Skeleton Action Recognition Based on Spatio-temporal Feature Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network
-
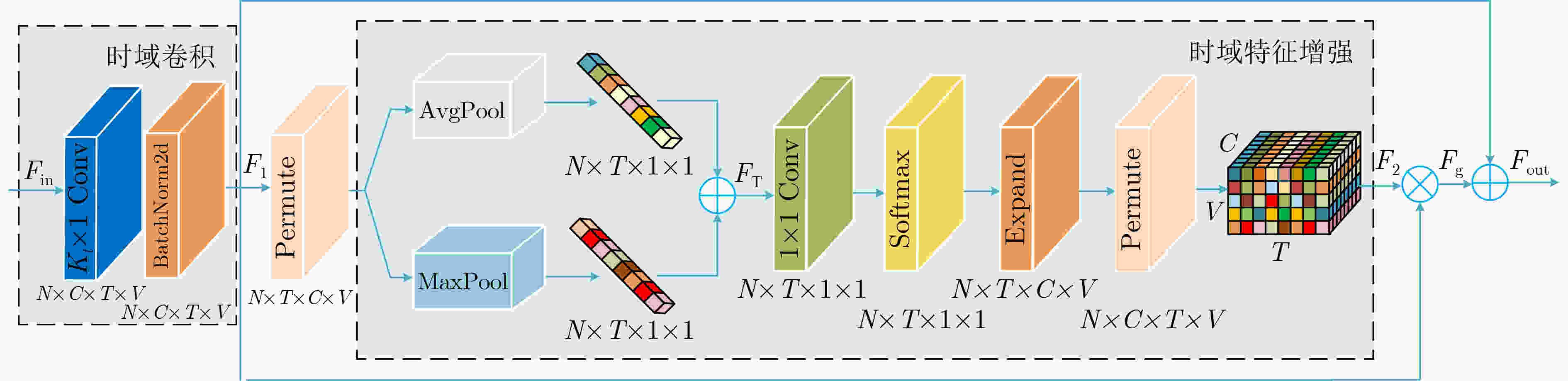
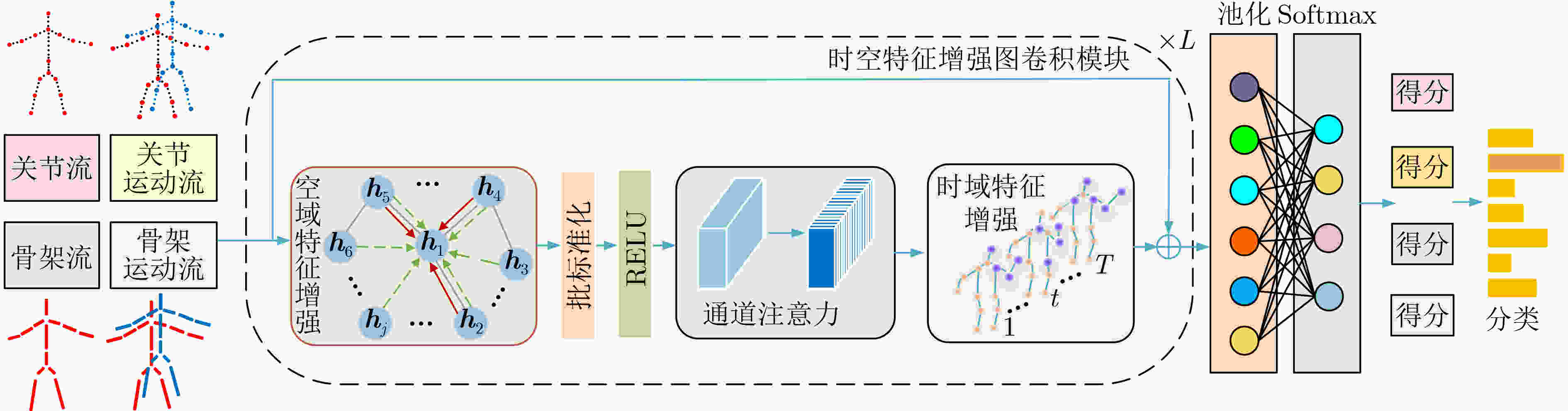
摘要: 针对骨架行为识别不能充分挖掘时空特征的问题,该文提出一种基于时空特征增强的图卷积行为识别模型(STFE-GCN)。首先,介绍表征人体拓扑结构邻接矩阵的定义及双流自适应图卷积网络模型的结构,其次,采用空域上的图注意力机制,根据邻居节点的重要性程度分配不同的权重系数,生成可充分挖掘空域结构特征的注意力系数矩阵,并结合非局部网络生成的全局邻接矩阵,提出一种新的空域自适应邻接矩阵,以期增强对人体空域结构特征的提取;然后,时域上采用混合池化模型以提取时域关键动作特征和全局上下文特征,并结合时域卷积提取的特征,以期增强对行为信息中时域特征的提取。再者,在模型中引入改进通道注意力网络(ECA-Net)进行通道注意力增强,更有利于模型提取样本的时空特征,同时结合空域特征增强、时域特征增强和通道注意力,构建时空特征增强图卷积网络模型在多流网络下实现端到端的训练,以期实现时空特征的充分挖掘。最后,在NTU-RGB+D和NTU-RGB+D120两个大型数据集上开展骨架行为识别研究,实验结果表明该模型具有优秀的识别准确率和泛化能力,也进一步验证了该模型充分挖掘时空特征的有效性。Abstract: Considering the problem that skeleton action recognition can not fully exploit spatio-temporal features, a skeleton action recognition model based on Spatio-Temporal Feature Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network (STFE-GCN) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the definition of adjacency matrix representing the topological structure of human body and the structure of one two-stream self-adaptive graph convolutional network model are introduced. Secondly, the graph attention network in spatial domain is used to assign different weight coefficients according to the importance of the neighbor nodes to generate an attention coefficient matrix, which can fully extract the spatial structure features of human body. Furthermore, a new spatial self-adaptive adjacency matrix is proposed to enhance furtherly the extraction of spatial structure features of human body combined with the global adjacency matrix generated by the non-local network; Then, a mixed pooling model is utilized in temporal domain to extract key action features and global contextual features, these two-above features can be furtherly combined with the features generated by the temporal convolution to enhance the extraction of temporal features from behavioral informations. Furthermore, an Efficient Channel Attention Network (ECA-Net)is introduced for channel attention to better extract the spatio-temporal features of the samples. Meanwhile, combining the spatial feature enhanced, the temporal feature enhanced with the channel attention, an novel model referred to as STFE-GCN is constructed and one end-to-end training can be realized based on mutil-stream network to achieve the full mining of spatio-temporal features. Finally, the researches on skeleton action recognition are carried on NTU-RGB+D and NTU-RGB+D120 datasets. The results show that this model has superior classification accuracy and generalization ability, which also further verifies the effectiveness of the model to fully mine spatio-temporal features.
-
表 1 STFE-GCN模型不同层数识别准确率对比(%)
7层STFE-GCN 8层STFE-GCN 9层STFE-GCN 10层STFE-GCN 11层STFE-GCN 关节流 93.6 93.9 94.0 94.4 94.1 骨架流
双流93.2
95.193.6
95.393.9
95.494.3
95.693.9
95.4表 2 时域不同卷积核大小的识别准确率对比(%)
5×1 7×1 9×1 11×1 13×1 关节流 94.5 94.3 94.4 94.0 93.8 骨架流
双流93.4
95.493.9
95.494.3
95.694.1
95.493.7
95.3表 3 NTU-RGB+D数据集X-View下消融实验的识别准确率(%)
模型 关节流 骨架流 双流 2s-AGCN 93.7 93.2 95.1 2s-AGCN+图注意力机制 94.1 93.4 95.3 2s-AGCN+混合池化 94.0 93.6 95.3 2s-AGCN+ECA-Net 94.0 94.1 95.4 STFE-GCN 94.4 94.3 95.6 表 4 NTU-RGB+D数据集上STFE-GCN模型各支流的识别准确率(%)
情景 关节流 骨架流 关节运动流 骨架运动流 双流 多流 X-View 94.4 94.3 92.8 93.0 95.6 96.0 X-Sub 87.7 87.4 85.7 85.6 89.3 89.8 表 5 NTU-RGB+D数据集上不同模型的识别准确率对比(%)
-
[1] 钱涛. 基于Kinect的动态姿势识别方法在医疗康复中的应用[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江工业大学, 2020.QIAN Tao. Application of Kinect-based dynamic posture recognition method in medical rehabilitation[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University of Technology, 2020. [2] 周风余, 尹建芹, 杨阳, 等. 基于时序深度置信网络的在线人体动作识别[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1030–1039. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150629ZHOU Fengyu, YIN Jianqin, YANG Yang, et al. Online recognition of human actions based on temporal deep belief neural network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1030–1039. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150629 [3] LIU Zhi, ZHANG Chenyang, and TIAN Yingli. 3D-based deep convolutional neural network for action recognition with depth sequences[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2016, 55: 93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2016.04.004 [4] XIA Rongjie, LI Yanshan, and LUO Wenhan. LAGA-Net: Local-and-global attention network for skeleton based action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022, 24: 2648–2661. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2021.3086758 [5] ZHANG Pengfei, LAN Cuiling, XING Junliang, et al. View adaptive neural networks for high performance skeleton-based human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(8): 1963–1978. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2896631 [6] JIANG Xinghao, XU Ke, and SUN Tanfeng. Action recognition scheme based on skeleton representation with DS-LSTM network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(7): 2129–2140. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2914137 [7] PLIZZARI C, CANNICI M, and MATTEUCCI M. Spatial temporal transformer network for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. International Conference on Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges, Milano, Italy, 2021: 694–701. [8] ZHANG Jiaxu, XIE Wei, WANG Chao, et al. Graph-aware transformer for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. The Visual Computer, To be published. [9] YAN Sijie, XIONG Yuanjun, and LIN Dahua. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 7444–7452. [10] SHI Lei, ZHANG Yifan, CHENG Jian, et al. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12018–12027. [11] CAO Yi, LIU Chen, HUANG Zhilong, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition with temporal action graph and temporal adaptive graph convolution structure[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(19): 29139–29162. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11136-z [12] PENG Wei, SHI Jingang, and ZHAO Guoying. Spatial temporal graph deconvolutional network for skeleton-based human action recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 244–248. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3049691 [13] YANG Hongye, GU Yuzhang, ZHU Jianchao, et al. PGCN-TCA: Pseudo graph convolutional network with temporal and channel-wise attention for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 10040–10047. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2964115 [14] CHEN Shuo, XU Ke, JIANG Xinghao, et al. Spatiotemporal-spectral graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Shenzhen, China, 2021: 1–6. [15] 石跃祥, 朱茂清. 基于骨架动作识别的协作卷积Transformer网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1485–1493.SHI Yuexiang and ZHU Maoqing. Collaborative convolutional transformer network for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(4): 1485–1493. [16] VELIČKOVIĆ P, CUCURULL G, CASANOVA A, et al. Graph attention networks[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1254–1263. [17] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. [18] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2575–7075. [19] SHAHROUDY A, LIU Jun, NG T T, et al. NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1010–1019. [20] LIU Jun, SHAHROUDY A, PEREZ M, et al. NTU RGB+D 120: A large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2684–2701. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2019.2916873 [21] ZHANG Pengfei, LAN Cuiling, ZENG Wenjun, et al. Semantics-guided neural networks for efficient skeleton-based human action recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 1109–1118. [22] LIU Jun, SHAHROUDY A, WANG Gang, et al. Skeleton-based online action prediction using scale selection network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(6): 1453–1467. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2898954 [23] LI Maosen, CHEN Siheng, CHEN Xu, et al. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2019: 3590–3598. -





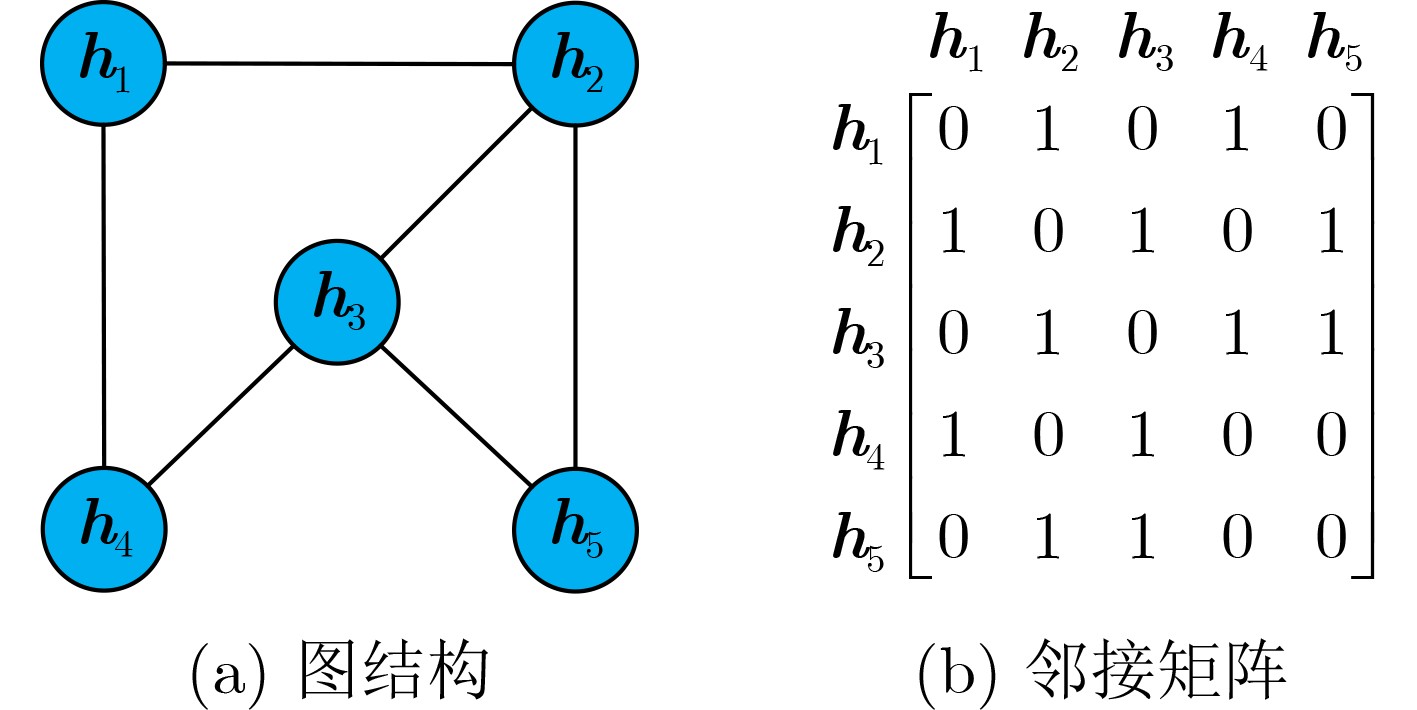
 下载:
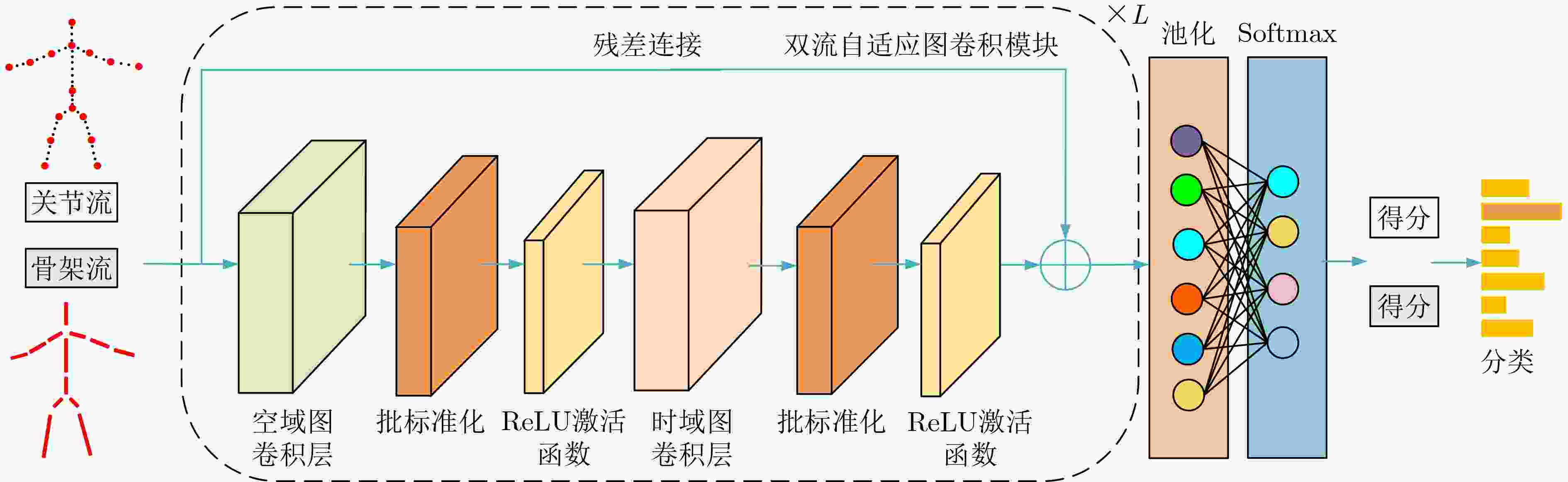
下载:
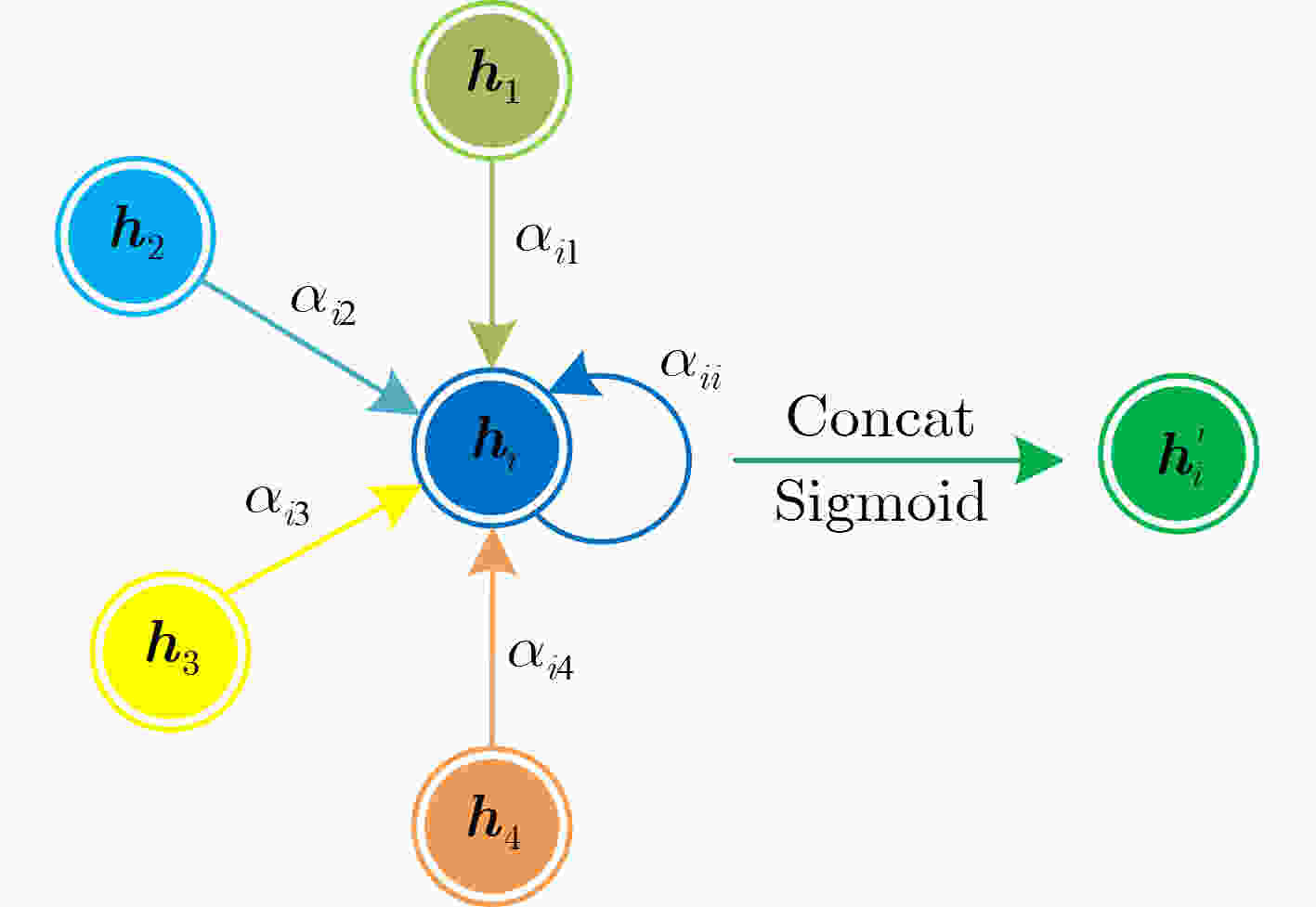
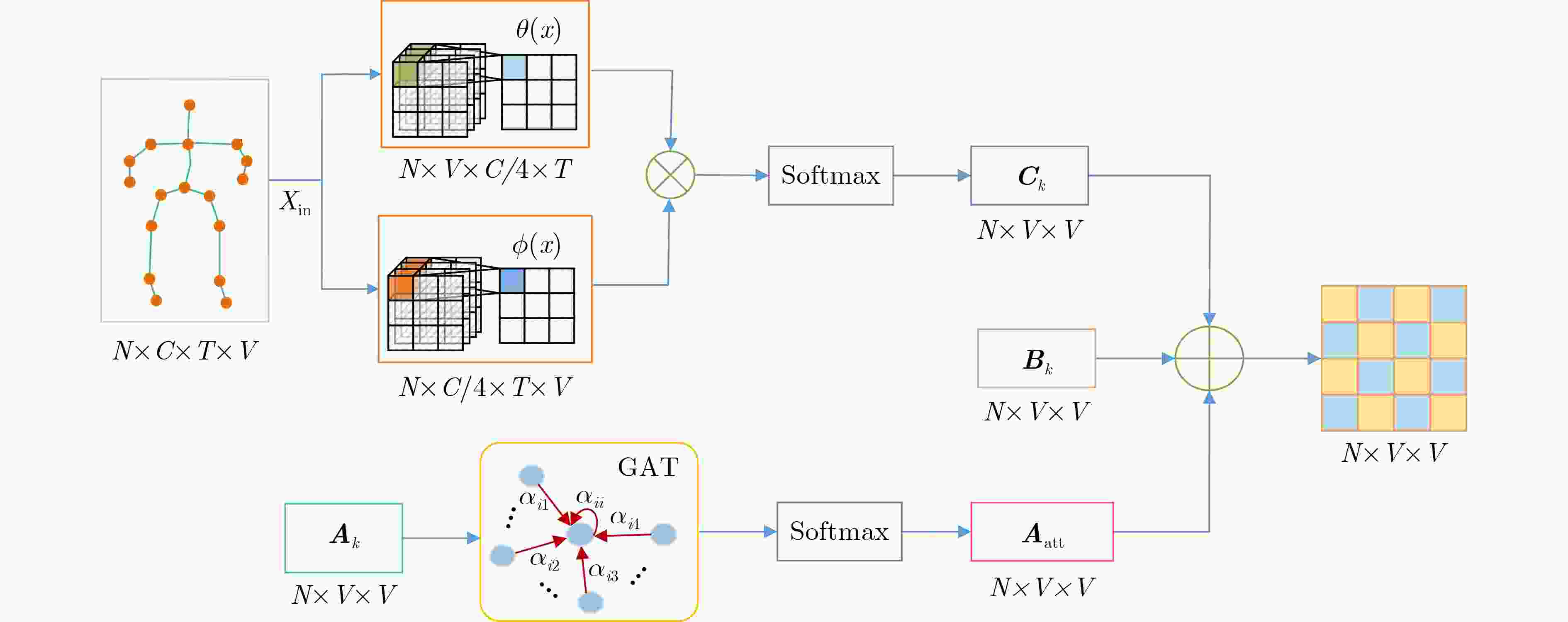


 下载:
下载:
