Research on Target Detection in Underground Coal Mines Based on Improved YOLOv5
-
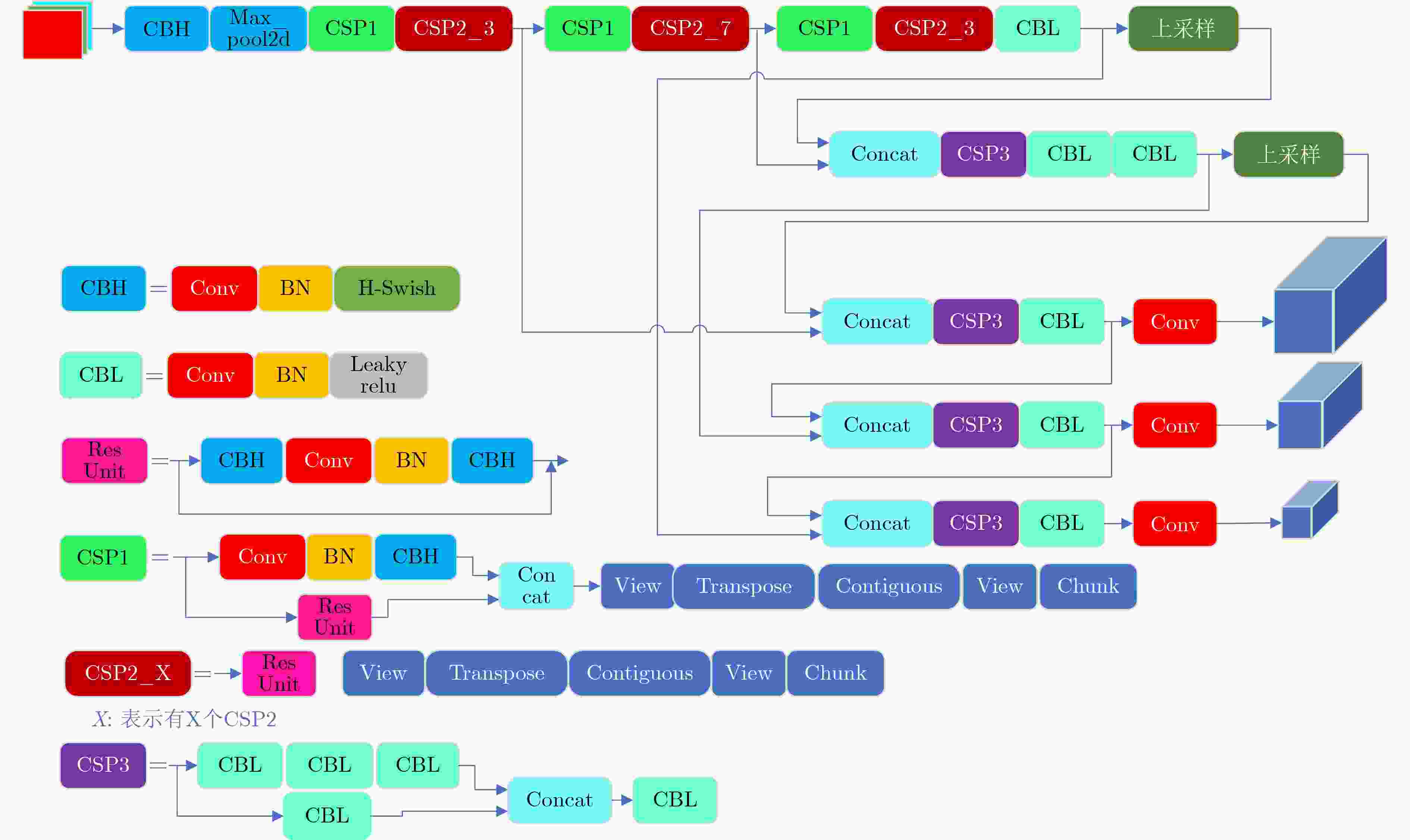
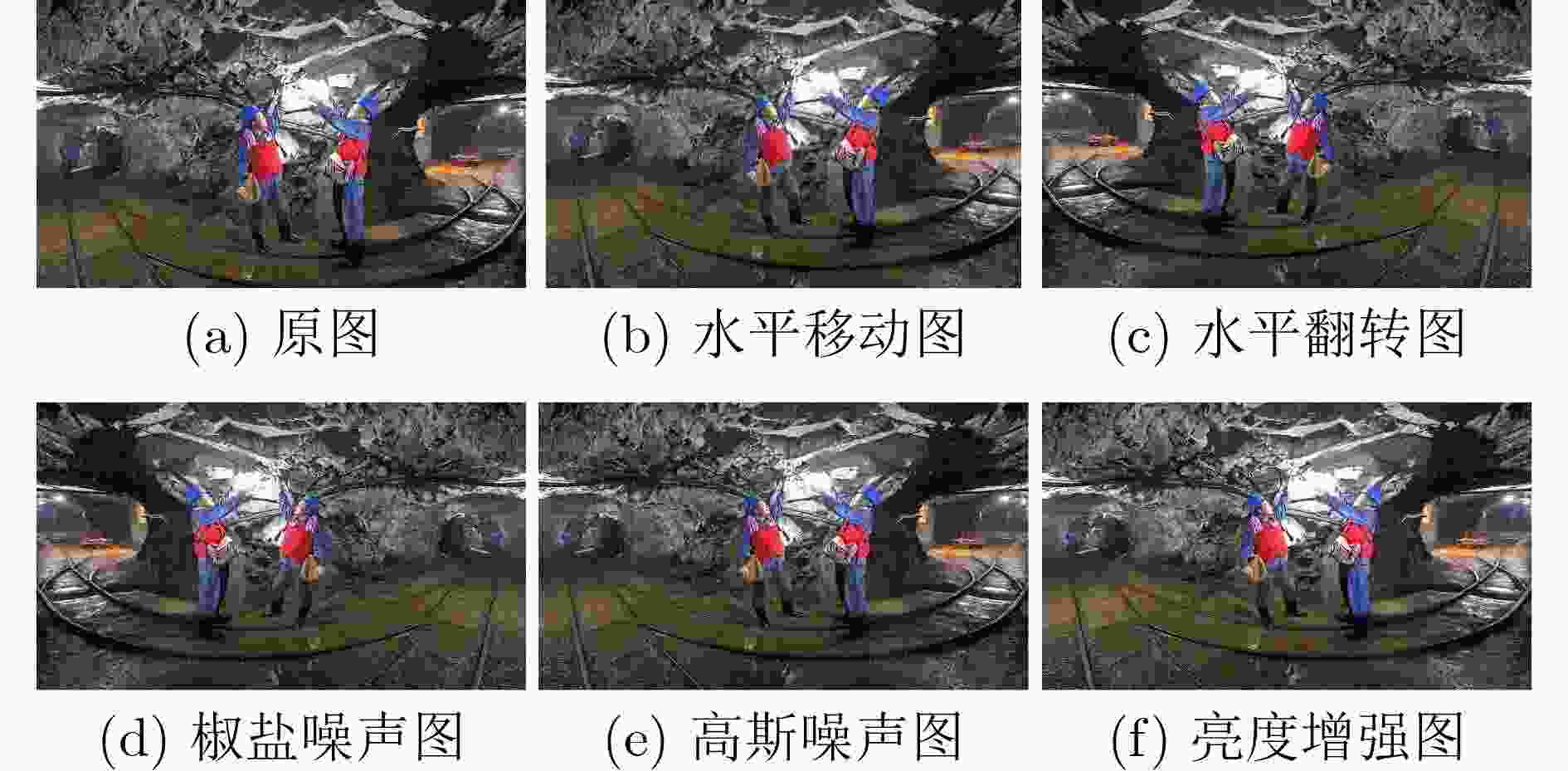
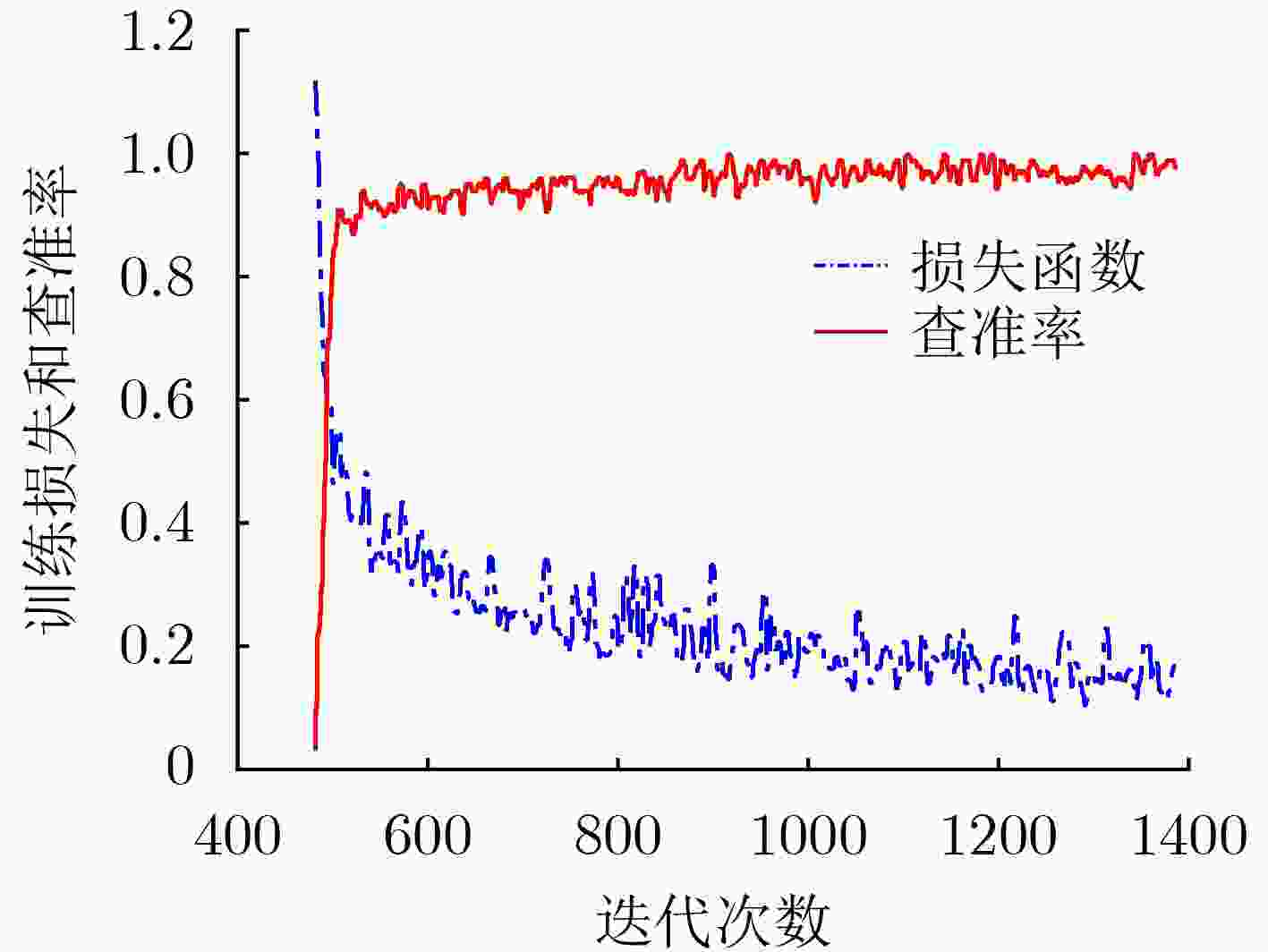
摘要: 针对煤矿井下环境多利用红外相机感知周边环境温度成像,但形成的图像存在纹理信息少、噪声多、图像模糊等问题,该文提出一种可用于煤矿井下实时检测的多尺度卷积神经网络(Ucm-YOLOv5)。该网络是在YOLOv5的基础上进行改进,首先使用PP-LCNet作为主干网络,用于加强CPU端的推理速度;其次取消Focus模块,使用shuffle_block模块替代C3模块,在去除冗余操作的同时减少了计算量;最后优化Anchor同时引入H-swish作为激活函数。实验结果表明,Ucm-YOLOv5比YOLOv5的模型参数量减少了41%,模型缩小了86%,该算法在煤矿井下具有更高的检测精度,同时在CPU端的检测速度达到实时检测标准,满足煤矿井下目标检测的工作要求。Abstract: In view of the underground coal mine environment, which uses mostly infrared cameras to sense the surrounding environment’s temperature, the images formed have the problems of less texture information, more noise, and blurred images. The detection of Underground targets in coal mines using YOLOv5(Ucm-YOLOv5), a neural network for real-time detection of coal mines, is suggested in this document. This network is an improvement on YOLOv5. Firstly, PP-LCNet is used as the backbone network for enhancing the inference speed on the CPU side. Secondly, the Focus module is eliminated, and the shuffle_block module is used to replace the C3 module in YOLOv5, which reduces the computation while removing redundant operations. Finally, the Anchor is optimized while introducing H-swish as the activation function. The experimental results show that Ucm-YOLOv5 has 41% fewer model parameters and an 86% smaller model than YOLOv5. The algorithm has higher detection accuracy in underground coal mines, while the detection speed at the CPU side reaches the real-time detection standard, which meets the working requirements for target detection in underground coal mines.
-
Key words:
- Coal mine underground target detection /
- Deep learning /
- YOLOv5
-
表 1 Anchor参数
原始Anchor 重构Anchor [10,13, 16,30, 55,220]
[30,61, 62,45, 59,119]
[116,90,156,198,373,326][30,27, 53,78, 172,35]
[128,115,90,225, 101,327]
[222,152,154,316,311,243]表 2 煤矿井下数据集参数
类别 扩充前标签数 扩充后标签数 Person 人 3658 21948 Rail 轨道 812 4872 Tip cards 提示牌 389 2334 Truck 车 352 2112 Machine 机器 479 2874 Pipe 管道 913 5478 Lamp 灯 1501 9006 Columns 支撑柱 585 3510 总计 8689 52134 表 3 网络检测结果对比(%)
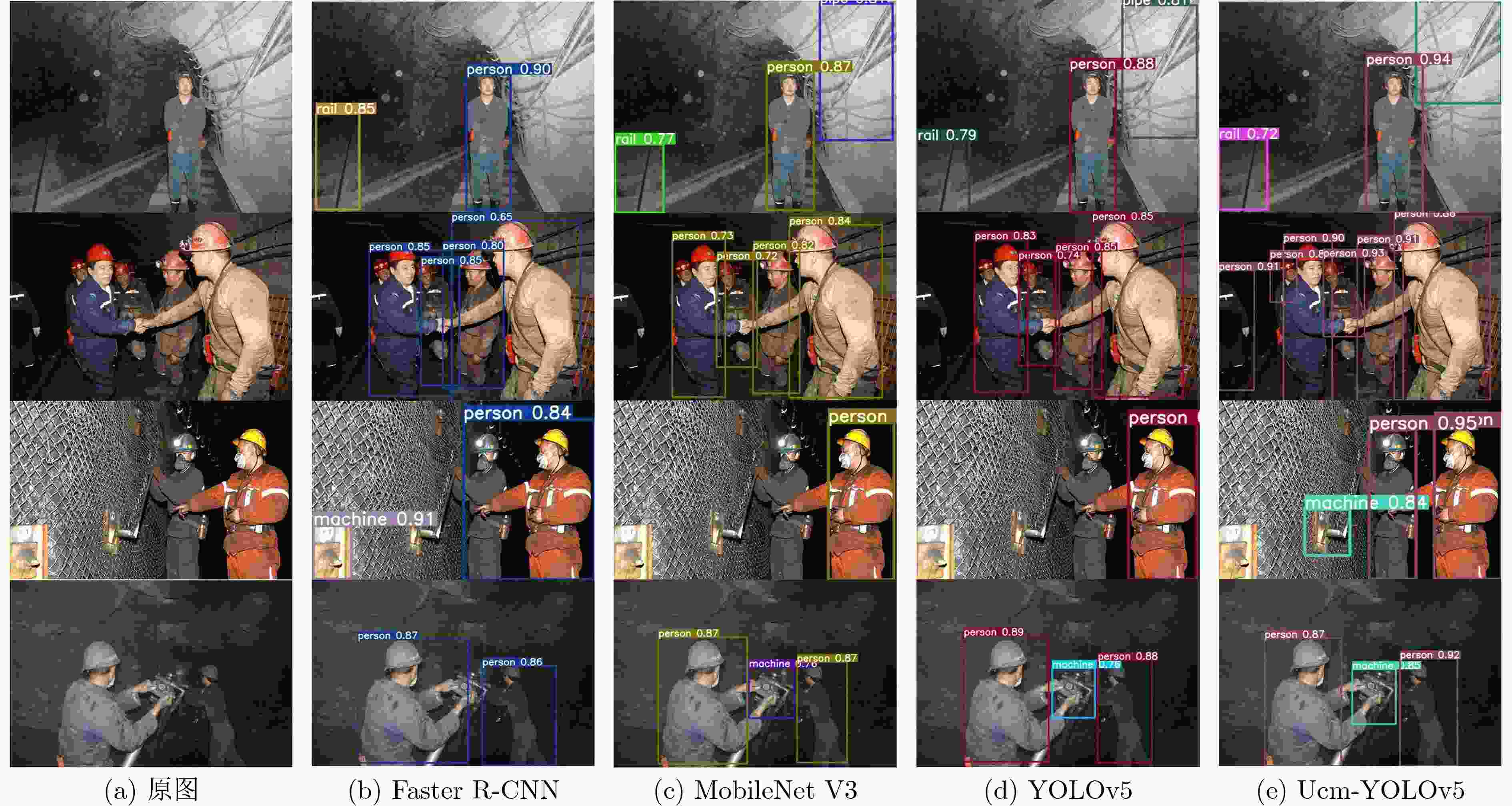
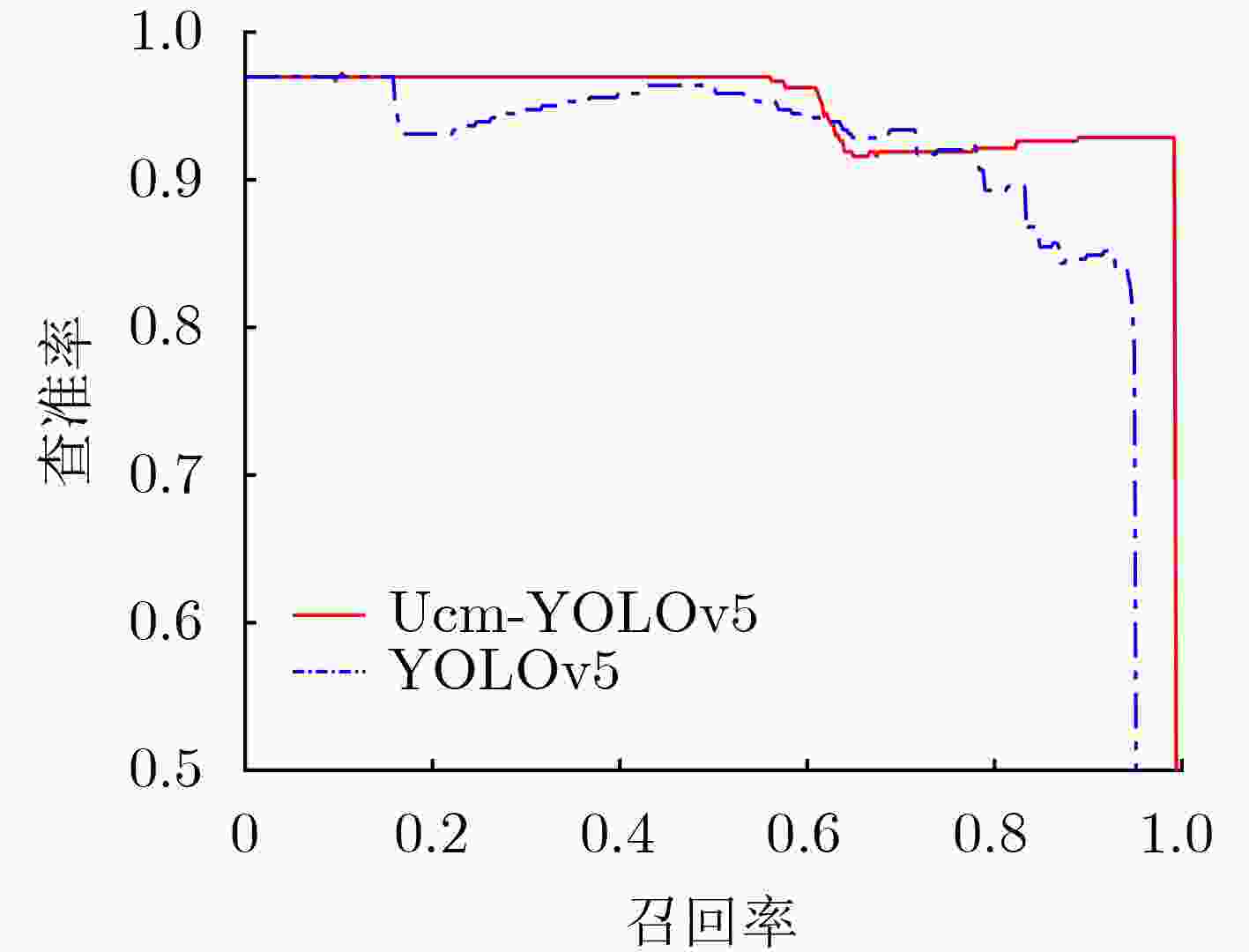
曝光状态 AP mAP 人类 轨道 提示牌 车 机器 管道 灯 支撑柱 强曝光 YOLOv5 89.6 88.2 89.5 84.5 85.2 89.4 89.3 83.5 88.2 Ucm-YOLOv5 99.3 99.6 98.7 99.4 99.5 99.6 98.2 96.1 98.8 弱曝光 YOLOv5 93.7 84.3 85.6 82.9 82.7 87.2 81.6 79.5 83.4 Ucm-YOLOv5 98.8 96.6 97.3 95.7 94.5 96.6 94.9 96.1 96.3 表 4 煤矿井下数据集不同方法结果比较
模型 Loss mAP(%) Faster R-CNN 0.0419 80.6 MobileNet V3 0.0119 86.2 YOLOv5 0.0206 85.8 Ucm-YOLOv5 0.0171 97.5 表 5 不同模型网络性能对比结果
模型 模型大小
(MByte)模型参数量
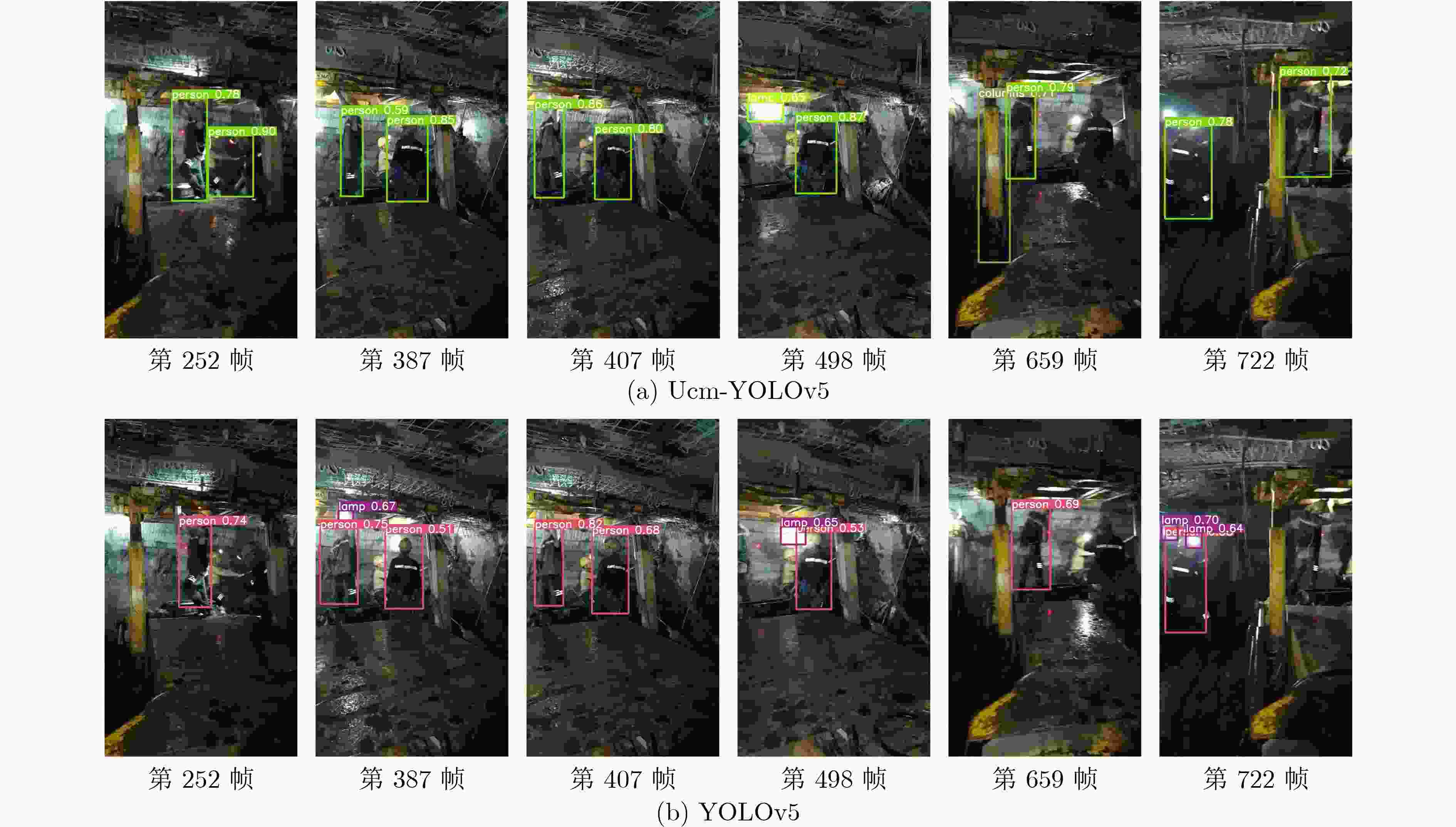
(MByte)平均检测速度(帧/s) GPU CPU Faster R-CNN 170 25.3 7.0 2.4 MobileNet V3 48 5.4 37 25 YOLOv5 90.4 7.3 85 7.6 Ucm-YOLOv5 12.5 4.3 51 28 表 6 煤矿井下复杂环境中Ucm-YOLOv5网络与YOLOv5的鲁棒性对比
类别 目标出现
总帧数目标检测总帧数 目标错误检测总帧数 平均精确率AP(%) 误检率(%) 平均检测率mAP(%) 平均检测速度(帧/s) Ucm-
YOLOv5YOLOv5 Ucm-
YOLOv5YOLOv5 Ucm-
YOLOv5YOLOv5 Ucm-
YOLOv5YOLOv5 Ucm-
YOLOv5YOLOv5 Ucm-
YOLOv5YOLOv5 Person 1986 1063 885 0 0 53.5 44.6 0 0 45.8 40.8 21.1 16.3 Rail 651 329 277 26 33 50.5 42.5 4 5 Tip cards 566 265 236 13 18 46.8 41.7 2.3 3.2 Truck 496 213 178 16 23 42.9 38.8 3.2 4.6 Machine 566 263 216 22 29 46.4 38.2 3.9 5.1 Pipe 648 298 269 0 0 45.9 41.5 0 0 Lamp 842 415 387 0 0 42.3 45.9 0 0 Columns 594 227 198 18 25 38.2 33.3 3 4.2 -
[1] LI Ailing, ZHANG Jixiong, ZHOU Nan, et al. A model for evaluating the production system of an intelligent mine based on unascertained measurement theory[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 38(2): 1865–1875. doi: 10.3233/JIFS-190329 [2] ZHANG Kexue, KANG Lei, CHEN Xuexi, et al. A review of intelligent unmanned mining current situation and development trend[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(2): 513. doi: 10.3390/en15020513 [3] HE Yunze, DENG Baoyuan, WANG Hongjin, et al. Infrared machine vision and infrared thermography with deep learning: A review[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2021, 116: 103754. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2021.103754 [4] WEI Dong, WANG Zhongbin, SI Lei, et al. Online shearer-onboard personnel detection method for the intelligent fully mechanized mining face[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2022, 236(6): 3058–3072. doi: 10.1177/09544062211030973 [5] RYU J and KIM S. Data driven proposal and deep learning-based small infrared drone detection[J]. Journal of Institute of Control, Robotics and Systems, 2018, 24(12): 1146–1151. doi: 10.5302/J.ICROS.2018.18.0157 [6] FAN Tao. Research and realization of video target detection system based on deep learning[J]. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing, 2020, 18(1): 1941010. doi: 10.1142/S0219691319410108 [7] 李宝奇, 黄海宁, 刘纪元, 等. 基于改进SSD的水下光学图像感兴趣目标检测算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3372–3378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210761LI Baoqi, HUANG Haining, LIU Jiyuan, et al. Underwater optical image interested object detection model based on improved SSD[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3372–3378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210761 [8] LI Xiaoyu, WANG Shuai, LIU Bin, et al. Improved YOLOv4 network using infrared images for personnel detection in coal mines[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2022, 31(1): 013017. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.31.1.013017 [9] JIANG Daihong, DAI Lei, LI Dan, et al. Moving-object tracking algorithm based on PCA-SIFT and optimization for underground coal mines[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 35556–35563. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899362 [10] DU Yuxin, TONG Minming, ZHOU Lingling, et al. Edge detection based on Retinex theory and wavelet multiscale product for mine images[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(34): 9625–9637. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.009625 [11] QIU Zhi, ZHAO Zuoxi, CHEN Shaoji, et al. Application of an improved YOLOv5 algorithm in real-time detection of foreign objects by ground penetrating radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(8): 1895. doi: 10.3390/RS14081895 [12] CUI Cheng, GAO Tingquan, WEI Shengyu, et al. PP-LCNet: A lightweight CPU convolutional neural network[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2109.15099, 2021. [13] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [14] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [15] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YoLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. [16] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [17] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YoLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [18] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7263–7271. [19] TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019. [20] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN Bo, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
