Byzantine Fault-Tolerance Consensus Algorithm Based on Perfect Binary Tree Communication
-
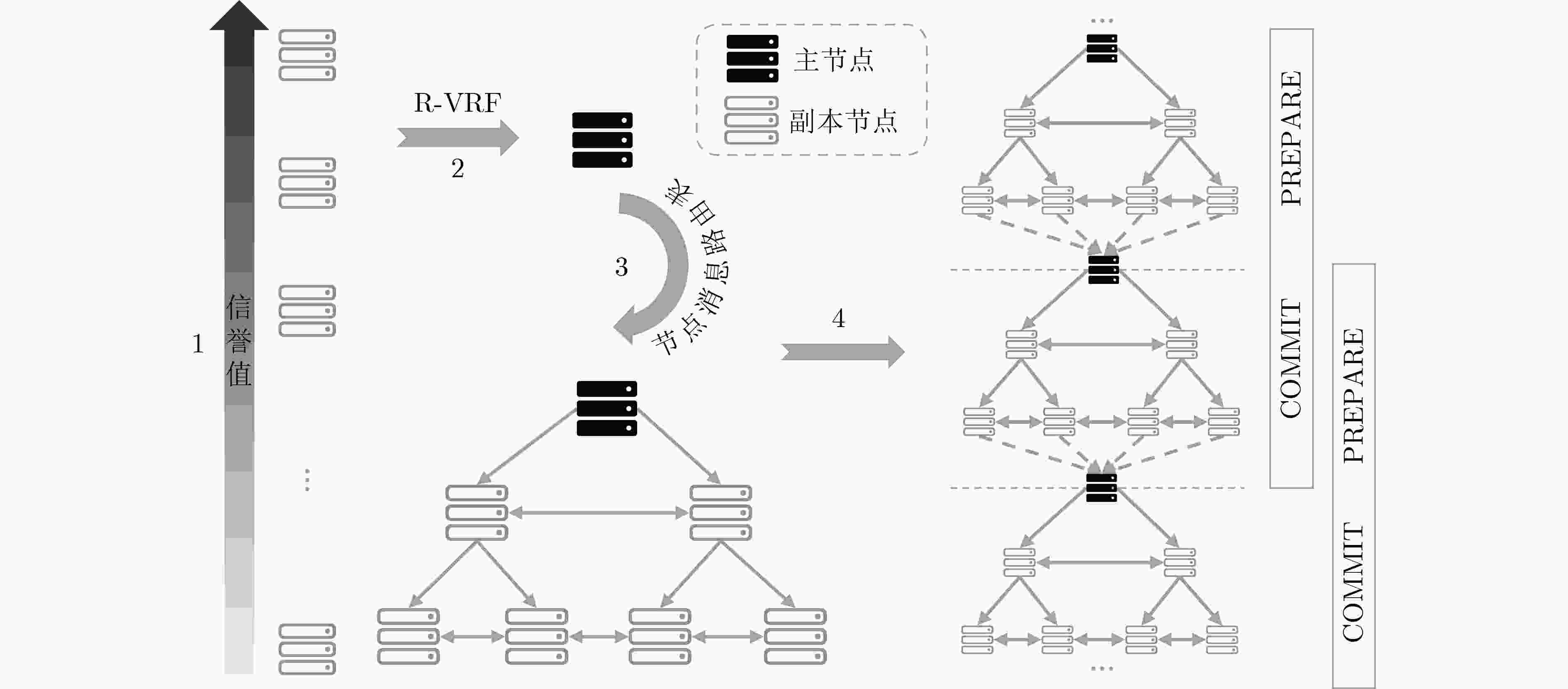
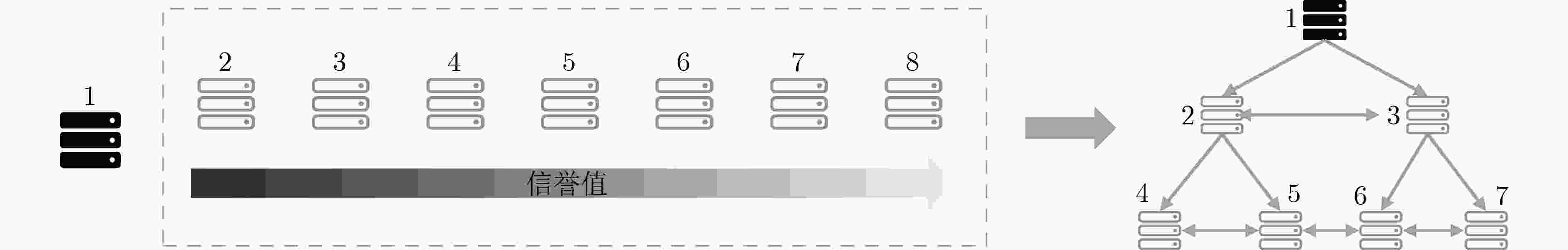
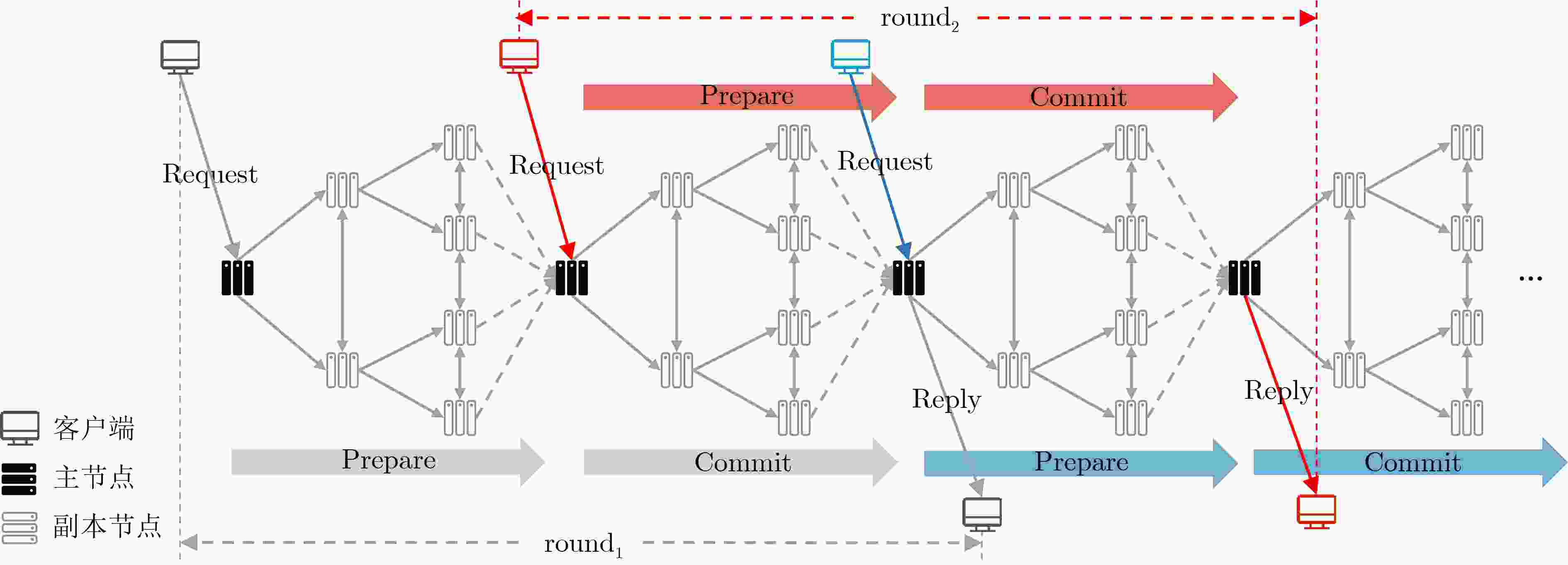
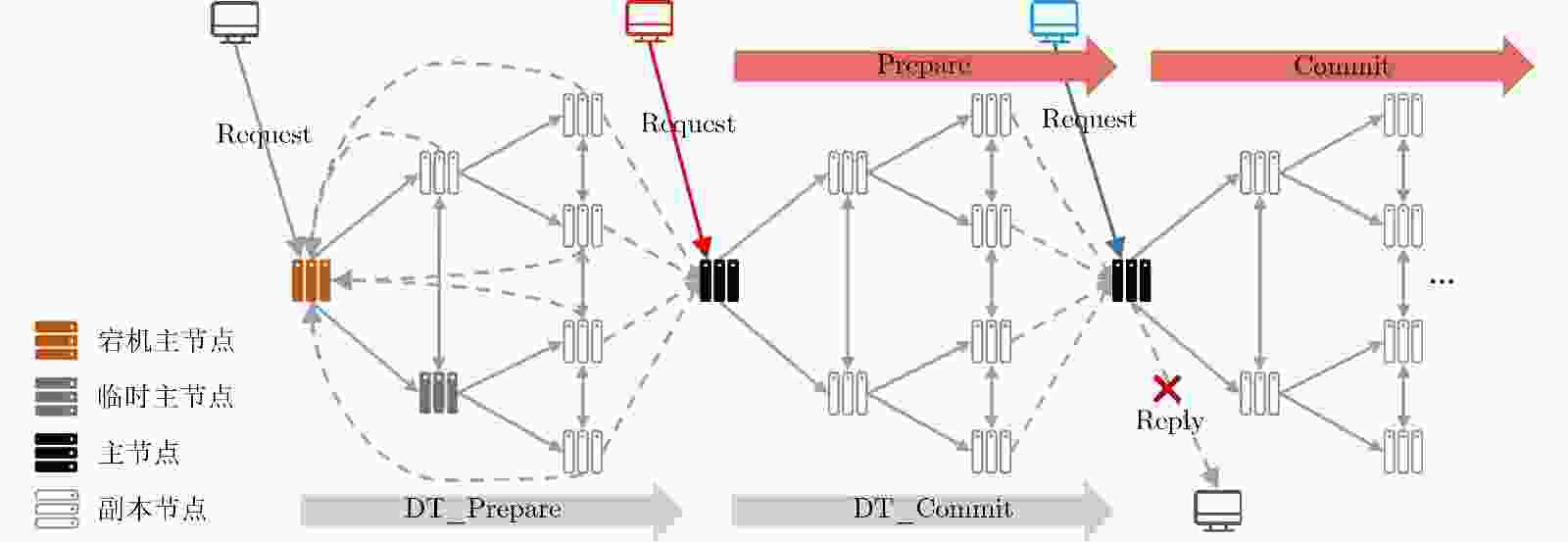
摘要: 针对实用拜占庭容错(PBFT)算法中主节点可预测、通信复杂度高和作恶节点缺少惩罚机制的问题,该文提出一种基于完美二叉树通信拓扑的联盟链拜占庭容错算法(PBT-BFT)。首先设计了信誉评估模型对节点的行为进行评估,同时提出基于信誉的可验证随机函数(R-VRF),使得随机抽取概率与信誉值呈正相关,保证了拥有不同信誉值的节点抽签的公平性和随机性。然后,设计了完美二叉树通信拓扑,将通信复杂度降低至线性复杂度,同时提出轮换主节点和流水线工作机制,提高了共识效率。实验结果表明,与PBFT相比,平均吞吐量提高了121.6%,平均时延降低了73.8%,能够很好地适用于大规模网络节点的联盟链。Abstract: Considering the problems of a predictable primary node, high communication complexity, and lack of punishment mechanism for malicious nodes in Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) algorithm, a consortium chain Byzantine Fault-Tolerant algorithm based on Perfect Binary Tree communication topology(PBT-BFT) is proposed. In PBT-BFT, a reputation evaluation model is designed to evaluate the behavior of nodes. At the same time, a Reputation-based Verifiable Random Function (R-VRF) is proposed, which makes the probability of random extraction positively correlated with the reputation value, and ensures the fairness and randomness of the lottery for nodes with different reputation values. Then, a perfect binary tree communication topology is designed to reduce the communication complexity to linear complexity, and a rotating primary node and Pipelining are proposed to improve the consensus efficiency. The experimental results show that compared with PBFT, the average throughput is increased by 121.6%, and the average delay is reduced by 73.8%, which can be well applied to the consortium chain of large-scale network nodes.
-
表 1 信誉评估指标
1级指标 2级指标 符号表示 节点贡献度 $C_r^i$ 转发消息数 ${\text{Info}}_r^i$ 最大转发消息数 ${\text{MaxInfo}}_r^i$ 创建有效区块 $B_r^i$ 节点作恶度 $W_r^i$ 出现宕机行为 ${\text{Down}}_r^i$ 出现作恶行为 ${\text{Bad}}_r^i$ 连续作恶系数 $\gamma $ 代价函数 ${\text{Cost}}\left( x \right)$ 历史信誉度 ${R_{{\text{old}}}}$ – – 表 2 节点消息路由表
节点序号 邻接节点 父节点 信誉值 1 {2, 3} – 0.5 2 {3, 4, 5} 1 0.6 3 {2, 6, 7} 1 0.5 -
[1] NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system[EB/OL]. https://bitcoin.org/en/bitcoin-paper, 2022. [2] 陈友荣, 章阳, 陈浩, 等. 面向车联网异构节点的区块链高效一致性共识算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 314–323. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201065CHEN Yourong, ZHANG Yang, CHEN Hao, et al. Efficient consistency consensus algorithm of blockchain for heterogeneous nodes in the internet of vehicles[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 314–323. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201065 [3] 陈友荣, 陈浩, 韩蒙, 等. 基于信用等级划分的医疗数据安全共识算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 279–287. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200893CHEN Yourong, CHEN Hao, HAN Meng, et al. Security consensus algorithm of medical data based on credit rating[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 279–287. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200893 [4] 邓小鸿, 王智强, 李娟, 等. 主流区块链共识算法对比研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(1): 1–8. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.06.0210DENG Xiaohong, WANG Zhiqiang, LI Juan, et al. Comparative research on mainstream blockchain consensus algorithms[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(1): 1–8. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.06.0210 [5] CASTRO M and LISKOV B. Practical Byzantine fault tolerance[C]. The Third Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, New Orleans, USA, 1999: 173–186. [6] 黄冬艳, 李浪, 陈斌, 等. RBFT: 基于Raft集群的拜占庭容错共识机制[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(3): 209–219. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021043HUANG Dongyan, LI Lang, CHEN Bin, et al. RBFT: A new Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus mechanism based on Raft cluster[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(3): 209–219. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021043 [7] 赖英旭, 薄尊旭, 刘静. 基于改进PBFT算法防御区块链中Sybil攻击的研究[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(9): 104–117. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020170LAI Yingxu, BO Zunxu, and LIU Jing. Research on Sybil attack in defense blockchain based on improved PBFT algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(9): 104–117. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020170 [8] 王日宏, 袁杉杉, 徐泉清, 等. 基于时间权重值的共识算法研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(11): 3243–3248. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.03.0097WANG Rihong, YUAN Shanshan, XU Quanqing, et al. Consensus algorithm based on time weight value[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(11): 3243–3248. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.03.0097 [9] ZHAN Yu, WANG Baocang, LU Rongxing, et al. DRBFT: Delegated randomization Byzantine fault tolerance consensus protocol for blockchains[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 559: 8–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.12.077 [10] LI Y X, QIAO Liang, and LV Zhihan. An optimized byzantine fault tolerance algorithm for consortium blockchain[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2021, 14(5): 2826–2839. doi: 10.1007/s12083-021-01103-8 [11] CHEN Yineng, LI Ming, ZHU Xinghui, et al. An improved algorithm for practical byzantine fault tolerance to large-scale consortium chain[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2022, 59(2): 102884. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2022.102884 [12] TANG Song, WANG Zhiqiang, JIANG Jian, et al. Improved PBFT algorithm for high-frequency trading scenarios of alliance blockchain[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 4426. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08587-1 [13] MICALI S, RABIN M, and VADHAN S. Verifiable random functions[C]. The 40th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, New York, USA, 1999: 120–130. [14] GILAD Y, HEMO R, MICALI S, et al. Algorand: Scaling byzantine agreements for cryptocurrencies[C]. The 26th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Shanghai, China, 2017: 51–68. [15] GOLDBERG S, REYZIN L, PAPADOPOULOS D, et al. Verifiable random functions (VRFs)[EB/OL], https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-irtf-cfrg-vrf/11/, 2022. [16] ALQAHTANI S and DEMIRBAS M. Bottlenecks in blockchain consensus protocols[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Omni-Layer Intelligent Systems (COINS), Barcelona, Spain, 2021: 1–8. [17] YIN Maofan, MALKHI D, REITER M K, et al. HotStuff: BFT consensus with linearity and responsiveness[C]. The 2019 ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing, Toronto, Canada, 2019: 347–356. -





 下载:
下载:
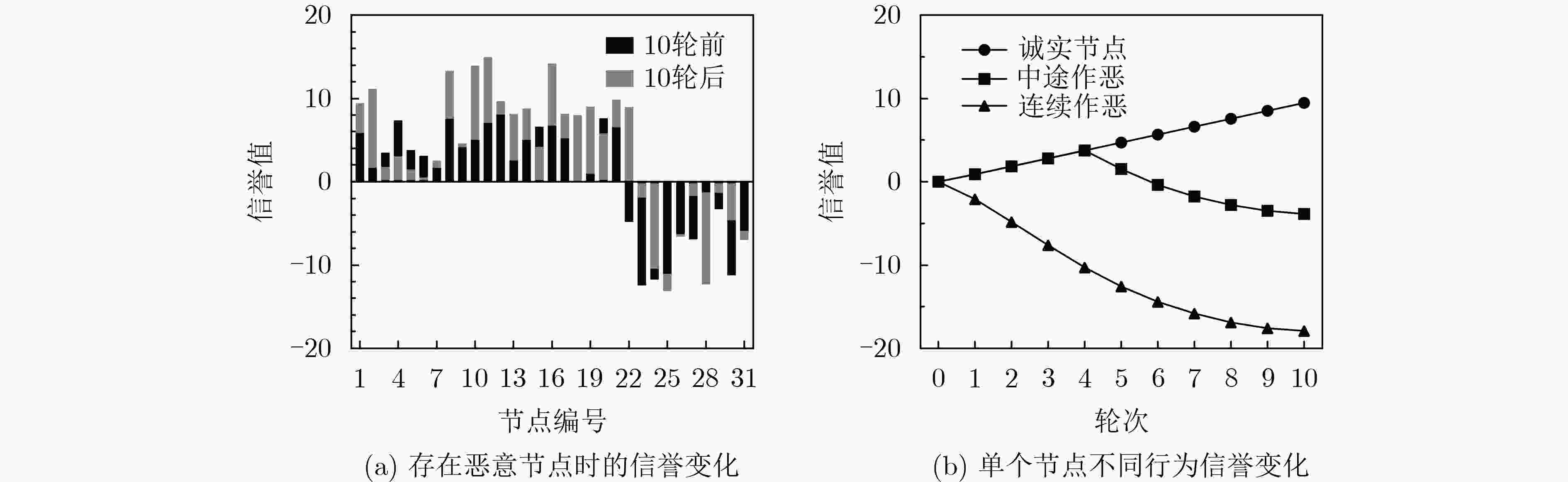
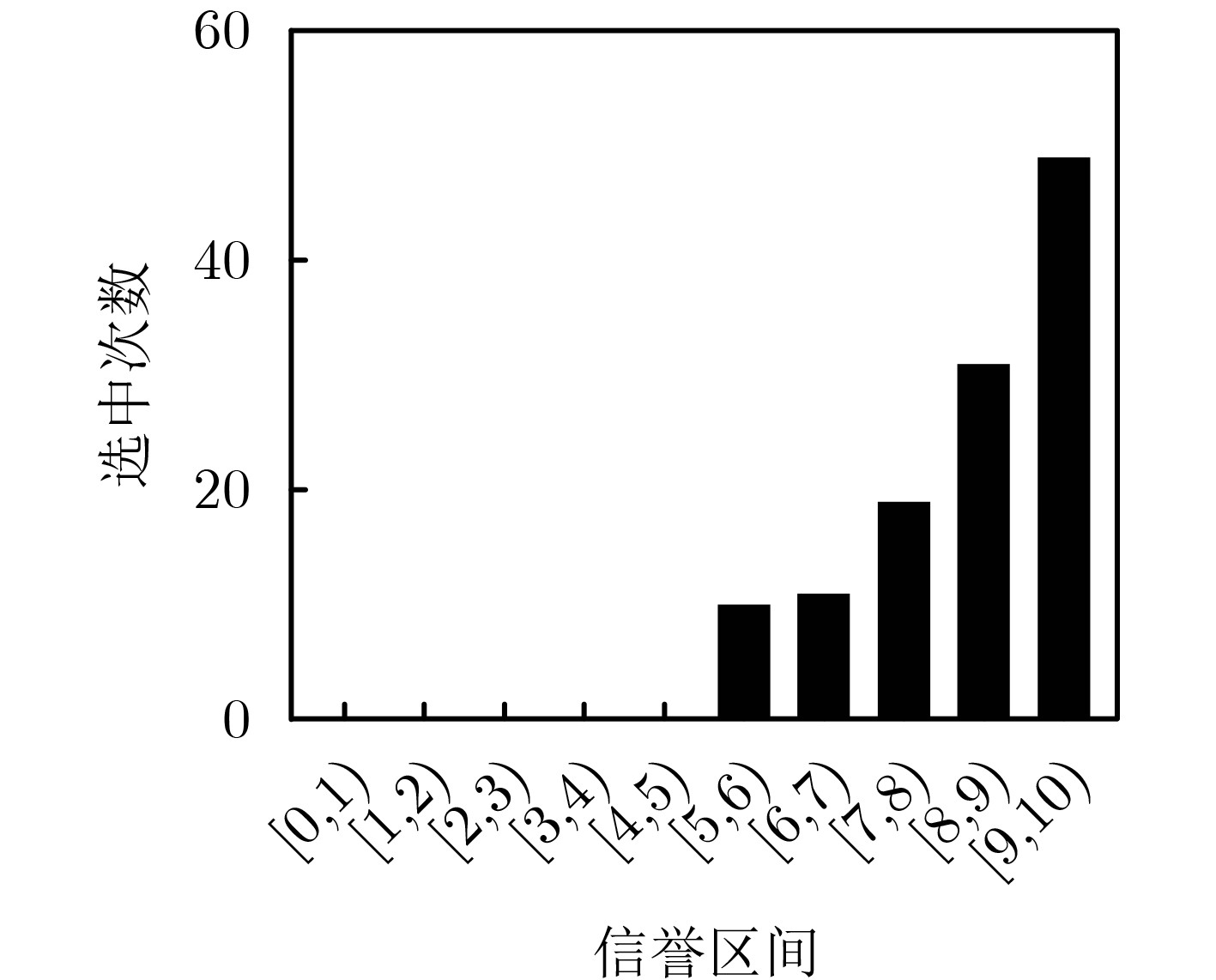
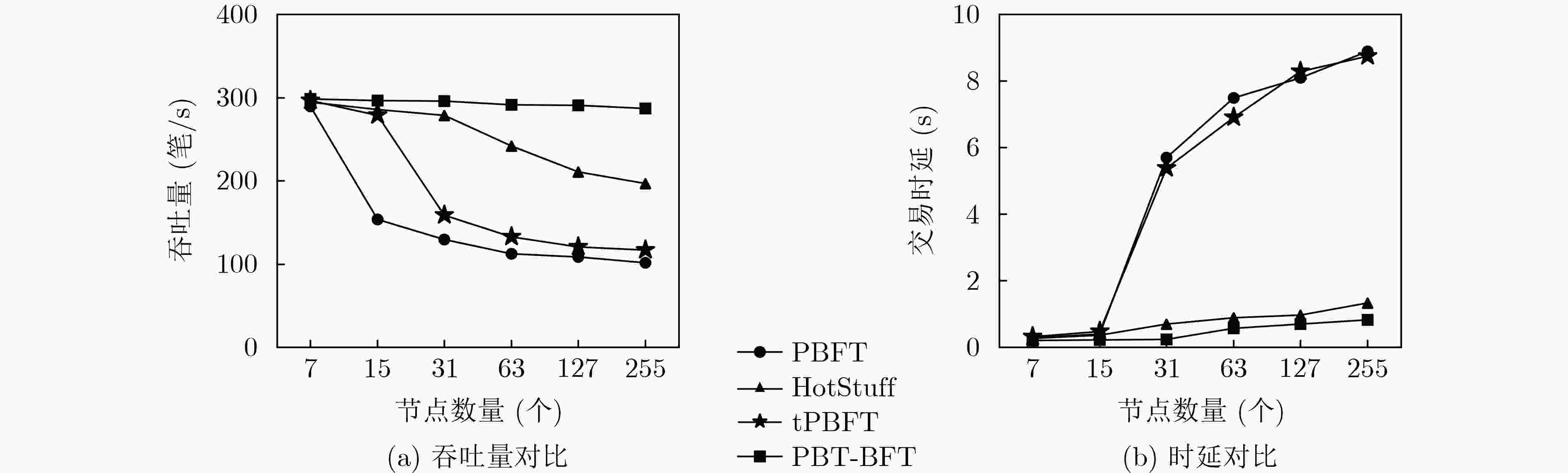
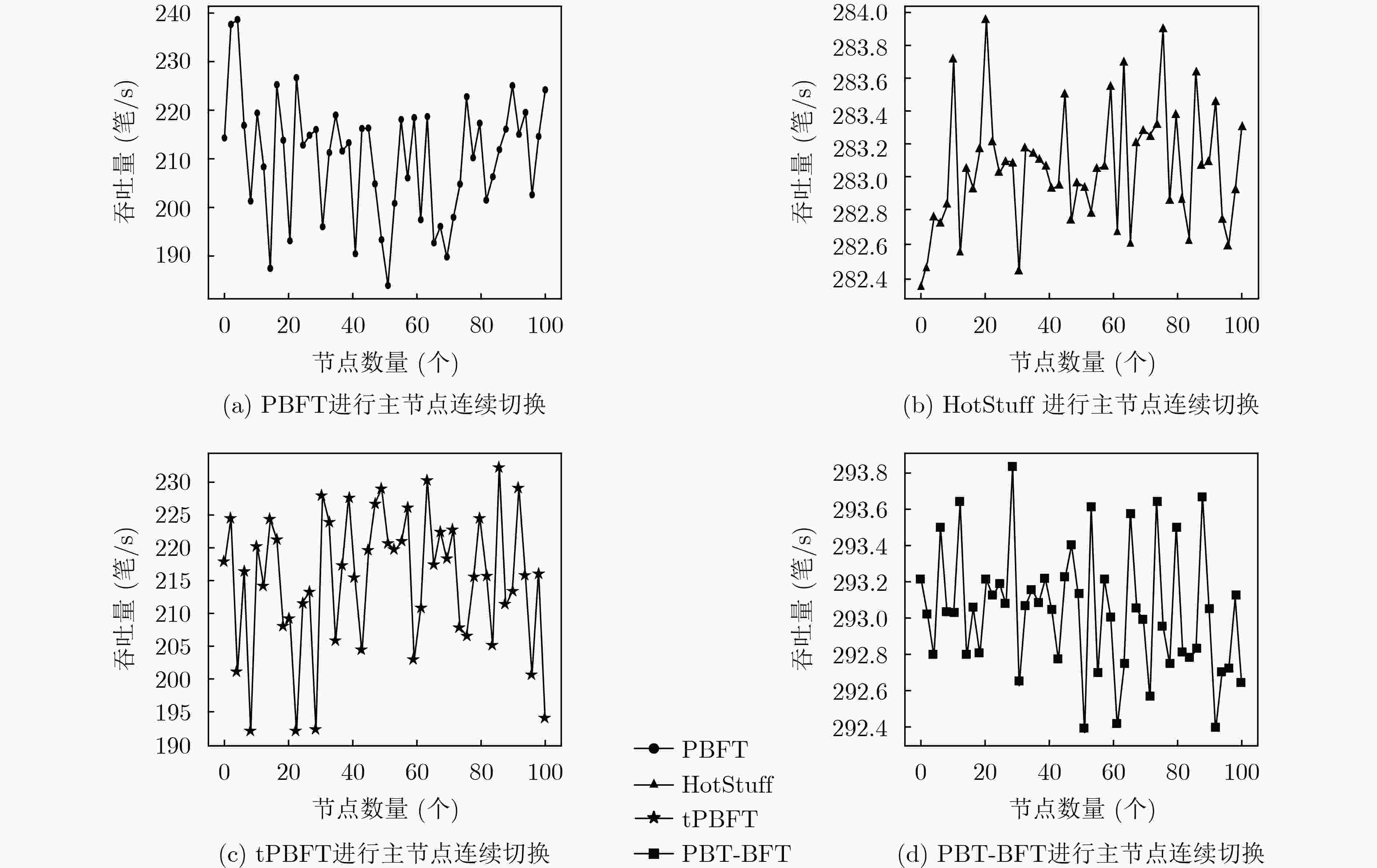


 下载:
下载:
