Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Path Planning Method Based on Search Rule and Cross Entropy Optimization
-
摘要: 针对快速扩展随机树(RRP)算法计算效率低、不具备渐进最优性等问题,该文提出一种基于搜索规则和交叉熵优化的改进RRT(IRRT)算法。在路径搜索过程中根据当前节点位置及搜索规则,调整搜索步长及搜索方向,实现高效、快速的初始路径规划。然后,利用交叉熵理论优化初始路径,使得路径具备渐进最优性。仿真实验1结果表明所提方法的有效性和收敛性,仿真实验2将该文所提算法与多种变体RRT算法进行比较,结果表明所提算法能够保证计算效率,同时使得路径具备渐进最优性。
-
关键词:
- 无人机 /
- 路径规划 /
- 改进快速扩展随机树算法 /
- 路径优化 /
- 交叉熵
Abstract: The Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT) algorithm has some shortcomings, including low computation efficiency and non-asymptotic optimality. An Improved RRT (IRRT) algorithm based on search rules and cross entropy optimization is presented in this paper. In the path search process, according to the current node position and search rules, the search step size and search direction are adjusted to achieve efficient and rapid initial path planning. Then, the cross entropy theory is applied to optimize the initial path, so that the path has the characteristic of asymptotic optimality. The simulation results of experiment 1 show the effectiveness and convergence of the proposed method, in the second simulation experiment, the proposed algorithm is compared with several variant RRT algorithms, and the results show that the proposed algorithm can ensure the computational efficiency and make the path has the characteristic of asymptotic optimality. -
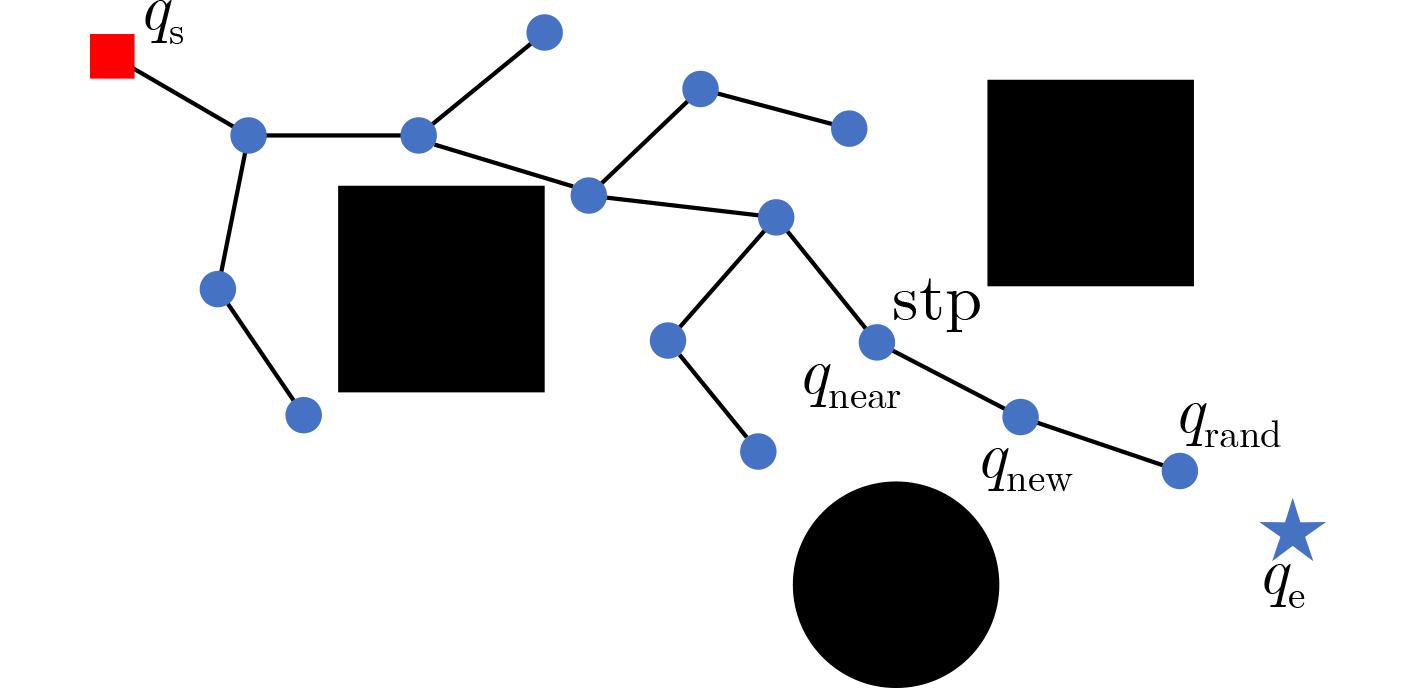
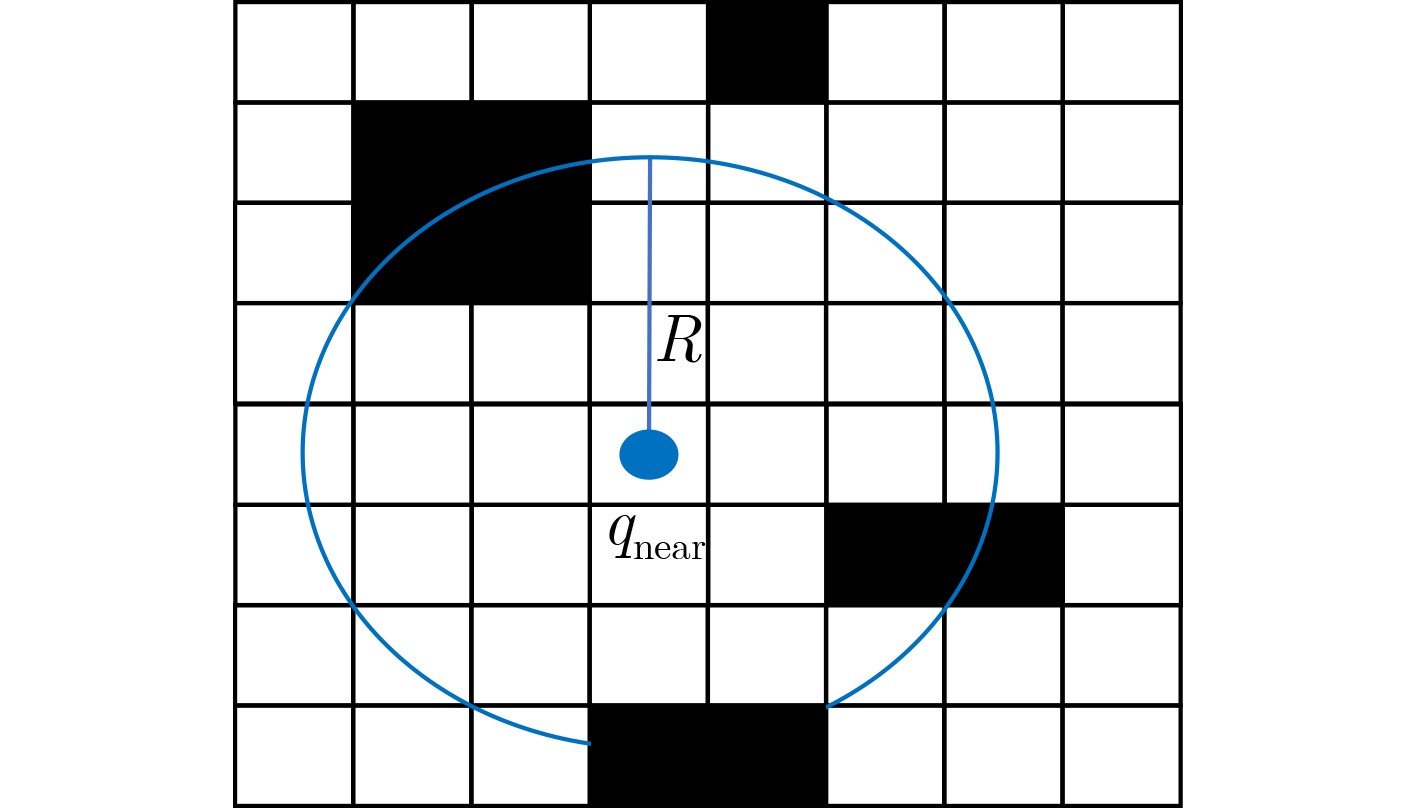
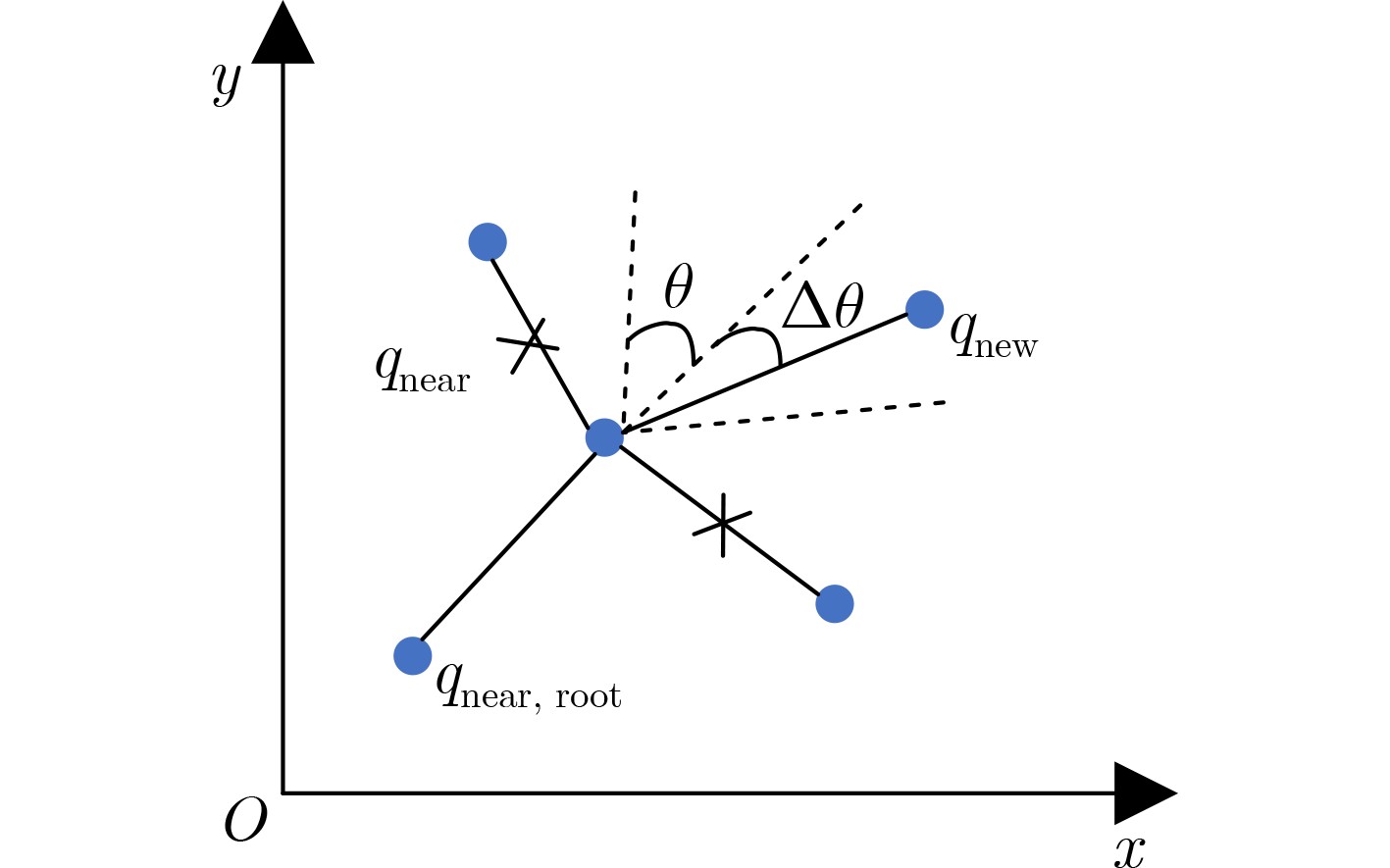
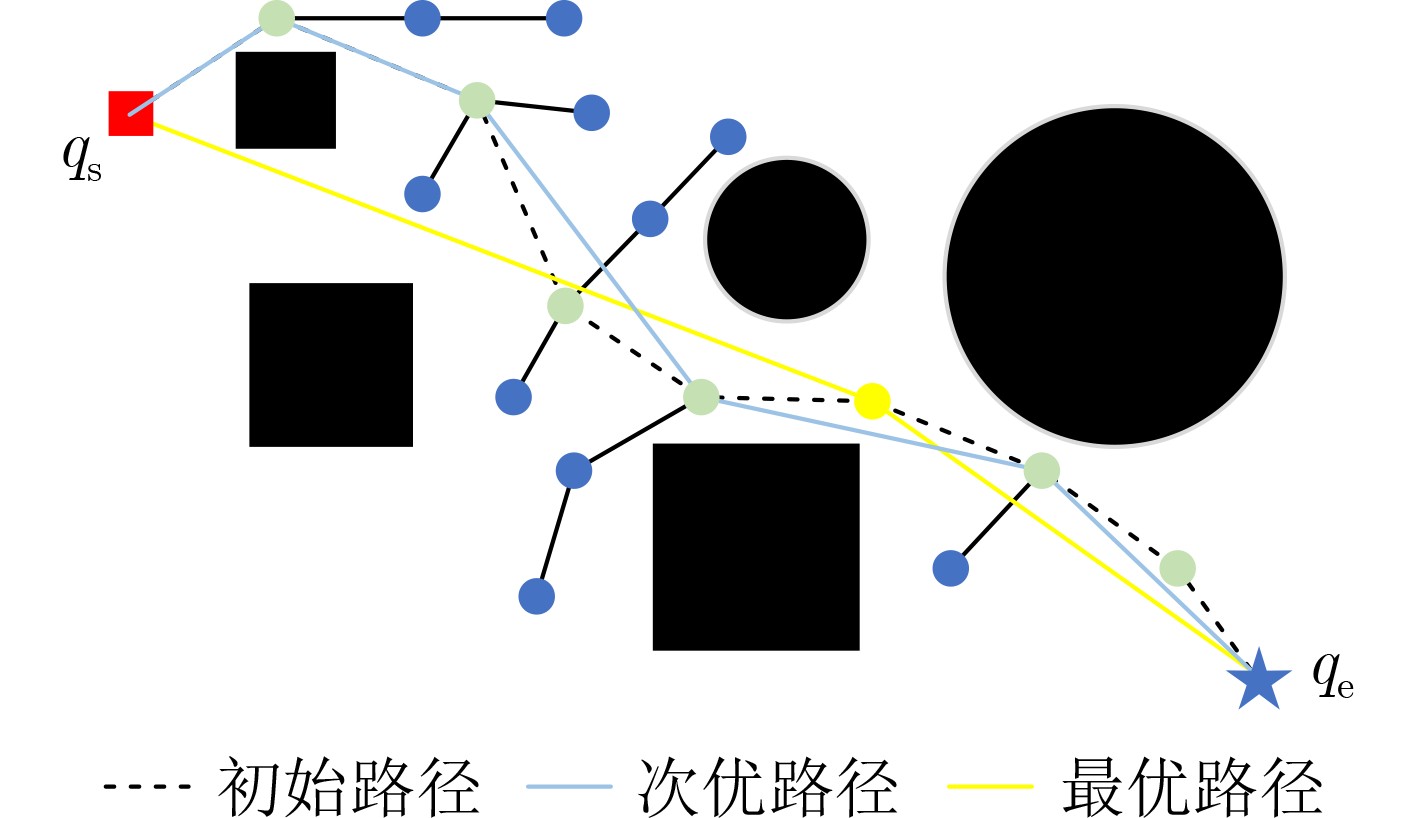
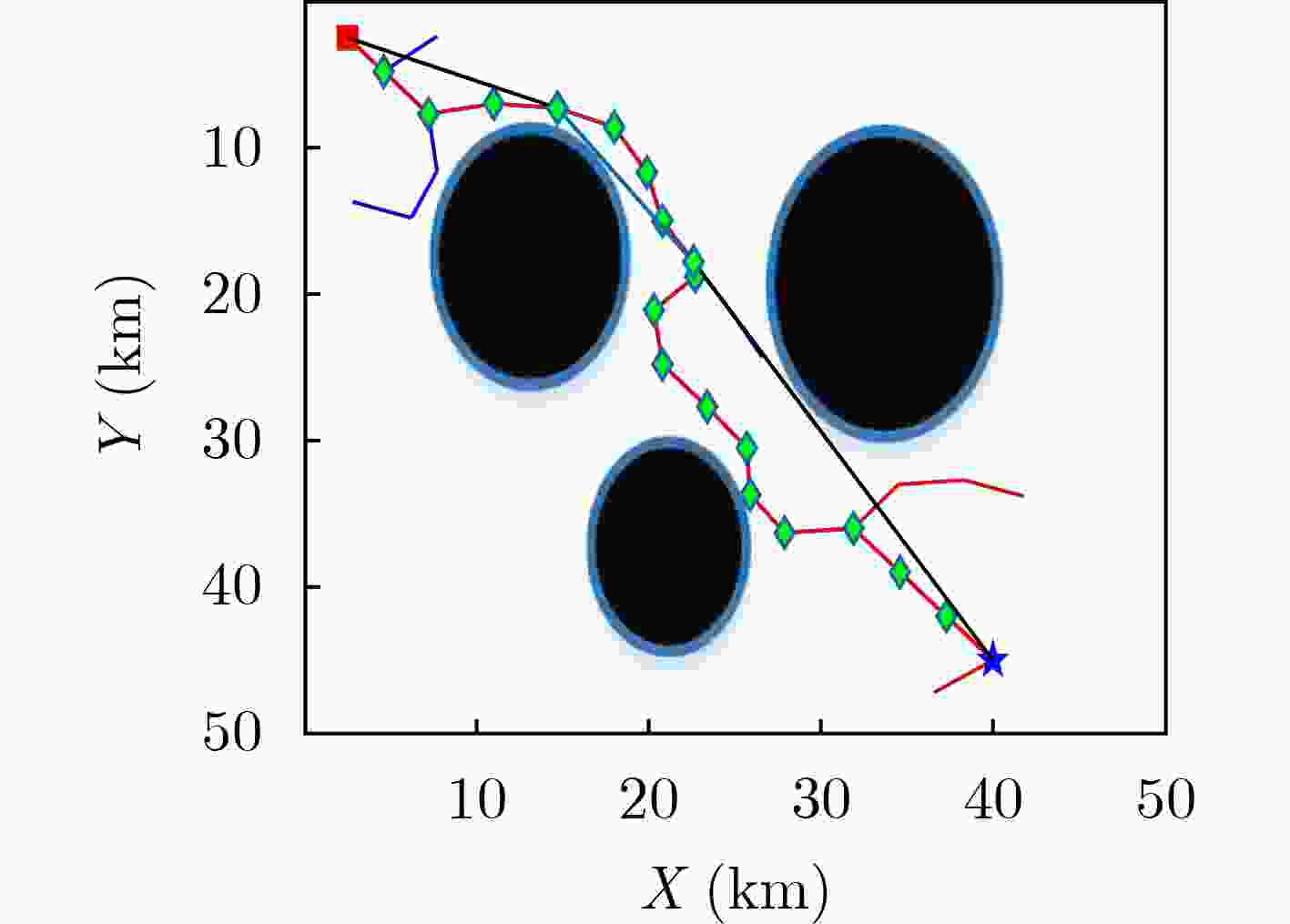
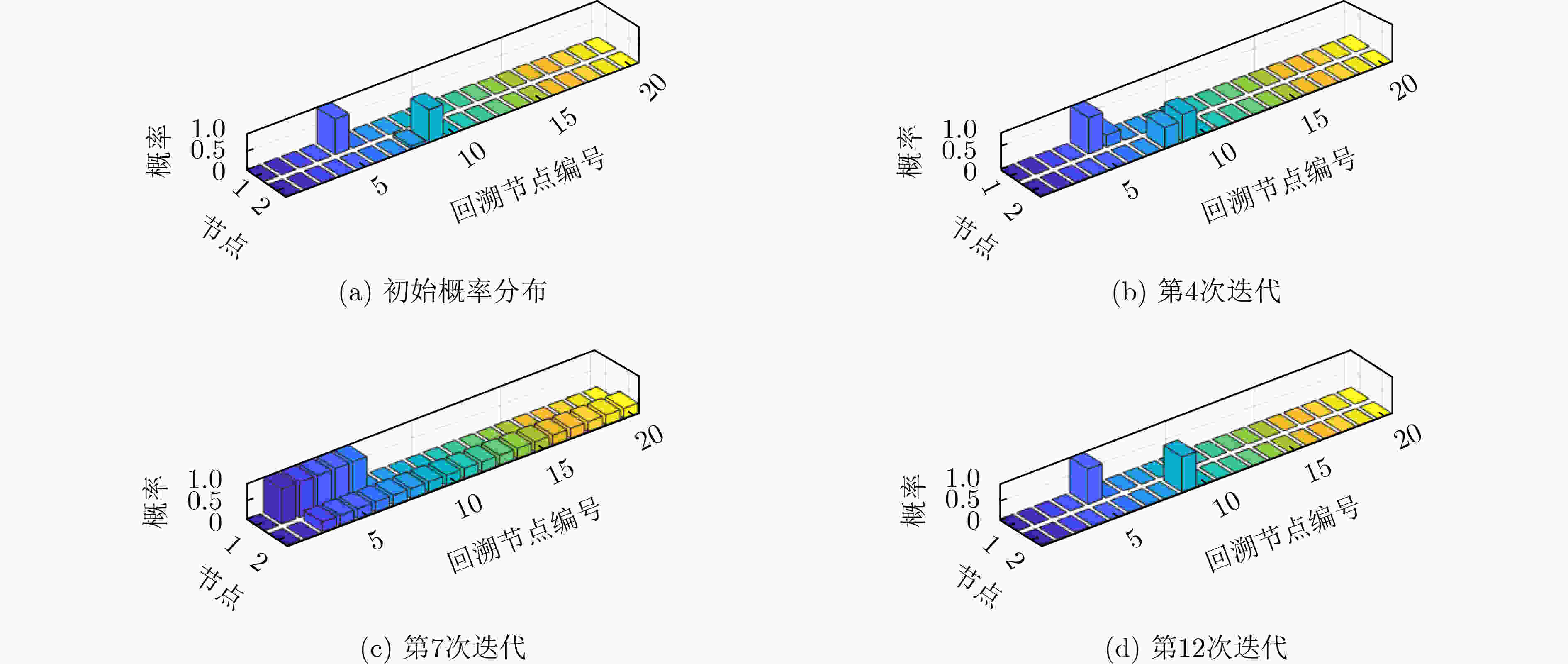
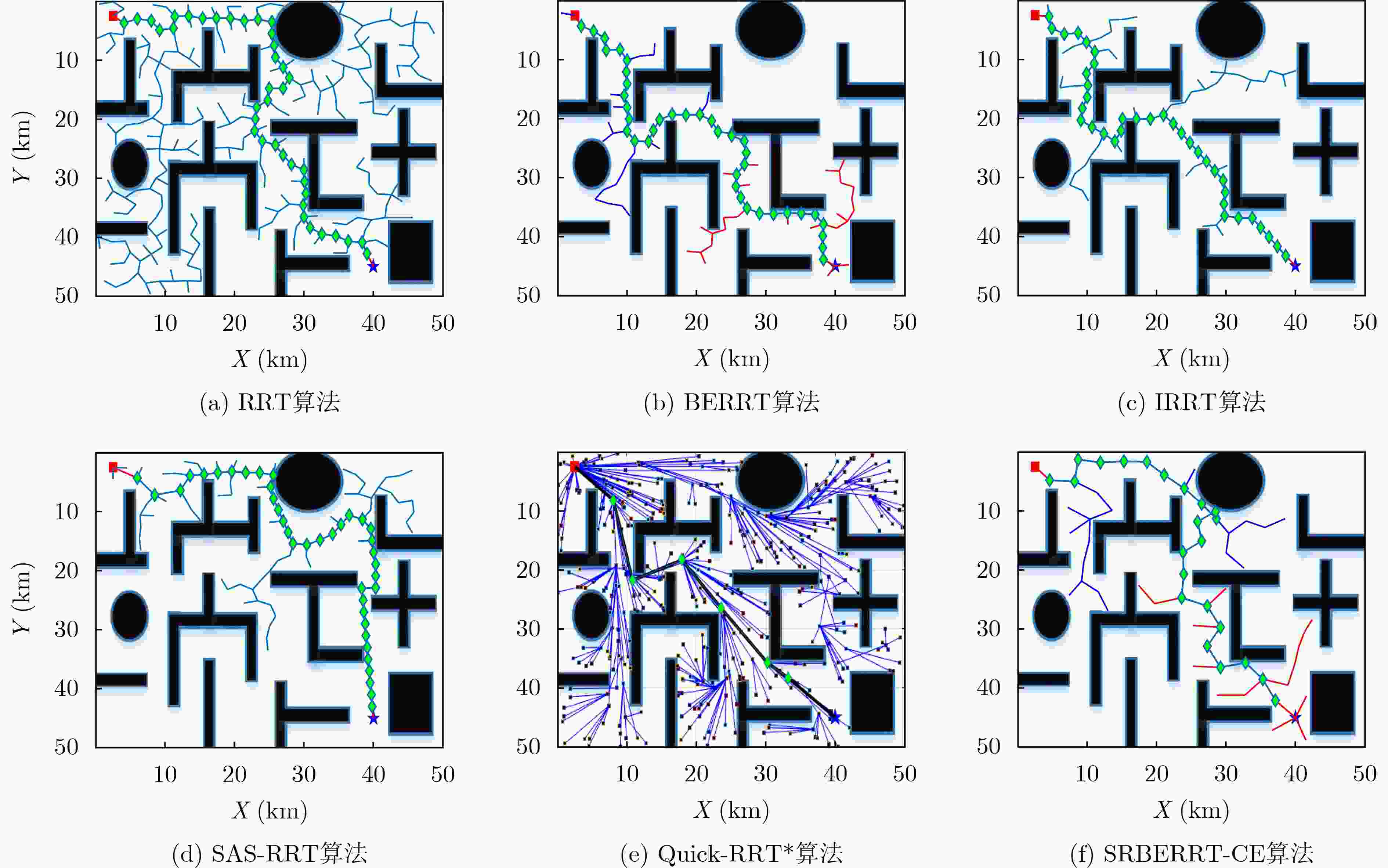
算法1 SRBERRT-CE算法 输入:$ {q_{\text{s}}} $,$ {q_{\text{e}}} $,$ {\text{st}}{{\text{p}}_0} $, $ G $, T, M, K 输出:$ \left\{ {{q_i}} \right\}_{i = 1}^N $, $ \left\{ {{q_i}} \right\}_{i = 1}^n $ (1) 将场景G二值化, 得到矩阵${\boldsymbol{H}}$。 (2) 在任务场景内随机采样两点$ {q_{{\text{s,rand}}}} $和$ {q_{{\text{e,rand}}}} $。 (3) 分别令$ {q_{{\text{rand}}}} = {q_{{\text{s,rand}}}} $, $ {q_{{\text{rand}}}} = {q_{{\text{e,rand}}}} $,分别执行步骤(4)—步骤(9)步。 (4) 根据搜索树,确定距离点$ {q_{{\text{rand}}}} $最近的点并记为$ {q_{{\text{near}}}} $。 (5) 在$ {q_{{\text{near}}}} $指向$ {q_{{\text{rand}}}} $的方向上移动单位步长$ {\text{stp}} $,并记为点$ {q_{{\text{new}}}} $。 (6) 判断从点$ {q_{{\text{near}}}} $到点$ {q_{{\text{new}}}} $的路径是否可行,若不可行则重新采样,若可行则进入下一步。 (7) 判断点$ {q_{{\text{near}}}} $到点$ {q_{{\text{new}}}} $的路径是否可行,是则进入下一步,否则回到步骤(2)。 (8) 扩展节点$ {q_{{\text{new}}}} $并记录其序号。 (9) 判断$ {q_{{\text{s,new}}}} $到$ {q_{{\text{e,new}}}} $的距离是否小于$ {\text{st}}{{\text{p}}_0} $,是则分别将$ {q_{{\text{s,new}}}} $加入始树,将$ {q_{{\text{e,new}}}} $加入终树,扩展结束,否则继续采样。 (10) 根据搜索树,反向回溯,获得路径$ \left\{ {{q_i}} \right\}_{i = 1}^N $。 (11) 从$ {q_0} $点出发,找到距离$ {q_0} $最远的点$ {q_i} $, 且$ F\left( {{q_0},{q_i}} \right) = 1 $。 (12) 从$ {q_i} $点出发,找到$ F\left( {{q_i},{q_j}} \right) = 1 $且距离$ {q_i} $最远的点$ {q_j} $。 (13) 重复步骤(12),直到点$ {q_j} $为点$ {q_{N + 1}} $。 (14) 确定节点数量n。 (15) 计算N个路径点之间任意两点的距离$ {\text{dist}}\left( {{q_i},{q_j}} \right) $。 (16) 计算任意两点之间构成路径的可行性判断函数$ F\left( {{q_i},{q_j}} \right) $。 (17) 计算初始概率矩阵${\boldsymbol{P}}$。 (18) 迭代循环1:T (19) 根据概率密度矩阵生成M个样本,并计算对应的路径长度值。 (20) 将M个样本对应的路径长度按照从小到大排列,同时将样本也对应排列。 (21) 选择前K个样本,并更新概率矩阵。 (22) 令$ {X^*} = {X_{\left( 1 \right)}} $。 (23) 判断是否满足停止条件,是则退出循环,否则继续迭代。 (24) 输出路径$ \left\{ {{q_i}} \right\}_{i = 1}^N $及优化后的路径$ \left\{ {{q_i}} \right\}_{i = 1}^n $。 表 1 各种算法仿真结果统计平均值
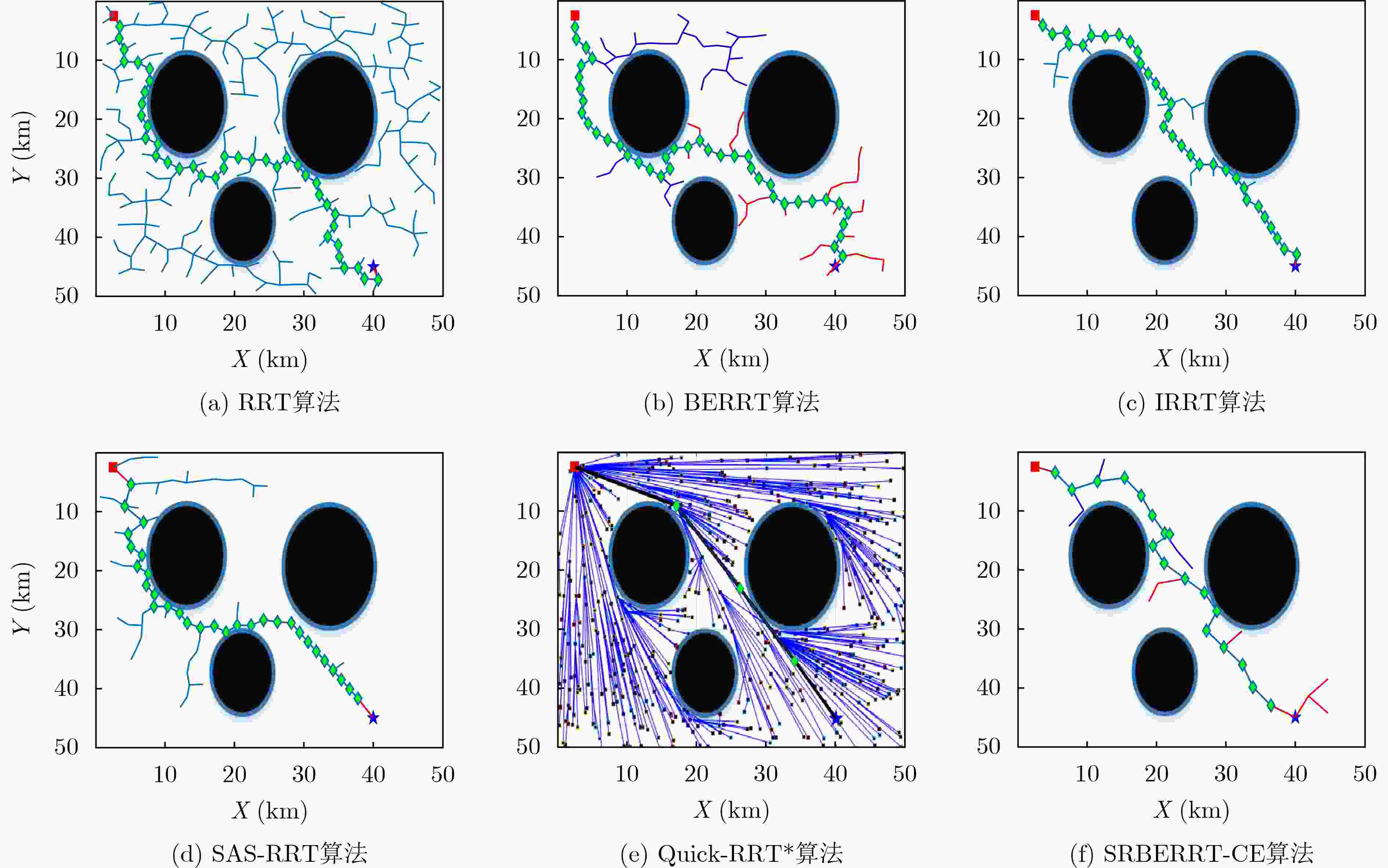
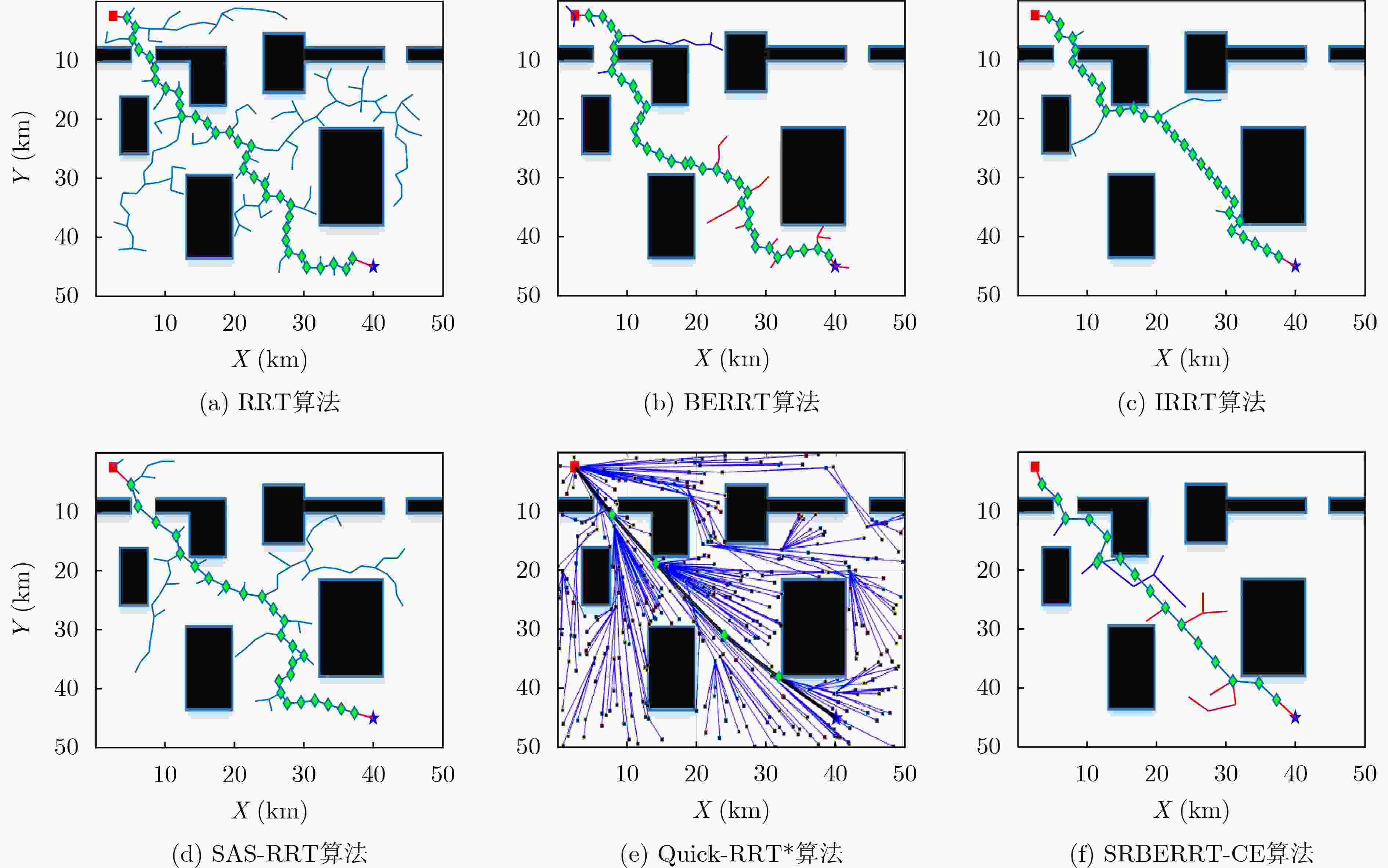
场景 算法 计算时长(s) 路径长度(km) 搜索树节点数量(个) 通路节点数量(个) 场景1 RRT 3.54 77.09 153 37 BERRT 1.78 78.16 84 30 IRRT 1.31 69.42 61 29 SAS-RRT 2.58 73.35 107 28 Quick-RRT* 3.25 59.48 204 6 SRBERRT-CE 1.05 59.87 32 3 场景2 RRT 3.71 73.95 162 36 BERRT 1.37 74.57 65 37 IRRT 1.34 68.49 62 29 SAS-RRT 1.42 70.28 62 29 Quick-RRT* 5.36 57.09 378 6 SRBERRT-CE 1.79 57.68 37 3 场景3 RRT 4.02 84.91 175 39 BERRT 2.53 83.75 118 41 IRRT 2.25 81.23 104 36 SAS-RRT 2.65 85.23 111 28 Quick-RRT* 6.32 66.97 326 9 SRBERRT-CE 3.11 66.76 65 6 -
[1] Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD). Unmanned aircraft systems roadmap 2005–2030[R]. Defense Technical Information Center, 2005. [2] MA Chunyao, FENG Zhuoqun, and ZHENG Zheng. Development of bionic UAVs cluster technology[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 35(S1): 1–8. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-1120.2018.S.001 [3] KHAN A, AFTAB F, and ZHANG Zhongshan. UAPM: An urgency aware packet management for disaster management using flying ad-hoc networks[J]. China Communications, 2019, 16(11): 167–182. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2019.11.014 [4] PERSSON S M and SHARF I. Sampling-based A* algorithm for robot path-planning[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2014, 33(13): 1683–1708. doi: 10.1177/0278364914547786 [5] SINGH Y, SHARMA S, SUTTON R, et al. A constrained A* approach towards optimal path planning for an unmanned surface vehicle in a maritime environment containing dynamic obstacles and ocean currents[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 169: 187–201. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.09.016 [6] HUANG Hanqiao, ZHANG Wei, ZHAO Xin, et al. Study on 4D path planning and tracking controlling of UCAV in multiple constraints dynamic condition[C]. The 33rd Chinese Control Conference, Nanjing, China, 2014: 31–36. [7] AOUDE G S, LUDERS B D, JOSEPH J M, et al. Probabilistically safe motion planning to avoid dynamic obstacles with uncertain motion patterns[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 35(1): 51–76. doi: 10.1007/s10514-013-9334-3 [8] KOTHARI M and POSTLETHWAITE I. A probabilistically robust path planning algorithm for UAVs using rapidly-exploring random trees[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2013, 71(2): 231–253. doi: 10.1007/s10846-012-9776-4 [9] PEHLIVANOGLU Y V. A new vibrational genetic algorithm enhanced with a Voronoi diagram for path planning of autonomous UAV[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2012, 16(1): 47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2011.02.006 [10] 刘冰雁, 叶雄兵, 王新波, 等. 基于改进人工势场的无人地面车辆路径规避算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28(6): 769–777. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2020.06.011LIU Bingyan, YE Xiongbing, WANG Xinbo, et al. Path avoidance algorithm of unmanned ground vehicle based on improved artificial potential field[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(6): 769–777. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2020.06.011 [11] 练青坡, 王宏健, 袁建亚, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的USV集群协同避碰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 2034–2040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.16LIAN Qingpo, WANG Hongjian, YUAN Jianya, et al. USV cluster collision avoidance based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 2034–2040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.16 [12] CONTRERAS-CRUZ M A, AYALA-RAMIREZ V, and HERNANDEZ-BELMONTE U H. Mobile robot path planning using artificial bee colony and evolutionary programming[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 30: 319–328. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.067 [13] LAVALLE S M and KUFFNER JR J J. Randomized kinodynamic planning[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 1999, 20(5): 378–400. doi: 10.1177/02783640122067453 [14] KUFFNER J J and LAVALLE S M. RRT-connect: An efficient approach to single-query path planning[C]. 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings, San Francisco, USA, 2000: 995–1001. [15] 王乐乐, 眭泽智, 蒲志强, 等. 一种改进RRT的多机器人编队路径规划算法[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(11): 2138–2145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.11.007WANG Lele, SUI Zezhi, PU Zhiqiang, et al. An improved RRT algorithm for multi-robot formation path planning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(11): 2138–2145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.11.007 [16] 李洋, 徐达, 周诚. 基于自适应步长RRT的双机器人协同路径规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(3): 358–367. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.03.041LI Yang, XU Da, and ZHOU Cheng. Cooperation path planning of dual-robot based on self-adaptive stepsize RRT[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(3): 358–367. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.03.041 [17] JEONG I B, LEE S J, and KIM J H. Quick-RRT*: Triangular inequality-based implementation of RRT* with improved initial solution and convergence rate[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 123: 82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.01.032 [18] HU Lei, YI Guoxing, HUANG Chao, et al. Research on dynamic weapon target assignment based on cross-entropy[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 8618065. doi: 10.1155/2020/8618065 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
