Dynamic Gesture Recognition Network Based on Multiscale Spatiotemporal Feature Fusion
-
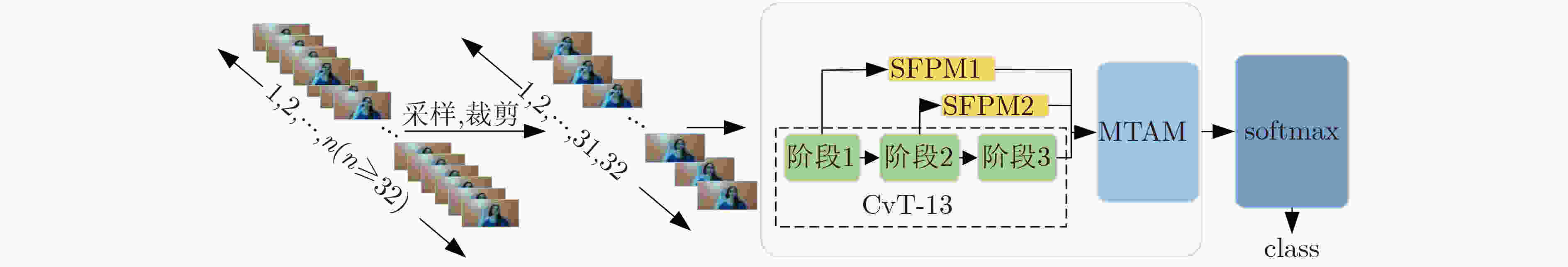
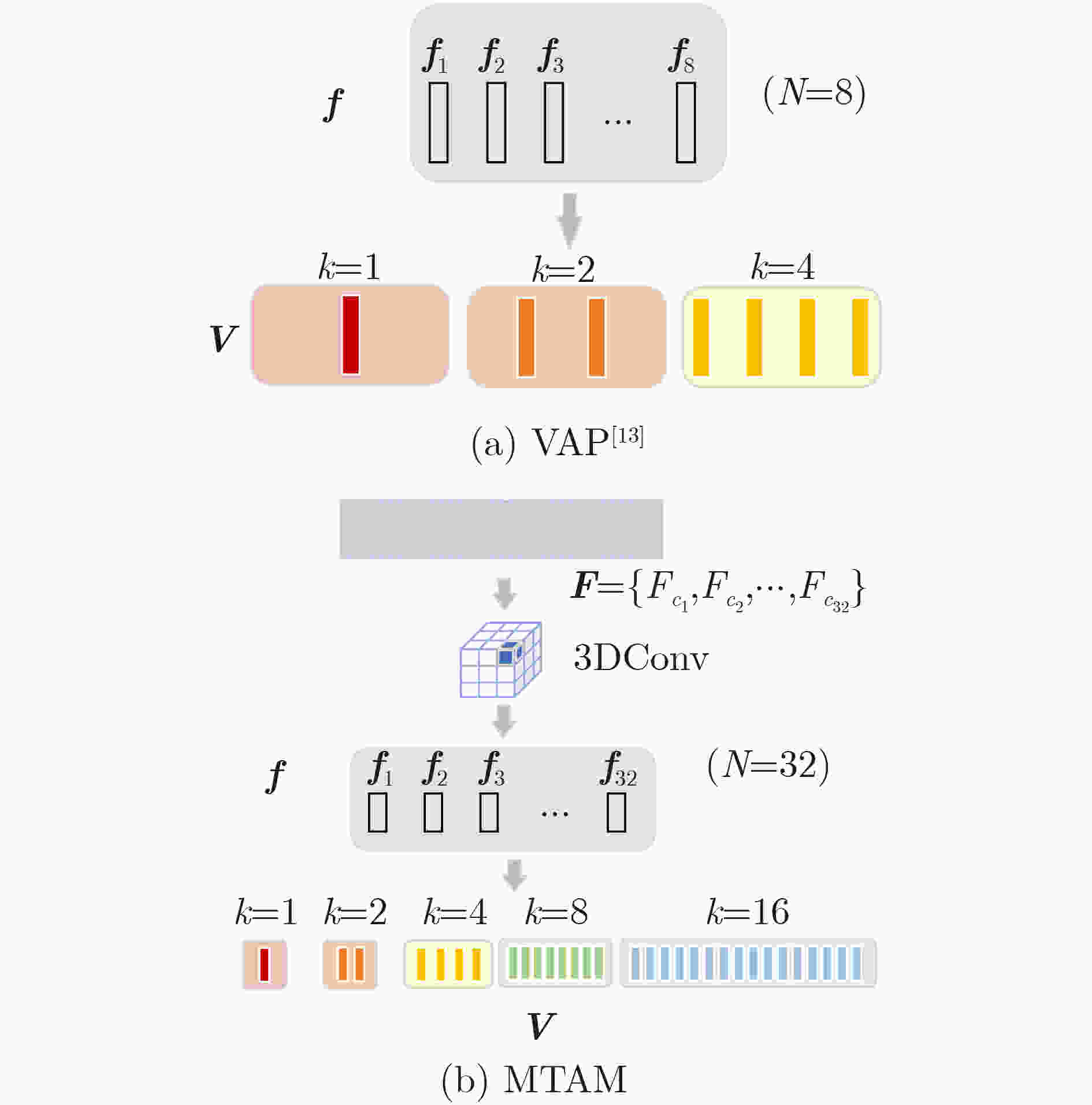
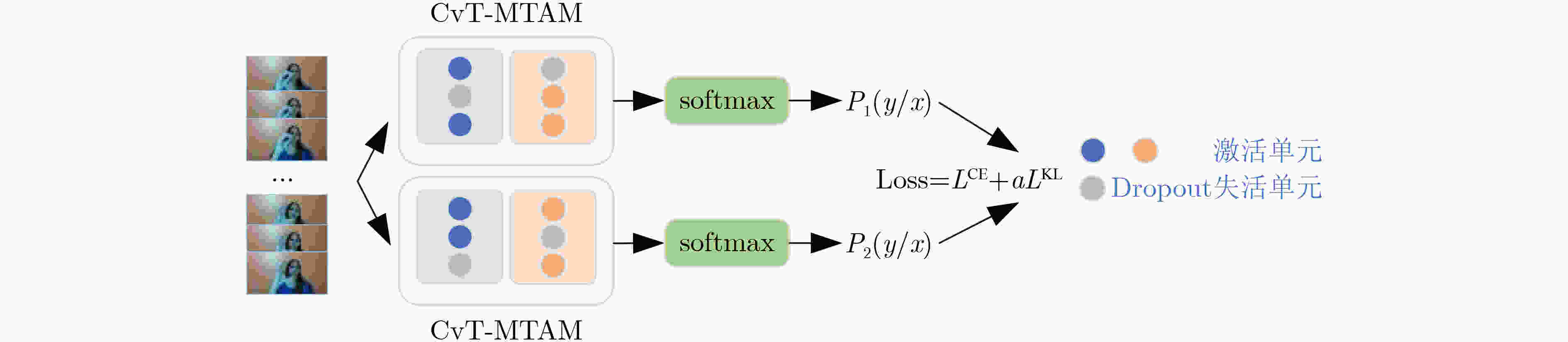
摘要: 由于动态手势数据具有时间复杂性以及空间复杂性,传统的机器学习算法难以提取准确的手势特征;现有的动态手势识别算法网络设计复杂、参数量大、手势特征提取不充分。为解决以上问题,该文提出一种基于卷积视觉自注意力模型(CvT)的多尺度时空特征融合网络。首先,将图片分类领域的CvT网络引入动态手势分类领域,用于提取单张手势图片的空间特征,将不同空间尺度的浅层特征与深层特征融合。其次,设计一种多时间尺度聚合模块,提取动态手势的时空特征,将CvT网络与多时间尺度聚合模块结合,抑制无效特征。最后为了弥补CvT网络中dropout层的不足,将R-Drop模型应用于多尺度时空特征融合网络。在Jester数据集上进行实验验证,与多种基于深度学习的动态手势识别方法进行对比,实验结果表明,该文方法在识别率上优于现有动态手势识别方法,在动态手势数据集Jester上识别率达到92.26%。
-
关键词:
- 动态手势识别 /
- 深度学习 /
- 卷积视觉自注意力模型 /
- 多尺度融合
Abstract: Because of the time complexity and space complexity of dynamic gesture data, traditional machine learning algorithms are difficult to extract accurate gesture features; The existing dynamic gesture recognition algorithms have complex network design, large amount of parameters and insufficient gesture feature extraction. To solve the above problems, a multiscale spatiotemporal feature fusion network based on Convolutional vision Transformer(CvT)is proposed. Firstly, the CvT network used in the field of image classification is introduced into the field of dynamic gesture classification. The CvT network is used to extract the spatial features of a single gesture image, and fuse the shallow features and deep features of different spatial scales. Secondly, a multi time scale aggregation module is designed to extract the spatio-temporal features of dynamic gestures. The CvT network is combined with the multi time scale aggregation module to suppress invalid features. Finally, in order to make up for the deficiency of dropout layer in CvT network, r-drop model is applied to multi-scale spatiotemporal feature fusion network. The experimental results on Jester dataset show that the proposed method is superior to the existing dynamic gesture recognition methods in recognition rate, and the recognition rate on Jester dataset reaches 92.26%. -
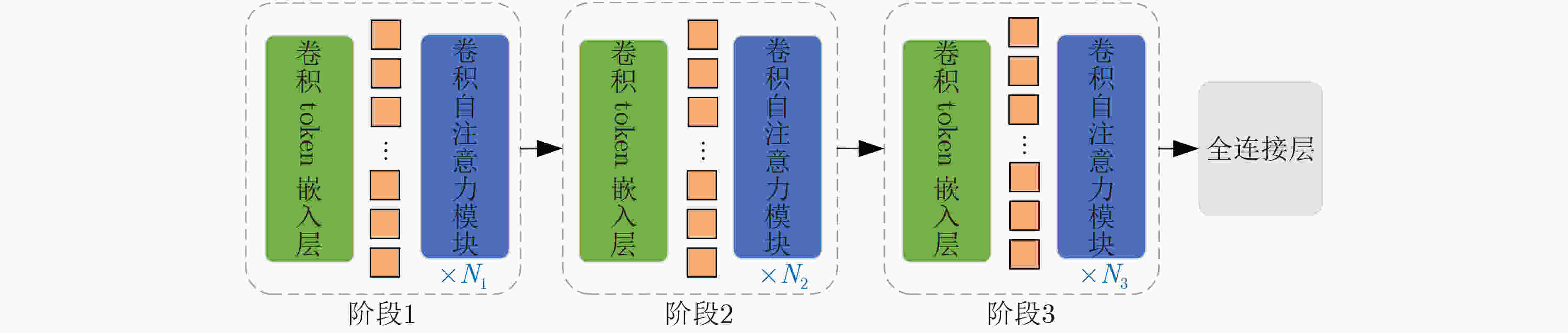
图 1 CvT网络结构图[19]
表 1 自建融合数据集(个)
手势类别 自建数量 原数据集数量 总数 停止动作 50 182 232 拇指向下 50 212 262 拇指向上 50 208 258 两指放大 50 199 249 两指缩小 50 200 250 表 2 多尺度特征融合以及MTAM模块消融实验结果
网络模型 算力(G) 参量数(M) 识别准确率(%) CvT 8.653 19.604 88.96 CvT+SFPM1 9.376 21.448 89.46 CvT+SFPM1+SFPM2 11.544 26.978 89.85 CvT-MTAM(CvT+SFPM1+SFPM2+MTAM) 11.544 26.979 91.21 表 3 R-Drop消融实验结果
网络模型 算力(G) 参量数(M) 识别准确率(%) CvT-MTAM 11.544 26.979 91.21 CvT-MTAM+R-Drop 11.544 26.979 92.26 表 4 本文方法与现有手势识别方法定量对比
网络方法 算力(G) 参量数(M) 识别准确率(%) R3D-34 25.420 63.791 85.48 R(2+1)D-34 25.813 63.748 84.75 STAM 137.464 104.807 88.94 PAN 9.128 23.866 90.74 SlowFast 13.176 35.17 87.62 ConvLSTM \ \ 82.76 本文方法 11.544 26.979 92.26 表 5 本文方法在自建数据集上的实验结果
网络方法 算力(G) 参量数(M) 识别准确率(%) 本文方法 11.544 26.979 92.46 -
[1] 张淑军, 张群, 李辉. 基于深度学习的手语识别综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1021–1032. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190416ZHANG Shujun, ZHANG Qun, and LI Hui. review of sign language recognition based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1021–1032. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190416 [2] ASADI-AGHBOLAGHI M, CLAPÉS A, BELLANTONIO M, et al. A survey on deep learning based approaches for action and gesture recognition in image sequences[C]. The 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Washington, USA, 2017: 476–483. [3] KOLLER O, NEY H, and BOWDEN R. Deep hand: How to train a CNN on 1 million hand images when your data is continuous and weakly labelled[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3793–3802. [4] WU J, ISHWAR P, and KONRAD J. Two-stream CNNs for gesture-based verification and identification: Learning user style[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 110–118. [5] JI Shuiwang, XU Wei, YANG Ming, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221–231. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 [6] HUANG Jie, ZHOU Wengang, LI Houqiang, et al. Sign language recognition using 3D convolutional neural networks[C] Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Turin, Italy, 2015: 1–6. [7] LIU Zhi, ZHANG Chenyang, and TIAN Yingli. 3D-based deep convolutional neural network for action recognition with depth sequences[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2016, 55(2): 93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2016.04.004 [8] 王粉花, 张强, 黄超, 等. 融合双流三维卷积和注意力机制的动态手势识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1389–1396. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200065WANG Fenhua, ZHANG Qiang, HUANG Chao, et al. Dynamic gesture recognition combining two-stream 3D convolution with attention mechanisms[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1389–1396. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200065 [9] TRAN D, RAY J, SHOU Zheng, et al. ConvNet architecture search for spatiotemporal feature learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05038, 2017. [10] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [11] TRAN D, WANG Heng, TORRESANI L, et al. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6450–6459. [12] FEICHTENHOFER C, FAN Haoqi, MALIK J, et al. SlowFast networks for video recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6201–6210. [13] ZHANG Can, ZOU Yuexian, CHEN Guang, et al. PAN: Towards fast action recognition via learning persistence of appearance[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.03462, 2020. [14] 胡凯, 陈旭, 朱俊, 等. 基于多尺度3D卷积神经网络的行为识别方法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 33(6): 970–976. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201910240366HU Kai, CHEN Xu, ZHU Jun, et al. Multiscale 3D convolutional neural network for action recognition[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2021, 33(6): 970–976. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.201910240366 [15] GAO Zan, GUO Leming, GUAN Weili, et al. A pairwise attentive adversarial spatiotemporal network for cross-domain few-shot action recognition-R2[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 767–782. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3038372 [16] 毛力, 张艺楠, 孙俊. 融合注意力与时域多尺度卷积的手势识别算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(7): 2196–2202. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.11.0620MAO Li, ZHANG Yinan, and SUN Jun. Gesture recognition algorithm combining attention and time-domain multiscale convolution[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(7): 2196–2202. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.11.0620 [17] SHARIR G, NOY A, and ZELNIK-MANOR L. An image is worth 16x16 words, what is a video worth?[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13915, 2021. [18] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929, 2020. [19] WU Haiping, XIAO Bin, CODELLA N, et al. CvT: Introducing convolutions to vision transformers[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021. [20] LIANG Xiaobo, WU Lijun, LI Juntao, et al. R-Drop: Regularized dropout for neural networks[C/OL]. Proceedings of the Thirty-fifth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021. [21] 谢昭, 周义, 吴克伟, 等. 基于时空关注度LSTM的行为识别[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(2): 261–274. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00261XIE Zhao, ZHOU Yi, WU Kewei, et al. Activity recognition based on spatial-temporal attention LSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(2): 261–274. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00261 [22] SHI Xingjian, CHEN Zhourong, WANG Hao, et al. Convolutional LSTM Network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 802–810. -





 下载:
下载:

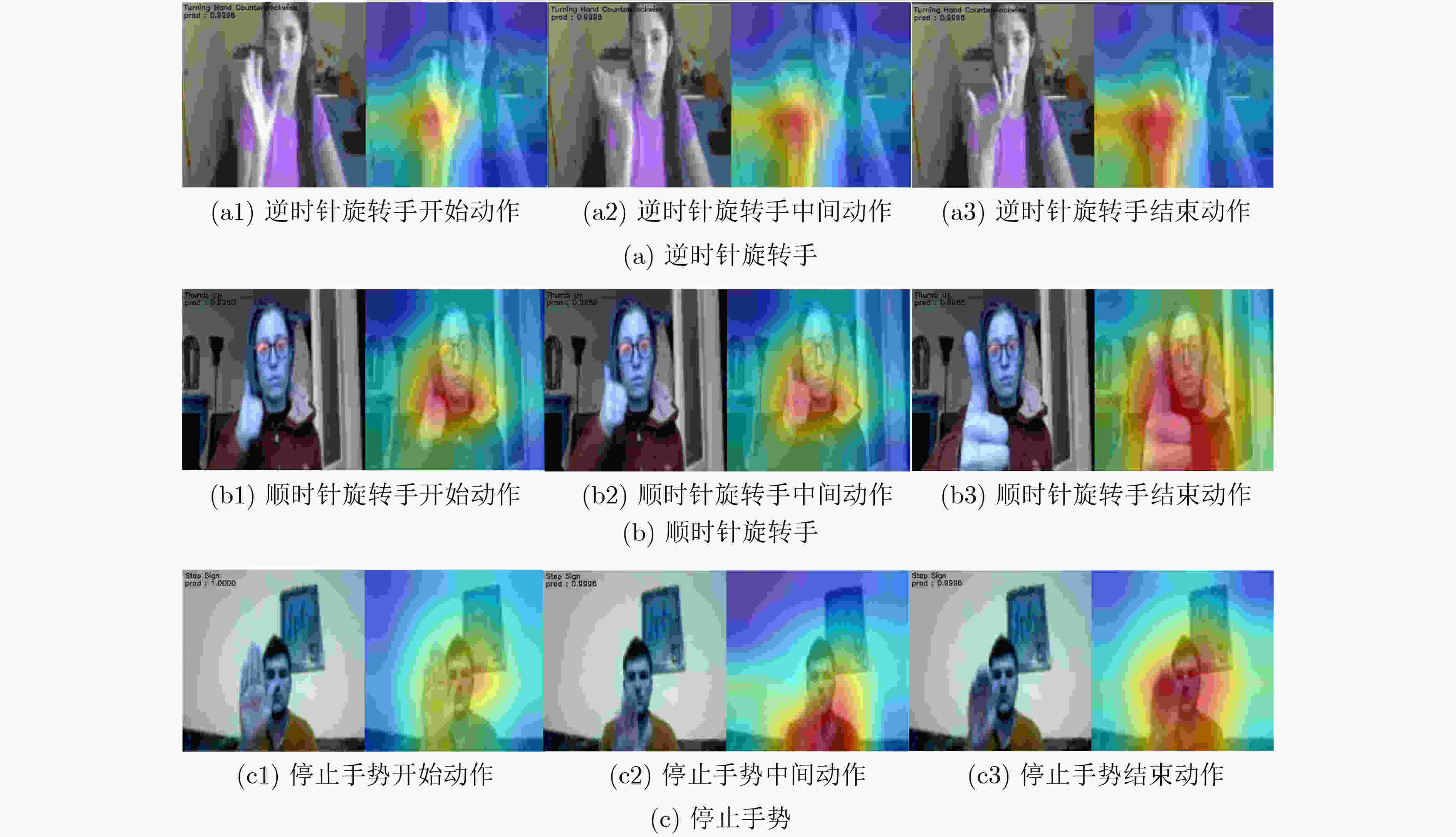

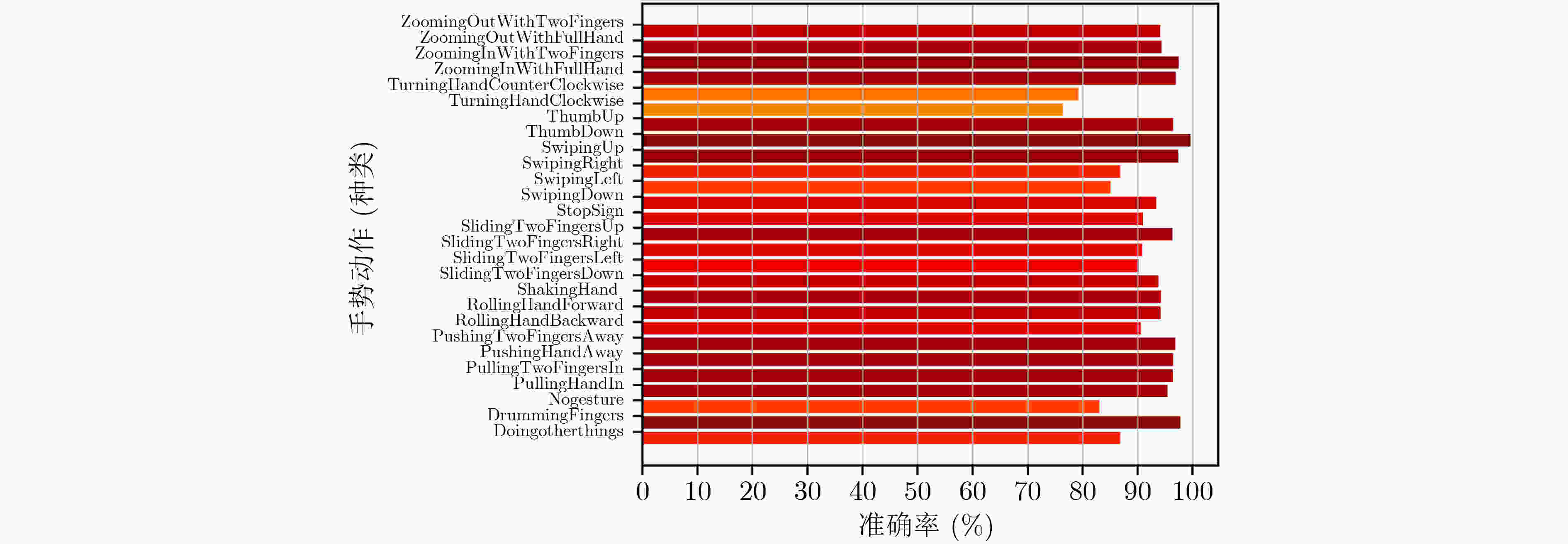


 下载:
下载:
