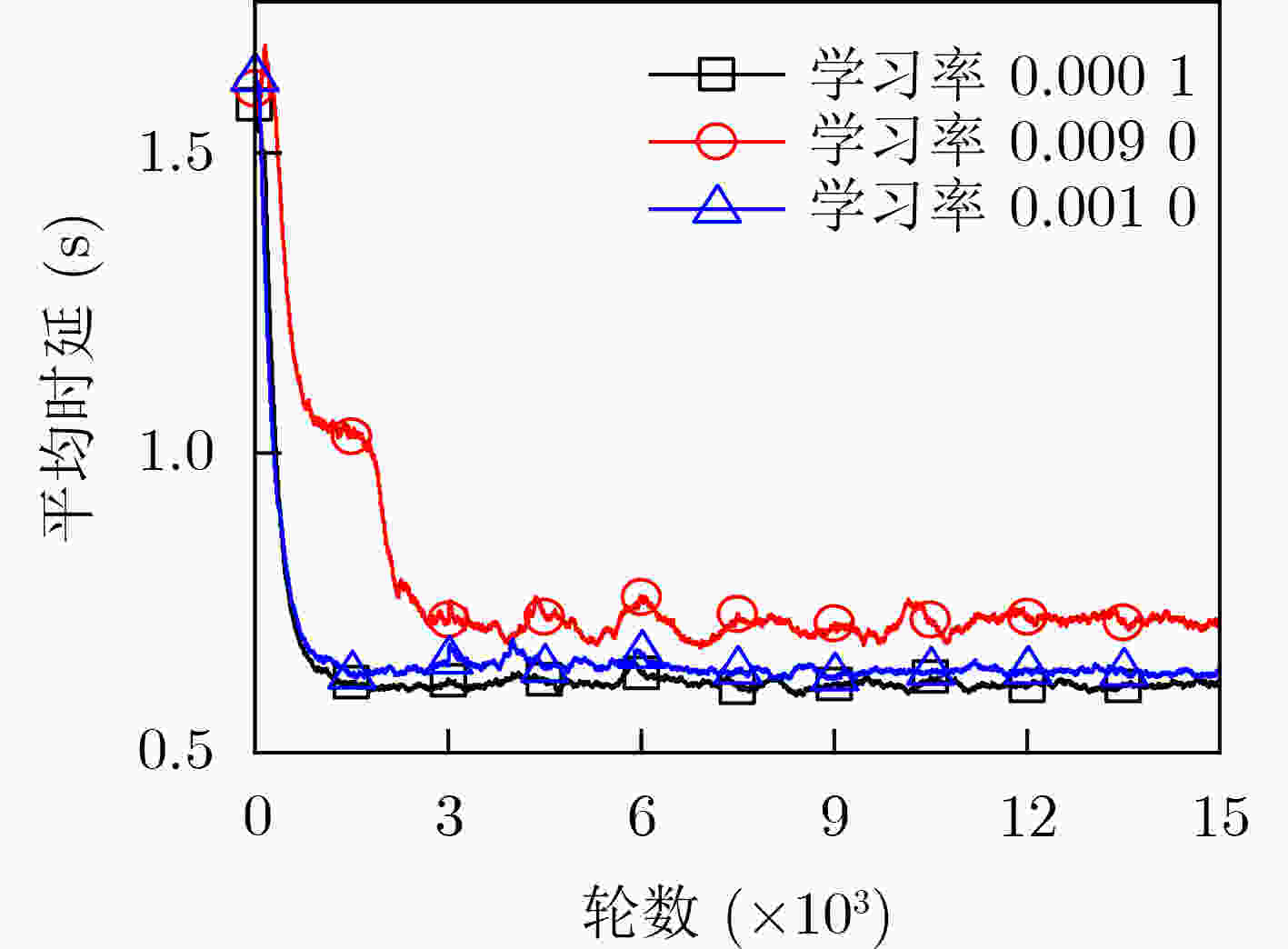


 下载:
下载:
