Salient Object Detection Based on Multiple Graph Neural Networks Collaborative Learning
-
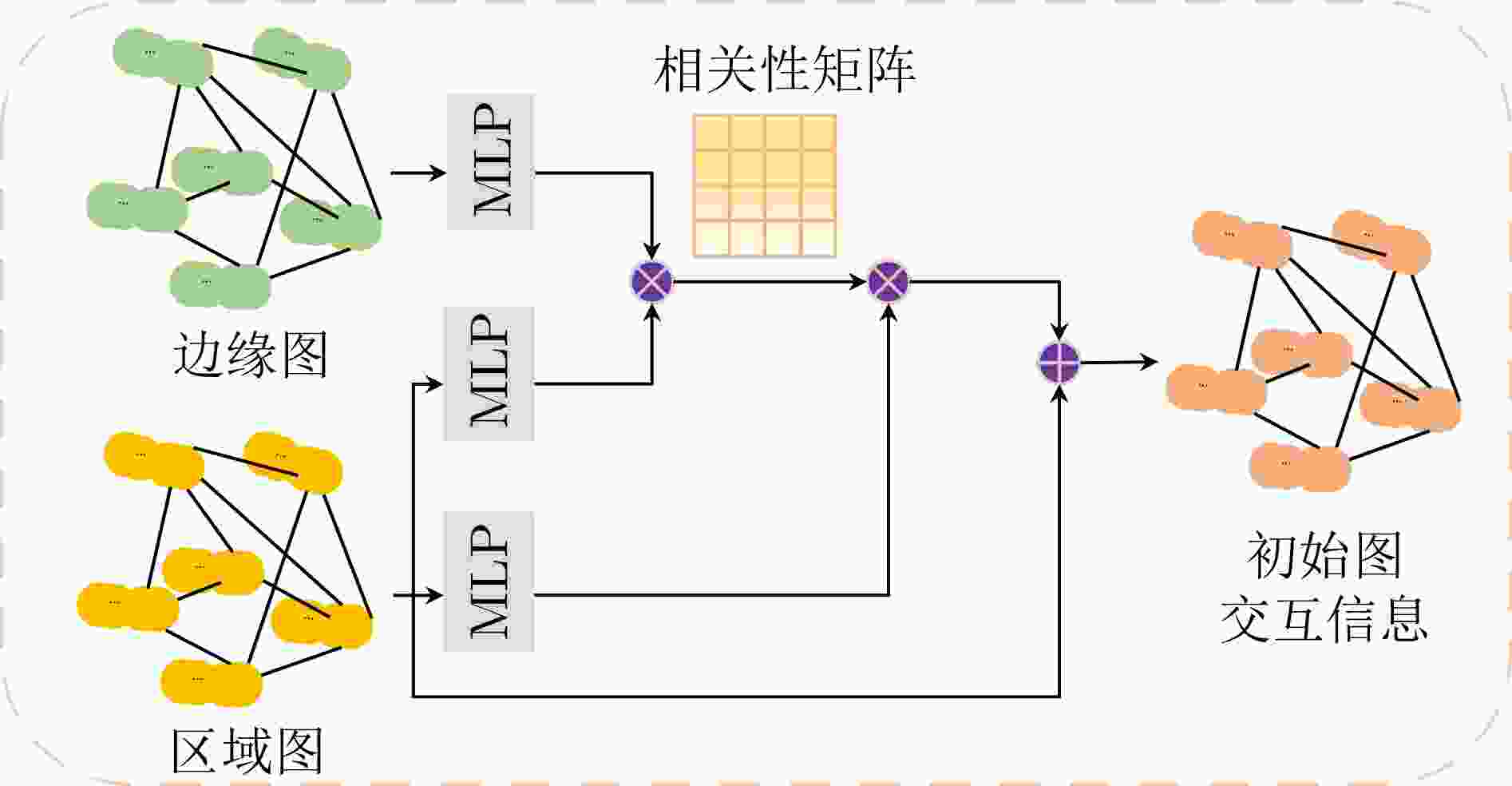
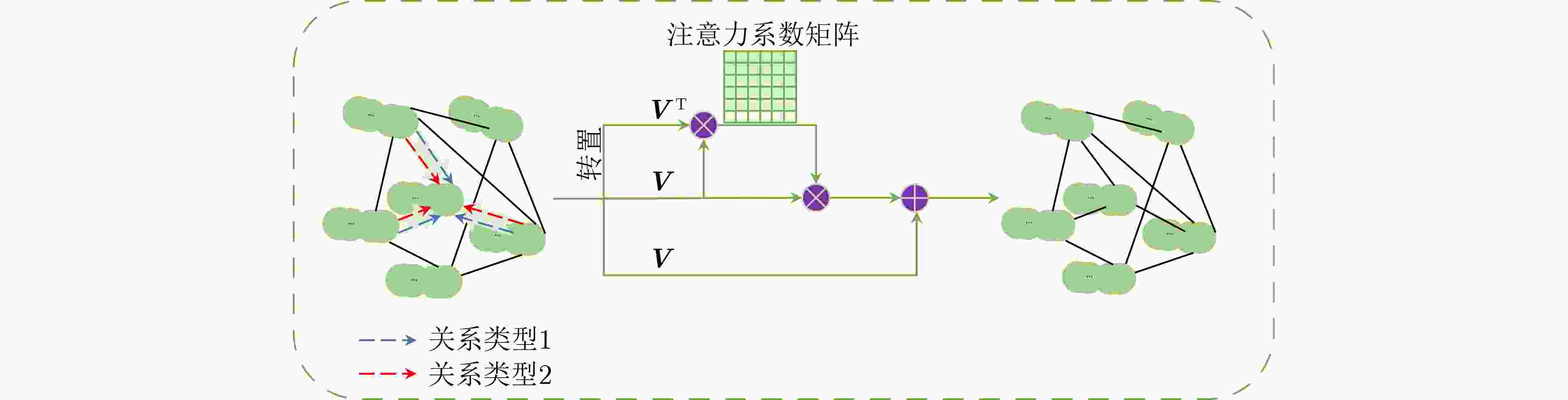
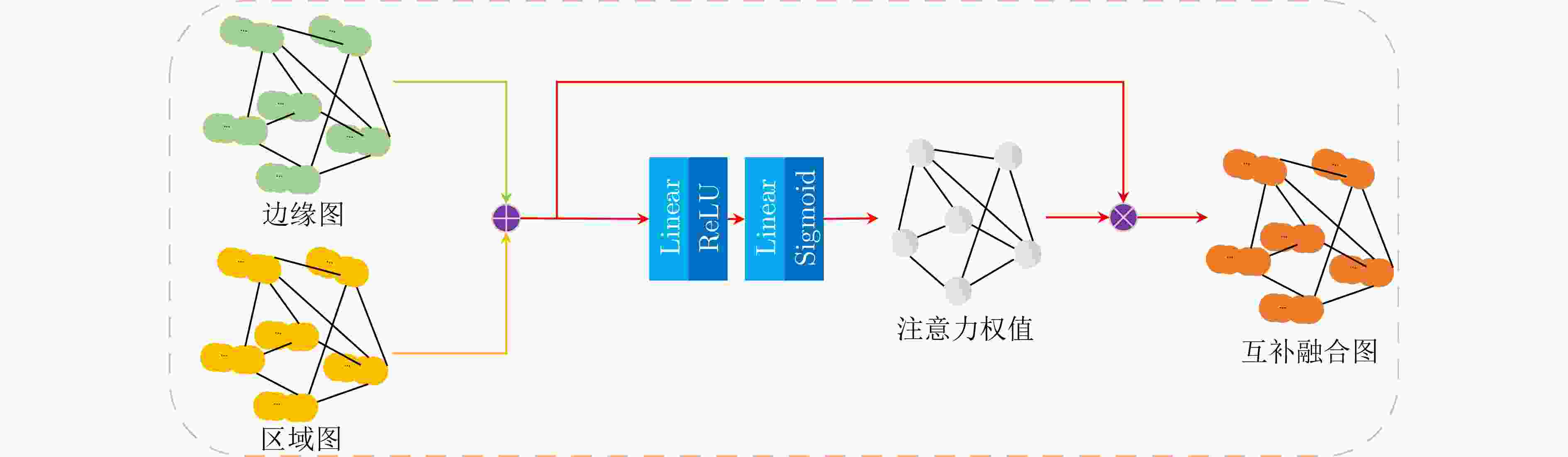
摘要: 目前基于深度卷积神经网络的显著性物体检测方法难以在非欧氏空间不规则结构数据中应用,在复杂视觉场景中易造成显著物体边缘及结构等高频信息损失,影响检测性能。为此,该文面向显著性物体检测任务提出一种端到端的多图神经网络协同学习框架,实现显著性边缘特征与显著性区域特征协同学习的过程。在该学习框架中,该文构造了一种动态信息增强图卷积算子,通过增强不同图节点之间和同一图节点内不同通道之间的信息传递,捕获非欧氏空间全局上下文结构信息,完成显著性边缘信息与显著性区域信息的充分挖掘;进一步地,通过引入注意力感知融合模块,实现显著性边缘信息与显著性区域信息的互补融合,为两种信息挖掘过程提供互补线索。最后,通过显式编码显著性边缘信息,指导显著性区域的特征学习,从而更加精准地定位复杂场景下的显著性区域。在4个公开的基准测试数据集上的实验表明,所提方法优于目前主流的基于深度卷积神经网络的显著性物体检测方法,具有较强的鲁棒性和泛化能力。Abstract: In complex visual scene, the performance of existing deep convolutional neural network based methods of salient object detection still suffer from the loss of high-frequency visual information and global structure information of the object, which can be attributed to the weakness of convolutional neural network in capability of learning from the data in non-Euclidean space. To solve these problems, an end-to-end multiple graph neural networks collaborative learning framework is proposed, which realizes the cooperative learning process of salient edge features and salient region features. In this learning framework, this paper constructs a dynamic message enhancement graph convolution operator, which captures non-Euclidean space global context structure information by enhancing message transfer between different graph nodes and between different channels within the same graph node. Further, by introducing an attention perception fusion module, the complementary fusion of salient edge information and salient region information is realized, providing complementary clues for the two information mining processes. Finally, by explicitly encoding the salient edge information to guide the feature learning of salient regions, salient regions in complex scenes can be located more accurately. The experiments on four open benchmark datasets show that the proposed method has strong robustness and generalization ability, which make it superior to the current mainstream deep convolutional neural network based salient object detection methods.
-
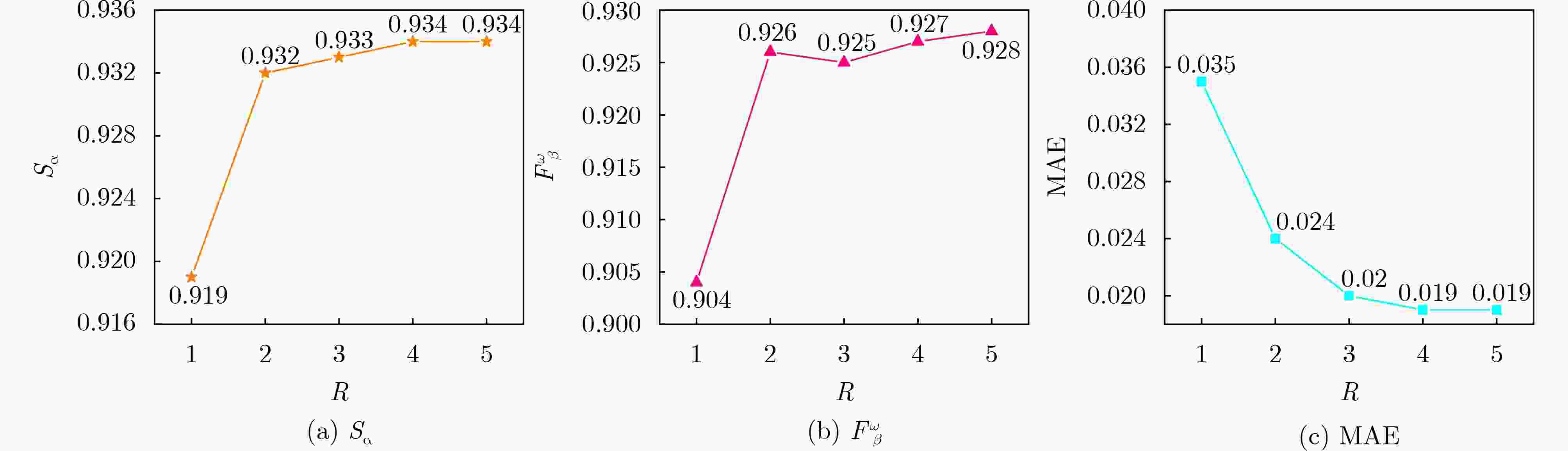
表 1 参数$ N $和$ k $在不同设置下的性能结果
ECSSD PASCAL-S $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ ${\rm{MAE}}( \downarrow )$ $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ ${\rm{MAE}}( \downarrow )$ 本文 ($ N = 48,k = 8 $) 0.933 0.924 0.024 0.881 0.841 0.047 本文 ($ N = 32,k = 8 $) 0.932 0.926 0.024 0.886 0.850 0.047 本文 ($ N = 16,k = 8 $) 0.929 0.923 0.028 0.879 0.830 0.057 本文 ($ N = 32,k = 16 $) 0.932 0.928 0.024 0.879 0.851 0.047 本文 ($ N = 32,k = 8 $) 0.932 0.926 0.024 0.886 0.850 0.047 本文 ($ N = 32,k = 4 $) 0.931 0.922 0.026 0.875 0.833 0.052 表 2 9种方法在4个标准数据集上的$ {S_\alpha } $, $ F_\beta ^\omega $和MAE指标
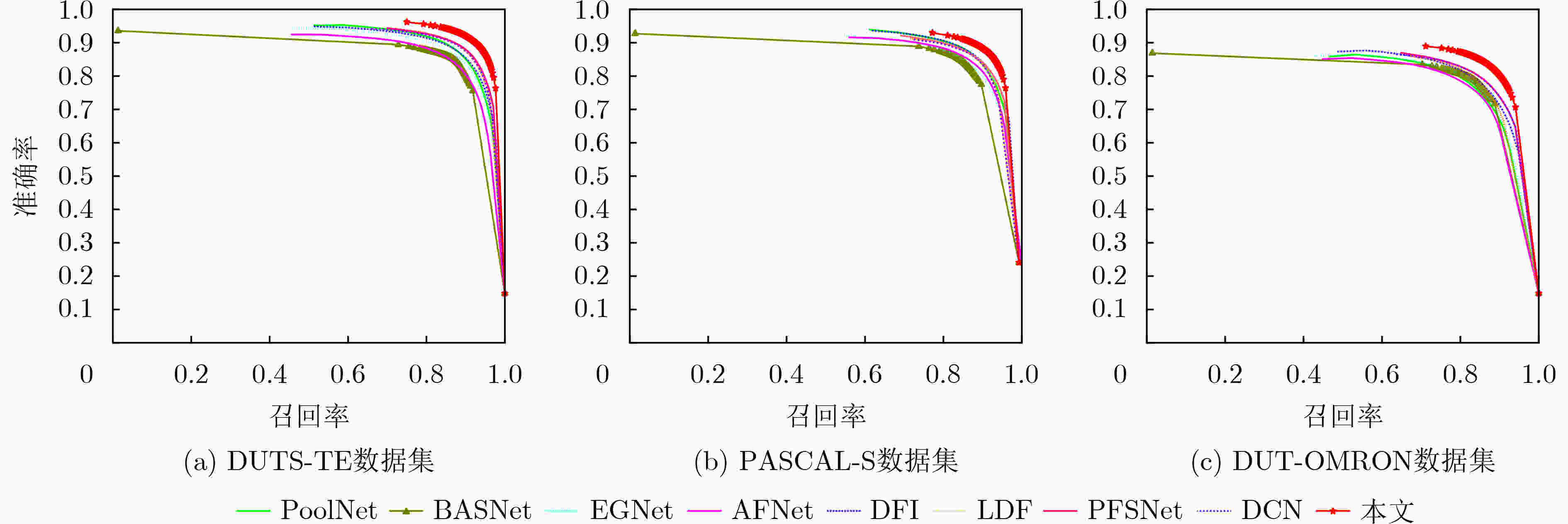
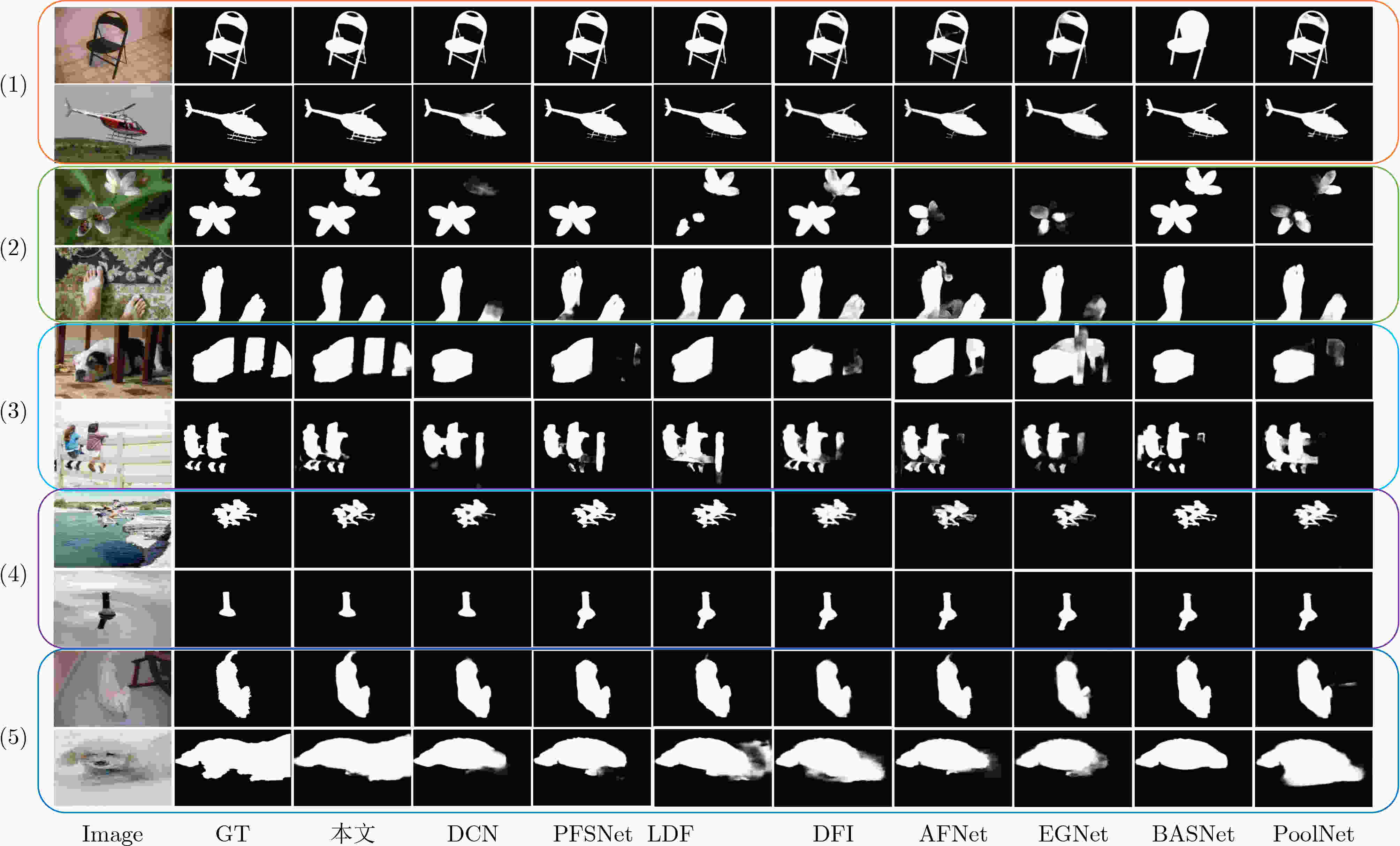
方法 DUTS-TE ECSSD PASCAL-S DUT-OMRON $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ $ {\rm{MAE}}( \downarrow ) $ $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ $ {\rm{MAE}}( \downarrow ) $ $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ $ {\rm{MAE}}( \downarrow ) $ $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ $ {\rm{MAE}}( \downarrow ) $ PoolNet 0.883 0.807 0.040 0.921 0.896 0.039 0.851 0.799 0.075 0.836 0.729 0.055 BASNet 0.866 0.803 0.048 0.916 0.904 0.037 0.836 0.795 0.077 0.836 0.751 0.057 EGNet 0.879 0.798 0.044 0.919 0.892 0.041 0.847 0.791 0.078 0.836 0.727 0.056 AFNet 0.867 0.785 0.046 0.914 0.887 0.042 0.850 0.797 0.071 0.826 0.717 0.057 DFI 0.886 0.817 0.039 0.927 0.906 0.035 0.866 0.819 0.065 0.839 0.736 0.055 LDF 0.892 0.845 0.034 0.924 0.915 0.034 0.862 0.825 0.061 0.839 0.751 0.052 PFSNet 0.900 0.898 0.036 0.927 0.912 0.031 0.844 0.791 0.063 0.802 0.743 0.055 DCN 0.892 0.840 0.035 0.928 0.920 0.032 0.862 0.825 0.062 0.845 0.760 0.051 本文 0.920 0.893 0.027 0.932 0.926 0.024 0.886 0.850 0.047 0.867 0.807 0.048 表 3 不同模块的性能影响
模块 ECSSD B DMEGC(R=2) AMF $ {S_\alpha }( \uparrow ) $ $ F_\beta ^\omega ( \uparrow ) $ $ {\rm {MAE}}( \downarrow ) $ √ 0.725 0.708 0.189 √ √ 0.911 0.898 0.040 √ √ √ 0.932 0.926 0.024 -
[1] VAN DE SANDE K E A, UIJLINGS J R R, GEVERS T, et al. Segmentation as selective search for object recognition[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1879–1886. [2] BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, HOU Qibin, et al. Salient object detection: A survey[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(2): 117–150. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1411.5878 [3] 刘桂池. 基于显著性和稀疏表示学习的光学遥感图像目标检测与分类[D]. [博士论文], 郑州大学, 2020.LIU Guichi. Saliency and sparse representation learning based optical remote sensing image object detection and classification[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhengzhou University, 2020. [4] 康凯, 杨磊, 李红艳. 基于视觉显著性的小型无人机目标检测方法[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2020, 18(3): 40–44. doi: 10.19519/j.cnki.1672-3392.2020.03.008KANG Kai, YANG Lei, and LI Hongyan. A novel small UAV detection method based on visual saliency[J]. Optics &Optoelectronic Technology, 2020, 18(3): 40–44. doi: 10.19519/j.cnki.1672-3392.2020.03.008 [5] REN Zhixiang, GAO Shenghua, CHIA L T, et al. Region-based saliency detection and its application in object recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2014, 24(5): 769–779. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2013.2280096 [6] FENG Wei, HAN Ruize, GUO Qing, et al. Dynamic saliency-aware regularization for correlation filter-based object tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3232–3245. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2895411 [7] RAMANISHKA V, DAS A, ZHANG Jianming, et al. Top-down visual saliency guided by captions[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3135–3144. [8] ZHOU Lian, ZHANG Yuejie, JIANG Yugang, et al. Re-caption: Saliency-enhanced image captioning through two-phase learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 694–709. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2928144 [9] HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, HU Xiaowei, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(4): 815–828. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2815688 [10] ZHANG Pingping, LIU Wei, LU Huchuan, et al. Salient object detection with lossless feature reflection and weighted structural loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(6): 3048–3060. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2893535 [11] 张文明, 姚振飞, 高雅昆, 等. 一种平衡准确性以及高效性的显著性目标检测深度卷积网络模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1201–1208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190229ZHANG Wenming, YAO Zhenfei, GAO Yakun, et al. A deep convolutional network for saliency object detection with balanced accuracy and high efficiency[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1201–1208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190229 [12] MA Mingcan, XIA Changqun, and LI Jia. Pyramidal feature shrinking for salient object detection[C]. The Thirty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2021: 2311–2318. [13] LIU Jiangjiang, HOU Qibin, and CHENG Mingming. Dynamic feature integration for simultaneous detection of salient object, edge, and skeleton[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 8652–8667. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3017352 [14] FENG Mengyang, LU Huchuan, and DING Errui. Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1623–1632. [15] ZHAO Jiaxing, LIU Jiangjiang, FAN Dengping, et al. EGNet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8778–8787. [16] LIU Jiangjiang, HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, et al. A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3912–3921. [17] QIN Xuebin, FAN Dengping, HUANG Chenyang, et al. Boundary-aware segmentation network for mobile and web applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.04704, 2021. [18] WEI Jun, WANG Shuhui, WU Zhe, et al. Label decoupling framework for salient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13022–13031. [19] WU Zhe, SU Li, and HUANG Qingming. Decomposition and completion network for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 6226–6239. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3093380 [20] KIPF T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]. The 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [21] WANG Lijun, LU Huchuan, WANG Yifan, et al. Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3796–3805. [22] SHI Jianping, YAN Qiong, LI Xu, et al. Hierarchical image saliency detection on extended CSSD[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(4): 717–729. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2465960 [23] LI Yin, HOU Xiaodi, KOCH C, et al. The secrets of salient object segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 280–287. [24] LI Cuiping, CHEN Zhenxue, LIU Chengyun, et al. Saliency detection: Multi-level combination approach via graph-based manifold ranking[C]. 2017 13th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Guilin, China, 2017: 604–609. [25] ZHAO Xiaoqi, PANG Youwei, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Self-supervised pretraining for RGB-D salient object detection[C]. The Thirty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2022: 3463–3471. [26] LI Yin and GUPTA A. Beyond grids: Learning graph representations for visual recognition[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 9245–9255. [27] ZHAI Qiang, LI Xin, YANG Fan, et al. Mutual graph learning for camouflaged object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 12992–13002. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
