Collision Warning Algorithm Based on Efficient Federated Learning in Mobile Edge Computing Assisted Intelligent Driving
-
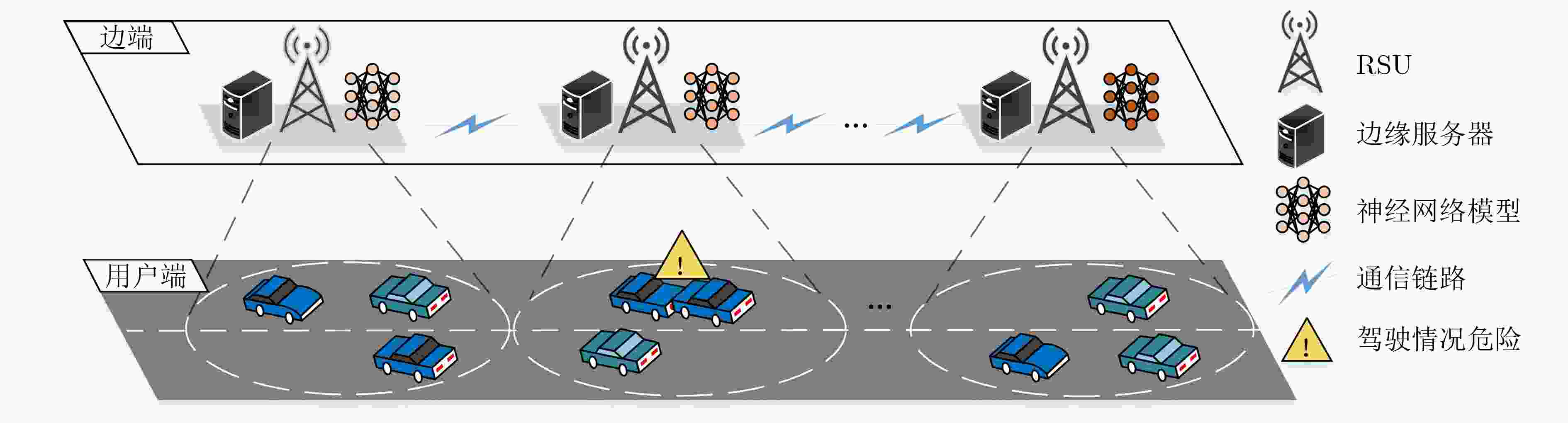
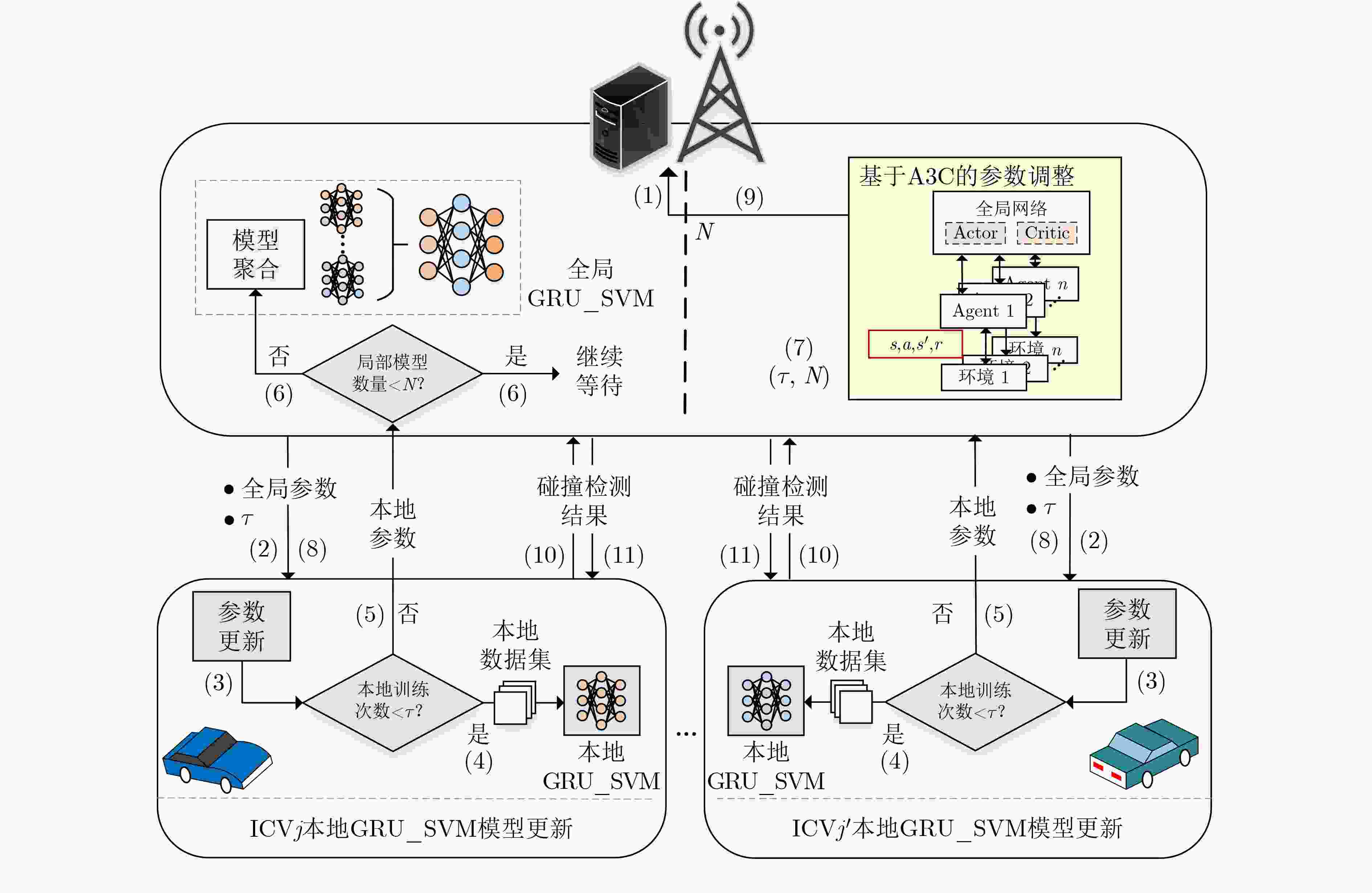
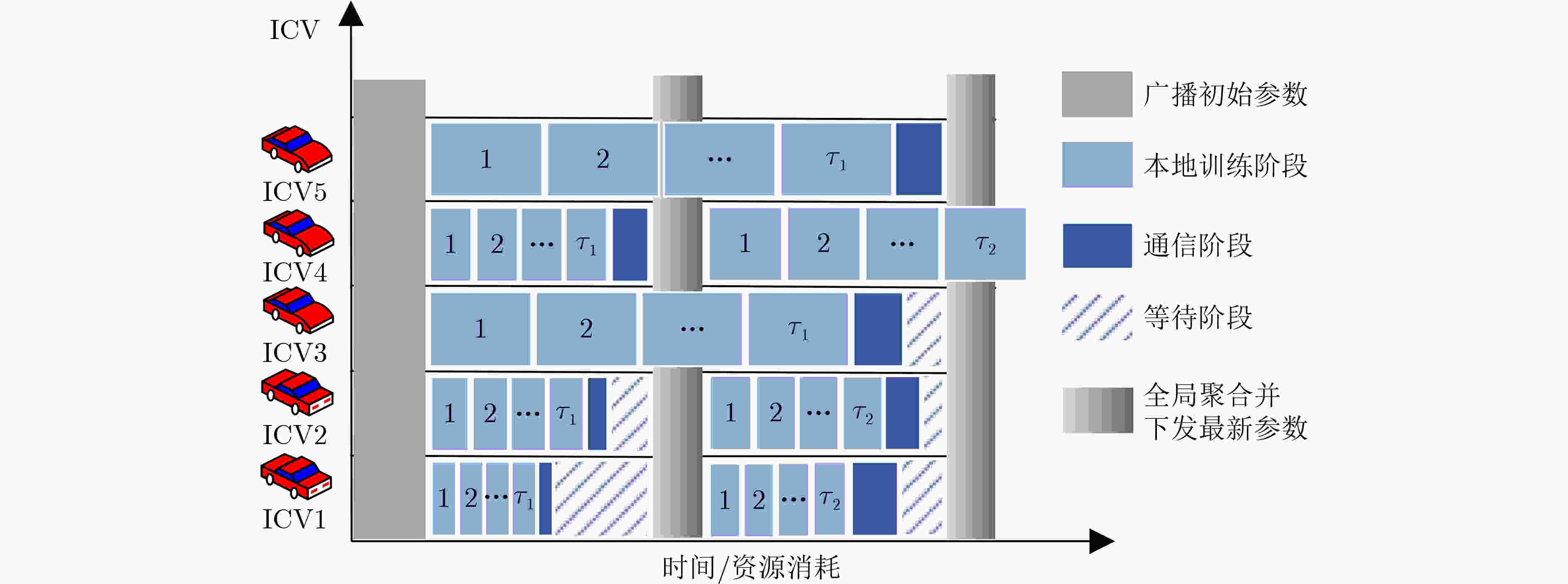
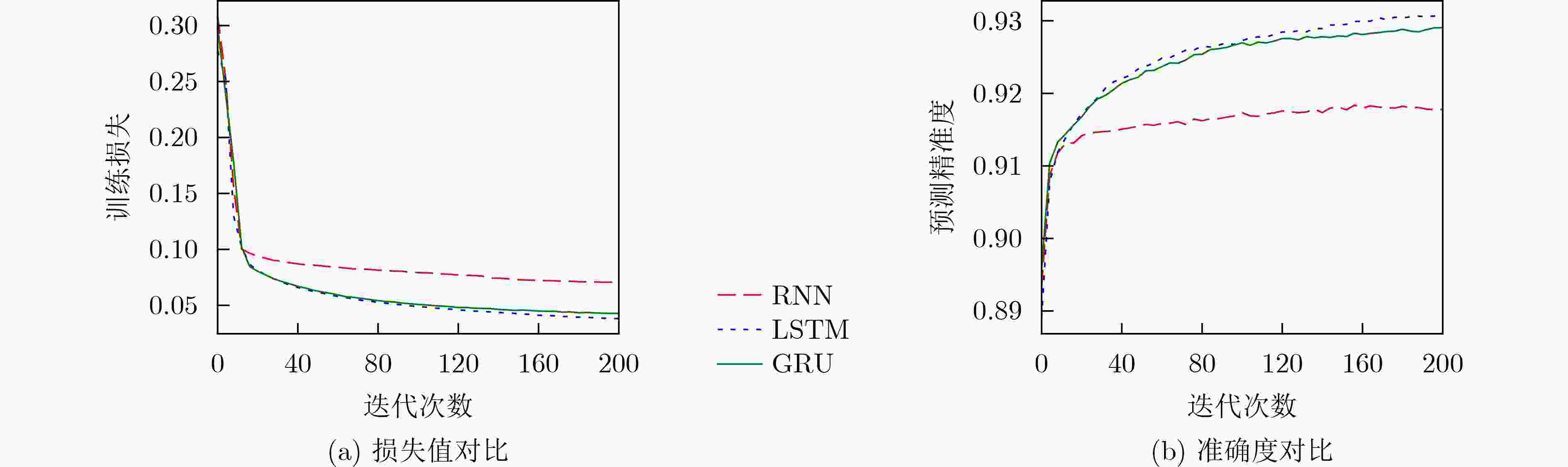
摘要: 智能驾驶中的碰撞避免任务存在对时延要求极高和隐私保护等挑战。首先,该文提出一种基于自适应调整参数的半异步联邦学习(SFLAAP)的门控循环单元联合支持向量机(GRU_SVM)碰撞多级预警算法,SFLAAP可根据训练和资源情况动态调整两个训练参数:本地训练次数和参与聚合的局部模型数量。然后,为解决资源受限的移动边缘计算(MEC)下碰撞预警模型协作训练的效率问题,根据上述参数与SFLAAP训练时延的关系,建立训练总时延最小化模型,并将其转化为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)。最后,在所建立的MDP中采用异步优势演员-评论家(A3C)学习求解,自适应地确定最优训练参数,从而减少碰撞预警模型的训练完成时间。仿真结果表明,所提算法有效地降低训练总时延并保证预测精度。
-
关键词:
- 碰撞预警 /
- 联邦学习 /
- 移动边缘计算 /
- 异步优势演员-评论家算法
Abstract: Collision avoidance tasks in intelligent driving have challenges such as extremely high latency requirements and privacy protection. First, a Gated Recurrent Unit_Support Vector Machine (GRU_SVM) collision multi-level warning algorithm based on Semi-asynchronous Federated Learning with Adaptive Adjustment of Parameters (SFLAAP) is proposed. SFLAAP can dynamically adjust two training parameters according to training and resource conditions: the number of local training times and the number of local models participating in aggregation. Then, in order to solve the efficiency problem of collaborative training of collision warning model under resource-constrained Mobile Edge Computing (MEC), according to the relationship between the above parameters and SFLAAP training delay, a model for minimizing the total training delay is established, and it is transformed into a Markov Decision Process (MDP). Finally, in the established MDP, the Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (A3C) algorithm is employed to determine adaptively the optimal training parameters, thereby reducing the training completion time of the collision warning model. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively reduce the total training delay and ensure prediction accuracy. -
算法1 基于A3C的SFLAAP算法 输入:全局参数$ {{\mathbf{\theta }}_a} $和$ {{\mathbf{\theta }}_c} $,折扣因子$\gamma $,熵超参数$\beta $,主Agent的最
大步数${T_{ {{\rm{global}} - {\rm{max}}} } }$和步数${t_{ { {\rm{global} } } } } = 0$,子Agent的最大步数
${T_{ {{\rm{local}} - {\rm{max}}} } }$和步数${t_{ {{\rm{local}}} } } = 0$,主Agent的更新频率${T_{ {{\rm{up}}} } }$,actor和
critic的学习步长${\alpha _1}$和${\alpha _2}$输出:最优动作$a'$ (1) for epoch $ k \in \{ 1,2,\cdots,K\} $ do (2) for ${t_{ {{\rm{global}}} } } \le {T_{ {{\rm{global}} - {\rm{max}}} } }$ do (3) ${\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_a} \leftarrow 0$, ${\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_c} \leftarrow 0$, ${ {\mathbf{\theta } }'_a} = { {\mathbf{\theta } }_a}$, ${ {\mathbf{\theta } }'_c} = { {\mathbf{\theta } }_c}$ (4) for ${t_{ {{\rm{local}}} } } \in \{ 0,1,\cdots,{T_{ {{\rm{local - {\rm{max}}}}} } }\}$ do (5) actor网络根据策略获得SFLAAP参数取值动作 (6) 由式(15)得到奖励${r_t}$和下一个状态${s_{t + 1}}$ (7) if ${s_t} \ne { {\rm{termina} } }{ {{\rm{l}}}^{} }{s_t}$或${t_{ {{\rm{local}}} } }\% ({T_{ {{\rm{up}}} } } - 1) \ne 0$ then (8) 将${\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_a}$,${\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_c}$推送至主Agent进行异步更新 (9) ${ {\mathbf{\theta } }_a} \leftarrow { {\mathbf{\theta } }_a} + {\alpha _1}{\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_a}$和${ {\mathbf{\theta } }_c} \leftarrow { {\mathbf{\theta } }_c} + {\alpha _2}{\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_c}$ (10) 子Agent的critic网络获得$V({s_t};{{\boldsymbol{\theta}} '_c} )$ (11) for $t = {t_{ { {\rm{local} } } } },{t_{ { {\rm{local} } } } } - 1,\cdots,{t_{ { {\rm{local} } } } } + 1 - {T_{ {{\rm{up}}} } }$ do (12) $V({s_t};{{\boldsymbol{\theta}} '_c} ) \leftarrow {r_t} + \gamma V({s_t};{{\boldsymbol{\theta}} '_c})$ (13) 计算全局actor网络的累积梯度:
${\boldsymbol{d} }{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_a} \leftarrow {\boldsymbol{d} }{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_a} + { { {\text{∇} } } _{ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} '_a} } }\log \pi ({a_t}|{s_t};{ {\boldsymbol{\theta} } '_a} )A({s_t},{a_t};{ {\boldsymbol{\theta} } '_c} )$
$+ \beta { {\text{∇} } _{ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} '_a} } }H(\pi ({s_t};{ {\boldsymbol{\theta} } '_a} ))$(14) 计算全局critic网络的累积梯度:
${\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_c} \leftarrow {\rm{d}}{ {\mathbf{\theta } }_c} + \partial {(A({s_t},{a_t};{ {\boldsymbol{\theta} }' _c} ))^2}/\partial { {\boldsymbol{\theta} } _c}$(15) end for (16) end if (17) end for (18) ${t_{ {{\rm{global}}} } } = {t_{ {{\rm{global}}} } } + 1$ (19) end for (20) 选择最优动作${a'_k} = ({\tau _k},{N_k})$ (21) 在图2的步骤(7)中,根据最优动作${a'_k}$更新${\tau _{k + 1}}$和${N_{k + 1}}$ (22) end for 表 1 SVM分类结果
准确度 召回率 F1分数 精度 0 0.97 0.98 0.97 0.96 1 0.84 0.78 0.80 2 0.90 0.91 0.90 宏平均 0.90 0.89 0.89 — -
[1] SONG Wenjie, YANG Yi, FU Mengyin, et al. Real-time obstacles detection and status classification for collision warning in a vehicle active safety system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 758–773. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2700628 [2] WINKLER S, WERNEKE J, and VOLLRATH M. Timing of early warning stages in a multi stage collision warning system: Drivers’ evaluation depending on situational influences[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2016, 36: 57–68. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2015.11.001 [3] LYU Nengchao, WEN Jiaqiang, DUAN Zhicheng, et al. Vehicle trajectory prediction and cut-in collision warning model in a connected vehicle environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(2): 966–981. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3019050 [4] XU Meiling, HAN Min, CHEN C L P, et al. Recurrent broad learning systems for time series prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(4): 1405–1417. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2863020 [5] XIANG Xuehai, QIN Wenhu, and XIANG Binfu. Research on a DSRC-based rear-end collision warning model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(3): 1054–1065. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2293771 [6] HUANG Chen, HE Ruisi, AI Bo, et al. Artificial intelligence enabled radio propagation for communications—part I: Channel characterization and antenna-channel optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(6): 3939–3954. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3149663 [7] HUANG Chen, HE Ruisi, AI Bo, et al. Artificial intelligence enabled radio propagation for communications—part II: Scenario identification and channel modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(6): 3955–3969. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3149665 [8] ZHOU Aojun, MA Yukun, ZHU Junnan, et al. Learning N: M fine-grained structured sparse neural networks from scratch[C/OL]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [9] DU Yuqing, YANG Sheng, and HUANG Kaibin. High-dimensional stochastic gradient quantization for communication-efficient edge learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2128–2142. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2983166 [10] YAO Xin, HUANG Chaofeng, and SUN Lifeng. Two-stream federated learning: Reduce the communication costs[C]. 2018 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Taichung, China, 2018: 1–4. [11] WANG Luping, WANG Wei, and LI Bo. CMFL: Mitigating communication overhead for federated learning[C]. 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Dallas, USA, 2019: 954–964. [12] LIU Jianchun, XU Hongli, WANG Lun, et al. Adaptive asynchronous federated learning in resource-constrained edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(3): 674–690. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2021.3096846 [13] SPRAGUE M R, JALALIRAD A, SCAVUZZO M, et al. Asynchronous federated learning for geospatial applications[C]. Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Dublin, Ireland, 2018: 21–28. [14] PUNZO V, BORZACCHIELLO M T, and CIUFFO B. On the assessment of vehicle trajectory data accuracy and application to the Next Generation SIMulation (NGSIM) program data[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2011, 19(6): 1243–1262. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2010.12.007 [15] WANG Xin, LIU Jing, QIU Tie, et al. A real-time collision prediction mechanism with deep learning for intelligent transportation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 9497–9508. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3003933 [16] LUO Bing, LI Xiang, WANG Shiqiang, et al. Cost-effective federated learning in mobile edge networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(12): 3606–3621. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3118436 -





 下载:
下载:
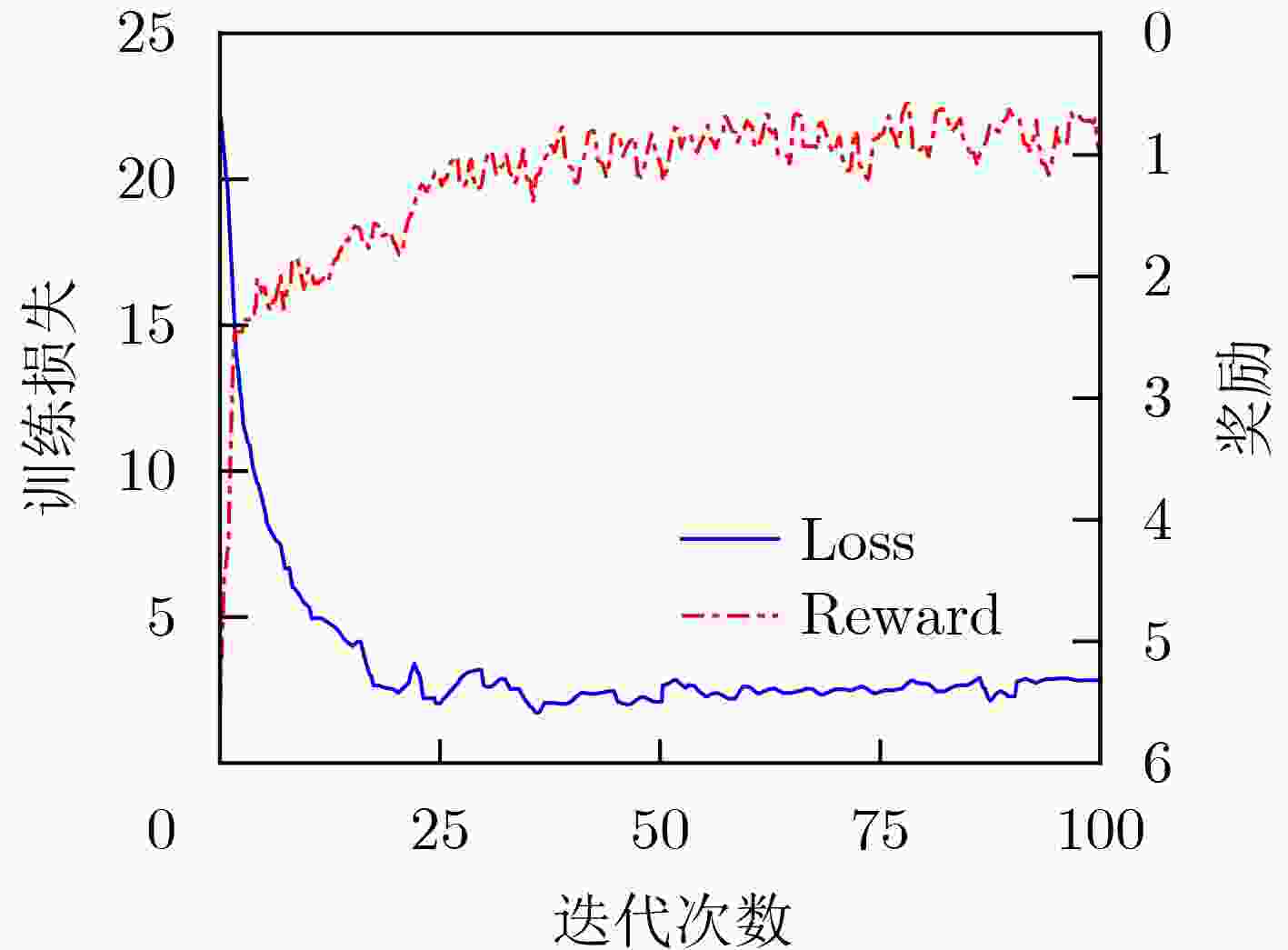
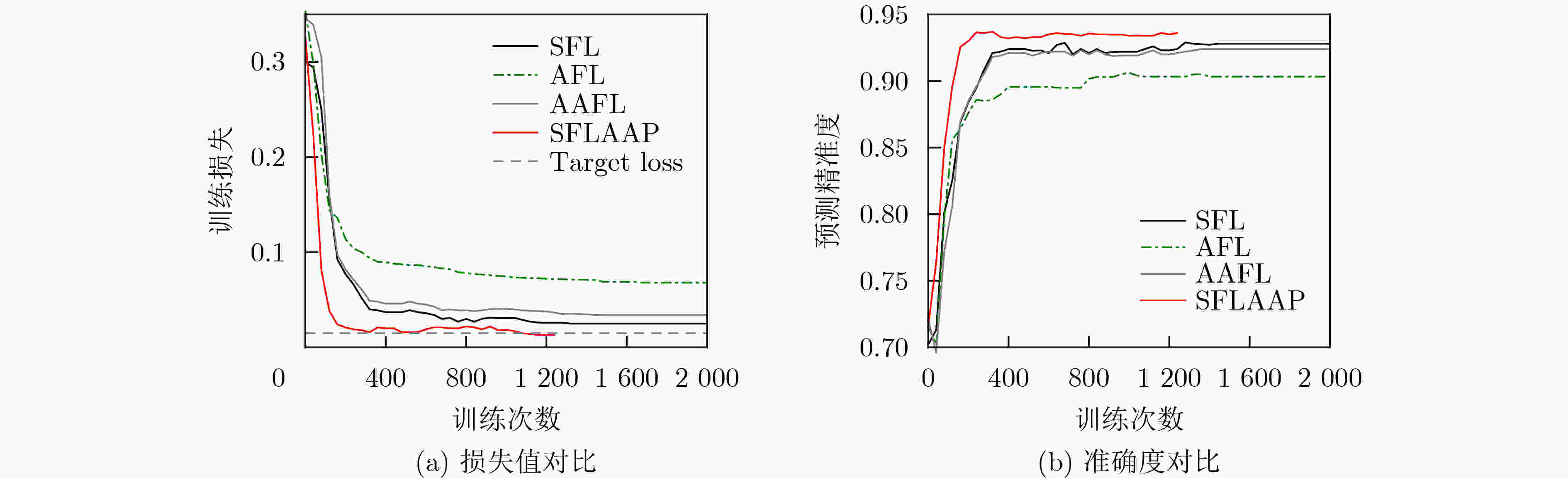


 下载:
下载:
