Automatic Modulation Recognition Based on Single-channel Multi-scale Graph Neural Network
-
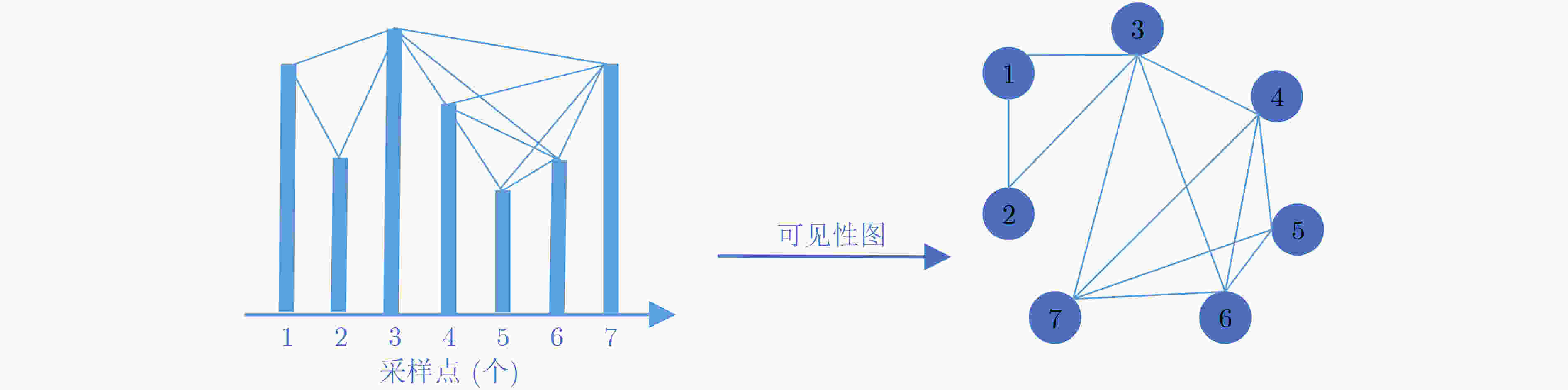
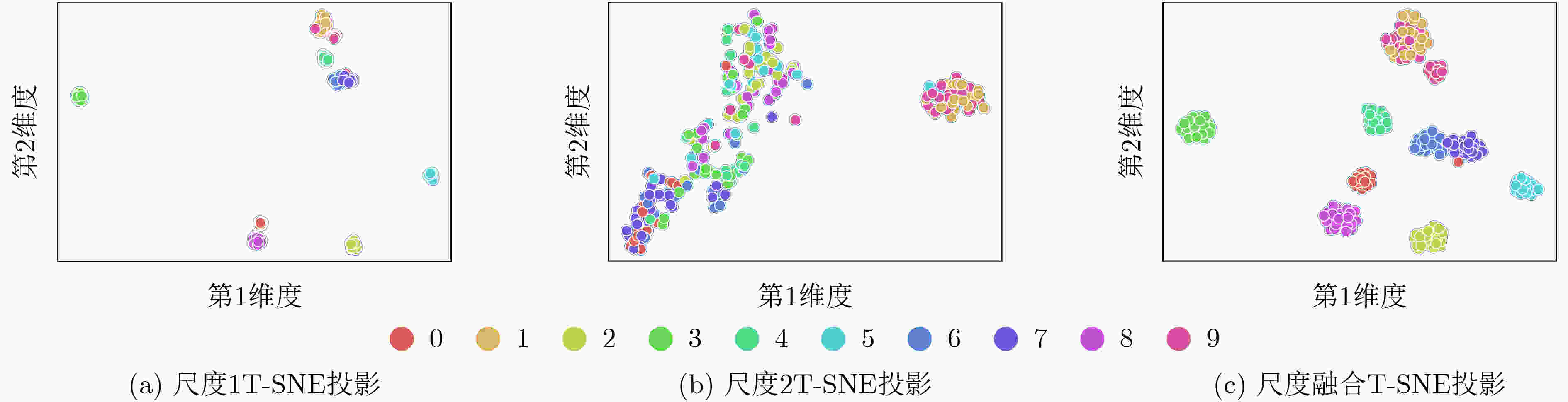
摘要: 针对自适应可见性图(AVG)算法复杂度过高且精度提升不明显的缺点,该文提出一种基于单通道多尺度图神经网络(SMGNN)的自动调制识别(AMR)框架,并对框架各个部分进行了可解释性研究。首先利用多层感知机和1维卷积自适应地实现了单通道信号序列和图之间的映射,有效降低了AVG算法的复杂度;其次,设计了一种多尺度图神经网络,将不同分辨率的特征进行融合,提升了模型识别准确率。实验表明,该文提出的SMGNN算法相比于AVG算法节省了近1/2的参数量,且识别精度得到了较大的提升。Abstract: Considering the shortcomings of the Adaptive Visibility Graph (AVG) algorithm being too complex and the accuracy improvement is not significant, an Automatic Modulation Recognition(AMR) framework based on Single-channel Multi-scale Graph Neural Network (SMGNN) is proposed and interpretability studies are conducted on the various parts of the framework. Firstly, the multi-layer perceptron and one-dimensional convolutional adaptive are used to realize the mapping between single-channel signal sequences and graphs, which reduces effectively the complexity of AVG algorithms. Secondly, a multi-scale graph neural network is designed to fuse the features of different resolutions, which improves the accuracy of model recognition. Experiments show that the SMGNN algorithm proposed in this paper saves nearly half of the parameter amount compared with the AVG algorithm, and the recognition accuracy has been greatly improved.
-
表 1 数据集RadioML2016.10b的参数设置
参数 定义值 采样速率(kHz) 200 信噪比(dB) –20~18,间隔为2 数据格式 IQ数据格式:2×128 信号数量 1 200 000 表 2 不同算法对数据集RML2016.10b的识别性能
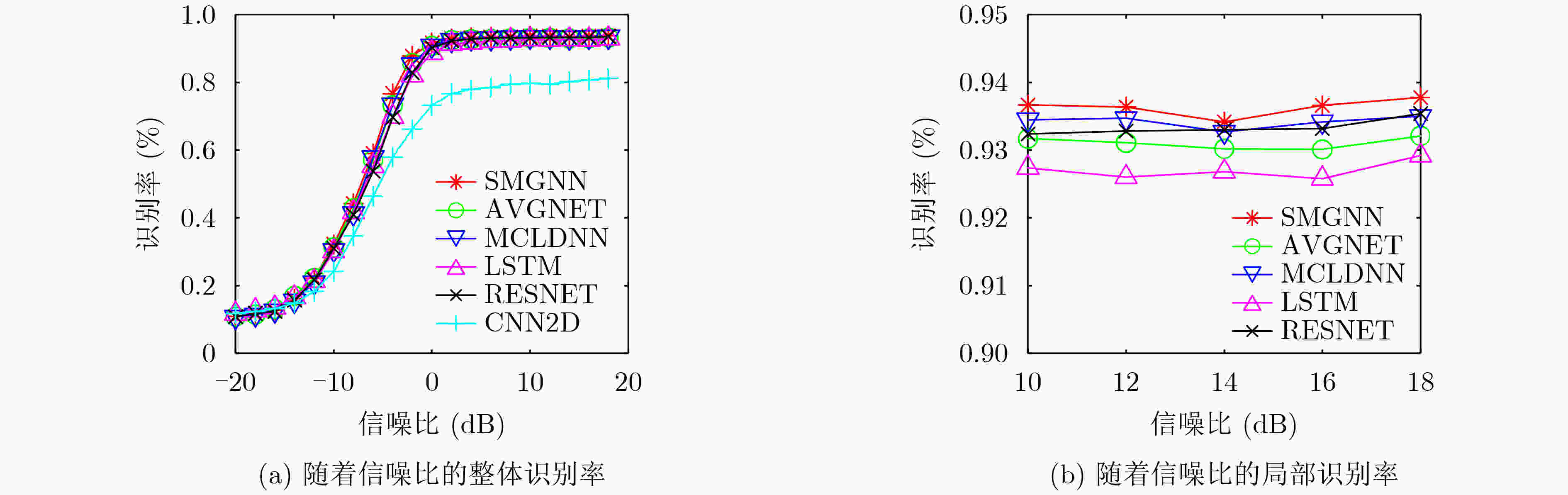
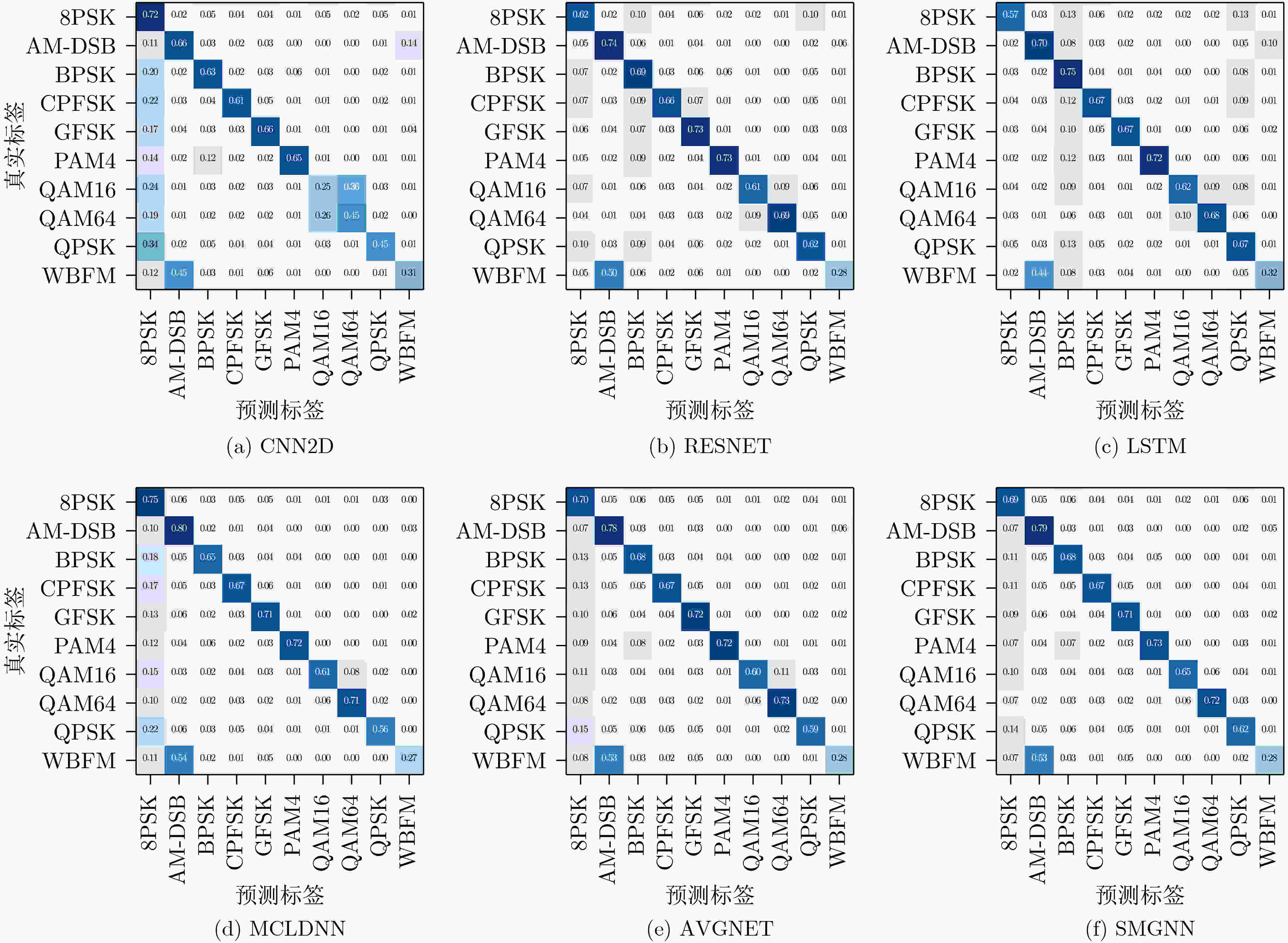
算法 识别精度(%) 参数量 平均推理时间(s) CNN2D 55.41 2706954 0.0192 RESNET 63.95 191946 0.0053 LSTM 63.72 197642 0.0064 MCLDNN 64.45 403722 0.0160 AVGNET 64.61 2311984 0.0310 SMGNN 65.36 1246720 0.0176 表 3 消融实验识别性能
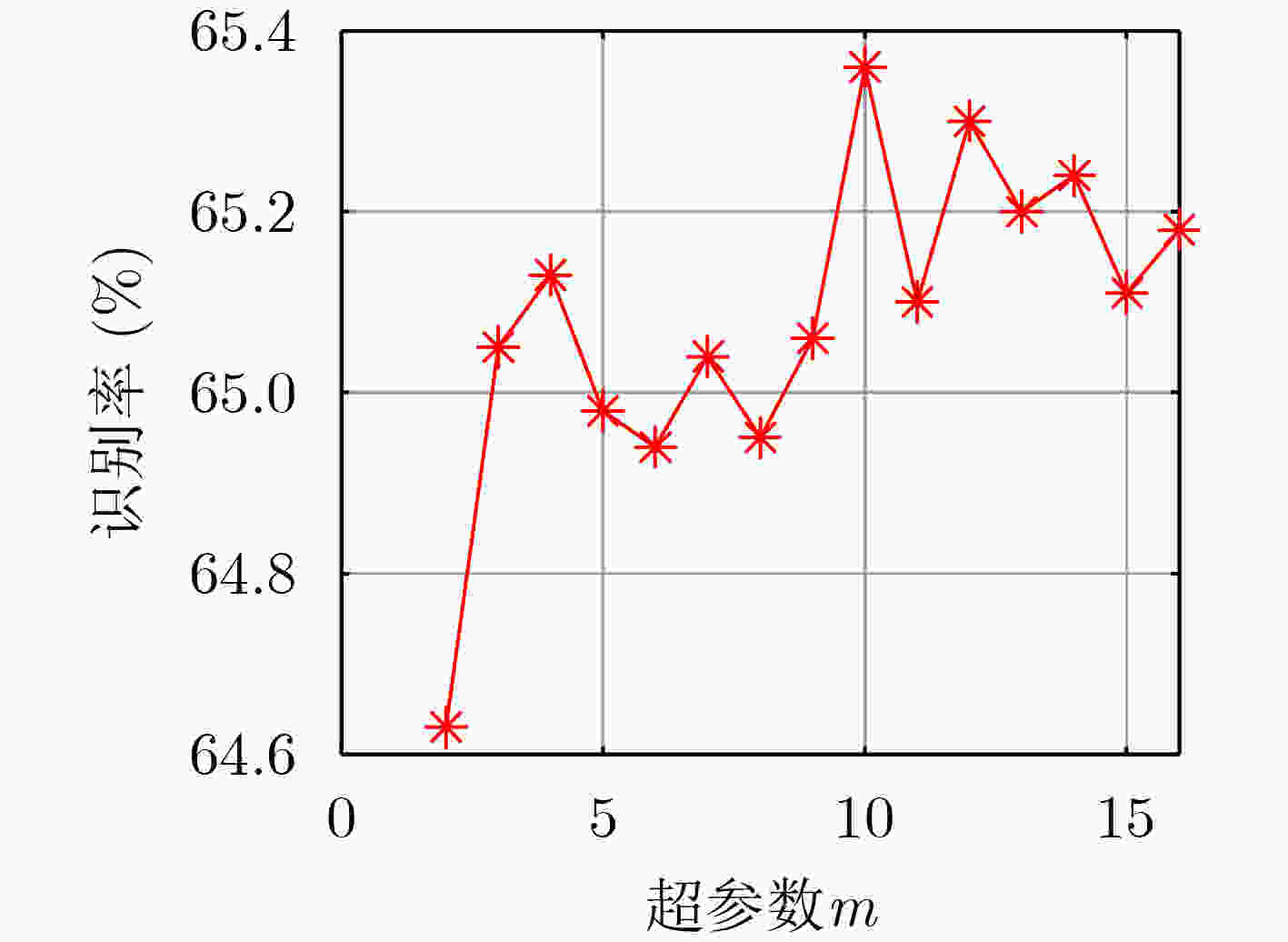
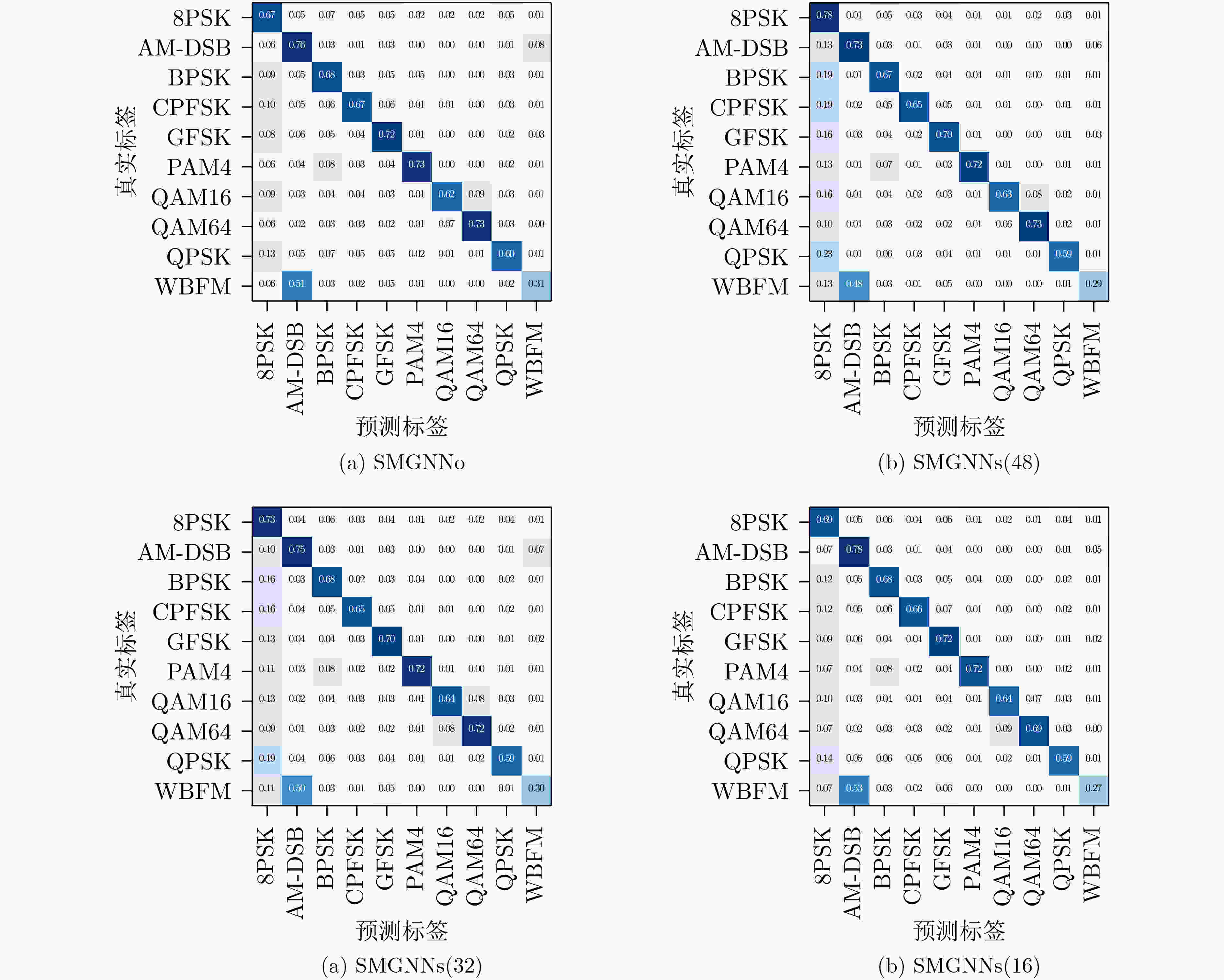
算法 识别精度(%) 参数量 平均推理时间(s) SMGNNo(单通道单尺度) 64.82 1156352 0.0165 SMGNNs(48维节点特征) 64.81 712976 0.0165 SMGNNs(32维节点特征) 64.67 327712 0.0154 SMGNNs(16维节点特征) 64.48 90928 0.0149 -
[1] LIANG Yingchang, TAN Junjie, and NIYATO D. Overview on intelligent wireless communication technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(7): 1–17. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020145 [2] XU J L, SU Wei, and ZHOU Mengchu. Likelihood-Ratio approaches to automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C, 2011, 41(4): 455–469. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2010.2076347 [3] XU J L, SU Wei, and ZHOU Mengchu. Software-Defined radio equipped with rapid modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2010, 59(4): 1659–1667. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2010.2041805 [4] O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, and CLANCY T C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks[C]. 17th International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Aberdeen, UK, 2016: 213–226. [5] WEST N E and O'SHEA T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–6. [6] 郭业才, 姚文强. 基于信噪比分类网络的调制信号分类识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825GUO Yecai and YAO Wenqiang. Modulation signal classification and recognition algorithm based on signal to noise ratio classification network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825 [7] 颜康, 金炜东, 黄颖坤, 等. 基于元学习的畸变雷达电磁信号识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1351–1357. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210190YAN Kang, JIN Weidong, HUANG Yingkun, et al. Distorted radar electromagnetic signal recognition based on meta-learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1351–1357. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210190 [8] XUE Fuzhao, SUN Aixin, ZHANG Hao, et al. GDPNet: Refining latent multi-view graph for relation extraction[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(16): 14194–14202. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i16.17670 [9] NAN Guoshun, LUO Guoqing, LENG Sicong, et al. Speaker-oriented latent structures for dialogue-based relation extraction[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2109.05182, 2021. [10] LACASA L, LUQUE B, BALLESTEROS F, et al. From time series to complex networks: The visibility graph[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(13): 4972–4975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709247105 [11] LUQUE B, LACASA L, BALLESTEROS F, et al. Horizontal visibility graphs: Exact results for random time series[J]. Physical Review E, 2009, 80(4 Pt 2): 046103. [12] QI Xuan, ZHOU Jinchao, QIU Kunfeng, et al. CLPVG: Circular limited penetrable visibility graph as a new network model for time series[J]. Chaos:An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2022, 32(1): 013130. doi: 10.1063/5.0048243 [13] WAN Tao, JIANG Kaili, TANG Yanli, et al. Automatic LPI radar signal sensing method using visibility graphs[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 159650–159660. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3020336 [14] LIU Yabo, LIU Yi, and YANG Cheng. Modulation recognition with graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 624–627. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2963828 [15] QI Xuan, ZHOU Jinchao, QIU Kunfeng, et al. AvgNet: Adaptive visibility graph neural network and its application in modulation classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(3): 1516–1526. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3146836 [16] YING R, YOU Jiaxuan, MORRIS C, et al. Hierarchical graph representation learning with differentiable pooling[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 4805–4815. [17] VAN DER MAATEN L and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(2605): 2579–2605. [18] 樊昌信, 曹丽娜. 通信原理[M]. 7版. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012: 176–225.FAN Changxin and CAO Lina. Principles of Communication[M]. 7th ed. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012: 176–225. [19] LIN T Y, DOLLAR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [20] O’SHEA T J, ROY T, and CLANCY T C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 168–179. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2797022 [21] RAJENDRAN S, MEERT W, GIUSTINIANO D, et al. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low-cost spectrum sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(3): 433–445. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2835460 [22] XU Jialang, LUO Chunbo, PARR G, et al. A spatiotemporal multi-channel learning framework for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629–1632. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2999453 [23] BASTIAN M, HEYMANN S, and JACOMY M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks[J]. Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, 2009, 3(1): 361–362. doi: 10.1609/icwsm.v3i1.13937 -






 下载:
下载:
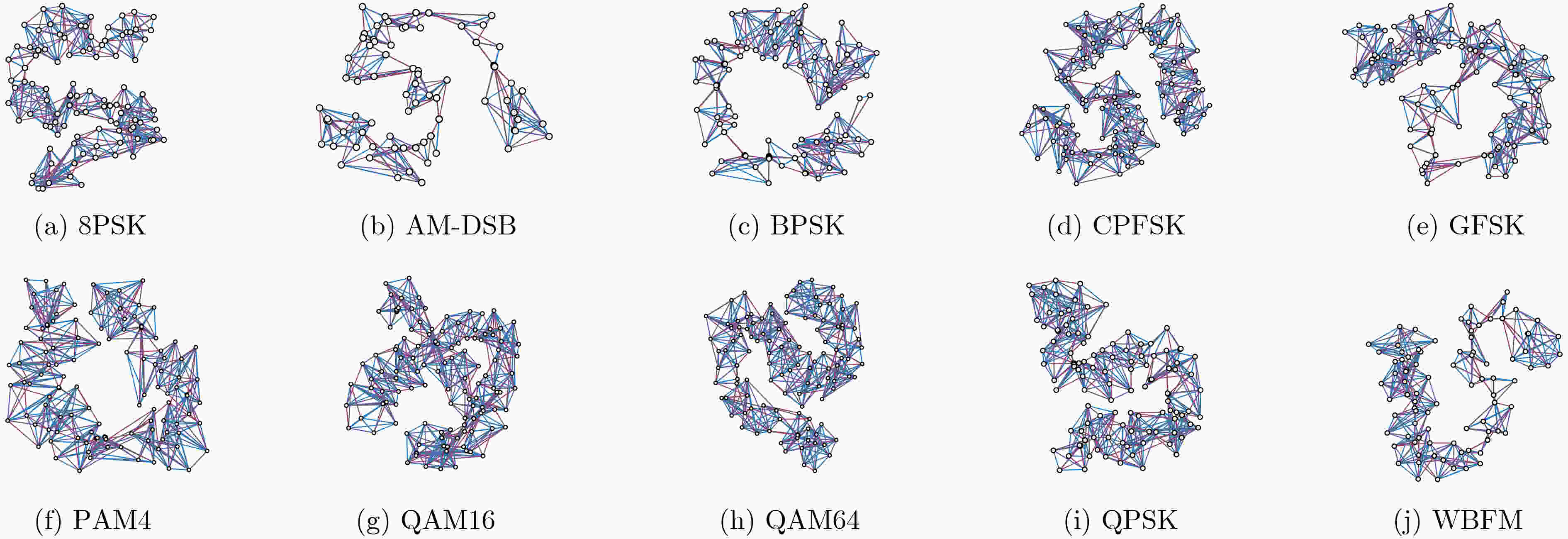


 下载:
下载:
