Resource Allocation and Load Balancing Strategy in Cloud-fog Hybrid Computing Based on Cluster-collaboration
-
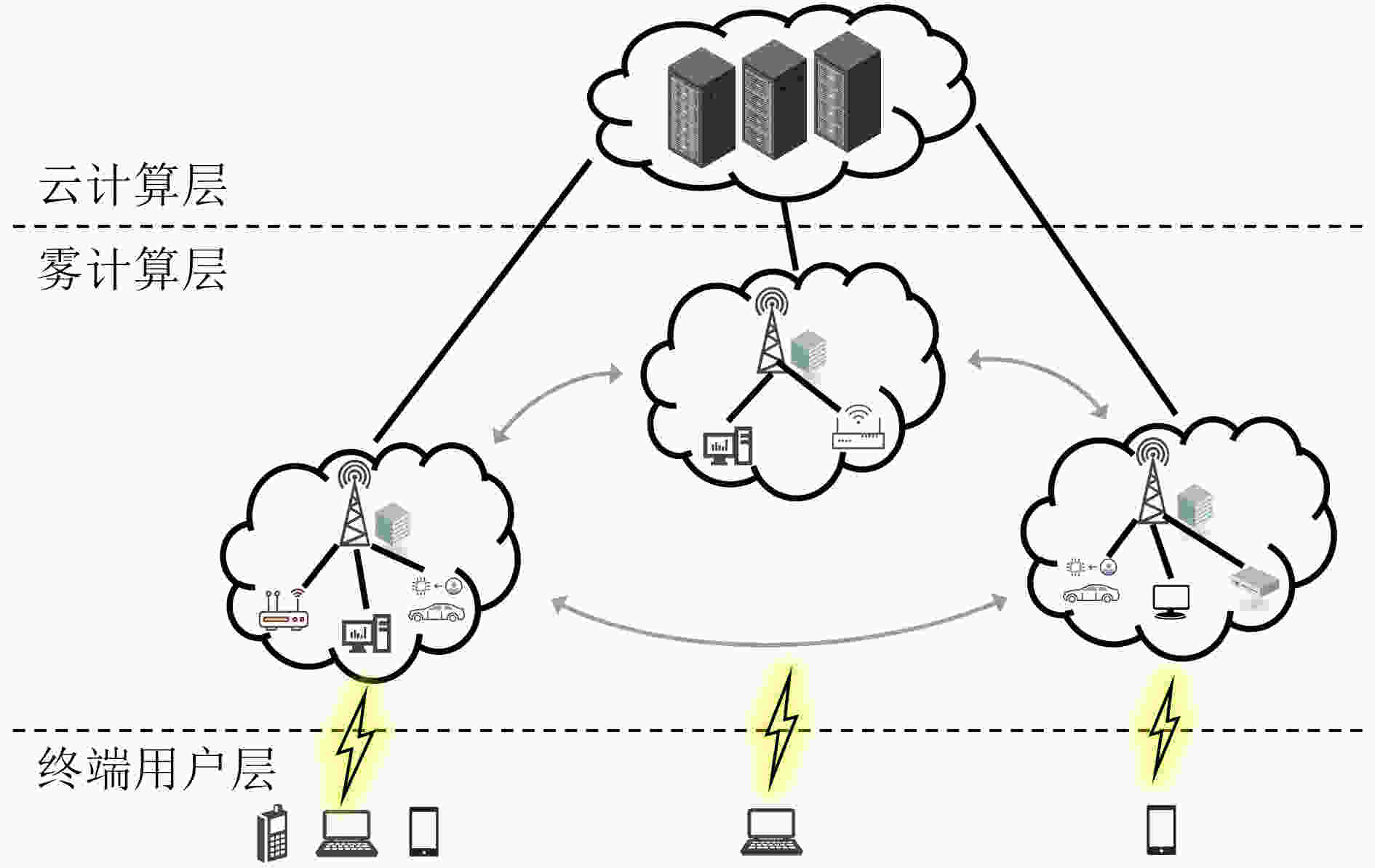
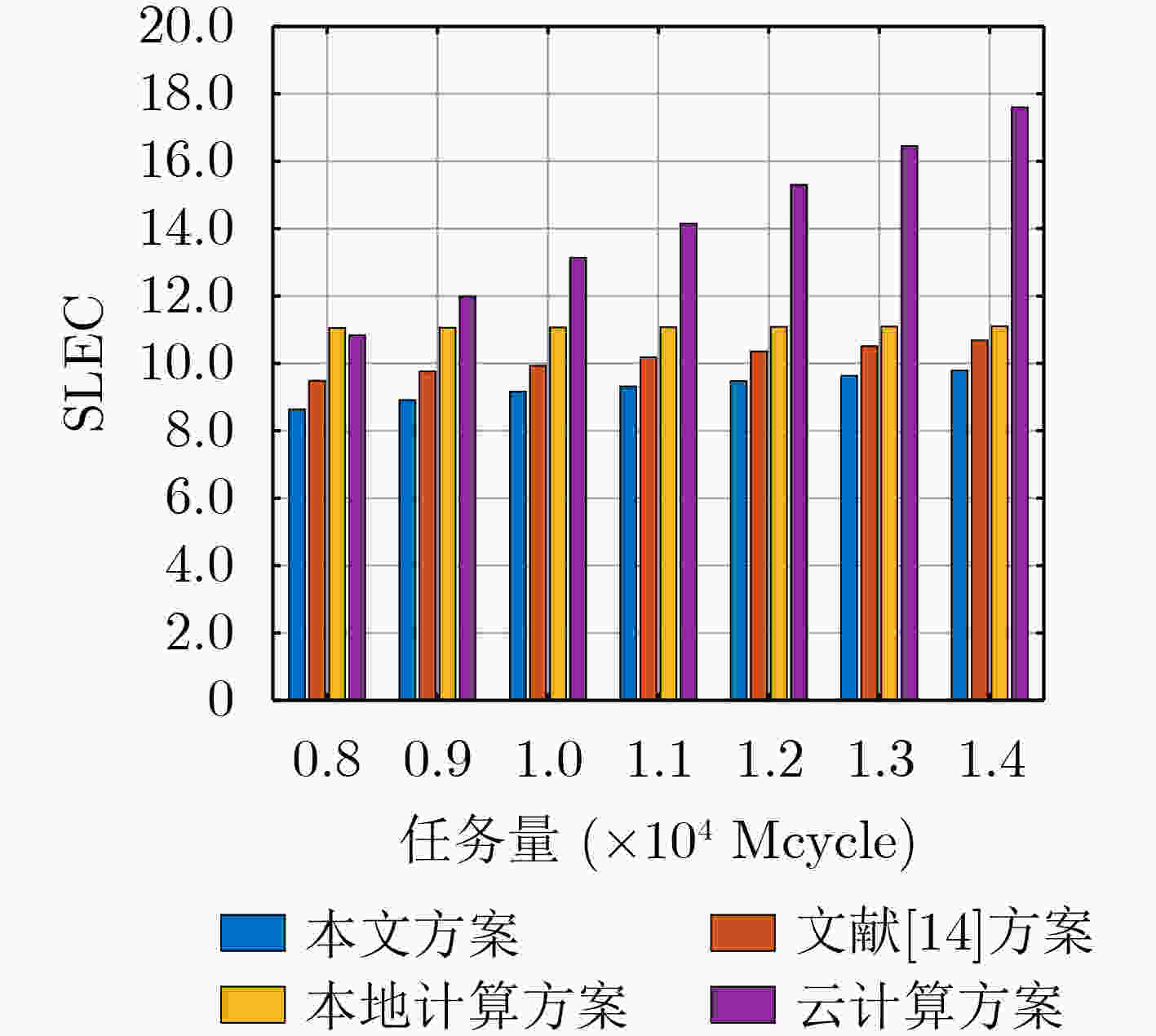
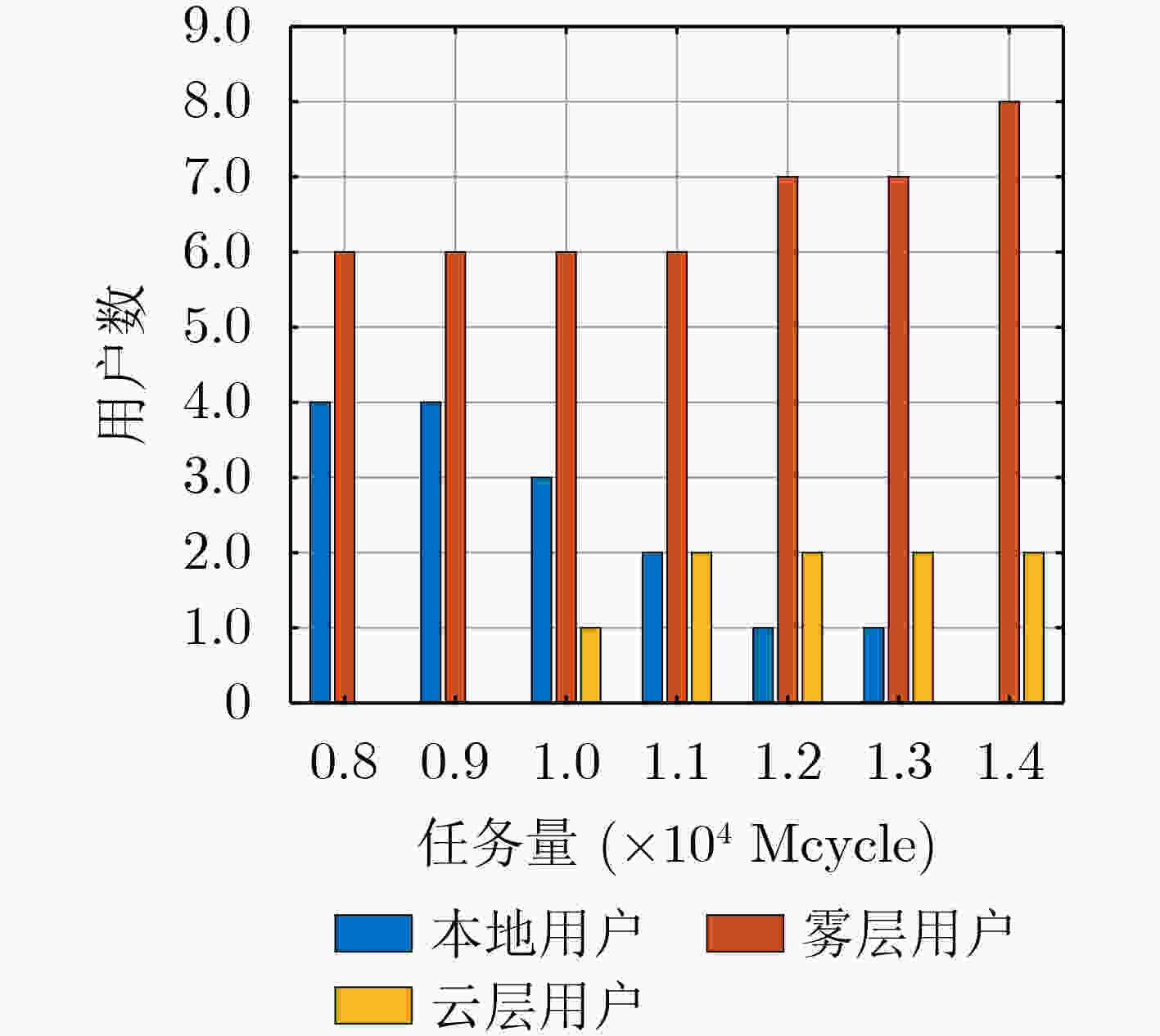
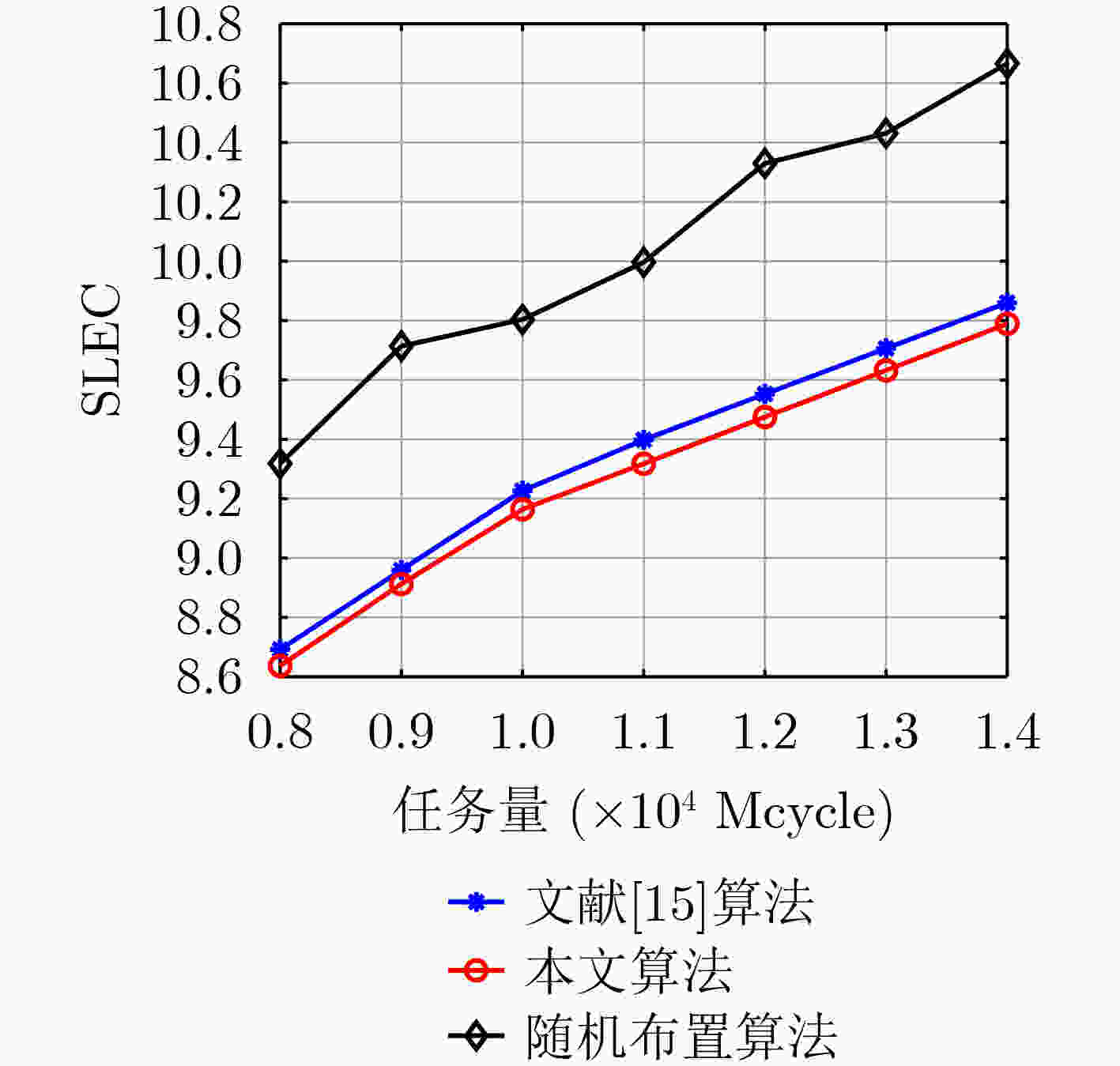
摘要: 针对物联网(IoT)中智能应用快速增长导致的移动网络数据拥塞问题,该文构建了一种基于雾集群协作的云雾混合计算模型,在考虑集群负载均衡的同时引入权重因子以平衡计算时延和能耗,最终实现系统时延能耗加权和最小。为了解决该混合整数非线性规划问题,将原问题分解后采用库恩塔克(KKT)条件和二分搜索迭代法对资源配置进行优化,提出一种基于分支定界的开销最小化卸载算法(BB-OMOA)获得最优卸载决策。仿真结果表明,集群协作模式显著提高了系统负载均衡度,且所提策略在不同参数条件下明显优于其他基准方案。Abstract: Considering the problem of data congestion in mobile networks caused by the rapid growth of smart applications in Internet of Things (IoT), a cloud-fog hybrid computing model based on cluster-collaboration is constructed. The cluster load balancing is considered while introducing weighting factors to balance the computational latency and energy consumption, and finally the minimum weighted sum of system latency and energy consumption is achieved. In order to solve this mixed integer nonlinear programming problem, the original problem is decomposed to optimize the resource allocation using Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) condition and bisection search iterative method. Then an Overhead Minimization Offloading Algorithm based on Branch and Brand (BB-OMOA) is proposed to obtain the optimal offloading decision. Simulation results show that the cluster-collaboration model improves significantly the system load balancing degree and the proposed strategy outperforms significantly other benchmark schemes.
-
Key words:
- Fog Computing (FC) /
- Cluster /
- Resource allocation /
- Load balancing /
- Branch brand
-
算法1 基于二分搜索迭代法的传输功率分配算法 初始化:传输功率范围0、$p_u^{\max }$,收敛阈值$\gamma $ (1) 根据式(23)计算$s(p_u^{\max })$ (2) if $\,s(p_u^{\max }) \le 0\,$ then (3) $p{_u^{t^*} } = p_u^{\max }$ (4) else (5) 初始化参数$p_u^{\text{v}} = 0,p_u^{\text{r}} = p_u^{\max }$ (6) $p_u^{\text{l}} = {{(p_u^{\text{v}} + p_u^{\text{r}})} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{(p_u^{\text{v}} + p_u^{\text{r}})} 2}} \right. } 2}$ (7) if $\,s(p_u^{\text{l}}) \le 0$ then (8) $p_u^{\text{v}} = p_u^{\text{l}}$ (9) else (10) $p_u^{\text{r}} = p_u^{\text{l}}$ (11) end if (12) until $\,(p_u^{\text{r} } - p_u^{\text{v} }) \le \gamma \,$ (13) $p_u^{\max } = {{(p_u^{\text{r}} + p_u^{\text{v}})} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{(p_u^{\text{r}} + p_u^{\text{v}})} 2}} \right. } 2}$ 算法2 BB-OMOA 初始化:用户任务及系统参量,最优计算频率$f{_u^{n,{\text{e} }^*} }$,最优功率
$p_u^{t^*}$,用户集合$U$,雾集群组$N$,求解精确度${\text{η }}$(1) for $u = 1,2, \cdots ,U$ do (2) 求解松弛问题$\widetilde { {\text{OPT} } } {\text{-}} 5$,得$ {\mathbf{b}} $和${\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}}$ (3) if ${b_{u,s}} \in Z,\forall u \in U$then (4) 现行解${{\mathbf{b}}^ * }$即为最优解 (5) else (6) 挑选不符合整数条件的变量${b_j}$构造约束${b_j} \le \left\lfloor {{v_j}} \right\rfloor $和
${b_j} \ge \left\lfloor {{v_j}} \right\rfloor + 1$进行分支形成子问题(7) 设定待更新上下界${\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}}$和${\tilde L_{{\text{upper}}}}$ (8) while ${\tilde L_{{\text{upper}}}} - {\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}} > {\text{η }}$ do (9) if 子问题${\widetilde { {\text{OPT} } }_i} {\text{-}} 5$有可行解 (10) if ${\tilde L_i} \ge {\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}}$且${\tilde L_i} \le {\tilde L_{{\text{upper}}}}$ (11) 令${\tilde L_i}$为新的下界,即${\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}} = {\tilde L_i}$ (12) 回到步骤(6)迭代分支定界操作 (13) else if ${\tilde L_i}$对应解的各分量都是整数then (14) return ${\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}}$ (15) else 进行剪支操作舍弃这一子问题 (16) end if (17) else 进行剪支操作舍弃这一子问题 (18) 令${\tilde L_i}^ * = \min \{ {\tilde L_{{\text{lower}}}}|i \in {N_ + }\} $ (19) $\tilde L_i^ * $为式(26)最优值${L^ * }$,对应解即最优策略${{\mathbf{b}}^ * }$。 表 1 仿真参数
参数 数值 系统带宽$ B\left(\mathrm{M}\mathrm{H}\mathrm{z}\right) $ 20 任务数据量$ L\left(\mathrm{M}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\right) $ 0.1~0.5 任务所需CPU周期数$ C\left(\mathrm{M}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{y}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{e}\right) $ 500~2500 本地计算能力${f}_{u}^{\rm{{l}}}\left(\mathrm{G}\mathrm{H}\mathrm{z}\right)$ 0.5~1.5 噪声功率谱密度$ {N}_{0}(\mathrm{d}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{H}\mathrm{z}) $ –174 最大传输功率$ {p}_{u}^{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}}\left(\mathrm{d}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{m}\right) $ 25 雾集群最大计算能力$ {F}_{n}\left(\mathrm{G}\mathrm{H}\mathrm{z}\right) $ 15~25 中心云总计算能力${f}_{{\rm{d}}}\left(\mathrm{G}\mathrm{H}\mathrm{z}\right)$ 50 -
[1] LYU X C, TIAN Hui, SENGUL C, et al. Multiuser joint task offloading and resource optimization in proximate clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(4): 3435–3447. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2593486 [2] HAO Wanming, ZENG Ming, SUN Gangcan, et al. Edge cache-assisted secure low-latency millimeter-wave transmission[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(3): 1815–1825. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2957351 [3] ZHANG Tiankui, WANG Yi, LIU Yuanwei, et al. Cache-enabling UAV communications: Network deployment and resource allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7470–7483. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3011881 [4] ZHANG Weizhe, ELGENDY I A, HAMMAD M, et al. Secure and optimized load balancing for multitier IoT and edge-cloud computing systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(10): 8119–8132. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3042433 [5] GOUDARZI M, WU Huaming, PALANISWAMI M, et al. An application placement technique for concurrent IoT applications in edge and fog computing environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2021, 20(4): 1298–1311. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.2967041 [6] LIU Zening, YANG Yang, CHEN Yu, et al. A multi-tier cost model for effective user scheduling in fog computing networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Paris, France, 2019: 1–6. [7] REHMAN A U, AHMAD Z, JEHANGIRI A I, et al. Dynamic energy efficient resource allocation strategy for load balancing in fog environment[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 199829–199839. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3035181 [8] ZENG Deze, GU Lin, GUO Song, et al. Joint optimization of task scheduling and image placement in fog computing supported software-defined embedded system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(12): 3702–3712. doi: 10.1109/TC.2016.2536019 [9] PHAM X Q and HUH E N. Towards task scheduling in a cloud-fog computing system[C]. 2016 18th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Kanazawa, Japan, 2016: 1–4. [10] DO C T, TRAN N H, PHAM C, et al. A proximal algorithm for joint resource allocation and minimizing carbon footprint in geo-distributed fog computing[C]. 2015 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Siem Reap, Cambodia, 2015: 324–329. [11] XU Xiaolong, FU Shucun, CAI Qing, et al. Dynamic resource allocation for load balancing in fog environment[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018, 2018: 6421607. doi: 10.1155/2018/6421607 [12] GAO Zihan, HAO Wanming, and YANG Shouyi. Joint offloading and resource allocation for multi-user multi-edge collaborative computing system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 3383–3388. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3139843 [13] SUN Yuxuan, GUO Xueying, SONG Jinhui, et al. Adaptive learning-based task offloading for vehicular edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3061–3074. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2895593 [14] GAO Zihan, HAO Wanming, ZHANG Ruizhe, et al. Markov decision process-based computation offloading algorithm and resource allocation in time constraint for mobile cloud computing[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(13): 2068–2078. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2020.0062 [15] TRAN T X and POMPILI D. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 856–868. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2881191 [16] DING Changfeng, WANG Junbo, ZHANG Hua, et al. Joint MU-MIMO precoding and resource allocation for mobile-edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(3): 1639–1654. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3035153 [17] HAO Yixue, CHEN Min, HU Long, et al. Energy efficient task caching and offloading for mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 11365–11373. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2805798 [18] ZHANG Ni, GUO Songtao, DONG Yifan, et al. Joint task offloading and data caching in mobile edge computing[C]. 2019 15th International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks (MSN), Shenzhen, China, 2019: 234–239. -





 下载:
下载:
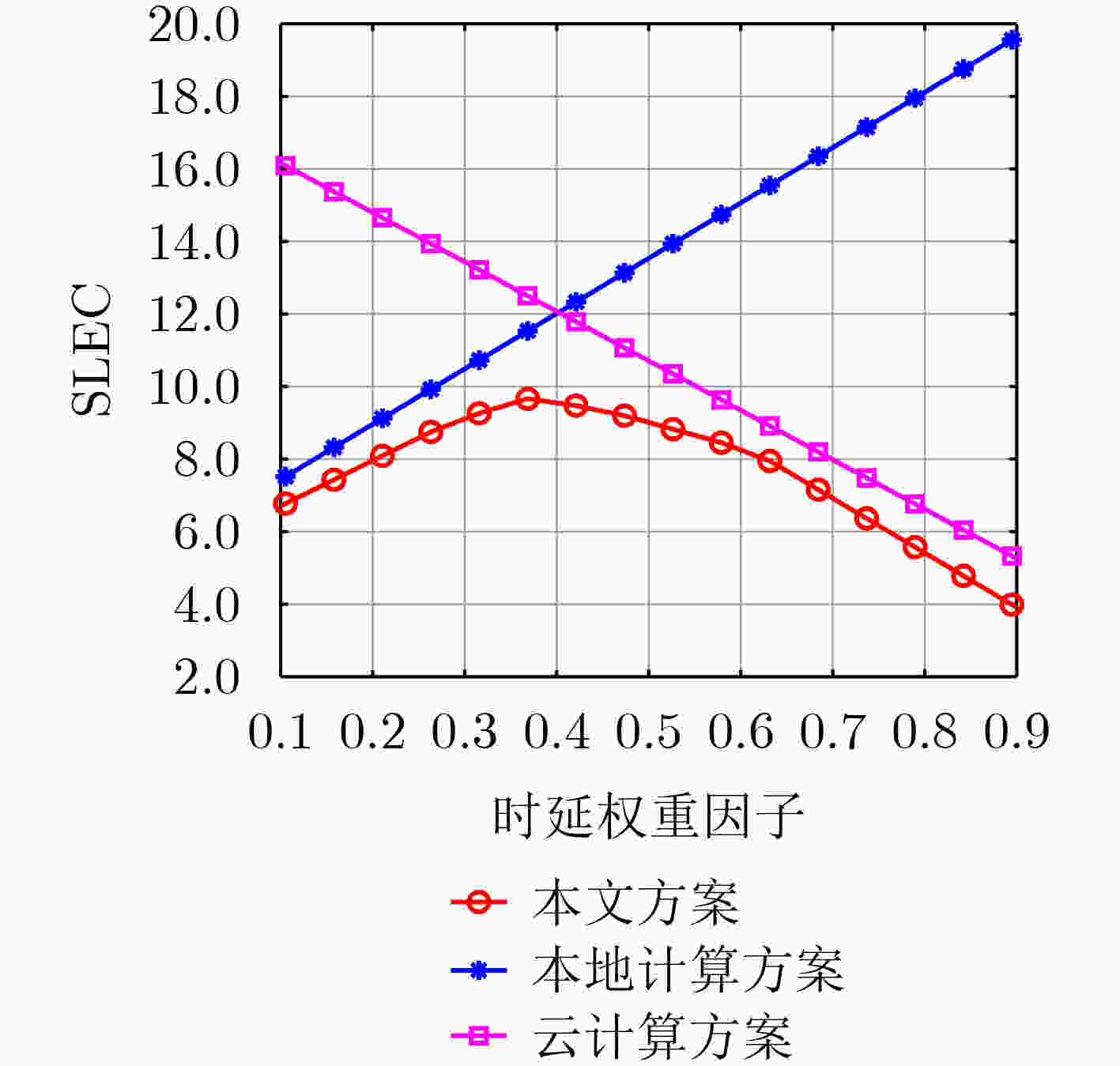
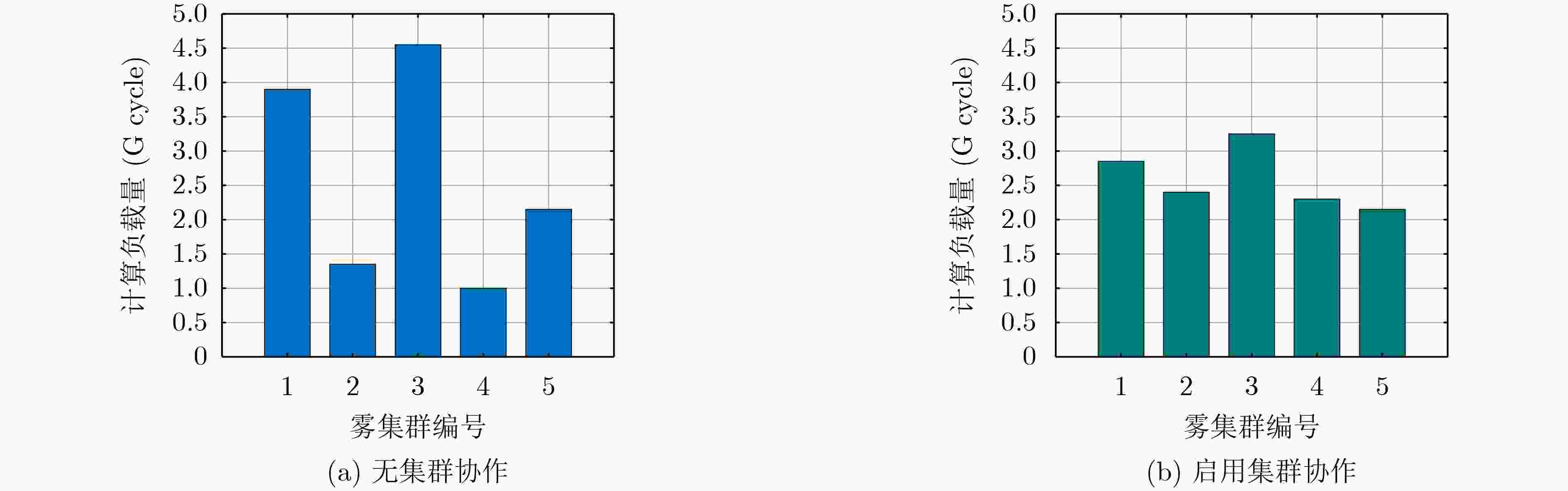


 下载:
下载:
