A Review of Adaptive Brain-Computer Interface Research
-
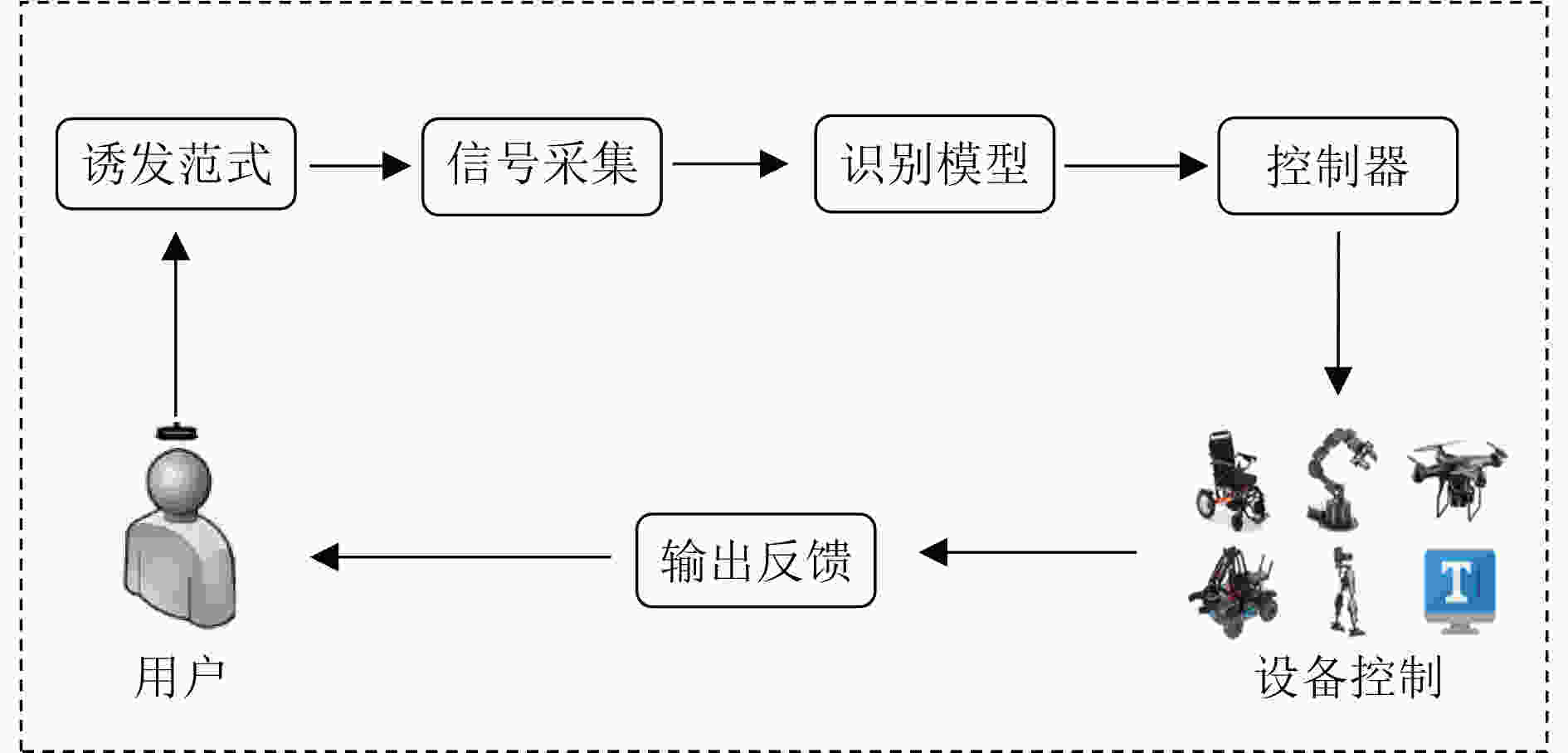
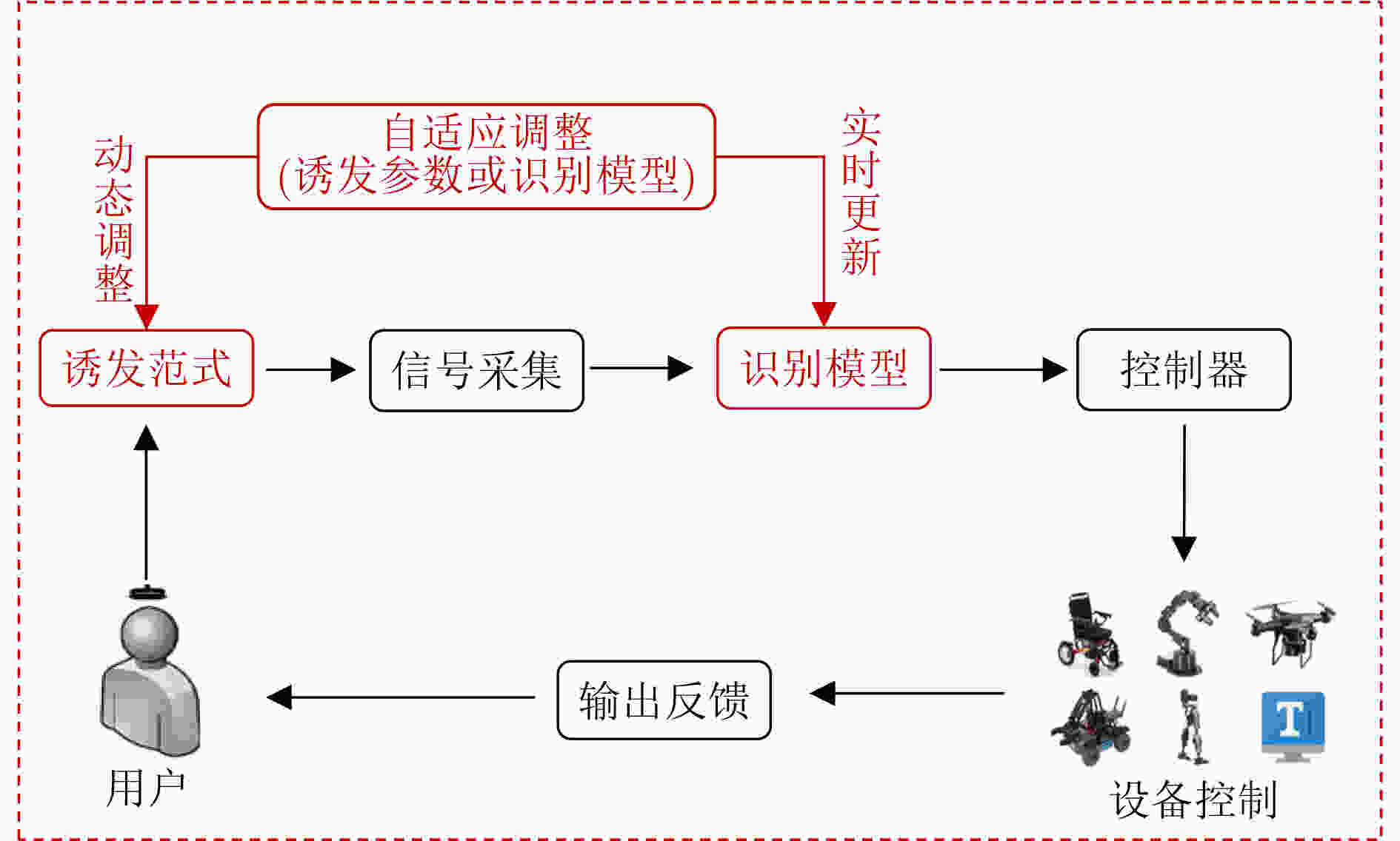
摘要: 脑机接口(BCI)不依赖于外周神经和肌肉,在大脑与外部设备之间建立起直接交流的通路。近年来,该技术在识别准确率和系统交互速率方面已取得巨大突破。然而,脑电(EEG)信号非平稳特性较强且用户主观状态波动较大,传统脑机接口技术对大脑活动的动态变化欠缺适应性,影响了脑机接口系统的控制稳定性,也限制了其智能化发展和应用。自适应脑机接口可根据大脑当前状态动态调整诱发范式和实时更新识别模型,从而增强脑控系统对非平稳大脑活动的适应性,提高其控制精度和鲁棒性,实现更加实用化的脑控系统,对推动脑机接口技术进一步发展极具意义。该文对自适应脑机接口的相关研究进行了回顾和总结,并对该技术未来发展的方向进行了展望。Abstract: Brain-Computer Interface(BCI) establishes a direct communication pathway between the brain and external devices without relying on peripheral nerves and muscles. In recent years, great breakthroughs in recognition accuracy and system interaction rate have been made by this technology. However, the non-stationary characteristics of ElectroEncephaloGram(EEG) signals are strong and the user's subjective state fluctuates greatly. Traditional BCI technology lacks adaptability to the dynamic changes of brain activity, so the control stability of the BCI system is affected and its intelligence development and application are limited. The adaptive BCI can dynamically adjust the evoked paradigm and update the recognition model in real time according to the current state of the brain, thereby enhancing the adaptability of the brain control system to non-stationary brain activities, improving its control accuracy and robustness, and achieving a more practical brain control system, which is highly meaningful to push the further development of BCI technology. The related research of adaptive BCI is reviewed and summarized in this paper, and an outlook of the future development direction of this technology is given.
-
表 1 传统脑机接口与自适应脑机接口对比
脑机接口类型 传统脑机接口 自适应脑机接口 诱发范式 诱发参数固定 诱发时长或刺激序列等参数可根据用户大脑状态动态调整 识别模型 模型参数固定 特征提取模型或模式识别模型可针对EEG高时变特点实时更新 小结 (1) 从诱发范式角度看,自适应脑机接口可最大化诱发特征的有效性,提升人机交互效率;
(2) 从识别模型角度看,自适应脑机接口可提高EEG特征的利用率,提升系统的稳定性和鲁棒性;
(3) 从实际应用角度看,两种类型的脑机接口应用场景相似,但自适应脑机接口由于其高适应性、高鲁棒性的特点,
优势更为突出。 -
[1] ABIRI R, BORHANI S, SELLERS E W, et al. A comprehensive review of EEG-based brain-computer interface paradigms[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2019, 16(1): 011001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aaf12e [2] MENG Jiayuan, XU Minpeng, WANG Kun, et al. Separable EEG features induced by timing prediction for active brain-computer interfaces[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(12): 3588. doi: 10.3390/s20123588 [3] WANG Kun, XU Minpeng, WANG Yijun, et al. Enhance decoding of pre-movement EEG patterns for brain–computer interfaces[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(1): 016033. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab598f [4] XU Lichao, XU Minpeng, JUNG T P, et al. Correction to: Review of brain encoding and decoding mechanisms for EEG-based brain–computer interface[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2021, 15(5): 921. doi: 10.1007/s11571-021-09686-x [5] XU Minpeng, XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yijun, et al. A brain—computer interface based on miniature-event-related potentials induced by very small lateral visual stimuli[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(5): 1166–1175. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2799661 [6] BUTTFIELD A, FERREZ P W, and MILLAN J R. Towards a robust BCI: Error potentials and online learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2006, 14(2): 164–168. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2006.875555 [7] SYKACEK P, ROBERTS S J, and STOKES M. Adaptive BCI based on variational Bayesian Kalman filtering: An empirical evaluation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 51(5): 719–727. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.824128 [8] MILLAN J R, RENKENS F, MOURINO J, et al. Noninvasive brain-actuated control of a mobile robot by human EEG[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 51(6): 1026–1033. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.827086 [9] CASTILLO-GARCIA J F, CAICEDO-BRAVO E F, and BASTOS T F. Adaptive spontaneous brain-computer interfaces based on software agents[J]. Advances in Data Science and Adaptive Analysis, 2018, 10(2): 1840004. doi: 10.1142/S2424922X18400041 [10] 姜俊. 自适应脑机接口控制系统研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011.JIANG Jun. Research on adaptive brain-computer interface control system[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011. [11] VIDAURRE C, SCHLOGL A, CABEZA R, et al. A fully on-line adaptive BCI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(6): 1214–1219. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.873542 [12] XU Minpeng, HE Feng, JUNG T P, et al. Current challenges for the practical application of electroencephalography-based brain–computer interfaces[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(12): 1710–1712. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.09.011 [13] JIANG Jing, YIN Erwei, WANG Chunhui, et al. Incorporation of dynamic stopping strategy into the high-speed SSVEP-based BCIs[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2018, 15(4): 046025. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aac605 [14] GU Zhenghui, CHEN Zhubing, ZHANG Jintao, et al. An online interactive paradigm for P300 brain-computer interface speller[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2019, 27(2): 152–161. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2892967 [15] HUANG Yihao, HE Feng, XU Minpeng, et al. Operate P300 speller when performing other task[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(5): 056022. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abb4a6 [16] WANG Fei, XU Zongfeng, ZHANG Weiwei, et al. An adaptive control approach for intelligent wheelchair based on BCI combining with QoO[C]. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 2020. [17] XU Minpeng, HAN Jin, WANG Yijun, et al. Implementing over 100 command codes for a high-speed hybrid brain-computer interface using concurrent P300 and SSVEP features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 67(11): 3073–3082. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2020.2975614 [18] MAINSAL B O, REEVES G, COLLINS L M, et al. Optimizing the stimulus presentation paradigm design for the P300-based brain-computer interface using performance prediction[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2017, 14(4): 046025. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aa7525 [19] COWLEY B R, WILLIAMSON R C, ACAR K, et al. Adaptive stimulus selection for optimizing neural population responses[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 30. [20] MAINSAH B O, KALIKA D, COLLINS L M, et al. Information-based adaptive stimulus selection to optimize communication efficiency in brain-computer interfaces[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montréal, Canada, 2018: 31. [21] CHEN X J, COLLINS L M, and MAINSAH B O. Mitigating the impact of psychophysical effects during adaptive stimulus selection in the P300 speller brain-computer interface[C]. The 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (IEEE EMBC), Mexico, 2021: 5796–5799. [22] PAN Hongguang, MI Wenyu, WEN Fan, et al. An adaptive decoder design based on the receding horizon optimization in BMI system[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2020, 14(3): 281–290. doi: 10.1007/s11571-019-09567-4 [23] SUN Shiliang and ZHOU Jin. A review of adaptive feature extraction and classification methods for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces[C]. 2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Beijing, China, 2014: 1746–1753. [24] COSTA A P, MØLLER J S, IVERSEN H K, et al. An adaptive CSP filter to investigate user independence in a 3-class MI-BCI paradigm[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2018, 103: 24–33. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.09.021 [25] SCHLÖEGL A, LUGGER K, and PFURTSCHELLER G. Using adaptive autoregressive parameters for a brain-computer-interface experiment[C]. The 19th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 'Magnificent Milestones and Emerging Opportunities in Medical Engineering' (Cat. No. 97CH36136), Chicago, USA, 1997. [26] YANG Banghua, YAN Guozheng, YAN Rongguo, et al. Adaptive subject-based feature extraction in brain–computer interfaces using wavelet packet best basis decomposition[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2007, 29(1): 48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2006.01.009 [27] 王江, 徐桂芝, 王磊, 等. 基于多通道自适应自回归模型脑-机接口系统特征的提取[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(48): 9007–9010. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2011.48.019WANG Jiang, XU Guizhi, WANG Lei, et al. Features extraction of brain-computer interface based on adaptive autoregressive models[J]. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research, 2011, 15(48): 9007–9010. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2011.48.019 [28] TALUKDAR U, HAZARIKA S M, and GAN J Q. Adaptive feature extraction in EEG-based motor imagery BCI: Tracking mental fatigue[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(1): 016020. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab53f1 [29] KIM C, SUN Jinwei, LIU Dan, et al. An effective feature extraction method by power spectral density of EEG signal for 2-class motor imagery-based BCI[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2018, 56(9): 1645–1658. doi: 10.1007/s11517-017-1761-4 [30] MOLLA K I, MORIKAWA N, ISLAM R, et al. Data-adaptive spatiotemporal ERP cleaning for single-trial BCI implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2018, 26(7): 1334–1344. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2018.2844109 [31] PARASHIVA P K and VINOD A P. Improving direction decoding accuracy during online motor imagery based brain-computer interface using error-related potentials[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 74: 103515. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103515 [32] AN Ying, SHI Tianwei, REN Ling, et al. UAV control in 2D space based on brain computer interface[C]. The 4th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), Hangzhou, China, 2017: 594–598. [33] CHIANG K J, EMMANOUILIDOU D, GAMPER H, et al. A closed-loop adaptive brain-computer interface framework: Improving the classifier with the use of error-related potentials[C]. The 10th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Italy, 2021: 487–490. [34] JIANG Qin, ZHANG Yi, GE Gengyu, et al. An adaptive CSP and clustering classification for online motor imagery EEG[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 156117–156128. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016700 [35] WONG C M, WANG Ze, NAKANISHI M, et al. Online adaptation boosts SSVEP-based BCI performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 69(6): 2018–2028. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3133594 [36] KOMIJANI H, PARSAEI M R, KHAJEH E, et al. EEG classification using recurrent adaptive neuro-fuzzy network based on time-series prediction[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2019, 31(7): 2551–2562. doi: 10.1007/s00521-017-3213-3 [37] MA Zheng, CHENG Jun, and TAO Dapeng. Online learning using projections onto shrinkage closed balls for adaptive brain-computer interface[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 97: 107017. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107017 [38] CHEN Yonghao, YANG Chen, CHEN Xiaogang, et al. A novel training-free recognition method for SSVEP-based BCIs using dynamic window strategy[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(3): 036007. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab914e [39] CHEN Lingling, CHEN Pengfei, ZHAO Shaokai, et al. Adaptive asynchronous control system of robotic arm based on augmented reality-assisted brain–computer interface[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(6): 066005. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac3044 [40] KE Yufeng, WANG Peiyuan, CHEN Yuqian, et al. Training and testing ERP-BCIs under different mental workload conditions[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2016, 13(1): 016007. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/13/1/016007 [41] ZHAO Yawei, TANG Jiabei, CAO Yong, et al. Effects of distracting task with different mental workload on steady-state visual evoked potential based brain computer interfaces—an offline study[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2018, 12: 79. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00079 [42] ALIAKBARYHOSSEINABADI S and MRACHACZ-KERSTING N. Adaptive brain-computer interface with attention alterations in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[C]. The 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, Canada, 2020: 3188–3191. [43] CECOTTI H. Adaptive time segment analysis for steady-state visual evoked potential based brain-computer interfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(3): 552–560. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.2968307 [44] DA CRUZ J N, WAN Feng, WONG C M, et al. Adaptive time-window length based on online performance measurement in SSVEP-based BCIs[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149: 93–99. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.01.062 [45] LIU Guangquan, ZHANG Dingguo, MENG Jianjun, et al. Unsupervised adaptation of electroencephalogram signal processing based on fuzzy C‐means algorithm[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2012, 26(6): 482–495. doi: 10.1002/acs.1293 [46] BENAROCH C, SADATNEJAD K, ROC A, et al. Long-term BCI training of a Tetraplegic user: Adaptive Riemannian classifiers and user training[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2021, 15: 635653. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.635653 [47] MYRDEN A and CHAU T. Towards psychologically adaptive brain-computer interfaces[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2016, 13(6): 066022. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/13/6/066022 [48] HAN S Y, KWAK N S, OH T, et al. Classification of pilots' mental states using a multimodal deep learning network[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 40(1): 324–336. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2019.12.002 [49] FAN Xiaoli, ZHAO Chaoyi, ZHANG Xin, et al. Assessment of mental workload based on multi-physiological signals[J]. Technology and Health Care, 2020, 28(S1): S67–S80. doi: 10.3233/THC-209008 [50] TAO Da, TAN Haibo, WANG Hailiang, et al. A systematic review of physiological measures of mental workload[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(15): 2716. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16152716 [51] HOGERVORST M A, BROUWER A M, and VAN ERP J B F. Combining and comparing EEG, peripheral physiology and eye-related measures for the assessment of mental workload[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2014, 8(322): 322. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00322 [52] LIU Yichuan, AYAZ H, and SHEWOKIS P A. Multisubject “Learning” for mental workload classification using concurrent EEG, fNIRS, and physiological measures[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2017, 11: 389. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00389 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
