MSIANet: Multi-scale Interactive Attention Crowd Counting Network
-
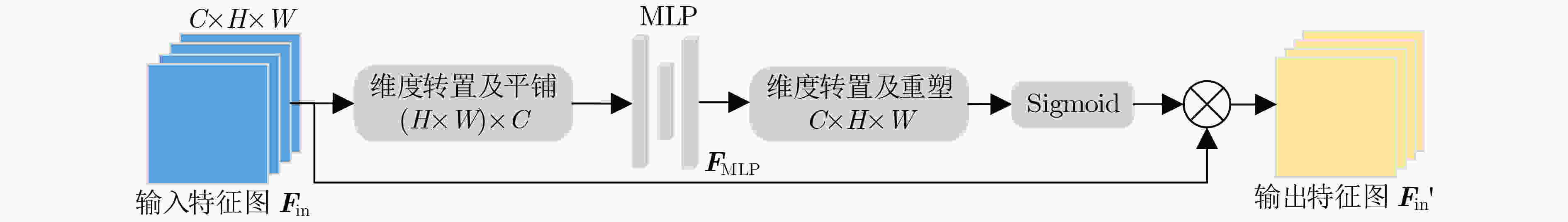
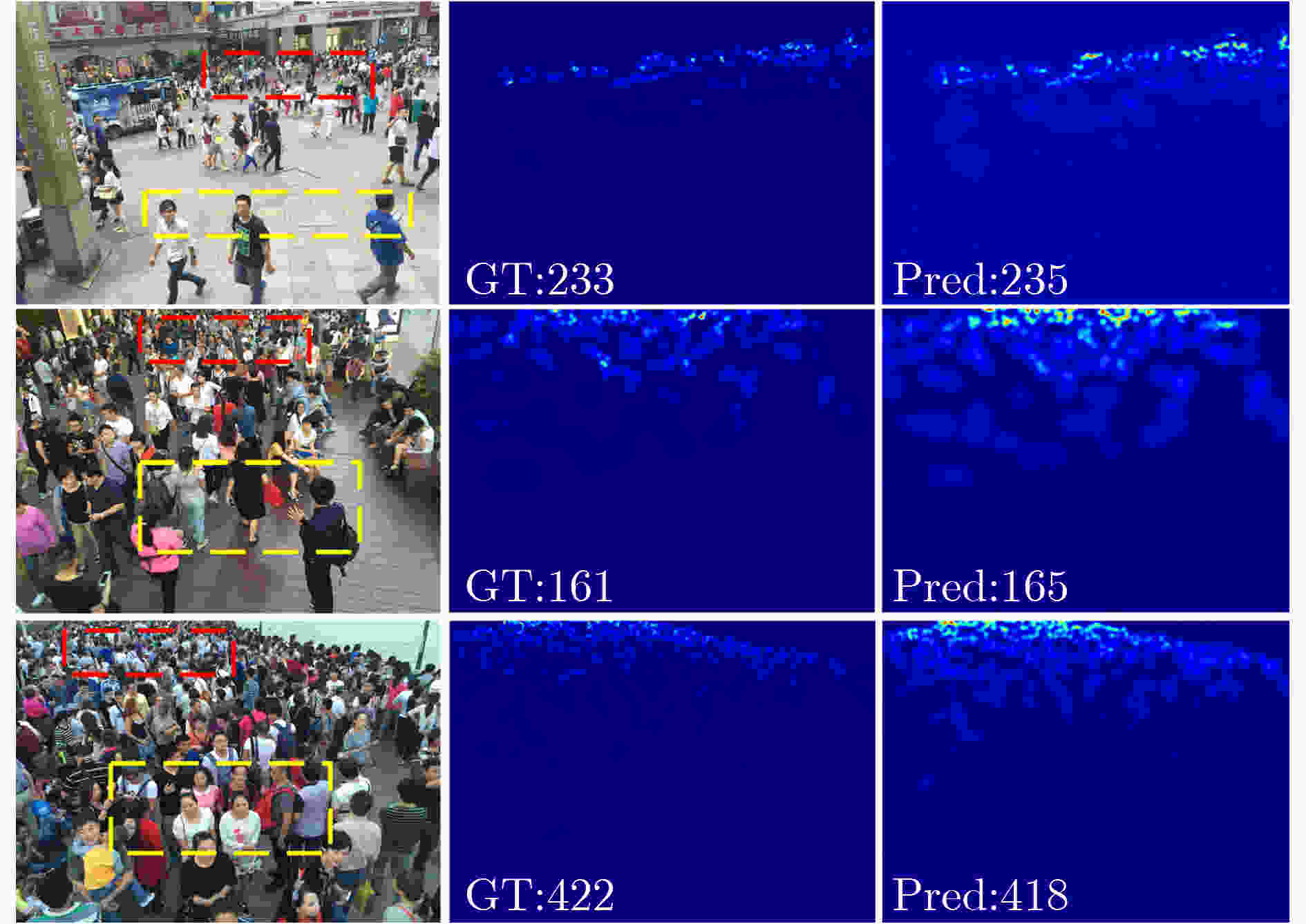
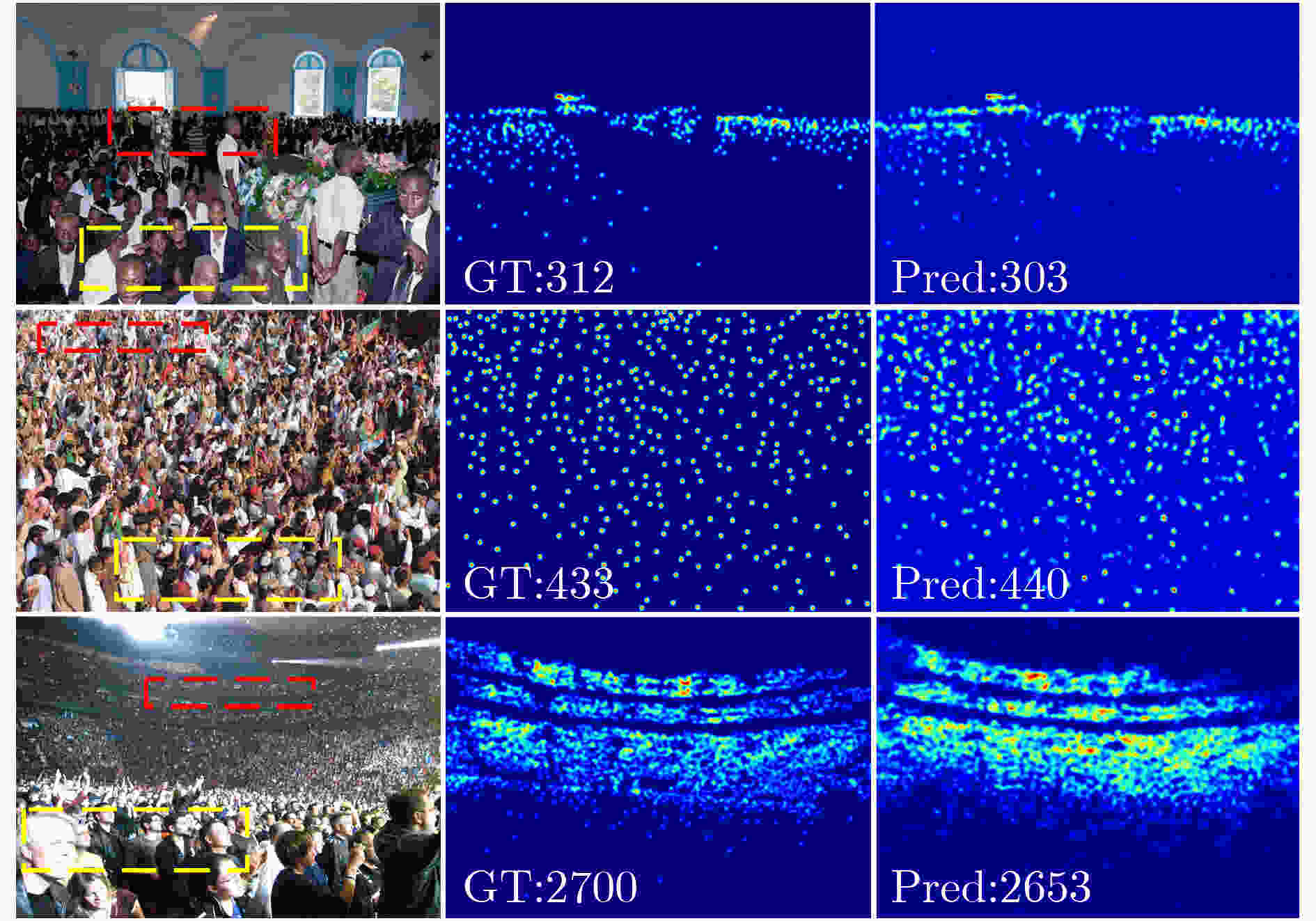
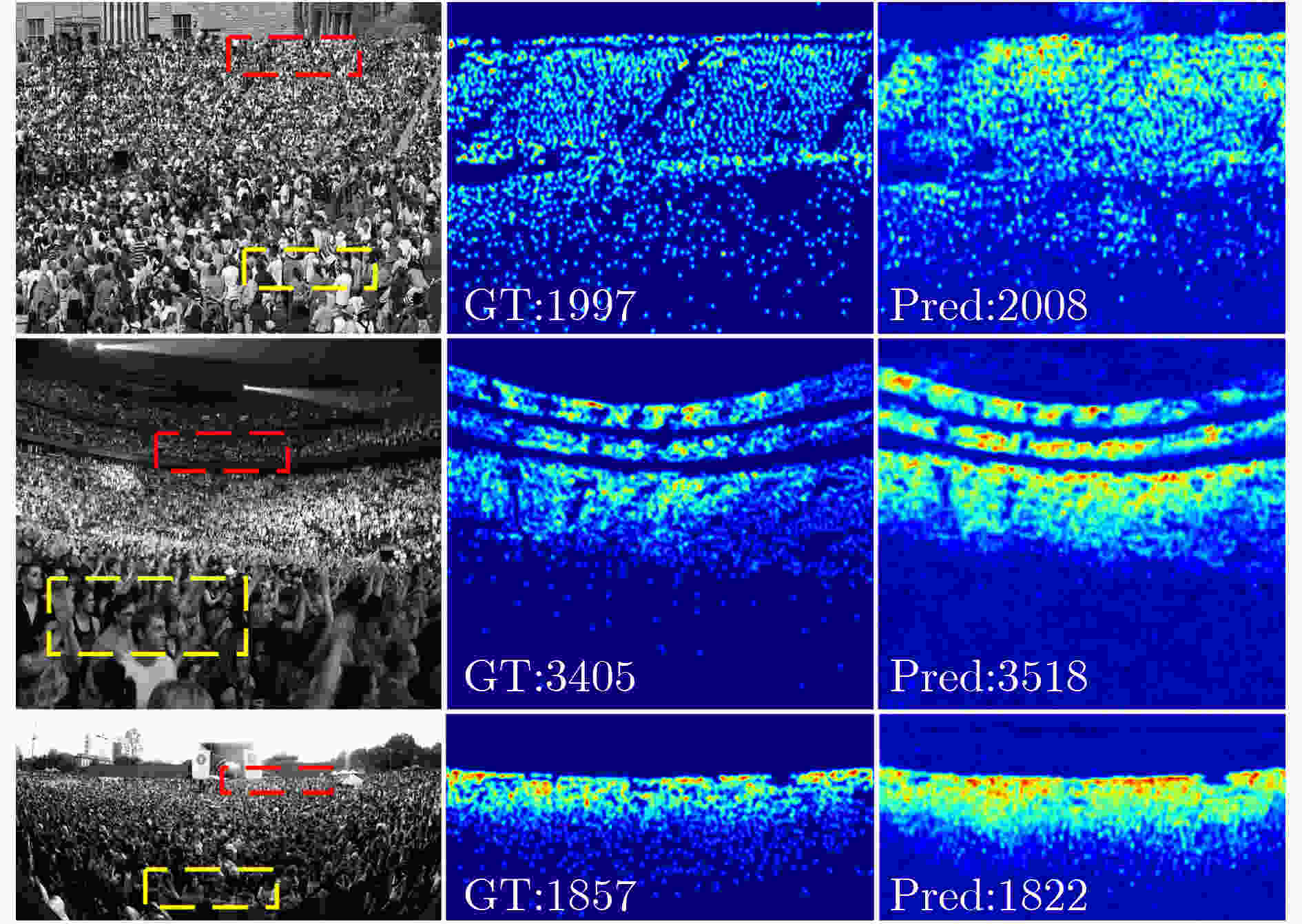
摘要: 尺度变化、遮挡和复杂背景等因素使得拥挤场景下的人群数量估计成为一项具有挑战性的任务。为了应对人群图像中的尺度变化和现有多列网络中规模限制及特征相似性问题,该文提出一种多尺度交互注意力人群计数网络(Multi-Scale Interactive Attention crowd counting Network, MSIANet)。首先,设计了一个多尺度注意力模块,该模块使用4个具有不同感受野的分支提取不同尺度的特征,并将各分支提取的尺度特征进行交互,同时,使用注意力机制来限制多列网络的特征相似性问题。其次,在多尺度注意力模块的基础上设计了一个语义信息融合模块,该模块将主干网络的不同层次的语义信息进行交互,并将多尺度注意力模块分层堆叠,以充分利用多层语义信息。最后,基于多尺度注意力模块和语义信息融合模块构建了多尺度交互注意力人群计数网络,该网络充分利用多层次语义信息和多尺度信息生成高质量人群密度图。实验结果表明,与现有代表性的人群计数方法相比,该文提出的MSIANet可有效提升人群计数任务的准确性和鲁棒性。Abstract: Factors such as scale variation, occlusion and complex backgrounds make crowd number estimation in crowded scenes a challenging task. To cope with the scale variation in crowd images and the scope limitation and the feature similarity problem in existing multi-column networks, a Multi-Scale Interactive Attention crowd counting Network (MSIANet) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, a multi-scale attention module is designed, which uses four branches with different perceptual fields to extract features at different scales and interacts the scale features extracted from each branch. At the same time, an attention mechanism is used to limit the feature similarity problem of the multi-column network. Secondly, a semantic information fusion module is designed based on the multi-scale attention module, which interacts different levels of semantic information of the backbone network and stacks the multi-scale attention module in layers to make full use of the multi-layer semantic information. Finally, a multi-scale interactive attention crowd counting network is constructed based on the multi-scale attention module and the semantic information fusion module, which makes full use of multi-level semantic information and multi-scale information to generate high-quality crowd density maps. The experimental results show that compared with the existing representative crowd counting methods, the proposed MSIANet can effectively improve the accuracy and robustness of the crowd counting task.
-
Key words:
- Crowd counting /
- Estimated density map /
- Attention mechanism /
- Multi-scale features
-
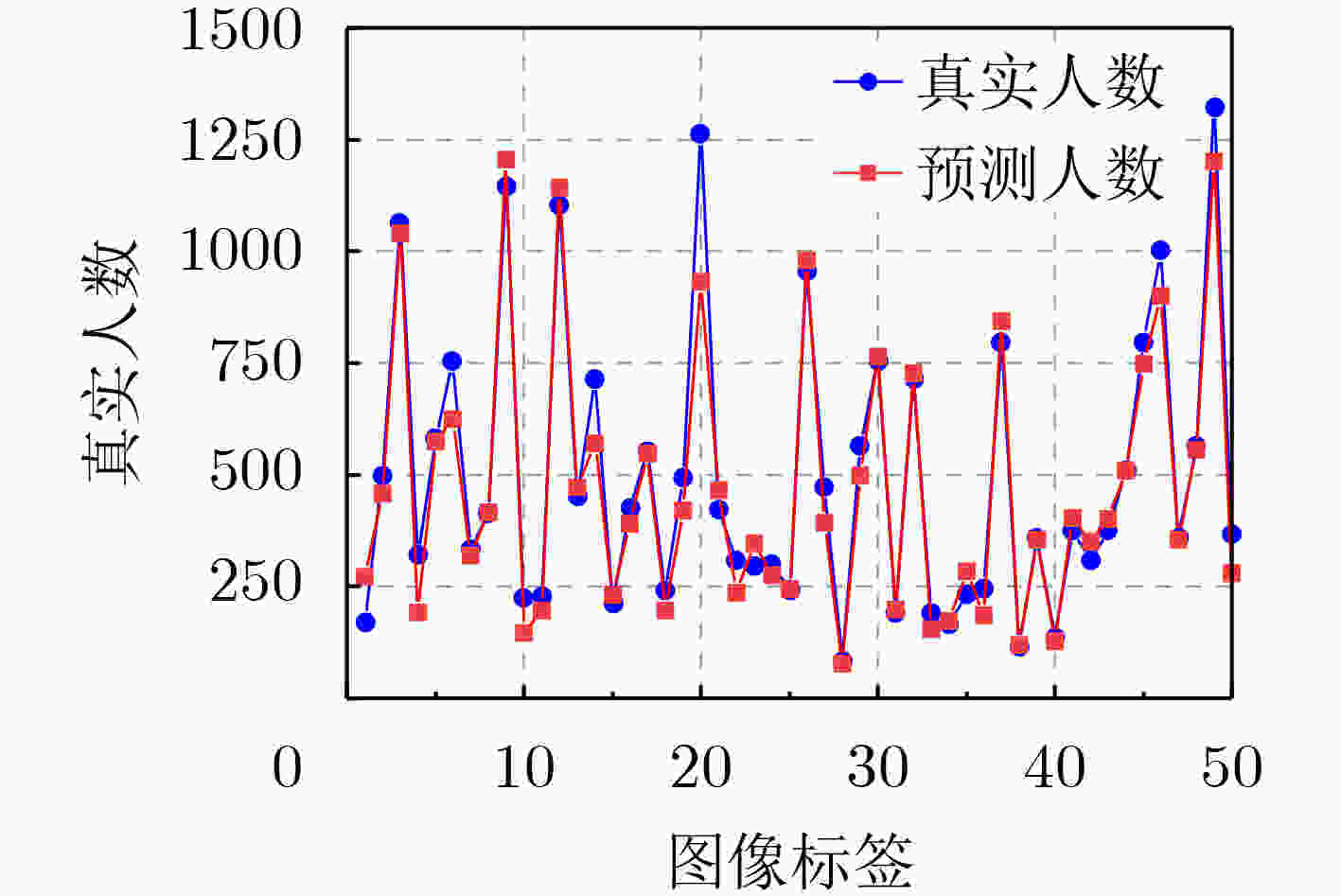
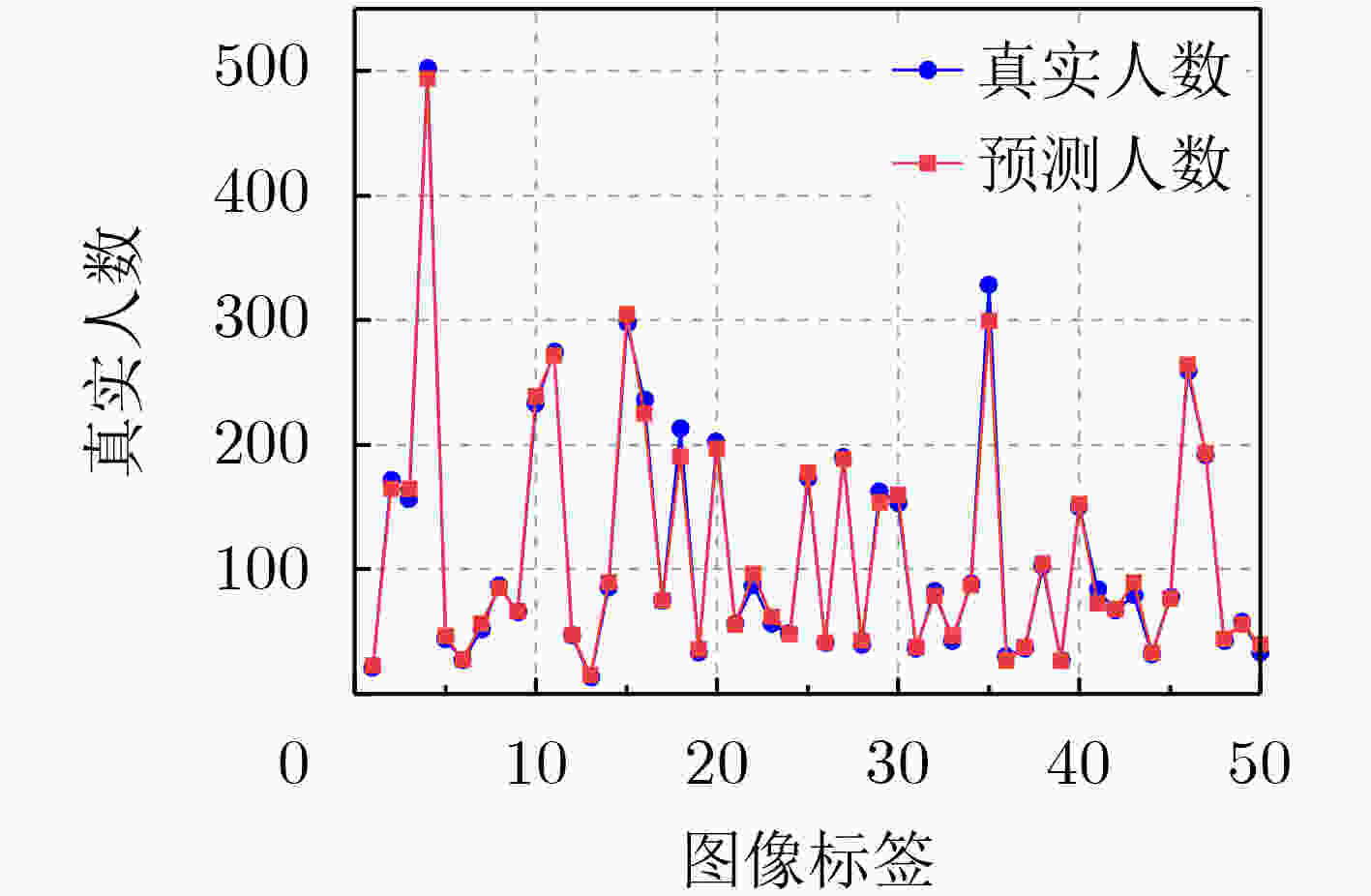
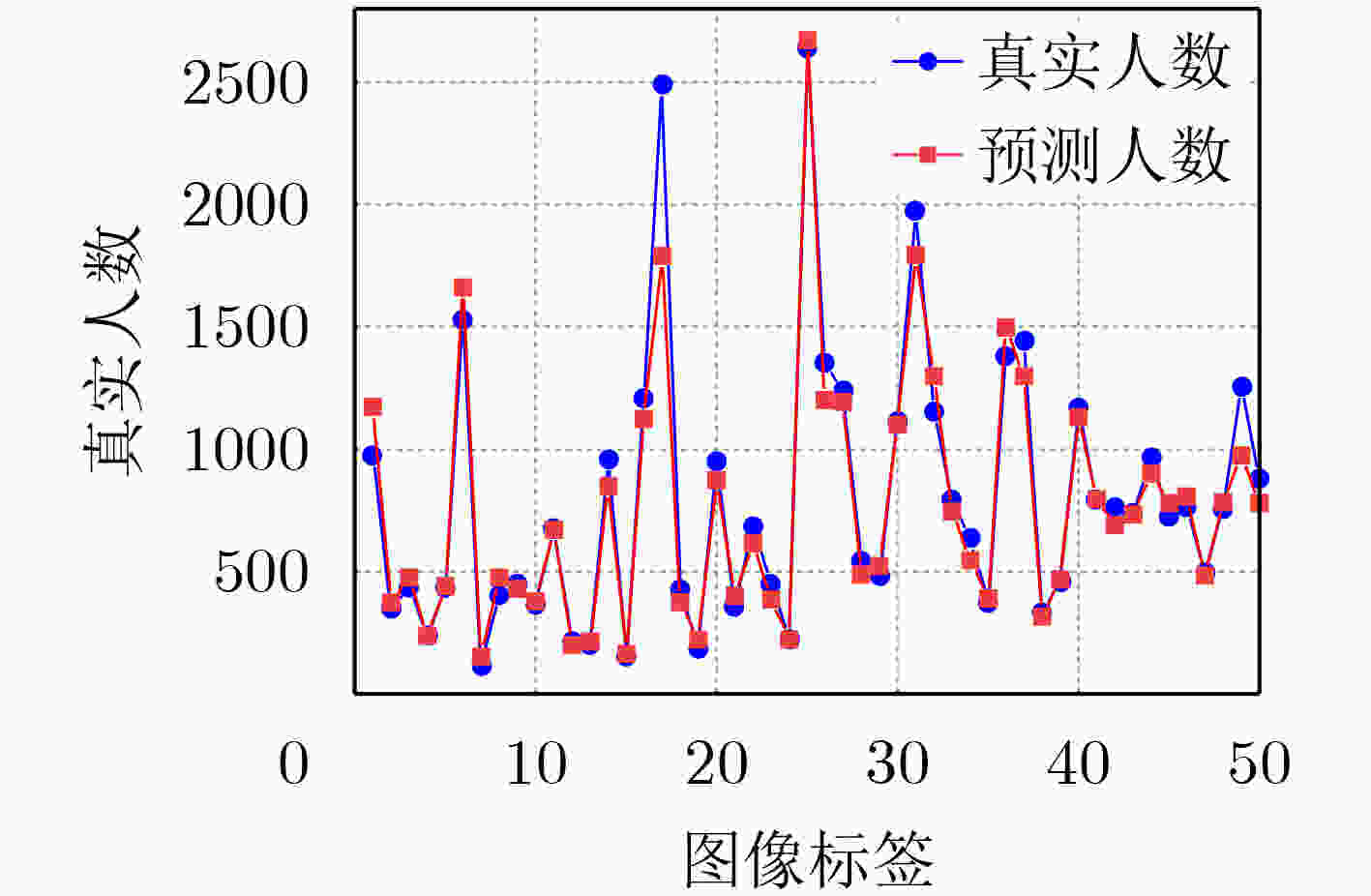
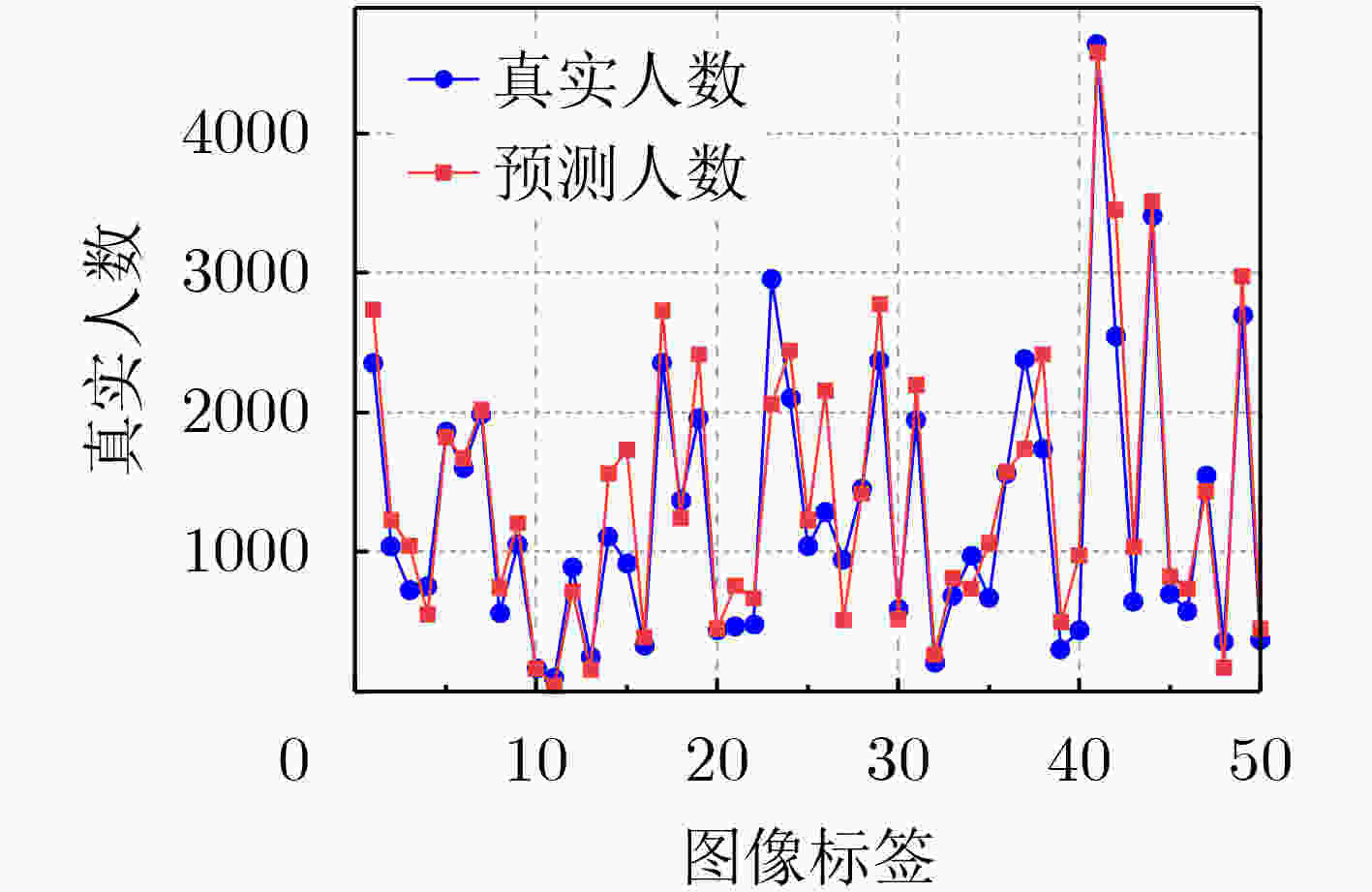
表 1 在3个人群计数基准数据集上使用MAE和RMSE指标进行评估(加粗表示最好结果)
方法 ShanghaiTech A ShanghaiTech B UCF_QNRF UCF_CC_50 MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MCNN [12] (2016) 110.2 173.2 26.4 41.3 277.0 426.0 377.6 509.1 SANet [13] (2018) 67.0 104.5 8.4 13.6 – – 258.4 334.9 CSRNet [7] (2018) 68.2 115.0 10.6 16.0 – – 266.1 397.5 Switch-CNN [14] (2017) 90.4 135.0 21.6 33.4 228.0 445.0 318.1 439.2 ADCrowdNet [19] (2019) 63.2 98.9 8.2 15.7 – – 266.4 358.0 TEDNet [15] (2019) 64.2 109.1 8.2 12.8 113.0 188.0 249.4 354.5 EPA [16] (2020) 60.9 91.6 7.9 11.6 – – 205.1 342.1 DUBNet [8] (2020) 64.6 106.8 7.7 12.5 105.6 180.5 243.8 329.3 DPDNet [17] (2021) 66.6 120.3 7.9 12.4 126.8 208.6 – – MLAttnCNN [20] (2021) – – 7.5 11.6 101.0 175.0 200.8 273.8 URC [9] (2021) 72.8 111.6 12.0 18.7 128.1 218.0 293.9 443.0 MPS [18] (2022) 71.1 110.7 9.6 15.0 – – – – AutoScale [10] (2022) 65.8 112.1 8.6 13.9 104.4 174.2 – – FusionCount [11] (2022) 62.2 101.2 6.9 11.8 – - – – MSIANet(本文) 55.6 99.2 6.6 11.0 94.8 184.6 194.5 273.3 表 2 消融实验结果
变体模型 MAE RMSE MSIANet的前端网络+后端网络 63.4 105.2 MSIANet的前端网络+MASM+后端网络 58.5 101.8 MSIANet w/o MSAM 60.7 101.0 MSIANet w/o GCAM 57.3 100.6 MSIANet w/o GSAM 57.1 99.5 MSIANet 55.6 99.2 -
[1] 徐涛, 段仪浓, 杜佳浩, 等. 基于多尺度增强网络的人群计数方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1764–1771. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200331XU Tao, DUAN Yinong, DU Jiahao, et al. Crowd counting method based on multi-scale enhanced network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1764–1771. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200331 [2] 万洪林, 王晓敏, 彭振伟, 等. 基于新型多尺度注意力机制的密集人群计数算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 1129–1136. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210163WAN Honglin, WANG Xiaomin, PENG Zhenwei, et al. Dense crowd counting algorithm based on new multi-scale attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 1129–1136. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210163 [3] TOPKAYA I S, ERDOGAN H, and PORIKLI F. Counting people by clustering person detector outputs[C]. Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Seoul, Korea (South), 2014: 313–318. [4] LI Min, ZHANG Zhaoxiang, HUANG Kaiqi, et al. Estimating the number of people in crowded scenes by MID based foreground segmentation and head-shoulder detection[C]. Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tampa, USA, 2008: 1–4. [5] CHAN A B, LIANG Z S J, and VASCONCELOS N. Privacy preserving crowd monitoring: Counting people without people models or tracking[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–7. [6] CHEN Ke, LOY C C, GONG Shaogang, et al. Feature mining for localised crowd counting[C]. Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, UK, 2012: 21.1–21.11. [7] LI Yuhong, ZHANG Xiaofan, and CHEN Deming. CSRNet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1091–1100. [8] OH M H, OLSEN P, and RAMAMURTHY K N. Crowd counting with decomposed uncertainty[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 11799–11806. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6852 [9] XU Yanyu, ZHONG Ziming, LIAN Dongze, et al. Crowd counting with partial annotations in an image[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 15550–15559. [10] XU Chenfeng, LIANG Dingkang, XU Yongchao, et al. AutoScale: Learning to scale for crowd counting[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(2): 405–434. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01542-z [11] MA Yiming, SANCHEZ V, and GUHA T. FusionCount: Efficient crowd counting via multiscale feature fusion[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Bordeaux, France, 2022. [12] ZHANG Yingying, ZHOU Desen, CHEN Siqin, et al. Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 589–597. [13] CAO Xinkun, WANG Zhipeng, ZHAO Yanyun, et al. Scale aggregation network for accurate and efficient crowd counting[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 757–773. [14] SAM D B, SURYA S, and BABU R V. Switching convolutional neural network for crowd counting[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4031–4039. [15] JIANG Xiaolong, XIAO Zehao, ZHANG Baochang, et al. Crowd counting and density estimation by trellis encoder-decoder networks[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6126–6135. [16] YANG Yifan, LI Guorong, DU Dawei, et al. Embedding perspective analysis into multi-column convolutional neural network for crowd counting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 30: 1395–1407. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3043122 [17] LIAN Dongze, CHEN Xianing, LI Jing, et al. Locating and counting heads in crowds with a depth prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, To be Published. [18] ZAND M, DAMIRCHI H, FARLEY A, et al. Multiscale crowd counting and localization by multitask point supervision[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Singapore, Singapore, 2022. [19] LIU Ning, LONG Yongchao, ZOU Changqing, et al. ADCrowdNet: An attention-injective deformable convolutional network for crowd understanding[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3220–3229. [20] TIAN Mengxiao, GUO Hao, and LONG Chengjiang. Multi-level attentive convoluntional neural network for crowd counting[J]. arXiv: 2105.11422, 2021. [21] LIU Yichao, SHAO Zongru, and HOFFMANN N. Global attention mechanism: Retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions[J]. arXiv: 2112.05561, 2021. [22] IDREES H, TAYYAB M, ATHREY K, et al. Composition loss for counting, density map estimation and localization in dense crowds[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 544–559. [23] IDREES H, SALEEMI I, SEIBERT C, et al. Multi-source multi-scale counting in extremely dense crowd images[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 2547–2554. -





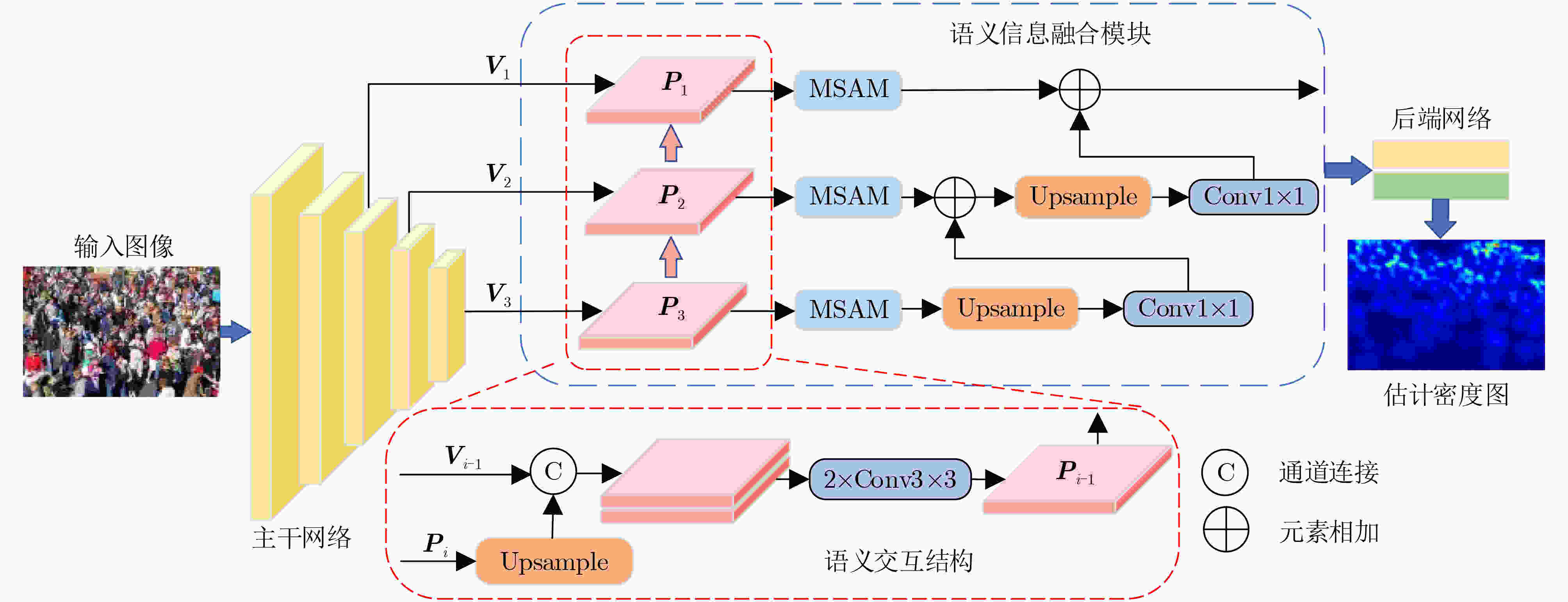
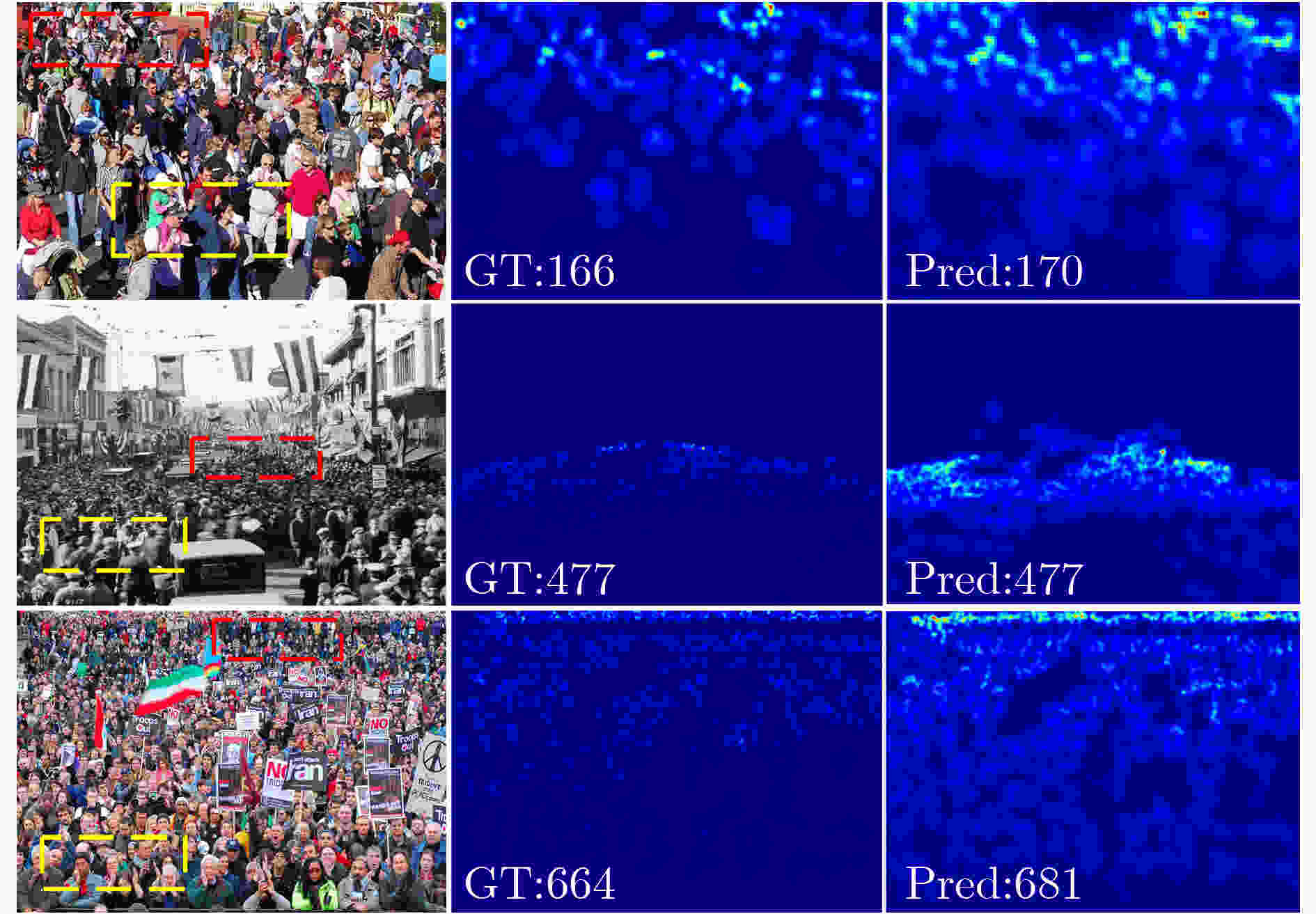
 下载:
下载:
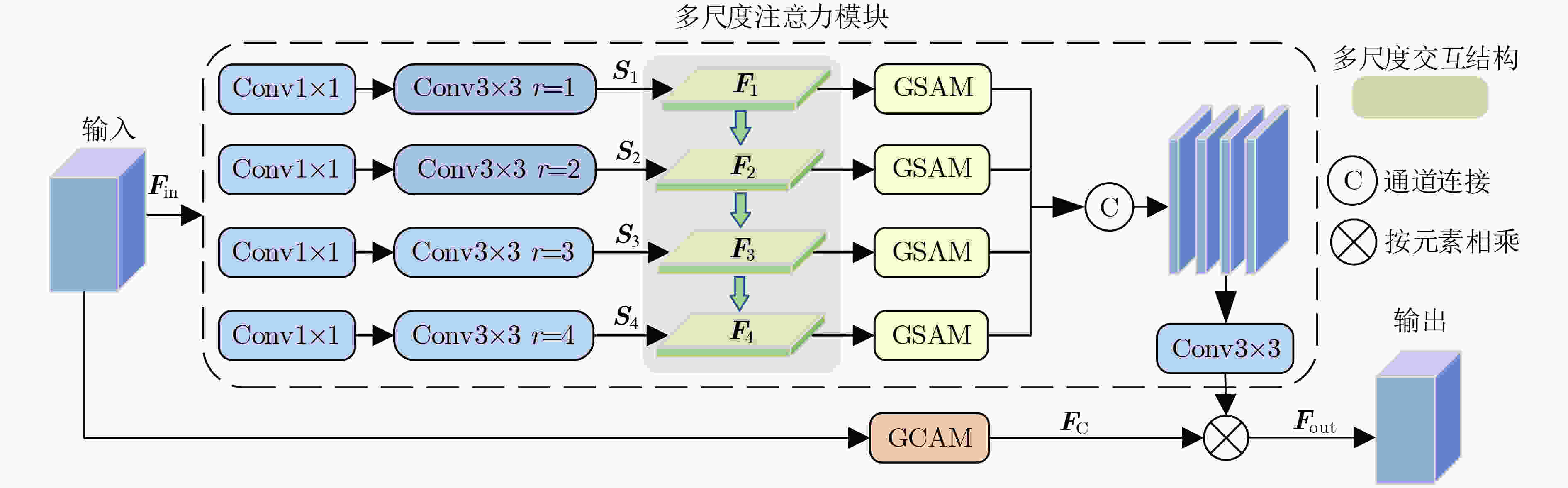
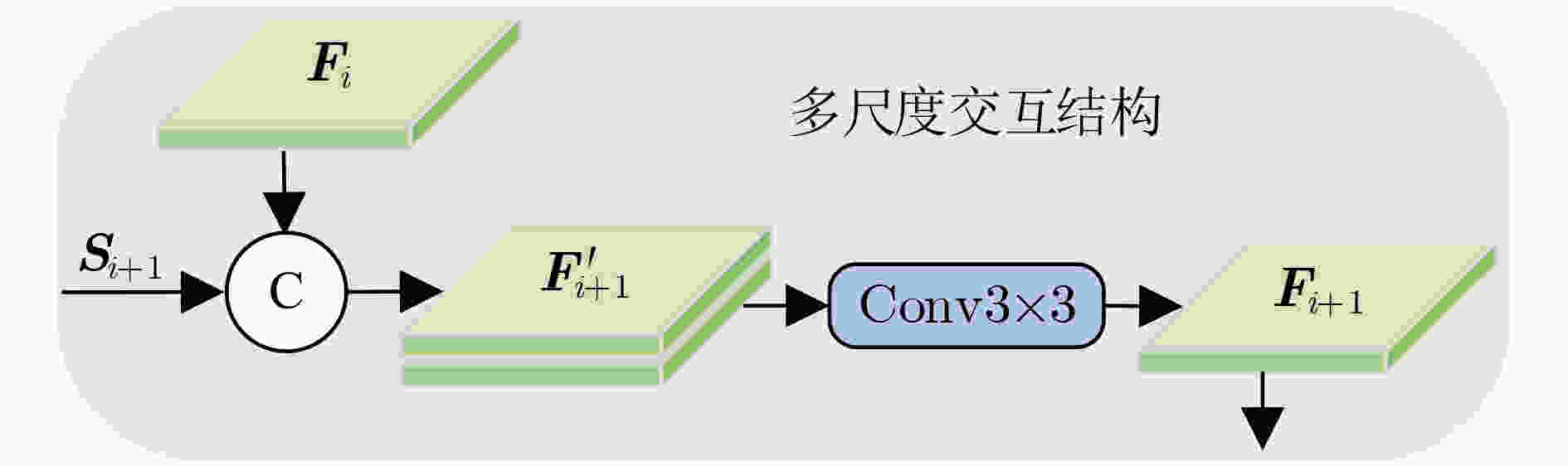
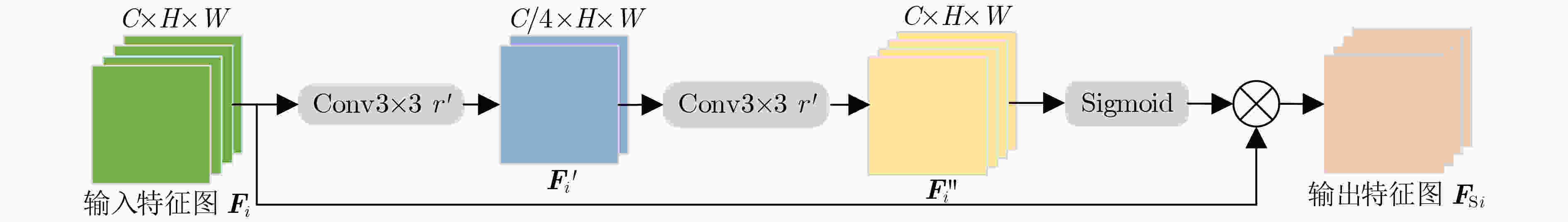



 下载:
下载:
