Handwriting Number Recognition Based on Millimeter-wave Radar with Dual-view Feature Fusion Network
-
摘要: 疫情常态化背景下,非接触式人机交互在医疗、健康领域蕴藏着巨大的应用前景,其中利用手势识别方法实现非接触式的仪器操控逐渐成为研究热点。对此,该文提出一种利用毫米波雷达双视角时序特征融合来实现手势数字识别的方法,以提高手势识别的鲁棒性和准确性。首先,该文同步采集正面、侧面视角的毫米波雷达手势数字0~9的时序回波数据;接着,对各视角的数据进行预处理,实现杂波抑制、数据压缩;随后提取两方向的距离、速度的时序特征,并就特征的时间相关性构建嵌入注意力机制的双视角时序特征融合网络(ADVFNet);最后,基于实测数据集完成了网络训练、时序特征融合、手势数字识别等步骤。实验结果表明,该文所提方法在实测数据集上识别准确率达到95%,网络收敛速度快、模型泛化能力好,与现有方法相比具有一定优势,为后续毫米波雷达人机交互提供了新思路。Abstract: Against the epidemic background, the contactless human-computer interaction has great application prospects in the medical and health field. Among them, using gesture recognition method to realize non-contact instrument control is becoming the hotspot. To improve the robustness and accuracy, a method is proposed to realize the digital gesture recognition based on dual-view sequential feature fusion of millimeter-wave radars in this paper. Firstly, time series echo data of gesture numbers 0~9 from positive and side perspectives are collected synchronously. Secondly, datasets from different perspectives are preprocessed by implementing clutter suppression and data compression. Furthermore, the Attention embedded Dual View Fusion Network (ADVFNet) is constructed based on the intrinsic correlation of temporal features. Finally, using the collected dataset, the task of training network, fusing sequential feature, and recognizing digital gesture could be completed. Experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of proposed method is about 95%, which has faster network convergence and better model generalization ability compared with several existing methods. Moreover, the method could provide a new idea for future human-computer interaction of millimeter-wave radars.
-
表 1 网络具体参数说明
类型 输入尺寸 输出尺寸 说明 正向输入(Postive Input) – (128×128×1) – 侧向输入(Side Input) – (128×128×1) – 双向LSTM(Bi-LSTM) (128×128) (128×128) units = 64 注意力模块(Attention Module) (128×128) (128×128) – 相乘层(Multiply) (128×128);(128×128) (128×128) – 平铺层(Flatten) (128×128) 16384 Activation = "ReLU" 特征融合层(Add) 16384;16384 16384 Dropout = 0.3 全连接层1(Dense) 16384 256 Activation = "ReLU" 全连接层2(Dense) 256 10 Activation = "Softmax" 表 2 雷达参数配置
参数 数值 参数 数值 发射天线数(个) 1 帧周期(ms) 20 接收天线数(个) 4 Chirp数(个) 128 带宽(GHz) 2 采样点数(个) 64 调频斜率(MHz/μs) 50 帧数(个) 100 采样率(MHz) 2 距离分辨率(cm) 7.5 表 3 不同情况下的纵向距离与径向距离的绝对差值与相对差值
x(cm) y=40 cm y=50 cm y=60 cm r(cm) AD(cm) RD(%) r(cm) AD(cm) RD(%) r(cm) AD(cm) RD(%) 0 40.000 0 0 50.000 0 0 60.000 0 0 1 40.012 0.012 0.031 50.010 0.010 0.020 60.008 0.008 0.014 2 40.049 0.049 0.124 50.040 0.040 0.080 60.033 0.033 0.056 3 40.112 0.112 0.280 50.090 0.090 0.180 60.075 0.075 0.125 4 40.199 0.199 0.498 50.160 0.160 0.319 60.133 0.133 0.222 5 40.311 0.311 0.778 50.249 0.249 0.499 60.208 0.208 0.347 6 40.447 0.447 1.118 50.359 0.359 0.717 60.299 0.299 0.499 7 40.607 0.607 1.519 50.488 0.488 0.975 60.407 0.407 0.678 8 40.792 0.792 1.980 50.636 0.636 1.272 60.531 0.531 0.885 9 41.000 1.000 2.500 50.804 0.804 1.607 60.671 0.671 1.119 10 41.231 1.231 3.077 50.990 0.990 1.980 60.828 0.828 1.379 表 4 手势识别准确率(%)
输入特征 网络类型 平均准确率 输入特征 网络类型 平均准确率 PRTM Bi-LSTM 84.95 PVTM Bi-LSTM 94.55 SRTM Bi-LSTM 80.34 SVTM Bi-LSTM 74.45 PRTM+SRTM DVFNet 92.54 PVTM+SVTM DVFNet 90.95 PRTM Bi-LSTM+Attention 88.45 PVTM Bi-LSTM+Attention 94.60 SRTM Bi-LSTM+Attention 86.59 SVTM Bi-LSTM+Attention 87.00 PRTM+SRTM ADVFNet 95.30 PVTM+SVTM ADVFNet 96.80 表 5 在单视角下ADVFNet的识别准确率
输入 网络类型 平均准确率(%) 训练时长(ms/step) SRTM+SVTM 双流卷积神经网络 89.95 323 PRTM+PVTM 双流卷积神经网络 92.65 320 SRTM+SVTM ADVFNet 93.70 57 PRTM+PVTM ADVFNet 95.12 58 -
[1] LI Xinyu, HE Yuan, FIORANELLI F, et al. Semisupervised human activity recognition with radar micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5103112. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3090106 [2] EROL B and AMIN M G. Radar data cube processing for human activity recognition using multisubspace learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3617–3628. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2910980 [3] 冯心欣, 李文龙, 何兆, 等. 基于调频连续波雷达的多维信息特征融合人体姿势识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 40(10): 3583–3591. doi: 10.11999JEIT220687FENG Xinxin, LI Wenlong, HE Zhao, et al. Multi-dimensional information feature fusion for posture recognition based on frequency modulated continuous wave radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 40(10): 3583–3591. doi: 10.11999JEIT220687 [4] ZHANG Zhenyuan, TIAN Zengshan, and ZHOU Mu. Latern: Dynamic continuous hand gesture recognition using FMCW radar sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(8): 3278–3289. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2808688 [5] SKARIA S, AL-HOURANI A, LECH M, et al. Hand-gesture recognition using two-antenna Doppler radar with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(8): 3041–3048. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2892073 [6] HAZRA S and SANTRA A. Robust gesture recognition using millimetric-wave radar system[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2018, 2(4): 1–4. doi: 10.1109/lsens.2018.2882642 [7] FAN Teng, MA Chao, GU Zhitao, et al. Wireless hand gesture recognition based on continuous-wave Doppler radar sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(11): 4012–4020. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2610427 [8] CRISÓSTOMO DE CASTRO FILHO H, ABÍLIO DE CARVALHO JÚNIOR O, FERREIRA DE CARVALHO O L, et al. Rice crop detection using LSTM, Bi-LSTM, and machine learning models from Sentinel-1 time series[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(16): 2655. doi: 10.3390/rs12162655 [9] SHRESTHA A, LI Haobo, LE KERNEC J, et al. Continuous human activity classification from FMCW radar with Bi-LSTM networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13607–13619. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3006386 [10] SUN Yuliang, FEI Tai, LI Xibo, et al. Real-time radar-based gesture detection and recognition built in an edge-computing platform[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(18): 10706–10716. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2994292 [11] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的手势动作雷达识别方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(6): 1117–1123. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0397WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Hand gesture recognition method by radar based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(6): 1117–1123. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0397 [12] 王勇, 王沙沙, 田增山, 等. 基于FMCW雷达的双流融合神经网络手势识别方法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(7): 1408–1415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.07.003WANG Yong, WANG Shasha, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Two-stream fusion neural network approach for hand gesture recognition based on FMCW radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(7): 1408–1415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.07.003 [13] 王勇, 吴金君, 田增山, 等. 基于FMCW雷达的多维参数手势识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485WANG Yong, WU Jinjun, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Gesture recognition with multi-dimensional parameter using FMCW radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485 [14] 夏朝阳, 周成龙, 介钧誉, 等. 基于多通道调频连续波毫米波雷达的微动手势识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 164–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190797XIA Zhaoyang, ZHOU Chenglong, JIE Junyu, et al. Micro-motion gesture recognition based on multi-channel frequency modulated continuous wave millimeter wave radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 164–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190797 [15] 靳标, 彭宇, 邝晓飞, 等. 基于串联式一维神经网络的毫米波雷达动态手势识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2743–2750. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200894JIN Biao, PENG Yu, KUANG Xiaofei, et al. Dynamic gesture recognition method based on millimeter-wave radar by one-dimensional series neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2743–2750. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200894 [16] SHEN Xiangyu, ZHENG Haifeng, FENG Xinxin, et al. ML-HGR-Net: A meta-learning network for FMCW radar based hand gesture recognition[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(11): 10808–10817. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3169231 [17] DONG Xichao, ZHAO Zewei, WANG Yupei, et al. FMCW radar-based hand gesture recognition using spatiotemporal deformable and context-aware convolutional 5-D feature representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5107011. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3122332 [18] RYU S J, SUH J S, BAEK S H, et al. Feature-based hand gesture recognition using an FMCW radar and its temporal feature analysis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(18): 7593–7602. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2859815 [19] 邵正途, 许登荣, 徐文利, 等. 基于LSTM和残差网络的雷达有源干扰识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(2): 416–423.SHAO Zhengtu, XU Dengrong, XU Wenli, et al. Radar active jamming recognition based on LSTM and residual network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 416–423. [20] SHERSTINSKY A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (RNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) network[J]. Physica D:Nonlinear Phenomena, 2020, 404: 132306. doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2019.132306 [21] JI Yuzhu, ZHANG Haijun, and WU Q M J. Salient object detection via multi-scale attention CNN[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 322: 130–140. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.061 [22] LI Liu, XU Mai, LIU Hanruo, et al. A large-scale database and a CNN model for attention-based glaucoma detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(2): 413–424. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2927226 [23] 韩崇, 韩磊, 孙力娟, 等. 基于时空压缩特征表示学习的毫米波雷达手势识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1274–1283. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211221HAN Chong, HAN Lei. SUN Lijuan, et al. Millimeter wave radar gesture recognition algorithm based on Spatio-temporal compression feature representation learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1274–1283. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211221 -





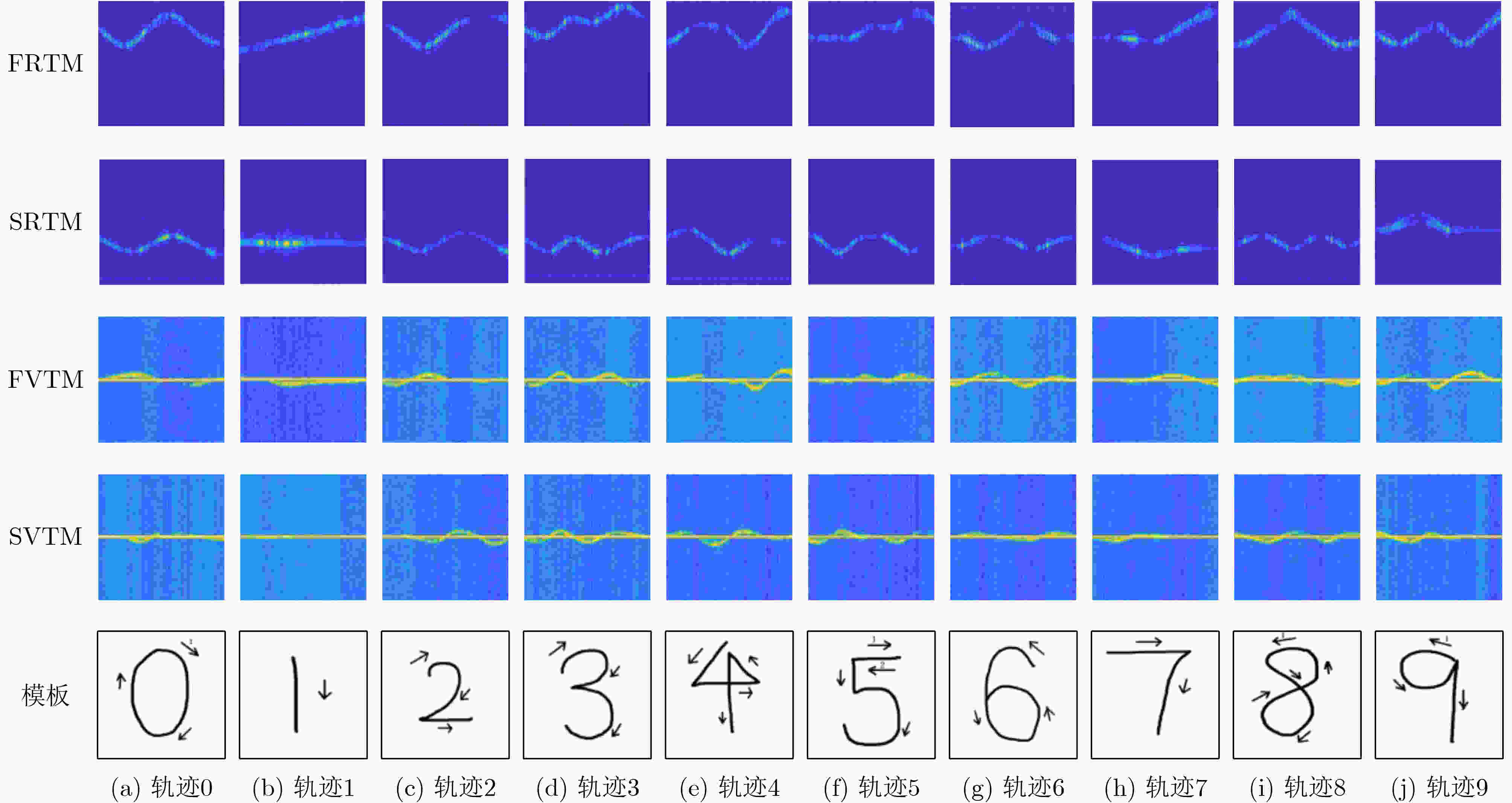
 下载:
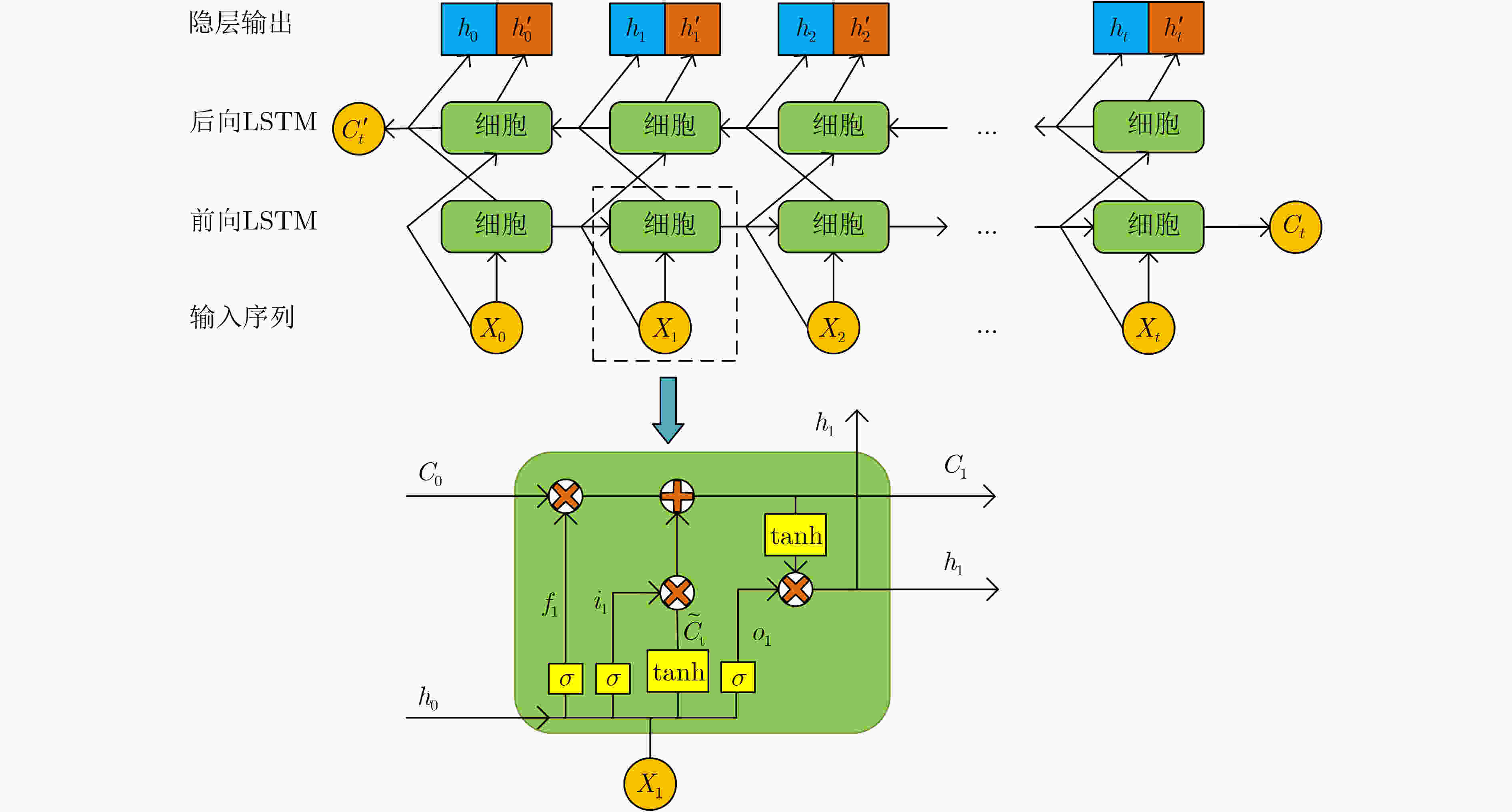
下载:
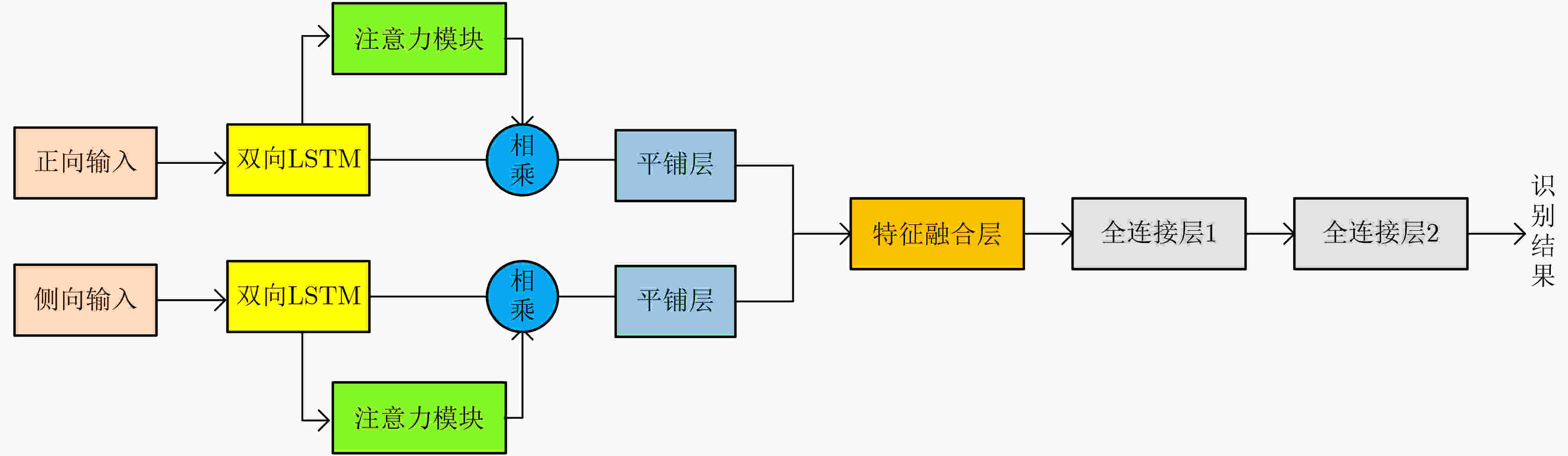
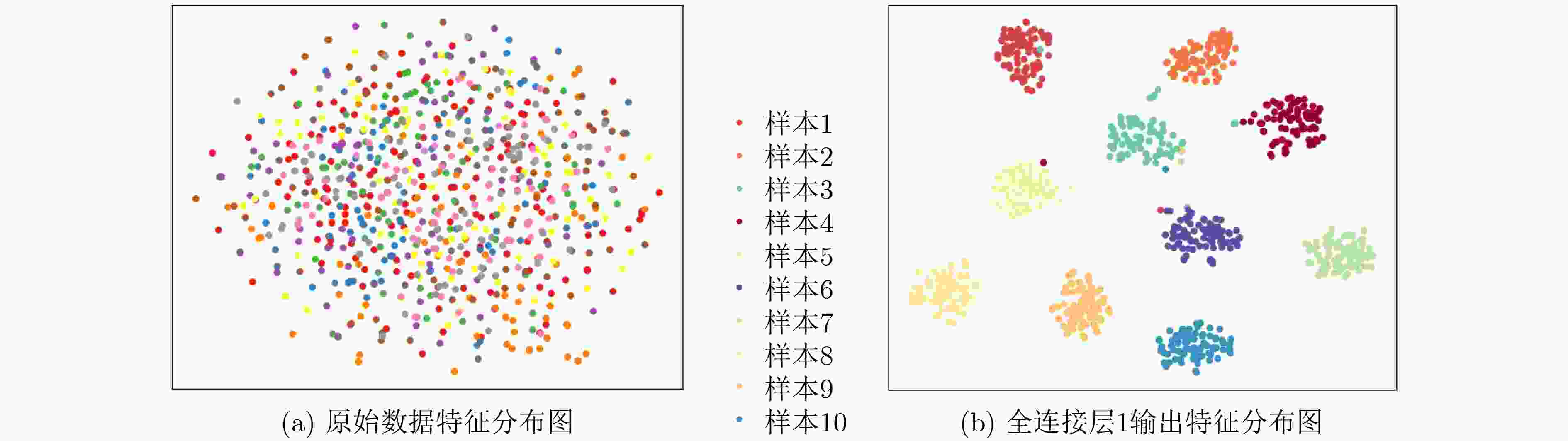
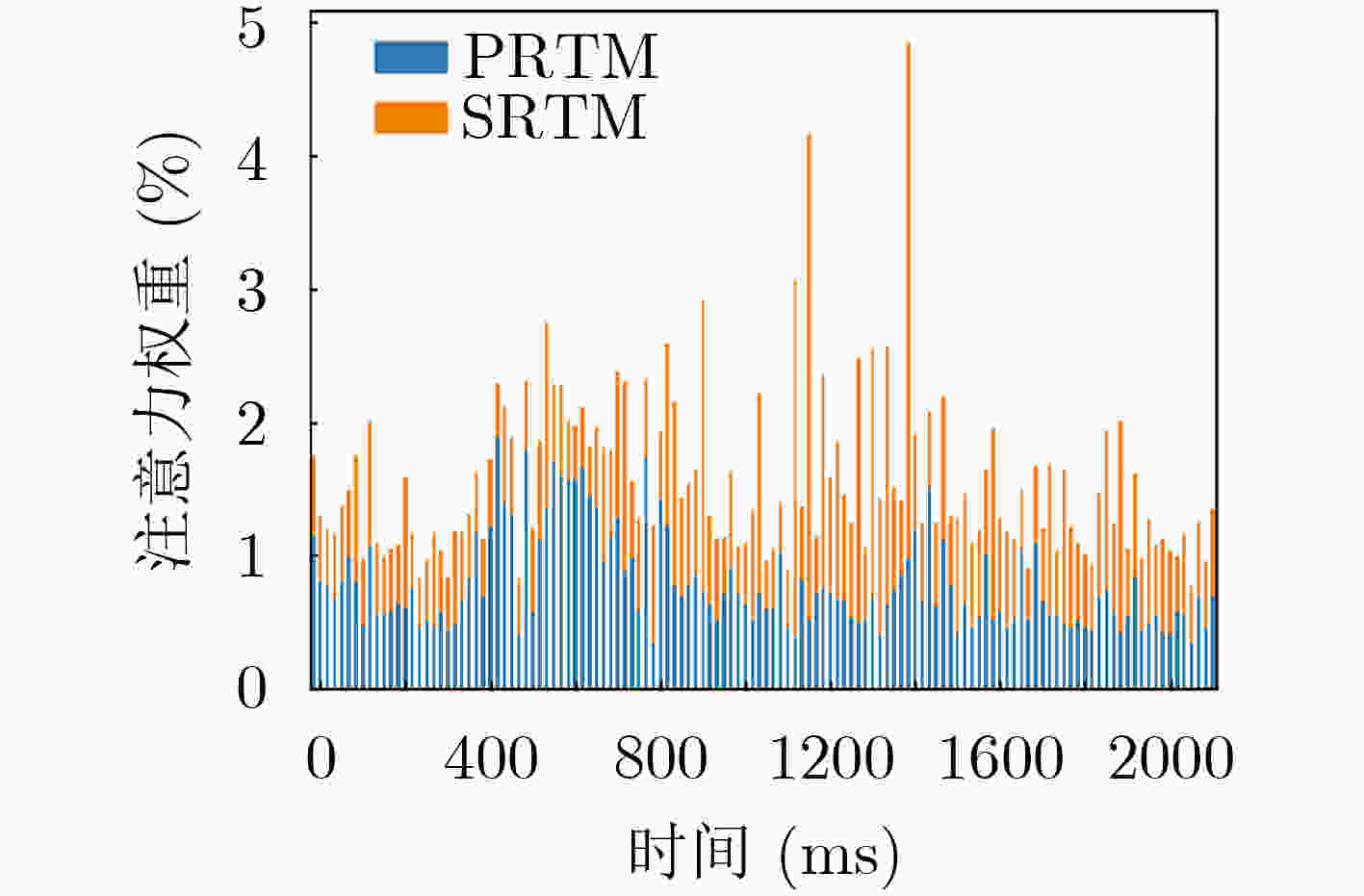
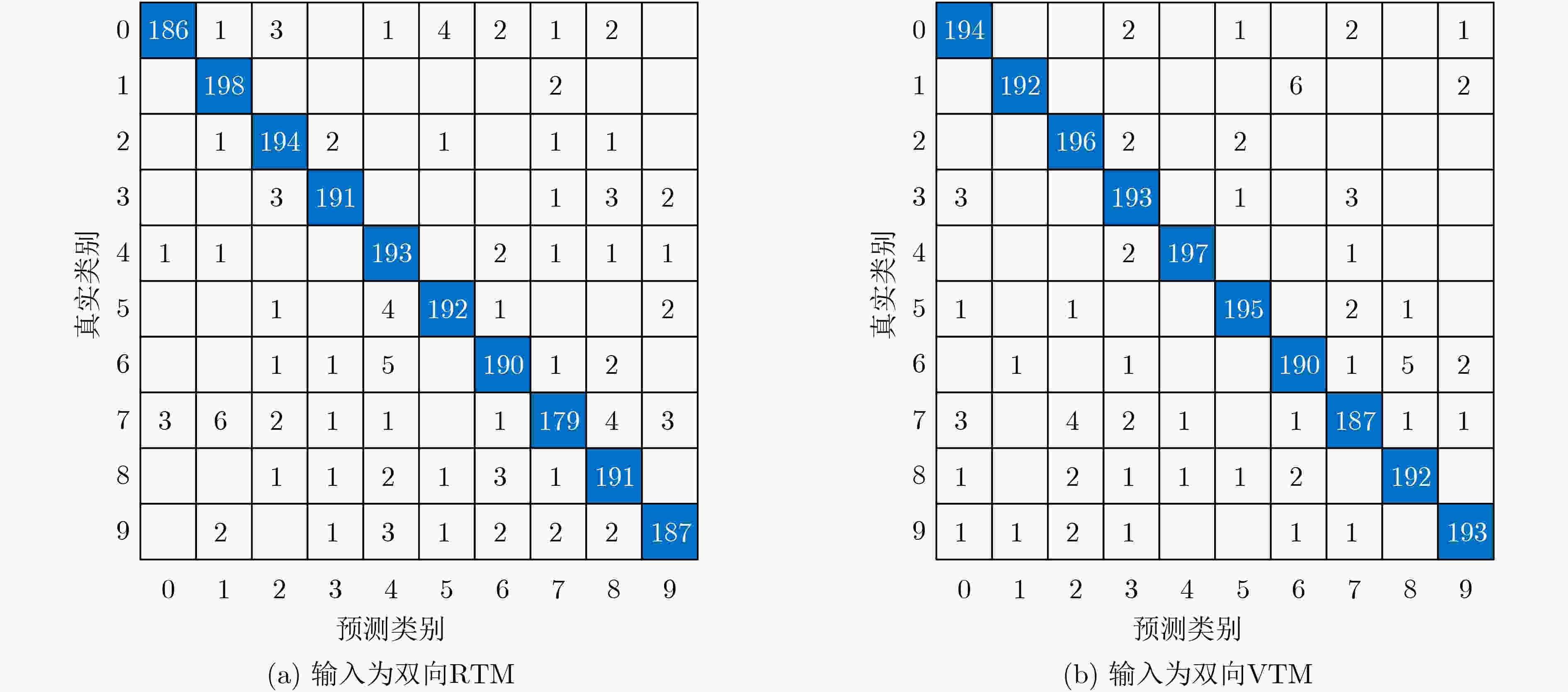


 下载:
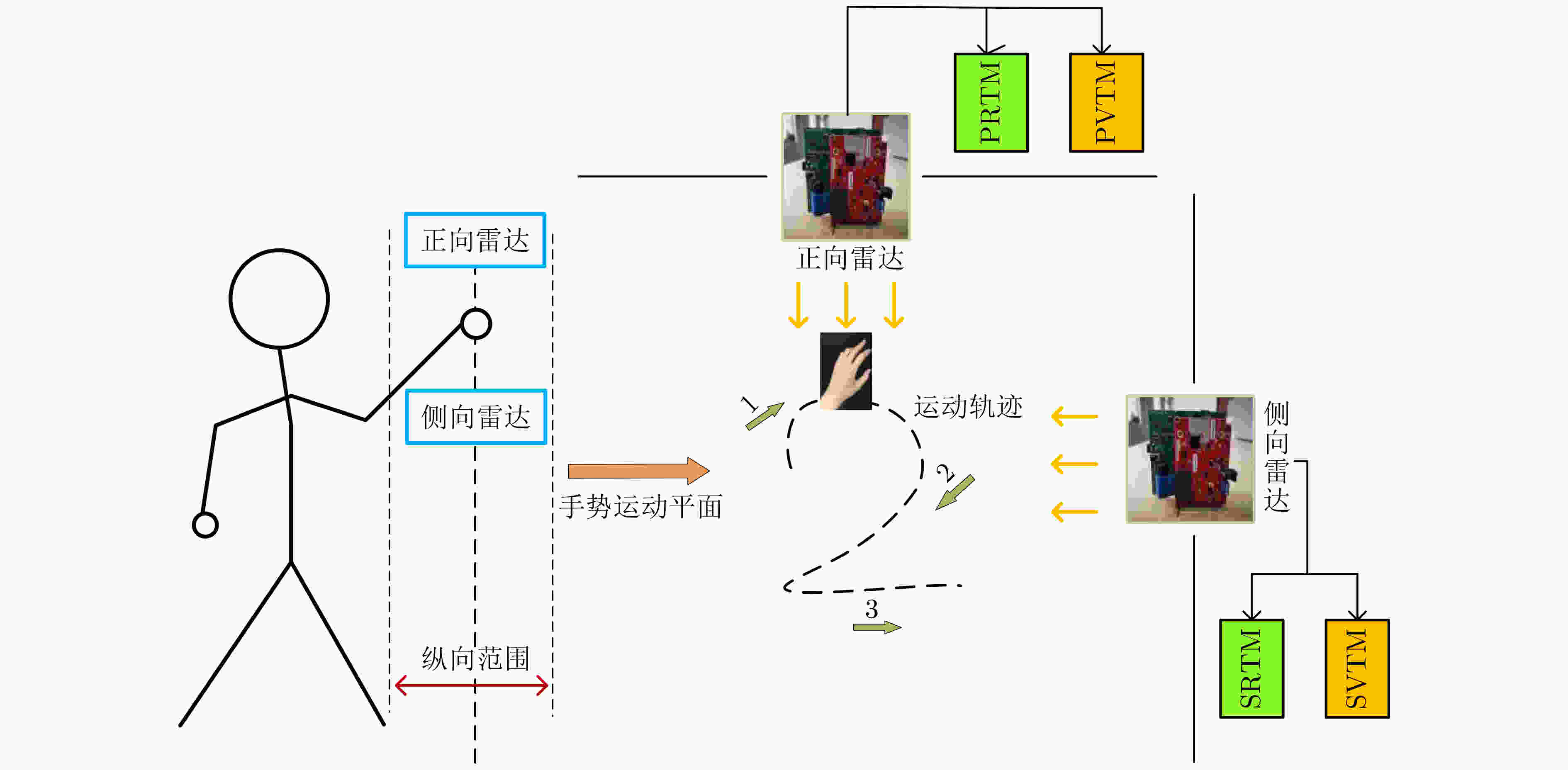
下载:
