Multi-feature Marine Small Target Detection Based on Multi-class Classifier
-
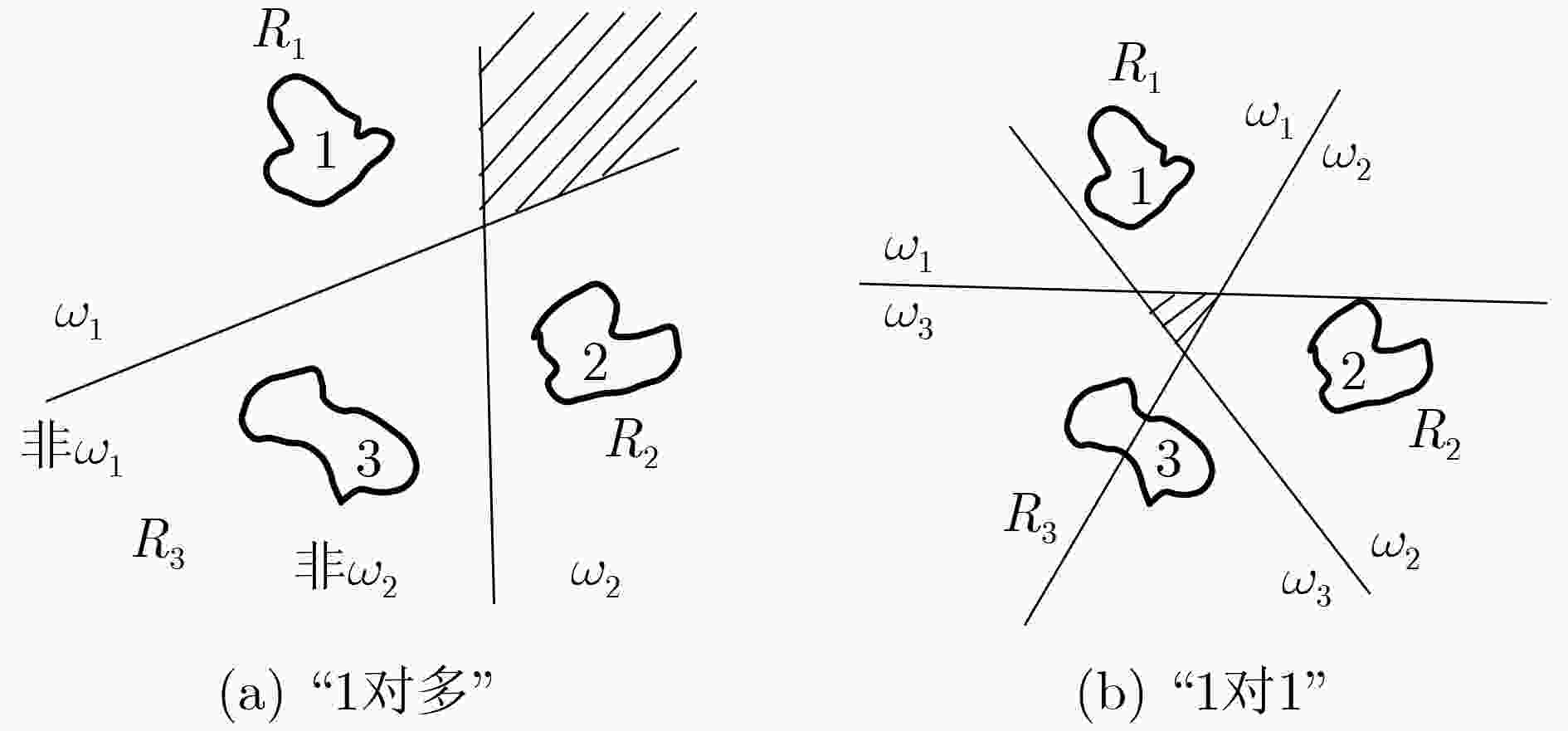
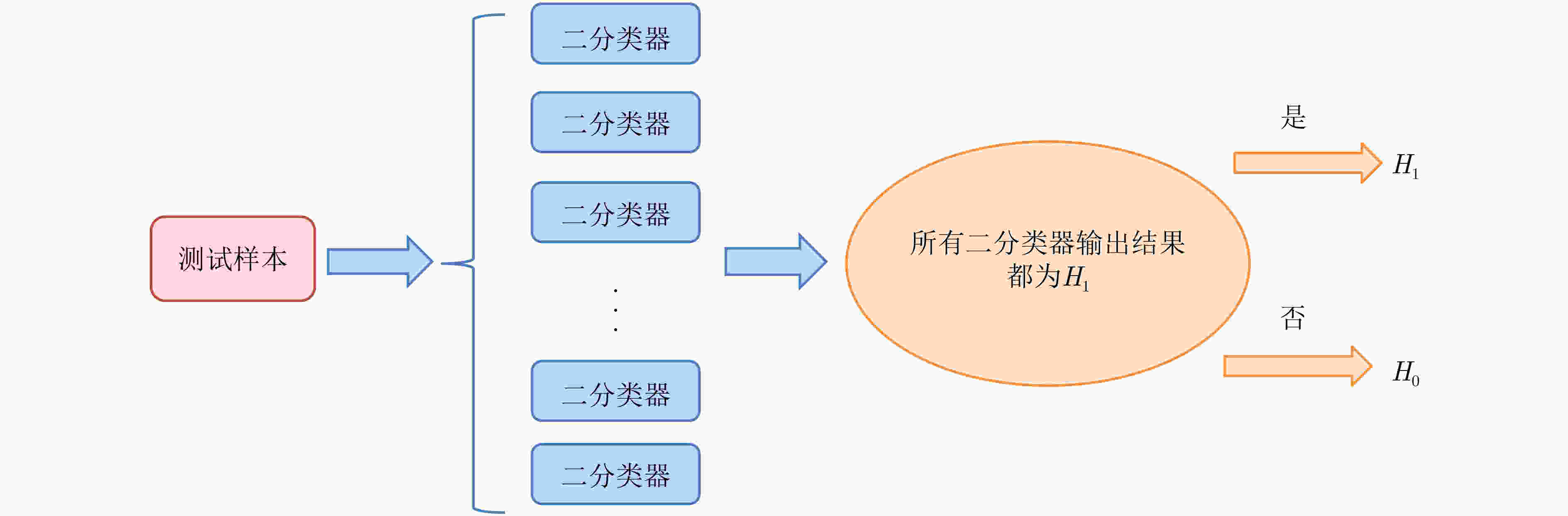
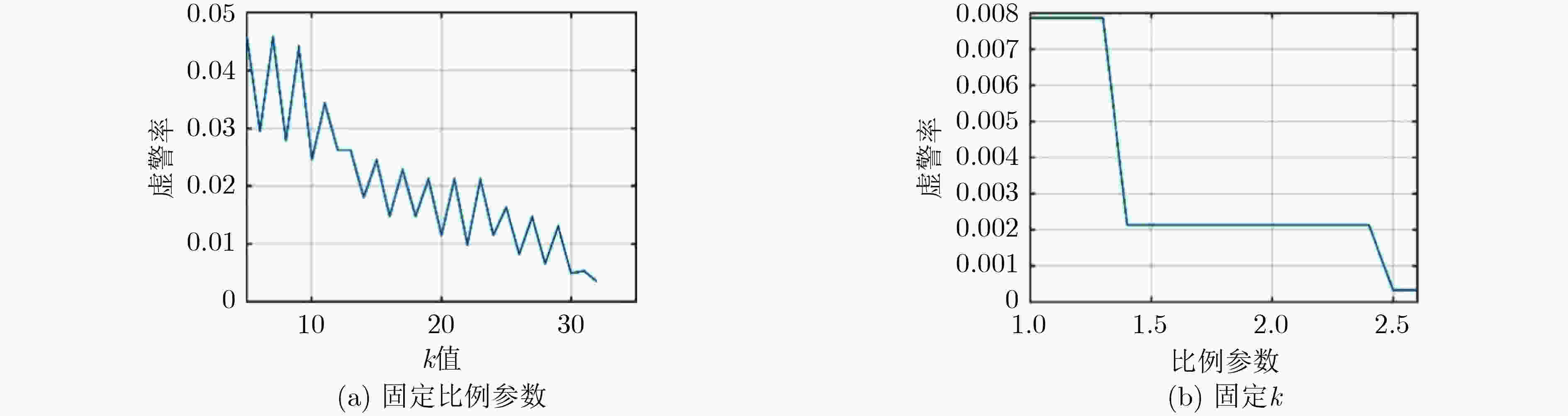
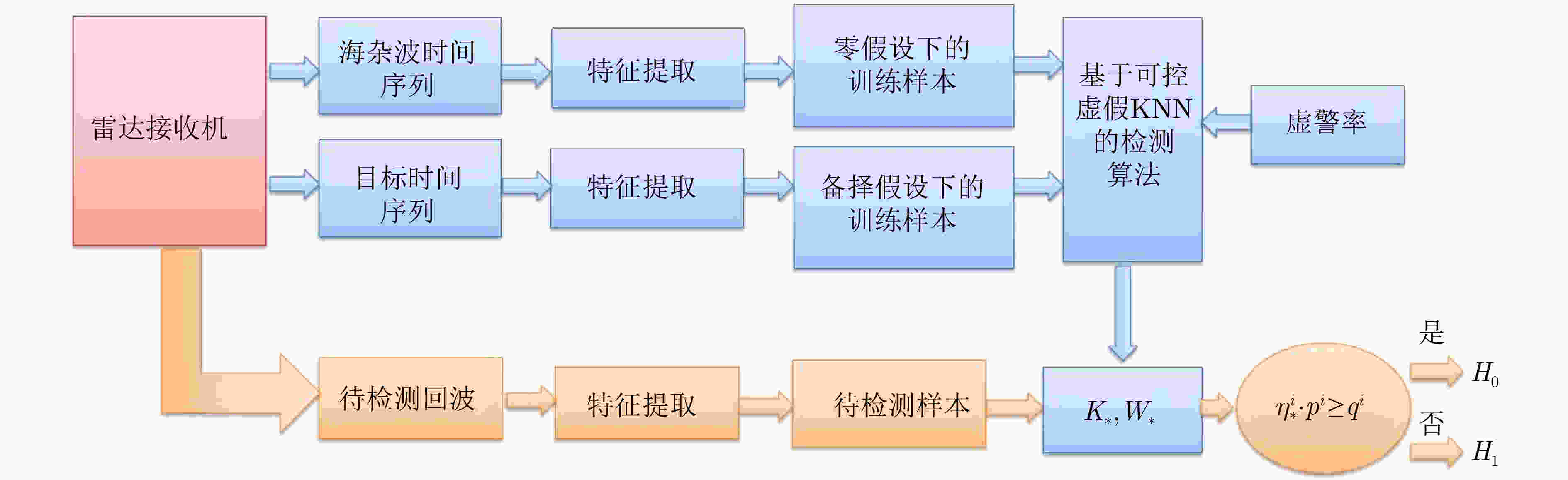
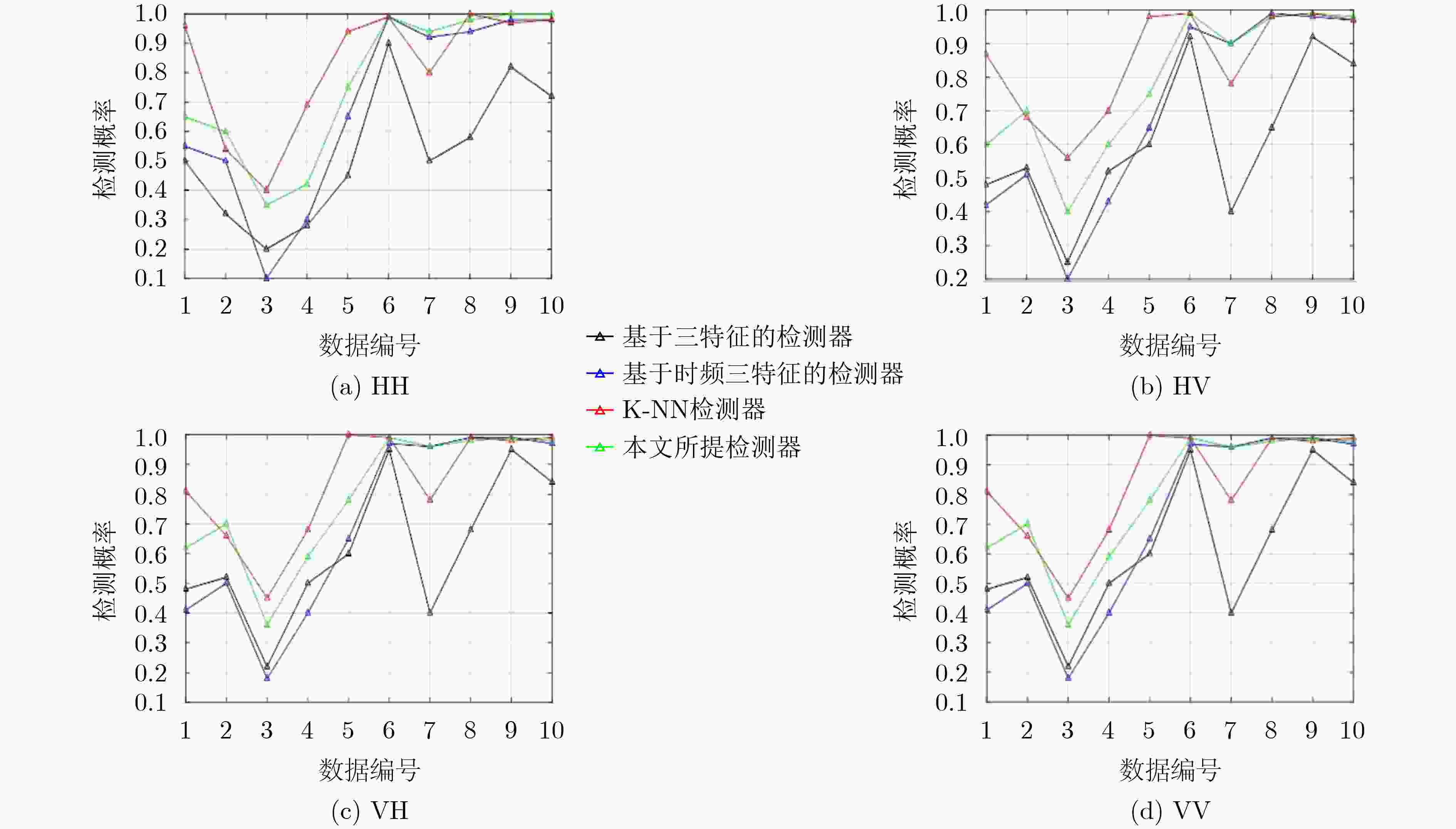
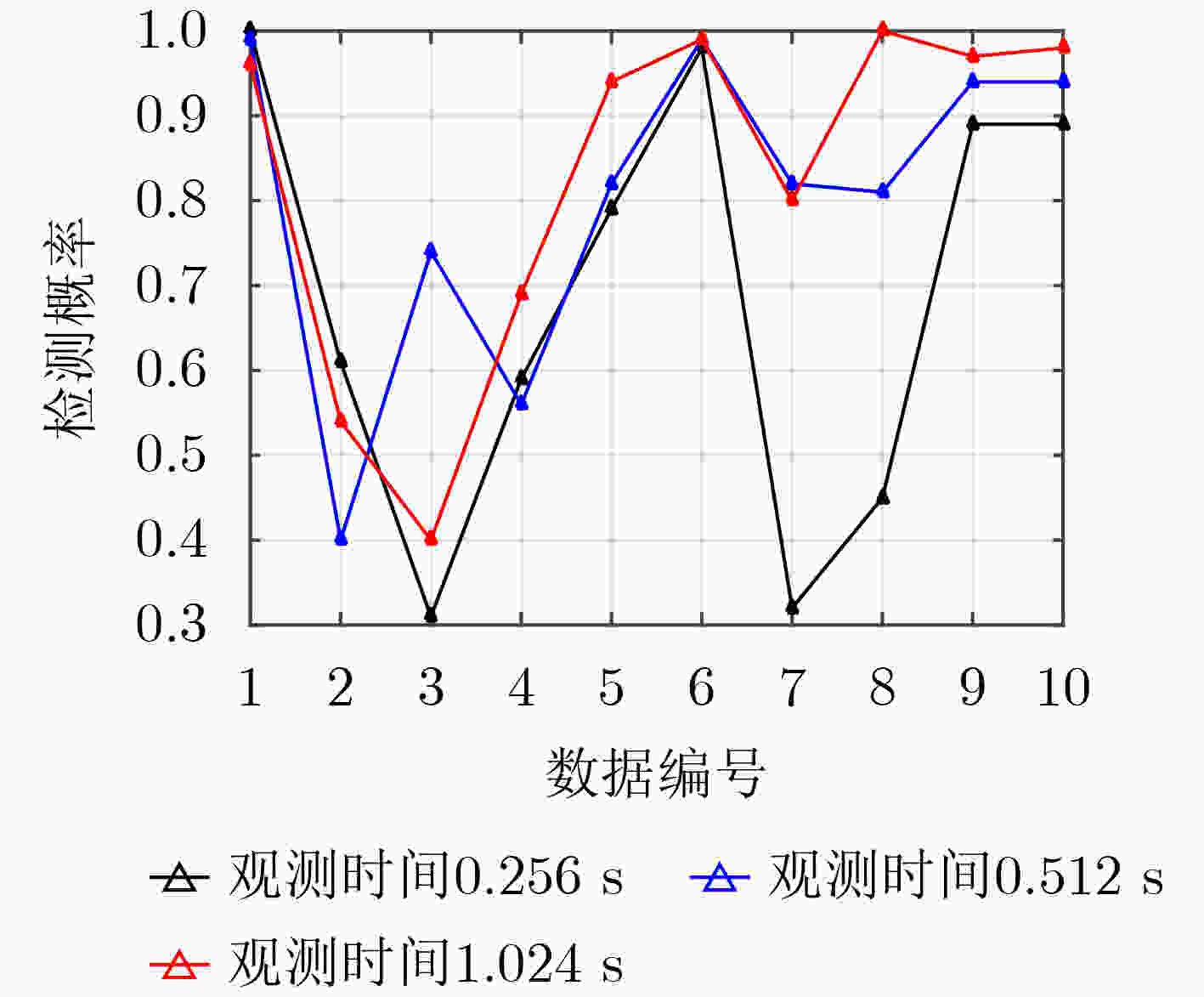
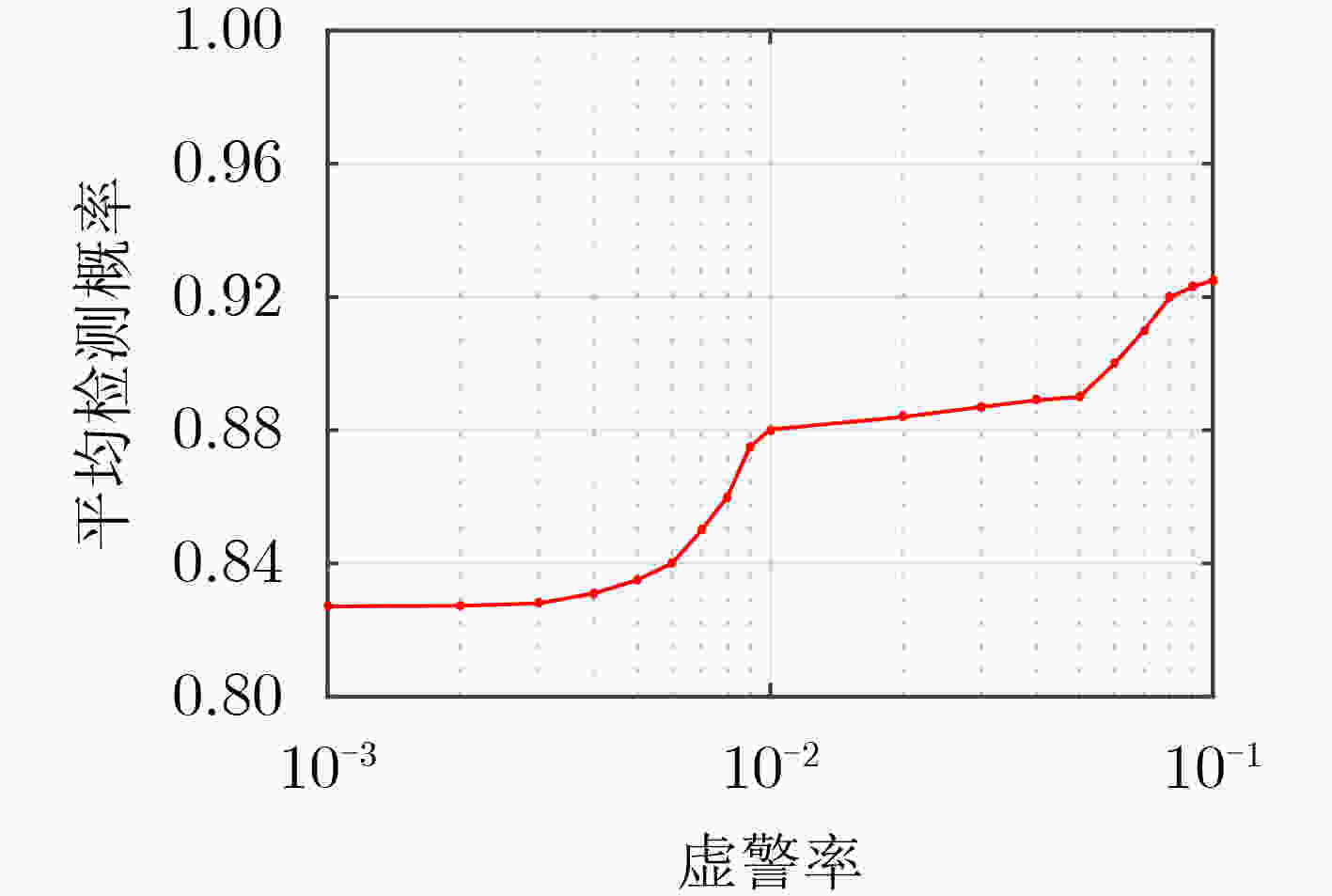
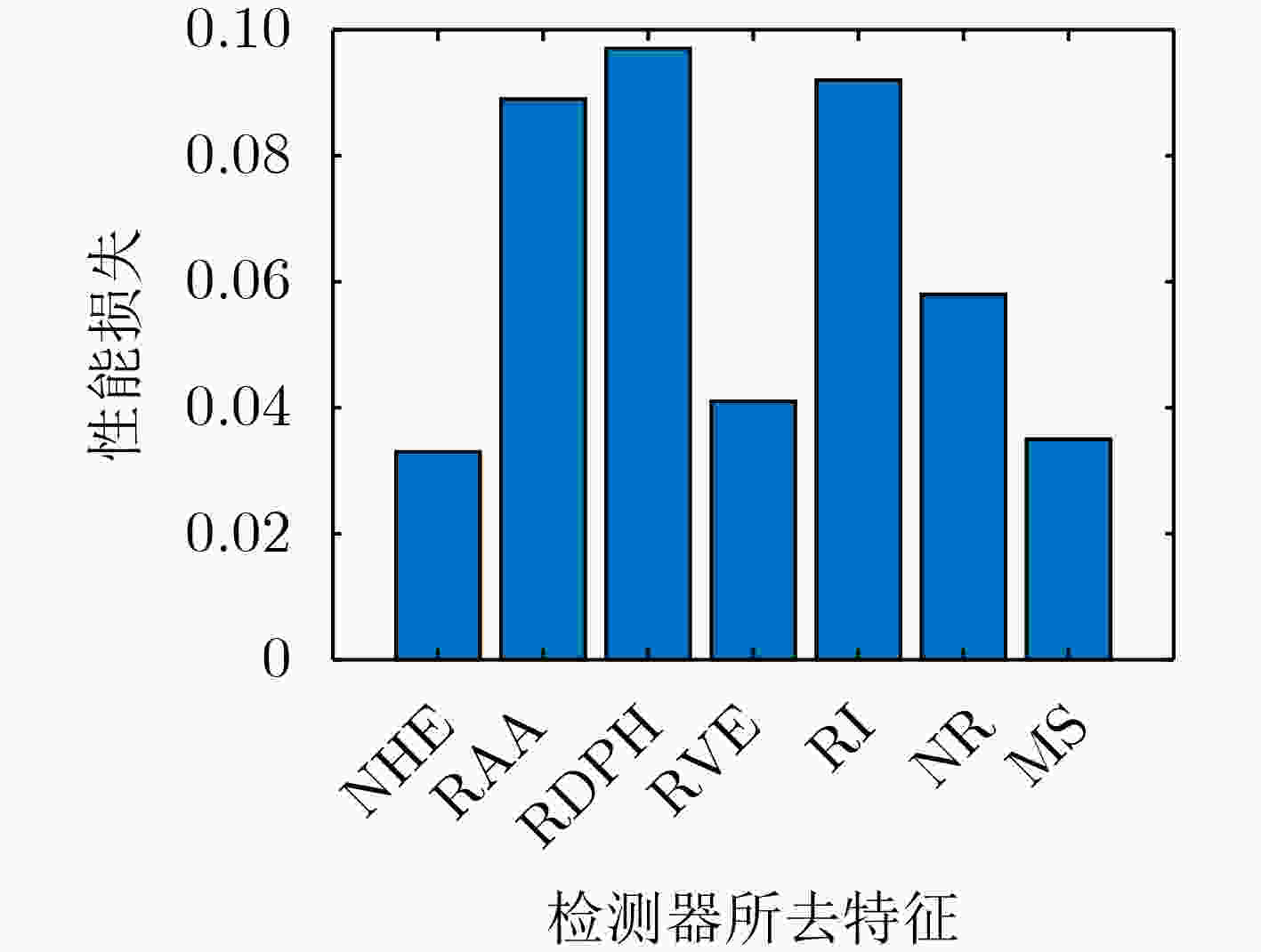
摘要: 模式识别技术已经广泛应用于海上目标检测,其中二分类的模式识别算法在处理该问题时会面临类别非均衡的困境。传统方法一般通过添加人工仿真目标回波扩充目标数据集,检测结果容易受到仿真精度的影响,且增加算法的复杂度。该文提出一种基于多分类思想的多特征海上小目标智能检测方法,先对海杂波数据与目标数据进行多维特征提取,构建高维特征空间;再基于多分类思想中的“1对1”方法,将海杂波特征空间划分成多个子空间,每个杂波子空间与目标数据特征空间等大,构造多个二分类器进行联合判决。该文选取的二分类器为改进的双参数K近邻 (K-NN)算法,可有效调节虚警率。经冰多参数成像X波段雷达(IPIX)数据集验证,所提方法在观测时间为1.024 s时获得了82.40%的检测概率,与基于K-NN的检测器做比较,获得了2%的性能提升。
-
关键词:
- 海杂波 /
- 小目标检测 /
- 多分类 /
- 双参数寻优K近邻(K-NN)算法 /
- 可控虚警
Abstract: The pattern recognition technology have been widely used in target detection within sea clutter, and the binary pattern recognition algorithm will face the dilemma of catgory disequilibrium when dealing with this problem. The traditional method expands the target data set by adding artificial simulated target echoes, however,the detection result is easily affected by the accuracy of simulation data, and the complexity of the algorithm increases.In this paper, a multi-feature intelligent detection method for small targets within sea clutter based on multi-class classifier is proposed. Firstly, multi-dimensional features are extracted from sea clutter and target data to construct a high-dimensional feature space. Then, based on the “one to one” method of multi-class classification, the sea clutter feature space is divided into multiple subspaces, which is as large as the target data feature space to biuld multiple binary classifiers for joint decision. The binary classifier selected in this paper is the improved two-parameter K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN) algorithm, which can effectively adjust the false alarm rate. Verified by Ice MultiParameter Imaging X-band radar (IPIX) radar data set, the detection probability of the proposed method is 82.40% when the observation time is 1.024 s, and the performance of the proposed method is improved by 2% compared with the existing feature detectors of the same type. -
表 1 1993年IPIX数据集说明
序号 数据名称 浪高(m) 风速(km/h) 目标所在单元 受影响单元 (1) #17 2.2 9 9 8,10,11 (2) #26 1.1 9 7 6,8 (3) #30 0.9 19 7 6,8 (4) #31 0.9 19 7 6,8,9 (5) #40 1.0 9 7 5,6,8 (6) #54 0.7 20 8 7,9,10 (7) #280 1.6 10 8 7,10 (8) #310 0.9 33 7 6,8,9 (9) #311 0.9 33 7 6,8,9 (10) #320 0.9 25 7 6,8,9 -
[1] LI Ying, YANG Yonghu, and ZHU Xueyuan. Target detection in sea clutter based on multifractal characteristics after empirical mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1547–1551. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2721463 [2] PETROV N, LE CHEVALIER F, and YAROVOY A G. Detection of range migrating targets in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 37–50. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2731558 [3] SHI Sainan, LIANG Xiang, SHUI Penglang, et al. Low-velocity small target detection with Doppler-guided retrospective filter in high-resolution radar at fast scan mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8937–8953. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923790 [4] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084 [5] FARINA A, GINI F, GRECO M V, et al. High resolution sea clutter data: Statistical analysis of recorded live data[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1997, 144(3): 121–130. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19971107 [6] CONTE E, DE MAIO A, and GALDI C. Statistical analysis of real clutter at different range resolutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(3): 903–918. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1337463 [7] WARD K D, TOUGH R J A, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. London: Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2006. [8] DE MAIO A, FOGLIA G, CONTE E, et al. CFAR behavior of adaptive detectors: An experimental analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(1): 233–251. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1413759 [9] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测目标探测技术[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(11): 30–38. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.11.004CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar low-observable target detection[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(11): 30–38. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.11.004 [10] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测动目标精细化处理及应用[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002 [11] WATTS S. Cell-averaging CFAR gain in spatially correlated K-distributed clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(5): 321–327. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960745 [12] 何友, 关键, 孟祥伟, 等. 雷达目标检测与恒虚警处理[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011.HE You, GUAN Jian, MENG Xiangwei, et al. Radar Target Detection and CFAR Processing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011. [13] ZHOU Wei, XIE Junhao, LI Gaopeng, et al. Robust CFAR detector with weighted amplitude iteration in nonhomogeneous sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1520–1535. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2671798 [14] KELLY E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745 [15] ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446 [16] 刘宁波, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 基于频域多尺度Hurst指数的海杂波中目标检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(3): 424–431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.002LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Target detection within sea clutter based on multi-scale Hurst exponent in frequency domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(3): 424–431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.002 [17] SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 [18] SHI Sainan and SHUI Penglang. Sea-surface floating small target detection by one-class classifier in time-frequency feature space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6395–6411. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838260 [19] 郭子薰, 水鹏朗, 白晓惠, 等. 海杂波中基于可控虚警K近邻的海面小目标检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 654–663. doi: 10.12000/JR20055GUO Zixun, SHUI Penglang, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Sea-surface small target detection based on K-NN with controlled false alarm rate in sea clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 654–663. doi: 10.12000/JR20055 [20] LI Yuzhou, XIE Pengcheng, TANG Zeshen, et al. SVM-based sea-surface small target detection: A false-alarm-rate-controllable approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1225–1229. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2894385 [21] CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744 [22] 董宏成, 文志云, 万玉辉, 等. 基于DPC聚类重采样结合ELM的不平衡数据分类算法[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2021, 43(10): 1856–1863. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2021.10.020DONG Hongcheng, WEN Zhiyun, WAN Yuhui, et al. An imbalanced data classification algorithm based on DPC clustering resampling combined with ELM[J]. Computer Engineering &Science, 2021, 43(10): 1856–1863. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2021.10.020 [23] 刘悦. 不平衡数据集下基于时序和高阶特征的硬盘故障预测[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2021(19): 152–156.LIU Yue. Hard disk failure prediction based on time series and higher-order features under imbalanced datasets[J]. Electronic Technology &Software Engineering, 2021(19): 152–156. [24] 余晨, 杨振泽, 谷建星, 等. 雷达差拍信号的欠采样智能重建[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2021, 40(9): 143–148. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2102832YU Chen, YANG Zhenze, GU Jianxing, et al. Intelligent under-sampling reconstruction of microwave photonic radar signal[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 40(9): 143–148. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2102832 [25] 张天翼, 丁立新. 一种基于SMOTE的不平衡数据集重采样方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(9): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2021.09.043ZHANG Tianyi and DING Lixin. A new resampling method based on SMOTE for imbalanced data set[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(9): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2021.09.043 [26] 万宇, 齐金平, 张儒, 等. 基于过采样支持向量机的煤与瓦斯突出预测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(28): 12080–12087. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.28.022WAN Yu, QI Jinping, ZHANG Ru, et al. Prediction of coal and gas outburst based on over-sampling support vector machine[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(28): 12080–12087. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.28.022 [27] 强冰冰, 尹红, 王瑞. 一种融合集成思想的不平衡数据分类方法[J]. 软件导刊, 2021, 20(9): 206–212. doi: 10.11907/rjdk.202513QIANG Bingbing, YIN Hong, and WANG Rui. An imbalanced data classification method integrating ensemble ideas[J]. Software Guide, 2021, 20(9): 206–212. doi: 10.11907/rjdk.202513 [28] 王德志, 梁俊艳. 不平衡数据集文本多分类深度学习算法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2021, 42(9): 2501–2508. doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2021.09.014WANG Dezhi and LIANG Junyan. Text multi-classification deep learning algorithm based on unbalanced data set[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2021, 42(9): 2501–2508. doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2021.09.014 [29] 左磊, 产秀秀, 禄晓飞, 等. 基于空域联合时频分解的海面微弱目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035ZUO Lei, CHAN Xiuxiu, LU Xiaofei, et al. A weak target detection method in sea clutter based on joint space-time-frequency decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
