Biological Inspired Goal-oriented Navigation Model Based on Spatial Exploration and Construction of Cognitive Map
-
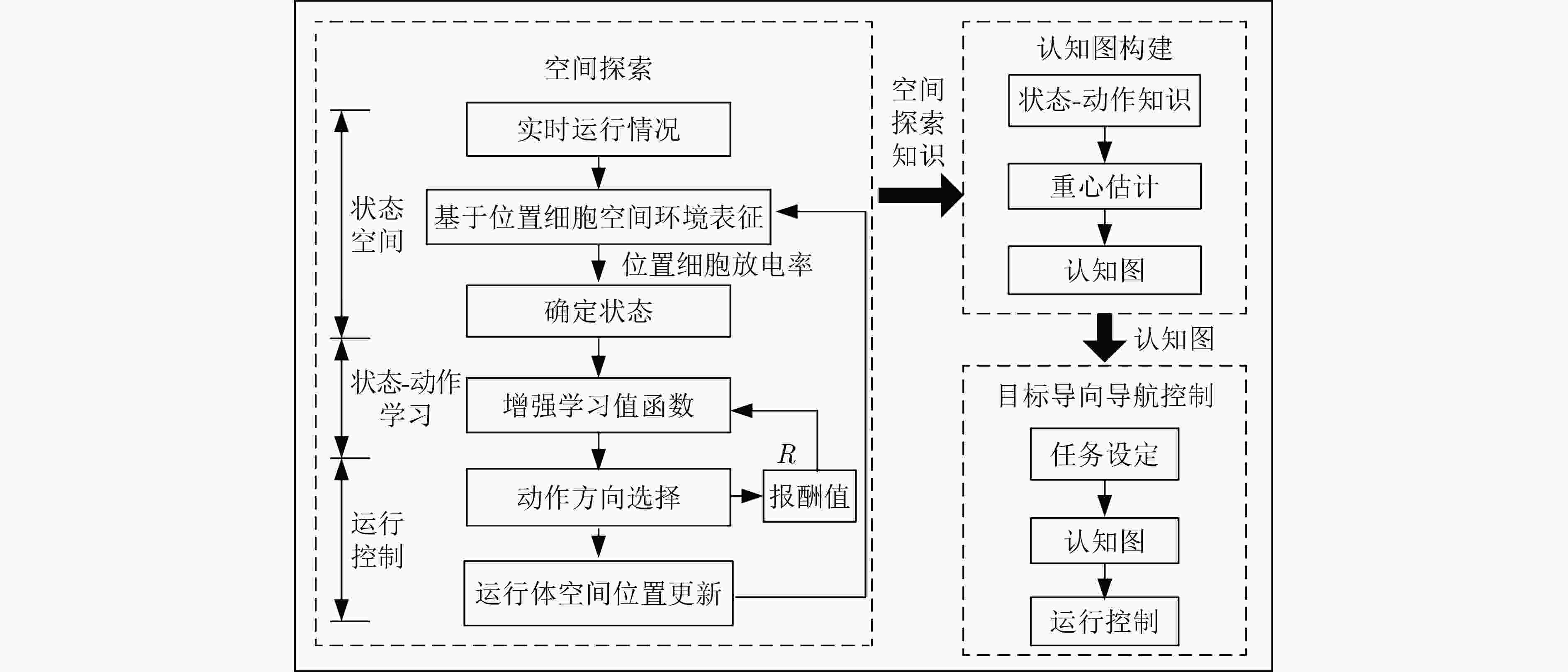
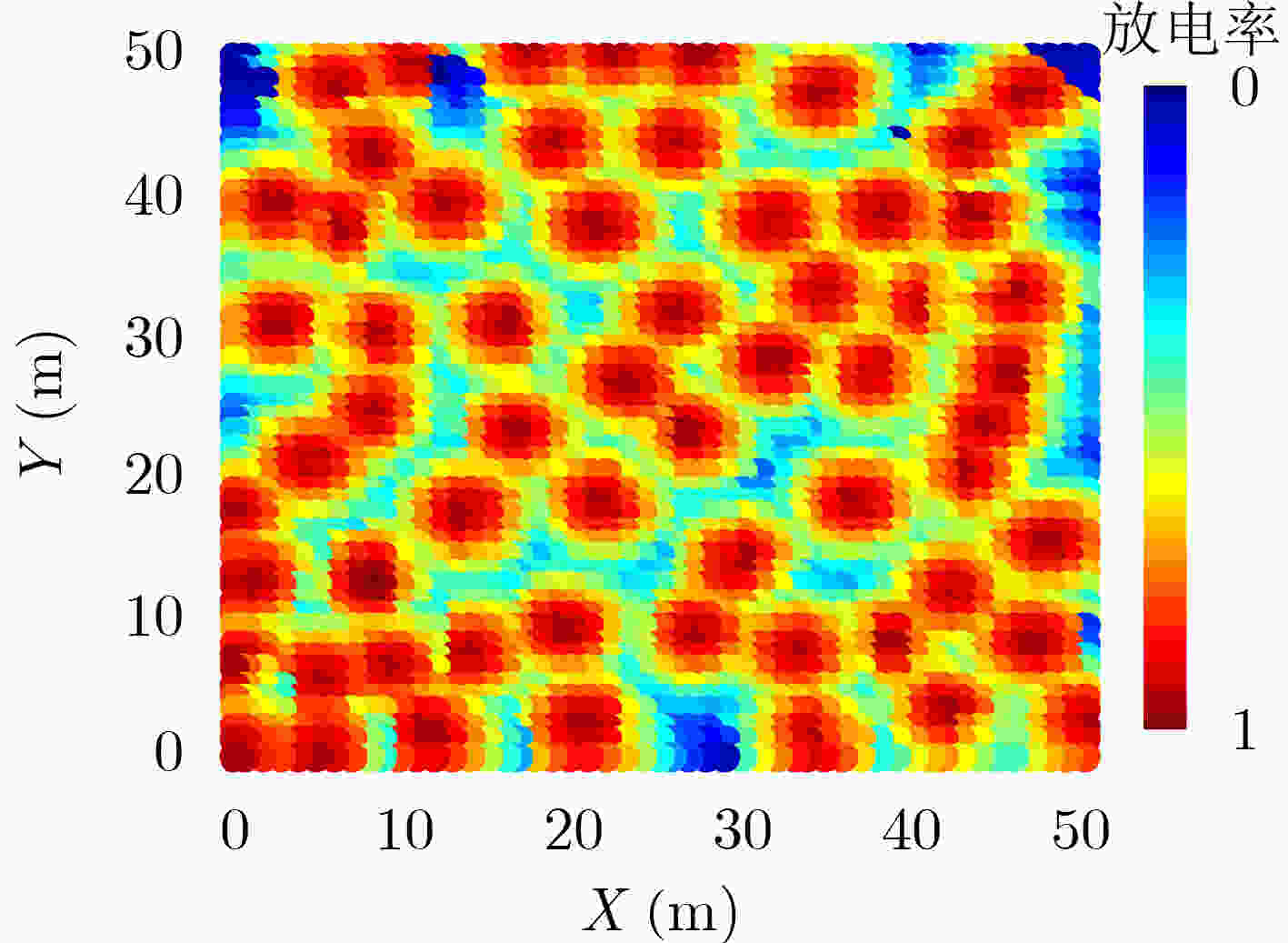
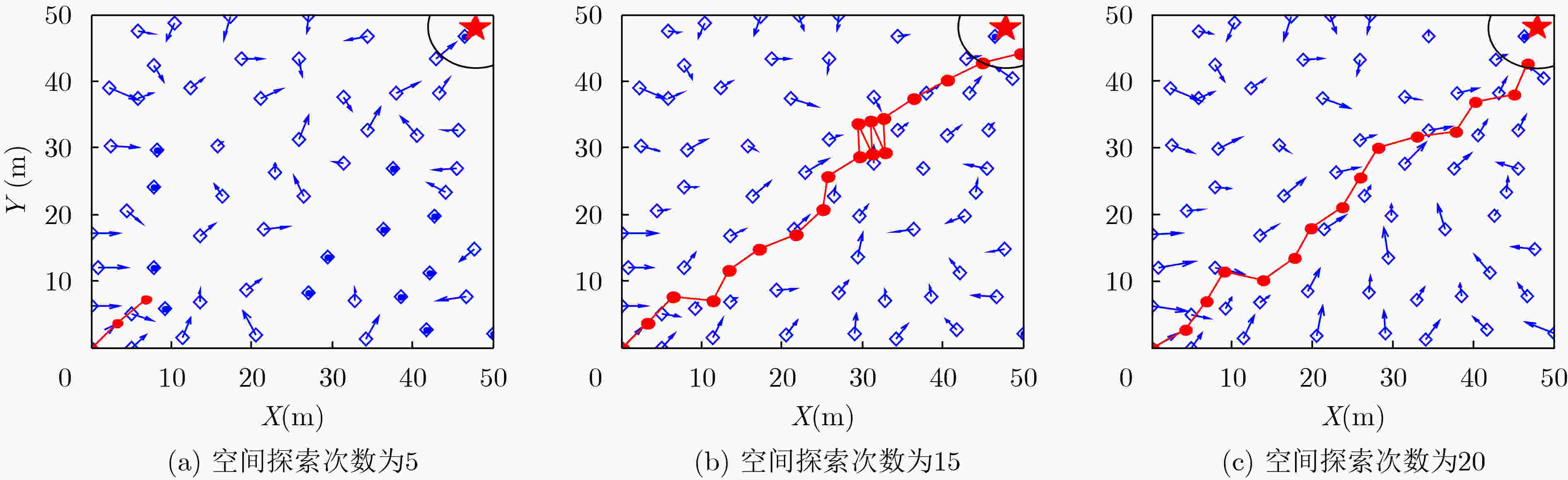
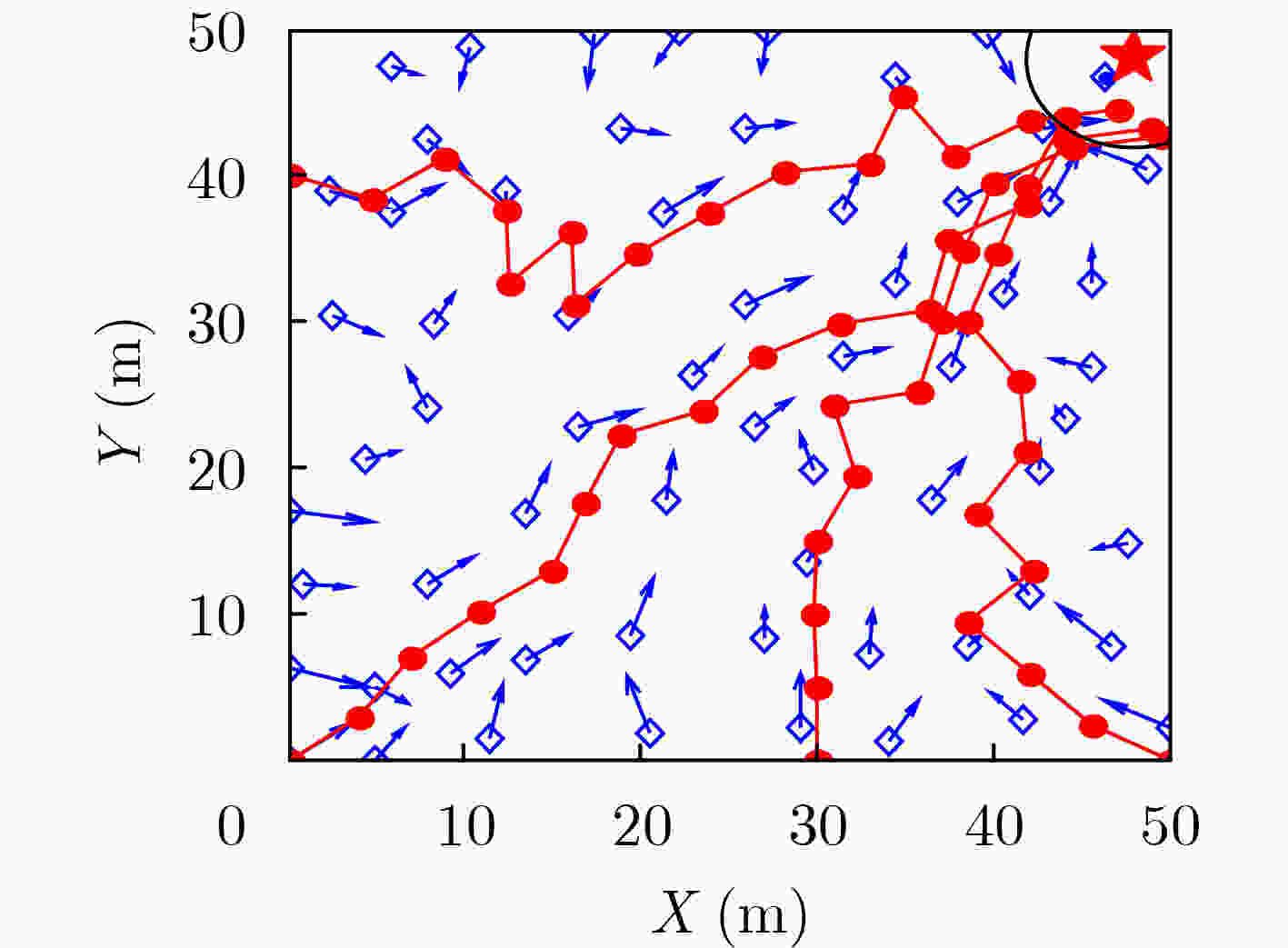
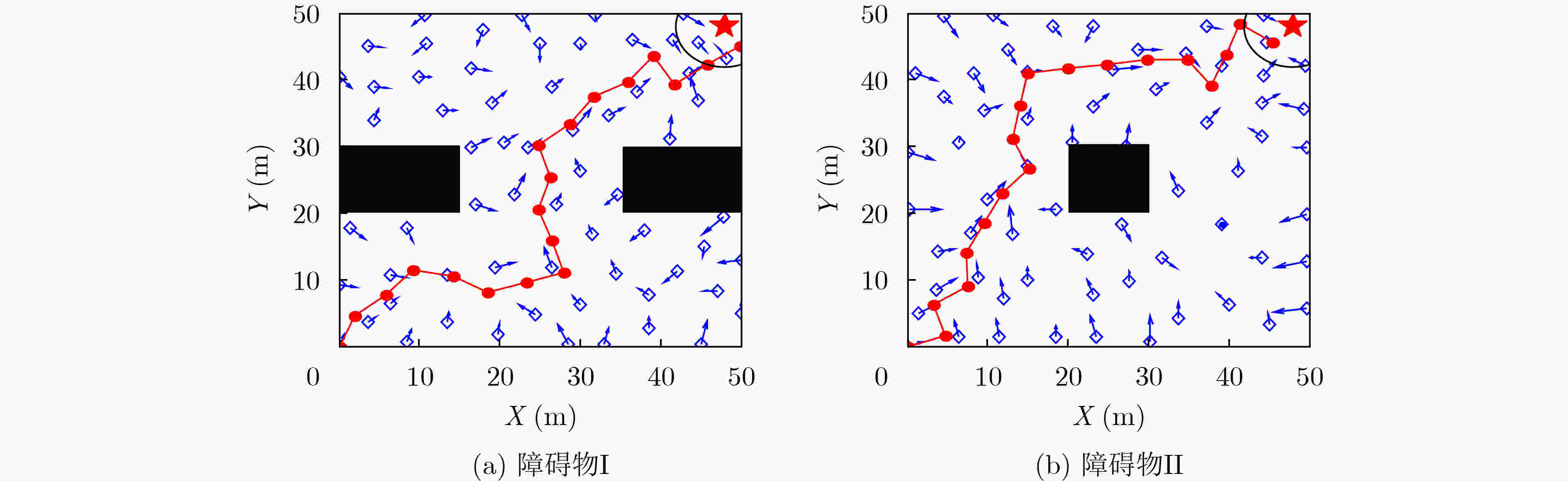
摘要: 为实现智能自主运行体面向目标的导航知识生成及运行控制,该文研究了一种基于空间探索和认知图构建的生物启发式目标导向(GO)导航模型,该模型由空间探索、认知图构建和GO导航控制3个部分组成。在空间探索中,将网格细胞(GCs)到位置细胞(PCs)模型和视觉位置细胞生成模型融合后生成的位置细胞表征当前状态,利用Q学习算法实现状态-动作的建立及更新,以此学习面向目标运行的导航知识;然后,在认知图构建中,利用重心估计原理对空间探索得到的知识进行处理,生成各位置细胞状态下面向目标的方向信息;最后,运行体在朝目标的运行中,根据得到的认知图实时控制运行方向,以此实现GO导航。仿真结果表明,该GO模型有效,运行体进行充分的空间探索可生成认知图,并以此实现GO导航,且在运行过程中能有效规避障碍物。Abstract: To realize the generation of the navigation knowledge and the running control driven by goal for the intelligent and autonomous vehicle, a biological inspired Goal-Oriented (GO) navigation model based on spatial exploration and construction of cognitive map is discussed in this paper. This model is made up of three parts, including spatial exploration, construction of cognitive map and control of goal-oriented navigation. During spatial exploration, the model from Grid Cells (GCs) to Place Cells (PCs) and visual place cells’ model are fused to represent current state, and Q-learning algorithm is used to build and update the state-action. As a result, the goal-oriented navigation knowledge is learned. Then, during the construction of cognitive map, the gravity center estimation principle is used to deal with the obtained spatial exploration knowledge, which can produce the direction information corresponding to the different place cells’ state. Finally, during goal-oriented navigation process, the vehicle controls its running direction based on the cognitive map. Therefore, the goal-oriented navigation can be realized. Simulation validates that this model is available. The vehicle can construct cognitive map after sufficient spatial exploration and realizes goal-oriented navigation based on the cognitive map. Besides, the vehicle can effectively avoid obstacles during running.
-
表 1 仿真中部分参数
参数 数值 学习率($ \beta $) 0.8 折扣因子($ \gamma $) 0.6 贪婪因子($ \varepsilon $) 0.75 动作细胞数量(NAC) 8 -
[1] O’KEEFE J and DOSTROVSKY J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat[J]. Brain Research, 1971, 34(1): 171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90358-1 [2] PASSINGHAM R E. The hippocampus as a cognitive map[J]. Neuroscience, 1979, 4(6): 863. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90015-0 [3] 赵菁, 赵东花, 王晨光, 等. 基于场景识别的惯性基类脑导航方法[J]. 导航与控制, 2020, 19(4): 119–125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5558.2020.h4.014ZHAO Jing, ZHAO Donghua, WANG Chenguang, et al. Inertial-based brain-like navigation strategy based on scene recognition[J]. Navigation and Control, 2020, 19(4): 119–125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5558.2020.h4.014 [4] 丛明, 邹强, 刘冬, 等. 定位细胞认知机理启发的机器人导航研究综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(23): 1–12. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.23.001CONG Ming, ZOU Qiang, LIU Dong, et al. Review of robot navigation inspired by the localization cells’ cognitive mechanism[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(23): 1–12. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.23.001 [5] TEJERA G, LLOFRIU M, BARRERA A, et al. Bio-inspired robotics: A spatial cognition model integrating place cells, grid cells and head direction cells[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2018, 91(1): 85–99. doi: 10.1007/s10846-018-0852-2 [6] MOSER E I, KROPFF E, and MOSER M B. Place cells, grid cells, and the brain’s spatial representation system[J]. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2008, 31: 69–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.061307.090723 [7] 杨闯, 刘建业, 熊智, 等. 由感知到动作决策一体化的类脑导航技术研究现状与未来发展[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(1): 023280. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23280YANG Chuang, LIU Jianye, XIONG Zhi, et al. Brain-inspired navigation technology integrating perception and action decision: A review and outlook[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 023280. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23280 [8] 李伟龙, 吴德伟, 卢虎, 等. 基于多尺度空间表征的生物启发目标指引导航模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1363–1370. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160892LI Weilong, WU Dewei, LU Hu, et al. Bio-inspired goal-directed navigation model based on multi-scale spatial representation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1363–1370. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160892 [9] HU Lingfang, HAO Kuangrong, CAI Xin, et al. A spatial cognitive cells inspired goal-directed navigation model[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA), Dalian, China, 2019: 211–215. [10] STRÖSSLIN T, SHEYNIKHOVICH D, CHAVARRIAGA R, et al. Robust self-localisation and navigation based on hippocampal place cells[J]. Neural Networks, 2005, 18(9): 1125–1140. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.08.012 [11] SHEYNIKHOVICH D, CHAVARRIAGA R, STRÖSSLIN T, et al. Spatial representation and navigation in a bio-inspired robot[M]. WERMTER S, PALM G, and ELSHAW M. Biomimetic Neural Learning for Intelligent Robots. Berlin: Springer, 2005: 245–264. [12] SHEYNIKHOVICH D and ARLEO A. A reinforcement learning approach to model interactions between landmarks and geometric cues during spatial learning[J]. Brain Research, 2010, 1365: 35–47. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.091 [13] SHEYNIKHOVICH D, DOLLÉ L, CHAVARRIAGA R, et al. Minimal model of strategy switching in the plus-maze navigation task[C]. The 11th International Conference on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior on From Animals to Animats 11, Clos Lucé, France, 2010: 390–401. [14] HASSELMO M E. A model of prefrontal cortical mechanisms for goal-directed behavior[J]. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 2005, 17(7): 1115–1129. doi: 10.1162/0898929054475190 [15] MARTINET L E, SHEYNIKHOVICH D, BENCHENANE K, et al. Spatial learning and action planning in a prefrontal cortical network model[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2011, 7(5): e1002045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002045 [16] LLOFRIU M, TEJERA G, and CONTRERAS M. Goal-oriented robot navigation learning using a multi-scale space representation[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 72: 62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2015.09.006 [17] 方略, 何洪军. 基于鼠脑海马位置细胞与Q学习面向目标导航[J]. 生物信息学, 2019, 17(1): 31–38. doi: 10.12113/j.issn.1672-5565.201809001FANG Lue and HE Hongjun. Goal oriented navigation based on place cells of rat’s brain hippocampus and Q-learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioinformatics, 2019, 17(1): 31–38. doi: 10.12113/j.issn.1672-5565.201809001 [18] ZHU Qing, WANG Rubin, and WANG Ziyin. A cognitive map model based on spatial and goal-oriented mental exploration in rodents[J]. Behavioural Brain Research, 2013, 256: 128–139. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.05.050 [19] 周阳, 吴德伟. 基于位置细胞的空间表征及位置估计模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(4): 488–494. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.04.015ZHOU Yang and WU Dewei. Spatial representation and location estimation model based on place cells[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(4): 488–494. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.04.015 [20] ZHOU Yang and WU Dewei. Grid-to-place cells model based on radial basis function network[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(3): 200–201. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.1750 [21] ZHOU Yang and WU Dewei. A model of generating visual place cells based on environment perception and similar measure[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2016, 2016: 3253678. doi: 10.1155/2016/3253678 [22] ARLEO A and GERSTNER W. Spatial cognition and neuro-mimetic navigation: A model of hippocampal place cell activity[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 2000, 83(3): 287–299. doi: 10.1007/s004220000171 [23] 赵辰豪, 吴德伟, 何晶, 等. 基于改进Q学习算法的导航认知图构建[J]. 空军工程大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 21(2): 53–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.02.008ZHAO Chenhao, WU Dewei, HE Jing, et al. Navigation cognitive map construction based on improved Q-learning algorithm[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 21(2): 53–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.02.008 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
