Optical Quantum Imaging Method Based on Filter Optimization of Coincidence Counting
-
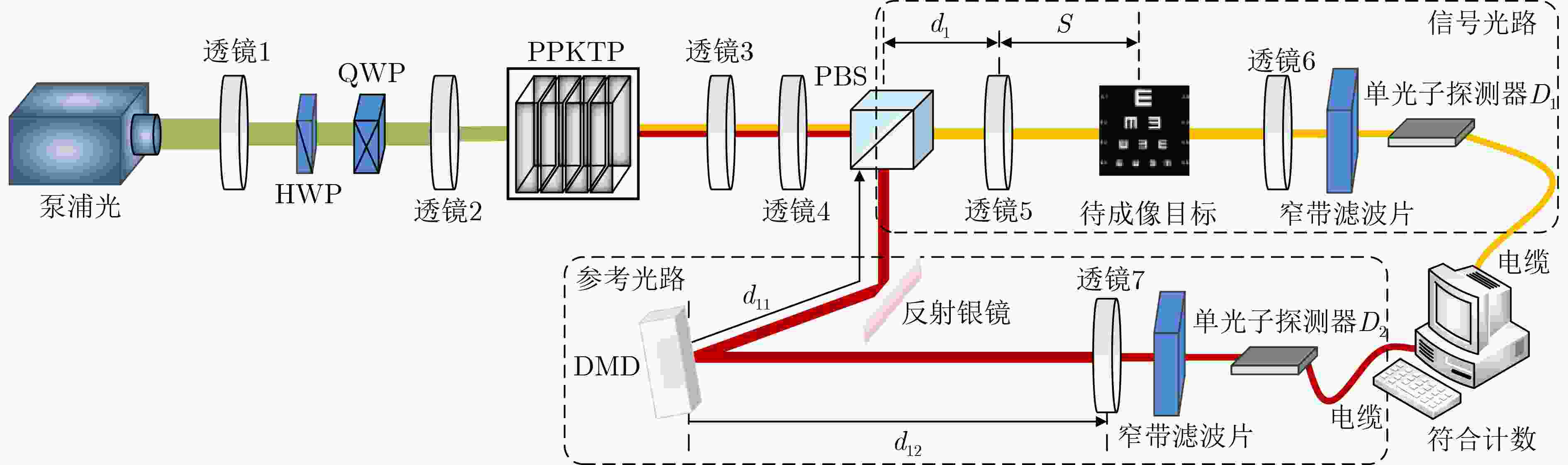
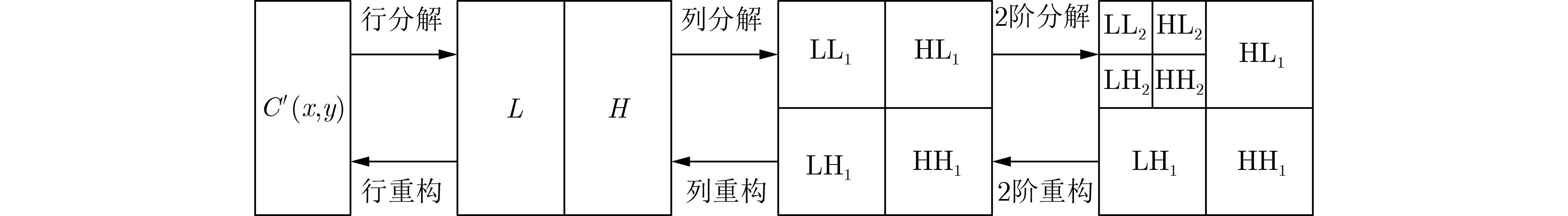
摘要: 量子成像(QI)具有抗侦察、抗干扰和高分辨力等特性,是量子光学领域重要的研究方向。为了解决实际量子成像过程中因环境光引起符合计数值异常所导致成像质量下降的问题,该文提出一种基于符合计数滤波优化的光量子成像方法。首先,对原始的符合计数值进行3层离散小波变换(DWT)得到相应的小波系数;然后,对小波系数中的高频成分进行高斯滤波去噪,并通过小波逆变换得到去噪后的符合计数值;最后,基于该符合计数值,利用线性映射方法实现对目标的量子成像。该文通过仿真分析了图像像素数、单像素曝光时间和符合门宽值对成像结果的影响,并搭建了实际的量子成像光路来验证仿真结果的有效性。Abstract: Quantum Imaging(QI) is an important research direction in the field of quantum optics due to its anti-reconnaissance, anti-interference and high resolution. In order to solve the problem of image quality degradation caused by the abnormal coincidence count value caused by ambient light in the actual quantum imaging process, a photon quantum imaging method based on coincidence count filter optimization is proposed in this paper. Firstly, three-layer Discrete Wavelet Transform(DWT) on the original coincident count values is performed to obtain the corresponding wavelet coefficients. Secondly, Gaussian filtering is performed to denoise the high-frequency components in the wavelet coefficients, and the denoised coincident count values through inverse wavelet transform is obtained in this paper. Finally, according to these coincidence count values, the linear mapping method is used to achieve quantum imaging of the target. In this paper, the influence of image pixel number, single pixel exposure time and coincidence gate width on imaging results by simulation are analyzed, and the actual quantum imaging optical path is built to verify the validity of the simulation analysis.
-
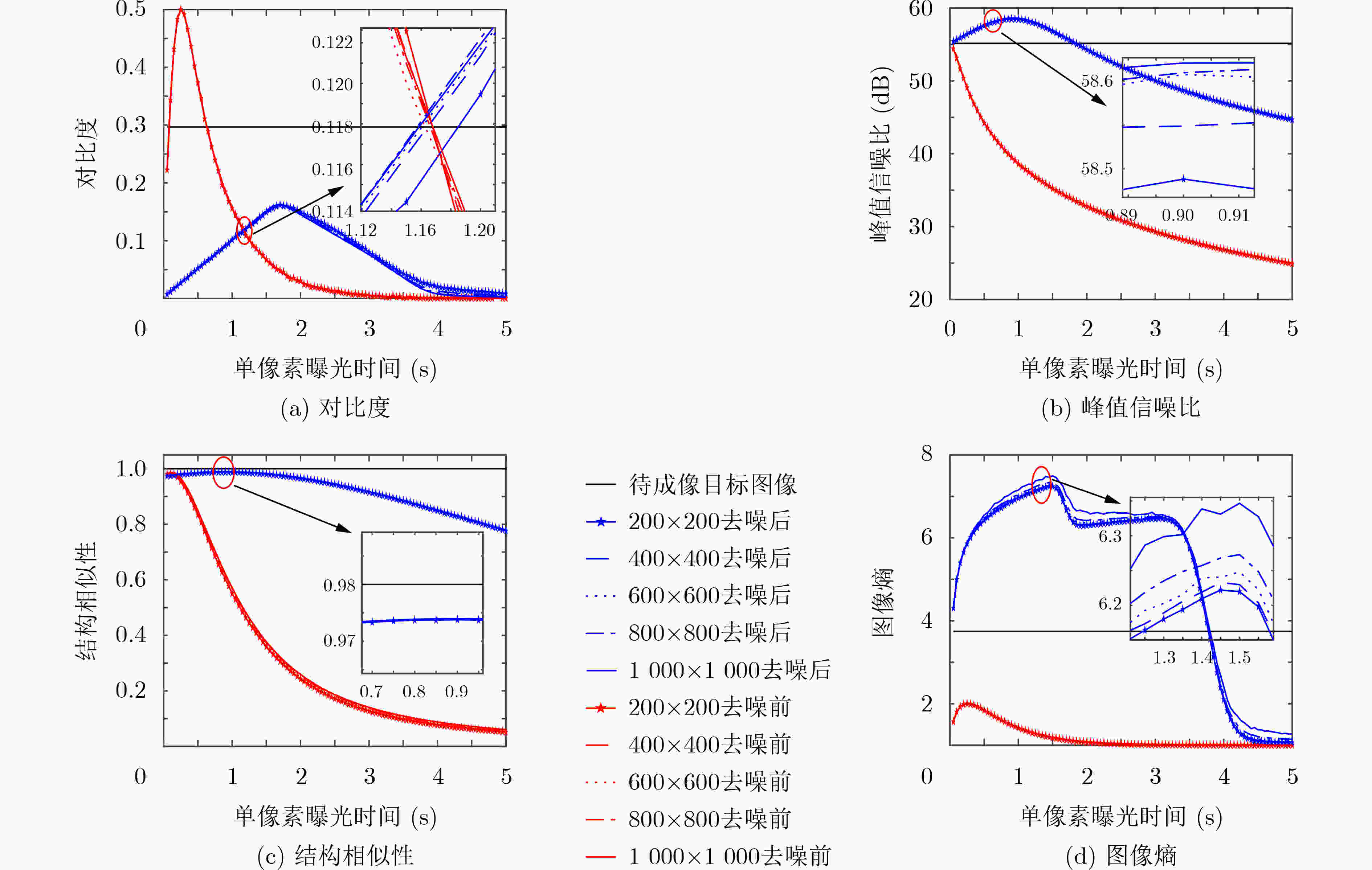
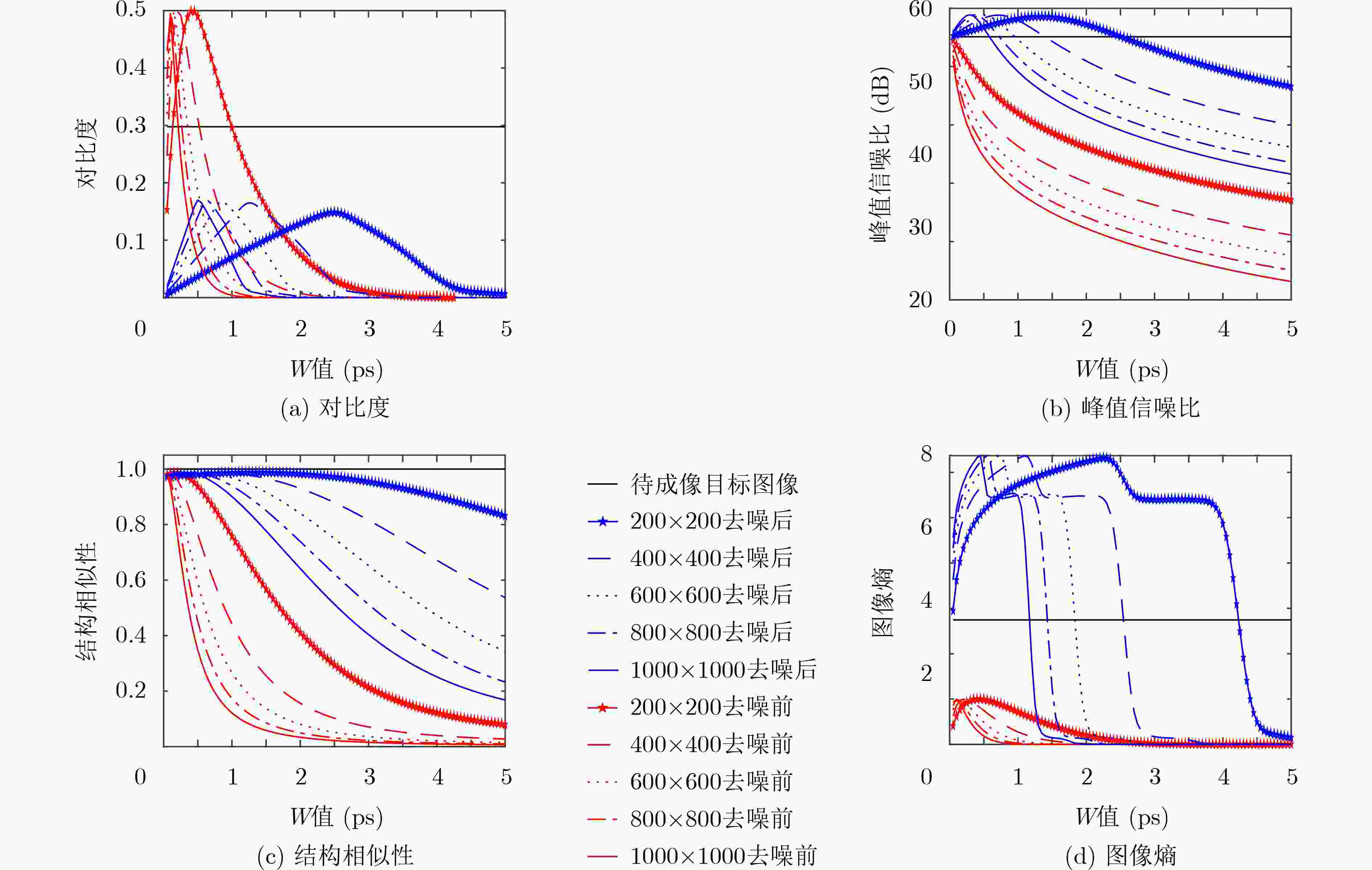
表 1 不同图像像素数对成像结果的影响
$ 200 \times 200 $ $ 400 \times 400 $ $ 600 \times 600 $ $ 800 \times 800 $ $1\;000 \times 1\;000$ 去噪前 




去噪后 




表 2 不同图像像素数下的成像结果
$8 \times 8$ $14 \times 14$ $20 \times 20$ 去噪前 


去噪前 


表 3 不同单像素曝光时间(SPET)下的成像结果
0.5 s 1.5 s 2.5 s 去噪前 


去噪后 


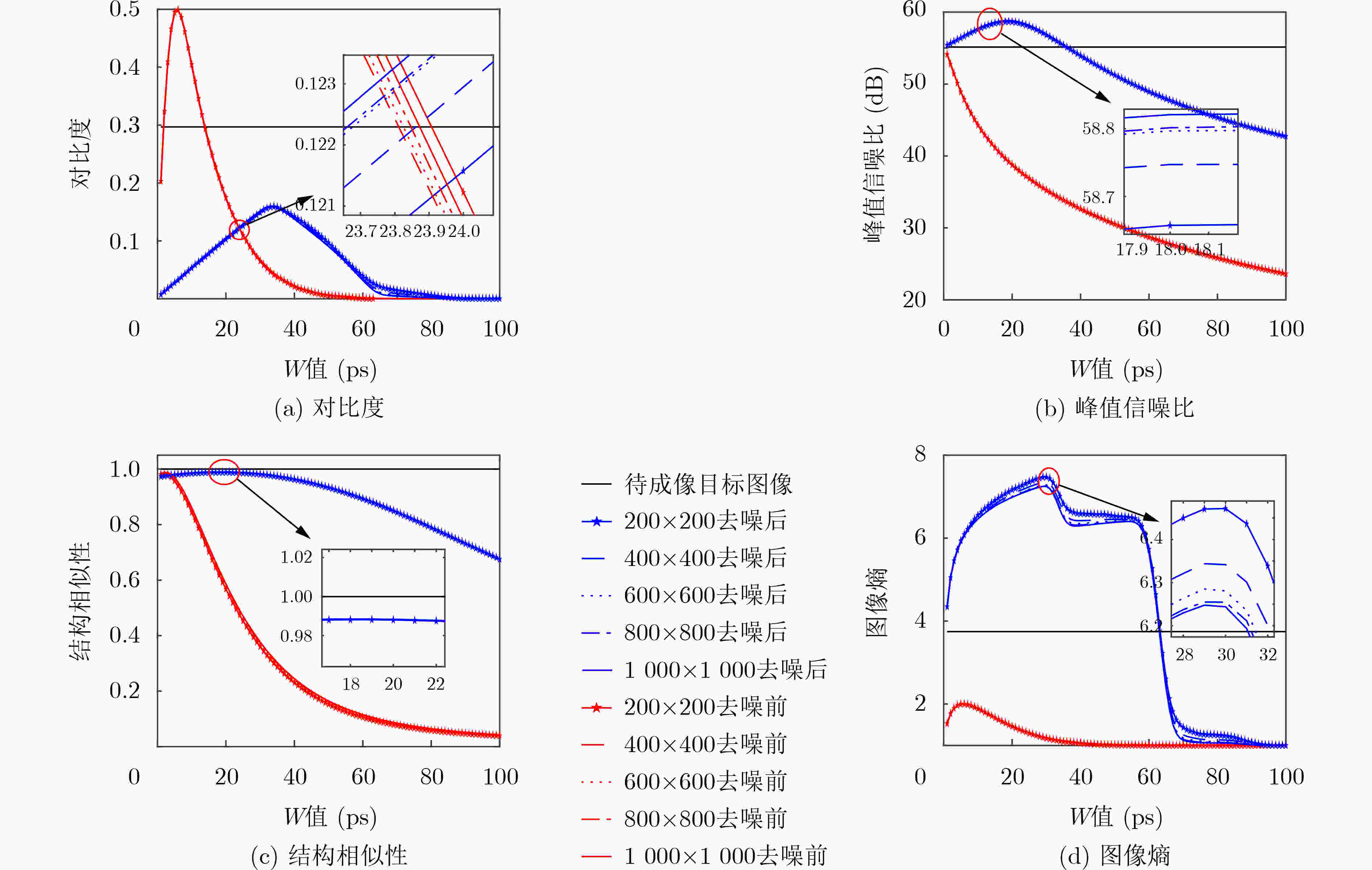
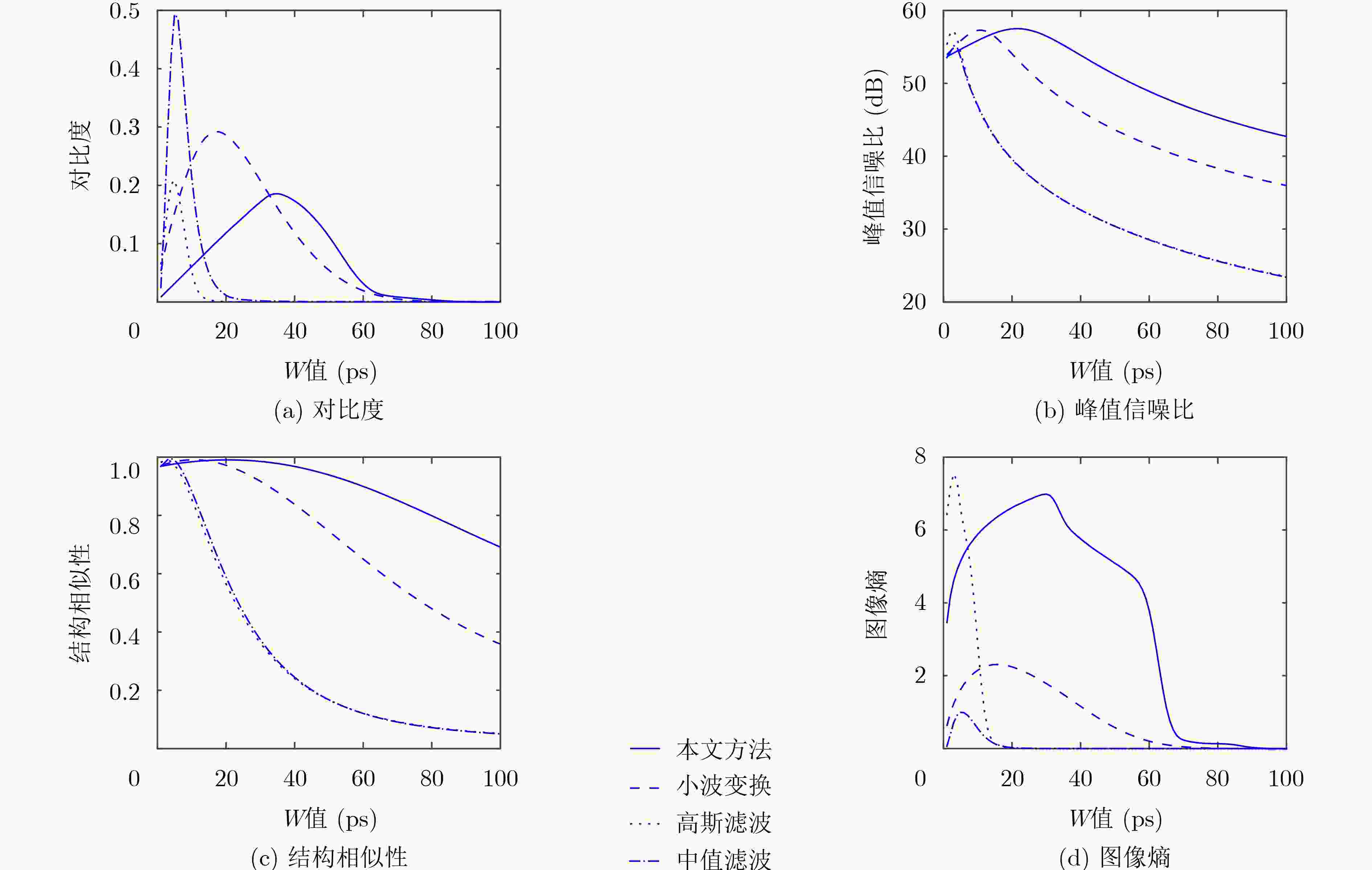
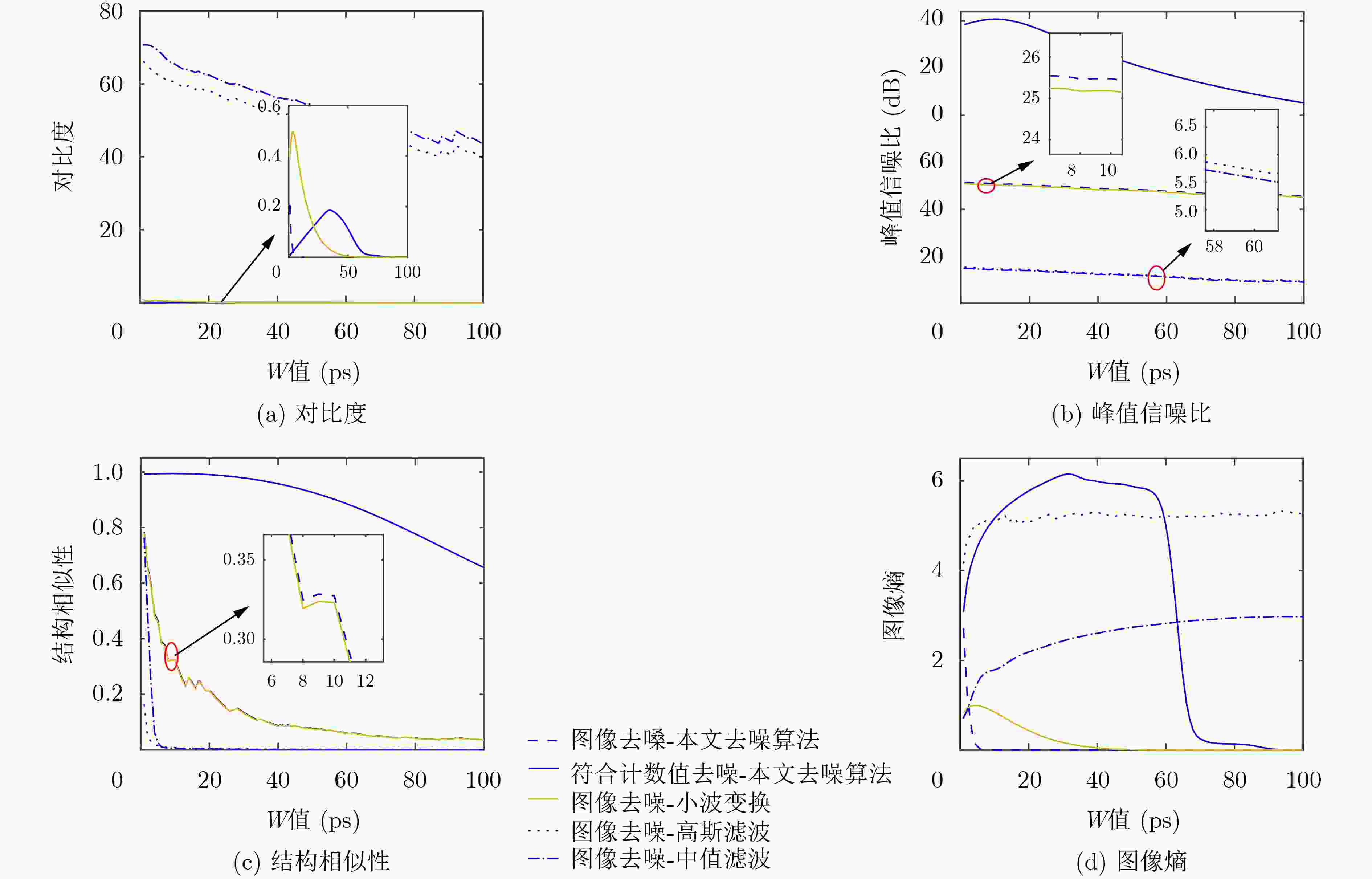
表 4 不同符合门宽值(W)下的成像结果
15 ps 30 ps 45 ps 去噪前 


去噪后 


-
[1] GILABERTE BASSET M, SETZPFANDT F, STEINLECHNER F, et al. Perspectives for applications of quantum imaging[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2019, 13(10): 1900097. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201900097 [2] 杨蕴, 李玉, 王玉. 一种数学形态学的量子图像去噪方法[J]. 遥感信息, 2018, 33(2): 17–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2018.02.003YANG Yun, LI Yu, and WANG Yu. A mathematical morphology method for quantum image denoising[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2018, 33(2): 17–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2018.02.003 [3] 王文远. 基于图像信噪比选择优化高斯滤波尺度[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(10): 2483–2487. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01392WANG Wenyuan. Selecting the optimal Gaussian filtering scale via the SNR of image[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(10): 2483–2487. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01392 [4] ZHAO Yuxing, LI Yue, and YANG Baojun. Low-frequency desert noise intelligent suppression in seismic data based on multiscale geometric analysis convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(1): 650–665. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2938836 [5] 张智, 林栩凌, 何红艳. 一种基于量子力学的遥感图像滤波方法研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2016, 45(S2): S226001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201645.S226001ZHANG Zhi, LIN Xuling, and HE Hongyan. Filtering method for remote sensing image based on quantum mechanics[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(S2): S226001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201645.S226001 [6] 毕思文, 陈浩, 帅通, 等. 一种基于双树复小波变换的图像去噪算法[J]. 无线电工程, 2019, 49(1): 27–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2019.01.06BI Siwen, CHEN Hao, SHUAI Tong, et al. An image denoising algorithm based on double-tree complex wavelet transform[J]. Radio Engineering, 2019, 49(1): 27–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2019.01.06 [7] CHEN Yan, NI Rui, WU Yaodong, et al. Phase-matching controlled orbital angular momentum conversion in periodically poled crystals[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(14): 143901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.143901 [8] MAGAÑA-LOAIZA O S and BOYD R W. Quantum imaging and information[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2019, 82(12): 124401. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ab5005 [9] ABEBE T, GEMECHU N, SHOGILE K, et al. Entanglement quantification using various inseparability criteria for correlated photons[J]. Romanian Journal of Physics, 2020, 65(3/4): 107. [10] SHAPIRO J H and BOYD R W. The physics of ghost imaging[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2012, 11(4): 949–993. doi: 10.1007/s11128-011-0356-5 [11] XU Chenni and WANG Ligang. Theory of light propagation in arbitrary two-dimensional curved space[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(12): 2486–2493. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.435993 [12] NDAGANO B, DEFIENNE H, LYONS A, et al. Imaging and certifying high-dimensional entanglement with a single-photon avalanche diode camera[J]. npj Quantum Information, 2020, 6(1): 94. doi: 10.1038/s41534-020-00324-8 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
