Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Improved Dual Path Generation Adversarial Network
-
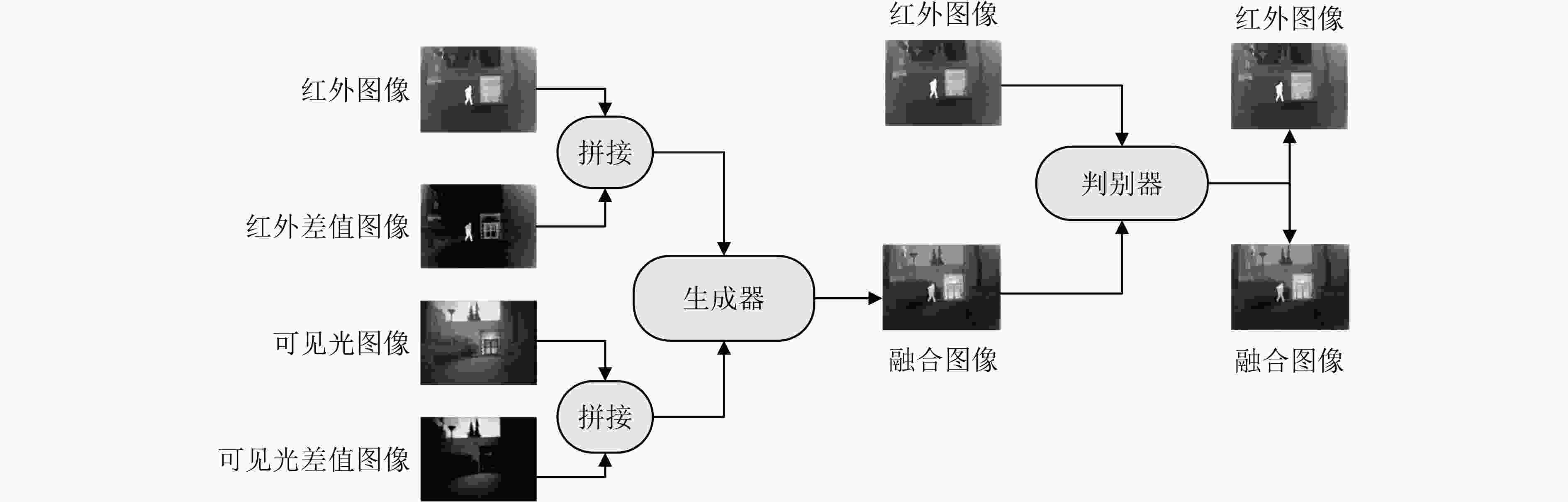
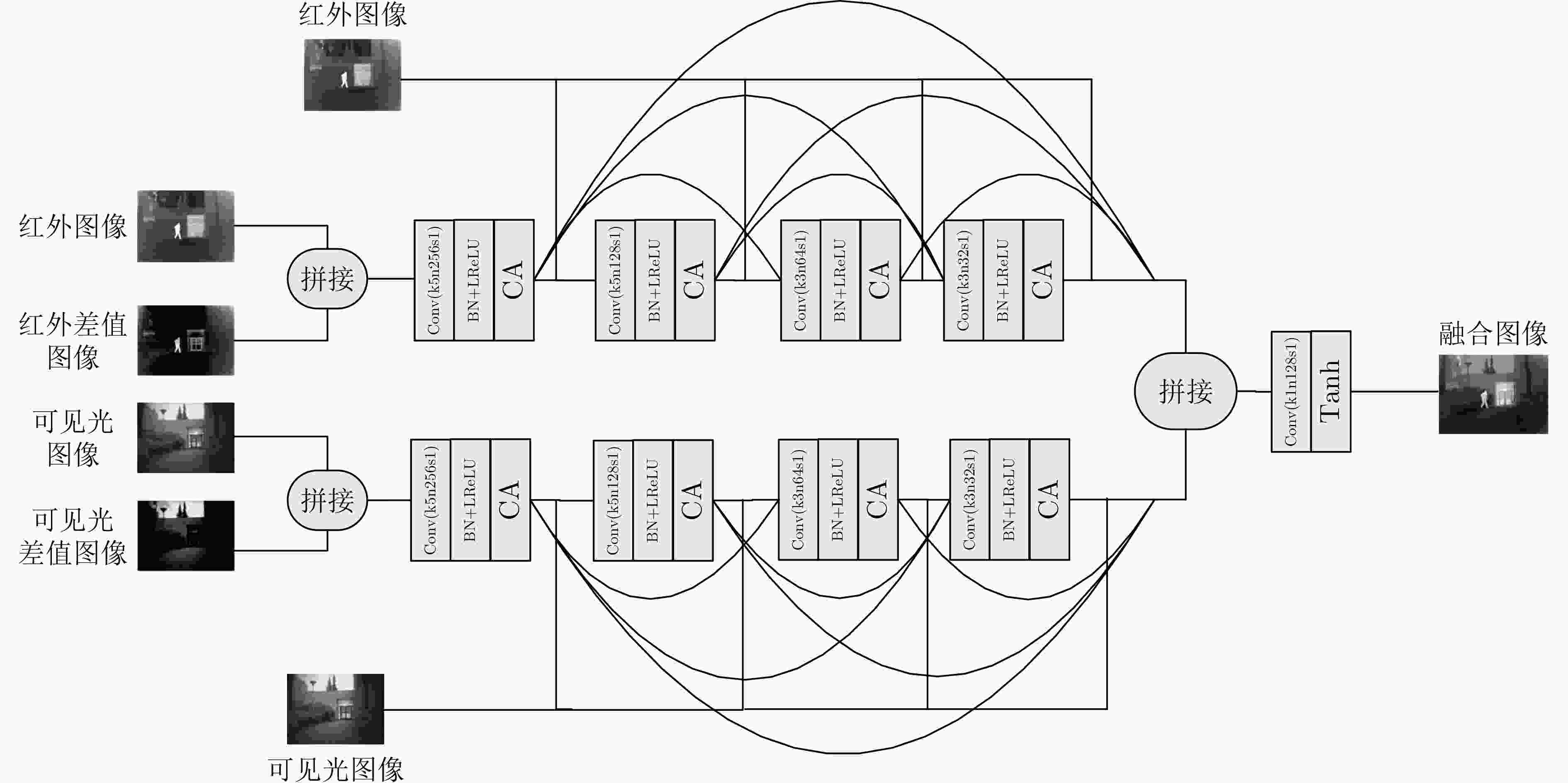
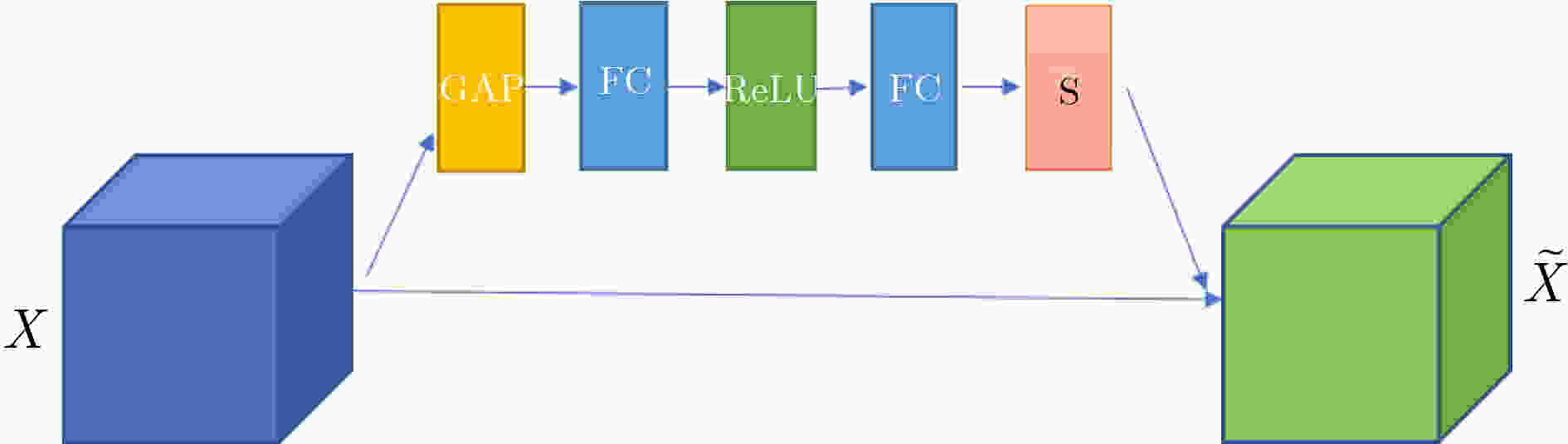
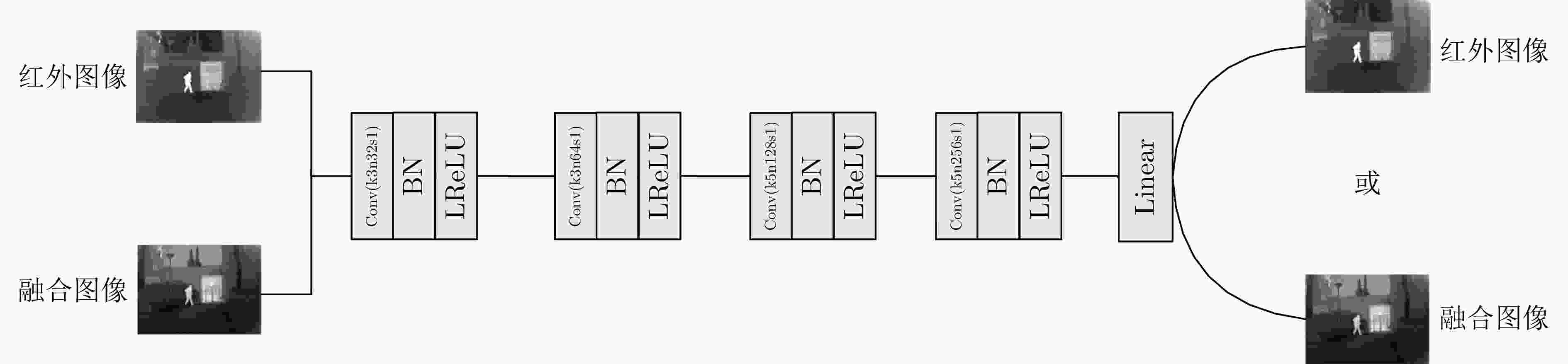
摘要: 为了使融合图像保留更多源图像的信息,该文提出一种端到端的双融合路径生成对抗网络(GAN)。首先,在生成器中采用结构相同、参数独立的双路径密集连接网络,构建红外差值路径和可见光差值路径以提高融合图像的对比度,引入通道注意力机制以使网络更聚焦于红外典型目标和可见光纹理细节;其次,将两幅源图像直接输入到网络的每一层,以提取更多的源图像特征信息;最后,考虑损失函数之间的互补,加入差值强度损失函数、差值梯度损失函数和结构相似性损失函数,以获得更具对比度的融合图像。实验表明,与多分类约束的生成对抗网络(GANMcC)、残差融合网络(RFnest)等相关融合算法相比,该方法得到的融合图像不仅在多个评价指标上均取得了最好的效果,而且具有更好的视觉效果,更符合人类视觉感知。Abstract: An end-to-end dual fusion path Generation Adversarial Network (GAN) is proposed to preserve more information from the source image. Firstly, in the generator, a double path dense connection network with the same structure and independent parameters is used to construct the infrared difference path and the visible difference path to improve the contrast of the fused image, and the channel attention mechanism is introduced to make the network focus more on the typical infrared targets and the visible texture details; Secondly, two source images are directly input into each layer of the network to extract more source image feature information; Finally, considering the complementarity between the loss functions, the difference intensity loss function, the difference gradient loss function and the structural similarity loss function are added to obtain a more contrast fused image. Experiments show that, compared with a Generative Adversarial Network with Multi-classification Constraints (GANMcC), Residual Fusion network for infrared and visible images (RFnest) and other related fusion algorithms, the fusion image obtained by this method not only achieves the best effect in multiple evaluation indicators, but also has better visual effect and is more in line with human visual perception.
-
Key words:
- Image fusion /
- Deep learning /
- Generate Adversarial Network(GAN) /
- Infrared image /
- Visible image
-
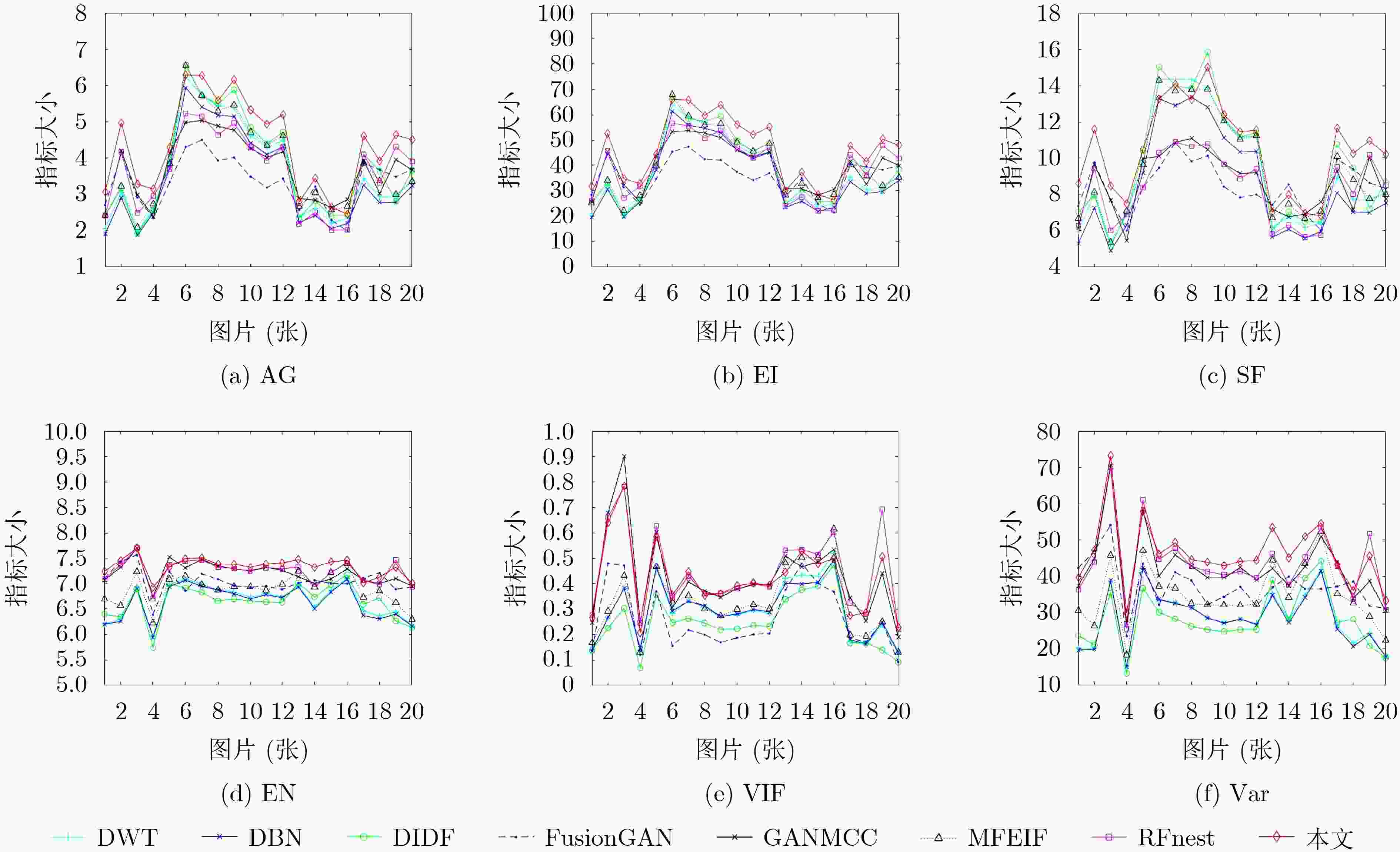
表 1 TNO定量对比实验结果
SF AG EI EN VIF Var DWT 6.8154 2.6473 26.0032 6.3753 0.2901 24.9950 DBN 6.1192 2.4574 24.8012 6.3375 0.2814 24.3822 DIDF 7.5609 2.9884 29.5566 6.5825 0.3417 30.0428 FusionGAN 6.2395 2.4168 24.1424 6.5761 0.2575 31.1204 GANMcC 6.1391 2.5457 25.8946 6.7474 0.4217 33.6386 MFEIF 7.2104 2.9034 29.3522 6.6568 0.3587 33.0184 RFnest 5.8727 2.6821 28.6441 6.9907 0.5133 37.2477 本文 9.0860 3.5805 35.1696 7.0731 0.4112 33.6727 表 2 FLIR定量对比实验结果
SF AG EI EN VIF Var DWT 9.0511 3.5425 37.0015 6.8426 0.3336 31.4294 DBN 8.3459 3.3623 35.3199 6.7845 0.3306 31.0446 DIDF 9.3434 3.6905 38.6017 6.7863 0.2943 31.5181 FusionGAN 8.1142 3.2045 34.4298 7.0167 0.2892 37.4859 GANMcC 8.6665 3.6744 39.4219 7.2089 0.4269 42.4833 MFEIF 9.4752 3.7719 39.8841 7.0171 0.3807 37.8447 RFnest 7.6279 3.3103 36.2151 7.2968 0.4503 44.1210 本文 9.7488 4.1359 44.1298 7.4163 0.4394 47.7148 表 3 不同融合方法计算效率对比结果(s)
DWT DBN DIDF FusionGAN GANMcC MFEIF RFnest 本文 40.0470 7.6031 10.0652 18.4680 31.8253 15.4883 19.8578 6.0944 表 4 4组融合模型定量对比结果
SF AG EI EN VIF Var No_both 4.3894 1.5310 15.7062 6.5230 0.1749 34.9732 No_dir 5.6119 2.2964 23.0950 6.7165 0.3504 41.0505 No_resource 4.9631 1.7396 18.6436 6.6073 0.2943 39.2500 本文 6.9145 2.8615 29.0777 7.1594 0.4093 48.0217 -
[1] GOSHTASBY A A and NIKOLOV S. Image fusion: Advances in the state of the art[J]. Information Fusion, 2007, 8(2): 114–118. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2006.04.001 [2] TOET A, HOGERVORST M A, NIKOLOV S G, et al. Towards cognitive image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2010, 11(2): 95–113. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2009.06.008 [3] 朱浩然, 刘云清, 张文颖. 基于对比度增强与多尺度边缘保持分解的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1294–1300. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170956ZHU Haoran, LIU Yunqing, and ZHANG Wenying. Infrared and visible image fusion based on contrast enhancement and multi-scale edge-preserving decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1294–1300. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170956 [4] GAO Yuan, MA Jiayi, and YUILLE A L. Semi-supervised sparse representation based classification for face recognition with insufficient labeled samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(5): 2545–2560. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2675341 [5] LIU C H, QI Y, and DING W R. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 83: 94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2017.04.018 [6] HE Changtao, LIU Quanxi, LI Hongliang, et al. Multimodal medical image fusion based on IHS and PCA[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 7: 280–285. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2010.11.045 [7] 张介嵩, 黄影平, 张瑞. 基于CNN的点云图像融合目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(5): 200418. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200418ZHANG Jiesong, HUANG Yingping, and ZHANG Rui. Fusing point cloud with image for object detection using convolutional neural networks[J]. Opto-electronic Engineering, 2021, 48(5): 200418. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200418 [8] 陈永, 张娇娇, 王镇. 多尺度密集连接注意力的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2022, 30(18): 2253–2266. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2253CHEN Yong, ZHANG Jiaojiao, and WANG Zhen. Infrared and visible image fusion based on multi-scale dense attention connection network[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(18): 2253–2266. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2253 [9] AN Wenbo and WANG Hongmei. Infrared and visible image fusion with supervised convolutional neural network[J]. Optik, 2020, 219: 165120. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165120 [10] LI Jing, HUO Hongtao, LIU Kejian, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion using dual discriminators generative adversarial networks with Wasserstein distance[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 529: 28–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.04.035 [11] MA Jiayi, YU Wei, LIANG Pengwei, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11–26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004 [12] MA Jiayi, ZHANG Hao, SHAO Zhenfeng, et al. GANMcC: A generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5005014. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3038013 [13] QU Guihong, ZHANG Dali, and YAN Pingfan. Information measure for performance of image fusion[J]. Electronics Letters, 2002, 38(7): 313–315. doi: 10.1049/el:20020212 [14] XYDEAS C S and PETROVIĆ V. Objective image fusion performance measure[J]. Electronics Letters, 2000, 36(4): 308–309. doi: 10.1049/el:20000267 [15] CUI Guangmang, FENG Huajun, XU Zhihai, et al. Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 341: 199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.12.032 [16] ESKICIOGLU A M and FISHER P S. Image quality measures and their performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1995, 43(12): 2959–2965. doi: 10.1109/26.477498 [17] LI H, MANJUNATH B S, and MITRA S K. Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet transform[J]. Graphical Models and Image Processing, 1995, 57(3): 235–245. doi: 10.1006/gmip.1995.1022 [18] FU Yu and WU Xiaojun. A dual-branch network for infrared and visible image fusion[C]. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 10675–10680. [19] ZHAO Zixiang, XU Shuang, ZHANG Chunxia, et al. DIDFuse: Deep image decomposition for infrared and visible image fusion[C]. Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 970–976. [20] LIU Jinyuan, FAN Xin, JIANG Ji, et al. Learning a deep multi-scale feature ensemble and an edge-attention guidance for image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(1): 105–119. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3056725 [21] LI Hui, WU Xiaojun, and KITTLER J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 72–86. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.023 [22] ROBERTS J W, AARDT J A V, and AHMED F B. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2008, 2(1): 023522. doi: 10.1117/1.2945910 [23] RAO Yunjiang. In-fibre Bragg grating sensors[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 1997, 8(4): 355–375. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/8/4/002 [24] HAN Yu, CAI Yunze, CAO Yin, et al. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(2): 127–135. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2011.08.002 [25] ZHANG Xingchen, YE Ping, and XIAO Gang. VIFB: A visible and infrared image fusion benchmark[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 468–478. -
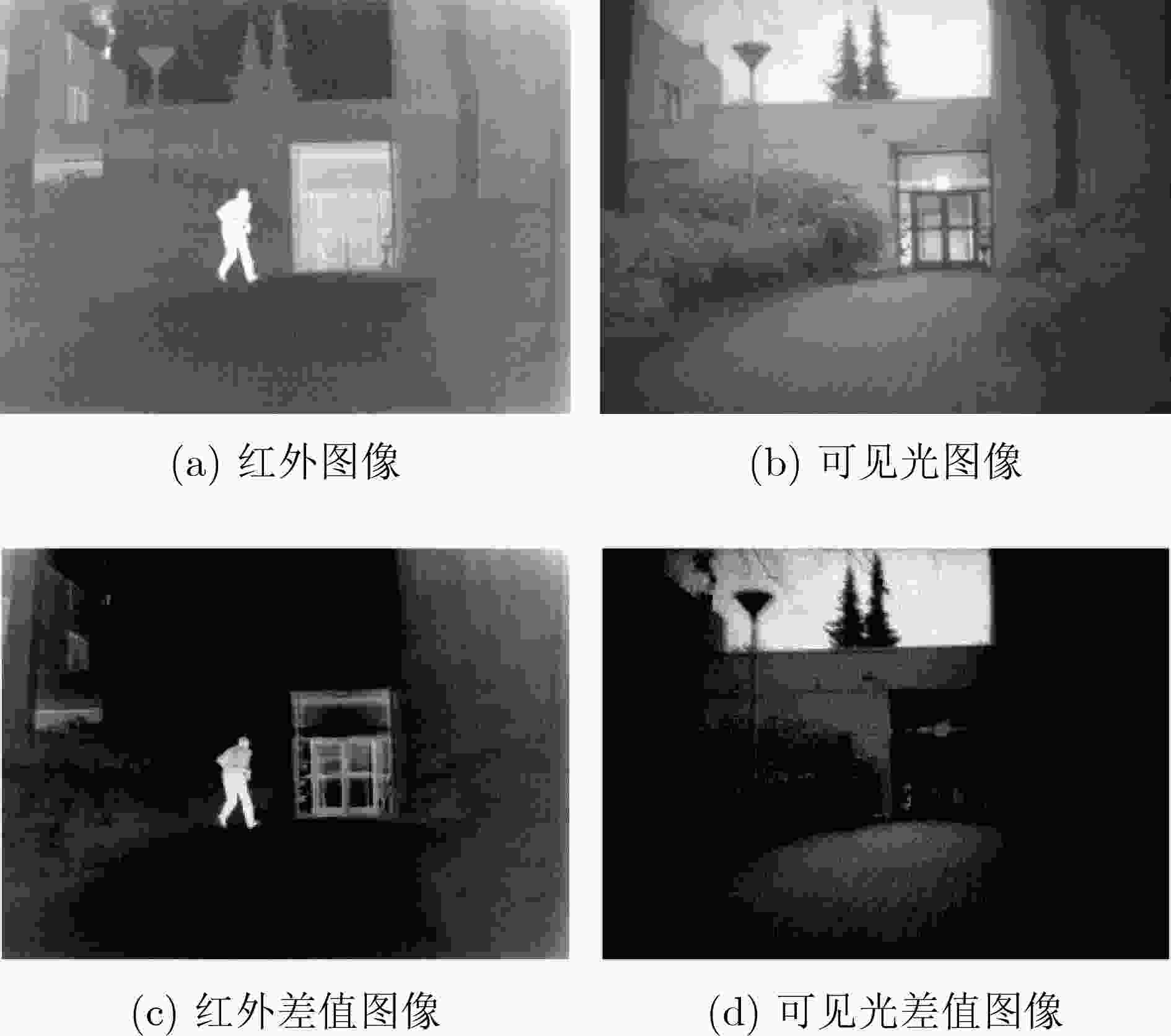






 下载:
下载:
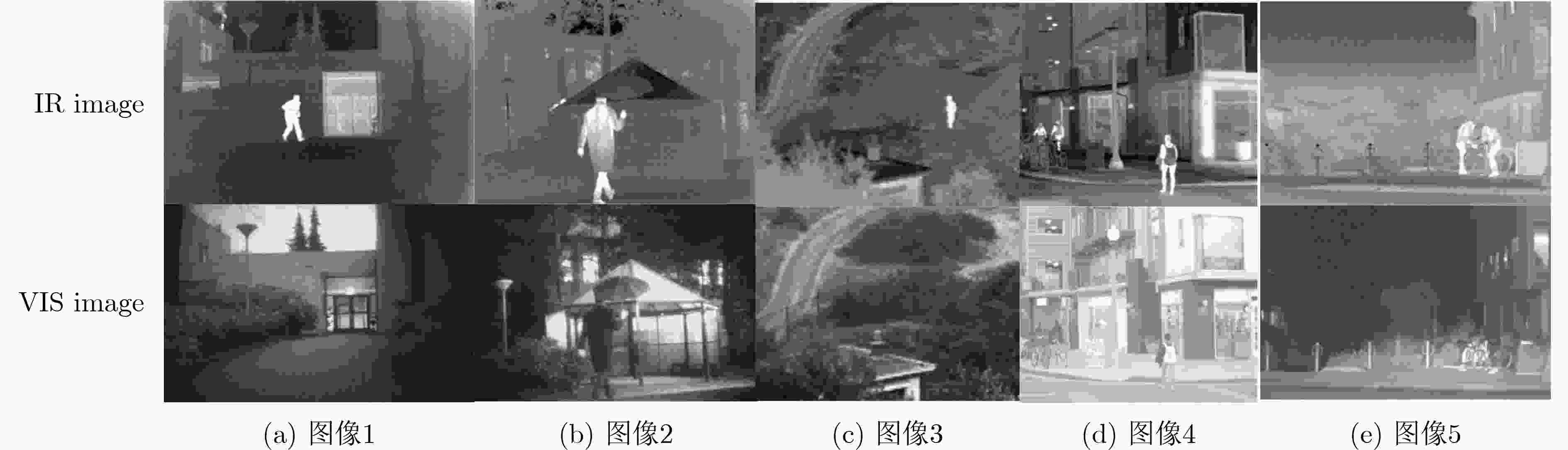





 下载:
下载:
