Artificial Intelligence Algorithms Based on Data-driven and Knowledge-guided Models
-
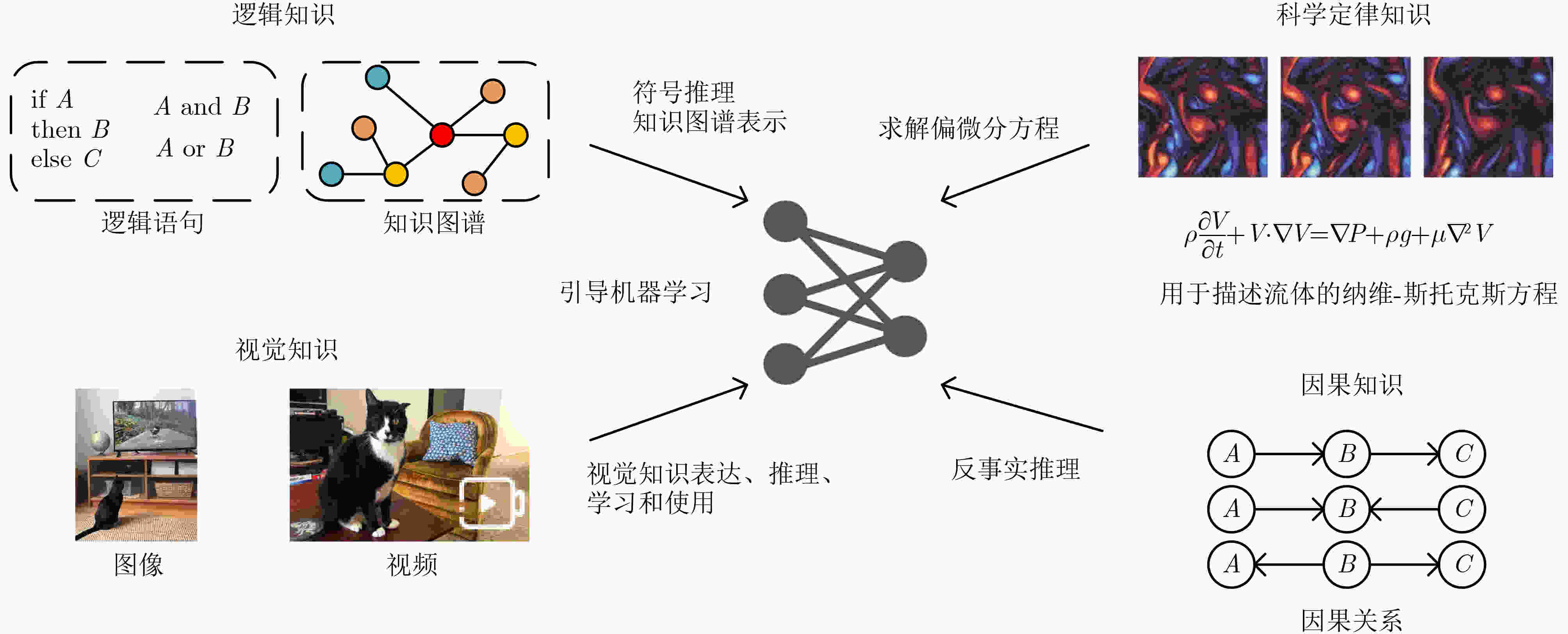
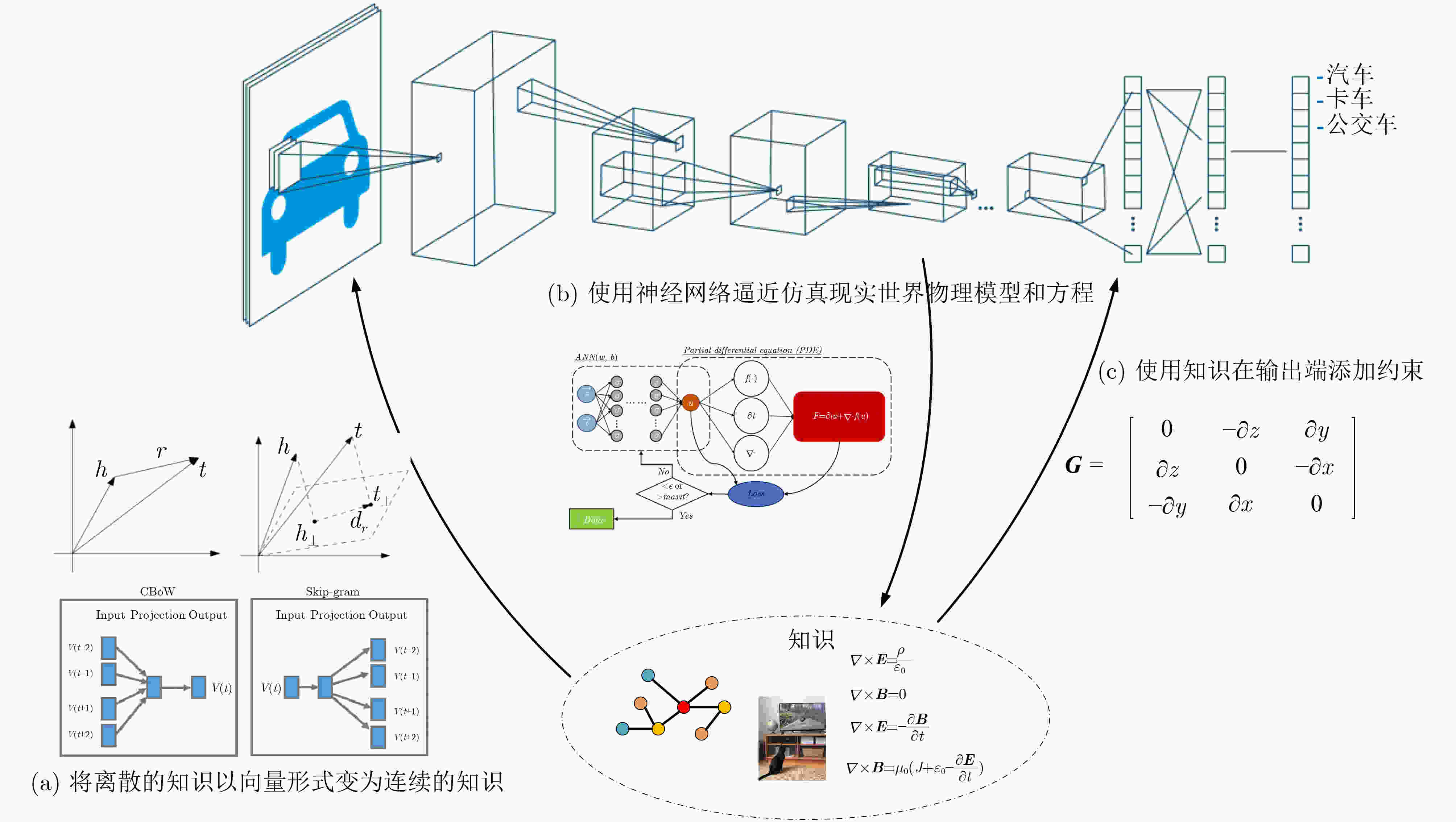
摘要: 当前人工智能的学习模式主要以数据驱动为主要手段,以深度神经网络为主流的机器学习算法取得了显著进展。但是这种数据驱动的人工智能手段依然面临数据获取成本高、可解释性弱、鲁棒性不强等不足。该文认为在现有机器学习算法中引入先验假设、逻辑规则和方程公式等知识,建立数据和知识双轮驱动的人工智能方法,将推动更通用计算范式的变革创新。该文将可用于引导人工智能算法模型知识归纳为4种——逻辑知识、视觉知识、物理定律知识和因果知识,探讨将这些知识与现有数据驱动模型相互结合的典型方法。Abstract: Nowadays, artificial intelligence is in the era of big data-driven manner. Machine learning algorithms with deep neural networks as the mainstream have achieved great development and achievements. However, data-driven artificial intelligence still faces problems such as the cost of annotating data, the lack of interpretability, and the weak robustness. The Introduction of knowledge such as prior hypothesis, logic rules and physical equations into existing machine learning algorithms will build artificial intelligence approaches powered by both data and knowledge which could promote innovations of computing paradigm. Four types of knowledge (logical knowledge, visual knowledge, laws of physics knowledge and causal knowledge) that can be used to guide artificial intelligence algorithm models are summarized in thus paper, and typical approaches to guide the combination of these knowledge with data-driven models are discussed.
-
Key words:
- Artificial intelligence /
- Big data /
- Data-drive /
- Knowledge-guided
-
表 1 知识引导的典型方法
知识 方法 具体思路 例子 逻辑知识 知识图谱表示 将知识图谱中的实体和关系表示为向量。 Bordes等人[35]、Lin等人[117]、Dettmers等人[118] 约束条件 使用知识作为优化的约束条件。 Hu等人[39]、Chen等人[40] 视觉知识 视觉知识抽取及应用 建立基于视觉知识的闭环学习机制。 Wu等人[65] 构建目标概念的视觉知识字典。 Pu等人[62] 科学定律知识 偏微分方程求解 流体力学中将不可压纳维-斯托克斯方程组与神经网络损失函数结合。 Raissi等人[76]、Jin等人[119] 生物医学中基于PINN求解心脏激活映射、心血管动脉压力相关函数。 Sahli Costabal等人[78]、Kissas等人[120] 材料领域中基于PINN解决频域麦克斯韦方程组和超材料设计问题、连续体固体力学的几何识别问题。 Fang等人[79]、Zhang等人[80] 电力学中基于PINN求解电力系统动力学中的摆动方程。 Misyris等人[121] 使用神经算子和深度算子网络求解。 Li等人[81]、Lu等人[82] 组合优化问题求解 基于自旋哈密顿函数、2元无约束优化等形式训练图神经网络的可微损失函数。 Schuetz等人[122] 先验知识与约束条件 蛋白质结构预测中结合蛋白质先验结构、氨基酸链的物理特性约束等知识。 Jumper等人[85]、Baek等人[87]、Humphreys等人[88] 逆合成分析中使用化学反应过程中变化的原子和键构建转化规则集,用于后续蒙特卡罗树搜索。 Segler等人[123] 晶体结构预测中建立晶体结构和生成焓之间的关联模型。 Cheng等人[124] 地表温度反演中使用辐射传递方程作为反演机制的数学推导。 Wang等人[125] 胸部X射线检查中使用基于X射线报告中的知识进行驱动的推理算法提高深度学习模型性能。 Jadhav等人[126] 因果知识 引入因果关系 尝试将因果关系引入机器学习模型中。 Kuang等人[45]、Kuang等
人[46] -
[1] PAN Yunhe. Heading toward artificial intelligence 2.0[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(4): 409–413. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2016.04.018 [2] 李国杰. 国内AI研究“顶不了天、落不了地”, 该想想了[EB/OL]. https://ysg.ckcest.cn/ysgNews/1738635.html, 2021.Li Guojie. Domestic AI research cannot be broken throuth and implemented. It is time to think about it. [EB/OL]. https://ysg.ckcest.cn/ysgNews/1738635.html, 2021. [3] PEARL J. Radical empiricism and machine learning research[J]. Journal of Causal Inference, 2021, 9(1): 78–82. doi: 10.1515/jci-2021-0006 [4] ZHANG Ningyu, JIA Qianghuai, DENG Shumin, et al. AliCG: Fine-grained and evolvable conceptual graph construction for semantic search at alibaba[C]. The 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Singapore, 2021: 3895–3905. [5] LUO Xusheng, BO Le, WU Jinhang, et al. AliCoCo2: Commonsense knowledge extraction, representation and application in E-commerce[C]. The 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Singapore, 2021: 3385–3393. [6] 凡友荣, 杨涛, 孔华锋, 等. 基于知识图谱的电信欺诈通联特征挖掘方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2019, 36(11): 182–187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.11.030FAN Yourong, YANG Tao, KONG Huafeng, et al. Calling features mining method of telecom fraud based on knowledge graph[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2019, 36(11): 182–187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.11.030 [7] 许振亮, 刘喜美. 电信诈骗研究的知识图谱分析[J]. 中国刑警学院学报, 2017(3): 50–56. doi: 10.14060/j.issn.2095-7939.2017.03.007XU Zhenliang and LIU Ximei. The knowledge mapping analysis of telecommunication fraud[J]. Journal of China Criminal Police University, 2017(3): 50–56. doi: 10.14060/j.issn.2095-7939.2017.03.007 [8] ANDERSON J R. Cognitive psychology[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1984, 23(1): 1–11. doi: 10.1016/0004-3702(84)90002-X [9] 潘云鹤. 形象思维中的形象信息模型的研究[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 1991, 4(4): 7–14.PAN Yunhe. Research on image information model in image thinking[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 1991, 4(4): 7–14. [10] 潘云鹤. 综合推理的研究[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 1996, 9(3): 201–208.PAN Yunhe. The synthesis reasoning[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 1996, 9(3): 201–208. [11] PAN Yunhe. On visual knowledge[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2019, 20(8): 1021–1025. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1910001 [12] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [13] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [14] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [15] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91–99. [16] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [17] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. [18] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [19] ZHU Chenchen, CHEN Fangyi, AHMED U, et al. Semantic relation reasoning for shot-stable few-shot object detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 8778–8787. [20] HU Hanzhe, BAI Shuai, LI Aoxue, et al. Dense relation distillation with context-aware aggregation for few-shot object detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10180–10189. [21] PAN Yunhe. Miniaturized five fundamental issues about visual knowledge[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2021, 22(5): 615–618. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2040000 [22] 曾庆存. 天气预报——由经验到物理数学理论和超级计算[J]. 物理, 2013, 42(5): 300–314. doi: 10.7693/wl20130501ZENG Qingcun. Weather forecast——from empirical to physicomathematical theory and super-computing system engineering[J]. Physics, 2013, 42(5): 300–314. doi: 10.7693/wl20130501 [23] 邓海游, 贾亚, 张阳. 蛋白质结构预测[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(17): 178701. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.178701DENG Haiyou, JIA Ya, and ZHANG Yang. Protein structure prediction[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(17): 178701. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.178701 [24] 杜其通, 刘朝雨, 闵剑, 等. 基于人工神经网络的动力学参数辨识法[J]. 高技术通讯, 2020, 30(5): 495–500. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2020.05.008DU Qitong, LIU Zhaoyu, MIN Jian, et al. Dynamic parameter identification method based on artificial neural network[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2020, 30(5): 495–500. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2020.05.008 [25] 黄铭枫, 刘国星, 王义凡, 等. 耦合台风天气预报模式和实测数据的神经网络风速预测[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2022, 43(3): 98–108. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2020.0563HUANG Mingfeng, LIU Guoxing, WANG Yifan, et al. Neural network forecasts of typhoon wind speeds coupled with WRF and measured data[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2022, 43(3): 98–108. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2020.0563 [26] BRIDGERS S, BUCHSBAUM D, SEIVER E, et al. Children’s causal inferences from conflicting testimony and observations[J]. Developmental Psychology, 2016, 52(1): 9–18. doi: 10.1037/a0039830 [27] MAICAS G, BRADLEY A P, NASCIMENTO J C, et al. Training medical image analysis systems like radiologists[C]. 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 2018: 546–554. [28] LI Liu, XU Mai, WANG Xiaofei, et al. Attention based glaucoma detection: A large-scale database and CNN model[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 10563–10572. [29] XIE Xiaozheng, NIU Jianwei, LIU Xuefeng, et al. A survey on incorporating domain knowledge into deep learning for medical image analysis[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 69: 101985. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.101985 [30] RATNER A, BACH S H, EHRENBERG H, et al. Snorkel: Rapid training data creation with weak supervision[J]. The VLDB Journal, 2020, 29(2/3): 709–730. doi: 10.1007/s00778-019-00552-1 [31] YU Yue, ZUO Simiao, JIANG Haoming, et al. Fine-tuning pre-trained language model with weak supervision: A contrastive-regularized self-training approach[C/OL]. The 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2021: 1063–1077. [32] LIEM C C S, LANGER M, DEMETRIOU A, et al. Psychology meets machine learning: Interdisciplinary perspectives on algorithmic job candidate screening[M]. ESCALANTE H J, ESCALERA S, GUYON I, et al. Explainable and Interpretable Models in Computer Vision and Machine Learning. Cham: Springer, 2018: 197–253. [33] JACKSON P T G, ATAPOUR-ABARGHOUEI A, BONNER S, et al. Style augmentation: Data augmentation via style randomization[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 83–92. [34] HWANG Y, CHO H, YANG Hongsun, et al. Mel-spectrogram augmentation for sequence to sequence voice conversion[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2001.01401, 2020. [35] BORDES A, USUNIER N, GARCIA-DURÁN A, et al. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data[C]. The 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2013: 2787–2795. [36] SUN Zhiqing, DENG Zhihong, NIE Jianyun, et al. RotatE: Knowledge graph embedding by relational rotation in complex space[C]. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2019. [37] KIPF T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [38] VELIČKOVIĆ P, CUCURULL G, CASANOVA A, et al. Graph attention networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.10903, 2017. [39] HU Zhiting, MA Xuezhe, LIU Zhengzhong, et al. Harnessing deep neural networks with logic rules[C]. The 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 2016: 2410–2420. [40] CHEN Xiang, ZHANG Ningyu, XIE Xin, et al. KnowPrompt: Knowledge-aware prompt-tuning with synergistic optimization for relation extraction[C]. The ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 2022: 2778–2788. [41] JIN Zhe, ZHANG Yin, KUANG Haodan, et al. Named entity recognition in traditional Chinese medicine clinical cases combining BiLSTM-CRF with knowledge graph[C]. 12th International Conference on Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management, Athens, Greece, 2019: 537–548. [42] HE Qizhen, WU Liang, YIN Yida, et al. Knowledge-graph augmented word representations for named entity recognition[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 7919–7926. [43] LOGAN R, LIU N F, PETERS M E, et al. Barack’s wife Hillary: Using knowledge graphs for fact-aware language modeling[C]. The 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 5962–5971. [44] ZHANG Zhengyan, HAN Xu, LIU Zhiyuan, et al. ERNIE: Enhanced language representation with informative entities[C]. The 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 1441–1451. [45] LIU Weijie, ZHOU Peng, ZHAO Zhe, et al. K-BERT: Enabling language representation with knowledge graph[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 2901–2908. [46] SUN Yu, WANG Shuohuan, LI Yukun, et al. ERNIE 2.0: A continual pre-training framework for language understanding[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 8968–8975. [47] CHEN Yu, WU Lingfei, and ZAKI M J. Bidirectional attentive memory networks for question answering over knowledge bases[C]. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, USA, 2019: 2913–2923. [48] BAUER L, WANG Yicheng, and BANSAL M. Commonsense for generative multi-hop question answering tasks[C]. The 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 2018: 4220–4230. [49] WANG Xiang, HE Xiangnan, CAO Yixin, et al. KGAT: Knowledge graph attention network for recommendation[C]. The 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, USA, 2019: 950–958. [50] WAN Guojia, PAN Shirui, GONG Chen, et al. Reasoning like human: Hierarchical reinforcement learning for knowledge graph reasoning[C]. The Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2021: 267. [51] WEN Zhang and PENG Yuxin. Multi-level knowledge injecting for visual commonsense reasoning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(3): 1042–1054. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2991866 [52] GAN Leilei, KUANG Kun, YANG Yi, et al. Judgment prediction via injecting legal knowledge into neural networks[C/OL]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 12866–12874. [53] 王玉萍, 曾毅. 人类视觉机制与ROI融合的红外行人检测[J]. 中国测试, 2021, 47(9): 87–93. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2020100100WANG Yuping and ZENG Yi. Pedestrian detection in infrared images using ROI fusion and human visual mechanism[J]. China Measurement &Test, 2021, 47(9): 87–93. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2020100100 [54] 许丽娜, 肖奇, 何鲁晓. 考虑人类视觉特征的融合图像评价方法[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2019, 44(4): 546–554. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20170168XU Lina, XIAO Qi, and HE Luxiao. Fused image quality assessment based on human visual characteristics[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(4): 546–554. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20170168 [55] 申天啸, 韩怡园, 韩冰, 等. 基于人类视觉皮层双通道模型的驾驶员眼动行为识别[J]. 智能系统学报, 2022, 17(1): 41–49. doi: 10.11992/tis.202106051SHEN Tianxiao, HAN Yiyuan, HAN Bing, et al. Recognition of driver's eye movement based on the human visual cortex two-stream model[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2022, 17(1): 41–49. doi: 10.11992/tis.202106051 [56] BAKHTIARI S, MINEAULT P, LILLICRAP T, et al. The functional specialization of visual cortex emerges from training parallel pathways with self-supervised predictive learning[C]. 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 25164–25178. [57] GREFF K, KAUFMAN R L, KABRA R, et al. Multi-object representation learning with iterative variational inference[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2424–2433. [58] ZHAO Yongheng, BIRDAL T, DENG Haowen, et al. 3D point capsule networks[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1009–1018. [59] LIANG Yuanzhi, FENG Qianyu, ZHU Linchao, et al. SEEG: Semantic energized Co-speech gesture generation[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10473–10482. [60] LUO Yawei, LIU Ping, GUAN Tao, et al. Adversarial style mining for one-shot unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1731. [61] WU Aming, HAN Yahong, ZHU Linchao, et al. Instance-invariant domain adaptive object detection via progressive disentanglement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(8): 4178–4193. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3060446 [62] PU Shiliang, ZHAO Wei, CHEN Weijie, et al. Unsupervised object detection with scene-adaptive concept learning[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2021, 22(5): 638–651. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2000567 [63] STEWART R and ERMON S. Label-free supervision of neural networks with physics and domain knowledge[C]. Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 2576–2582. [64] PEARL J and MACKENZIE D. The Book of Why: The New Science of Cause and Effect[M]. New York: Basic Books, 2018. [65] WU Anpeng, YUAN Junkun, KUANG Kun, et al. Learning decomposed representations for treatment effect estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering. 2022, 35(5): 4989–5001. [66] YUAN Junkun, WU Anpeng, KUANG Kun, et al. Auto IV: Counterfactual prediction via automatic instrumental variable decomposition[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2022, 16(4): 74. doi: 10.1145/3494568 [67] KUANG Kun, LI Yunzhe, LI Bo, et al. Continuous treatment effect estimation via generative adversarial de-confounding[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2021, 35(6): 2467–2497. doi: 10.1007/s10618-021-00797-x [68] LOSCH M, FRITZ M, and SCHIELE B. Interpretability beyond classification output: Semantic bottleneck networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1907.10882, 2019. [69] KUANG Kun, ZHANG Hengtao, WU Runze, et al. Balance-subsampled stable prediction across unknown test data[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2022, 16(3): 45. doi: 10.1145/3477052 [70] KUANG Kun, LI Bo, CUI Peng, et al. Stable prediction via leveraging seed variable[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2006.05076, 2020. [71] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, and KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics informed deep learning (Part I): Data-driven solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.10561, 2017. [72] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, and KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics informed deep learning (Part II): Data-driven discovery of nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.10566, 2017. [73] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, and KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686–707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [74] BAYDIN A G, PEARLMUTTER B A, RADUL A A, et al. Automatic differentiation in machine learning: A survey[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(1): 5595–5637. [75] 李野, 陈松灿. 基于物理信息的神经网络: 最新进展与展望[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(4): 254–262. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210500158LI Ye and CHEN Songcan. Physics-informed neural networks: Recent advances and prospects[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(4): 254–262. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210500158 [76] RAISSI M, YAZDANI A, and KARNIADAKIS G E. Hidden fluid mechanics: Learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6481): 1026–1030. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw4741 [77] RAISSI M, WANG Zhicheng, TRIANTAFYLLOU M S, et al. Deep learning of vortex-induced vibrations[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 861: 119–137. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.872 [78] SAHLI COSTABAL F, YANG Yibo, PERDIKARIS P, et al. Physics-informed neural networks for cardiac activation mapping[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2020, 8: 42. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2020.00042 [79] FANG Zhiwei and ZHAN J. Deep physical informed neural networks for metamaterial design[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24506–24513. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963375 [80] ZHANG Enrui, DAO Ming, KARNIADAKIS G E, et al. Analyses of internal structures and defects in materials using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(7): eabk0644. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abk0644 [81] LI Zongyi, KOVACHKI N B, AZIZZADENESHELI K, et al. Fourier neural operator for parametric partial differential equations[C/OL]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [82] LU Lu, JIN Pengzhan, PANG Guofei, et al. Learning nonlinear operators via DeepONet based on the universal approximation theorem of operators[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3(3): 218–229. doi: 10.1038/s42256-021-00302-5 [83] BRANDSTETTER J, WORRALL D E, and WELLING M. Message passing neural PDE solvers[C/OL]. The Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022. [84] SENIOR A W, EVANS R, JUMPER J, et al. Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning[J]. Nature, 2020, 577(7792): 706–710. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1923-7 [85] JUMPER J, EVANS R, PRITZEL A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 583–589. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2 [86] GABLER F, NAM S Z, TILL S, et al. Protein sequence analysis using the MPI bioinformatics toolkit[J]. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 2020, 72(1): e108. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.108 [87] BAEK M, DIMAIO F, ANISHCHENKO I, et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6557): 871–876. doi: 10.1126/science.abj8754 [88] HUMPHREYS I R, PEI Jimin, BAEK M, et al. Computed structures of core eukaryotic protein complexes[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6573): eabm4805. doi: 10.1126/science.abm4805 [89] KENNEDY J. Swarm intelligence[M]. ZOMAYA A Y. Handbook of Nature-Inspired and Innovative Computing: Integrating Classical Models with Emerging Technologies. New York: Springer, 2006: 187–219. [90] CHU Shuchuan, RODDICK J F, SU C J, et al. Constrained ant colony optimization for data clustering[C]. 8th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Auckland, New Zealand, 2004: 534–543. [91] 陈健瑞, 王景璟, 侯向往, 等. 挺进深蓝: 从单体仿生到群体智能[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(12): 2458–2467. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20201448CHEN Jianrui, WANG Jingjing, HOU Xiangwang, et al. Advance into ocean: From bionic monomer to swarm intelligence[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(12): 2458–2467. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20201448 [92] SILVER D, HUANG A, MADDISON C J, et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 484–489. doi: 10.1038/nature16961 [93] SILVER D, SCHRITTWIESER J, SIMONYAN K, et al. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354–359. doi: 10.1038/nature24270 [94] LI Wei, WU Wenjun, WANG Huaimin, et al. Crowd intelligence in AI 2.0 era[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2017, 18(1): 15–43. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1601859 [95] COLORNI A, DORIGO M, and MANIEZZO V. Distributed optimization by ant colonies[C]. The First European Conference on Artificial Life, Paris, France, 1991: 134–142. [96] KENNEDY J and EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization[C]. Proceedings of ICNN'95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 1995: 1942–1948. [97] 吴虎胜, 张凤鸣, 吴庐山. 一种新的群体智能算法——狼群算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(11): 2430–2438.WU Husheng, ZHANG Fengming, and WU Lushan. New swarm intelligence algorithm—wolf pack algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(11): 2430–2438. [98] 邢立宁, 陈英武. 基于知识的智能优化引导方法研究进展[J]. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(11): 1285–1289. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.01285XING Lining and CHEN Yingwu. Research progress on intelligent optimization guidance approaches using knowledge[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(11): 1285–1289. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.01285 [99] CUCKER F and SMALE S. Emergent behavior in flocks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(5): 852–862. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.895842 [100] LEE M, TAROKH M, and CROSS M. Fuzzy logic decision making for multi-robot security systems[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2010, 34(2): 177–194. doi: 10.1007/s10462-010-9168-8 [101] NGUYEN T T, NGUYEN N D, and NAHAVANDI S. Deep reinforcement learning for multiagent systems: A review of challenges, solutions, and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 3826–3839. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977374 [102] 孙长银, 穆朝絮. 多智能体深度强化学习的若干关键科学问题[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1301–1312. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200159SUN Changyin and MU Chaoxu. Important scientific problems of multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1301–1312. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200159 [103] 蒲志强, 易建强, 刘振, 等. 知识和数据协同驱动的群体智能决策方法研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 627–643. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210118PU Zhiqiang, YI Jianqiang, LIU Zhen, et al. Knowledge-based and data-driven integrating methodologies for collective intelligence decision making: A survey[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 627–643. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210118 [104] 刘云浩. 群智感知计算[J]. 中国计算机学会通讯, 2012, 8(10): 38–41.LIU Yunhao. Crowd sensing computing[J]. Communications of the CCF, 2012, 8(10): 38–41. [105] HAN Tao, SUN Hailong, SONG Yangqiu, et al. Incorporating external knowledge into crowd intelligence for more specific knowledge acquisition[C]. The Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2016: 1541–1547. [106] RIVEST R L, ADLEMAN L, and DERTOUZOS M L. On data banks and privacy homomorphisms[J]. Foundations of Secure Computation, 1978, 4(11): 169–180. [107] KONEČNÝ J, MCMAHAN H B, YU F X, et al. Federated learning: Strategies for improving communication efficiency[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.05492, 2016. [108] MCMAHAN H B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282. [109] ZHAO Ning, WU Hao, YU F R, et al. Deep-reinforcement-learning-based latency minimization in edge intelligence over vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(2): 1300–1312. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3078480 [110] SHI Dingyuan, TONG Yongxin, ZHOU Zimu, et al. Learning to assign: Towards fair task assignment in large-scale ride hailing[C]. The 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Singapore, 2021: 3549–3557. [111] KELLER J. DARPA to develop swarming unmanned vehicles for better military reconnaissance[J]. Military & Aerospace Electronics, 2017, 28(2): 4–6. [112] ARNOLD R, JABLONSKI J, ABRUZZO B, et al. Heterogeneous UAV multi-role swarming behaviors for search and rescue[C]. 2020 IEEE Conference on Cognitive and Computational Aspects of Situation Management (CogSIMA), Victoria, Canada, 2020: 122–128. [113] HARDY S, HENECKA W, IVEY-LAW H, et al. Private federated learning on vertically partitioned data via entity resolution and additively homomorphic encryption[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.10677, 2017. [114] ZHENG Wenbo, YAN Lan, GOU Chao, et al. Federated meta-learning for fraudulent credit card detection[C]. The Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 4654–4660. [115] BADDELEY A. Working memory: Looking back and looking forward[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2003, 4(10): 829–839. doi: 10.1038/nrn1201 [116] BADDELEY A D and HITCH G. Working memory[J]. Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 1974, 8: 47–89. doi: 10.1016/S0079-7421(08)60452-1 [117] LIN Yankai, LIU Zhiyuan, SUN Maosong, et al. Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion[C]. The Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, USA, 2015: 2181–2187. [118] DETTMERS T, MINERVINI P, STENETORP P, et al. Convolutional 2D knowledge graph embeddings[C]. The Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirtieth Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Eighth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 1811–1818. [119] JIN Xiaowei, CAI Shengze, LI Hui, et al. NSFnets (Navier-Stokes flow nets): Physics-informed neural networks for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 426: 109951. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109951 [120] KISSAS G, YANG Yibo, HWUANG E, et al. Machine learning in cardiovascular flows modeling: Predicting arterial blood pressure from non-invasive 4D flow MRI data using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 358: 112623. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2019.112623 [121] MISYRIS G S, VENZKE A, and CHATZIVASILEIADIS S. Physics-informed neural networks for power systems[C]. 2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Montreal, Canada, 2020: 1–5. [122] SCHUETZ M J A, BRUBAKER J K, and KATZGRABER H G. Combinatorial optimization with physics-inspired graph neural networks[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2022, 4(4): 367–377. doi: 10.1038/s42256-022-00468-6 [123] SEGLER M H S, PREUSS M, and WALLER M P. Planning chemical syntheses with deep neural networks and symbolic AI[J]. Nature, 2018, 555(7698): 604–610. doi: 10.1038/nature25978 [124] CHENG Guanjian, GONG Xingao, and YIN Wanjian. Crystal structure prediction by combining graph network and optimization algorithm[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1492. doi: 10.1038/S41467-022-29241-4 [125] WANG Han, MAO Kebiao, YUAN Zijin, et al. A method for land surface temperature retrieval based on model-data-knowledge-driven and deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 265: 112665. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112665 [126] JADHAV A, WONG K C L, WU J T, et al. Combining deep learning and knowledge-driven reasoning for chest X-ray findings detection[C]. American Medical Informatics Association Annual Symposium, Chicago, USA, 2020: 593–601. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
