Trusted Geographic Routing Protocol Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Network
-
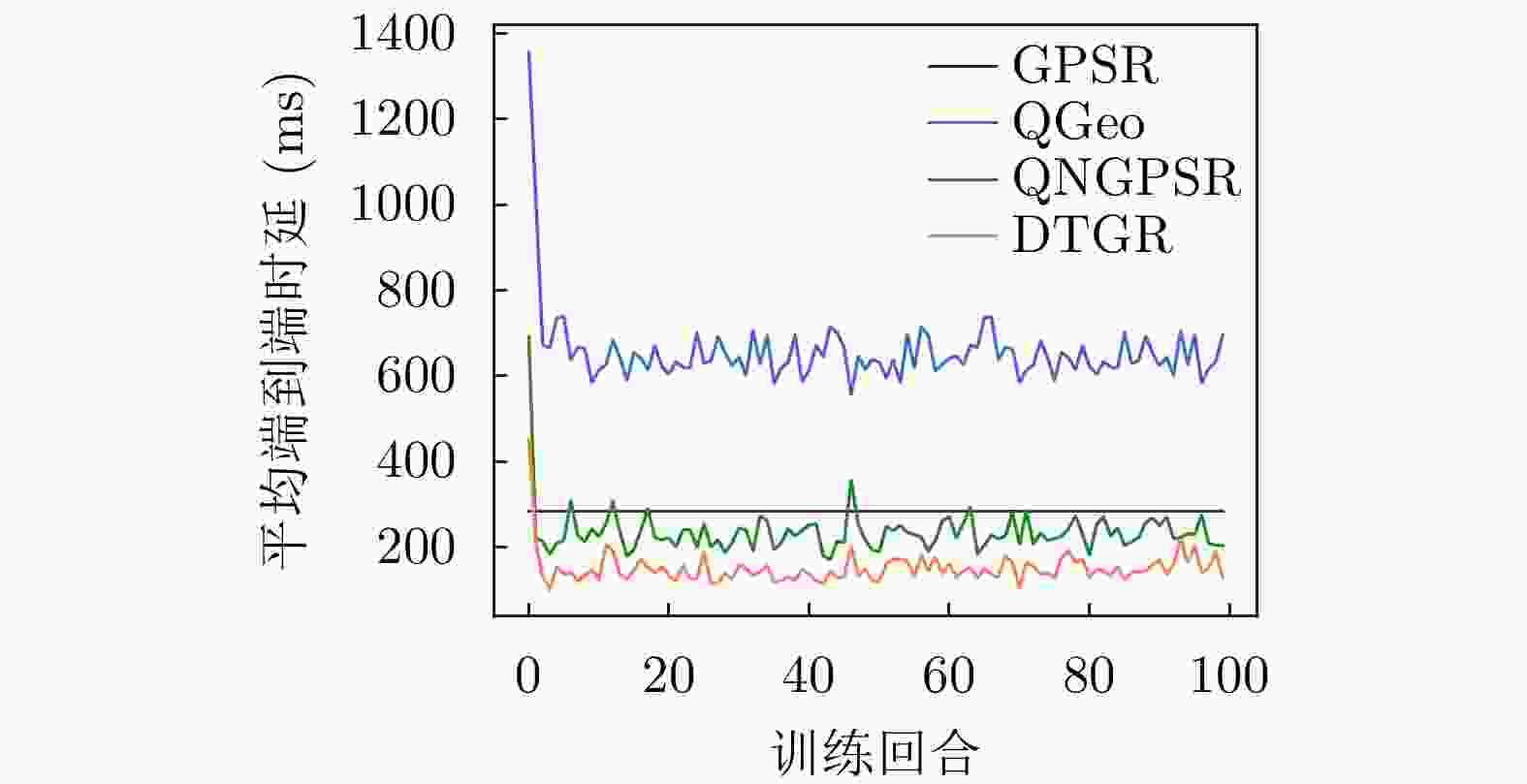
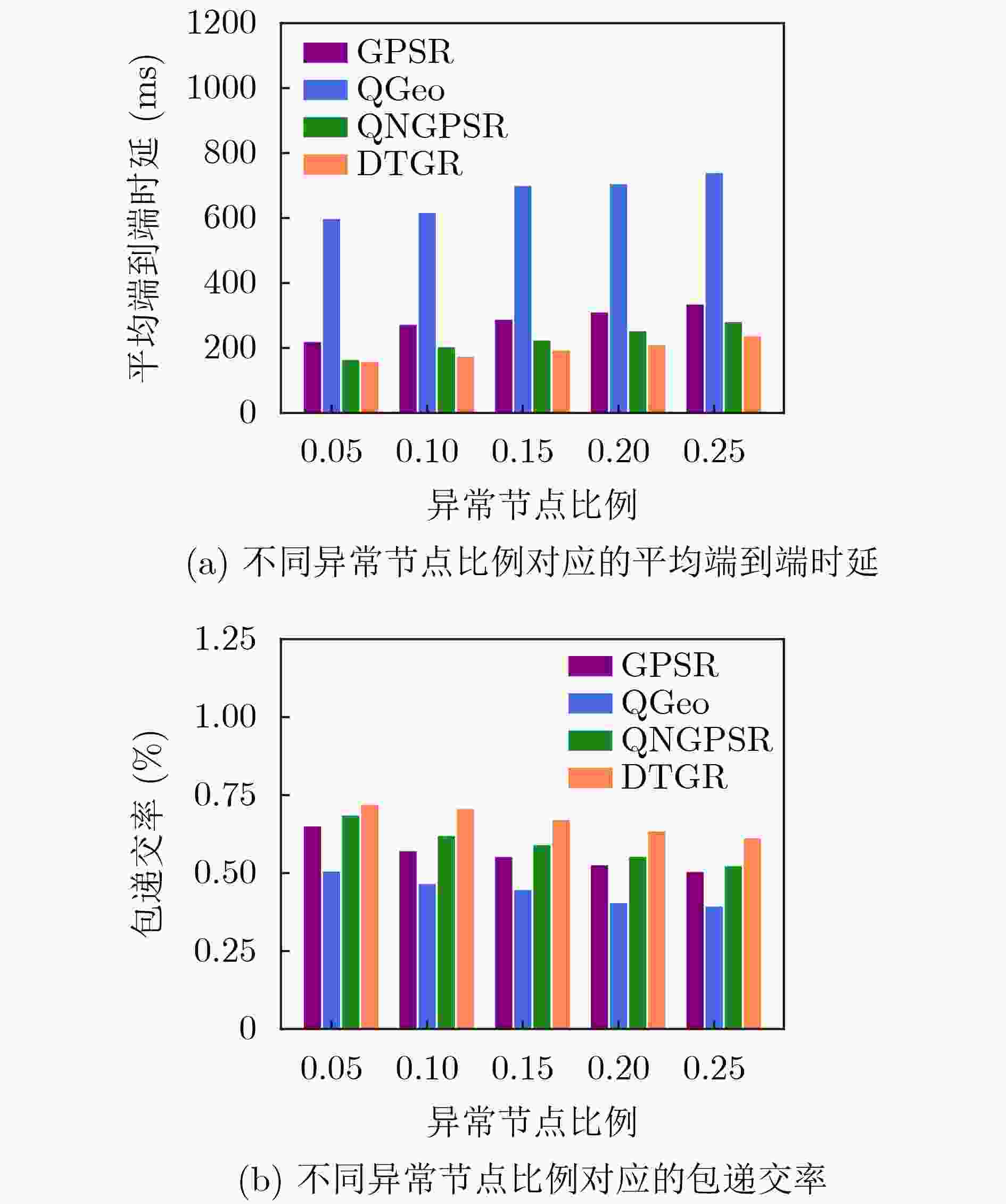
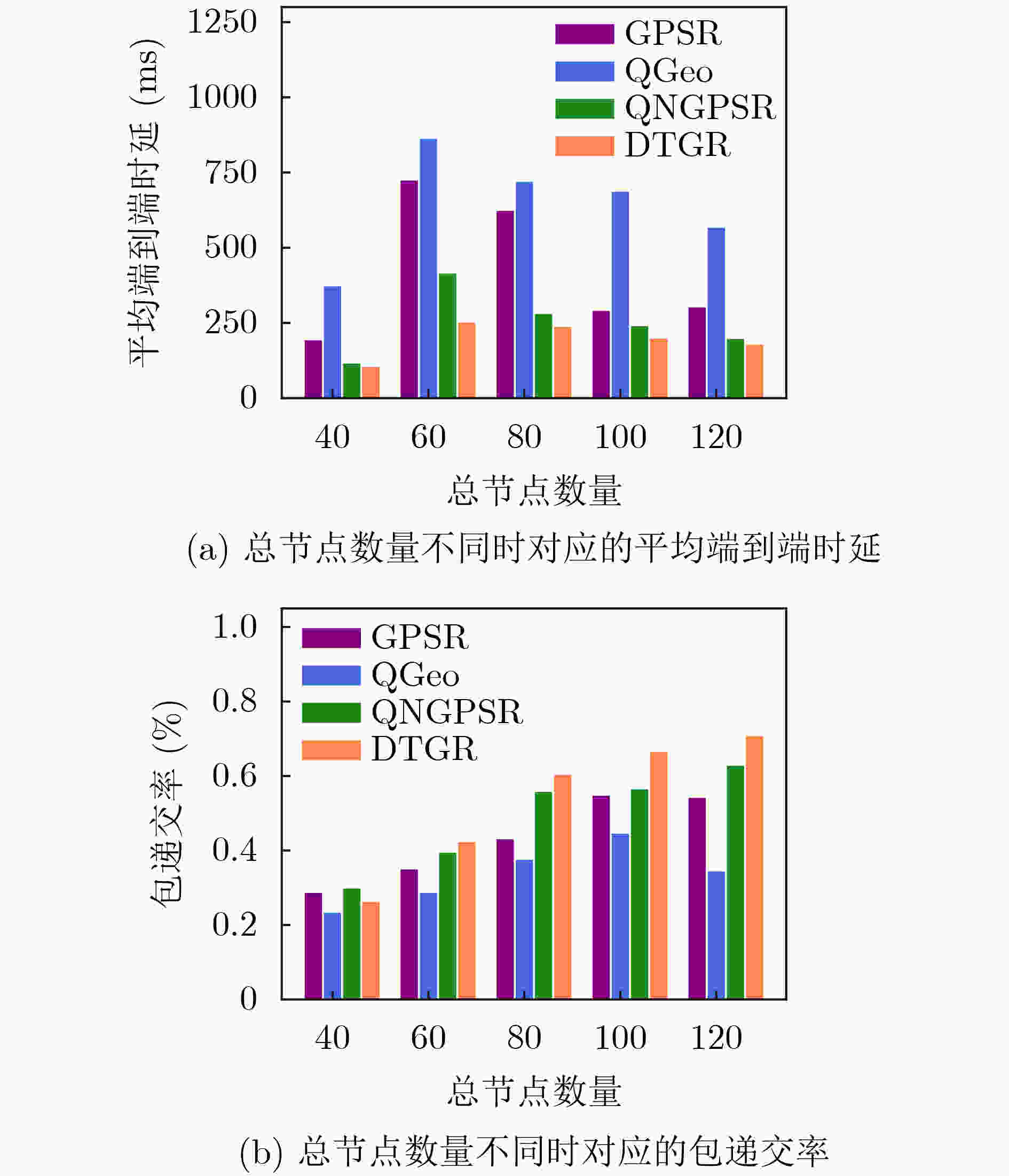
摘要: 针对无人机(UAV)通信过程中存在的高移动性和节点异常问题,该文提出一种基于深度强化学习的无人机可信地理位置路由协议(DTGR)。引入可信第三方提供节点的信任度,使用理论与真实的时延偏差和丢包率作为信任度的评估因子,将路由选择建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),基于节点信任度、地理位置和邻居拓扑信息构建状态空间,然后通过深度Q网络(DQN)输出路由决策。在奖励函数中结合信任度调整动作的价值,引导节点选择最优下一跳。仿真结果表明,在包含异常节点的无人机自组网(UANET)中,DTGR与现有方案相比具有更低的平均端到端时延和更高的包递交率。当异常节点数量或者比例变化时,DTGR能感知环境并高效智能地完成路由决策,保障网络性能。Abstract: Considering the problems of high mobility and abnormal nodes in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) communication, a Deep reinforcement learning based Trusted Geographic Routing protocol (DTGR) is proposed. A trusted third party is introduced to provide the trust of nodes. The difference between theoretical delay and real delay, and packet loss ratio are used as evaluation factors of trust degree. Routing selection is modeled as the Markov Decision Process (MDP). The state are constructed based on the neighbor nodes’ geographic location, the trust degree and the topology information. Then the routing decision can be output through the Deep Q Network(DQN). The action-value is adjusted by combining trust in reward function, to guide nodes to select the optimal next-hop. The simulation results show that DTGR has a lower average end-to-end delay and higher packet delivery ratio compared with existing schemes in UAV Ad hoc NETwork (UANET) with abnormal nodes. Besides, DTGR can effectively implement route selection and ensure network performance when the number or proportion of abnormal nodes changes.
-
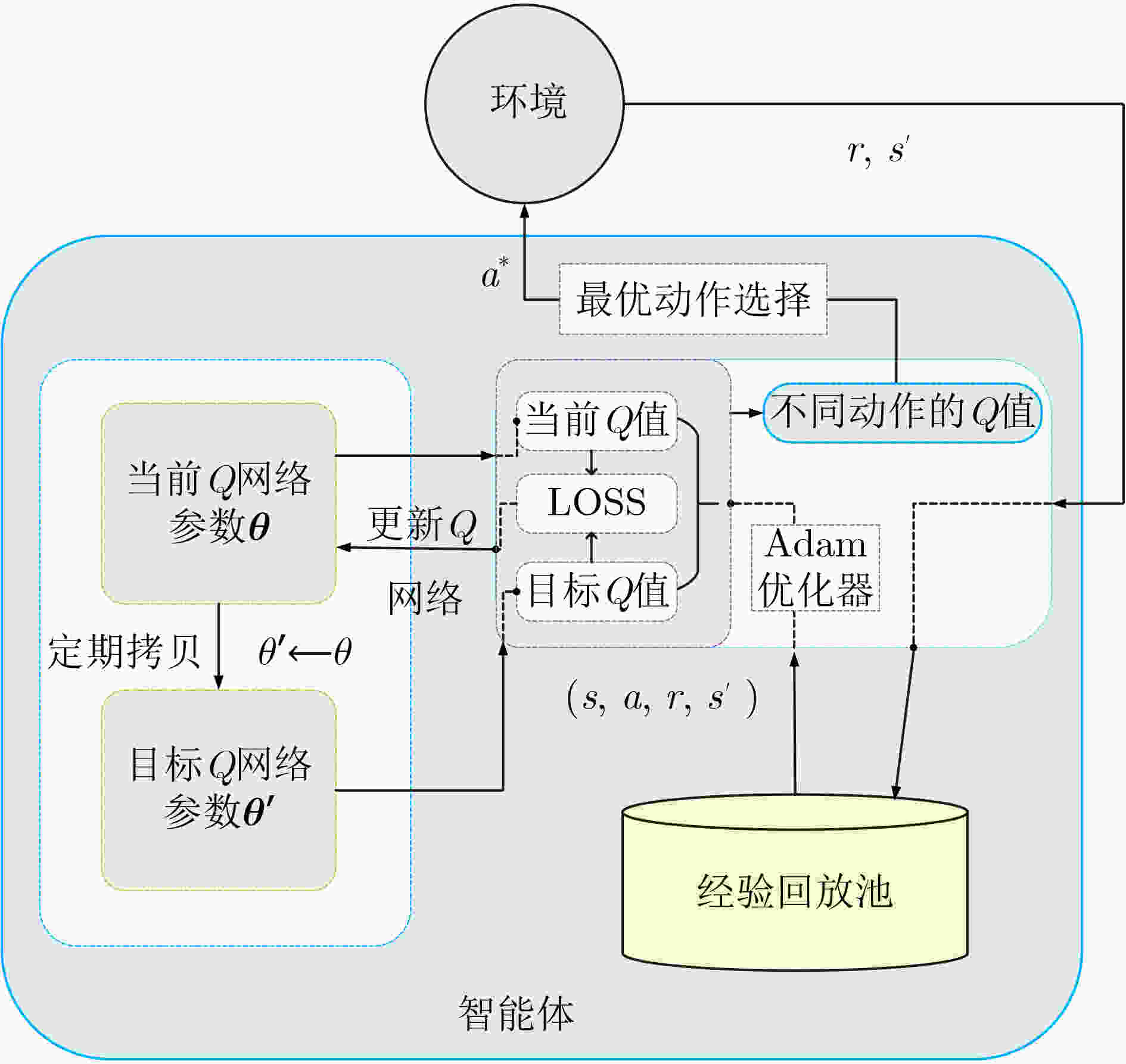
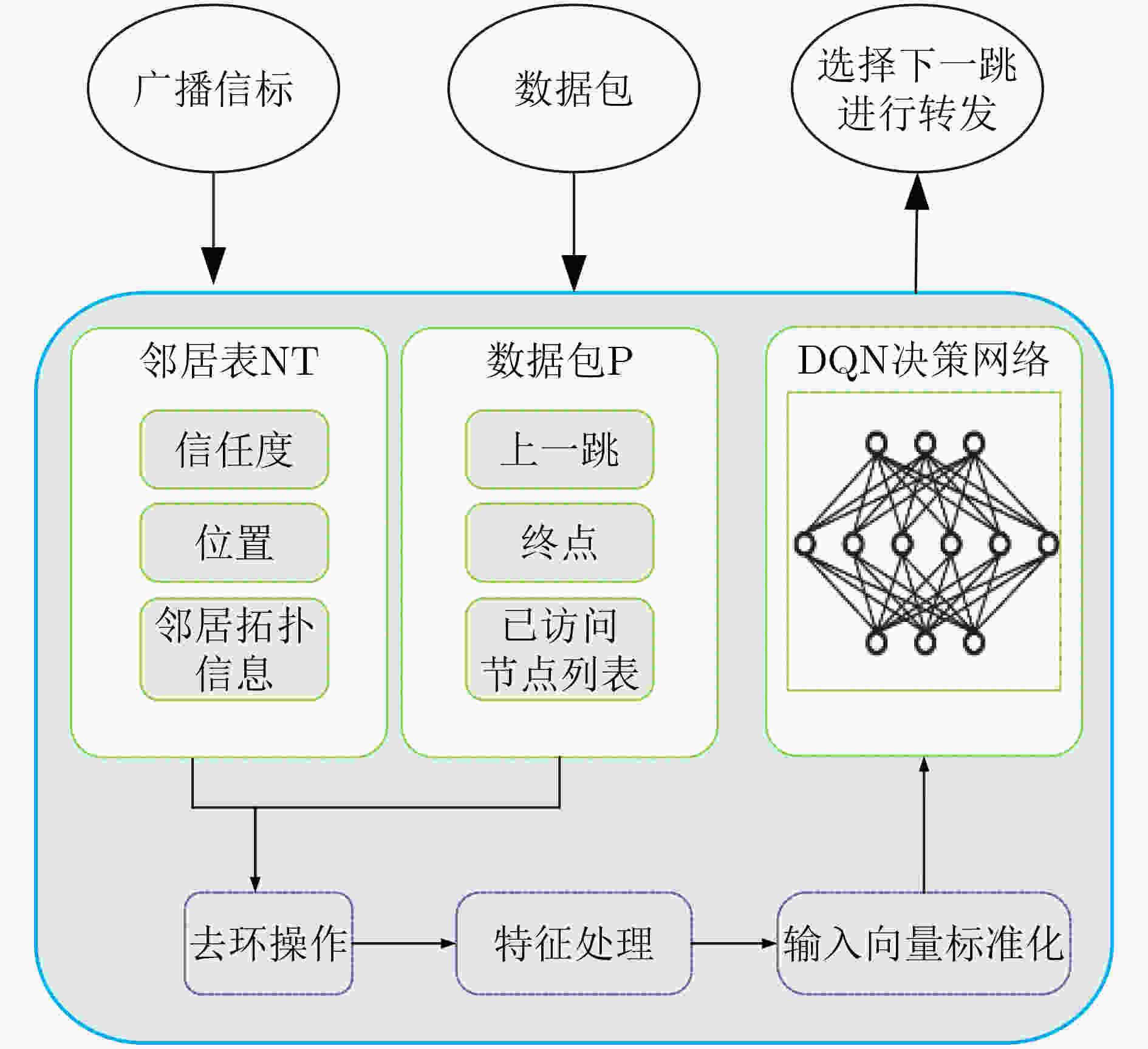
表 1 DTGR路由选择算法(算法1)
输入:当前节点位置${L_c} $,数据包$p $,邻居表${{\rm{NT}}_c}$。 输出:动作${a^*} $。 步骤1:if当前节点$c $是终点则算法结束; else转步骤2~11; 步骤2:根据${{\rm{NT}}_c}$构建邻居编号集合${V_0} $; 步骤3:构建可选下一跳集合${V_l} = {V_0} - {\rm{HVN}}$; 步骤4:if ${V_l} $为空集则算法结束; else转步骤5~11; 步骤5:对节点集
$\forall {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\rm{ID}}_i} \in {V_l},i = 1,2, \cdots ,|{V_l}|$迭代步骤6;步骤6:构建${ {\rm{ID} }_i}$的输入特征向量:
${\bf{in}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} [i] = {\rm{feature}}({L_c},p,{{\rm{NT}}_c})$;步骤7:将${[{\bf{in}}]_{\left| { {V_l} } \right| \times 5} }$归一化后使用DQN网络预测可选下一跳的
${{Q} }$值向量${\boldsymbol{Q} }_c $:${ {\boldsymbol{Q} }_c} = {\rm{DQN} }({\bf{in} }) = [{q_1},{q_2}, \cdots ,{q_{\left| { {V_l} } \right|} }]_{1 \times |{V_l}|}^{\rm{T} }$; 步骤8:if当前处在训练阶段,转步骤9,10; else转步骤11; 步骤9:将本次决策获得的经验e放入经验回放池,更新DQN网
络参数;步骤10:根据式(13)和${{\boldsymbol{Q}}_c}$选择动作${a^*} $;
步骤11:根据公式${a^*} = {\mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{ {q_a} \in { {\boldsymbol{Q} }_c} } }\;\hat Q(s,a;{\boldsymbol{\theta} } )$选择动作${a^*} $。算法结束 表 2 仿真实验参数
仿真参数 设定值 仿真区域大小(km) 2×2 无人机数量 40~120 无人机移动速度(m/s) 3~10 通信半径(m) 350 信标广播周期(s) 0.5 数据包发送频率(Hz) 1 数据包大小(kb) 1 数据包传输速率(Mbps) 1 异常节点比例 0.05~0.25 正常节点信任度阈值 0.7~1.0 异常节点信任度阈值 0.3~0.6 经验回放池大小 2000 DQN学习率$ \alpha $ 0.001 信任权重$ \tau $ 5 折扣因子$ \gamma $ 0.99 贪心算法参数$ \varepsilon $ 0.05 -
[1] BUSHNAQ O M, CHAABAN A, and AL-NAFFOURI T Y. The role of UAV-IoT networks in future wildfire detection[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(23): 16984–16999. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3077593 [2] FENG Wanmei, TANG Jie, YU Yu, et al. UAV-enabled SWIPT in IoT networks for emergency communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(5): 140–147. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900656 [3] BOURSIANIS A D, PAPADOPOULOU M S, DIAMANTOULAKIS P, et al. Internet of things (IoT) and agricultural unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in smart farming: A comprehensive review[J]. Internet of Things, 2022, 18: 100187. doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2020.100187 [4] KHAWAJA W, OZDEMIR O, and GUVENC I. UAV air-to-ground channel characterization for mmWave systems[C]. IEEE 86th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Toronto, Canada, 2017: 1–5. [5] CHEN I R, BAO Fenye, CHANG M J, et al. Dynamic trust management for delay tolerant networks and its application to secure routing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(5): 1200–1210. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.116 [6] CHO J H, SWAMI A, and CHEN I R. A survey on trust management for mobile ad hoc networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2011, 13(4): 562–583. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2011.092110.00088 [7] HYLAND M T, MULLINS B E, BALDWIN R O, et al. Simulation-based performance evaluation of mobile ad hoc routing protocols in a swarm of unmanned aerial vehicles[C]. 21st International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (AINAW'07), Niagara Falls, Canada, 2007: 249–256. [8] KARP B and KUNG H T. GPSR: Greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks[C]. The 6th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Boston, USA, 2000: 243–254. [9] JUNG W S, YIM J, and KO Y B. QGeo: Q-learning-based geographic ad hoc routing protocol for unmanned robotic networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(10): 2258–2261. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2656879 [10] LYU Niqi, SONG Guanghua, YANG Bowei, et al. QNGPSR: A Q-network enhanced geographic ad-hoc routing protocol based on GPSR[C]. 2018 IEEE 88th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Chicago, USA, 2018: 1–6. [11] LIU Jianmin, WANG Qi, HE Chentao, et al. QMR: Q-learning based multi-objective optimization routing protocol for flying ad hoc networks[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 150: 304–316. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2019.11.011 [12] ZHU Haojin, DU Suguo, GAO Zhaoyu, et al. A probabilistic misbehavior detection scheme toward efficient trust establishment in delay-tolerant networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(1): 22–32. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.36 [13] CHO J H and CHEN I R. PROVEST: Provenance-based trust model for delay tolerant networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2018, 15(1): 151–165. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2016.2530705 [14] GE Chunpeng, ZHOU Lu, HANCKE G P, et al. A provenance-aware distributed trust model for resilient unmanned aerial vehicle networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(16): 12481–12489. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3014947 [15] DJEDJIG N, TANDJAOUI D, MEDJEK F, et al. Trust-aware and cooperative routing protocol for IoT security[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2020, 52: 102467. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2020.102467 [16] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
