Prognostic Prediction of Gastric Cancer Based on Ensemble Deep Learning of Pathological Images
-
摘要: 病理图像分析对胃癌的诊断和预后具有重要意义,但在临床应用上仍然面临着目视阅片一致性低、多分辨率图像差异大等挑战。为此,该文提出一种基于病理图像集成深度学习的胃癌预后预测方法。首先,对患者不同分辨率下的病理图像进行切分、筛选等预处理;然后,采用ResNet, MobileNetV3, EfficientNetV2深度学习方法分别对不同分辨率下的切片(Tile)进行深度特征提取和融合,以此获得患者层面(Patient-level)的单分辨率子分类器预测结果;最终,采用双重集成策略对不同分辨率下异质子分类器预测结果进行融合以获得患者层面的预后预测结果。实验中收集了250例胃癌患者的组织病理图像,并以远处转移预测为例进行验证,实验结果表明,所提方法在测试集上的预测准确率为89.10%,敏感度为89.57%,特异度为88.61%,马修斯相关系数为78.19%,相比于单模型预测结果获得了显著提升,可为胃癌患者的治疗和预后提供重要参考。Abstract: The analysis of pathological images is of great significance for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. However, its clinical application still faces challenges such as low consistency of visual reading and large differences in multi-resolution images. To address these issues, a prognostic prediction method of gastric cancer based on ensemble deep learning of pathological images is proposed. First, the pathological images at different resolutions of patient are preprocessed by slicing and filtering. Then, the deep feature extraction and fusion of slices at different resolutions are carried out by using three deep learning methods, i.e., ResNet, MobileNetV3, and EfficientNetV2, respectively, which aims to obtain the single-resolution prediction results of individual classifier at patient level. Finally, a double-level ensemble strategy is used to fuse the prediction results of heterogeneous individual classifiers at different resolutions to obtain the patient-level prognostic prediction results. In the experiment, the pathological images of 250 gastric cancer patients are collected, and the prediction of distant metastases is used as an example for verification. The experimental results show that the prediction accuracy of the proposed method on the test set is 89.10%, the sensitivity is 89.57%, the specificity is 88.61%, and the Matthews correlation coefficient is 78.19%. Compared with the single-model prediction results, the prediction performance of the proposed method has been significantly improved, which can provide an important reference for the treatment and prognosis of gastric cancer patients.
-
Key words:
- Pathological image /
- Ensemble learning /
- Deep learning /
- Gastric cancer /
- Prognosis prediction
-
表 1 250例胃癌患者临床随访信息
指标 特征 数量 年龄 ≤50 61 51~70 153 >70 36 性别 男性 163 女性 87 远处转移 发生转移 125 未发生转移 125 病理类型 腺癌 177 黏液腺癌 11 印戎细胞癌 56 其他 6 Lauren分型 肠型 27 弥漫型 71 混合型 32 未标明 120 表 2 不同量级子分类器网络在切片(10×分辨率)层面的预测性能(%)对比
方法 ACC SEN SPE MCC ResNet-18 76.42 76.72 76.10 52.81 ResNet-34 78.37 75.79 81.08 56.90 ResNet-50 79.67 79.43 79.86 59.29 MobileNetV3-small 77.03 71.30 83.04 54.62 MobileNetV3-large 79.21 75.38 82.87 58.46 EfficientNetV2-s 81.18 85.78 76.36 62.49 EfficientNetV2-m 82.94 85.27 80.50 65.88 EfficientNetV2-l 83.69 86.52 80.85 67.48 表 3 不同量级子分类器网络在切片(40×分辨率)层面的预测性能(%)对比
方法 ACC SEN SPE MCC ResNet-18 74.84 73.55 76.19 49.73 ResNet-34 76.33 75.95 76.73 52.66 ResNet-50 78.05 76.78 79.38 56.15 MobileNetV3-small 73.46 74.30 72.58 46.89 MobileNetV3-large 76.24 78.01 74.47 52.52 EfficientNetV2-s 79.58 82.81 76.20 59.19 EfficientNetV2-m 80.23 82.93 77.39 60.45 EfficientNetV2-l 81.16 83.94 78.24 62.32 表 4 不同分辨率下子分类器网络与集成模型在切片层面的预测性能(%)对比
方法 ACC SEN SPE MCC ResNet-50(10×) 79.67 79.43 79.86 59.29 MobileNetV3-large(10×) 79.21 75.38 82.87 58.46 EfficientNetV2-l(10×) 83.69 86.52 80.85 67.48 集成模型(10×) 86.16 87.64 84.66 72.34 ResNet-50(40×) 78.05 76.78 79.38 56.15 MobileNetV3-large(40×) 76.24 78.01 74.47 52.52 EfficientNetV2-l(40×) 81.16 83.94 78.24 62.32 集成模型(40×) 84.64 86.42 82.80 69.29 表 5 不同模型在患者层面的预测性能(%)对比
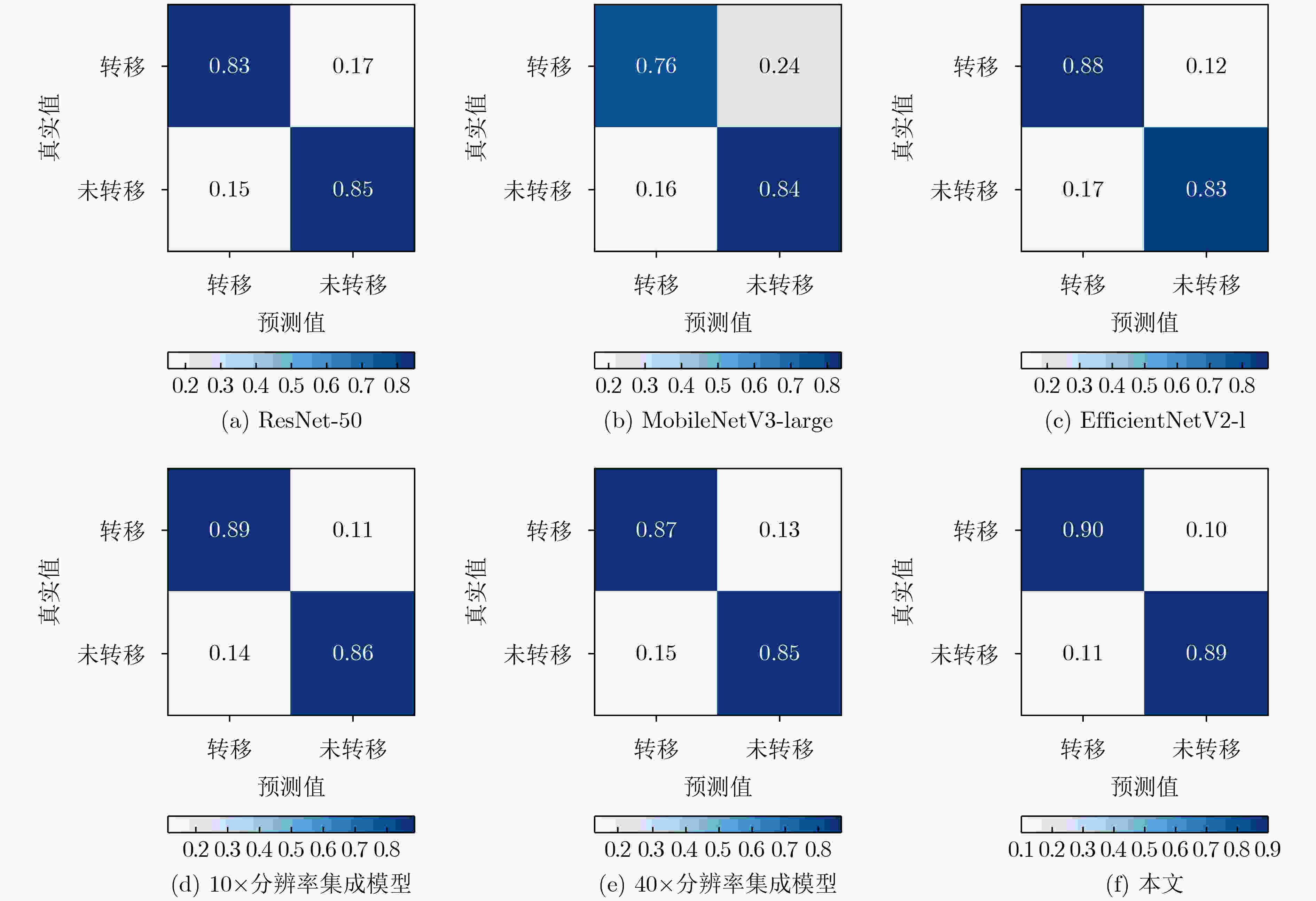
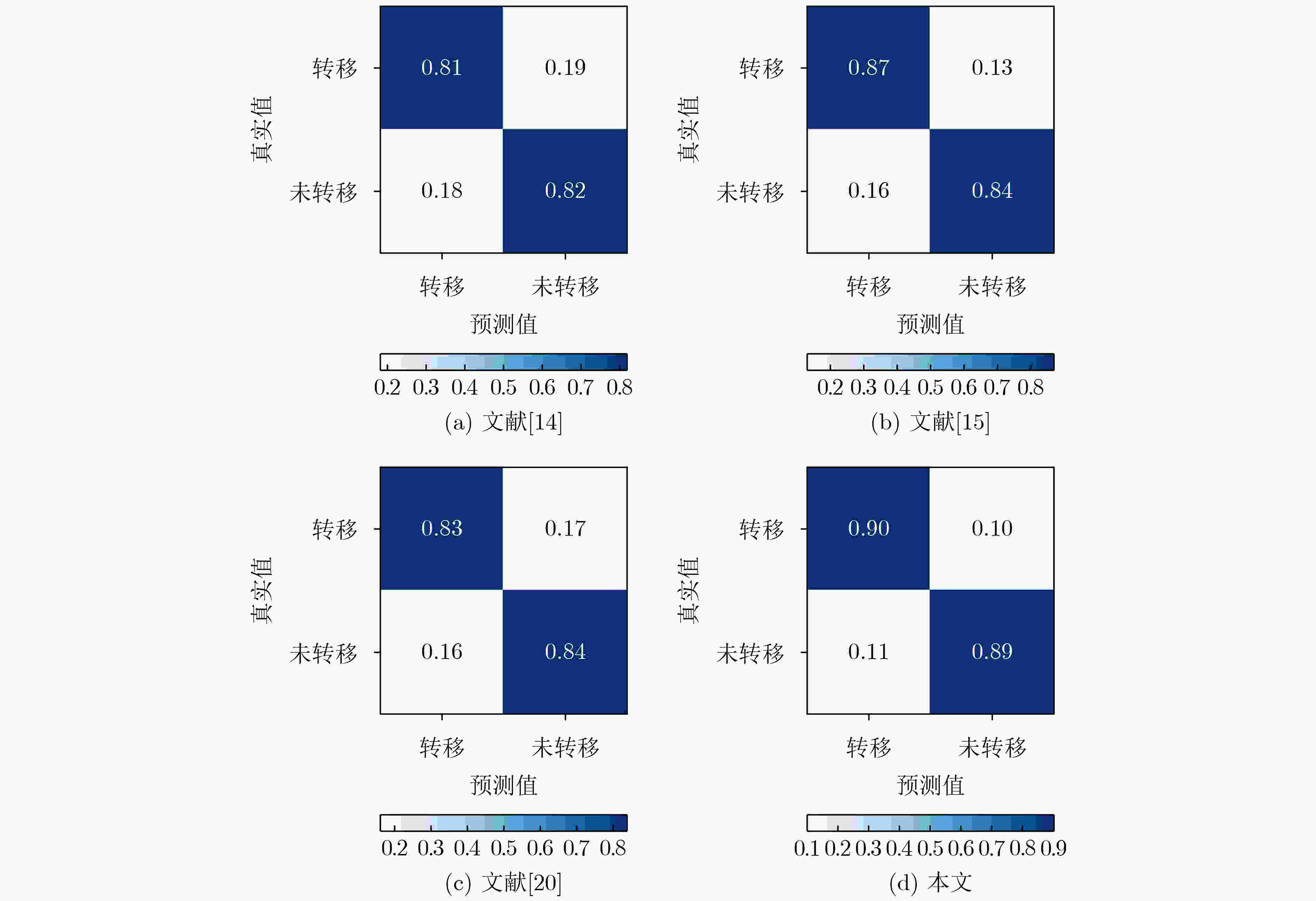
方法 ACC SEN SPE MCC ResNet-50 83.78 83.06 84.53 67.57 MobileNetV3-large
EfficientNetV2-l80.21
85.6476.27
87.8684.35
83.3160.74
71.2910×分辨率集成模型 87.54 88.96 86.08 75.09 40×分辨率集成模型 86.19 87.23 85.44 72.70 本文 89.10 89.57 88.61 78.19 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2021, 71(3): 209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] DAGOGO-JACK I and SHAW A T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies[J]. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 2018, 15(2): 81–94. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166 [3] TAKTAK A F G and FISHER A C. Outcome Prediction in Cancer[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006: 16-17. [4] GORLIA T, VAN DEN BENT M J, HEGI M E, et al. Nomograms for predicting survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Prognostic factor analysis of EORTC and NCIC trial 26981-22981/CE. 3[J]. The Lancet Oncology, 2008, 9(1): 29–38. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70384-4 [5] YU Chaoran and ZHANG Yujie. Development and validation of prognostic nomogram for young patients with gastric cancer[J]. Annals of Translational Medicine, 2019, 7(22): 641. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.10.77 [6] ZHANG Yanbo and YU Hengyong. Convolutional neural network based metal artifact reduction in X-ray computed tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1370–1381. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2823083 [7] HAMEED A A, KARLIK B, and SALMAN M S. Back-propagation algorithm with variable adaptive momentum[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 114: 79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2016.10.001 [8] 徐莹莹, 沈红斌. 基于模式识别的生物医学图像处理研究现状[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 201–213. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190657XU Yingying and SHEN Hongbin. Review of research on biomedical image processing based on pattern recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 201–213. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190657 [9] GREENSPAN H, VAN GINNEKEN B, and SUMMERS R M. Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: Overview and future promise of an exciting new technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1153–1159. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2553401 [10] LUO J, WU Min, GOPUKUMAR D, et al. Big data application in biomedical research and health care: A literature review[J]. Biomedical Informatics Insights, 2016, 8: 1–10. doi: 10.4137/BII.S31559 [11] ESTEVA A, KUPREL B, NOVOA R A, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 115–118. doi: 10.1038/nature21056 [12] JIANG Yuming, JIN Cheng, YU Heng, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning CT signature to predict survival and chemotherapy benefit in gastric cancer: A multicenter, retrospective study[J]. Annals of Surgery, 2021, 274(6): e1153–e1161. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003778 [13] 陈雯, 王旭, 段辉宏, 等. 深度学习在癌症预后预测模型中的应用研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2020, 37(5): 918–929. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201909066CHEN Wen, WANG Xu, DUAN Huihong, et al. Application of deep learning in cancer prognosis prediction model[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 37(5): 918–929. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201909066 [14] KATHER J N, PEARSON A T, HALAMA N, et al. Deep learning can predict microsatellite instability directly from histology in gastrointestinal cancer[J]. Nature Medicine, 2019, 25(7): 1054–1056. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0462-y [15] SKREDE O J, DE RAEDT S, KLEPPE A, et al. Deep learning for prediction of colorectal cancer outcome: A discovery and validation study[J]. The Lancet, 2020, 395(10221): 350–360. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0462-y [16] 杨昆, 常世龙, 王尉丞, 等. 基于sECANet通道注意力机制的肾透明细胞癌病理图像ISUP分级预测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 138–148. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210900YANG Kun, CHANG Shilong, WANG Yucheng, et al. Predict the ISUP grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma using pathological images based on sECANet Chanel attention[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 138–148. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210900 [17] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xianyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [18] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN Bo, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1314–1324. [19] TAN Mingxing and LE Q. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training[C/OL]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 10096–10106. [20] 于凌涛, 夏永强, 闫昱晟, 等. 利用卷积神经网络分类乳腺癌病理图像[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2021, 42(4): 567–573. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201909052YU Lingtao, XIA Yongqiang, YAN Yusheng, et al. Breast cancer pathological image classification based on a convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2021, 42(4): 567–573. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201909052 [21] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336–359. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01228-7 -





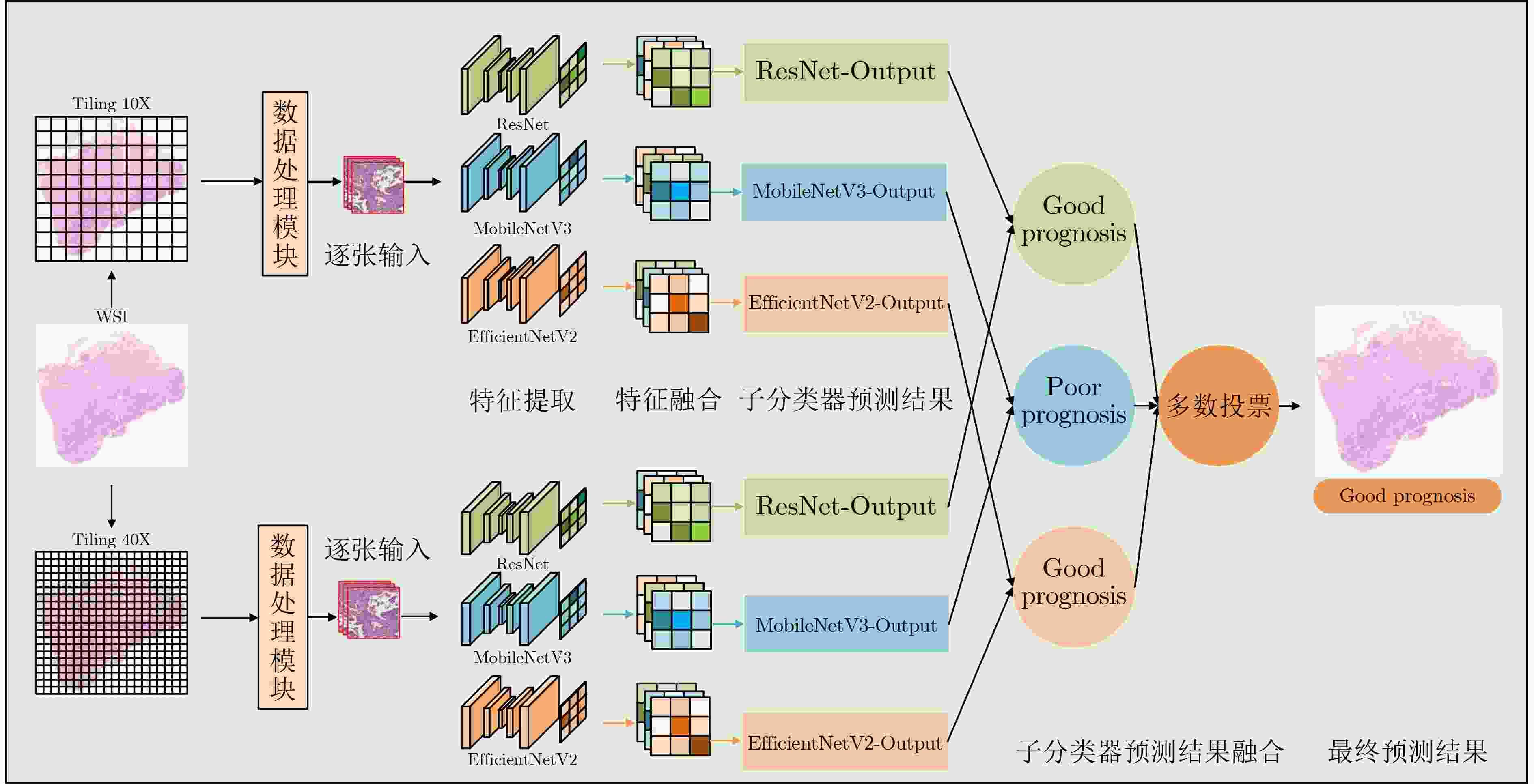
 下载:
下载:
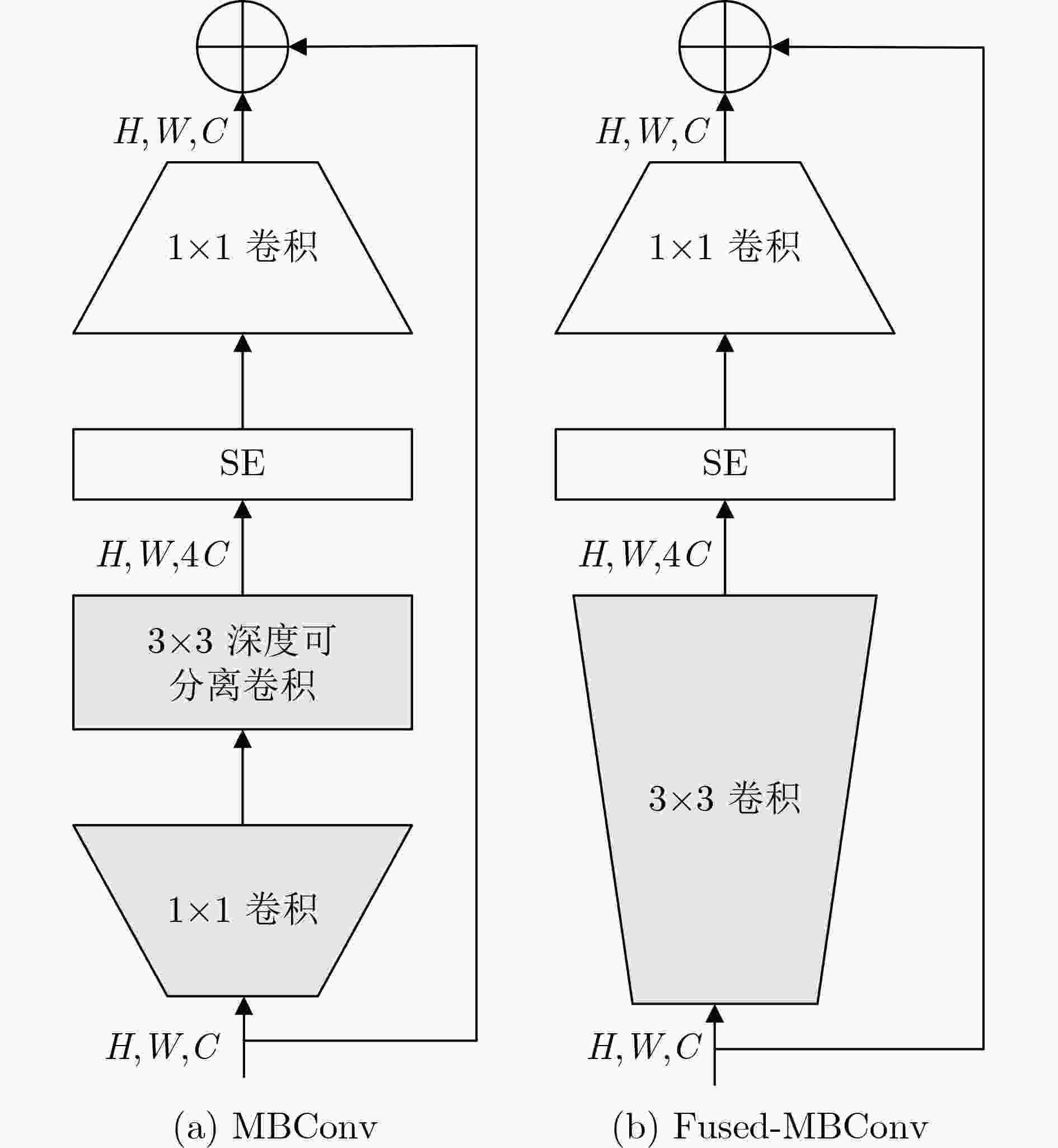
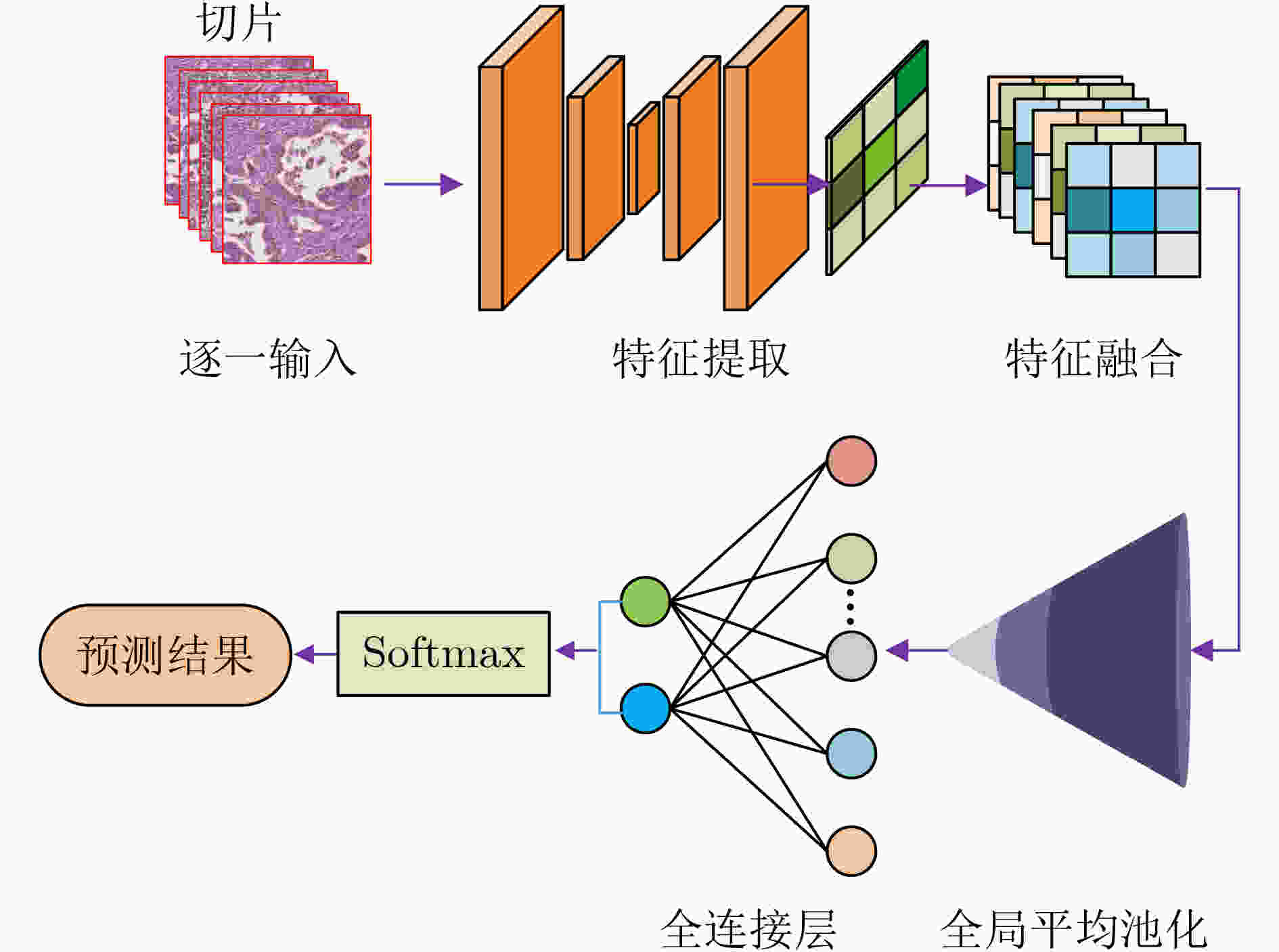

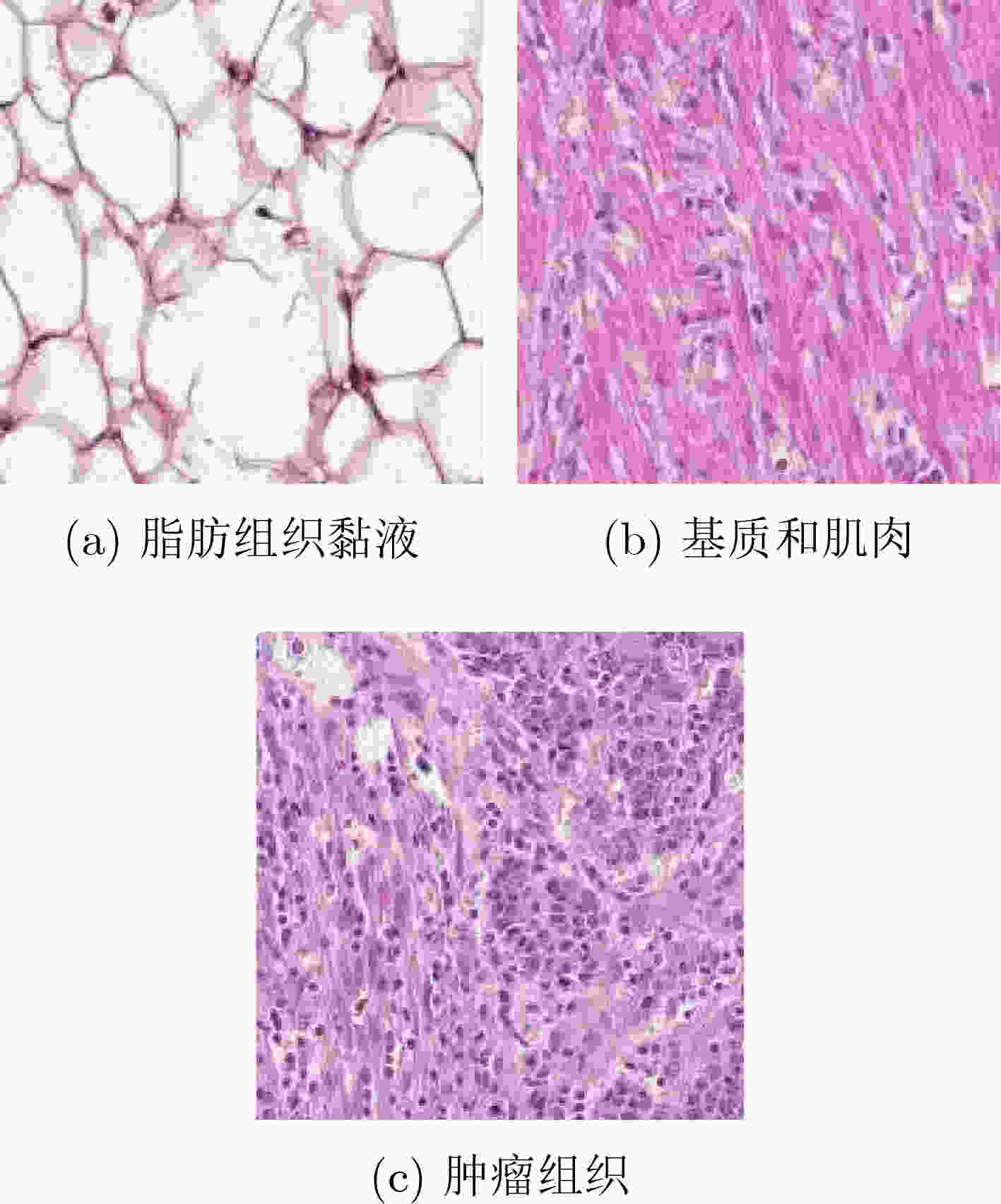
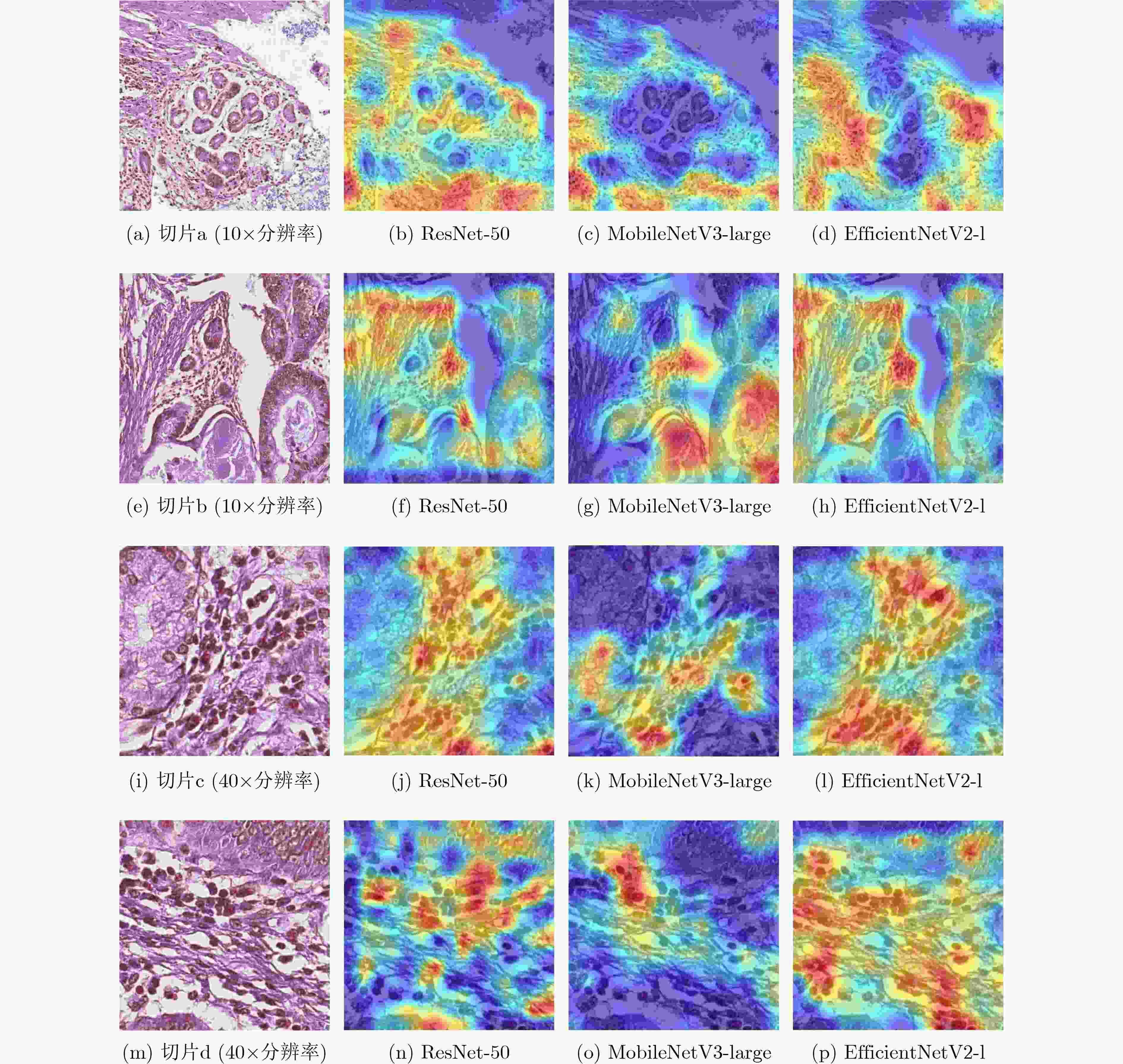


 下载:
下载:
