Design of Hybrid Multimode Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Electrocardiogram Detection
-
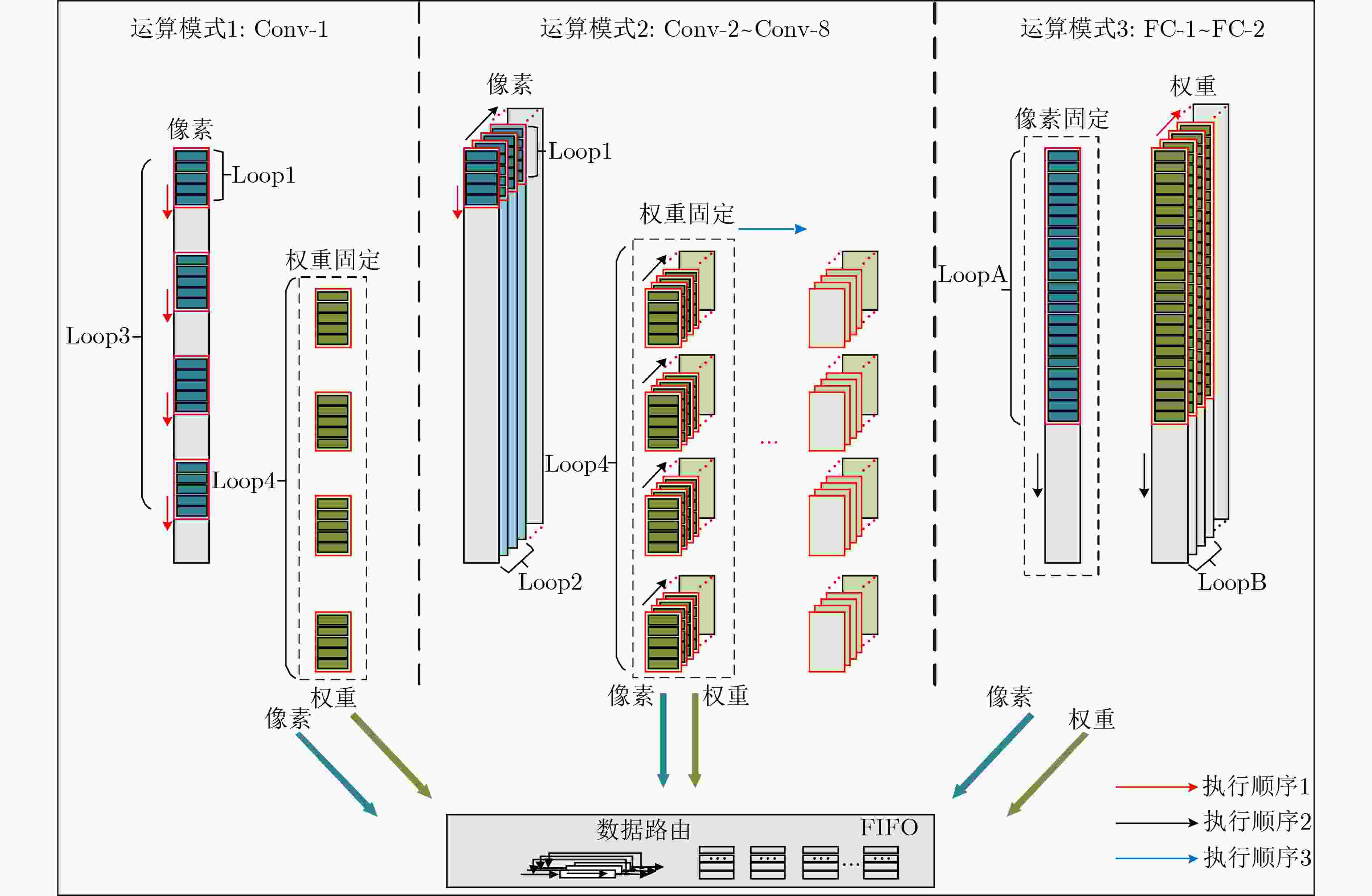
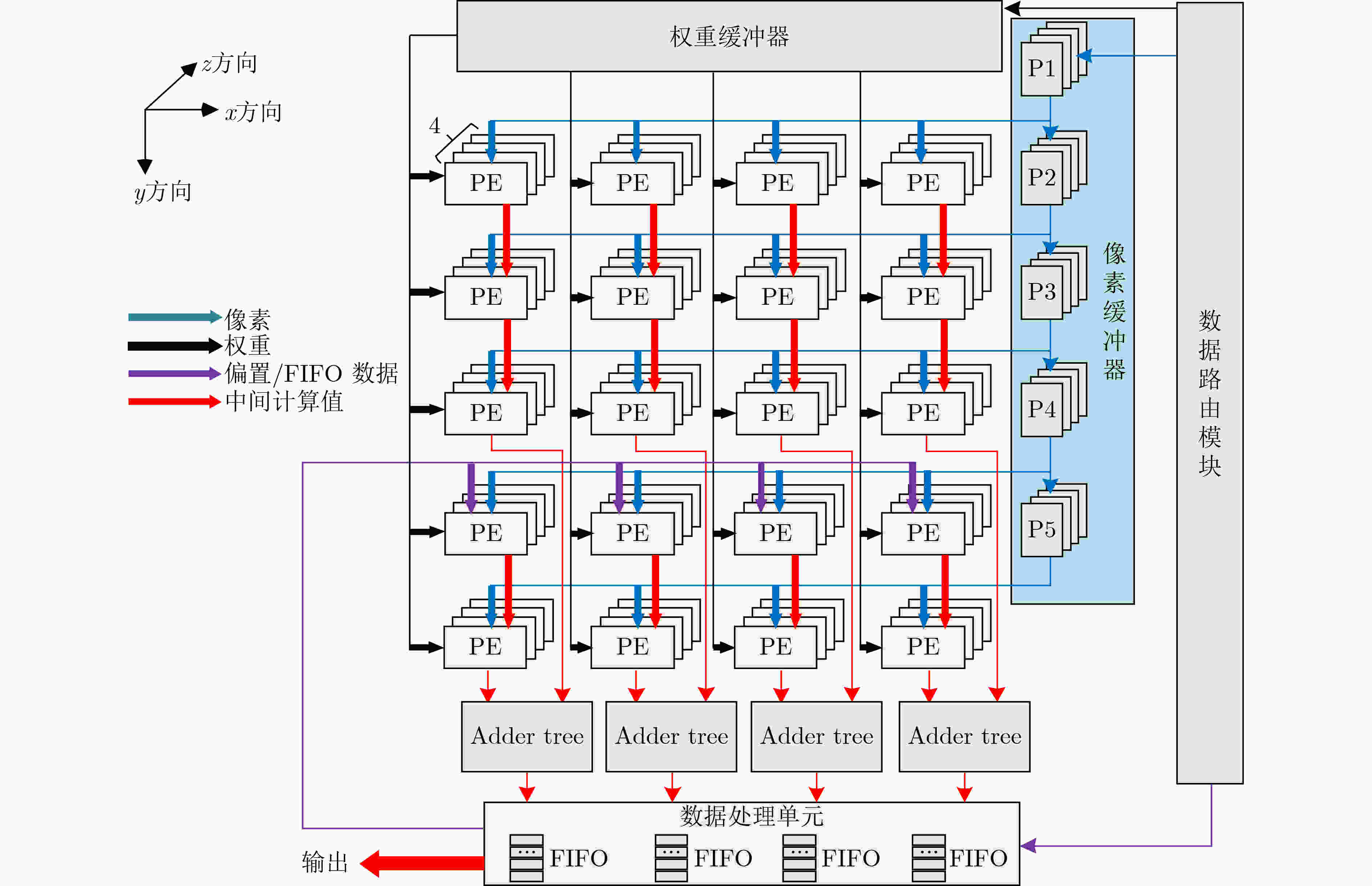
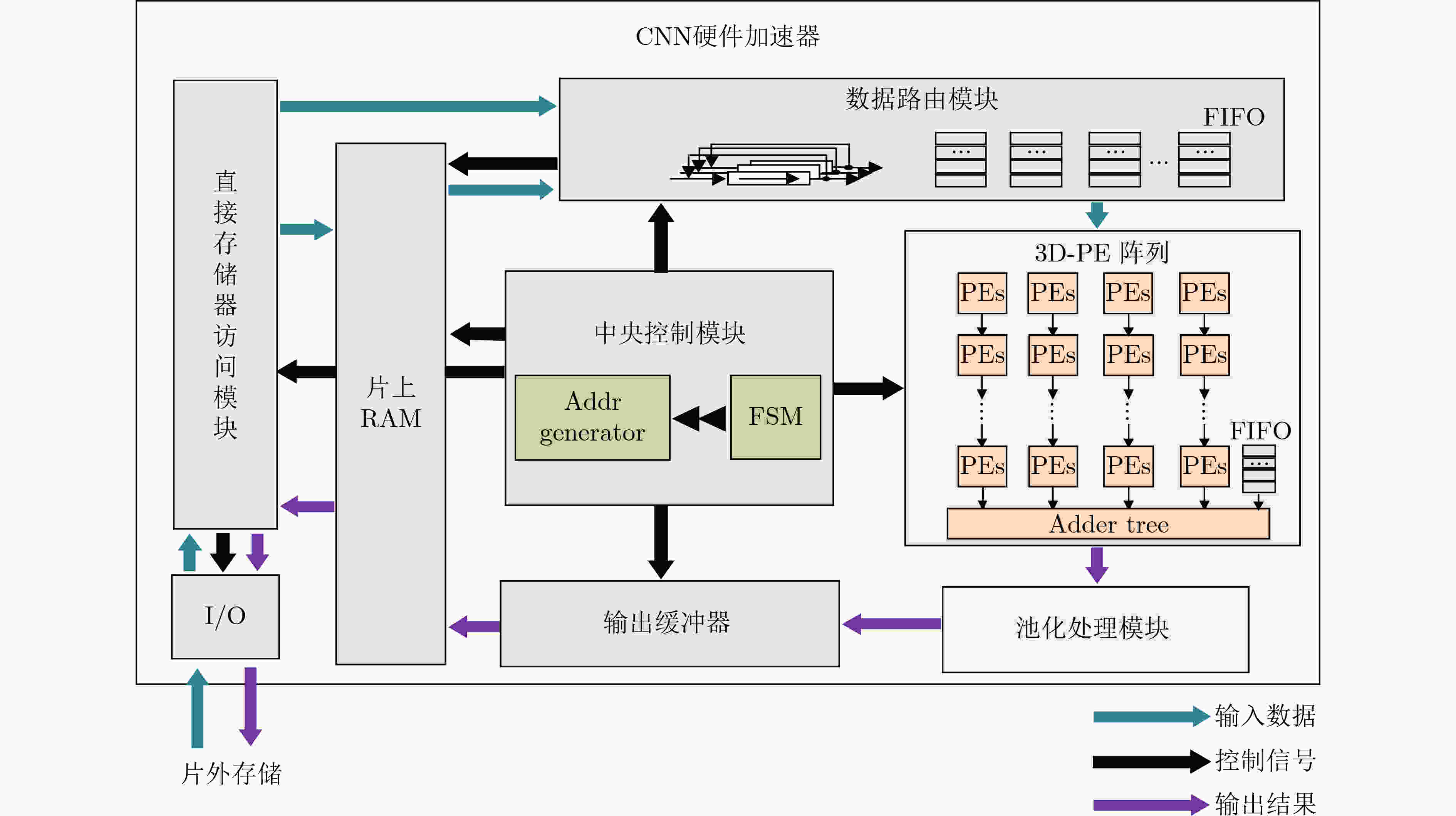
摘要: 随着医疗资源日益匮乏以及人口老龄化日趋严重,心血管疾病已对人类健康造成了极大的威胁。具有心电(ECG)检测的便携式设备能有效降低心血管疾病对患者的威胁,因此该文设计了一种面向心电检测的混合多模卷积神经网络加速器。该文首先介绍了一种用于心电信号分类的1维卷积神经网络(1D-CNN)模型,随后针对该模型设计了一种高效的卷积神经网络(CNN)加速器,该加速器采用了一种多并行展开策略和多数据流的运算模式完成了卷积循环的加速和优化,能在时间上和空间上高度复用数据,同时提高了硬件资源利用率,从而提升了硬件加速器的硬件效率。最后基于Xilinx ZC706硬件平台完成了原型验证,结果显示,所设计卷积神经网络加速器消耗的资源为2247 LUTs, 80 DSPs。在200 MHz的工作频率下,该设计的整体性能可达到28.1 GOPS,并且硬件效率达到了12.82 GOPS/kLUT。Abstract: With the increasing scarcity of medical resources and the aging of the population, cardiovascular disease has posed a great threat to human health. Portable devices with ElectroCardioGram (ECG) detection can effectively reduce the threat of cardiovascular disease to patients. In this paper, a hybrid multi-mode Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) accelerator is designed for monitoring the patient's ECG. Firstly, a one-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network(1D-CNN) model is introduced for ECG classification, then an efficient accelerator is designed for this model, which adopts a multi-parallel expansion strategy and multi-data stream operation mode to complete the acceleration and optimization of convolution loops. The proposed operation mode can highly reuse data in time and space, and improve the utilization of hardware resources, thereby improving the hardware efficiency of the hardware accelerator. Finally, the prototype verification is completed based on the Xilinx ZC706 hardware platform. The results show 2247 LUTs and 80 DSPs are consumed. At 200 MHz operating frequency, the overall performance can reach 28.1 GOPS, and the hardware efficiency reaches 12.82 GOPS/kLUT.
-
图 4 1D-CNN模型结构图[13]
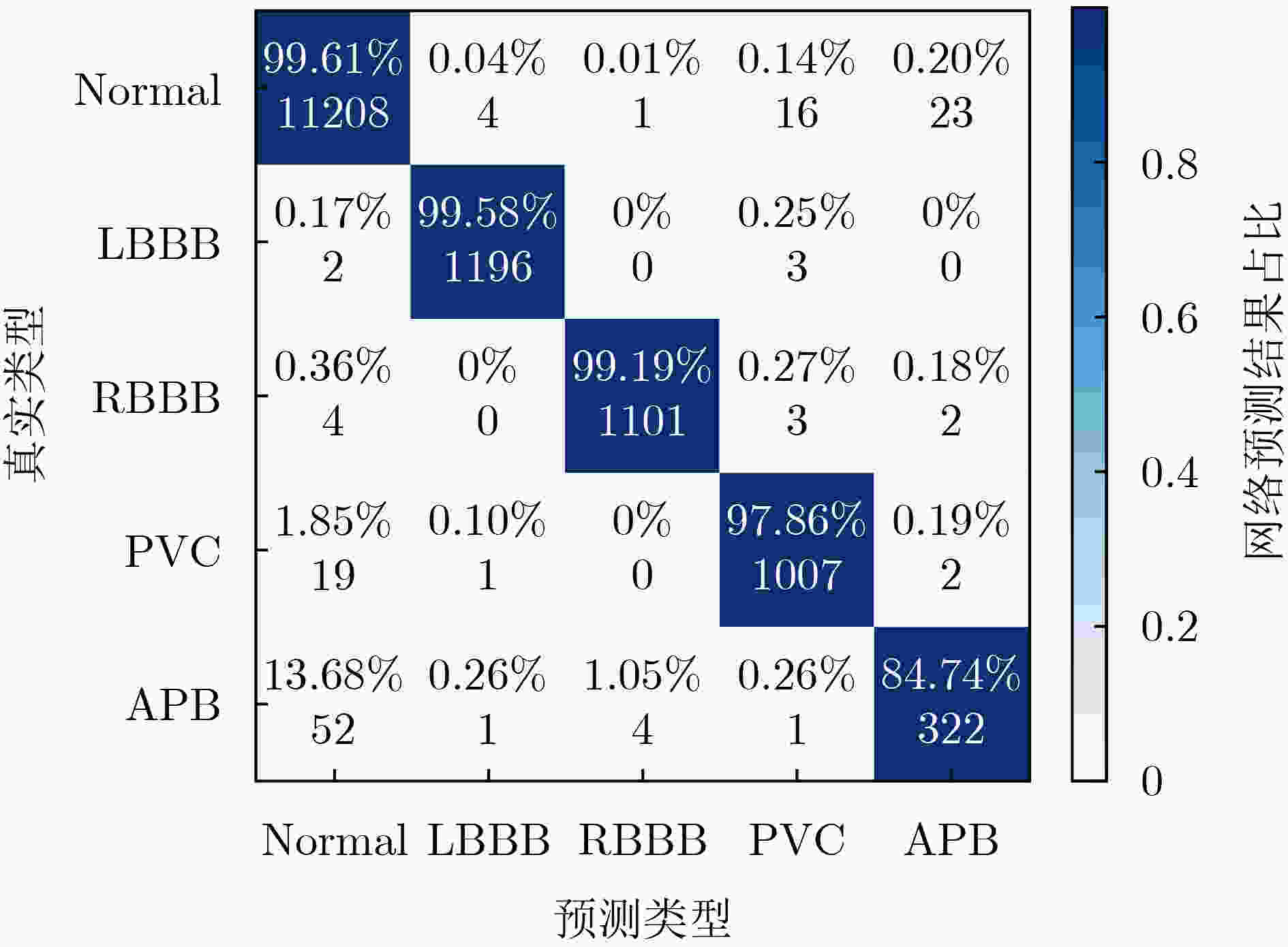
表 1 软硬件平台测试集的性能指标(%)
平台 Acc Sen Spec Ppr Intel Core i5-10400 99.20 97.97 99.60 98.80 ZYNQ 7000 ZC706 99.19 97.92 99.60 98.80 表 2 CNN加速器性能比较
文献 FPGA Bit-width CNN Model Clock
(MHz)DSP
UtilizationResource
(kLUT)Throughput
(GOPS)Efficiency
(GOPS/kLUT)DSP Efficiency
(GOPS/DSP)[7] Arria 10
GX 115016 bit Fixed VGG-16 200 3036 235k 1030.2 4.384 0.339 [17] Zynq XC7Z045 16 bit Fixed VGG-16 150 780 183k 137.0 0.749 0.175 [18] Zynq
ZCU 10216 bit Fixed VGG-16 200 1352 390k 495.4 1.270 0.366 [19] Zynq XC7Z045 16 bit Fixed VGG-16 172 576 59k 316.2 5.358 0.549 本设计 Zynq ZC706 16 bit Fixed 1D-CNN 200 80 2.2k 28.1 12.820 0.360 -
[1] United Nations. World population ageing 2017: highlights[R]. ST/ESA/SER. A/397, 2017. [2] ZHANG Jiancan. Construction and application of “internet” mental health cloud platform based on trinity model analysis[C]. 2021 International Conference on Internet, Education and Information Technology (IEIT), Suzhou, China, 2021: 1–5. [3] LI Feiteng, WU Jiaquan, JIA Menghan, et al. Automated heartbeat classification exploiting convolutional neural network with channel-wise attention[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 122955–122963. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2938617 [4] QIAN Yanmin, BI Mengxiao, TAN Tian, et al. Very deep convolutional neural networks for noise robust speech recognition[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24(12): 2263–2276. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2602884 [5] LI Zhen, WANG Yuqing, ZHI Tian, et al. A survey of neural network accelerators[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2017, 11(5): 746–761. doi: 10.1007/s11704-016-6159-1 [6] WANG Ying, WANG Yongchen, SHI Cong, et al. An edge 3D CNN accelerator for low-power activity recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2021, 40(5): 918–930. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.3011042 [7] MA Yufei, CAO Yu, VRUDHULA S, et al. Optimizing the convolution operation to accelerate deep neural networks on FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2018, 26(7): 1354–1367. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2815603 [8] PARK S W, PARK J, BONG K, et al. An energy-efficient and scalable deep learning/inference processor with tetra-parallel MIMD architecture for big data applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2015, 9(6): 838–848. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2015.2504563 [9] TU Fengbin, WU Weiwei, WANG Yang, et al. Evolver: A deep learning processor with on-device quantization–voltage–frequency tuning[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(2): 658–673. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3021661 [10] ZHU Lingsong, LIU Dongsheng, LI Xiaohuan, et al. An efficient hardware architecture for epileptic seizure detection using EEG signals based on 1D-CNN[C]. 2021 IEEE 14th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), Kunming, China, 2021: 1–4. [11] LIU Xinheng, CHEN Yao, HAO Cong, et al. WinoCNN: Kernel sharing winograd systolic array for efficient convolutional neural network acceleration on FPGAs[C]. 2021 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP), NJ, USA, 2021: 258–265. [12] YUAN Zhe, LIU Yongpan, YUE Jinshan, et al. STICKER: An energy-efficient multi-sparsity compatible accelerator for convolutional neural networks in 65-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(2): 465–477. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2946771 [13] WEI Lai, LIU Dongsheng, LU Jiahao, et al. A low-cost hardware architecture of convolutional neural network for ECG classification[C]. 2021 9th International Symposium on Next Generation Electronics (ISNE), Changsha, China, 2021: 1–4. [14] DU Li, DU Yuan, LI Yilei, et al. A reconfigurable streaming deep convolutional neural network accelerator for internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2018, 65(1): 198–208. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2735490 [15] MA Yufei, CAO Yu, VRUDHULA S, et al. An automatic RTL compiler for high-throughput FPGA implementation of diverse deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 27th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Ghent, Belgium, 2017: 1–8. [16] MA Yufei, SUDA N, CAO Yu, et al. Scalable and modularized RTL compilation of convolutional neural networks onto FPGA[C]. 2016 26th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Lausanne, Switzerland, 2016: 1–8. [17] GUO Kaiyuan, SUI Lingzhi, QIU Jiantao, et al. Angel-eye: A complete design flow for mapping CNN onto embedded FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(1): 35–47. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2705069 [18] ZHU Chaoyang, HUANG Kejie, YANG Shuyuan, et al. An efficient hardware accelerator for structured sparse convolutional neural networks on FPGAs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2020, 28(9): 1953–1965. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3002779 [19] WANG Jichen, LIN Jun, and WANG Zhongfeng. Efficient hardware architectures for deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2018, 65(6): 1941–1953. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2767204 -





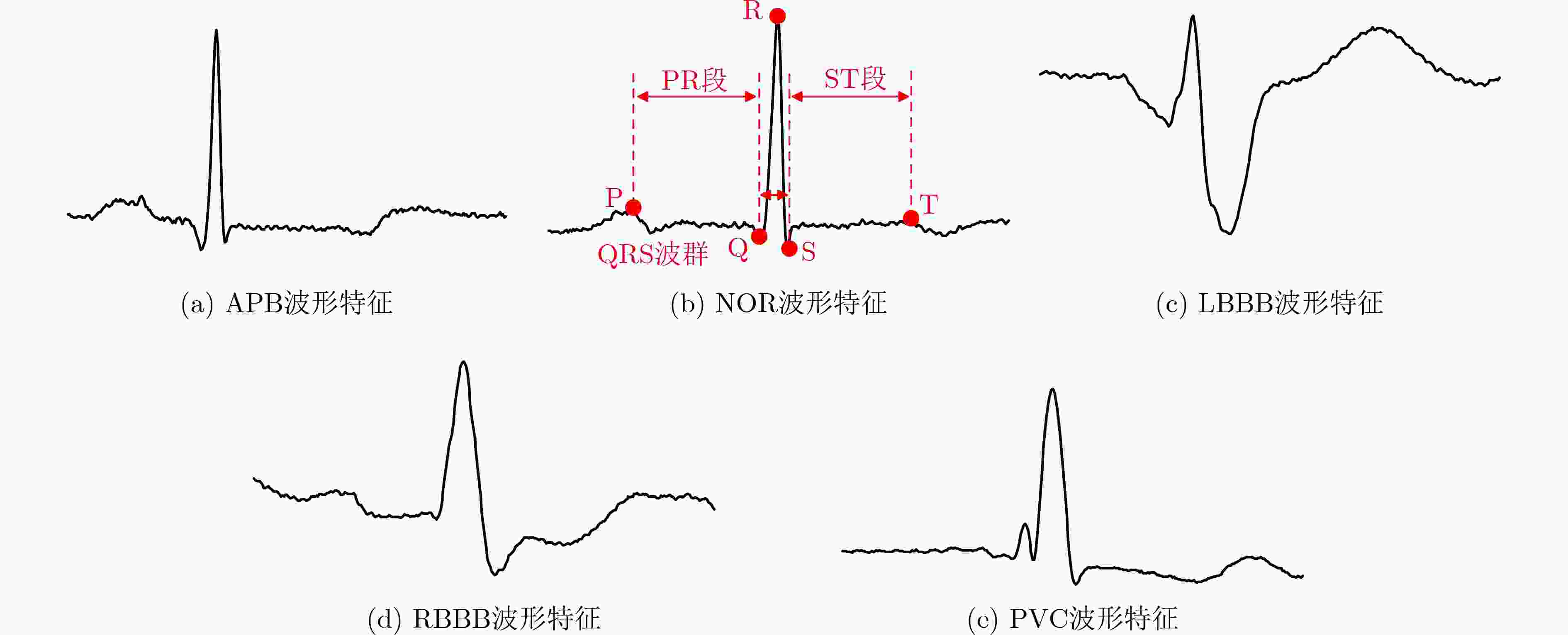
 下载:
下载:
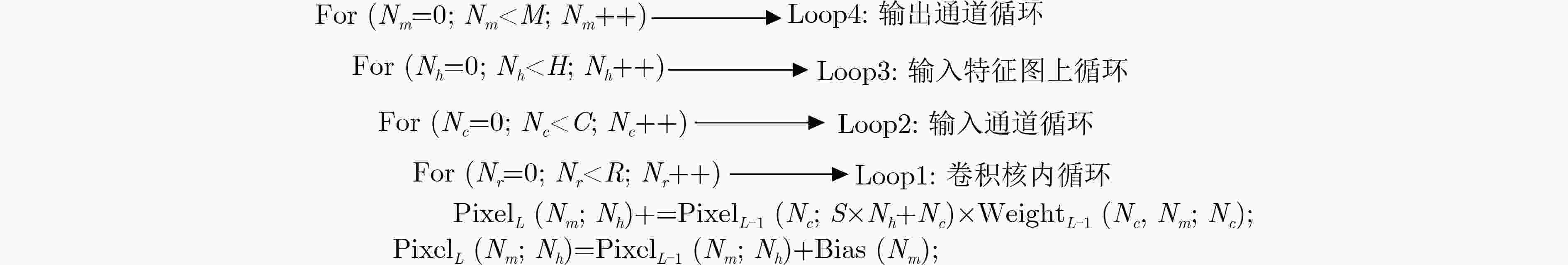
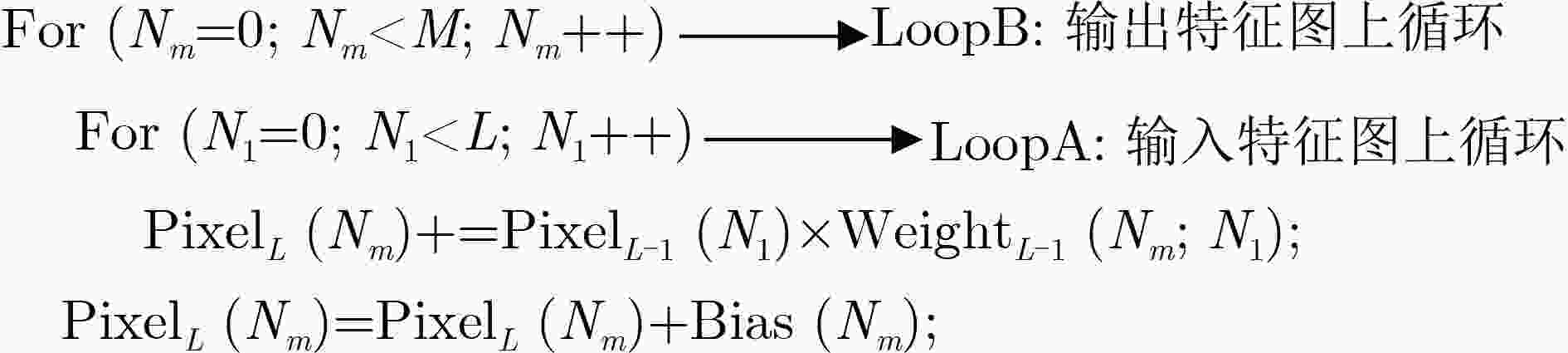
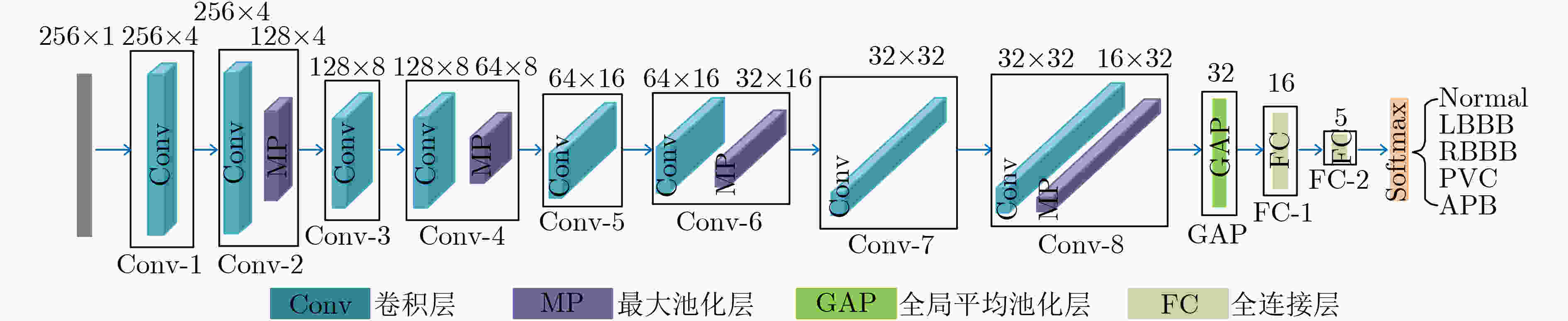


 下载:
下载:
