Compressed Sensing Reconstruction of Hyperspectral Images Based on Adaptive Blocking
-
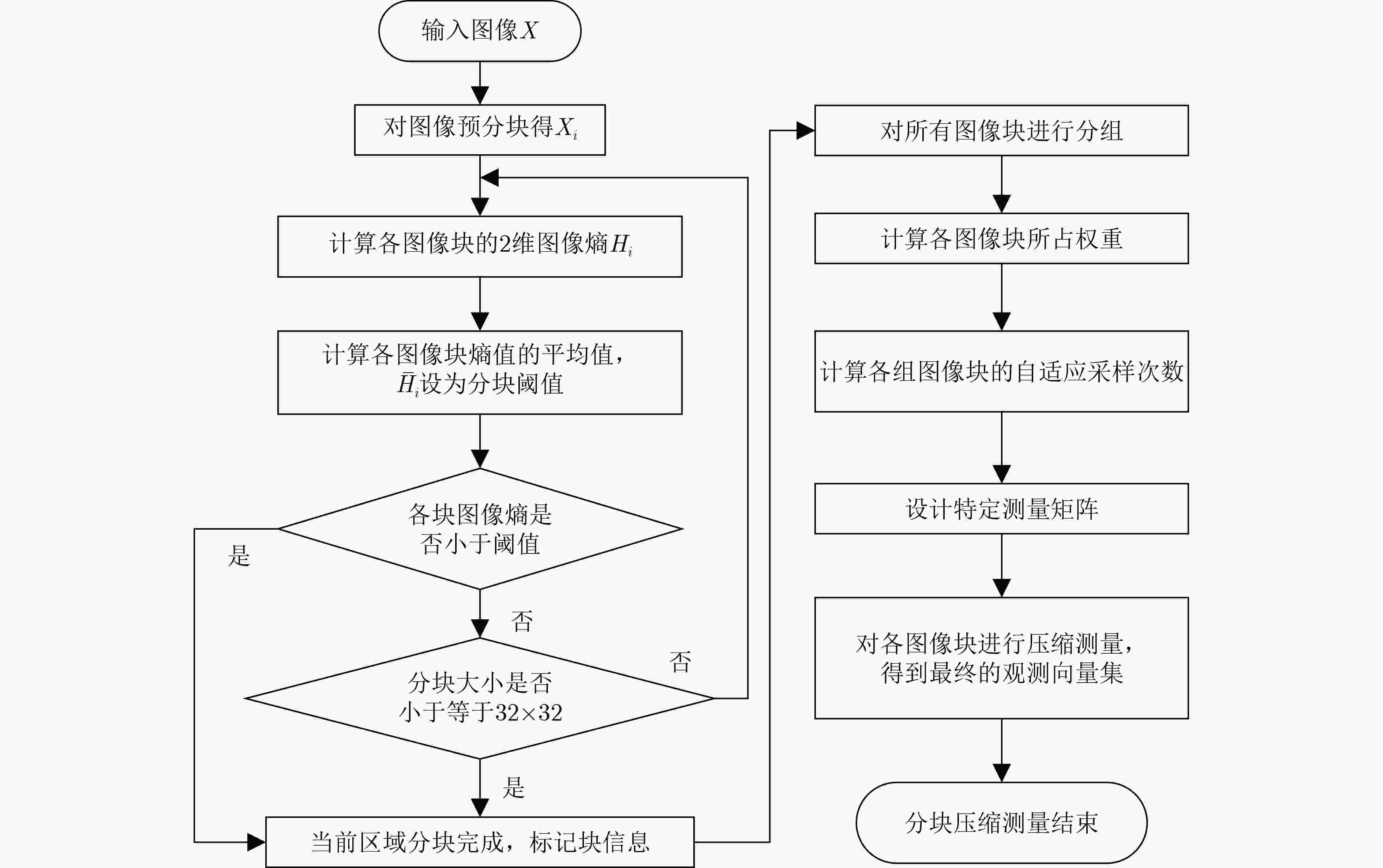
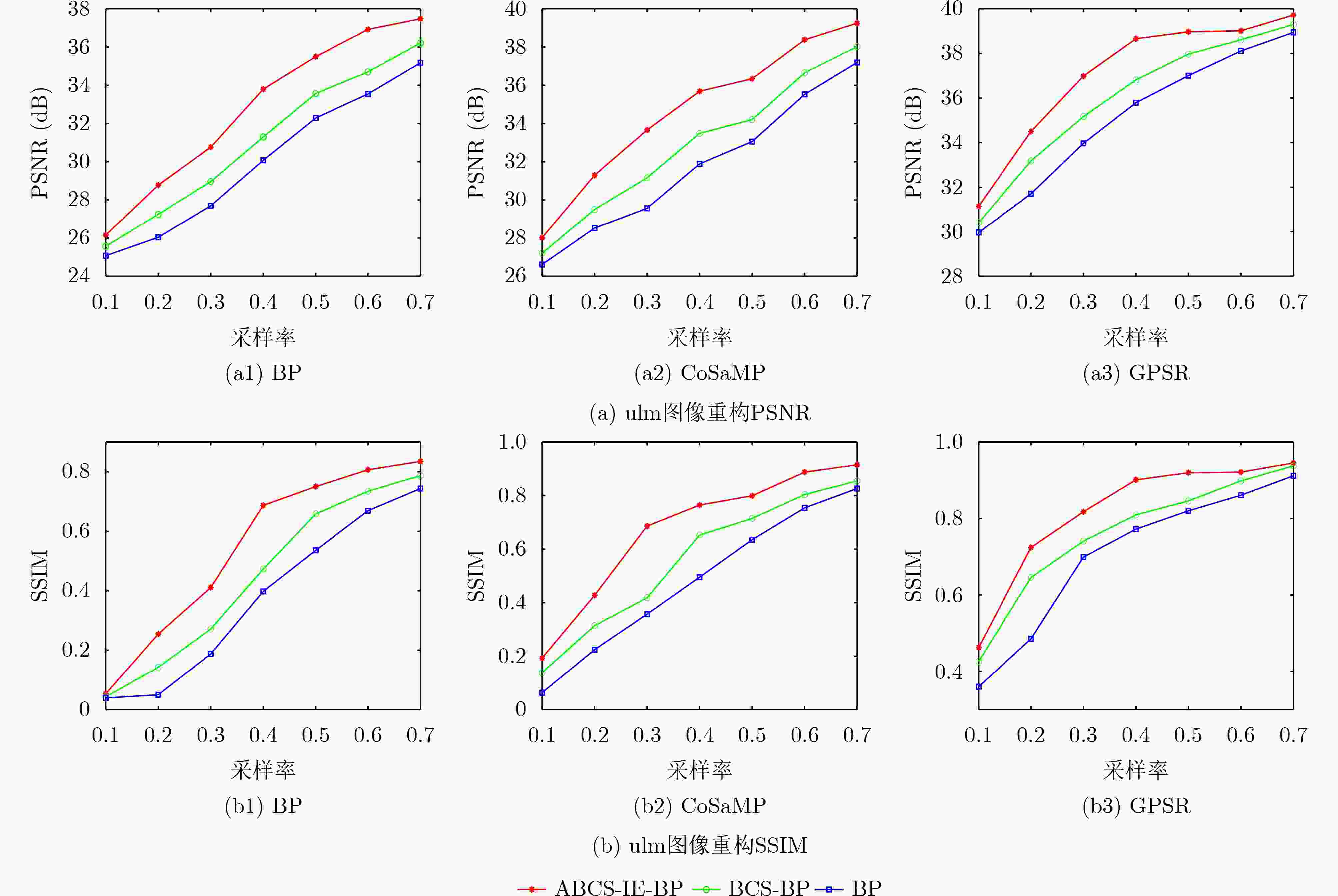
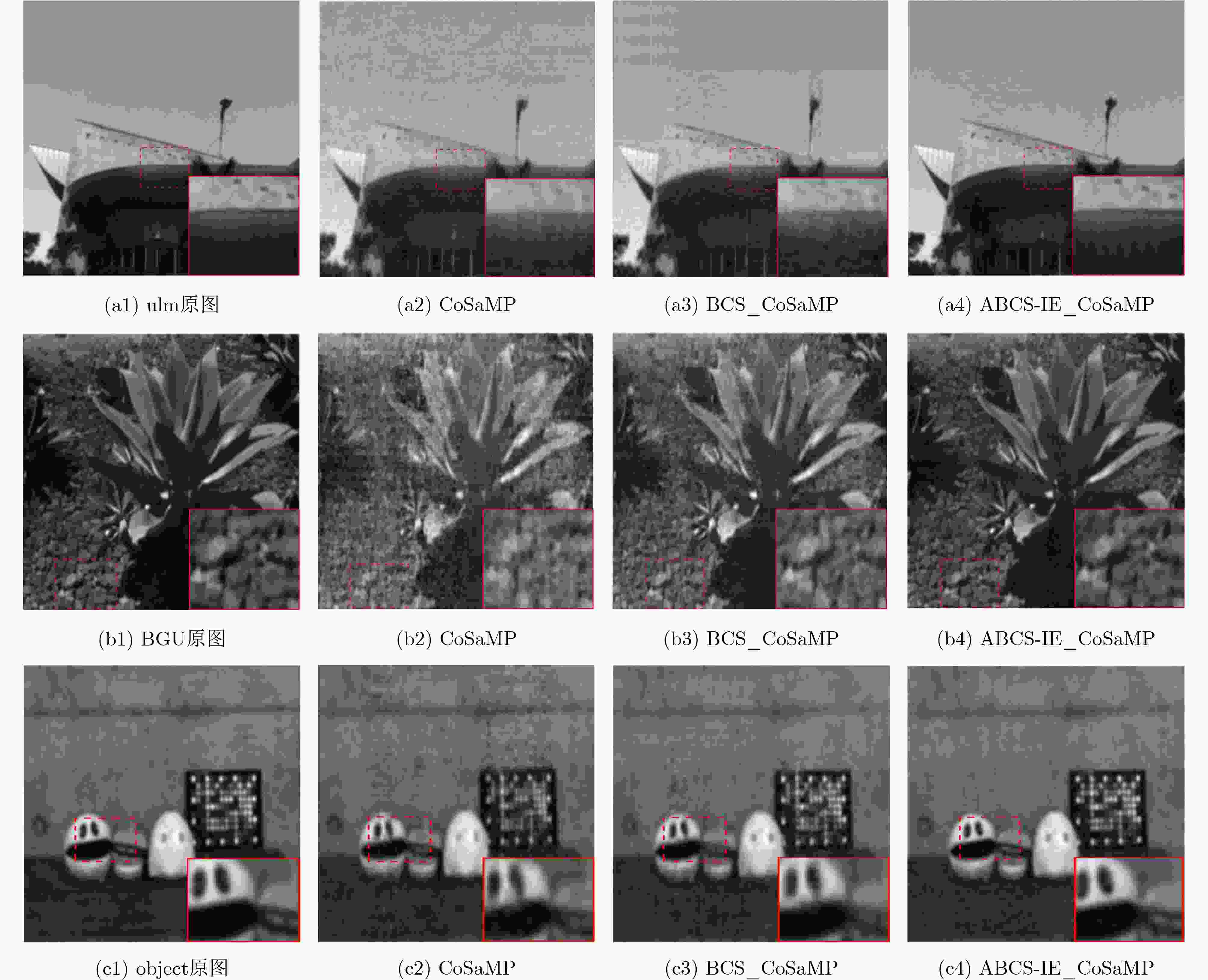
摘要: 在对高光谱图像采样重构的研究中,整体采样和固定分块采样没有考虑到高光谱图像复杂的纹理特征分布,使用了相同的测量矩阵导致图像的重构质量较差。针对此问题,该文提出基于2维图像熵自适应分块压缩感知重构方法(ABCS-IE),该方法以图像2维熵作为高光谱图像纹理细节的度量,根据图像的纹理细节分布自适应改变图像子块的大小,然后为不同的图像块分配特定的采样值,根据分配的采样值设计专有的测量矩阵对图像块进行压缩测量,将采样测量值代入重构算法中进行重构。实验结果表明,与整体采样重构和固定分块采样重构相比,将该方法应用到压缩感知重构算法中对高光谱图像进行采样重构后,重构的图像在视觉效果上有明显的提高,取得的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似度(SSIM)最大,采样率为0.4时,PSNR提高了2~4 dB,SSIM最大提高了0.27,均方根误差(RMSE)和信息熵差值(ΔH)也有所降低,说明重构的图像更加接近原始图像。而且运算时间也减少了1~1.5 s。可见,该方法能充分利用高光谱图像的纹理特征,有效提高图像的重构质量,同时减少重构的运算时间。Abstract: In the study of sampling and reconstruction of hyperspectral images, global sampling and fixed block sampling do not take into account the complex texture distribution of hyperspectral images, and the use of the same measurement matrix results in poor image reconstruction quality. To solve this problem, an Adaptive Block Compressed Sensing-Image Entropy (ABCS-IE) is presented. In this method, 2-dimensional image entropy is used as a measure of texture details of hyperspectral images. The size of image blocks is adaptively changed according to the texture details distribution of the image. Then, specific sampling values are assigned to different image blocks, and a special measurement matrix is designed to compress the image blocks according to the assigned sampling values, and the sampled measurements are brought into the reconstruction algorithm for reconstruction. The experimental results show that when this method is applied to the compression-aware reconstruction algorithm to sample and reconstruct the hyperspectral image, the visual effect of the reconstructed image is significantly improved. The maximum Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) are obtained. When the sampling rate is 0.4, the PSNR is increased by 2~4 dB and the SSIM is increased by 0.27, the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and the information entropy difference (ΔH) are also reduced, indicating that the reconstructed image is closer to the original image. Moreover, the operation time is reduced by 1~1.5 s. It can be seen that this method can make full use of texture features of hyperspectral images and improve effectively the quality of image reconstruction, and reduce the operation time of reconstruction.
-
表 1 不同测量矩阵下重构图像的PSNR结果对比(dB)
目标图像 算法 测量矩阵 高斯矩阵 伯努利矩阵 循环矩阵 ulm CoSaMP 31.8891 31.4468 30.6240 BCS-CoSaMP 33.4864 33.0751 32.5439 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 35.6857 34.9760 33.4807 BGU CoSaMP 30.0709 29.6891 28.6254 BCS-CoSaMP 31.1368 30.8649 29.7950 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 32.9268 32.1008 31.5431 object CoSaMP 31.1605 30.5438 29.2670 BCS-CoSaMP 32.4569 31.7902 30.9657 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 34.5967 33.9961 32.5935 表 2 重构图像的RMSE结果对比
目标图像 算法 采样率 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 ulm CoSaMP 0.2429 0.2052 0.1850 0.1461 0.1258 0.0852 0.0545 BCS-CoSaMP 0.2308 0.1851 0.1490 0.1107 0.1056 0.0653 0.0347 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 0.2113 0.1487 0.1077 0.0715 0.0670 0.0293 0.0096 BGU CoSaMP 0.2149 0.1947 0.1844 0.1592 0.1214 0.0621 0.0187 BCS-CoSaMP 0.2073 0.1746 0.1554 0.1342 0.0926 0.0417 0.0168 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 0.1967 0.1453 0.1194 0.0977 0.0594 0.0105 0.0073 object CoSaMP 0.1574 0.1422 0.1221 0.0956 0.0631 0.0230 0.0031 BCS-CoSaMP 0.1428 0.1297 0.1020 0.0725 0.0447 0.0121 0.0026 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 0.1271 0.1061 0.0763 0.0423 0.0207 0.0063 0.0017 表 3 重构图像的ΔH结果对比
目标图像 算法 采样率 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 ulm CoSaMP 3.2887 2.2157 1.5800 1.0037 0.6808 0.4247 0.2657 BCS-CoSaMP 2.8893 1.6728 1.3594 0.6121 0.4301 0.2867 0.2200 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 1.9695 1.3302 0.5293 0.3393 0.3291 0.1338 0.0299 BGU CoSaMP 0.9519 0.8377 0.8182 0.6289 0.3832 0.1881 0.0601 BCS-CoSaMP 0.8786 0.7334 0.5948 0.4747 0.2828 0.1383 0.0077 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 0.8273 0.5269 0.4370 0.3526 0.1972 0.0774 0.0045 object CoSaMP 1.6118 1.4790 1.2130 0.8118 0.3988 0.1276 0.0401 BCS-CoSaMP 1.5231 1.2472 0.9248 0.4871 0.2917 0.0490 0.0249 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 1.2859 0.9757 0.5653 0.4551 0.1838 0.0456 0.0099 表 4 不同重构算法的运行时间t对比(s)
算法 目标图像 ulm BGU object BP 8.75 7.54 7.32 BCS-BP 8.52 7.03 7.25 ABCS-IE-BP 7.08 5.87 6.03 CoSaMP 6.35 5.83 5.80 BCS-CoSaMP 6.18 5.79 5.75 ABCS-IE-CoSaMP 4.67 4.34 4.36 GPSR 8.42 8.21 7.84 BCS-GPSR 8.36 8.17 7.76 ABCS-IE-GPSR 6.84 6.73 6.35 -
[1] LIU Lei, SUN Min, REN Xiang, et al. Hyperspectral image quality based on convolutional network of multi-scale depth[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2020, 71: 102721. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2019.102721 [2] FABELO H, ORTEGA S, SZOLNA A, et al. In-vivo hyperspectral human brain image database for brain cancer detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39098–39116. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904788 [3] 王建成, 朱猛. 高光谱侦察技术的发展[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2019, 35(3): 37–45. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2019.03.009WANG Jiancheng and ZHU Meng. Development status of hyperspectral reconnaissance[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2019, 35(3): 37–45. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2019.03.009 [4] LU Bing, HE Yuhong, and DAO P D. Comparing the performance of multispectral and hyperspectral images for estimating vegetation properties[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(6): 1784–1797. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2910558 [5] 王立国, 王丽凤. 结合高光谱像素级信息和CNN的玉米种子品种识别模型[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(11): 2234–2244.WANG Liguo and WANG Lifeng. Variety identification model for maize seeds using hyperspectral pixel-level information combined with convolutional neural network[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(11): 2234–2244. [6] 邓亚美, 王秀娟, 杨敏莉, 等. 成像技术在食品安全与质量控制中的研究进展[J]. 色谱, 2020, 38(7): 741–749. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.202DENG Yamei, WANG Xiujuan, YANG Minli, et al. Research advances in imaging technology for food safety and quality control[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2020, 38(7): 741–749. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.202 [7] HU Meiqi, WU Chen, ZHANG Liangpei, et al. Hyperspectral anomaly change detection based on autoencoder[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 3750–3762. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3066508 [8] LUO Jiqiang, XU Tingfa, PAN Teng, et al. An efficient compression method of hyperspectral images based on compressed sensing and joint Optimization[J]. Integrated Ferroelectrics, 2020, 208(1): 194–205. doi: 10.1080/10584587.2020.1728625 [9] SUN Zheng and YAN Xiangyang. Image reconstruction based on compressed sensing for sparse-data endoscopic photoacoustic tomography[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2020, 116: 103587. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103587 [10] LI Denghui and WANG Yanhong. Implementation of image resampling algorithm based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2021, 1732: 012071. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1732/1/012071 [11] WANG Rongfang, QIN Yali, WANG Zhenbiao, et al. Group-based sparse representation for compressed sensing image reconstruction with joint regularization[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(2): 182. doi: 10.3390/electronics11020182 [12] 赵首博, 李秀红. 基于压缩感知的反射光谱重构算法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(4): 1092–1096. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2021)04-1092-05ZHAO Shoubo and LI Xiuhong. Research on reflection spectrum reconstruction algorithm based on compressed sensing[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(4): 1092–1096. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2021)04-1092-05 [13] WEI Ziran, ZHANG Jianlin, XU Zhiyong, et al. Optimization methods of compressively sensed image reconstruction based on single-pixel imaging[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(9): 3288. [14] TAO Chenning, ZHU Huanzheng, SUN Peng, et al. Simultaneous coded aperture and dictionary optimization in compressive spectral imaging via coherence minimization[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(18): 26587–26600. doi: 10.1364/OE.396260 [15] ZHANG Hao, MA Xu, LAU D L, et al. Compressive spectral imaging based on hexagonal blue noise coded apertures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 749–763. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2020.2979373 [16] ZHAO Yushi, HE Wenjun, LIU Zhiying, et al. Optical design of an offner coded aperture snapshot spectral imaging system based on dual-DMDs in the mid-wave infrared band[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(24): 39271–39283. doi: 10.1364/OE.444460 [17] WANG Zhongliang, HE Mi, YE Zhen, et al. Reconstruction of hyperspectral images from spectral compressed sensing based on a multitype mixing model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2304–2320. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2994334 [18] 谌德荣, 吕海波, 李秋富, 等. 分块压缩感知的全变差正则化重构算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2217–2223. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180931CHEN Derong, LÜ Haibo, LI Qiufu, et al. Total variation regularized reconstruction algorithms for block compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2217–2223. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180931 [19] DAI Guangzhi, HE Zhiyong, and SUN Hongwei. Ultrasonic block compressed sensing imaging reconstruction algorithm based on wavelet sparse representation[J]. Current Medical Imaging, 2020, 16(3): 262–272. doi: 10.2174/1573405615666191209151746 [20] ZHANG Zheng, BI Hongbo, KONG Xiaoxue, et al. Adaptive compressed sensing of color images based on salient region detection[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(21): 14777–14791. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-7062-6 [21] WANG Xiaodong, LI Yunhui, WANG Zhi, et al. Self-adaptive block-based compressed sensing imaging for remote sensing applications[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2020, 14(1): 016513. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.14.016513 [22] KAZEMI V, SHAHZADI A, and BIZAKIi H K. Multifocus image fusion using adaptive block compressive sensing by combining spatial frequency[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(11): 15153–15170. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12072-2 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
